Effects of Contaminations on Electric Arc Behavior and Occurrence of Defects in Wire Arc Additive Manufacturing of 316L-Si Stainless Steel
Abstract
1. Introduction
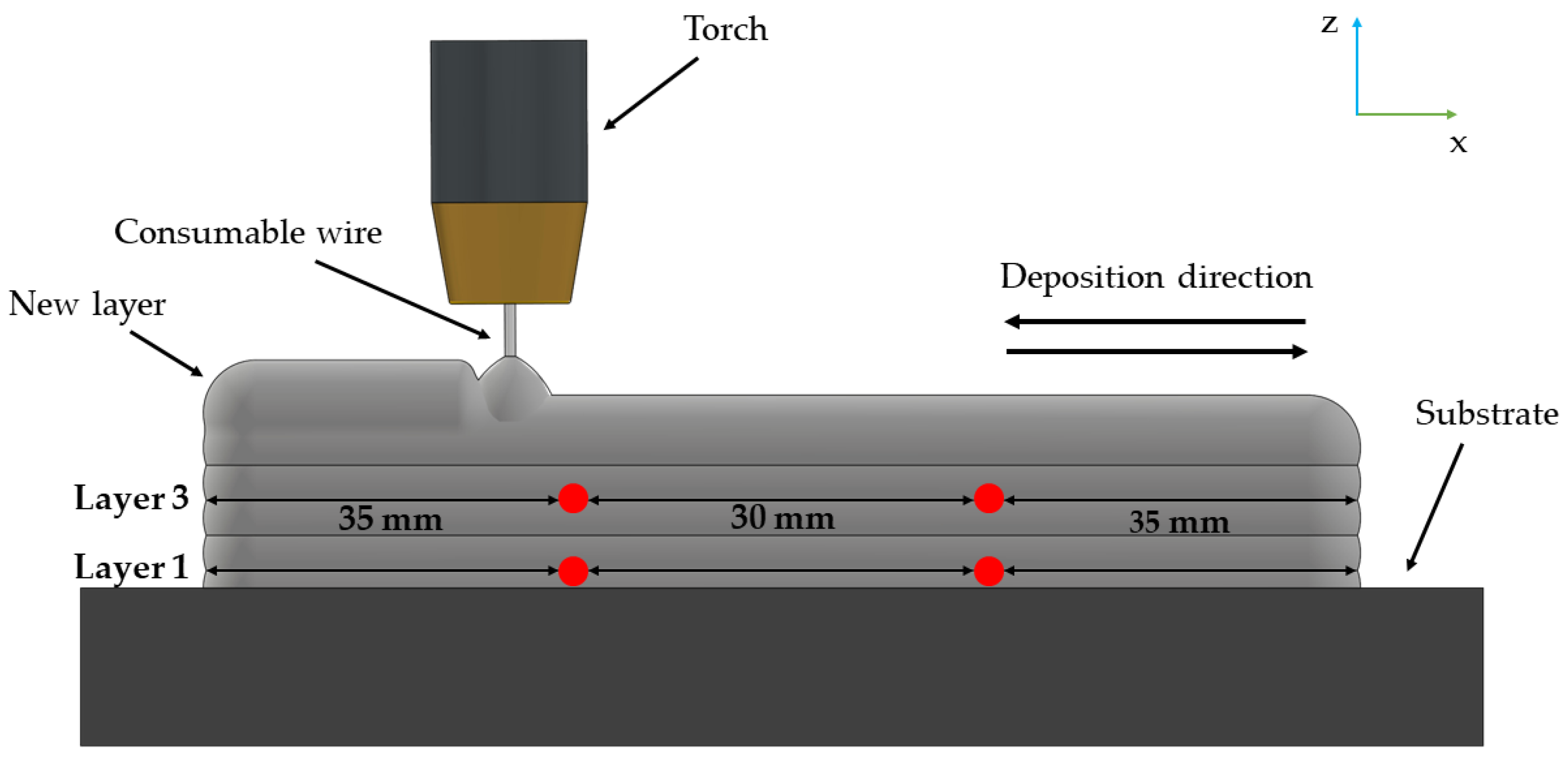
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
