Effect of Strain Localization on Pitting Corrosion of an AlMgSi0.5 Alloy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
| Material and processing | Effect of pass number on Epit | Dominant pit initiation | Pit morphology with increasing pass number | Analytical techniques | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| high purity Al 2, 6, 10 ECAP passes (route Bc) | lowered | dislocations, grain boundaries | PP | [6] | |
| Al-2.5 wt% Cu-1.5 wt% Mg alloy aging, no ECAP | unaffected/lowered | critical size of GP zones (solute enriched regions) | PP, CT | [10] | |
| Al-Mg model alloys (varying Mg content) 4, 8, 12 ECAP passes (route Bc) | lowered/unaffected | deformation state more dominant than grain size | after PP: pits deeper and more localized, hindered repassivation with increasing pass number, filiform, decreasing crystallographic character | PP, EIS | [7] |
| high purity Al 1, 4, 8 ECAP passes (route Bc) | unaffected | more reactive surfaces for passivation (grain size, grain boundaries) | PP | [8] | |
| AA 1050 1, 2, 3, 5 passes | raised | fragmentation of Si-containing constituent particles | after PT: decreased pit size, less severe attack | PP, PT, EIS | [11] |
| AA 1100 8 ECAP passes (route Bc); AA5052 4 ECAP passes (route Bc) | raised | fragmentation of Fe-Al impurities, increased formation rate of passivation film | after PT: decreased pit size, crystallographic pits | PP, EIS | [12] |
