Rejuvenation-to-Relaxation Transition Induced by Elastostatic Compression and Its Effect on Deformation Behavior in a Zr-Based Bulk Metallic Glass
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- modifying compositions of BMGs;
2. Experimental Methods
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Mechanical Performance
3.2. Differential Scanning Calorimetry Measurement
3.3. Nanoindentation Creep Deformation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ghidelli, M.; Orekhov, A.; Bassi, A.L.; Terraneo, G.; Djemia, P.; Abadias, G.; Nord, M.; Béché, A.; Gauquelin, N.; Verbeeck, J.; et al. Novel class of nanostructured metallic glass films with superior and tunable mechanical properties. Acta Mater. 2021, 213, 116955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.H. Roles of minor additions in formation and properties of bulk metallic glasses. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2007, 52, 540–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.H.; Wang, G.; Wang, R.J.; Zhao, D.Q.; Pan, M.X.; Wang, W.H. Super plastic bulk metallic glasses at room temperature. Science 2007, 315, 1385–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nandam, S.H.; Ivanisenko, Y.; Schwaiger, R.; Śniadecki, Z.; Mu, X.; Wang, D.; Chellali, R.; Boll, T.; Kilmametov, A.; Bergfeldt, T.; et al. Cu-Zr nanoglasses: Atomic structure, thermal stability and indentation properties. Acta Mater. 2017, 136, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazlov, A.I.; Igrevskaya, A.G.; Tabachkova, N.Y.; Chen, C.; Cheverikin, V.V.; Pozdniakov, A.V.; Jiang, J.; Louzguine-Luzgin, D.V. Thermo-mechanical processing of a Zr62.5Cu22.5Fe5Al10 glassy alloy as a way to obtain tensile ductility. J. Alloy. Compd. 2021, 853, 157138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Zhao, Z.; Mu, J.; Wang, Y. Effect of pre-plastic-deformation on mechanical properties of TiZr-based amorphous alloy composites. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2018, 716, 23–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, S.D.; Chan, K.C.; Zhao, L.; Pan, S.P.; Qi, L.; Wang, L.M.; Liu, R.P. Rejuvenation by weakening the medium range order in Zr46Cu46Al8 metallic glass with pressure preloading: A molecular dynamics simulation study. Mater. Des. 2018, 158, 248–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Shen, J.; Sun, Y.H.; Ke, H.B.; Sun, B.A.; Wang, W.H.; Bai, H.Y. Composition and size dependent torsion fracture of metallic glasses. