Antioxidant Therapy as an Effective Strategy against Noise-Induced Hearing Loss: From Experimental Models to Clinic
Abstract
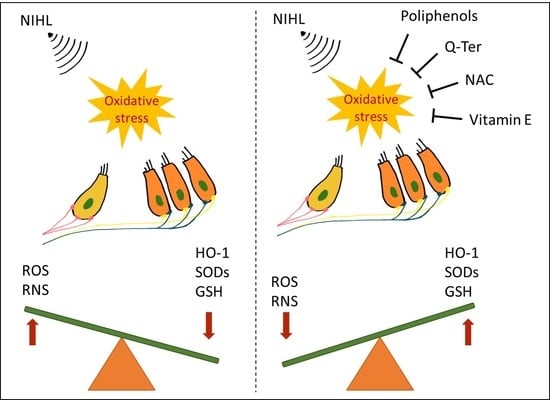
:1. Introduction
2. Cochlear Oxidative Damage in NIHL: A Brief Overview
3. Effectiveness of Antioxidant Treatments in Animal Models of NIHL
3.1. Polyphenols
3.2. Coenzyme Q10
3.3. Vitamin E and N-acetylcysteine
4. Clinical Relevance for the Use of Antioxidants
Antioxidant Treatment against Noise-Induced Temporary Threshold Shift (TTS)
5. Conclusions
6. Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nelson, D.I.; Nelson, R.Y.; Concha-Barrientos, M.; Fingerhut, M. The global burden of occupational noise-induced hearing loss. Am. J. Ind. Med. 2005, 48, 446–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deafness and Hearing Loss. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/deafness-and-hearing-loss (accessed on 21 February 2023).
- Chen, K.-H.; Su, S.-B.; Chen, K.-T. An overview of occupational noise-induced hearing loss among workers: Epidemiology, pathogenesis, and preventive measures. Environ. Health Prev. Med. 2020, 25, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Prell, C.G.; Yamashita, D.; Minami, S.B.; Yamasoba, T.; Miller, J.M. Mechanisms of noise-induced hearing loss indicate multiple methods of prevention. Heart Res. 2007, 226, 22–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fetoni, A.R.; Paciello, F.; Rolesi, R.; Paludetti, G.; Troiani, D. Targeting dysregulation of redox homeostasis in noise-induced hearing loss: Oxidative stress and ROS signaling. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2019, 135, 46–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, D.; Bielefeld, E.C.; Harris, K.; Hu, B.H. The Role of Oxidative Stress in Noise-Induced Hearing Loss. Ear Heart 2006, 27, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paciello, F.; Ripoli, C.; Fetoni, A.R.; Grassi, C. Redox Imbalance as a Common Pathogenic Factor Linking Hearing Loss and Cognitive Decline. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciorba, A.; Gasparini, P.; Chicca, M.; Pinamonti, S.; Martini, A. Reactive oxygen species in human inner ear perilymph. Acta Oto-Laryngol. 2010, 130, 240–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Van De Water, T.R.; Bonny, C.; de Ribaupierre, F.; Puel, J.L.; Zine, A. A Peptide Inhibitor of c-Jun N-Terminal Kinase Protects against Both Aminoglycoside and Acoustic Trauma-Induced Auditory Hair Cell Death and Hearing Loss. J. Neurosci. 2003, 23, 8596–8607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crane, F.L. Biochemical Functions of Coenzyme Q10. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2001, 20, 591–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saini, R. Coenzyme Q10: The essential nutrient. J. Pharm. Bioallied Sci. 2011, 3, 466–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sergi, B.; Fetoni, A.R.; Paludetti, G.; Ferraresi, A.; Navarra, P.; Mordente, A.; Troiani, D. Protective properties of idebenone in noise-induced hearing loss in the guinea pig. Neuroreport 2006, 17, 857–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fetoni, A.R.; Ferraresi, A.; La Greca, C.; Rizzo, D.; Sergi, B.; Tringali, G.; Piacentini, R.; Troiani, D. Antioxidant protection against acoustic trauma by coadministration of idebenone and vitamin E. Neuroreport 2008, 19, 277–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mordente, A.; Martorana, G.E.; Minotti, G.; Giardina, B. Antioxidant Properties of 2,3-Dimethoxy-5-methyl-6-(10-hydroxydecyl)-1,4-benzoquinone (Idebenone). Chem. Res. Toxicol. 1998, 11, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Seo, A.Y.; Vorobyeva, D.A.; Carter, C.S.; Anton, S.D.; Lezza, A.M.S.; Leeuwenburgh, C. Beneficial Effects of a Q-ter® Based Nutritional Mixture on Functional Performance, Mitochondrial Function, and Oxidative Stress in Rats. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e10572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergamini, C.; Moruzzi, N.; Sblendido, A.; Lenaz, G.; Fato, R. A Water Soluble CoQ10 Formulation Improves Intracellular Distribution and Promotes Mitochondrial Respiration in Cultured Cells. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e33712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keithley, E.M.; Wang, X.; Barkdull, G.C. Tumor Necrosis Factor α Can Induce Recruitment of Inflammatory Cells to the Cochlea. Otol. Neurotol. 2008, 29, 854–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oishi, N.; Schacht, J. Emerging treatments for noise-induced hearing loss. Expert Opin. Emerg. Drugs 2011, 16, 235–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.-Y.; Wu, J.-L.; Shih, T.-S.; Tsai, P.-J.; Sun, Y.-M.; Guo, Y.L. Glutathione S-transferase M1, T1, and P1 polymorphisms as susceptibility factors for noise-induced temporary threshold shift. Hear. Res. 2009, 257, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sliwinska-Kowalska, M.; Pawelczyk, M. Contribution of genetic factors to noise-induced hearing loss: A human studies review. Mutat. Res. Mol. Mech. Mutagen. 