Diagnostics 2023, 13(2), 181; https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13020181 - 4 Jan 2023
Cited by 5 | Viewed by 2700
Abstract
Glioblastoma (GBM) is regarded as an aggressive brain tumor that rarely develops extracranial metastases. Despite well-investigated molecular alterations in GBM, there is a limited understanding of these associated with the metastatic potential. We herein present a case report of a 43-year-old woman with
[...] Read more.
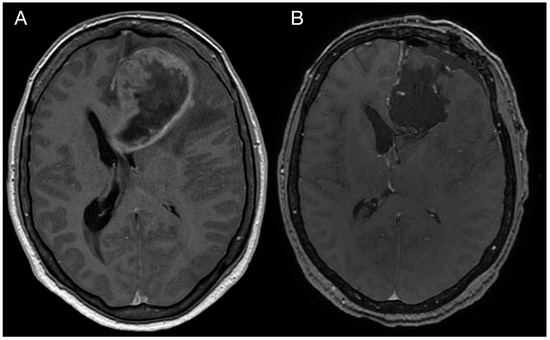
Glioblastoma (GBM) is regarded as an aggressive brain tumor that rarely develops extracranial metastases. Despite well-investigated molecular alterations in GBM, there is a limited understanding of these associated with the metastatic potential. We herein present a case report of a 43-year-old woman with frontal GBM with primitive neuronal component who underwent gross total resection followed by chemoradiation. Five months after surgery, the patient was diagnosed with an intraspinal GBM metastasis. Next-generation sequencing analysis of both the primary and metastatic GBM tissues was performed using the Illumina TruSight Tumor 170 assay. The number of single nucleotide variants observed in the metastatic sample was more than two times higher. Mutations in TP53, PTEN, and RB1 found in the primary and metastatic tissue samples indicated the mesenchymal molecular GBM subtype. Among others, there were two inactivating mutations (Arg1026Ile, Trp1831Ter) detected in the NF1 gene, two novel NOTCH3 variants of unknown significance predicted to be damaging (Pro1505Thr, Cys1099Tyr), one novel ARID1A variant of unknown significance (Arg1046Ser), and one gene fusion of unknown significance, EIF2B5-KIF5B, in the metastatic sample. Based on the literature evidence, the alterations of NF1, NOTCH3, and ARID1A could explain, at least in part, the acquired invasiveness and metastatic potential in this particular GBM case.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Advances in the Pathology of Lung, Brain, and Heart Diseases)
►
Show Figures