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2021, 82, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, G.H.; Jiang, M.Q.; Liu, X.F.; Dai, L.H.; Li, J.X. In-situ observations on shear-banding process during tension of a Zr-based bulk metallic glass composite with dendrites. J. Non Cryst. Solids 2021, 565, 120841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmann, D.C.; Suh, J.Y.; Wiest, A.; Duan, G.; Lind, M.L.; Demetriou, M.D.; Johnson, W.L. Designing metallic glass matrix composites with high toughness and tensile ductility. Nature 2008, 451, 1085–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, R.; Yang, S.; Chang, Y.; Li, Y.F.; Zhang, C.J.; He, L. Mechanical property degradation of a CuZr-based bulk metallic glass composite induced by sub-Tg annealing. Mater. Des. (1980–2015) 2014, 56, 128–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, J.C.; Wang, Q.; Pelletier, J.M.; Kato, H.; Casalini, R.; Crespo, D.; Pineda, E.; Yao, Y.; Yang, Y. Structural heterogeneities and mechanical behavior of amorphous alloys. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2019, 104, 250–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Maaß, R. Elastic Fluctuations and Structural Heterogeneities in Metallic Glasses. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1800388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Yin, Y.Y.; Gong, Y.; Gu, L.; Wang, W.H.; Bai, H.Y. High stored energy of metallic glasses induced by high pressure. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2017, 110, 111901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.W.; Cao, Q.P.; Chen, L.Y.; Wang, X.D.; Jiang, J.Z. Shear band evolution and hardness change in cold-rolled bulk metallic glasses. Acta Mater. 2010, 58, 4827–4840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di, S.Y.; Wang, Q.Q.; Zhou, J.; Shen, Y.Y.; Li, J.Q.; Zhu, M.Y.; Yin, K.B.; Zeng, Q.S.; Sun, L.T.; Shen, B.L. Enhancement of plasticity for FeCoBSiNb bulk metallic glass with superhigh strength through cryogenic thermal cycling. Scr. Mater. 2020, 187, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ketov, S.V.; Trifonov, A.S.; Ivanov, Y.P.; Churyumov, A.Y.; Lubenchenko, A.V.; Batrakov, A.A.; Jiang, J.; Louzguine-Luzgin, D.V.; Eckert, J.; Orava, J.; et al. On cryothermal cycling as a method for inducing structural changes in metallic glasses. NPG Asia Mater. 