The Structural Evolution and Segregation in a Dual Alloy Ingot Processed by Electroslag Remelting
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
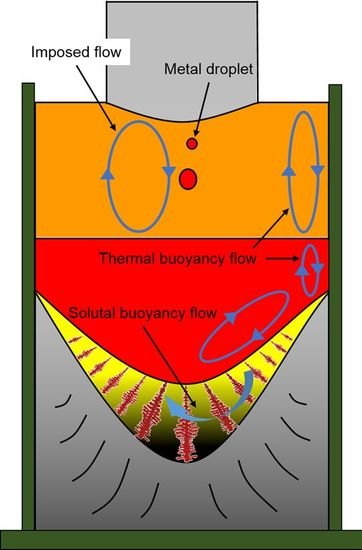
2.1. Experimental Apparatus and Method
2.2. Specimen Preparation and Analyzing Methods
3. Results and Discussions
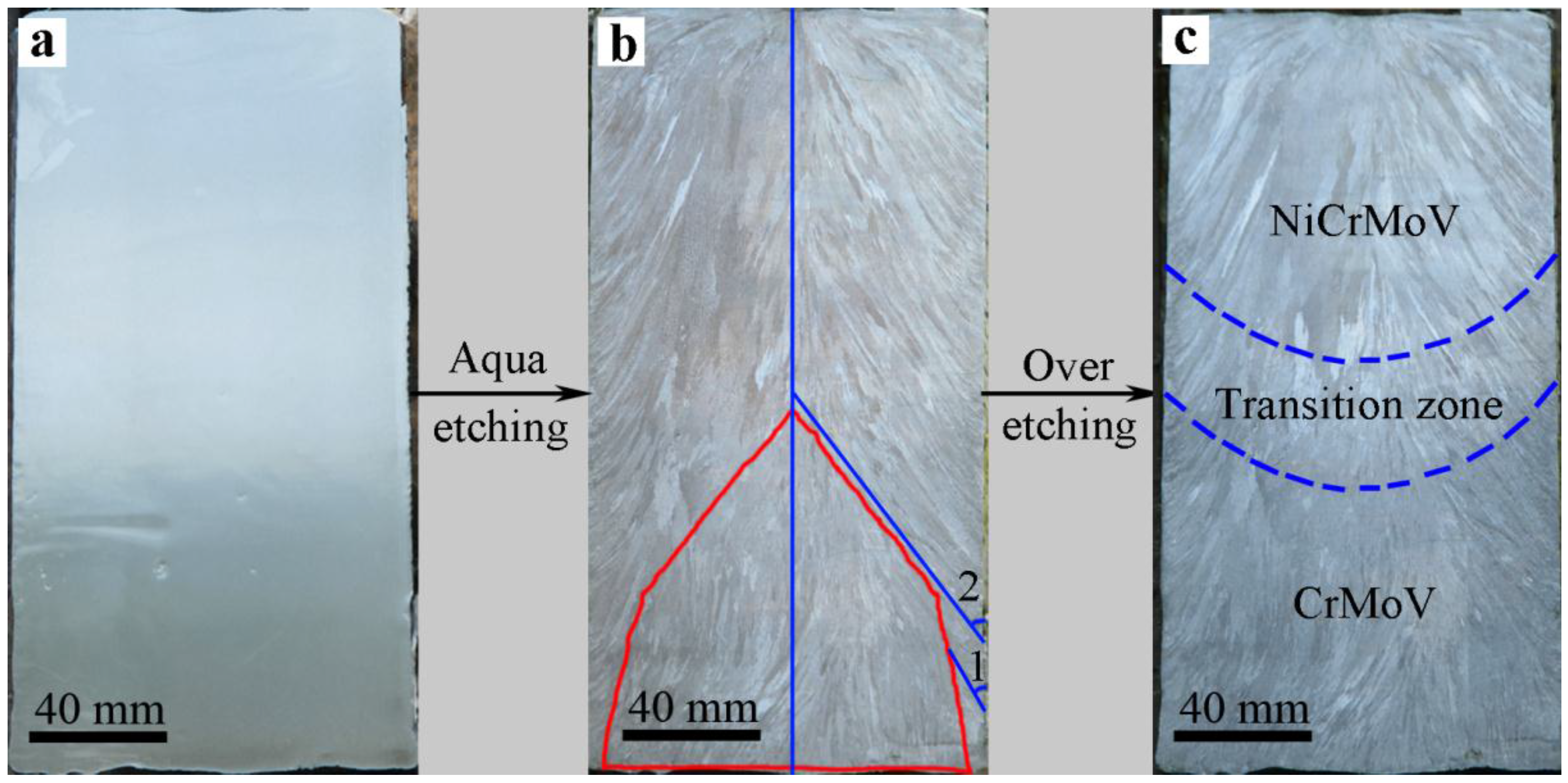
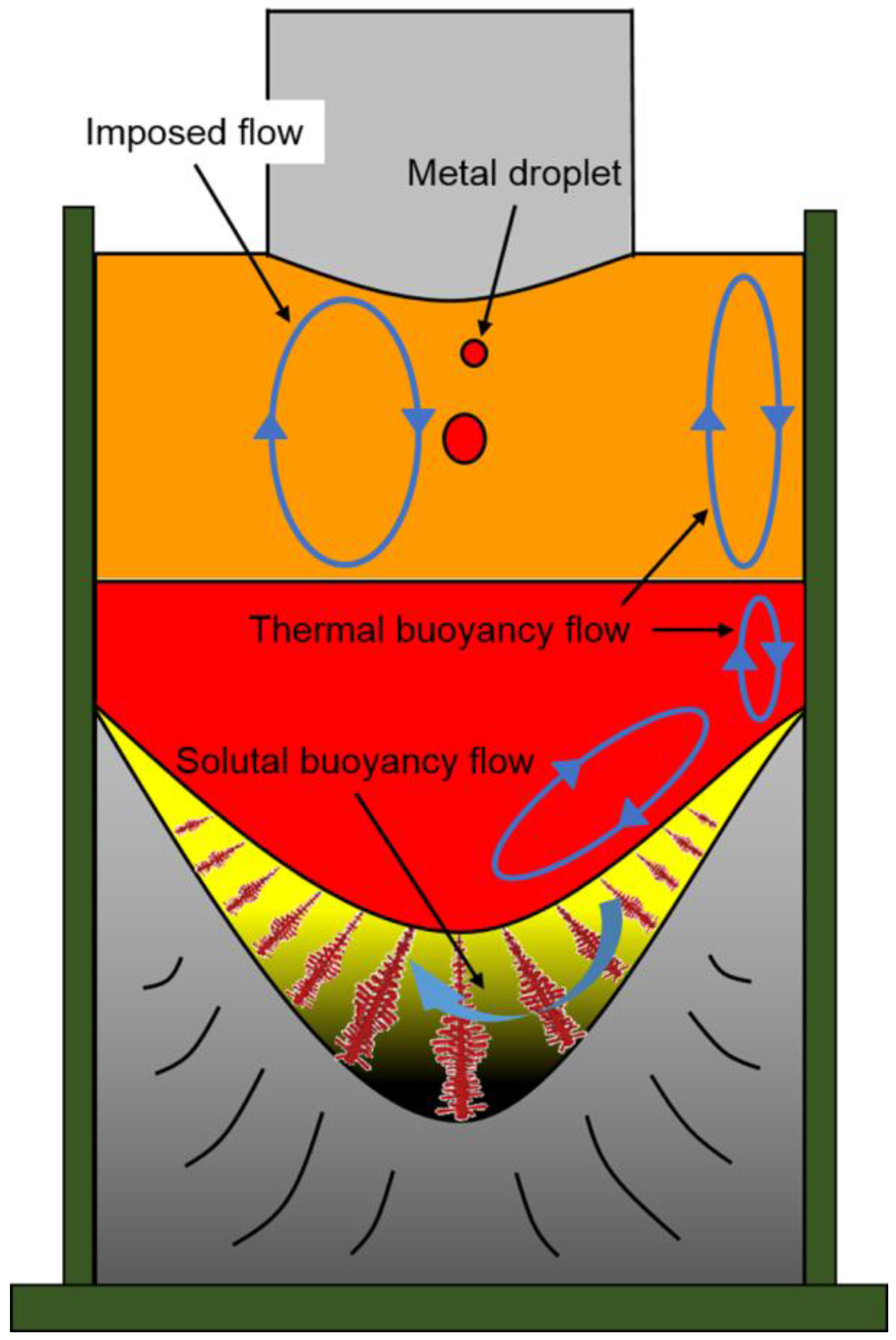
