Experimental Study on Cross Wedge Rolling of 21-4N Heat Resistant Steel
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Design of CWR Process
3. Experiments and Results
3.1. Experiments Conditions
3.2. Experiment Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Surface Quality
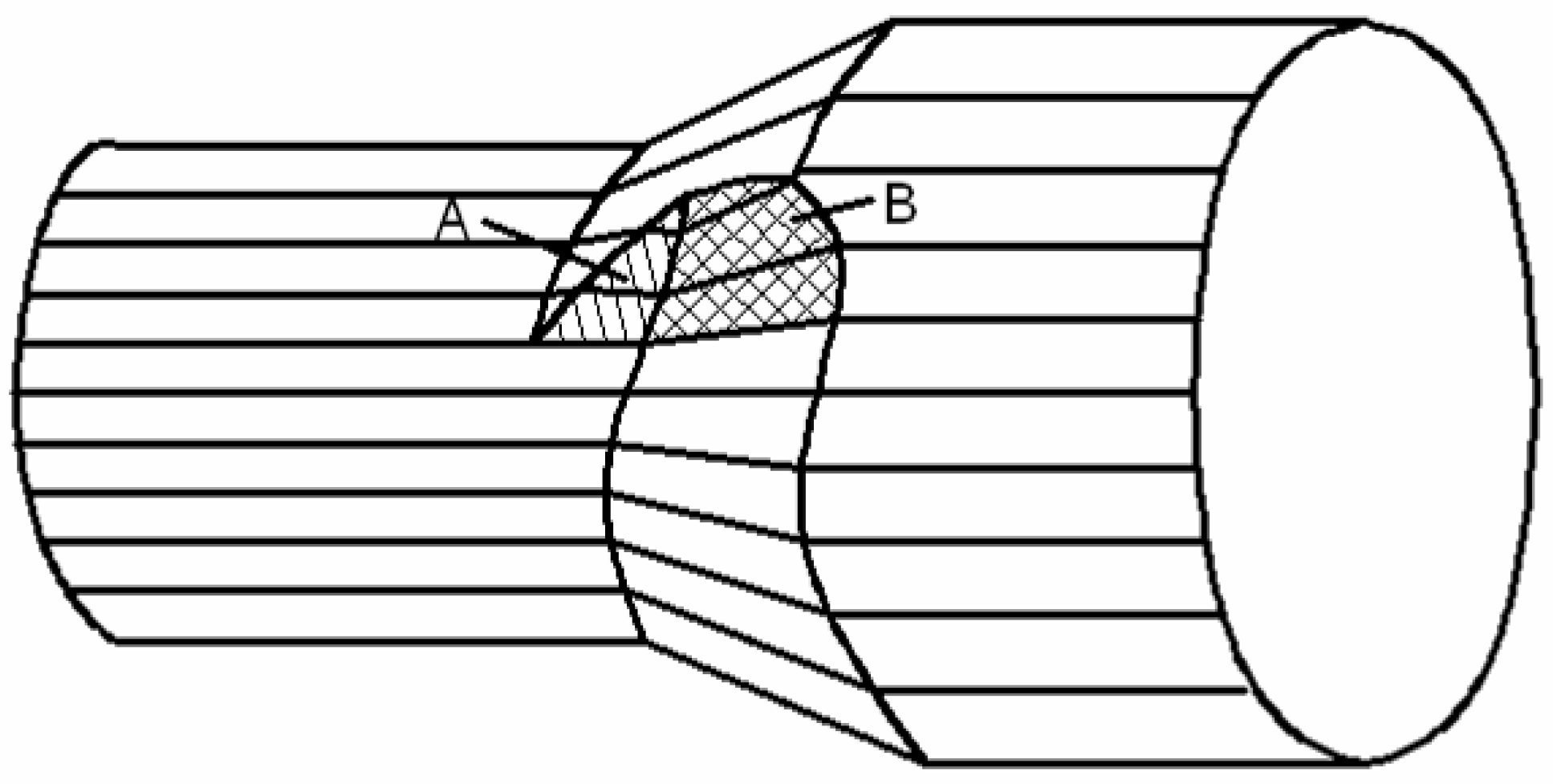
4.2. Central Quality
5. Conclusions
- (1)
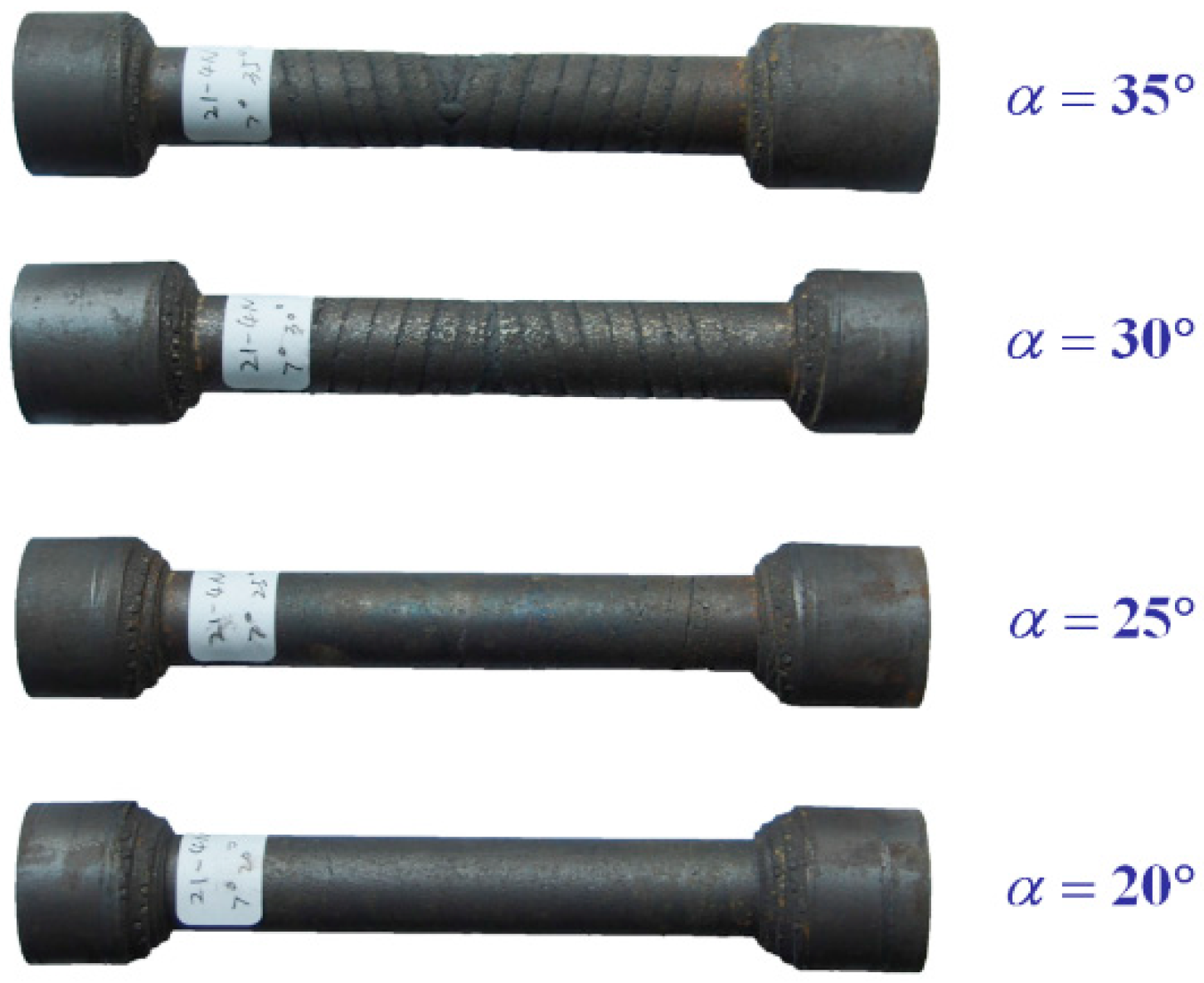
- A larger stretching angle and smaller forming angle are good for the surface quality. When the stretching angle is 7° and forming angle is 20°, the surface quality reaches the best level.