| Al-5.4 wt% Ni and Al-5 wt% Cu 2, 4, 6 ECAP passes (route Bc) | raised | fragmentation of constituent particles, microstructural homogenization | after PP: fewer pits in the shear bands | PP | [6] |
| EN AW-6082 1, 2, 8 ECAP passes (route E), 1 ECAP pass + post ageing | raised | fragmentation and redistribution of constituent particles | after PP: decreased pit depth | PP, EIS, CV | [13,14] |
| low purity Al (Al-0.5 wt% Si-0.15 wt% Fe) 16 ECAP passes | raised | more stable passivation film due to strain induced crystalline defects and residual (micro)stress | after PT: decreased pit size uniform distribution | PP, PT, IT, EIS | [15] |
| low purity Al (99.1 wt%) with α-AlFeSi phases 2, 4 ECAP passes (route A) | lowered | fragmentation of constituent particles (α-phase), grain refinement and higher dislocation density | after IT: crystallographic pitting | IT, PP, EIS | [16] |
| low purity Al (99.1 wt%) with Al8Fe2Si phase 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 ECAP passes (route A) | unaffected | fragmentation of constituent particles, increased volume fraction of grain boundaries | after IT and PP: reduced intergranular corrosion increased pitting increased density and decreased pit depths | IT, PP, EIS, 3D optical profilometry | [17] |
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Sample Preparation
