Abstract
The aim of this study was to investigate the effects of the cryogenic treatment (CT) using liquid nitrogen on tensile properties and microstructures of the 2024-T351 aluminum alloy. Tensile tests were carried out, and tensile fractures were observed using a scanning electron microscope (SEM). The microstructure evolution of 2024-T351 subjected to CT was also studied using both an optic microscope (OM) and a SEM. The components of the second phase were tested with an energy dispersive spectrometer (EDS). The results showed that both the ultimate strength and the yield strength of the 2024-T351 aluminum alloy could be improved through CT without the sacrifice of elongation. In addition, tensile fractures showed that the plasticity of 2024-T351 aluminum might also be improved, as the dimples in the fracture of the CTed specimens were markedly more uniform compared with the untreated specimen. The phenomenon of grains refinement (GR) was found through microstructure observation. It was also found that the second phases were distributed more uniformly after CT. A conceivable mechanism concerning the shrinking effect and crystal grain movement was raised to explain the experimental phenomena. The effects of CT on residual stress in the 2024-T351 aluminum alloy are discussed herein. Measurements showed that tensile residual stress in 2024-T351 was removed, and slight compressive residual stress was generated after CT. This may also contribute to the improvement of the tensile properties of the alloy.
1. Introduction
2024-T351 is a typical high strength aluminum that is widely used in aircraft structures, automobile parts, and several other engineering applications [1,2,3]. In order to improve the mechanical properties of this alloy, numerous treatment processes have been invented and investigated in the past several decades. In general terms, the treatment processes could be classified into two categories: body treatments such as heat treatments (HTs), particle reinforced metal matrix composites (PRMMCs) [4,5,6], and surface treatments such as surface melting (SM) [7], shot peening (SP) [8,9], and laser peening (LP) [10,11,12,13]. For example, Hong et al. [6], from Shanghai Jiaotong University, investigated the effect of cryogenic pre-treatment on aging behavior of in-situ TiB2/Al-Cu-Mg composites and found that the ultimate tensile strength and the elongation of the samples aged with a cryogenic pre-treatment were lower than the samples without cryogenic pre-treatment, while the hardness and the yield strength were higher. Correa et al. [13] from Universidad Politécnica de Madrid studied laser shock peening without absorbing coating (LSPwAC) in the 2024-T351 aluminum alloy and found that a random-type scanning pattern could reduce residual stress anisotropy, improving the mechanical properties of 2024-T351 aluminum treated by LP.
Recently, an increasing number of scholars investigated the valid combination of body treatments and surface treatment in order to improve the mechanical properties of several alloys. For example, in 2015, Liao et al. [14] reviewed the processing techniques of warm laser shock peening (WLSP) and thermal engineered-laser shock peening (TE-LSP) systematically and explained the fundamental process mechanisms clearly. According to the review, a dislocation pinning effect based on the dynamic strain aging (DSA) and dynamic precipitation (DP) is the main reason for improvement of residual stress and microstructure stability of WLSP [14,15]. Chen et al. [16] in Jiangsu University studied the effects of warm laser peening (WLP) on thermal stability of the A356 alloy and found that WLP can effectively improve the thermal stability of residual stress compared with LP. From 2011 to 2015, Ye et al. [17,18,19] studied the effect of CLSP on the mechanical properties of copper and 304 stainless steel; it was found that due to the generation of nanotwinned microstructure during CLSP, the strength and ductility of the materials could be improved simultaneously. In 2015, Singh et al. [20] found that cryoforging followed by aging can simultaneously improve strength, ductility, and corrosion resistance of the Al2024 alloy. However, to the best of our knowledge, few studies purely concerned the influence of cryogenic treatment (CT) on the 2024-T351 aluminum alloy have been published yet.