2013, 752, 61–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamasoba, T.; Pourbakht, A.; Sakamoto, T.; Suzuki, M. Ebselen prevents noise-induced excitotoxicity and temporary threshold shift. Neurosci. Lett. 2005, 380, 234–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traber, M.G.; Atkinson, J. Vitamin E, antioxidant and nothing more. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2007, 43, 4–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fetoni, A.R.; Ralli, M.; Sergi, B.; Parrilla, C.; Troiani, D.; Paludetti, G. Protective properties of antioxidant drugs in noise-induced hearing loss in the guinea pig. Audiol. Med. 2008, 6, 271–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohlemiller, K.K.; McFadden, S.L.; Ding, D.-L.; Lear, P.M.; Ho, Y.-S. Targeted Mutation of the Gene for Cellular Glutathione Peroxidase (Gpx1) Increases Noise-Induced Hearing Loss in Mice. J. Assoc. Res. Otolaryngol. 2000, 1, 243–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borel, P.; Desmarchelier, C. Bioavailability of Fat-Soluble Vitamins and Phytochemicals in Humans: Effects of Genetic Variation. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2018, 38, 69–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niforou, A.; Konstantinidou, V.; Naska, A. Genetic Variants Shaping Inter-individual Differences in Response to Dietary Intakes—A Narrative Review of the Case of Vitamins. Front. Nutr. 2020, 7, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, F.; Wang, S.; Zhai, S.; Hu, Y.; Yang, W.; He, L. Effects of α-tocopherol on noise-induced hearing loss in guinea pigs. Hear. Res. 2003, 179, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rybak, L.P.; Dhukhwa, A.; Mukherjea, D.; Ramkumar, V. Local Drug Delivery for Prevention of Hearing Loss. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopke, R.D.; Weisskopf, P.A.; Boone, J.L.; Jackson, R.L.; Wester, D.C.; Hoffer, M.E.; Lambert, D.C.; Charon, C.C.; Ding, D.-L.; McBride, D. Reduction of noise-induced hearing loss using L-NAC and salicylate in the chinchilla. Hear. Res. 2000, 149, 138–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, M.; Qiu, J.; Laurell, G.; Olofsson, Å.; Counter, S.A.; Borg, E. Dose and time-dependent protection of the antioxidant N-l-acetylcysteine against impulse noise trauma. Hear. Res. 2004, 192, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loukzadeh, Z.; Hakimi, A.; Esmailidehaj, M.; Mehrparvar, A.H. Effect of Ascorbic Acid on Noise Induced Hearing Loss in Rats. Iran. J. Otorhinolaryngol. 2015, 27, 267–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A Pryor, W. Vitamin E and heart disease: Basic science to clinical intervention trials. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2000, 28, 141–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Leeuw, F.A.; Honer, W.G.; Schneider, J.A.; Morris, M.C. Brain γ-Tocopherol levels are associated with presynaptic protein levels in elderly human midfrontal cortex. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2020, 77, 619–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, F.; Wang, S. Preventive effects of vitamin E on short-term noise-induced hearing loss in guinea pigs. Zhonghua Lao Dong Wei Sheng Zhi Ye Bing Za Zhi 2005, 23, 408–410. [Google Scholar]
- Fetoni, A.R.; Sergi, B.; Scarano, E.; Paludetti, G.; Ferraresi, A.; Troiani, D. Protective Effects of α-Tocopherol Against Gentamicin-induced Oto-vestibulo Toxicity: An Experimental Study. Acta Oto-Laryngol. 2003, 123, 192–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopke, R.; Slade, M.D.; Jackson, R.; Hammill, T.; Fausti, S.; Lonsbury-Martin, B.; Sanderson, A.; Dreisbach, L.; Rabinowitz, P.; Torre, P.; et al. Efficacy and safety of N-acetylcysteine in prevention of noise induced hearing loss: A randomized clinical trial. Hear. Res. 2015, 323, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohinata, Y.; Miller, J.M.; Schacht, J. Protection from noise-induced lipid peroxidation and hair cell loss in the cochlea. Brain Res. 2003, 966, 265–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, E.D.; Kil, J. Compounds for the prevention and treatment of noise-induced hearing loss. Drug Discov. Today 2005, 10, 1291–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niki, E.; Noguchi, N. Dynamics of Antioxidant Action of Vitamin E. Acc. Chem. Res. 2004, 37, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco-Llamero, C.; Fonseca, J.; Durazzo, A.; Lucarini, M.; Santini, A.; Señoráns, F.J.; Souto, E.B. Nutraceuticals and Food-Grade Lipid Nanoparticles: From Natural Sources to a Circular Bioeconomy Approach. Foods 2022, 11, 2318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Prell, C.G.; Lobarinas, E. Strategies for Evaluating Antioxidant Efficacy in Clinical Trials Assessing Prevention of Noise-Induced Hearing Loss. In Free Radicals in ENT Pathology; Miller, J., Le Prell, C.G., Rybak, L., Eds.; Oxidative Stress in Applied Basic Research and Clinical Practice; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 163–192. ISBN 978-3-319-13473-4. [Google Scholar]
