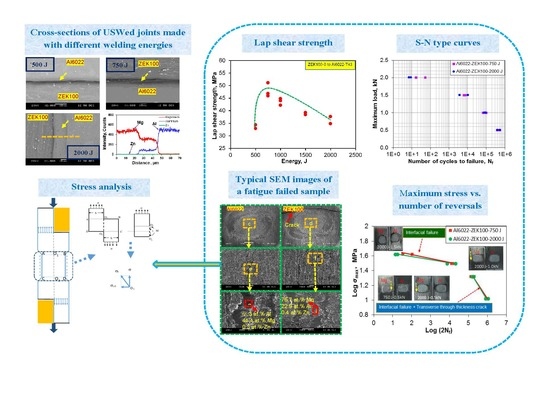
Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Ultrasonic Spot Welded Mg/Al Alloy Dissimilar Joints
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
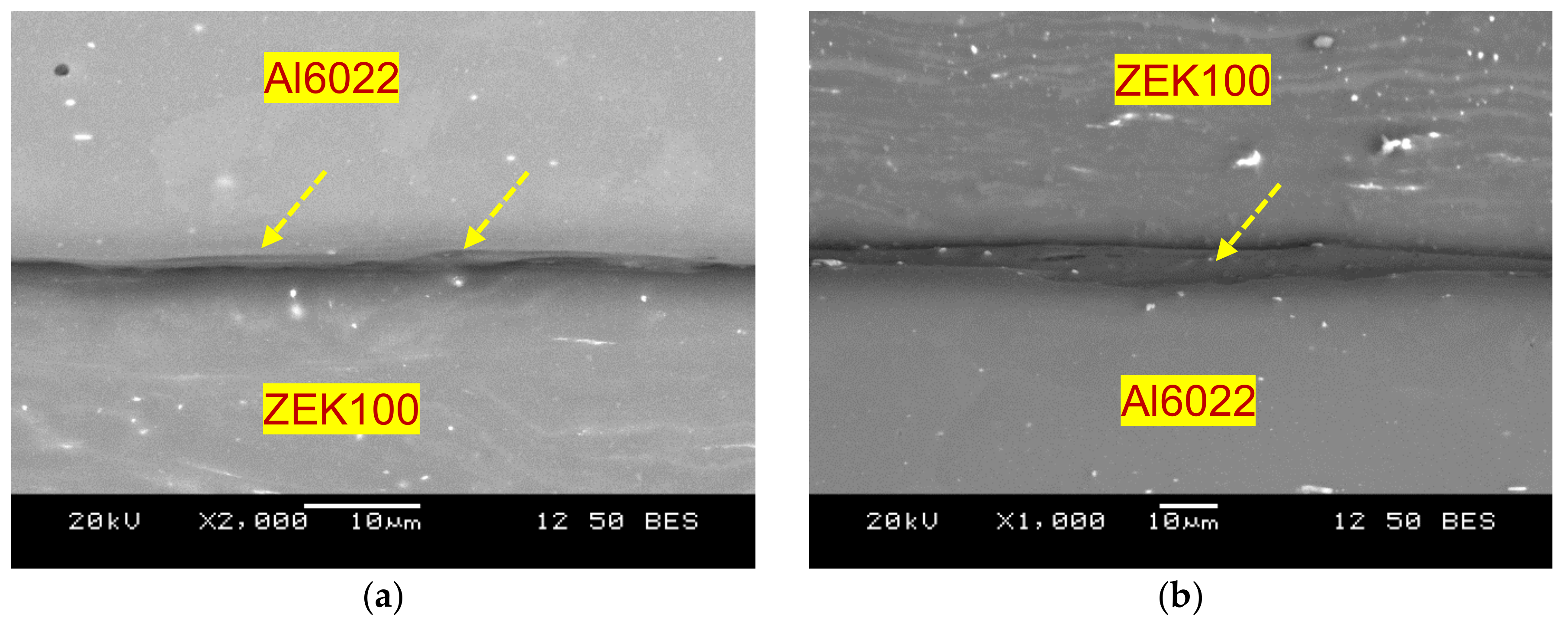
3.1. Microstructural Characterization
3.2. Tensile Lap Shear Load
3.3. Fractography: Tensile Lap Shear Fracture Surface Examinations
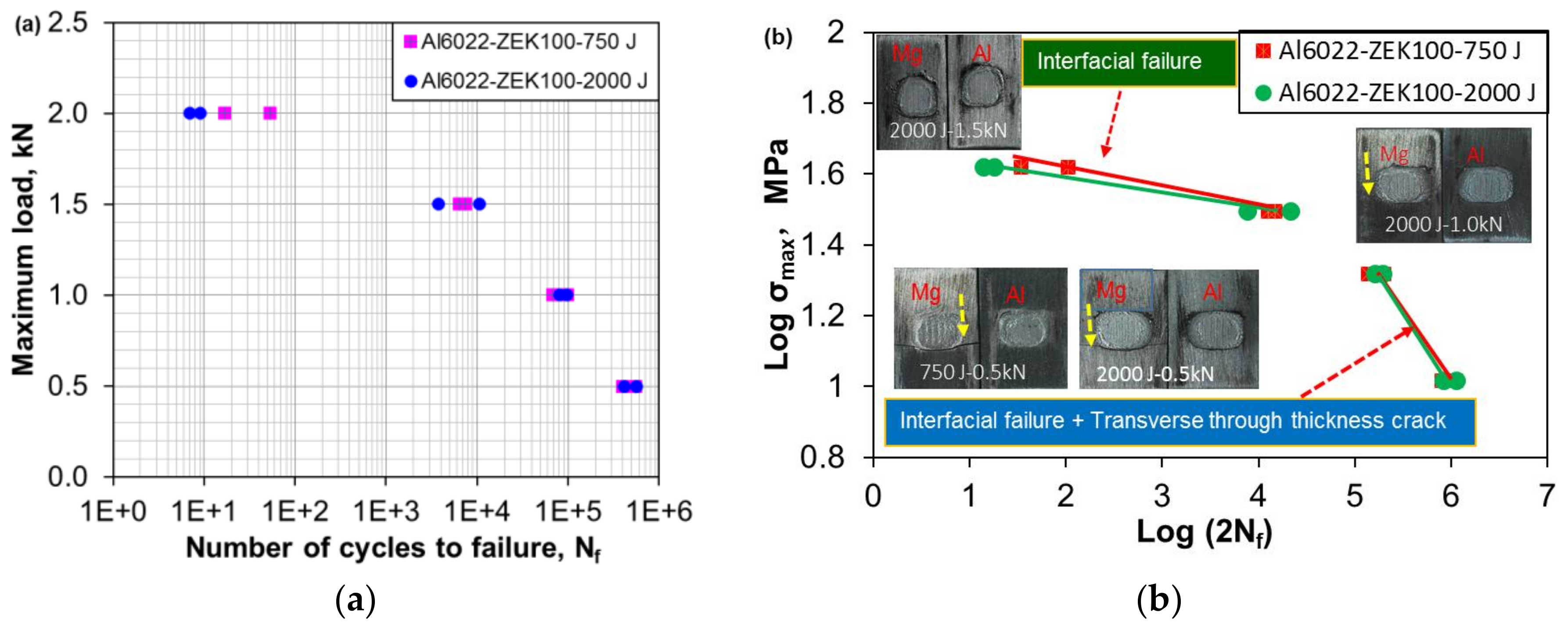
3.4. Fatigue Strength and Failure Mode
4. Conclusions
- An interface diffusion layer consisting of eutectic structure of α-Mg and Al12Mg17 was observed during welding at the energy levels from 500 J to 2000 J. The thickness of the interface diffusion layer increased from 0.5 µm to 30 µm with increasing welding energy.
- As the welding energy increased, the tensile lap shear peak load and critical stress intensity of the USWed joints first increased, reached their maximum values, and then decreased, while the interfacial failure mode occurred in the tensile lap shear tests at all levels of welding energy due to the presence of interface diffusion layer.
- The desirable interface diffusion layer was observed to be thin (about 3~5 µm in thickness) and continuous, which was achieved at a welding energy of 750 J, corresponding to the highest peak load of ~2 kN and the highest critical stress intensity of ~4.7 MPam1/2, respectively.
- The peak load of USWed ZEK100-Al6022 dissimilar joints reached about 68% of that of USWed ZEK100-ZEK100 similar joints and about 56% of that of USWed Al6022-Al6022 similar joints, while the peak critical stress intensity of ZEK100-Al6022 dissimilar joints arrived at about 75% and 49% of that of ZEK100-ZEK100 and Al6022-Al6022 similar joints, respectively. This was mainly related to the existence of interface diffusion layer in the ZEK100-Al6022 dissimilar joints and the difference in the ductility and formability between Al alloy and Mg alloy.