For the very first time, the effects of CT on tensile properties and microstructures of the 2024-T351 aluminum alloy are systematically investigated in this publication, in order to better study the combined techniques. In addition, the fractures of the tensile specimens have been analyzed. The components of the second phase were tested with an energy dispersive spectrometer (EDS), and the precipitate distribution of both treated and untreated specimens were observed using a Nova NanoSEM 450. Experimental results indicate that the precipitates changed their size after cryogenic treatment. Spacing among the fine precipitates was also changed to increase resistance of dislocation bowing. As a result, both the ultimate strength and the yield strength of the 2024-T351 aluminum alloy were improved through CT without the sacrifice of elongation. A mechanism concerning the shrinking effect and crystal grain movement was conceived to further explain the experimental phenomena. Measurements of residual stress in both untreated and CTed specimens were all carried out. The effects of CT on residual stress in the 2024-T351 aluminum alloy were discussed. Measurements showed that tensile residual stress in 2024-T351 was removed, and slight compressive residual stress was generated after CT. This may also contribute to the improvement of tensile properties of the alloy.
2. Materials and Experiments
2.1. Materials
Commercial 2024-T351 aluminum was selected for this study. The chemical composition and mechanical properties of the untreated samples at room temperature are shown in Table 1 and Table 2, respectively. The dimension and schematic diagrams of specimens used in CT and tensile tests are shown in Figure 1. Before experiments, all the specimens were polished with Al2O3 sandpaper with different grades of roughness (from 400# to 1500#), and then cleaned up by acetone and industrial alcohol carefully. The physical specimens used in the experiments are shown in Figure 2.

Table 1.
Chemical composition of the 2024-T351 alloy (wt %).

Table 2.
Mechanical properties of the 2024-T351 alloy tested at room temperature.
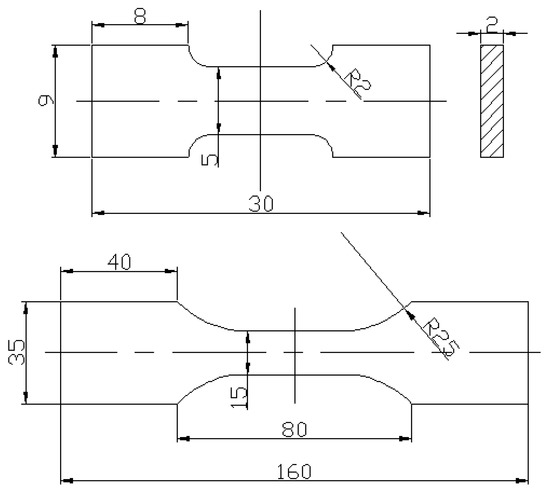
Figure 1.
The dimension of specimens used for cryogenic treatment (CT) and tensile tests.

Figure 2.
The specimens used in CT and tensile tests.
2.2. Cryogenic Treatments and Microstructure Observations
We placed the specimens in the foam box, infunded the liquid nitrogen, and covered the box, soaking the specimen under the temperature of 77 K for 2 h, 4 h, 6 h, 8 h, and 12 h, respectively. When the cryogenic treatments were complete, the specimens were initially polished using water sandpaper with different grades of roughness (from 800# to 2000#), after which they were polished using the polishing machine, and each sample was thereafter placed in a Keller reagent (1.0% HF + 1.5% HCl + 2.5% HNO3 + 95% H2O) for 30–60 s. The specimens were observed later under OM.
2.3. Tensile Tests and Fracture Observation
The tensile tests were conducted on a WDW-200G electronic universal testing machine (Jinan, China). The maximum force of this machine is 200 kN, with a displacement velocity of 0.005–500 mm/min and a maximum tensile travel up to 700 mm. The tensile strain rate used was 2.0 × 10−4 s−1. After the tensile tests, the fracture was observed using a Nova NanoSEM 450 (Hillsboro, OR, USA).