- Fetoni, A.R.; Garzaro, M.; Ralli, M.; Landolfo, V.; Sensini, M.; Pecorari, G.; Mordente, A.; Paludetti, G.; Giordano, C. The monitoring role of otoacoustic emissions and oxidative stress markers in the protective effects of antioxidant administration in noise-exposed subjects: A pilot study. Experiment 2009, 15, 8. [Google Scholar]
- Passali, D.; Staffa, P.; Bellussi, L.; Cambi, J.; Mezzedimi, C. Activity of coenzyme Q10(Q-Ter multicomposite) on recovery time in noise-induced hearing loss. Noise Health 2014, 16, 265–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nam, D.W.; Park, S.S.; Lee, S.M.; Suh, M.-W.; Park, M.K.; Song, J.-J.; Choi, B.Y.; Lee, J.H.; Oh, S.H.; Moon, K.C.; et al. Effects of CoQ10 Replacement Therapy on the Audiological Characteristics of Pediatric Patients with COQ6 Variants. BioMed Res. Int. 2022, 2022, 5250254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joachims, H.Z.; Segal, J.; Golz, A.; Netzer, A.; Goldenberg, D. Antioxidants in Treatment of Idiopathic Sudden Hearing Loss. Otol. Neurotol. 2003, 24, 572–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gopinath, B.; Flood, V.M.; McMahon, C.M.; Burlutsky, G.; Spankovich, C.; Hood, L.J.; Mitchell, P. Dietary antioxidant intake is associated with the prevalence but not incidence of age-related hearing loss. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2011, 15, 896–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hatano, M.; Uramoto, N.; Okabe, Y.; Furukawa, M.; Ito, M. Vitamin E and vitamin C in the treatment of idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Acta Oto-Laryngol. 2008, 128, 116–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-J.; Um, J.-Y.; Kim, S.-H.; Hong, S.-H. Protective Effect of Rosmarinic Acid is Through Regulation of Inflammatory Cytokine in Cadmium-Induced Ototoxicity. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2013, 41, 391–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, T.; Tan, B.; Yin, Y.; Blachier, F.; Tossou, M.C.; Rahu, N. Oxidative Stress and Inflammation: What Polyphenols Can Do for Us? Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2016, 2016, 7432797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.-N.; Li, S.; Zhang, Y.-J.; Xu, X.-R.; Chen, Y.-M.; Li, H.-B. Resources and Biological Activities of Natural Polyphenols. Nutrients 2014, 6, 6020–6047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paciello, F.; Di Pino, A.; Rolesi, R.; Troiani, D.; Paludetti, G.; Grassi, C.; Fetoni, A.R. Anti-oxidant and anti-inflammatory effects of caffeic acid: In vivo evidences in a model of noise-induced hearing loss. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2020, 143, 111555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fetoni, A.R.; De Bartolo, P.; Eramo, S.L.M.; Rolesi, R.; Paciello, F.; Bergamini, C.; Fato, R.; Paludetti, G.; Petrosini, L.; Troiani, D. Noise-Induced Hearing Loss (NIHL) as a Target of Oxidative Stress-Mediated Damage: Cochlear and Cortical Responses after an Increase in Antioxidant Defense. J. Neurosci. 2013, 33, 4011–4023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang-Chien, J.; Yen, Y.-C.; Li, S.-Y.; Hsu, T.-C.; Yang, J.-J. Ferulic acid-mediated protection against neomycin-induced hair cell loss in transgenic zebrafish. J. Funct. Foods 2017, 28, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akdemir, F.; Gozeler, M.; Yildirim, S.; Askin, S.; Dortbudak, M.; Kiziltunc, A. The effect of ferulic acid against cisplatin-induced ototoxicit. Med. Sci. Int. Med. J. 2018, 7, 528–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fetoni, A.R.; Eramo, S.L.M.; DI Pino, A.; Rolesi, R.; Paciello, F.; Grassi, C.; Troiani, D.; Paludetti, G. The Antioxidant Effect of Rosmarinic Acid by Different Delivery Routes in the Animal Model of Noise-Induced Hearing Loss. Otol. Neurotol. 2018, 39, 378–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shetty, K. Rosmarinic Acid Biosynthesis and Mechanism of Action. Food Biotechnol. 2005, 165, 825–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tepe, B.; Eminagaoglu, O.; Akpulat, H.A.; Aydin, E. Antioxidant potentials and rosmarinic acid levels of the methanolic extracts of Salvia verticillata (L.) subsp. verticillata and S. verticillata (L.) subsp. amasiaca (Freyn & Bornm.) Bornm. Food Chem. 2007, 100, 985–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, X.; Ci, X.; He, J.; Jiang, L.; Wei, M.; Cao, Q.; Guan, M.; Xie, X.; Deng, X. Effects of a Natural Prolyl Oligopeptidase Inhibitor, Rosmarinic Acid, on Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Acute Lung Injury in Mice. Molecules 2012, 17, 3586–3598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kantar-Gok, D.; Hidisoglu, E.; Er, H.; Acun, A.D.; Olgar, Y.; Yargıcoglu, P. Changes of auditory event-related potentials in ovariectomized rats injected with d-galactose: Protective role of rosmarinic acid. Neurotoxicology 2017, 62, 64–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Hirose, K.; Liberman, M.C. Dynamics of Noise-Induced Cellular Injury and Repair in the Mouse Cochlea. J. Assoc. Res. Otolaryngol. 