| Si | Fe | Cu | Mn | Mg | Zn | Al | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EN AW-6060 | 0.45 | 0.16 | 0.003 | 0.026 | 0.49 | 0.003 | bal. |
2.2. Electrochemical Measurements
2.3. Microstructural Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Evolution of Microstructure



3.2. Pitting Corrosion Potential Derived from Macro- and Micro-Electrochemical Tests
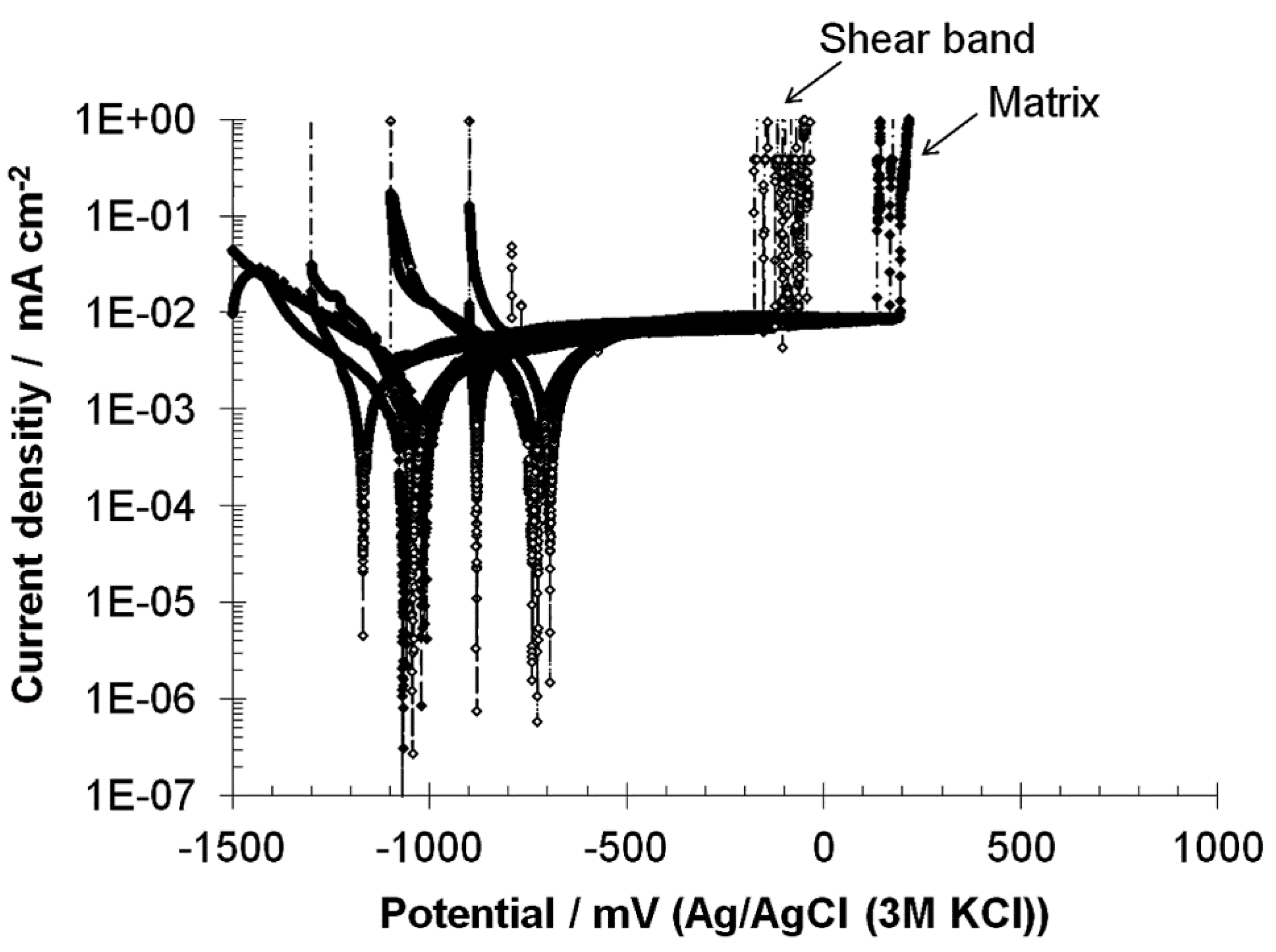
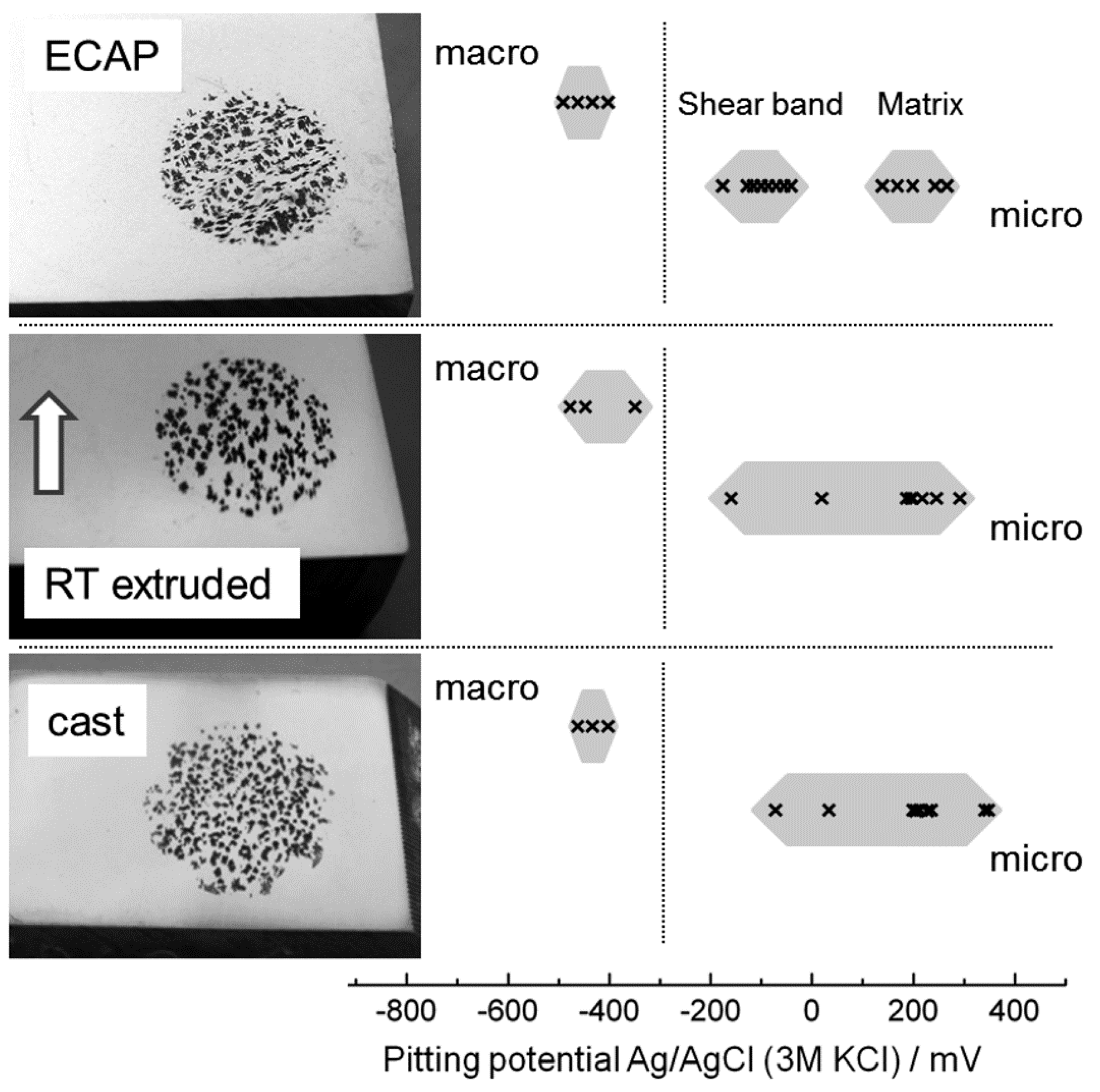
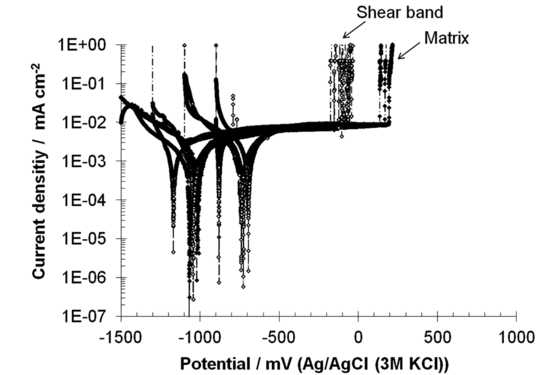
3.3. Pit Morphology




| State | Corroded area fraction (%) | Corroded volume (mm³) | Average corrosion depth (µm) | Maximal pit depth (µm) | Average pit depth (µm) | Density of pits (pits/mm²) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| cast | 34 | 0.57 | 7.3 | 100 | 19.6 | 4.6 |
| RT-extruded | 37 | 0.75 | 9.6 | 120 | 28.1 | 3.9 |
| ECAP | ||||||
| sum | 38 | 0.43 | 5.1 | 75 | 13.5 | 8.7 |
| matrix | 45 | 0.24 | 6.0 | 75 | 13.3 | 8.0 |
| shear band | 32 | 0.19 | 4.4 | 75 | 13.6 | 9.3 |

4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Segal, V.M. Equal channel angular extrusion: from macromechanics to structure formation. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 1999, 271, 322–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segal, V.M. The Method of Material Preparation for Subsequent Working. Patent of the USSR 1977 No. 575892.