2018, 10, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ketov, S.V.; Sun, Y.H.; Nachum, S.; Lu, Z.; Checchi, A.; Beraldin, A.R.; Bai, H.Y.; Wang, W.H.; Louzguine-Luzgin, D.V.; Carpenter, M.A.; et al. Rejuvenation of metallic glasses by non-affine thermal strain. Nature 2015, 524, 200–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, B.S.; Xie, S.; Kruzic, J.J. Toughness enhancement and heterogeneous softening of a cryogenically cycled Zr–Cu–Ni–Al–Nb bulk metallic glass. Acta Mater. 2019, 176, 278–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.C.; Lee, C.M.; Lee, J.C.; Kim, H.J.; Shibutani, Y.; Fleury, E.; Falk, M.L. Structural disordering process of an amorphous alloy driven by the elastostatic compression at room temperature. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2008, 92, 151906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.C.; Lee, C.M.; Yang, J.W.; Lee, J.C. Microstructural evolution of an elastostatically compressed amorphous alloy and its influence on the mechanical properties. Scr. Mater. 2008, 58, 591–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.C. Irreversible Structural Change Induced by Elastostatic Stress imposed on an Amorphous Alloy and Its Influence on the Mechanical Properties. Met. Mater. Int. 2008, 14, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashim, I.M.; Ghazi, I.F.; Kuzichkin, O.R.; Shakirova, I.A.; Surendar, A.; Thangavelu, L.; Dorofeev, A.E.; Zhu, Y. Effects of Primary Stored Energy on Relaxation Behavior of High Entropy Bulk Metallic Glasses Under Compressive Elastostatic Loading. Trans. Indian Inst. Met. 2021, 74, 1295–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samavatian, M.; Gholamipour, R.; Amadeh, A.A.; Mirdamadi, S. Role of tensile elastostatic loading on atomic structure and mechanical properties of Zr55Cu30Ni5Al10 bulk metallic glass. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2019, 753, 218–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, R.; Chang, Y.; Li, Y.F.; Li, G.; Yang, S.; Zhang, C.J.; He, L. Effect of lateral pre-compression on the compressive behavior of a CuZr-based bulk metallic glass composite containing B2-CuZr phase. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2013, 587, 233–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Q.; Zhang, K.; Wang, Y.; Leng, J.; Jia, H.; Liaw, P.K.; Wang, Y. Effects of pre-compression on the microstructure, mechanical properties and corrosion resistance of RE65Co25Al10 (RE=Ce, La, Pr, Sm and Gd) bulk metallic glasses. Intermetallics 2015, 67, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, Y.; Dmowski, W.; Bei, H.; Yokoyama, Y.; Egami, T. Mechanical rejuvenation in bulk metallic glass induced by thermo-mechanical creep. Acta Mater. 