2002, 3, 248–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shizuki, K.; Ogawa, K.; Matsunobu, T.; Kanzaki, J.; Ogita, K. Expression of c-Fos after noise-induced temporary threshold shift in the guinea pig cochlea. Neurosci. Lett. 2002, 320, 73–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fetoni, A.; Paciello, F.; Rolesi, R.; Eramo, S.; Mancuso, C.; Troiani, D.; Paludetti, G. Rosmarinic acid up-regulates the noise-activated Nrf2/HO-1 pathway and protects against noise-induced injury in rat cochlea. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2015, 85, 269–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ealvarado, J.C.; Fuentes-Santamarã a, V.; Emelgar-Rojas, P.; Valero, M.L.; Gabaldã³N-Ull, M.C.; Miller, J.M.; Juiz, J.M. Synergistic effects of free radical scavengers and cochlear vasodilators: A new otoprotective strategy for age-related hearing loss. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2015, 7, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lenaz, G.; Baracca, A.; Fato, R.; Genova, M.L.; Solaini, G. New Insights into Structure and Function of Mitochondria and Their Role in Aging and Disease. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2006, 8, 417–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamasoba, T.; Someya, S.; Yamada, C.; Weindruch, R.; Prolla, T.A.; Tanokura, M. Role of mitochondrial dysfunction and mitochondrial DNA mutations in age-related hearing loss. Heart Res. 2007, 226, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birben, E.; Sahiner, U.M.; Sackesen, C.; Erzurum, S.; Kalayci, O. Oxidative Stress and Antioxidant Defense. World Allergy Organ. J. 2012, 5, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, R.; de Almodovar, C.R.; Bulteau, A.-L.; Gomes, C.M. Neurodegeneration, Neurogenesis, and Oxidative Stress. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2013, 2013, 730581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamm, K.; Arnold, W. The effect of blood flow promoting drugs on cochlear blood flow, perilymphatic pO2 and auditory function in the normal and noise-damaged hypoxic and ischemic guinea pig inner ear. Heart Res. 2000, 141, 199–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamane, H.; Nakai, Y.; Takayama, M.; Iguchi, H.; Nakagawa, T.; Kojima, A. Appearance of free radicals in the guinea pig inner ear after noise-induced acoustic trauma. Eur. Arch. Oto-Rhino-Laryngol. 1995, 252, 504–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, J.M.; Brown, J.N.; Schacht, J. 8-Iso-Prostaglandin F2α, a Product of Noise Exposure, Reduces Inner Ear Blood Flow. Audiol. Neurotol. 2003, 8, 207–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valencia, A.; Morán, J. Reactive oxygen species induce different cell death mechanisms in cultured neurons. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2004, 36, 1112–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.-H.; Miller, J.M.; Tucker, K.L.; Hu, H.; Park, S.K. Antioxidant vitamins and magnesium and the risk of hearing loss in the US general population. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2014, 99, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, M.; Pourrajab, B.; Tokhi, M.O. Protective effects of vitamins/antioxidants on occupational noise-induced hearing loss: A systematic review. J. Occup. Health 2021, 63, e12217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohinata, Y.; Yamasoba, T.; Schacht, J.; Miller, J.M. Glutathione limits noise-induced hearing loss. Heart Res. 2000, 146, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sataloff, R.T.; Bittermann, T.; Marks, L.; Lurie, D.; Hawkshaw, M. The effects of glutathione enhancement on sensorineural hearing loss. Ear Nose Throat J. 2010, 89, 422–433. [Google Scholar]
- Minami, S.B.; Yamashita, D.; Ogawa, K.; Schacht, J.; Miller, J.M. Creatine and tempol attenuate noise-induced hearing loss. Brain Res. 2007, 1148, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murashita, H.; Tabuchi, K.; Hoshino, T.; Tsuji, S.; Hara, A. The effects of tempol, 3-aminobenzamide and nitric oxide synthase inhibitors on acoustic injury of the mouse cochlea. Hear. Res. 2006, 214, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourbakht, A.; Yamasoba, T. Ebselen attenuates cochlear damage caused by acoustic trauma. Hear. Res. 2003, 181, 100–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kil, J.; Harruff, E.E.; Longenecker, R.J. Development of ebselen for the treatment of sensorineural hearing loss and tinnitus. Hear. Res. 2022, 413, 108209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorito, G.; Giordano, P.; Prosser, S.; Martini, A.; Hatzopoulos, S. Noise-induced hearing loss: A study on the pharmacological protection in the Sprague Dawley rat with N-acetyl-cysteine. Acta Otorhinolaryngol. Ital. 2006, 26, 133–139. [Google Scholar]