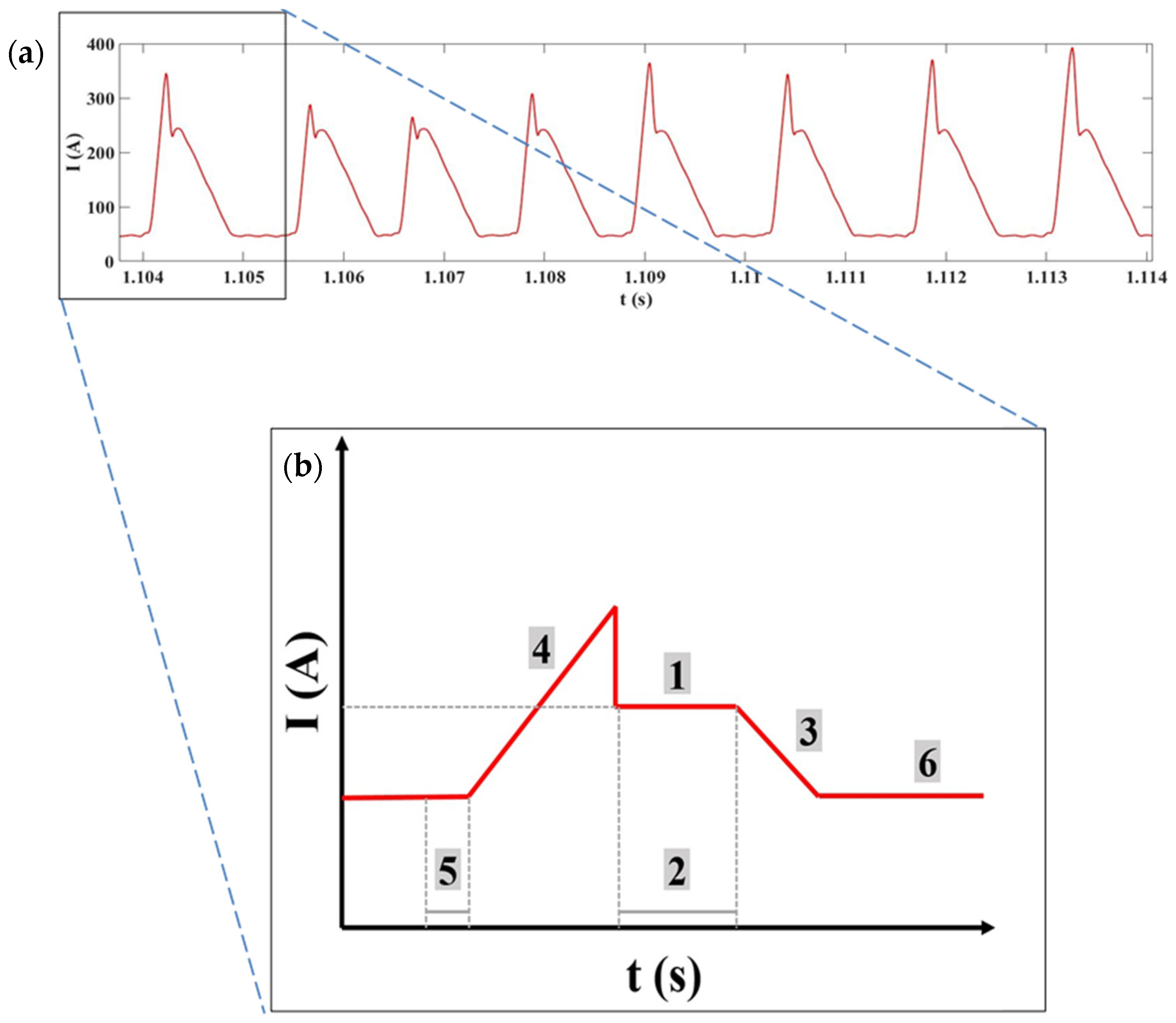
3.1. Effects of Contaminants on Electric Arc
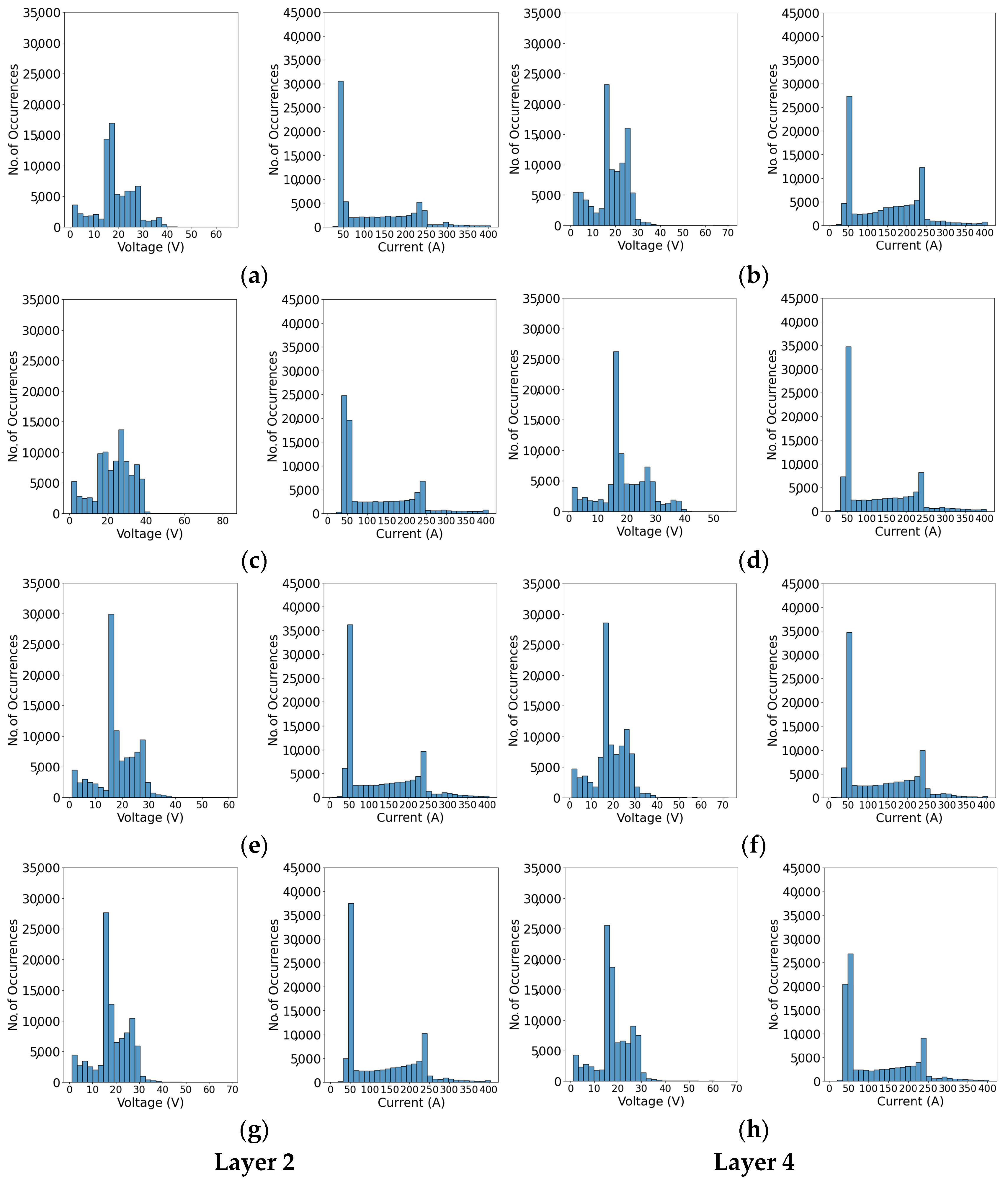
3.2. Effects of Contaminants on Arc Stability
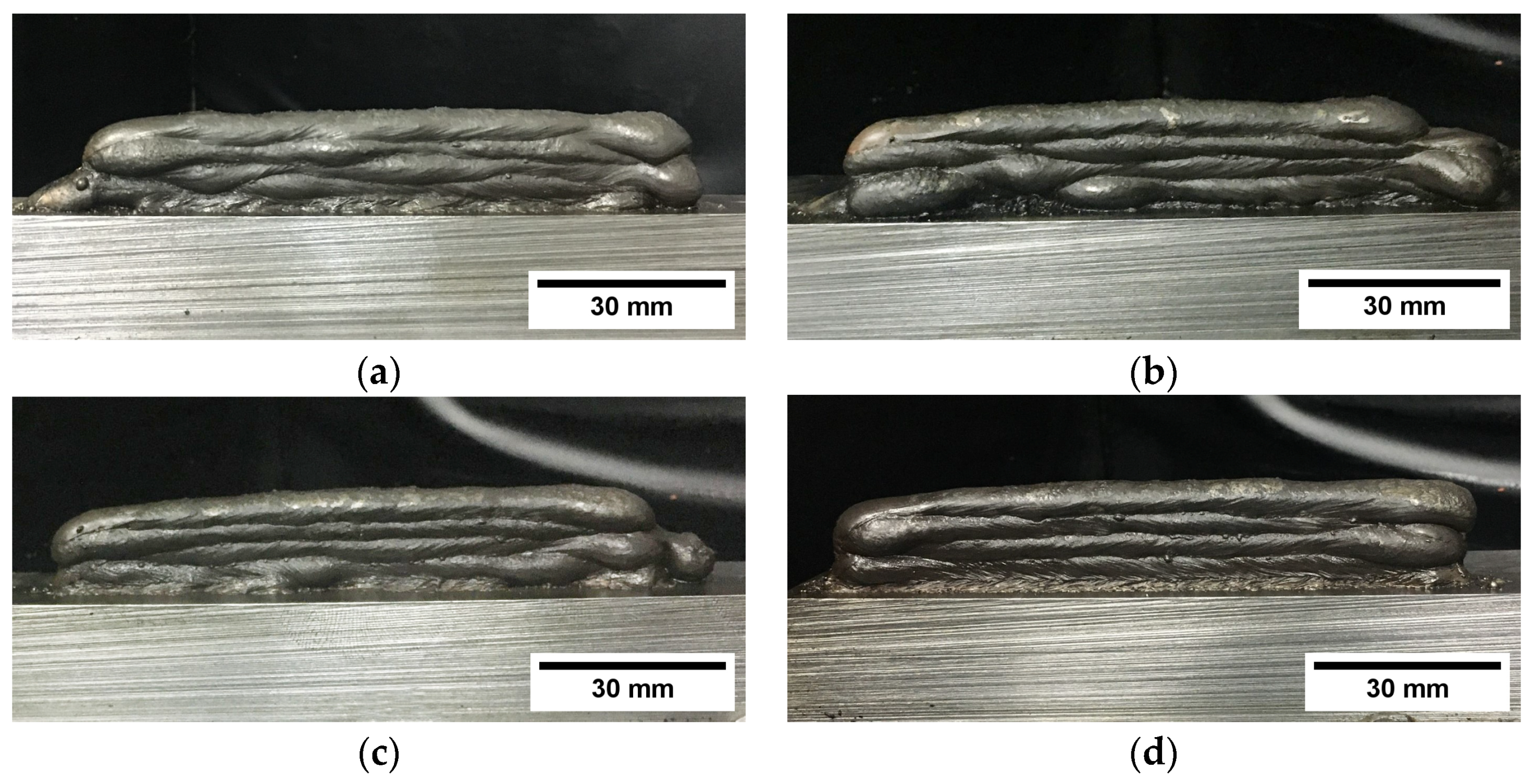
3.3. Metallographic Characterization of Thin Walls
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- The visual inspection of the WAAM-based thin walls preliminarily showed the negative effect of contaminants on the visual appearance of the preforms, showing discontinuities related to geometric variation and excessive spatter.
