Tensile Strength Reliability Analysis of Cu48Zr48Al4 Amorphous Microwires
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Details
3. Results and Discussion
4. Summary
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Johnson, W.L. Bulk glass-forming metallic alloys: Science and technology. MRS Bull. 1999, 24, 42–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, A. Stabilization of metallic supercooled liquid and bulk amorphous alloys. Acta Mater. 2000, 48, 279–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.H.; Dong, C.; Shek, C.H. Bulk metallic glasses. Mater. Sci. Eng. R 2004, 44, 45–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vázquez, M.; Zhukov, A.P. Magnetic properties of glass-coated amorphous and nanocrystalline microwires. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 1996, 160, 223–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vajquez, M.; Polo, C.G.; Chen, D.X.; Hemando, A. Magnetic Bistability of Amorphous Wires and Sensor Applications. IEEE Trans. Magn. 1994, 30, 907–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panina, L.V.; Mohri, K. Magneto-impedance effect in amorphous wires. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1994, 65, 1189–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.S.; Qin, F.X.; Chen, D.M.; Shen, H.X.; Wang, H.; Xing, D.W.; Phan, M.H.; Sun, J.F. Combined current-modulation annealing induced enhancement of giant magnetoimpedance effect of Co-rich amorphous microwires. J. Appl. Phys. 2014, 115, 17A326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.M.; Xing, D.W.; Qin, F.X.; Liu, J.S.; Wang, H.; Wang, X.D.; Sun, J.F. Correlation of magnetic domains, microstructure and GMI effect of