- Bielefeld, E.C.; Kopke, R.D.; Jackson, R.L.; Coleman, J.K.; Liu, J.; Henderson, D. Noise protection with N-acetyl-l-cysteine (NAC) using a variety of noise exposures, NAC doses, and routes of administration. Acta Oto-Laryngol. 2007, 127, 914–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopke, R.D.; Coleman, J.K.M.; Liu, J.; Campbell, K.C.M.; Riffenburgh, R.H. Enhancing Intrinsic Cochlear Stress Defenses to Reduce Noise-Induced Hearing Loss. Laryngoscope 2002, 112, 1515–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, K.; Claussen, A.; Meech, R.; Verhulst, S.; Fox, D.; Hughes, L. d-methionine (d-met) significantly rescues noise-induced hearing loss: Timing studies. Hear. Res. 2011, 282, 138–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rana, A.; Samtiya, M.; Dhewa, T.; Mishra, V.; Aluko, R.E. Health benefits of polyphenols: A concise review. J. Food Biochem. 2022, 46, e14264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganesan, K.; Xu, B. Polyphenol-Rich Lentils and Their Health Promoting Effects. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Prell, C.G.; Ohlemiller, K.K.; Gagnon, P.M.; Bennett, D.C. Reduction in Permanent Noise-Induced Threshold Deficits in Mice Fed a Combination of Dietary Agents. Abs. Assoc. Res. Otolaryngol. 2009, 32, 280. [Google Scholar]
- Fetoni, A.; Mancuso, C.; Eramo, S.; Ralli, M.; Piacentini, R.; Barone, E.; Paludetti, G.; Troiani, D. In vivo protective effect of ferulic acid against noise-induced hearing loss in the guinea-pig. Neuroscience 2010, 169, 1575–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancuso, C.; Scapagini, G.; Currò, D.; Giuffrida Stella, A.M.; De Marco, C.; Butterfield, D.A.; Calabrese, V. Mitochondrial Dysfunction, Free Radical Generation and Cellular Stress Response in Neurodegenerative Disorders. Front. Biosci. 2007, 12, 1107–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calabrese, V.; Calafato, S.; Puleo, E.; Cornelius, C.; Sapienza, M.; Morganti, P.; Mancuso, C. Redox regulation of cellular stress response by ferulic acid ethyl ester in human dermal fibroblasts: Role of vitagenes. Clin. Dermatol. 2008, 26, 358–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barone, E.; Calabrese, V.; Mancuso, C. Ferulic acid and its therapeutic potential as a hormetin for age-related diseases. Biogerontology 2009, 10, 97–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, E.-R.; Youn, C.K.; Jun, Y.; Cho, S.I. The protective role of ferulic acid against cisplatin-induced ototoxicity. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2019, 120, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, L.; Cui, X.; Wei, W.; Yang, J.; Li, X. Ferulic acid promotes survival and differentiation of neural stem cells to prevent gentamicin-induced neuronal hearing loss. Exp. Cell Res. 2017, 360, 257–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paciello, F.; Fetoni, A.R.; Mezzogori, D.; Rolesi, R.; Di Pino, A.; Paludetti, G.; Grassi, C.; Troiani, D. The dual role of curcumin and ferulic acid in counteracting chemoresistance and cisplatin-induced ototoxicity. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gok, D.K.; Hidisoglu, E.; Er, H.; Acun, A.D.; Yargıcoglu, P. Decrease of Auditory Evoked Delta, Alpha and Beta Oscillatory Responses in d-galactose Induced Aging Model: Effects of Rosmarinic Acid. Int. J. Gerontol. 2018, 12, 255–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, H.-J.; Choi, Y.; Kim, M.-H.; Kang, I.-C.; Lee, J.-H.; Park, C.; Park, R.; Kim, H.-M. Rosmarinic Acid, Active Component of Dansam-Eum Attenuates Ototoxicity of Cochlear Hair Cells through Blockage of Caspase-1 Activity. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e18815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakır, S.; Ozbay, M.; Gun, R.; Yorgancilar, E.; Kınış, V.; Keles, A.; Abakay, A.; Gökalp, O.; Topcu, I.; Yorgancılar, E.; et al. The protective role of caffeic acid phenethyl ester against streptomycin ototoxicity. Am. J. Otolaryngol. 2013, 34, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.; Kim, S.H.; Rah, Y.C.; Chae, S.W.; Lee, J.D.; Lee, B.D.; Park, M.K. Effects of caffeic acid on cisplatin-induced hair cell damage in HEI-OC1 auditory cells. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2014, 78, 2198–2204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozbay, M.; Sengul, E.; Kinis, V.; Alabalik, U.; Yilmaz, B.; Topcu, I. Effects of caffeic acid phenethyl ester on cisplatin ototoxicity. B-ENT 2016, 12, 211–218. [Google Scholar]