- (2)
- The electric voltage and current data analysis showed dissimilar electric arc behavior when comparing the contaminating preforms with the reference one (S3). For the analyses involving electrical current values, it was noticed that contaminants tended to present a reduced number of occurrences throughout the observed range of values, taking into account the peaks related to the predefined peak and base current values.
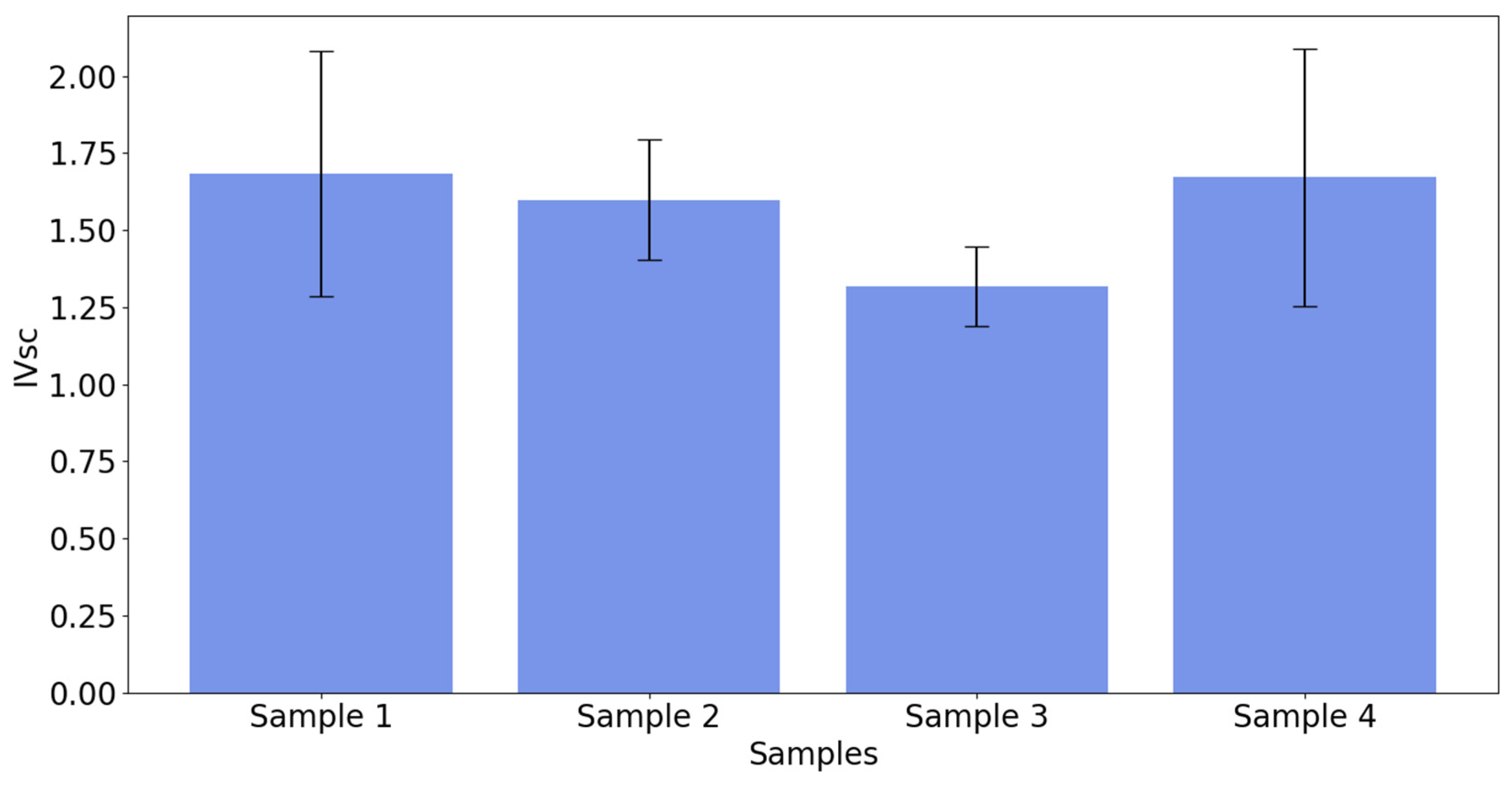
- (3)
- In all cases, the insertion of contaminants significantly harmed the stability of the electric arc, so the IVsc values for all the contaminants were higher compared to the reference sample (S3), and the sample with the insertion of sand (S4) presented the worst index for arc stability, followed by the samples contaminated with chalk (S1) and oil (S2).