- Fatigue life of the USWed ZEK100-Al6022 dissimilar joints made at energy levels of 750 J and 2000 J was equivalent at the lower cyclic loads, while the joints made at 750 J exhibited a longer fatigue life at the higher cyclic loading levels. When the cyclic loading levels changed from high to low, the fatigue fracture mode changed from the interfacial failure to a mixed mode of interfacial failure and TTT crack growth that occurred on the Mg side, which corresponded well to the bi-linear characteristic of S-N curves.
- In both tensile lap shear and fatigue tests, the crack initiation was observed to occur basically at the weld nugget edge and at the interface between the two sheets. A theoretical stress analysis indicated that this was due to the presence of the maximum triaxial stresses at that location.
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Anenberg, S.C.; Miller, J.; Minjares, R.; Du, L.; Henze, D.K.; Lacey, F.; Malley, C.S.; Emberson, L.; Franco, V.; Klimont, Z.; et al. Impacts and mitigation of excess diesel-related NOx emissions in 11 major vehicle markets. Nature 2017, 545, 467–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rockström, J.; Gaffney, O.; Rogelj, J.; Meinshausen, M.; Nakicenovic, N.; Schellnhuber, H.J. A roadmap for rapid decarbonization. Science 2017, 355, 1269–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosen, J. After the ice goes. Nature 2017, 542, 152–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gielen, D.; Boshell, F.; Saygin, D. Climate and energy challenges for materials science. Nat. Mater. 2016, 15, 117–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, S.; Majumdar, A. Opportunities and challenges for a sustainable energy future. Nature 2012, 488, 294–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McNutt, M. Climate change impacts. Science 2013, 341, 435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, Z.R.; Nie, J.F.; Xu, S.W.; Davies, C.H.J.; Birbilis, N. Super-formable pure magnesium at room temperature. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nie, J.F.; Zhu, Y.M.; Liu, J.Z.X.; Fang, Y. Periodic segregation of solute atoms in fully coherent twin boundaries. Science 2013, 340, 957–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.X.; Curtin, W.A. The origins of high hardening and low ductility in magnesium. Nature 2015, 526, 62–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frankel, G.S. Magnesium alloys: Ready for the road. Nat. Mater. 2015, 14, 1189–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, W.Q.; Birbilis, G.; Sha, N.; Wang, Y.; Daniels, J.E.; Xiao, Y.; Ferry, M. A high-specific-strength and corrosion-resistant magnesium alloy. Nat. Mater. 2015, 14, 1229–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirsch, J. Aluminum in innovative light-weight car design. Mater. Trans. 2011, 52, 818–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taub, A.I.; Luo, A.A. Advanced lightweight materials and manufacturing processes for automotive applications. MRS Bull. 2015, 40, 1045–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Li, Y.J.; Geng, H.R.; Wang, J. Microstructure characteristics in TIG welded joint of Mg Al dissimilar materials. Mater. Lett. 2007, 61, 1288–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, V.K.; Bhole, S.D.; Chen, D.L. Microstructure and mechanical properties of dissimilar welded Mg-Al joints by ultrasonic spot welding technique. Sci. Technol. Weld. Join. 2012, 17, 202–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Chen, D.L.; Jiang, X.Q. Microstructure and mechanical properties of an ultrasonic spot welded aluminum alloy: The effect of welding energy. Materials 2017, 10, 449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.C.; Nakata, K. Friction stir lap joining aluminum and magnesium alloys. Scr. Mater. 2008, 58, 433–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panteli, A.; Chen, Y.C.; Strong, D.; Zhang, X.; Prangnell, P.B. Optimization of aluminium-to-magnesium ultrasonic spot welding. JOM 2012, 64, 414–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pouranvari, M. Fracture toughness of martensitic stainless steel resistance spot welds. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2017, 680, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Ren, D.; Liu, F. A review of dissimilar welding techniques for magnesium alloys to aluminum alloys. Materials 2014, 7, 3735–3757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, V.K.; Bhole, S.D.; Chen, D.L. Improving weld strength of magnesium to aluminum dissimilar joints via tin interlayer during ultrasonic spot welding. Sci. Technol. Weld. Join. 2012, 17, 342–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panteli, A.; Robson, J.D.; Brough, I.; Prangnell, P.B. The effect of high strain rate deformation on intermetallic reaction during ultrasonic welding aluminum to magnesium. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2012, 556, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panteli, A.; Robson, J.D.; Chen, Y.C. Prangnell, P.B. The effectiveness of surface coatings on preventing interfacial reaction during ultrasonic welding of aluminum to magnesium. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2013, 44, 5773–5781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macwan, A.; Chen, D.L. Ultrasonic spot welding of rare-earth containing ZEK100 magnesium alloy to 5754 aluminum alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2016, 666, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macwan, A.; Chen, D.L. Microstructure and mechanical properties of ultrasonic spot welded copper-to-magnesium alloy joints. Mater. Des. 2015, 84, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macwan, A.; Patel, V.K.; Jiang, X.Q.; Li, C.; Bhole, S.D.; Chen, D.L. Ultrasonic spot welding of Al/Mg/Al tri-layered clad sheets. Mater. Des. 2014, 62, 344–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakavos, D.; Prangnell, P.B. Mechanisms of joint and microstructure formation in high power ultrasonic spot welding 6111 aluminum automotive sheet. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2010, 527, 6320–6334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gould, J.E. Joining aluminum sheet in the automotive industry—A 30 year history. Weld. J. 2012, 91, 23s–34s. [Google Scholar]
- Patel, V.K.; Chen, D.L.; Bhole, S.D. Dissimilar ultrasonic spot welding of Mg-Al and Mg-high strength low alloy steel. Theor. Appl. Mech. Lett. 2014, 4, 041005-1–041005-8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macwan, A.; Mirza, F.A.; Bhole, S.D.; Chen, D.L. Similar and dissimilar ultrasonic spot welding of 5754 aluminum alloy for automotive applications. Mater. Sci. Forum 2017, 877, 561–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, D.; Davis, B.; Robson, J.D. The Influence of strain path on rare earth recrystallization textures in a magnesium-zinc-rare earth alloy. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2018, 49, 321–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boba, M.; Butcher, C.; Panahi, N.; Worswick, M.J.; Mishra, R.K.; Carter, J.T. Warm forming limits of rare earth-magnesium alloy ZEK100 sheet. Int. J. Mater. Form. 2017, 10, 181–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, H.M.; Rodriguez, R.I.; Jordon, J.B.; Barkey, M.E.; Guo, Y.B.; Badarinarayan, H.; Yuan, W. Friction stir spot welding of rare-earth containing ZEK100 magnesium alloy sheets. Mater. Des. 2014, 56, 750–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, X.P.; Skszek, T.; Fabischek, M.; Zak, A. Low temperature warm forming of magnesium ZEK 100 sheets for automotive applications. Mater. Sci. Forum 2014, 783–786, 431–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokdad, F.; Chen, D.L. Strain-controlled low cycle fatigue properties of a rare-earth containing ZEK100 magnesium alloy. Mater. Des. 2015, 67, 436–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokdad, F.; Chen, D.L. Cyclic deformation and anelastic behavior of ZEK100 magnesium alloy: Effect of strain ratio. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2015, 640, 243–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirza, F.A.; Chen, D.L.; Li, D.J.; Zeng, X.Q. Effect of rare earth elements on deformation behavior of an extruded Mg-10Gd-3Y-0.5Zr alloy during compression. Mater. Des. 2013, 46, 411–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahreen, N.; Zhang, D.F.; Pan, F.S.; Jiang, X.Q.; Li, D.Y.; Chen, D.L. Hot deformation and processing map of an as-extruded Mg-Zn-Mn-Y alloy containing I and W phases. Mater. Des. 2015, 87, 245–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, J.E.; Luan, B. Protective coatings on magnesium and its alloys—A critical review. J. Alloy. Compd. 2002, 336, 88–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamasaki, M.; Hayashi, N.; Izumi, S.; Kawamura, Y. Corrosion behavior of rapidly solidified Mg-Zn-rare earth element alloys in NaCl solution. Corros. Sci. 2007, 49, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wielage, B.; Mucklich, S.; Grund, T. Corrosion behavior of soldered joints of magnesium alloys and dissimilar materials. Microchim. Acta 2007, 156, 151–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishak, M.; Yamasaki, K.; Maekawa, K. Micmstnlcture and Corrosion Behavior of Laser Welded Magnesium Alloys with Silver NaIloparticles. World Acad. Sci. Eng. Technol. 2010, 70, 354–358. [Google Scholar]