- Vinogradov, A.; Mimaki, T.; Hashimoto, S.; Valiev, R. On the corrosion behaviour of ultra-fine grain copper. Scripta Mater. 1999, 41, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valiev, R.Z.; Langdon, T.G. Principles of equal-channel angular pressing as a processing tool for grain refinement. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2006, 51, 881–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, A.E.; Birbilis, N.; Mol, J.M.C.; Garcia, S.J.; Zhou, X.; Thompson, G.E. High Strength Al-Alloys: Microstructure, Corrosion and Principles of Protection. In Recent Trends in Processing and Degradation of Aluminium Alloys; InTech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Akiyama, E.; Zhang, Z.; Watanabe, Y.; Tsuzaki, K. Effects of severe plastic deformation on the corrosion behavior of aluminum alloys. J. Solid State Electrochem. 2009, 13, 277–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunner, J.G.; May, J.; Höppel, H.W.; Göken, M.; Virtanen, S. Localized corrosion of ultrafine-grained Al–Mg model alloys. Electrochim. Acta 2010, 55, 1966–1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ralston, K.D.; Fabianic, D.; Birbilis, N. Effect of grain size on corrosion of high purity aluminium. Electrochim. Acta 2011, 56, 1729–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ralston, K.D.; Birbilis, N. Effect of grain size on corrosion: A review. Corrosion 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ralston, K.D.; Birbilis, N.; Weyand, M.; Hutchinson, C.R. The effect of precipitate size on the yield strength-pitting corrosion correlation in Al-Cu-Mg alloys. Acta Mater. 2010, 58, 5941–5948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, M.K.; Choi, Y.S.; Kim, J.G.; Kim, Y.M.; Lee, J.C. Effect of the number of ECAP pass time on the electrochemical properties of 1050 Al alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2004, 366, 282–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, I.J.; Nakano, H.; Oue, S.; Kobayashi, S.; Fukushima, H.; Horita, Z. Pitting corrosion resistance of ultrafine-grained aluminum processed by severe plastic deformation. Mater. Trans. 2006, 47, 1163–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hockauf, M.; Meyer, L.W.; Nickel, D.; Alisch, G.; Lampke, T.; Wielage, B.; Krüger, L. Mechanical properties and corrosion behaviour of ultrafine-grained AA6082 produced by equal channel angular pressing. J. Mater. Sci. 2008, 43, 7409–7417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wielage, B.; Nickel, D.; Lampke, T.; Alisch, G.; Podlesak, H.; Darwich, S.; Hockauf, M. Corrosion characteristics of an ultrafine-grained Al-Mg-Si alloy (AA6082). Mater. Sci. Forum 2008, 584–586, 988–993. [Google Scholar]
- Song, D.; Ma, A.B.; Jiang, J.H.; Lin, P.H.; Yang, D.H. Corrosion behavior of ultra-fine grained industrial pure Al fabricated by ECAP. Trans. Nonferrous Metals Soc. China 2009, 19, 1065–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korchef, A.; Kahoul, A. Corrosion Behavior of Commercial Aluminum Alloy Processed by Equal Channel Angular Pressing. Inter. J. Corros. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jilani, O.; Njah, N.; Ponthiaux, P. Transition from intergranular to pitting corrosion in fine grained aluminum processed by equal channel angular pressing. Corros. Sci. 2014, 87, 259–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naeini, M.F.; Shariat, M.H.; Eizadjou, M. On the chloride induced pitting of ultra fine grains 5052 aluminum alloy produced by accumulative roll bonding process. J. Alloys Compd. 2011, 509, 4696–4700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Wei, K.X.; Du, Q.B. Corrosion and tensile behaviors of ultra-fine grained Al–Mn alloy produced by accumulative roll bonding. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2007, 454, 536–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suter, T.; Peter, T.; Böhni, H. Microelectrochemical investigations of MnS inclusions. Mater. Sci. Forum 1995, 192–194, 25–39. [Google Scholar]