- (4)
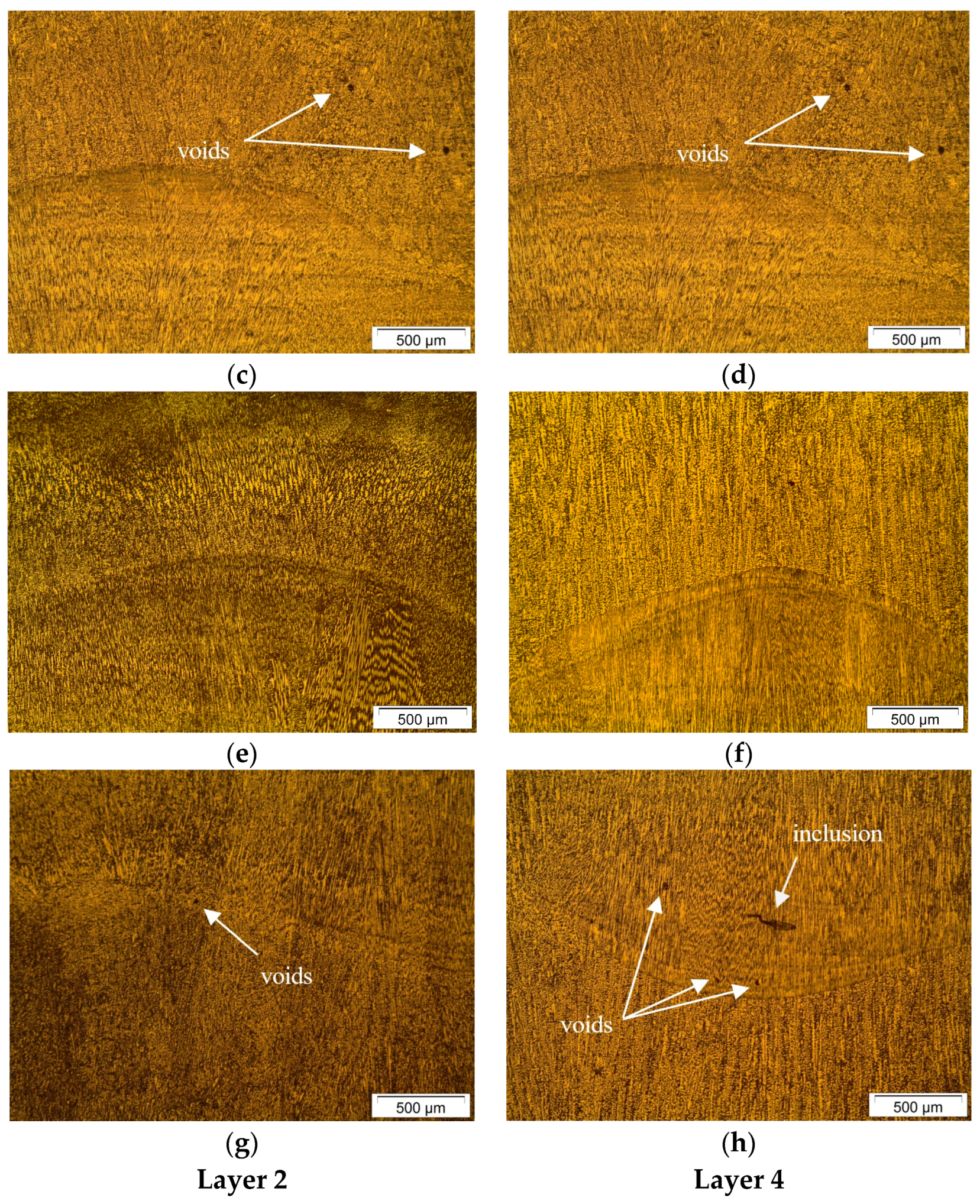
- Through the metallographic characterization, the anomalous behavior of the electric arc and its instability were confirmed, in addition to visual indications of discontinuities confirmed by visual inspection, by identifying microscopic defects in the interpass regions of the preforms, related to the contamination zones.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kumar, N.; Bhavsar, H.; Mahesh, P.V.S.; Srivastava, A.K.; Bora, B.J.; Saxena, A.; Dixit, A.R. Wire Arc Additive Manufacturing—A Revolutionary Method in Additive Manufacturing. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2022, 285, 126144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmer, J.W.; Gibbs, G. Mechanical Rolling and Annealing of Wire-Arc Additively Manufactured Stainless Steel Plates. Sci. Technol. Weld. Join. 2022, 27, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DebRoy, T.; Wei, H.L.; Zuback, J.S.; Mukherjee, T.; Elmer, J.W.; Milewski, J.O.; Beese, A.M.; Wilson-Heid, A.; De, A.; Zhang, W. Additive Manufacturing of Metallic Components—Process, Structure and Properties. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2018, 92, 112–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Waddell, C.; Hamilton, C.; Xiao, H. Quality Prediction and Control in Wire Arc Additive Manufacturing via Novel Machine Learning Framework. Micromachines 2022, 13, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Souto, J.I.V.; Ferreira, S.D.; de Lima, J.S.; de Castro, W.B.; Grassi, E.N.D.; de Abreu Santos, T.F. Effect of GMAW Process Parameters and Heat Input on Weld Overlay of Austenitic Stainless Steel 316L-Si. Soldag. Inspeção 2023, 28, e2809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinovitzer, M.; Chen, X.; Laliberte, J.; Huang, X.; Frei, H. Effect of Wire and Arc Additive Manufacturing (WAAM) Process Parameters on Bead Geometry and Microstructure. Addit. Manuf. 2019, 26, 138–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Lima, J.S.; da Silva Neto, J.F.; Maciel, T.M.; López, E.A.T.; de Santana, R.A.C.; de Abreu Santos, T.F. Effect of Wire Arc Additive Manufacturing Parameters on Geometric, Hardness, and Microstructure of 316LSi Stainless Steel Preforms. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2024, accepted. [Google Scholar]
- He, X.; Wang, T.; Wu, K.; Liu, H. Automatic Defects Detection and Classification of Low Carbon Steel WAAM Products Using Improved Remanence/Magneto-Optical Imaging and Cost-Sensitive Convolutional Neural Network. Measurement 2021, 173, 108633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaloo, M.; Schnall, M.; Klein, T.; Huber, N.; Reitinger, B. A Review of Non-Destructive Testing (NDT) Techniques for Defect Detection: Application to Fusion Welding and Future Wire Arc Additive Manufacturing Processes. Materials 2022, 15, 3697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Su, C.; Zhu, J. Comprehensive Review of Wire Arc Additive Manufacturing: Hardware System, Physical Process, Monitoring, Property Characterization, Application and Future Prospects. Results Eng. 2022, 13, 100330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Ding, D.; Pan, Z.; Cuiuri, D.; Li, H.; Han, J.; Fei, Z. Effects of Heat Accumulation on the Arc Characteristics and Metal Transfer Behavior in Wire Arc Additive Manufacturing of Ti6Al4V. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2017, 250, 304–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, S.J.; Hong, S.H.; Jadhav, S.; Kim, D.B. Detecting Balling Defects Using Multisource Transfer Learning in Wire Arc Additive Manufacturing. J. Comput. Des. Eng. 2023, 10, 1423–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brennan, M.C.; Keist, J.S.; Palmer, T.A. Defects in Metal Additive Manufacturing Processes. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2021, 30, 4808–4818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomar, B.; Shiva, S.; Nath, T. A Review on Wire Arc Additive Manufacturing: Processing Parameters, Defects, Quality Improvement and Recent Advances. Mater. Today Commun. 2022, 31, 103739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Pan, Z.; Ding, D.; Cuiuri, D.; Li, H.; Xu, J.; Norrish, J. A Review of the Wire Arc Additive Manufacturing of Metals: Properties, Defects and Quality Improvement. J. Manuf. Process. 2018, 35, 127–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, N.; Vázquez, L.; Huarte, I.; Arruti, E.; Tabernero, I.; Alvarez, P. Wire and Arc Additive Manufacturing: A Comparison between CMT and TopTIG Processes Applied to Stainless Steel. Weld. World 2018, 62, 1083–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, D.; Pan, Z.; Cuiuri, D.; Li, H. Wire-Feed Additive Manufacturing of Metal Components: Technologies, Developments and Future Interests. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2015, 81, 465–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, C.; Pan, Z.; Polden, J.; Li, H.; Xu, Y.; Chen, S.; Zhang, Y. A Review on Wire Arc Additive Manufacturing: Monitoring, Control and a Framework of Automated System. J. Manuf. Syst. 2020, 57, 31–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimermann, R.; Mohseni, E.; Vasilev, M.; Loukas, C.; Vithanage, R.K.W.; Macleod, C.N.; Lines, D.; Javadi, Y.; Espirindio E Silva, M.P.; Fitzpatrick, S.; et al. Collaborative Robotic Wire + Arc Additive Manufacture and Sensor-Enabled In-Process Ultrasonic Non-Destructive Evaluation. Sensors 2022, 22, 4203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramalho, A.; Santos, T.G.; Bevans, B.; Smoqi, Z.; Rao, P.; Oliveira, J.P. Effect of Contaminations on the Acoustic Emissions during Wire and Arc Additive Manufacturing of 316L Stainless Steel. Addit. Manuf. 2022, 51, 102585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pringle, A.M.; Oberloier, S.; Petsiuk, A.L.; Sanders, P.G.; Pearce, J.M. Open Source Arc Analyzer: Multi-Sensor Monitoring of Wire Arc Additive Manufacturing. HardwareX 2020, 8, e00137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Sun, B.; Zhang, C.; Lou, X.; Zhao, Z.; Han, J. Wire Composition and Shielding Gas Flow Monitoring Based on Image and Spectrum Multimodal Network. Measurement 2020, 160, 107797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, H.W.; Shin, S.J.; Seo, G.J.; Kim, D.B.; Lee, D.H. Real-Time Anomaly Detection Using Convolutional Neural Network in Wire Arc Additive Manufacturing: Molybdenum Material. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2022, 302, 117495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauser, T.; Reisch, R.T.; Seebauer, S.; Parasar, A.; Kamps, T.; Casati, R.; Volpp, J.; Kaplan, A.F.H. Multi-Material Wire Arc Additive Manufacturing of Low and High Alloyed Aluminium Alloys with in-Situ Material Analysis. J. Manuf. Process. 2021, 69, 378–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.; Seo, G.; Kim, D.B.; Kim, M.; Shin, J.-H. Development of Defect Detection AI Model for Wire + Arc Additive Manufacturing Using High Dynamic Range Images. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 7541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Polden, J.; Pan, Z.; Cui, J.; Xia, C.; He, F.; Mu, H.; Li, H.; Wang, L. A Defect Detection System for Wire Arc Additive Manufacturing Using Incremental Learning. J. Ind. Inf. Integr. 2022, 27, 100291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reisch, R.; Hauser, T.; Lutz, B.; Pantano, M.; Kamps, T.; Knoll, A. Distance-Based Multivariate Anomaly Detection in Wire Arc Additive Manufacturing. In Proceedings of the 2020 19th IEEE International Conference on Machine Learning and Applications (ICMLA), Miami, FL, USA, 14–17 December 2020; pp. 659–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- So, M.S.; Seo, G.J.; Kim, D.B.; Shin, J.