2.4. Measurements of Residual Stress
The residual stresses of both untreated specimen and CTed specimens were measured by the X-ray diffraction (XRD) technique using an X-ray diffractometer X-350A (Handan, China). The testing points were the center of each square specimen. The S1 stress, which was parallel with the scanning direction, was measured. The X-ray beam diameter was about 2 mm. The X-ray source was a Co Kα beam, and the diffraction plane was a phase (420) plane in the stress calculation. The feed angle of the ladder scanning was 0.1 deg.·s−1. The scanning starting angle and terminating angle were typical 123° and 116°. The measurements were repeated three times for each condition, and an average value was used.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Tensile Tests and Fracture Analysis
As shown in Table 3 and Figure 3, compared with the untreated specimen, the ultimate strength and the yield strength of the CTed specimens improved simultaneously. For example, after CT for 6 h, the tensile strength and the yield strength of the specimen were 478.2 MPa and 339 MPa, respectively. The tensile strength and the yield strength improved 13.5% and 10.4%, respectively. The elongation was all around 19.7% for the specimens N.1-0–N.1-5. Clearly, the strength of the 2024-T351 aluminum alloy improved without the sacrifice of ductility as tested. It should be pointed out that the elongation tested was largely related to the dimension of the specimen; as for specimens N.2-0–N.2-3, the elongation was around 17.6%. In fact, the ultimate strength and the yield strength tested were also related to the geometry of the specimens.

Table 3.
Tensile properties of 2024-T351 before and after CT.
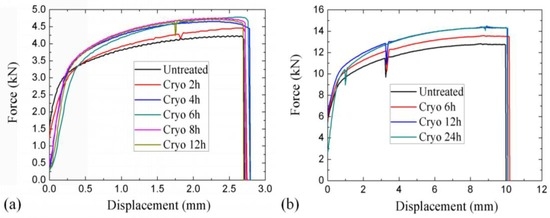
Figure 3.
The tensile curves of 2024-T351 specimens: (a) N.1-0–N.1-5; (b) N.2-0–N.2-3.
It was found that the improvement of tensile properties was largely related to the CT time. It can be reasonably inferred that the appropriate cryogenic time is interrelated to the specific material as well as the geometry of the specimen. As for 2024-T35l aluminum and the specimens N.1-0–N.1-5 used in this study, the appropriate CT time was 6 h. After CT of the specimens for 2 h, 4 h, and 6 h, both the tensile strength and the yield strength improved as cryogenic time increased. However, after the CT of the specimens for 8 h and 12 h, the ultimate strength as well as the yield strength decreased slightly compared with the earlier specimen after CT for 6 h. This phenomenon considerably confused us at first, but it was later found that it was related to the “aging time” of the specimens after CT. The phase “aging time” has a similar meaning to the generic term used in the heat treatments of metals.
The fractures of the tensile specimens were observed with SEM, as shown in Figure 4. The basic fracture mode of the 2024-T351 aluminum alloy is ductile fracture. The formation process of the dimples is shown in Figure 5. Hollow points are usually formed at the location of the second phases. If the second phases are too large, local quasi-cleavage characteristic might take shape, as shown in Figure 4a,c. A typical fracture was observed in Specimen N.1-0. As the second phases were diminished and equalized during the CT process, uniform and homogenized dimples were observed, as shown in Figure 4b,d. The quasi-cleavage characteristic might have transformed to torn edges as the second phases were diminished. In fact, the plasticity of 2024-T351 aluminum might also have improved through CT as the fracture of the CTed specimen became more homogenized.


Figure 4.
Tensile fractures observed with a scanning electron microscope (SEM): (a) N.1-0, 1000×; (b) N.1-3, 1000×; (c) N.1-0, 5000×; (d) N.1-4, 5000×.
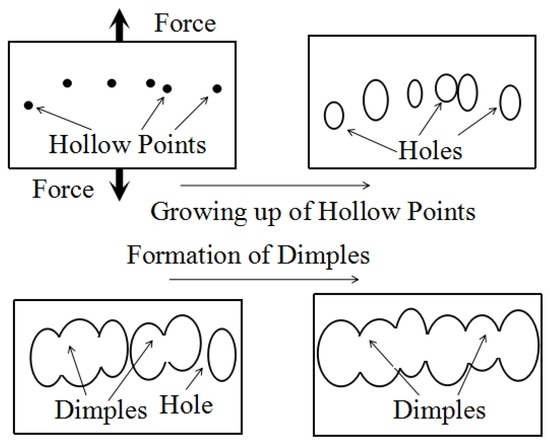
Figure 5.