3.1. Macro- and Microstructure Evolution of Steel Ingot Made via the Electroslag Remelting (ESR) Process
3.2. Macrosegregation of the ESR Ingot
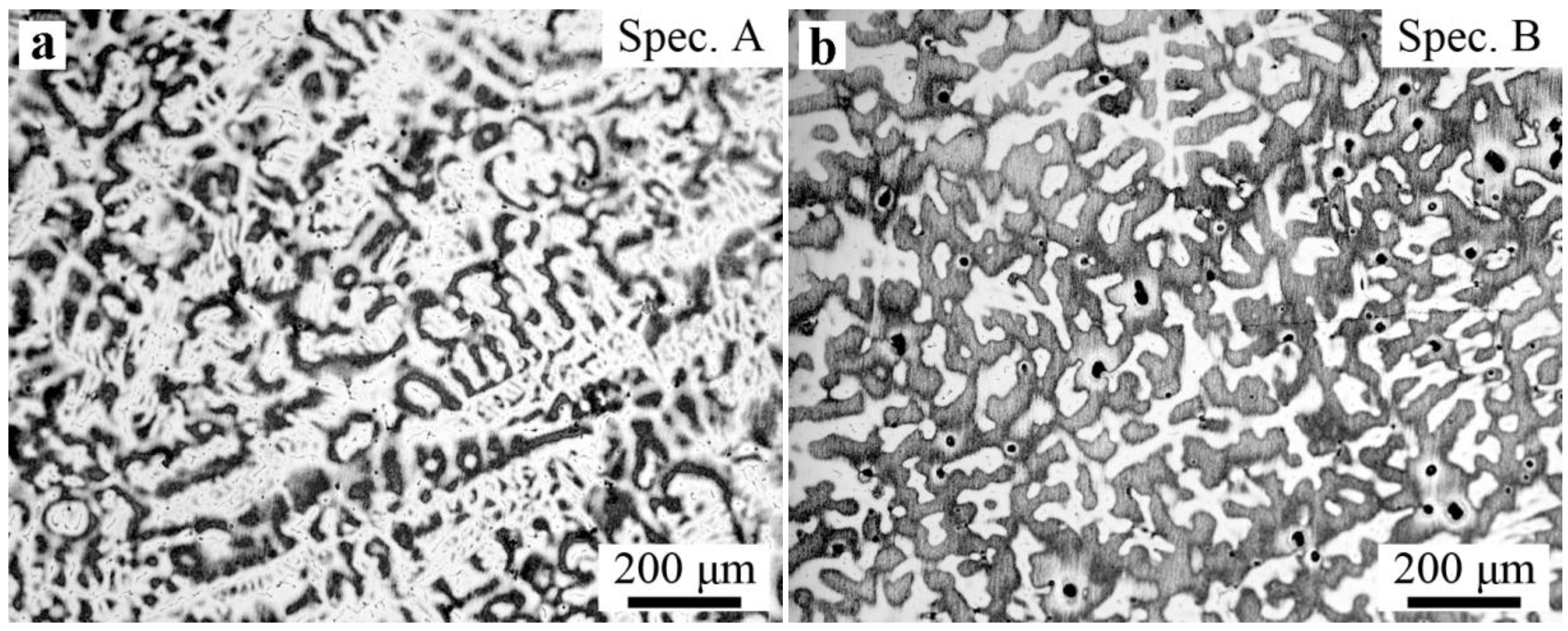
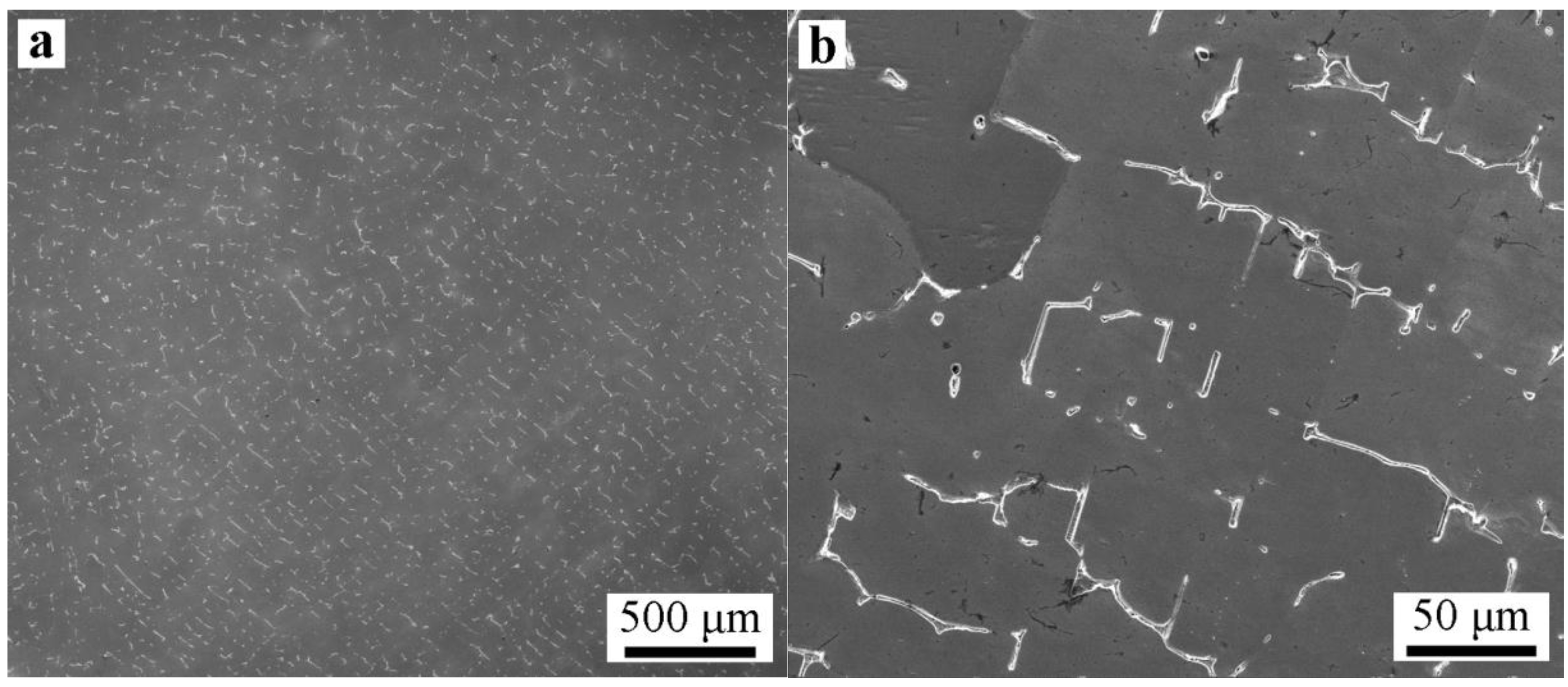
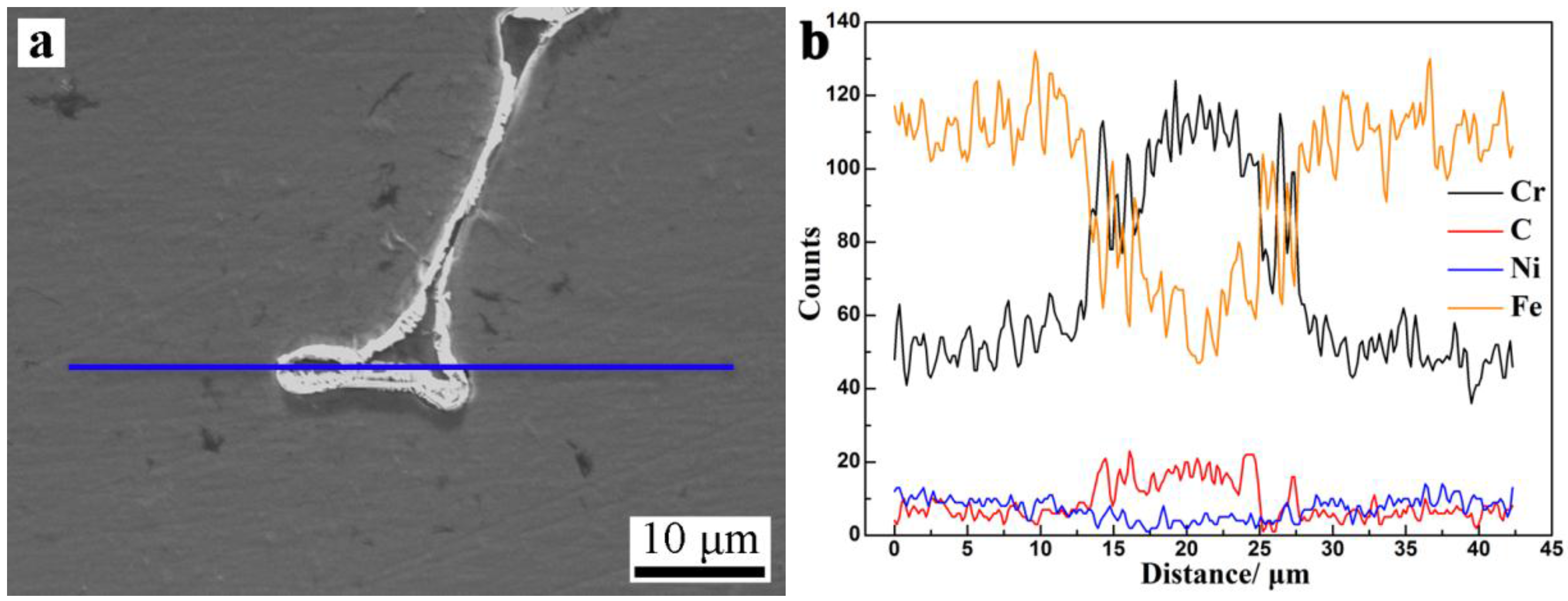
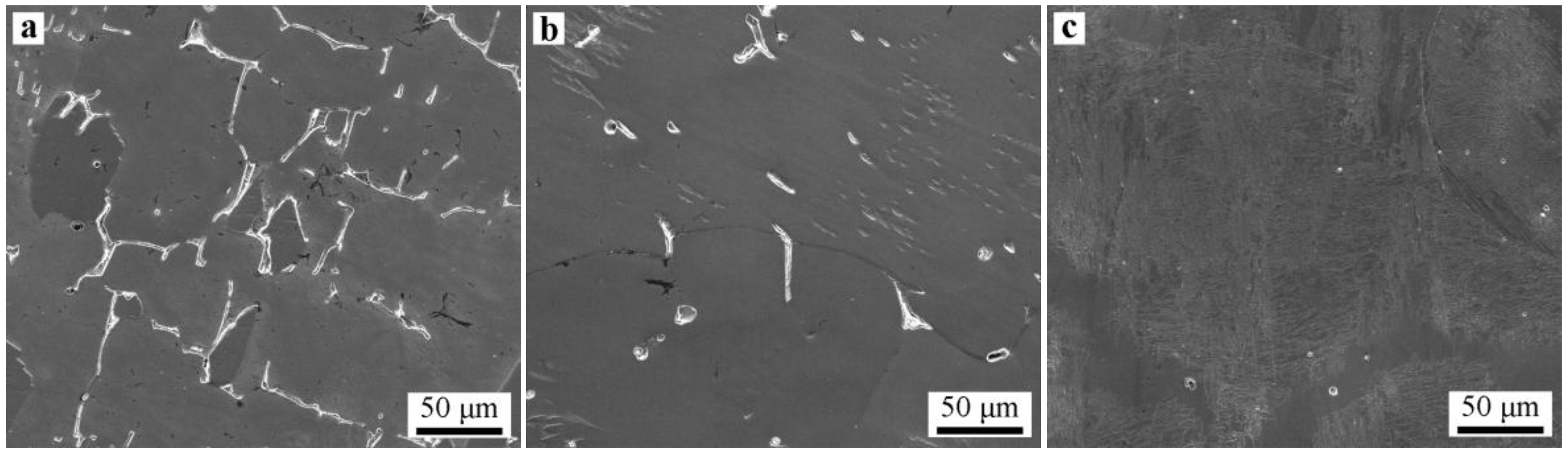
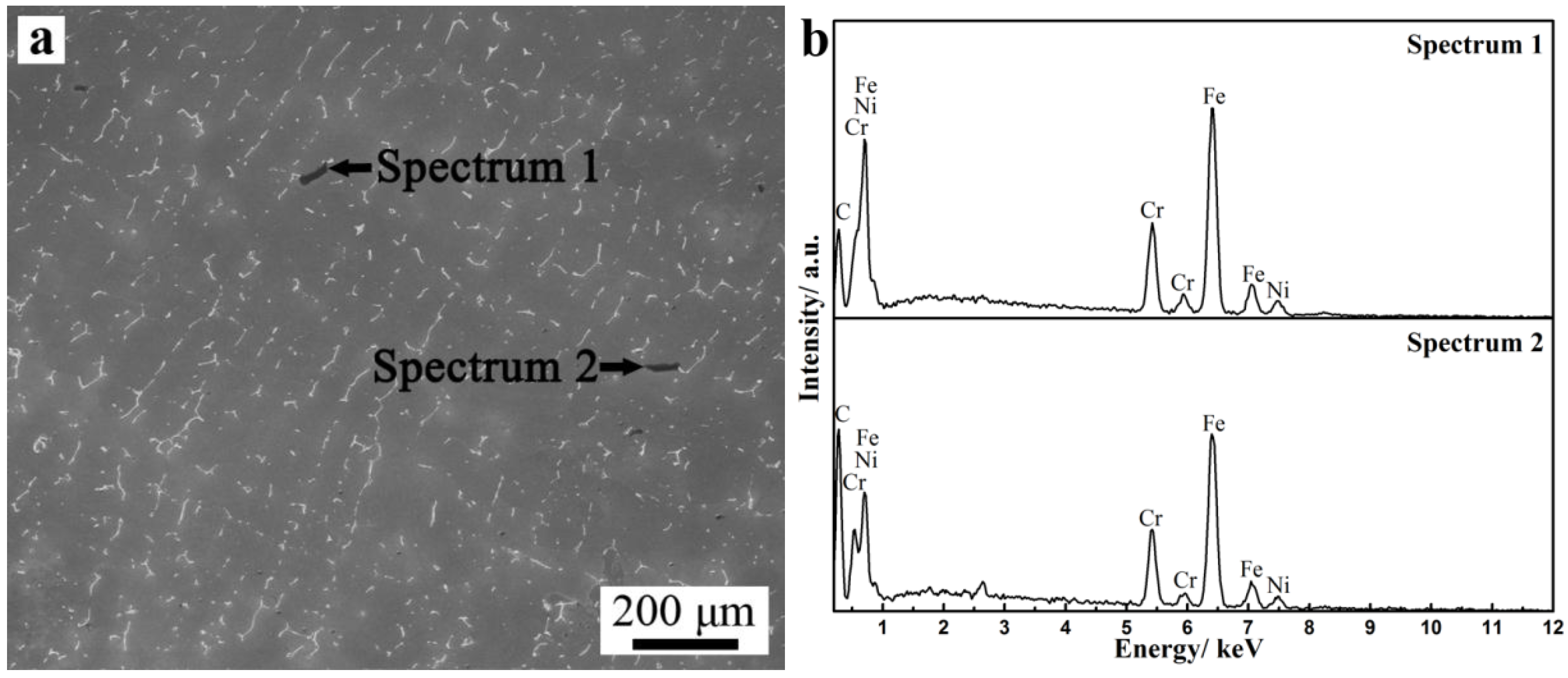
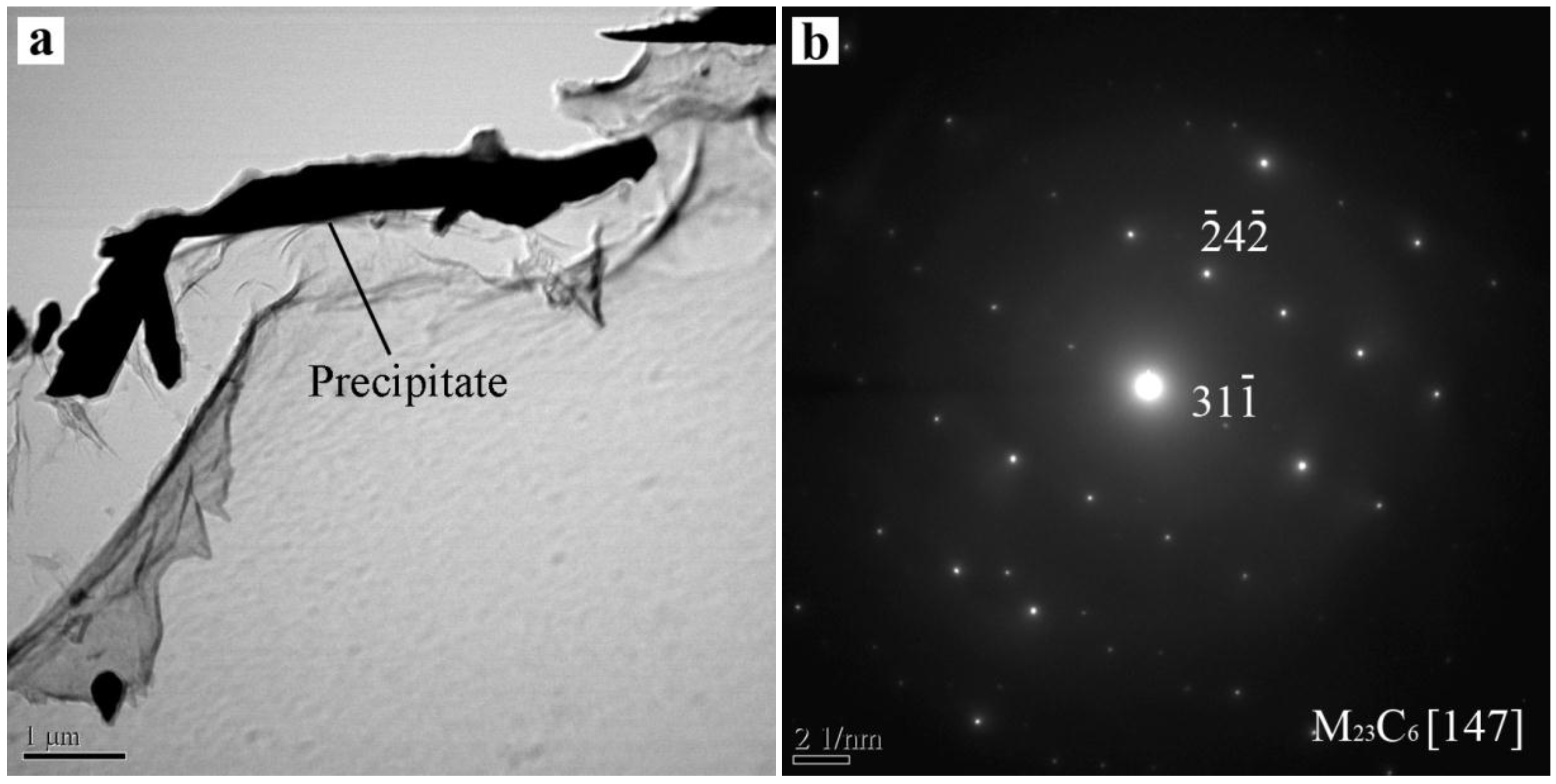