2018, 148, 384–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samavatian, M.; Gholamipour, R.; Amadeh, A.A.; Mirdamadi, S. Extra rejuvenation of Zr55Cu30Al10Ni5 bulk metallic glass using elastostatic loading and cryothermal treatment interaction. J. Non Cryst. Solids 2019, 506, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.D.; Song, S.L.; Zhu, Z.W.; Zhang, H.F.; Ren, X.C. Structural evolution under elastic cyclic loading in a Ti-based metallic glass. J. Non Cryst. Solids 2022, 577, 121263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samavatian, M.; Gholamipour, R.; Amadeh, A.A.; Samavatian, V. Inherent relation between atomic-level stresses and nanoscale heterogeneity in Zr-based bulk metallic glass under a rejuvenation process. Phys. B Condens. Matter 2020, 595, 412390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Shi, B.; Wang, J.; Xu, Y.; Jin, P. Rejuvenation of a naturally aged bulk metallic glass by elastostatic loading. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2021, 806, 140843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.W.; Lee, C.M.; Wakeda, M.; Shibutani, Y.; Falk, M.L.; Lee, J.C. Elastostatically induced structural disordering in amorphous alloys. Acta Mater. 2008, 56, 5440–5450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argon, A.S.; Salama, M. The Mechanism of fracture in glassy materials capable of some inelastic deformation. Mater. Sci. Eng. 1976, 23, 219–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghidelli, M.; Gravier, S.; Blandin, J.J.; Raskin, J.P.; Lani, F.; Pardoen, T. Size-dependent failure mechanisms in ZrNi thin metallic glass films. Scr. Mater. 2014, 89, 9–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Wang, L.; Ge, J.; Wu, Z.; Ke, Y.; Li, Q.; Sun, B.; Feng, T.; Wu, Y.; Wang, J.T.; et al. Deformation-enhanced hierarchical multiscale structure heterogeneity in a Pd-Si bulk metallic glass. Acta Mater. 2020, 200, 42–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.B.; Qu, D.D.; Wang, X.H.; Cao, Y.; Liao, X.Z.; Kawasaki, M.; Ringer, S.P.; Shan, Z.W.; Langdon, T.G.; Shen, J. Introducing a strain-hardening capability to improve the ductility of bulk metallic glasses via severe plastic deformation. Acta Mater. 