Joule-annealed melt-extracted Co68.15Fe4.35Si12.25B13.75Nb1Cu0.5 microwires for double functional sensors. Phys. Status Solid. A 2013, 210, 2515–2520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McHenry, M.E.; Willard, M.A.; Laughlin, D.E. Amorphous and nanocrystalline materials for applications as soft magnets. Prog. Mater. Sci. 1999, 44, 291–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.X.; Wang, H.; Liu, J.S.; Xing, D.W.; Qin, F.X.; Cao, F.Y.; Chen, D.M.; Liu, Y.F.; Sun, J.F. Enhanced magnetocaloric and mechanical properties of melt-extracted Gd55Al25Co20 micro-fibers. J. Alloy. Compd. 2014, 603, 167–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauly, S.; Gorantla, S.; Wang, G.; Kuhn, U.; Eckert, J. Transformation-mediated ductility in CuZr–based bulk metallic glasses. Nat. Mater. 2010, 9, 473–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, J.; Liu, L.; Chan, K.C. The effect of microalloying on mechanical properties in CuZrAl bulk metallic glass. J. Alloy. Compd. 2010, 504, S74–S77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Wang, H.; Wu, H.H.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Hui, X.D.; Chen, G.L.; Ma, D.; Wang, X.L.; Lu, Z.P. Formation of Cu–Zr–Al bulk metallic glass composites with improved tensile properties. Acta Mater. 2011, 59, 2928–2936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, G.; Ohkubo, T.; Mukai, T.; Hono, K. Plasticity and microstructure of Zr–Cu–Al bulk metallic glasses. Scr. Mater. 2007, 57, 173–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, A.; Kawase, D.; Tsai, A.P.; Zhang, T.; Masumoto, T. Stability and transformation to crystalline phases of amorphous Zr–Al–Cu alloys with significant supercooled liquid region. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 1994, 178, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, W.B.; Zhao, Y.Y.; He, J.P.; Zhang, Y. Tensile deformation behaviors and damping properties of small-sized Cu–Zr–Al metallic glasses. J. Alloy. Compd. 2013, 555, 357–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.H.; Wang, J.Q.; Lu, L.; Li, Y. High tensile strength reliability in a bulk metallic glass. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2008, 92, 041905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conner, R.D.; Johnson, W.L.; Paton, N.E.; Nix, W.D. Shear bands and cracking of metallic glass plates in bending. J. Appl. Phys. 2003, 94, 904–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Xing, D.W.; Wang, X.D.; Sun, J. Fabrication and characterization of melt-extracted Co-based amorphous wires. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2010, 42, 1103–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.H. Correlations between elastic moduli and properties in bulk metallic glasses. J. Appl. Phys. 2006, 99, 093506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharpe, W.N.; Pulskamp, J.; Gianola, D.S.; Eberl, C.; Polcawich, R.G.; Thompson, R.J. Strain measurements of silicon dioxide microspecimens by digital imaging processing. Exp. Mech. 2007, 47, 649–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weibull, W.; Sweden, S. A statistical distribution function of wide applicability. J. Appl. Mech. 1951, 18, 293–297. [Google Scholar]