3.3. Microsegregation and Precipitates of the ESR Ingot
4. Conclusions
- (1)
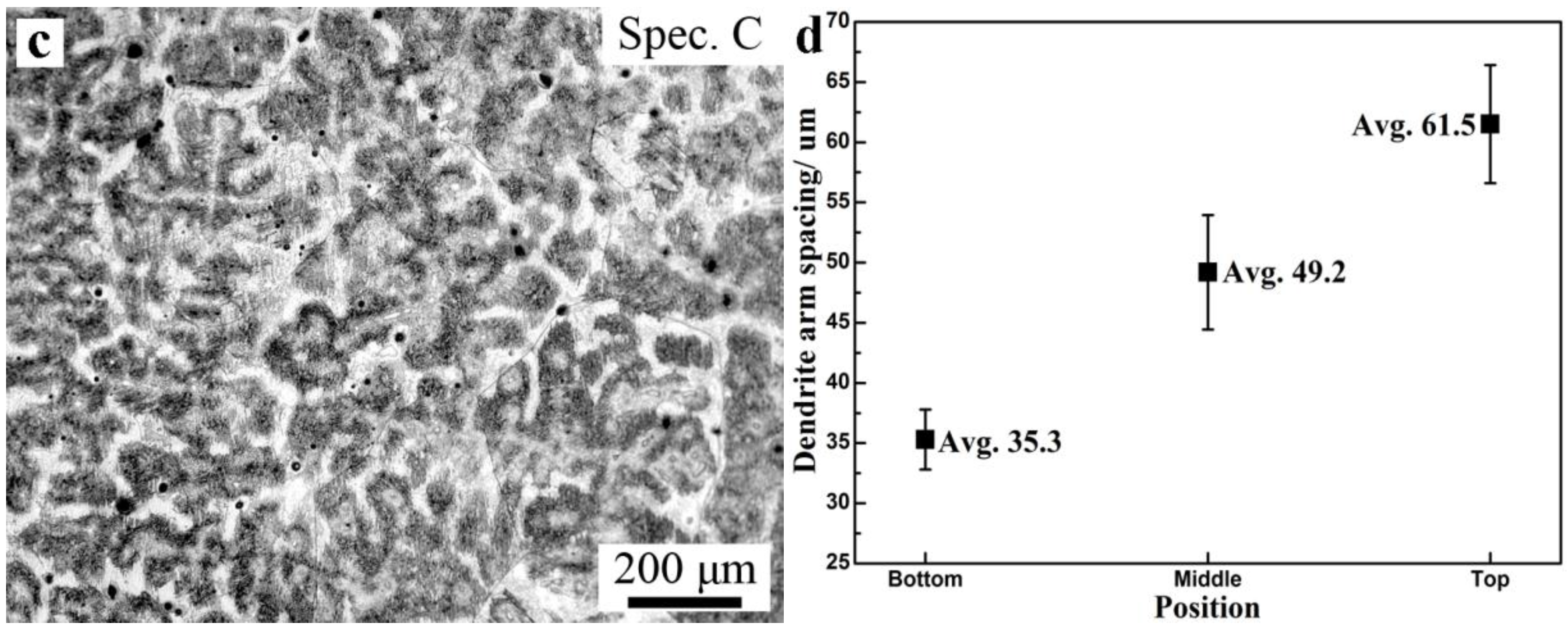
- Two crystallization structures were observed in the ESR ingot: one is a quite narrow, fine, equiaxed grain region at the edge of the ingot, and the other is a columnar grain region, which plays a leading role. The typical columnar structure shows no