- Pandey, K.B.; Rizvi, S.I. Plant polyphenols as dietary antioxidants in human health and disease. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2009, 2, 270–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosme, P.; Rodríguez, A.B.; Espino, J.; Garrido, M. Plant Phenolics: Bioavailability as a Key Determinant of Their Potential Health-Promoting Applications. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidalgo-Gutiérrez, A.; González-García, P.; Díaz-Casado, M.; Barriocanal-Casado, E.; López-Herrador, S.; Quinzii, C.; López, L. Metabolic Targets of Coenzyme Q10 in Mitochondria. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fetoni, A.R.; Piacentini, R.; Fiorita, A.; Paludetti, G.; Troiani, D. Water-soluble Coenzyme Q10 formulation (Q-ter) promotes outer hair cell survival in a guinea pig model of noise induced hearing loss (NIHL). Brain Res. 2009, 1257, 108–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paciello, F.; Pisani, A.; Rolesi, R.; Escarrat, V.; Galli, J.; Paludetti, G.; Grassi, C.; Troiani, D.; Fetoni, A. Noise-Induced Cochlear Damage Involves PPAR Down-Regulation through the Interplay between Oxidative Stress and Inflammation. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fetoni, A.R.; Troiani, D.; Eramo, S.L.M.; Rolesi, R.; Troiani, G.P. Efficacy of different routes of administration for Coenzyme Q10 formulation in noise-induced hearing loss: Systemic versus transtympanic modality. Acta Oto-Laryngol. 2012, 132, 391–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wakabayashi, K.; Fujioka, M.; Kanzaki, S.; Okano, H.J.; Shibata, S.; Yamashita, D.; Masuda, M.; Mihara, M.; Ohsugi, Y.; Ogawa, K.; et al. Blockade of interleukin-6 signaling suppressed cochlear inflammatory response and improved hearing impairment in noise-damaged mice cochlea. Neurosci. Res. 2010, 66, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, W.J.T.; Thorne, P.R.; Vlajkovic, S.M. Characterisation of cochlear inflammation in mice following acute and chronic noise exposure. Histochem. Cell Biol. 2016, 146, 219–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Someya, S.; Xu, J.; Kondo, K.; Ding, D.; Salvi, R.J.; Yamasoba, T.; Rabinovitch, P.S.; Weindruch, R.; Leeuwenburgh, C.; Tanokura, M.; et al. Age-related hearing loss in C57BL/6J mice is mediated by Bak-dependent mitochondrial apoptosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 19432–19437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarado, J.C.; Fuentes-Santamaría, V.; Juiz, J.M. Antioxidants and Vasodilators for the Treatment of Noise-Induced Hearing Loss: Are They Really Effective? Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McFadden, S.L.; Woo, J.M.; Michalak, N.; Ding, D. Dietary vitamin C supplementation reduces noise-induced hearing loss in guinea pigs. Hear. Res. 2005, 202, 200–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clifford, R.E.; Coleman, J.K.M.; Balough, B.J.; Liu, J.; Kopke, R.D.; Jackson, R.L. Low-Dose D-Methionine and N-Acetyl-L-Cysteine for Protection from Permanent Noise-Induced Hearing Loss in Chinchillas. Otolaryngol. Neck Surg. 2011, 145, 999–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricciarelli, R.; Zingg, J.-M.; Azzi, A. Vitamin E: Protective role of a Janus molecule. FASEB J. 2001, 15, 2314–2325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meulmeester, F.L.; Luo, J.; Martens, L.G.; Mills, K.; van Heemst, D.; Noordam, R. Antioxidant Supplementation in Oxidative Stress-Related Diseases: What Have We Learned from Studies on Alpha-Tocopherol? Antioxidants 2022, 11, 2322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gugliandolo, A.; Bramanti, P.; Mazzon, E. Role of Vitamin E in the Treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease: Evidence from Animal Models. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fetoni, A.R.; Ralli, M.; Sergi, B.; Parrilla, C.; Troiani, D.; Paludetti, G. Protective effects of N-acetylcysteine on noise-induced hearing loss in guinea pigs. Acta Otorhinolaryngol. Ital. 2009, 29, 70–75. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, C.-H.; Chen, K.; Vasquez-Weldon, A.; Jackson, R.L.; Floyd, R.A.; Kopke, R.D. Effectiveness of 4-hydroxy phenyl N-tertbutylnitrone (4-OHPBN) alone and in combination with other antioxidant drugs in the treatment of acute acoustic trauma in chinchilla. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2008, 44, 1772–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marie, A.; Meunier, J.; Brun, E.; Malmstrom, S.; Baudoux, V.; Flaszka, E.; Naert, G.; Roman, F.; Cosnier-Pucheu, S.; Gonzalez-Gonzalez, S. N-acetylcysteine Treatment Reduces Age-related Hearing Loss and Memory Impairment in the Senescence-Accelerated Prone 8 (SAMP8) Mouse Model. Aging Dis. 2018, 9, 664–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feghali, J.G.; Liu, W.; Van De Water, T.R. L-N-Acetyl-Cysteine Protection Against Cisplatin-Induced Auditory Neuronal and Hair Cell Toxicity. Laryngoscope 2001, 111, 1147–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamernik, R.P.; Qiu, W.; Davis, B. The effectiveness of N-acetyl-l-cysteine (l-NAC) in the prevention of severe noise-induced hearing loss. Hear. Res. 2008, 239, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fetoni, A.R.; Sergi, B.; Ferraresi, A.; Paludetti, G.; Troiani, D. Protective effects of α-tocopherol and tiopronin against cisplatin-induced ototoxicity. Acta Oto-Laryngol. 