2012, 60, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores, K.M.; Sherer, E.; Bharathula, A.; Chen, H.; Jean, Y.C. Sub-nanometer open volume regions in a bulk metallic glass investigated by positron annihilation. Acta Mater. 2007, 55, 3403–3411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhowmick, R.; Raghavan, R.; Chattopadhyay, K.; Ramamurty, U. Plastic flow softening in a bulk metallic glass. Acta Mater. 2006, 54, 4221–4228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, Z.L.; Hufnagel, T.C. Characterization of nanometer-scale defects in metallic glasses by quantitative high-resolution transmission electron microscopy. Phys. Rev. B 2002, 65, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, J.; Spaepen, F.; Hufnagel, T.C. Nanometre scale defects in shear bands in a metallic glass. Philos. Mag. A 2002, 82, 2623–2630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, W.; Wei, X.; Liu, S.N.; Liu, Y.; Lan, S.; Wang, J.T. Negative Strain Rate Sensitivity Induced by Structure heterogeneity in ZrCuAlNi bulk metallic glasses. Metals 2021, 11, 339. [Google Scholar]
- Dubach, A.; Dallatorre, F.; Loffler, J. Constitutive model for inhomogeneous flow in bulk metallic glasses. Acta Mater. 2009, 57, 881–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, C.C.; Lv, Z.W.; Pang, C.M.; Zhu, W.W.; Wang, X.L.; Shen, B.L. Pronounced nanoindentation creep deformation in Cu-doped CoFe-based metallic glasses. J. Alloy. Compd. 2019, 806, 246–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Z.W.; Yuan, C.C.; Ke, H.B.; Shen, B.L. Defects activation in CoFe-based metallic glasses during creep deformation. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2021, 69, 42–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.C.; Lu, J.; Liu, C.T.; Wang, Q.; Yang, Y. Atomistic free-volume zones and inelastic deformation of metallic glasses. Nat. Mater. 2010, 9, 619–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, H.B.; Zhang, P.; Sun, B.A.; Zhang, P.G.; Liu, T.W.; Chen, P.H.; Wu, M.; Huang, H.G. Dissimilar nanoscaled structural heterogeneity in U-based metallic glasses revealed by nanoindentation. J. Alloy. Compd. 2019, 788, 391–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, C.C.; Liu, R.; Pang, C.M.; Zuo, X.F.; Li, B.F.; Song, S.C.; Hu, J.Y.; Zhu, W.W.; Shen, B.L. Anelastic and viscoplastic deformation in a Fe-based metallic glass. J. Alloy. Compd. 2021, 853, 157233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, C.C.; Lv, Z.W.; Pang, C.M.; Li, X.; Liu, R.; Yang, C.; Ma, J.; Ke, H.B.; Wang, W.H.; Shen, B.L. Ultrasonic-assisted plastic flow in a Zr-based metallic glass. Sci. China Mater. 2020, 64, 448–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