Schematic of the formation of dimples.
3.2. Microstructure before and after CT
In order to understand the mechanism behind the improvement of tensile properties, especially the simultaneous improvement of the strength and ductility of the 2024-T351 aluminum alloy subjected to CT, the microstructures of the specimens before and after CT were all observed under OM, as shown in Figure 6. It could be clearly observed that the specimen after CT for 6 h obtained much fewer defects compared with the untreated specimen. The grains of the treated specimen were also more clear and uniform. As shown in Figure 7, the precipitates changed their size after CT. Spacing among fine precipitates also changed. In other words, the precipitates were distributed uniformly in the CTed specimen. The precipitates might be an S phase containing Cu, Mg, and the base element Al, according to EDS analysis. CT was thus considered to have great effects on the defects and precipitate distribution in the 2024-T351 aluminum alloy. Furthermore, the defects and the distribution of the precipitates in the alloy might affect the tensile properties of the aluminum alloy greatly, including the tensile fracture mechanism.
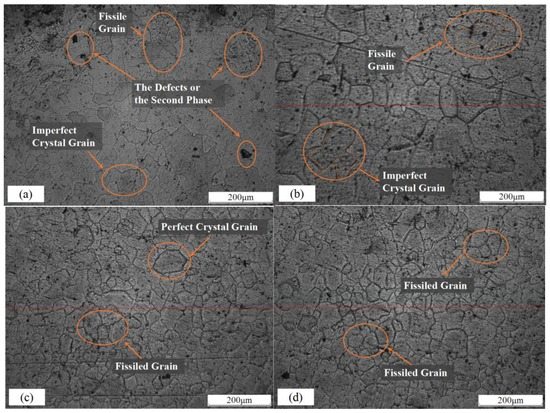

Figure 6.
The microstructure of the 2024-T351 aluminum alloy: (a) untreated specimen; (b) CTed Specimen, 2 h; (c) CTed Specimen, 6 h; (d) CTed Specimen, 12 h.

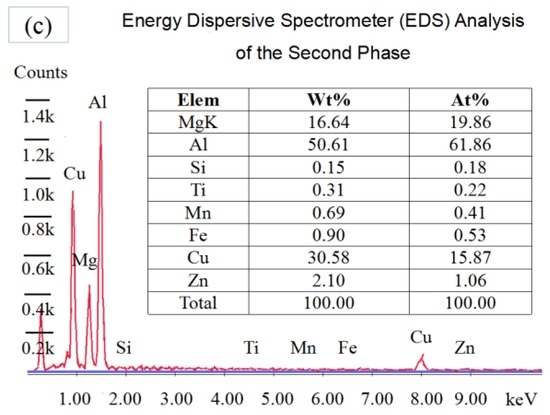
Figure 7.
SEM and energy dispersive spectrometer (EDS) images of the specimens: (a) untreated; (b) CT for 6 h; (c) EDS.
During the tensile process, due to the effect of stress concentration, it is likely to develop hollow points, especially where the precipitates are. As shown in Figure 5, hollow points may grow up to holes and then form the dimples. It is conceivable that the dimples will be more uniform when the precipitates are distributed more uniformly. In addition, smaller spacing among fine precipitates could increase the resistance of dislocation bowing and thus improve the ultimate strength and the yield strength of the 2024-T351 aluminum alloy.
A mechanism concerning the shrinking effect and crystal grain movement was conceived to explain the experimental phenomena, as shown in Figure 8. Firstly, dislocation density increased during the CT process. The grain movement and precipitate movement were unlocked, and dislocation movement promoted the process of grain refinement and precipitate redistribution. Finally, the precipitate distribution was more uniform, and the grains became finer and more perfect after the CT process. As a result, both the ultimate strength and the yield strength of the 2024-T351 aluminum alloy improved through CT without the sacrifice of elongation. In other words, the tensile properties of the 2024-T351 aluminum alloy were greatly improved.