2004, 124, 421–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tillinger, J.A.; Gupta, C.; Ila, K.; Ahmed, J.; Mittal, J.; Van De Water, T.R.; Eshraghi, A.A. l-N-acetylcysteine protects outer hair cells against TNFα initiated ototoxicity in vitro. Acta Oto-Laryngol. 2018, 138, 676–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tardiolo, G.; Bramanti, P.; Mazzon, E. Overview on the Effects of N-Acetylcysteine in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Molecules 2018, 23, 3305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.-P.; Hsu, C.-J.; Cheng, T.-J.; Guo, Y.L. N-acetylcysteine attenuates noise-induced permanent hearing loss in diabetic rats. Hear. Res. 2010, 267, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopke, R.; Bielefeld, E.; Liu, J.; Zheng, J.; Jackson, R.; Henderson, D.; Coleman, J.K.M. Prevention of impulse noise-induced hearing loss with antioxidants. Acta Oto-Laryngol. 2005, 125, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCleery, J.; Abraham, R.P.; A Denton, D.; Rutjes, A.W.S.; Chong, L.-Y.; Al-Assaf, A.S.; Griffith, D.J.; Rafeeq, S.; Yaman, H.; A Malik, M.; et al. Vitamin and mineral supplementation for preventing dementia or delaying cognitive decline in people with mild cognitive impairment. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2018, 2019, CD011905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akhondzadeh, S.; Noroozian, M.; Mohammadi, M.; Ohadinia, S.; Jamshidi, A.H.; Khani, M. Salvia officinalis extract in the treatment of patients with mild to moderate Alzheimer’s disease: A double blind, randomized and placebo-controlled trial. J. Clin. Pharm. Ther. 2003, 28, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halliwell, B. The antioxidant paradox. Lancet 2000, 355, 1179–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhakta-Guha, D.; Efferth, T. Hormesis: Decoding Two Sides of the Same Coin. Pharmaceuticals 2015, 8, 865–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abourashed, E.A. Bioavailability of Plant-Derived Antioxidants. Antioxidants 2013, 2, 309–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, M.-K.; Itoh, K.; Yamamoto, M.; Kensler, T.W. Enhanced Expression of the Transcription Factor Nrf2 by Cancer Chemopreventive Agents: Role of Antioxidant Response Element-Like Sequences in the nrf2 Promoter. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2002, 22, 2883–2892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghunath, A.; Sundarraj, K.; Nagarajan, R.; Arfuso, F.; Bian, J.; Kumar, A.P.; Sethi, G.; Perumal, E. Antioxidant response elements: Discovery, classes, regulation and potential applications. Redox Biol. 2018, 17, 297–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, D. Pharmacogenetics: An Important Part of Drug Development with A Focus on Its Application. Int. J. Biomed. Investig. 2018, 1, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadros, S.F.; D’Souza, M.; Zhu, X.; Frisina, R.D. Gene Expression Changes for Antioxidants Pathways in the Mouse Cochlea: Relations to Age-related Hearing Deficits. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e90279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.-M.; Xue, X.-M.; Yu, N.; Guo, W.-W.; Yuan, S.-L.; Jiang, Q.-Q.; Yang, S.-M. The Role of Genetic Variants in the Susceptibility of Noise-Induced Hearing Loss. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabinowitz, P.M.; Wise, J.P.; Mobo, B.H.; Antonucci, P.G.; Powell, C.; Slade, M. Antioxidant status and hearing function in noise-exposed workers. Hear. Res. 2002, 173, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortunato, G.; Marciano, E.; Zarrilli, F.; Mazzaccara, C.; Intrieri, M.; Calcagno, G.; Vitale, D.F.; La Manna, P.; Saulino, C.; Marcelli, V.; et al. Paraoxonase and Superoxide Dismutase Gene Polymorphisms and Noise-Induced Hearing Loss. Clin. Chem. 2004, 50, 2012–2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldim, I.; Oliveira, A.M.; Souto, E.B.; Oliveira, W.P. Cyclodextrins-in-Liposomes: A Promising Delivery System for Lippia sidoides and Syzygium aromaticum Essential Oils. Life 2022, 12, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, I.; Yehye, W.A.; Etxeberria, A.E.; Alhadi, A.A.; Dezfooli, S.M.; Julkapli, N.B.M.; Basirun, W.J.; Seyfoddin, A. Nanoantioxidants: Recent Trends in Antioxidant Delivery Applications. Antioxidants 2019, 9, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ulasov, A.V.; Rosenkranz, A.A.; Georgiev, G.P.; Sobolev, A.S. Nrf2/Keap1/ARE signaling: Towards specific regulation. Life Sci. 2022, 291, 120111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Dong, M. Nrf2 as a potential target for Parkinson’s disease therapy. J. Mol. Med. 2021, 99, 917–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, M.E.D.C.A.D.; da Costa, K.V.T.; Vitorino, P.A.; Bueno, N.; Menezes, P. Effect of antioxidant supplementation on the auditory threshold in sensorineural hearing loss: A meta-analysis. Braz. J. Otorhinolaryngol. 