- Han, Z.; Tang, L.C.; Xu, J.; Li, Y. A three-parameter Weibull statistical analysis of the strength variation of bulk metallic glasses. Scr. Mater. 2009, 61, 923–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, J.D.; Lauzon, P.H. Experimental probability estimators for Weibull plots. J. Mater. Sci. Lett. 1986, 5, 1245–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.F.; Li, Y.; Schuh, C.A. Strength, plasticity and brittleness of bulk metallic glasses under compression: Statistical and geometric effects. Philos. Mag. 2008, 88, 71–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Soboyejo, W. A statistical approach to the prediction of brittle fracture in heat-affected zones of A707 steel welds. Mater. Manuf. Process. 2004, 19, 921–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zberg, B.; Arata, E.R.; Uggowitzer, P.J.; Löffler, J.F. Tensile properties of glassy MgZnCa wires and reliability analysis using Weibull statistics. Acta Mater. 2009, 57, 3223–3231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.L.; Shen, Y.; Xu, J. Weibull analysis of fracture strength for Zr55Ti2Co28Al15 bulk metallic glass: Tension-compression asymmetry and porosity effect. J. Mater. Res. 2011, 26, 2087–2097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.Y.; Ma, E.; Xu, J. Reliability of compressive fracture strength of Mg–Zn–Ca bulk metallic glasses: Flaw sensitivity and Weibull statistics. Scr. Mater. 2008, 58, 496–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Qin, F.X.; Xing, D.W.; Cao, F.Y.; Peng, H.X.; Sun, J.F. Fabrication and characterization of nano/amorphous dual-phase FINEMET microwires. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2013, 178, 1483–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stief, P.S.; Spaepen, F.; Hutchinson, J.W. Strain localization in amorphous metals. Acta Metall. 