- Macwan, A.; Jiang, X.Q.; Chen, D.L. Interfacial characterization of dissimilar joints between Al/Mg/Al-trilayered clad sheet to high-strength low-alloy steel. JOM 2015, 67, 1468–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, S.H.; Chen, D.L.; Bhole, S.D.; Cao, X.; Wanjara, P. Lap shear strength and fatigue life of friction stir spot welded AZ31 magnesium and 5754 aluminum alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2012, 556, 500–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, S.H.; Chen, D.L.; Bhole, S.D.; Cao, X.; Wanjara, P. Lap shear strength and fatigue behavior of friction stir spot welded dissimilar magnesium-to-aluminum joints with adhesive. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2013, 562, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firouzdor, V.; Kou, S. Formation of liquid and intermetallics in Al-to-Mg friction stir welding. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2010, 41, 3238–3251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Niknejad, S.T.; Zhang, G.; Lee, M.K.; Wu, L.; Zhou, Y. Microstructure and mechanical properties of resistance spot welded AZ31/AA5754 using a nickel interlayer. Mater. Des. 2015, 87, 905–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, Y.S.; Shiota, A.; Kokawa, H.; Okamoto, K.; Yang, Q.; Kim, C. Effect of interfacial microstructure on lap shear strength of friction stir spot weld of aluminum alloy to magnesium alloy. Sci. Technol. Weld. Join. 2010, 15, 319–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, J.; Wang, K.H.; Zhou, Q.; Zhang, D.K.; Huang, J.; Li, G. Microstructure characteristics and mechanical properties of cold metal transfer welding Mg/Al dissimilar metals. Mater. Des. 2012, 34, 559–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Q.B.; Li, Y.L.; Yang, J.; Wang, Y.B.; Xiao, X. Effects of chemical plating Sn coating on the ultrasonic spot welding of Mg/Al dissimilar metals. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2017, 25, 35–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.R.; Liang, W.; Zhao, X.G.; Zhang, Y.; Fu, X.P.; Liu, F.C. Bonding of Mg and Al with Mg–Al eutectic alloy and its application in aluminum coating on magnesium. J. Alloy. Compd. 2009, 471, 408–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, D.; Ahn, B.; Lee, C.; Yeon, Y.; Song, K.; Jung, S. Formation of intermetallic compounds in Al and Mg alloy interface during friction stir spot welding. Intermetallics 2011, 19, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carboni, M.; Annoni, M. Ultrasonic metal welding of AA 6022-T4 lap joints: Part II—Fatigue behavior, failure analysis and modelling. Sci. Technol. Weld. Join. 2011, 16, 116–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, V.K.; Bhole, S.D.; Chen, D.L. Fatigue life estimation of ultrasonic spot welded Mg alloy joints. Mater. Des. 2014, 62, 124–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Liu, L.; Zhou, Y.; Mori, H.; Chen, D.L. Tensile and fatigue properties of weld-bonded and adhesive-bonded magnesium alloy joints. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2012, 563, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Material | Zn | Zr | Si | Nd | Ti | Mn | Fe | Cr | Mg | Cu | Al |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZEK100 Mg alloy | 1.3 | 0.25 | 0.2 | 0.01 | Bal | ||||||
| 6022Al alloy | 0.2 | 1.0 | 0.1 | 0.7 | 0.5 | 0.25 | 1.0 | 0.1 | Bal |
| Ultrasonic Power | Clamping Pressure | Welding Energy | Welding Time | Impedance Setting | Frequency |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2000 W | 0.40 MPa | 500–2000 J | 0.25–1 s | 5 | 20 kHz |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Peng, H.; Jiang, X.; Bai, X.; Li, D.; Chen, D. Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Ultrasonic Spot Welded Mg/Al Alloy Dissimilar Joints. Metals 2018, 8, 229. https://doi.org/10.3390/met8040229
Peng H, Jiang X, Bai X, Li D, Chen D. Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Ultrasonic Spot Welded Mg/Al Alloy Dissimilar Joints. Metals. 2018; 8(4):229. https://doi.org/10.3390/met8040229
Chicago/Turabian StylePeng, He, Xianquan Jiang, Xuefei Bai, Dongyang Li, and Daolun Chen. 2018. "Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Ultrasonic Spot Welded Mg/Al Alloy Dissimilar Joints" Metals 8, no. 4: 229. https://doi.org/10.3390/met8040229
APA StylePeng, H., Jiang, X., Bai, X., Li, D., & Chen, D. (2018). Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Ultrasonic Spot Welded Mg/Al Alloy Dissimilar Joints. Metals, 8(4), 229. https://doi.org/10.3390/met8040229