- Yulinova, A.; Nickel, D.; Frint, P.; Lampke, T. Electrochemical properties of AL-6060 alloy after industrial scale ECAP. Mater. Sci. 2012, 48, 191–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frint, P.; Hockauf, M.; Halle, T.; Strehl, G.; Lampke, T.; Wagner, M.F.X. Microstructural features and mechanical properties after industrial scale ECAP of an Al-6060 alloy. Mater. Sci. Forum 2011, 667–669, 1153–1158. [Google Scholar]
- Frint, P.; Hockauf, M.; Dietrich, D.; Halle, T.; Wagner, M.F.X.; Lampke, T. Influence of strain gradients on the grain refinement during industrial scale ECAP. Mater. Sci. Eng. Technol. 2011, 42, 680–685. [Google Scholar]
- Iwahashi, Y.; Wang, J.T.; Horita, Z.; Nemoto, M.; Langdon, T.G. Principle of equal-channel angular pressing for the processing of ultra-fine grained materials. Scripta Mater. 1996, 35, 143–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietrich, D.; Berek, H.; Schulze, A.; Scharf, I.; Lampke, T. EBSD and STEM on aluminium alloys subjected to severe plastic deformation. Prac. Metall. 2011, 43, 136–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böhni, H.; Suter, T.; Schreyer, A. Micro- and nanotechniques to study localized corrosion. Electrochim. Acta 1995, 40, 1361–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birbilis, N.; Buchheit, R.G. Electrochemical characteristics of intermetallic phases in aluminum alloys—An experimental survey and discussion. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2005, 152, B140–B151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couper, M.J.; Rinderer, B.; Yao, J.Y. Characterisation of AlFeSi intermetallics in 6000 series aluminium alloy extrusions. Mater. Sci. Forum 2006, 519–521, 303–308. [Google Scholar]
- Milkereit, B.; Wanderka, N.; Schick, C.; Kessler, O. Continuous cooling precipitation diagrams of Al–Mg–Si alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2012, A550, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birol, Y. Precipitation during homogenization cooling in AlMgSi alloys. Trans. Nonferrous Metals Soc. China 2013, 23, 1875–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bournane, M.; Berezina, A.; Davydenko, O.; Monastyrska, T.; Molebny, O.; Spuskanyuk, V.; Kotko, A. Effect of severe plastic deformation on structure and properties of Al-Mg-Si alloy of 6060 type. Mater. Sci. Metall. Eng. 2013, 1, 13–21. [Google Scholar]
- Hockauf, K.; Wagner, M.F.X.; Halle, T.; Niendorf, T.; Hockauf, M.; Lampke, T. Influence of precipitates on low-cycle fatigue and crack growth behavior in an ultrafine-grained aluminum alloy. Acta Mater. 2014, 80, 250–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suter, T.; Alkire, R.C. Microelectrochemical studies of pit initiation at single inclusions in Al 2024-T3. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2001, 148, B36–B42. [Google Scholar]
- Wloka, J.; Hack, T.; Virtanen, S. Local electrochemical properties of laser beam-welded high-strength Al–Zn–Mg–Cu alloys. Mater. Corros. 2008, 59, 5–13. [Google Scholar]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nickel, D.; Dietrich, D.; Mehner, T.; Frint, P.; Spieler, D.; Lampke, T. Effect of Strain Localization on Pitting Corrosion of an AlMgSi0.5 Alloy. Metals 2015, 5, 172-191. https://doi.org/10.3390/met5010172
Nickel D, Dietrich D, Mehner T, Frint P, Spieler D, Lampke T. Effect of Strain Localization on Pitting Corrosion of an AlMgSi0.5 Alloy. Metals. 2015; 5(1):172-191. https://doi.org/10.3390/met5010172
Chicago/Turabian StyleNickel, Daniela, Dagmar Dietrich, Thomas Mehner, Philipp Frint, Dagobert Spieler, and Thomas Lampke. 2015. "Effect of Strain Localization on Pitting Corrosion of an AlMgSi0.5 Alloy" Metals 5, no. 1: 172-191. https://doi.org/10.3390/met5010172
APA StyleNickel, D., Dietrich, D., Mehner, T., Frint, P., Spieler, D., & Lampke, T. (2015). Effect of Strain Localization on Pitting Corrosion of an AlMgSi0.5 Alloy. Metals, 5(1), 172-191. https://doi.org/10.3390/met5010172