Figure 8.
Schematic of the CT process—a conceivable mechanism.
3.3. Discussion of Residual Stress
The analysis of residual stress in the alloy is an important issue of several treatment processes. In general, residual stress in metals could be classified into three categories. The first category of residual stress is related to macroscopic deformation, while the second and the third categories of residual stress are related to the microstructures of the alloy. Traditional applications of CT include the removal of residual stress generated in the machining processes.
As shown in Table 4, the first category of residual stress in 2024-T351 was measured both before and after CT. The value of residual stress in the untreated specimen was about 26 MPa. Tensile residual stress was removed, and slight compressive residual stress was generated after CT. The values were all around 10 MPa. This may also contribute to the improvement of the ultimate strength and the yield strength of the 2024-T351 aluminum alloy. It could be hypothesized that the second and the third categories of residual stress were also removed since the microstructures of 2024-T351 aluminum were refined after CT. This could be further investigated in the future.

Table 4.
Residual stress in 2024-T351 before and after CT.
4. Conclusions
The effects of CT on 2024-T351 aluminum were investigated through both macroscopic and microscopic methods. It was found that both the ultimate strength and the yield strength of the 2024-T351 aluminum alloy could be improved through CT without the sacrifice of elongation. Tensile fractures showed that the plasticity of 2024-T351 aluminum might also be improved as the dimples of CTed specimens were more uniform. In the microscopic method, it was found that the grains of CTed specimens were finer, and the second phase of CTed specimens were distributed much more uniformly than the untreated specimen. These phenomena might be due to the shrinking effect and crystal grain movement during the CT process. In terms of residual stress, measurements showed that tensile residual stress in 2024-T351 was removed, and slight compressive residual stress was generated after CT. This may also contribute to the improvement of tensile properties of the alloy. In addition, it could be hypothesized that the second and the third categories of residual stress were also removed since the microstructures of 2024-T351 aluminum were refined after CT. The present study can help us better understand the effects of CT on 2024-T351 aluminum and push forward further studies on the 2024-T351 alloy.
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51575247), the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation Funded Project (No. 2014T70477 and 2013M540417), the Research Fund for the Doctoral Program of Higher Education of China (No. 20123227110022), Jiangsu Planned Projects for Postdoctoral Research Funds (No. 140l065B), the Advanced Talent Foundation of Jiangsu University of China (No. 13JDG109), and the Scientific Research Project for Jiangsu University Student (No. 14A114).
Author Contributions
Jiangzhong Zhou provided the investigating theme and offered several suggestions on the experiments. Suqiang Xu carried out the experiments and wrote the paper. Shu Huang, Xiankai Meng, and Jie Sheng provided some advice on the writing of the paper. Haifeng Zhang, Jing Li, and Yunhui Sun performed literature research on the background of this study. Emmanuel Agyenim Boateng polished up the language and discussed some parts of the study with Suqiang Xu.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Lu, J.Z.; Luo, K.Y.; Zhang, Y.K.; Cui, C.Y.; Sun, G.F.; Zhou, J.Z.; Zhang, L.; You, J.; Chen, K.M.; Zhong, J.W. Grain refinement of LY2 aluminum alloy induced by ultra-high plastic strain during multiple laser shock processing impacts. Acta Mater. 2010, 58, 3984–3994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaroog, O.S.; Ali, A.; Sahari, B.B.; Zahari, R. Modeling of residual stress relaxation of fatigue in 2024-T351 aluminium alloy. Int. J. Fatigue 2011, 33, 279–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodopoulos, C.A.; Kermanidis, A.T.; Statnikov, E.; Vityazev, V.; Korolkov, O. The Effect of Surface Engineering Treatments on the Fatigue Behavior of 2024-T351 Aluminum Alloy. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2007, 16, 30–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, J.; Chen, G.; Ji, X.; Song, X.; Hu, N.; Han, F. Effect of reaction temperature on the microstructures and mechanical properties of high-intensity ultrasonic assisted in-situ Al3Ti/2024 Al composites. J. Alloy. Compd. 2016, 666, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emamy, M.; Oliayee, M.; Tavighi, K. Microstructures and tensile properties of Al/2024–Al4Sr composite after hot extrusion and T6 heat treatment. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2015, 625, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, T.; Shen, Y.; Geng, J.; Chen, D.; Li, X.; Zhou, C. Effect of cryogenic pre-treatment on aging behavior of in-situ TiB2/Al-Cu-Mg composites. Mater. Character. 2016, 119, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalita, S.J. Microstructure and corrosion properties of diode laser melted friction stir weld of aluminum alloy 2024-T351. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2011, 257, 3985–3997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; An, X.; Rodopoulos, C.A.; Brown, M.W.; O′Hara, P.; Levers, A.; Gardiner, S. The effect of controlled shot peening on the fatigue behaviour of 2024-T3 aluminium friction stir welds. Int. J. Fatigue 2007, 29, 1531–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novelli, M.; Fundenberger, J.J.; Bocher, P.; Grosdidier, T. On the effectiveness of surface severe plastic deformation by shot peening at cryogenic temperature. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 389, 1169–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodopoulos, C.A.; Romero, J.S.; Curtis, S.A.; Curtis, S.A.; de los Rios, E.R.; Peyre, P. Effect of controlled shot peening and laser shock peening on the fatigue performance of 2024-T351 aluminum alloy. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2003, 12, 414–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Zhou, J.Z.; Sheng, J.; Luo, K.Y.; Lu, J.Z.; Xu, Z.C.; Meng, X.K.; Dai, L.; Zuo, L.D.; Ruan, H.Y.; et al. Effects of laser peening with different coverage areas on fatigue crack growth properties of 6061-T6 aluminum alloy. Int. J. Fatigue 2013, 47, 292–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montross, C.S.; Wei, T.; Ye, L.; Clark, G.; Mai, Y.W. Laser shock processing and its effects on microstructure and properties of metal alloys: A review. Int. J. Fatigue 2002, 24, 1021–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correa, C.; Peral, D.; Porro, J.A.; Diaz, M.; Ruiz de Lara, L.; Garcia-Beltran, A.; Ocana, J.L. Random-type scanning patterns in laser shock peening without absorbing coating in 2024-T351 Al alloy: A solution to reduce residual stress anisotropy. Opt. Laser Technol. 2015, 73, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.; Ye, C.; Cheng, G.J. A review: Warm laser shock peening and related laser processing technique. Opt. Laser Technol. 2015, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.; Ye, C.; Gao, H.; Kim, B.J. Dislocation pinning effects induced by nano-precipitates during warm laser shock peening: Dislocation dynamic simulation and experiments. J. Appl. Phys. 2011, 110, 023518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zhou, J.; Sheng, J.; Meng, X.; Huang, S.; Xie, X. Effects of Warm Laser Peening on Thermal Stability and High Temperature Mechanical Properties of A356 Alloy. Metals 2016, 6, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, C.; Suslov, S.; Lin, D.; Liao, Y.; Fei, X.; Cheng, G.J. Microstructure and mechanical properties of copper subjected to cryogenic laser shock peening. J. Appl. Phys. 2011, 110, 083504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, C.; Suslov, S.; Lin, D.; Liao, Y. Cryogenic ultrahigh strain rate deformation induced hybrid nanotwinned microstructure for high strength and high ductility. J. Appl. Phys. 2014, 115, 213519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, C.; Suslov, S.; Lin, D.; Cheng, G.J. Deformation-induced martensite and nanotwins by cryogenic laser shock peening of AISI 304 stainless steel and the effects on mechanical properties. Philos. Mag. 2011, 92, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.K.; Ghosh, S.; Mula, S. Simultaneous improvement of strength, ductility and corrosion resistance of Al2024 alloy processed by cryoforging followed by ageing. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2015, 651, 774–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).