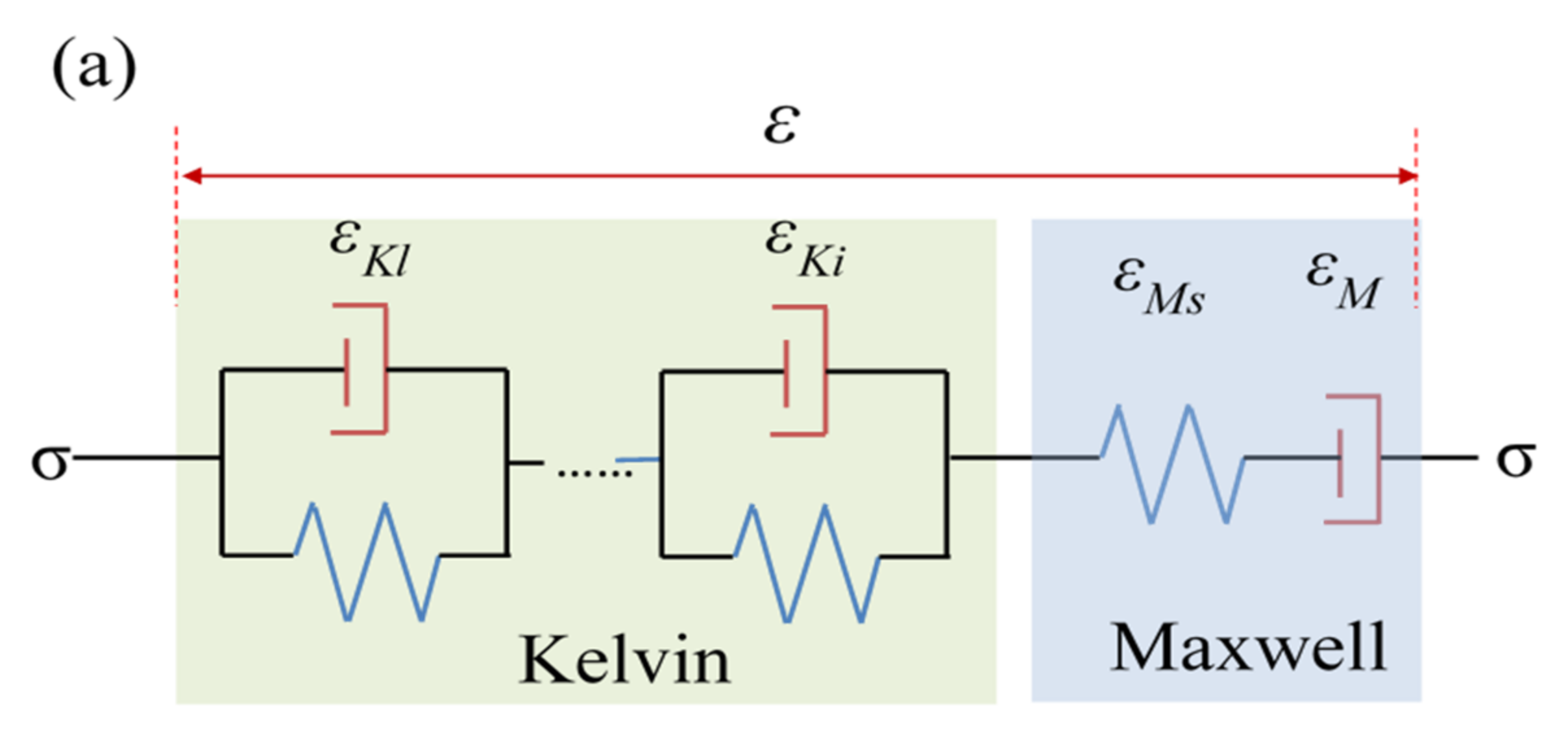
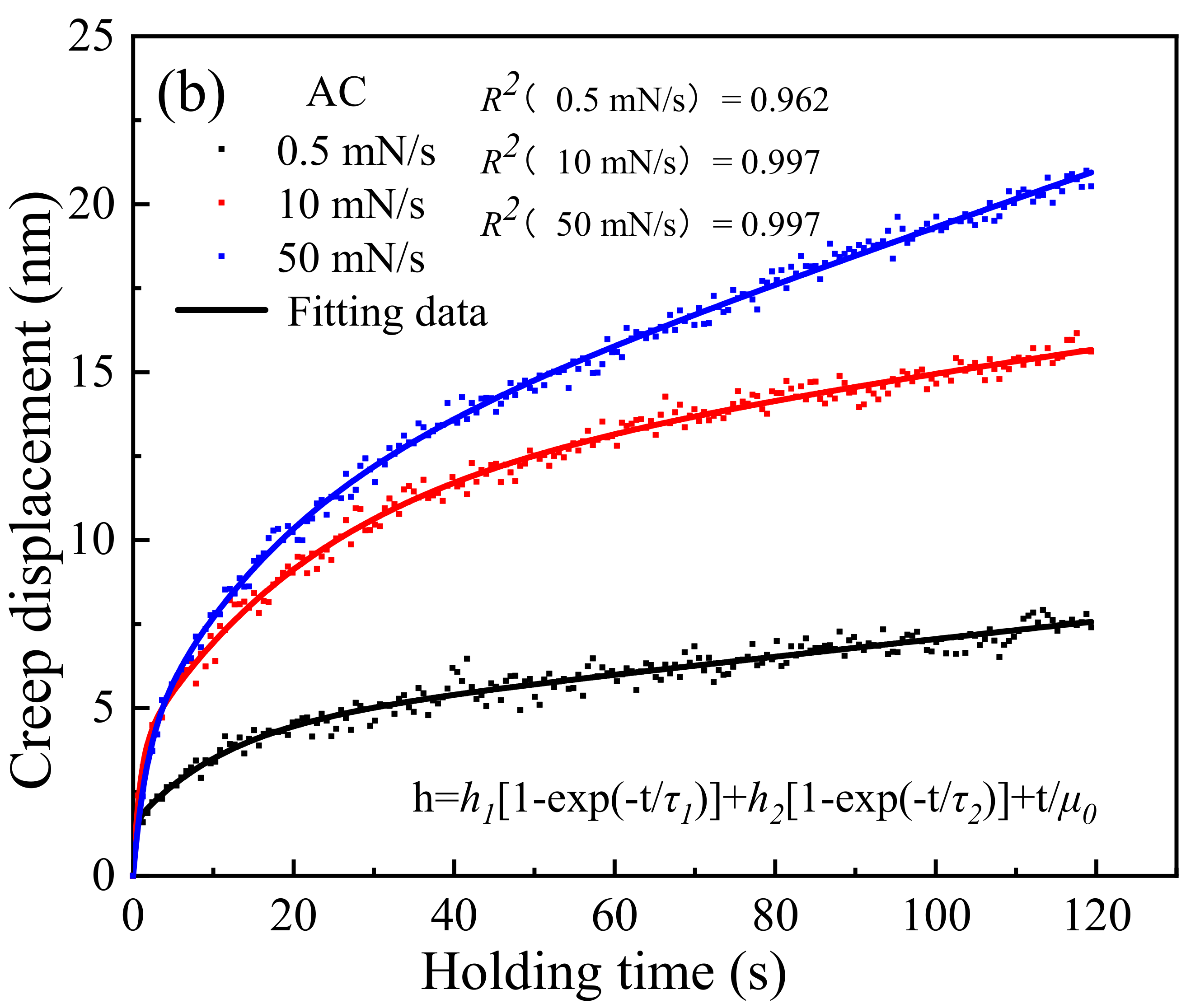

| Sample | Loading Rate (mN/s) | h1 (nm) | τ1 (s) | h2 (nm) | τ2 (s) | μ0−1 (nm/s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AC | 0.5 | 1.54 ± 0.18 | 0.30 ± 0.23 | 2.88 ± 0.17 | 11.36 ± 1.39 | 0.03 |
| 10 | 4.83 ± 0.20 | 1.76 ± 0.18 | 8.06 ± 0.46 | 30.13 ± 3.20 | 0.06 | |
| 50 | 3.68 ± 0.27 | 1.62 ± 0.24 | 7.34 ± 0.21 | 17.56 ± 1.24 | 0.083 | |
| T20 | 0.5 | 2.38 ± 0.21 | 8.28 ± 1.12 | 1.24 ± 0.23 | 0.62 ± 0.33 | 0.04 |
| 10 | 12.59 ± 0.15 | 18.43 ± 0.59 | 3.81 ± 0.17 | 1.06 ± 0.14 | 0.18 | |
| 50 | 5.42 ± 0.20 | 1.41 ± 0.13 | 12.92 ± 0.19 | 20.61 ± 0.82 | 0.15 | |
| T40 | 0.5 | 0.69 ± 0.17 | 0.52 ± 0.50 | 3.14 ± 0.15 | 11.89 ± 1.17 | 0.02 |
| 10 | 5.06 ± 0.17 | 1.45 ± 0.14 | 14.34 ± 0.51 | 32.09 ± 1.89 | 0.05 | |
| 50 | 3.70 ± 0.17 | 1.15 ± 0.15 | 10.13 ± 0.18 | 21.28 ± 0.98 | 0.05 | |
| T60 | 0.5 | 1.05 ± 0.15 | 0.24 ± 0.31 | 2.59 ± 0.14 | 11.87 ± 1.38 | 0.07 |
| 10 | 14.28 ± 0.25 | 24.87 ± 0.92 | 5.07 ± 0.15 | 1.10 ± 0.10 | 0.12 | |
| 50 | 6.05 ± 0.20 | 1.30 ± 0.12 | 12.35 ± 0.24 | 23.10 ± 1.11 | 0.15 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cui, J.; Luo, Q.; Di, S.; Zhang, Z.; Shen, B. Rejuvenation-to-Relaxation Transition Induced by Elastostatic Compression and Its Effect on Deformation Behavior in a Zr-Based Bulk Metallic Glass. Metals 2022, 12, 282. https://doi.org/10.3390/met12020282
Cui J, Luo Q, Di S, Zhang Z, Shen B. Rejuvenation-to-Relaxation Transition Induced by Elastostatic Compression and Its Effect on Deformation Behavior in a Zr-Based Bulk Metallic Glass. Metals. 2022; 12(2):282. https://doi.org/10.3390/met12020282
Chicago/Turabian StyleCui, Jingxian, Qiang Luo, Siyi Di, Zhengguo Zhang, and Baolong Shen. 2022. "Rejuvenation-to-Relaxation Transition Induced by Elastostatic Compression and Its Effect on Deformation Behavior in a Zr-Based Bulk Metallic Glass" Metals 12, no. 2: 282. https://doi.org/10.3390/met12020282
APA StyleCui, J., Luo, Q., Di, S., Zhang, Z., & Shen, B. (2022). Rejuvenation-to-Relaxation Transition Induced by Elastostatic Compression and Its Effect on Deformation Behavior in a Zr-Based Bulk Metallic Glass. Metals, 12(2), 282. https://doi.org/10.3390/met12020282