1982, 30, 447–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; He, Y.; Shiflet, G.J.; Poon, S.J. Deformation-induced nanocrystal formation in shear bands of amorphous alloys. Nature 1994, 367, 541–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores, K.M.; Dauskardt, R.H. Local heating associated with crack tip plasticity in Zr–Ti–Ni–Cu–Be bulk amorphous metals. J. Mater. Res. 1999, 14, 638–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewandowski, J.J.; Greer, A.L. Temperature rise at shear bands in metallic glasses. Nat. Mater. 2005, 5, 15–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Jiang, M.Q.; Jiang, F.; He, L.; Sun, J. The ductile to brittle transition behavior in a Zr–based bulk metallic glass. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2015, 625, 393–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barekar, N.S.; Pauly, S.; Kumar, R.B.; Kühn, U.; Dhindaw, B.K.; Eckert, J. Structure-property relations in bulk metallic Cu–Zr–Al alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2010, 527, 5867–5872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


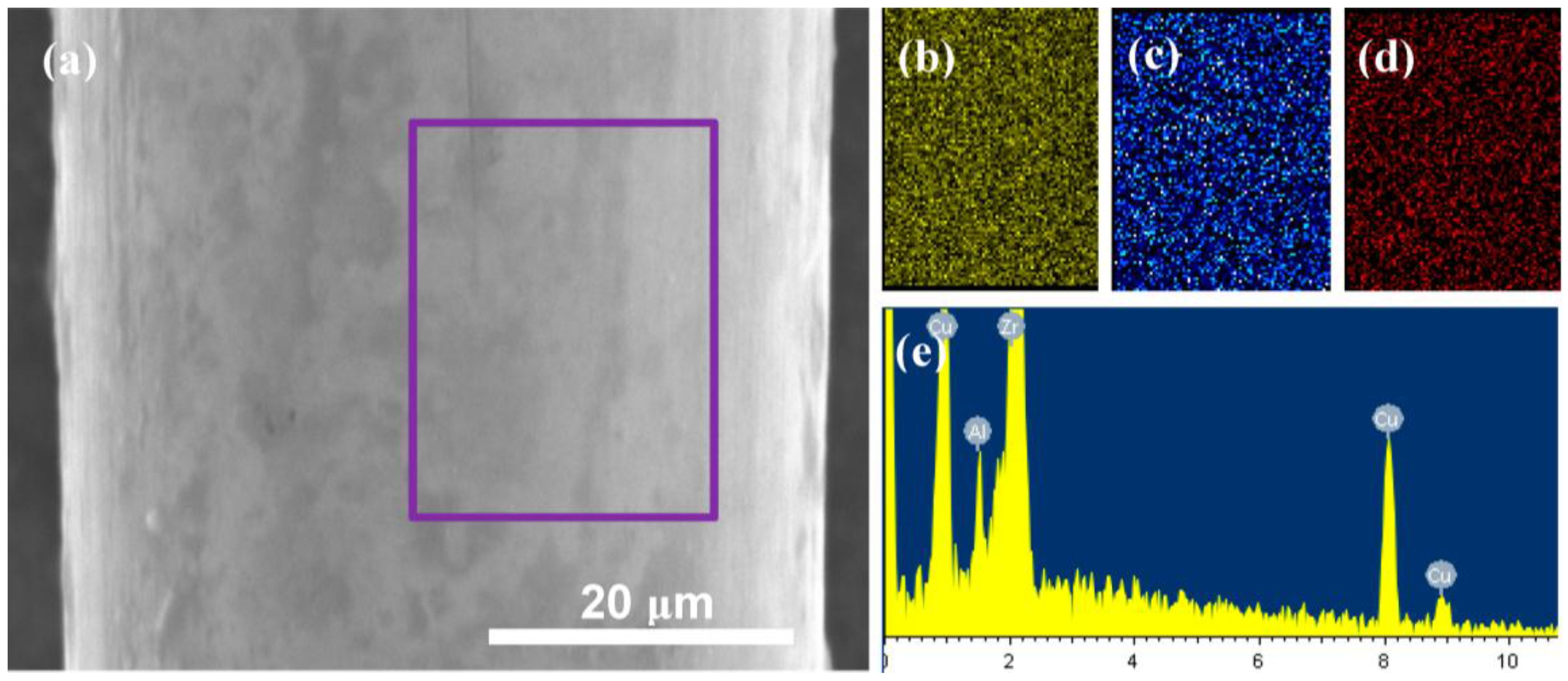

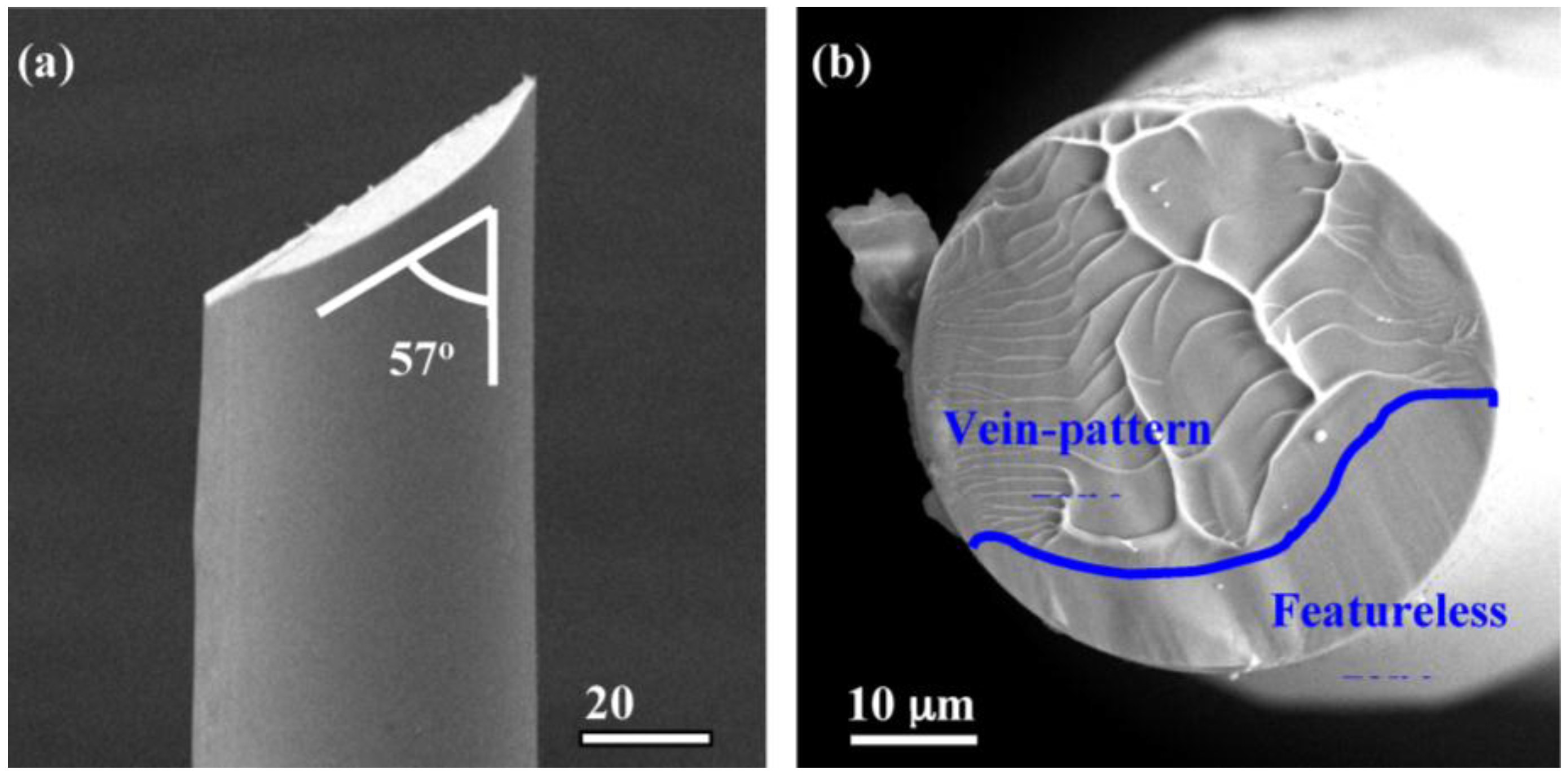
| No. | Zr, at. % | Cu, at. % | Al, at. % |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 46.72 | 48.76 | 4.52 |
| 2 | 49.75 | 47.02 | 3.22 |
| 3 | 47.47 | 48.63 | 3.90 |
| 4 | 46.06 | 48.55 | 5.39 |
| 5 | 48.65 | 47.32 | 4.03 |
| Average | 47.73 | 48.057 | 4.213 |
| Material | Test Method | Sample Sizes | No. of Test Samples | Fracture Strength | Weibull Modulus | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mg66Zn30Ca4 | Compression | Φ5 mm | 25 | 716–854 | 26 | [23] |
| Mg71Zn25Ca4 | Compression | Φ2 mm | 25 | 672–752 | 44 | [23] |