-H. Prediction of Metal Additively Manufactured Surface Roughness Using Deep Neural Network. Sensors 2022, 22, 7955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Lu, J.; Zhao, Z.; Deng, W.; Han, J.; Bai, L.; Yang, X.; Yao, J. Active Disturbance Rejection Control of Layer Width in Wire Arc Additive Manufacturing Based on Deep Learning. J. Manuf. Process. 2021, 67, 364–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Li, W.; Jiao, Y.; Paniagua, C.; Ren, Y.; Lu, H. Porosity Evolution under Increasing Tension in Wire-Arc Additively Manufactured Aluminum Using in-Situ Micro-Computed Tomography and Convolutional Neural Network. Scr. Mater. 2023, 225, 115172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kah, P.; Edigbe, G.O.; Ndiwe, B.; Kubicek, R. Assessment of Arc Stability Features for Selected Gas Metal Arc Welding Conditions. SN Appl. Sci. 2022, 4, 268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puñales, E.M.M.; Alfaro, S.C.A. Stability on the GMAW Process. In Welding—Modern Topics; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2021; Volume 11, p. 13. ISBN 0000957720. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, T.; Xu, C.; Cheng, J.; Chen, Z.; Wang, L.; Wang, K. Research of Surface Oxidation Defects in Copper Alloy Wire Arc Additive Manufacturing Based on Time-Frequency Analysis and Deep Learning Method. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 25, 511–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, S.; Jin, C.; Yu, J.; Rhee, S. Real-Time Detection of Weld Defects for Automated Welding Process Base on Deep Neural Network. Metals 2020, 10, 389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, G.R.B.; Filho, R.M.M.; Scotti, A.; Lagares, M.L. Exploring a Locus of Maximum Metal Transfer Stability of the Short-Circuiting GMAW Process Based on the Reignition Voltage Peaks. J. Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 2021, 43, 503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truppel, G.H.; Angerhausen, M.; Pipinikas, A.; Reisgen, U.; dos Santos Paes, L.E. Stability Analysis of the Cold Metal Transfer (CMT) Brazing Process for Galvanized Steel Plates with ZnAl4 Filler Metal. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2019, 103, 2485–2494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Shen, J.; Hu, S.; Chen, Y.; Yin, C.; Bu, X. Optimization of CMT Characteristic Parameters for Swing Arc Additive Manufacturing of AZ91 Magnesium Alloy Based on Process Stability Analysis. Materials 2023, 16, 3236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Li, H.; Gong, H.; Wu, Y.; Chen, X.; Zhang, X. Study on Location-Related Thermal Cycles and Microstructure Variation of Additively Manufactured Inconel 718. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2022, 18, 3056–3072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodideal, N.; Machado, C.M.; Infante, V.; Braga, D.F.O.; Santos, T.G.; Vidal, C. Mechanical Characterization and Fatigue Assessment of Wire and Arc Additively Manufactured HSLA Steel Parts. Int. J. Fatigue 2022, 164, 107146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liskevych, O.; Scotti, A. Influence of the CO2 Content on Operational Performance of Short-Circuit GMAW. Weld. World 2015, 59, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Meneses, V.A.; Gomes, J.F.P.; Scotti, A. The Effect of Metal Transfer Stability (Spattering) on Fume Generation, Morphology and Composition in Short-Circuit MAG Welding. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2014, 214, 1388–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bevans, B.; Ramalho, A.; Smoqi, Z.; Gaikwad, A.; Santos, T.G.; Rao, P.; Oliveira, J.P. Monitoring and Flaw Detection during Wire-Based Directed Energy Deposition Using in-Situ Acoustic Sensing and Wavelet Graph Signal Analysis. Mater. Des. 2023, 225, 111480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Yue, C.; Tan, X.; Zhou, Z.; Li, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, C.; Peng, Y.; Wang, K. Quality Prediction for Wire Arc Additive Manufacturing Based on Multi-Source Signals, Whale Optimization Algorithm–Variational Modal Decomposition, and One-Dimensional Convolutional Neural Network. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, H.; Zhang, W.; Li, X.; Pei, K.; Lin, S.; Tian, J.; Wang, Z. Effect of Pulse Current on Droplet Transfer Behavior and Weld Formation of 304 Stainless Steel in Local Dry Underwater Pulse MIG Welding. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2022, 122, 869–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauné, E.; Bonnet, C.; Liu, S. Assessing Metal Transfer Stability and Spatter Severity in Flux Cored Arc Welding. Sci. Technol. Weld. Join. 2001, 6, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assunção, M.T.; Bracarense, A.Q. Evaluation of the Effect of the Water in the Contact Tip on Arc Stability and Weld Bead Geometry in Underwater Wet FCAW. Soldag. Inspeção 2017, 22, 401–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.H.; Kim, C.; Kang, M. Effects of Electrode Negative Pulsing Ratio in Direct Energy Deposition via Variable-Polarity Cold Metal Transfer Process on the Deposition Behavior and Microstructural Characteristics. Metals 2022, 12, 475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauser, T.; Reisch, R.T.; Kamps, T.; Kaplan, A.F.H.; Volpp, J. Acoustic Emissions in Directed Energy Deposition Processes. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2022, 119, 3517–3532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcaraz, J.Y.; Foqué, W.; Sharma, A.; Tjahjowidodo, T. Indirect Porosity Detection and Root-Cause Identification in WAAM. J. Intell. Manuf. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zimmer-Chevret, S.; Léonard, F.; Bourlet, C.; Abba, G. In Situ Monitoring of Internal Defects by a Laser Sensor for CMT Based Wire-Arc Additive Manufacturing Parts. Defect Diffus. Forum 2022, 417, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.P.; Wang, C.R.; Du, X.D.; Tian, W.; Zhang, T.; Hu, J.S.; Bo, L.; Li, P.C.; Liao, W.H. Research Status and Quality Improvement of Wire Arc Additive Manufacturing of Metals. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2023, 33, 969–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Steel | C | Ni | Cr | Mn | Si | Mo | Cu | P | S | Fe |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AISI 1015 (AISI, USA) | 0.148 | - | 0.043 | 0.419 | - | - | - | - | - | Bal. |
| ABNT 316L-Si (ABNT, Brazil) | 0.030 | 12.5 | 19.0 | 1.75 | 0.83 | 2.5 | 0.75 | 0.03 | 0.03 | Bal. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Souto, J.I.V.d.; Lima, J.S.d.; Castro, W.B.d.; Santana, R.A.C.d.; Silva, A.A.; Abreu Santos, T.F.d.; Tavares, J.M.R.S. Effects of Contaminations on Electric Arc Behavior and Occurrence of Defects in Wire Arc Additive Manufacturing of 316L-Si Stainless Steel. Metals 2024, 14, 286. https://doi.org/10.3390/met14030286
Souto JIVd, Lima JSd, Castro WBd, Santana RACd, Silva AA, Abreu Santos TFd, Tavares JMRS. Effects of Contaminations on Electric Arc Behavior and Occurrence of Defects in Wire Arc Additive Manufacturing of 316L-Si Stainless Steel. Metals. 2024; 14(3):286. https://doi.org/10.3390/met14030286
Chicago/Turabian StyleSouto, Joyce Ingrid Venceslau de, Jefferson Segundo de Lima, Walman Benício de Castro, Renato Alexandre Costa de Santana, Antonio Almeida Silva, Tiago Felipe de Abreu Santos, and João Manuel R. S. Tavares. 2024. "Effects of Contaminations on Electric Arc Behavior and Occurrence of Defects in Wire Arc Additive Manufacturing of 316L-Si Stainless Steel" Metals 14, no. 3: 286. https://doi.org/10.3390/met14030286
APA StyleSouto, J. I. V. d., Lima, J. S. d., Castro, W. B. d., Santana, R. A. C. d., Silva, A. A., Abreu Santos, T. F. d., & Tavares, J. M. R. S. (2024). Effects of Contaminations on Electric Arc Behavior and Occurrence of Defects in Wire Arc Additive Manufacturing of 316L-Si Stainless Steel. Metals, 14(3), 286. https://doi.org/10.3390/met14030286