discontinuity between the CrMoV zone, the NiCrMoV zone, and the transition zone. The average second arm-spacing is coarsened from 35.3 to 49.2 μm and 61.5 μm from the bottom to the top of the ingot. The distinctive features of the structure are attributed to different cooling conditions during the ESR process.
- (2)
- The Ni, Cr, and C show a slight increase from the end to the top and from the surface to the center of the ESR ingot due to the partition ratios, gravity segregation, the thermal buoyancy flow, the solutal buoyancy flow, and the inward Lorentz force. The Ni, Cr, and C contents markedly increase in the transition zone until it reaches the nominal concentration of Elec. NiCrMoV.
- (3)
- Severe dendrite segregation was observed in the ESR ingot, which becomes severer from the bottom to the top of the ingot. Less dendrite segregation exists in the CrMoV zone and the transition zone due to a stronger cooling rate (11.1 and 4.5 °C/s) and lower Cr and C contents. The precipitation of carbides was observed in the ESR ingot due to a lower solid solubility of the carbon element in the α phase. The massive carbides are detrimental to the strength of the matrix. An appropriate heat treatment process is expected to eliminate the severer dendrite segregation and dissolve the massive carbides. The result of the present work provides a reference for the manufacture of the dual alloy rotor to be used in steam turbines using a combined cycle, which would provide significant improvements in power generating efficiency.