2018, 84, 368–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meydani, S.N.; Meydani, M.; Blumberg, J.B.; Leka, L.S.; Pedrosa, M.; Diamond, R.; Schaefer, E.J. Assessment of the safety of supplementation with different amounts of vitamin E in healthy older adults. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1998, 68, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsueh, Y.-J.; Chen, Y.-N.; Tsao, Y.-T.; Cheng, C.-M.; Wu, W.-C.; Chen, H.-C. The Pathomechanism, Antioxidant Biomarkers, and Treatment of Oxidative Stress-Related Eye Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grover, A.K.; Samson, S.E. Benefits of antioxidant supplements for knee osteoarthritis: Rationale and reality. Nutr. J. 2016, 15, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tenório, M.C.d.S.; Graciliano, N.G.; Moura, F.; de Oliveira, A.C.M.; Goulart, M.O.F. N-Acetylcysteine (NAC): Impacts on Human Health. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, X.; Wang, M.; Niu, X.; Yu, H.; Yue, J.; Sun, Y. Effect of N-acetyl-cysteine treatment on sensorineural hearing loss: A meta-analysis. World J. Otorhinolaryngol.-Head Neck Surg. 2022, 8, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilles, A.; Ihtijarevic, B.; Wouters, K.; Van de Heyning, P. Using prophylactic antioxidants to prevent noise-induced hearing damage in young adults: A protocol for a double-blind, randomized controlled trial. Trials 2014, 15, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotfi, Y.; Moossavi, A.; Bakhshi, E.; Talasaz, A.H.; Hoorzad, A.; Doosti, A. Comparison of the effects of N-acetyl-cysteine and ginseng in prevention of noise induced hearing loss in male textile workers. Noise Health 2014, 16, 223–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.-Y.; Wu, J.-L.; Shih, T.-S.; Tsai, P.-J.; Sun, Y.-M.; Ma, M.-C.; Guo, Y.L. N-Acetyl-cysteine against noise-induced temporary threshold shift in male workers. Hear. Res. 2010, 269, 42–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angeli, S.I.; Abi-Hachem, R.N.; Vivero, R.J.; Telischi, F.T.; Machado, J.J. L-N-Acetylcysteine treatment is associated with improved hearing outcome in sudden idiopathic sensorineural hearing loss. Acta Oto-Laryngol. 2012, 132, 369–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-H.; Young, Y.-H. N-acetylcysteine as a single therapy for sudden deafness. Acta Oto-Laryngol. 2017, 137, 58–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.-L.; Ho, C.-Y.; Chin, S.-C. Effects of oral N-acetylcysteine combined with oral prednisolone on idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Medicine 2022, 101, e29792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Antioxidant Compound | Molecular Mechanisms | Experimental Studies | Clinical Studies |
|---|---|---|---|
| CoQ10, Q-Ter (soluble form) and Idebeneone (Q-Ter analogue) | ↓ROS ↓antiapoptosis ↓NF-κB ↓pro-inflammatory cytokines ↑SOD | [9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17] | [18,19,20] |
| Vitamin E and α-tocopherol | ↑GSH ↑SOD | [21,22,23] | [24,25,26] |
| N-acetyl, L-cysteine (NAC) | ↓ROS ↑GSH synthesis ↓NF-κB | [27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37] | [38,39,40,41,42,43,44,45,46,47] |
| Caffeic acid | ↓ROS and RNS ↓NF-κB and IL-1β ↑Nrf2/HO-1 pathway ↑SOD and GSH | [48,49,50,51] | -------- |
| Ferulic acid | ↑Nrf2/HO-1 pathway ↓vascular damage | [41,43,44,45,46,47,48,49] | --------- |
| Rosmarinic acid | ↑Nrf2/HO-1 pathway ↓NF-κB | [52,53,54,55,56,57,58,59] | ---------- |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pisani, A.; Paciello, F.; Montuoro, R.; Rolesi, R.; Galli, J.; Fetoni, A.R. Antioxidant Therapy as an Effective Strategy against Noise-Induced Hearing Loss: From Experimental Models to Clinic. Life 2023, 13, 1035. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13041035
Pisani A, Paciello F, Montuoro R, Rolesi R, Galli J, Fetoni AR. Antioxidant Therapy as an Effective Strategy against Noise-Induced Hearing Loss: From Experimental Models to Clinic. Life. 2023; 13(4):1035. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13041035
Chicago/Turabian StylePisani, Anna, Fabiola Paciello, Raffaele Montuoro, Rolando Rolesi, Jacopo Galli, and Anna Rita Fetoni. 2023. "Antioxidant Therapy as an Effective Strategy against Noise-Induced Hearing Loss: From Experimental Models to Clinic" Life 13, no. 4: 1035. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13041035
APA StylePisani, A., Paciello, F., Montuoro, R., Rolesi, R., Galli, J., & Fetoni, A. R. (2023). Antioxidant Therapy as an Effective Strategy against Noise-Induced Hearing Loss: From Experimental Models to Clinic. Life, 13(4), 1035. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13041035