| Mg67Zn28Ca5 microwires | Tension | ~Φ100 μm | 23 | 675–894 | 20.6 | [21] |
| Gd55Al25Co20 | Tension | ~Φ30 μm | 11 | 1067–1286 | 19.9 | [30] |
| Zr55Ti2Co28Al15 | Compression | Φ6 mm | 31 | 1840–2080 | 36.2 | [22] |
| (Zr48Cu45Al7)98Y2 | Compression | Φ1.5 mm | 47 | 1430–1780 | 25.5 | [22] |
| (Zr48Cu45Al7)99Y1 | Compression | Φ1.5 mm | 30 | 1636–1883 | 34.9 | [22] |
| (Zr48Cu45Al7)99.5Y0.5 | Compression | Φ1.5 mm | 27 | 1667–1838 | 55.9 | [22] |
| Zr48Cu45Al7 | Compression | Φ1.5 mm | 28 | 1791–1898 | 73.7 | [17] |
| Zr48Cu45Al7 | Tension | 1 × 0.7 mm2 | 22 | 1790–1890 | 36.5 | [12] |
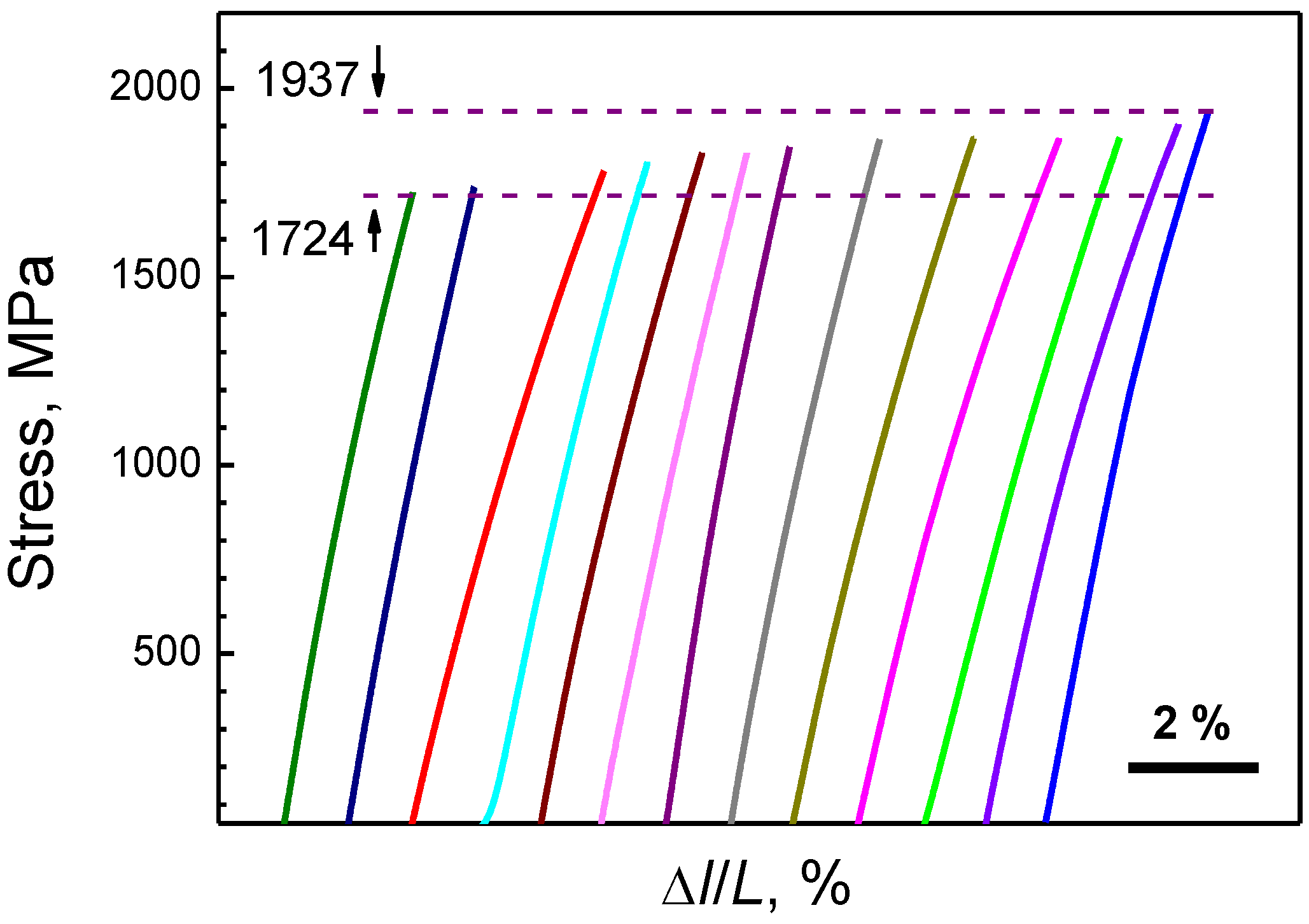
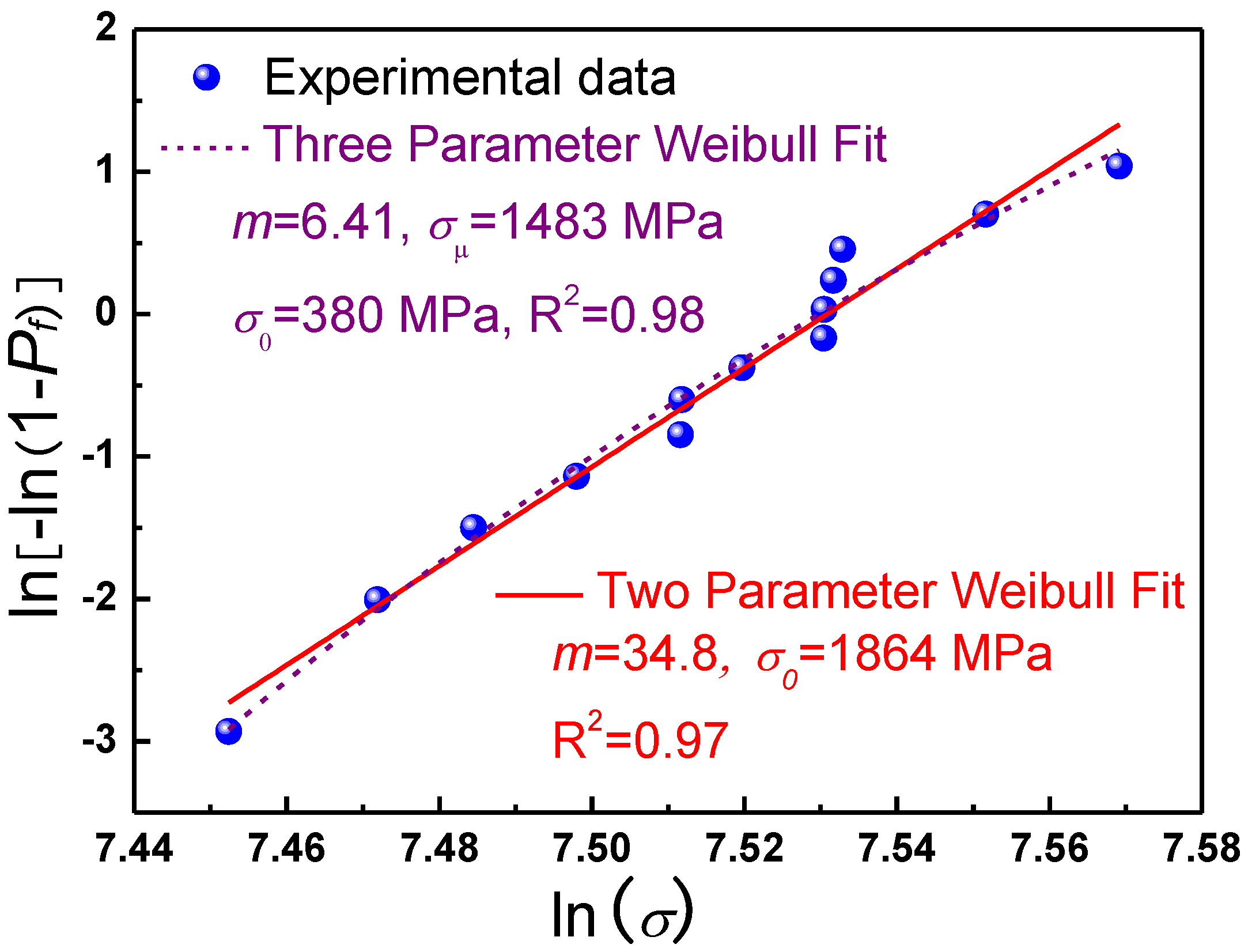
| Cu48Zr48Al4 microwires | Tension | ~Φ30 μm | 13 | 1724–1937 | 34.8 | This work |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, H.; Ning, Z.; Wang, G.; Liang, W.; Shen, H.; Sun, J.; Xue, X. Tensile Strength Reliability Analysis of Cu48Zr48Al4 Amorphous Microwires. Metals 2016, 6, 296. https://doi.org/10.3390/met6120296
Sun H, Ning Z, Wang G, Liang W, Shen H, Sun J, Xue X. Tensile Strength Reliability Analysis of Cu48Zr48Al4 Amorphous Microwires. Metals. 2016; 6(12):296. https://doi.org/10.3390/met6120296
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Haichao, Zhiliang Ning, Gang Wang, Weizhong Liang, Hongxian Shen, Jianfei Sun, and Xiang Xue. 2016. "Tensile Strength Reliability Analysis of Cu48Zr48Al4 Amorphous Microwires" Metals 6, no. 12: 296. https://doi.org/10.3390/met6120296
APA StyleSun, H., Ning, Z., Wang, G., Liang, W., Shen, H., Sun, J., & Xue, X. (2016). Tensile Strength Reliability Analysis of Cu48Zr48Al4 Amorphous Microwires. Metals, 6(12), 296. https://doi.org/10.3390/met6120296