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ESR | electroslag remelting |
| TZ | transition zone |
| ICP-AES | inductively coupled plasma-atomic emission spectroscopy |
| OM | optical microscopy |
| SEM | scanning electron microscopy |
| EDS | energy dispersive spectrometer |
| TEM | transmission electron microscopy |
References
- Wang, Q.; Yan, H.; Ren, N.; Li, B. Effect of current on solute transport in electroslag remelting dual alloy ingot. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2016, 101, 546–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Yan, H.; Ren, N.; Li, B. Effect of slag thickness on macrosegregation and transition zone width of electroslag remelting dual alloy ingot. JOM 2016, 68, 397–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kajikawa, K.; Ganesh, S.; Kimura, K.; Kudo, H.; Nakamura, T.; Tanaka, Y.; Schwant, R.; Gatazka, F.; Yang, L. Forging for advanced trubine applications: Development of multiple alloy rotor forging for turbine application. Ironmak. Steelmak. 2007, 34, 216–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, L.; Zhao, J.H.; Zhao, Z.X.; Ding, G.; Geng, M.P. Macro-and microstructure evolution of 5CrNiMo steel ingots during electroslag remelting process. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 2014, 21, 644–652. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, L.Z.; Shi, X.F.; Yang, H.S.; Li, Z.B. Effect of low-frequency AC power supply during electroslag remelting on qualities of alloy steel. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 2009, 16, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Wang, Q.; Wang, F.; Chen, M. A coupled cellular automaton-finite-element mathematical model for the multiscale phenomena of electroslag remelting H13 die steel ingot. JOM 2014, 66, 1153–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, D.; Zhou, J.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, Q.; Li, D. Influence of thermal homogenization treatment on structure and impact toughness of H13 ESR steel. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 2009, 16, 56–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fezi, K.; Yanke, J.; Krane, M.J.M. Macrosegregation during electroslag remelting of alloy 625. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2015, 46, 766–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Wang, F.; Li, B.; Tsukihashi, F. A three-dimensional comprehensive model for prediction of macrosegregation in electroslag remelting ingot. ISIJ Int. 2015, 55, 1010–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Won, Y.M.; Thomas, B.G. Simple model of microsegregation during solidification of steels. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2001, 32, 1755–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Li, B. Numerical investigation on the effect of fill ratio on macrosegregation in electroslag remelting ingot. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2015, 91, 116–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Cui, J.; Zeng, X.; Ding, W. Effect of low-frequency electromagnetic field on microstructures and macrosegregation of Φ270 mm DC ingots of an Al-Zn-Mg-Cu-Zr alloy. Mater. Lett. 2005, 59, 1502–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Cui, J.; Lu, G. Effect of low-frequency magnetic field on macrosegregation of continuous casting aluminum alloys. Mater. Lett. 2003, 57, 1707–1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, M.C.; Beckermann, C. Formation of macrosegregation by multicomponent thermosolutal convection during the solidification of steel. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 1995, 26, 2373–2388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, V.; Jardy, A.; Dussoubs, B.; Ablitzer, D.; Ryberon, S.; Schmitt, V.; Hans, S.; Poisson, H. A comprehensive model of the electroslag remelting process: Description and validation. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2009, 40, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Ward, R.M.; Jacobs, M.H.; Barratt, M.D. Effect of variation in process parameters on the formation of freckle in inconel 718 by vacuum arc remelting. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2008, 39, 2981–2989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, A. Solidification in remelting processes. Mat. Sci. Eng. A 2005, 413, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Z.; Bao, H.; He, X.; Li, Q.; Liu, Z. Strengthening mechanisms of heat resistant alloys used for steam turbine rotor working at 700 °C. J. Iron Steel Res. 2015, 27, 1–6. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Jiao, S.Y.; Zhang, M.C.; Zheng, L.; Dong, J.X. Investigation of carbide precipitation process and chromium depletion during thermal treatment of Alloy 690. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2010, 41, 26–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angeliu, T.M.; Was, G.S. Behavior of grain boundary chemistry and precipitates upon thermal treatment of controlled purity alloy 690. Metall. Trans. A 1990, 21, 2097–2107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Electrode | C | Mn | Si | P | S | Cr | Ni | Mo | Al | Ti | T.[O] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Elec. NiCrMoV | 0.106 | 1.67 | 0.37 | 0.018 | 0.039 | 16.28 | 7.45 | 0.117 | 0.009 | 0.012 | 0.0156 |
| Elec. CrMoV | 0.074 | 3.94 | 0.40 | 0.020 | 0.011 | 12.25 | 5.85 | 0.14 | 0.014 | 0.008 | 0.0121 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Li, G.; Wang, Q.; Wang, L.; Li, B. The Structural Evolution and Segregation in a Dual Alloy Ingot Processed by Electroslag Remelting. Metals 2016, 6, 325. https://doi.org/10.3390/met6120325
Liu Y, Zhang Z, Li G, Wang Q, Wang L, Li B. The Structural Evolution and Segregation in a Dual Alloy Ingot Processed by Electroslag Remelting. Metals. 2016; 6(12):325. https://doi.org/10.3390/met6120325
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Yu, Zhao Zhang, Guangqiang Li, Qiang Wang, Li Wang, and Baokuan Li. 2016. "The Structural Evolution and Segregation in a Dual Alloy Ingot Processed by Electroslag Remelting" Metals 6, no. 12: 325. https://doi.org/10.3390/met6120325
APA StyleLiu, Y., Zhang, Z., Li, G., Wang, Q., Wang, L., & Li, B. (2016). The Structural Evolution and Segregation in a Dual Alloy Ingot Processed by Electroslag Remelting. Metals, 6(12), 325. https://doi.org/10.3390/met6120325