- (2)
- The influence of forming angle on central quality is significant. When the stretching angles are 5° and 7°, no damage was found at the central area with the forming angle of 30° and 35°.
- (3)
- Considering the balance of surface quality and central quality, when forming a 21-4N workpiece with an area reduction of 65%, stretching angle of 7° and forming angle of 30° can be chosen as suitable parameters for cross wedge rolling.
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, Y. Introduction to Engine Valvetrains; SAE International: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.; Sun, Y. Review of forming technique development for engine valves. China Met. Form. Equip. Manuf. Technol. 2007, 42, 18–21. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, X.; Zhang, Z.; Sun, Y.; Liu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Luo, T. Product defect reasons analysis and quality control strategy in electric upsetting deformation. Hot Work. Technol. 2001, 30, 45–48. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, H.; Liu, J.; Wang, B.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, T.; Hu, Z. Numerical analysis and experiment on cross wedge rolling and forging for engine valves. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2015, 221, 233–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, H.; Liu, J.; Wang, B.; Zheng, Z.; Huang, J.; Hu, Z. Cross-wedge rolling of a 4Cr9Si2 hollow valve: Explorative experiment and finite element simulation. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2015, 77, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, H.; Liu, J.; Wang, B.; Fu, X.; Xiao, W.; Hu, Z. A new method for manufacturing hollow valves via cross wedge rolling and forging: Numerical analysis and experiment validation. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2017, 240, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Yang, C.; Wang, B. Development of part rolling technology in China. J. Mech. Eng. 2012, 48, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pater, Z. Tools optimization in cross-wedge rolling. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2003, 138, 176–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Lovell, M.R. The establishment of a failure criterion in cross wedge rolling. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2004, 24, 180–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Lovell, M.R. Cross wedge rolling failure mechanisms and industrial application. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2008, 37, 265–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Li, X.; Du, F. Analysis of Metal Forming in Two-Roll Cross Wedge Rolling Process Using Finite Element Method. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 2009, 16, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pater, Z.; Gontarz, A.; Tofil, A. Analysis of the cross-wedge rolling process of toothed shafts made from 2618 aluminium alloy. J. Shanghai Jiaotong Univ. Sci. 2011, 16, 162–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pater, Z. Cross-Wedge Rolling of Shafts with an Eccentric Step. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 2011, 18, 26–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulzak, T.; Pater, Z.; Tomczak, J. Numerical and experimental analysis of a cross wedge rolling process for producing ball studs. Arch. Civ. Mech. Eng. 2017, 17, 729–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, W.F.; Zhang, J.H.; Huang, G.X.; Liu, W.P.; Shu, X.D.; Zhu, J. Stress distributions during the cross-wedge rolling of composite 42CrMo/Q235 laminated shafts. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2016, 83, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.J.; Peng, W.F.; Shu, X.D. Influence of rolling temperature on interface properties of the cross wedge rolling of 42CrMo/Q235 laminated shaft. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2017, 91, 517–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Xu, J.; Peng, W.; Shu, X.; Yin, A.; Huang, G. Experimental investigation on cross wedge rolling of composite 42CrMo/Q235 laminated shaft. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2018, 96, 895–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çakırcalı, M.; Kılıçaslan, C.; Güden, M.; Kıranlı, E.; Shchukin, V.Y.; Petronko, V.V. Cross wedge rolling of a Ti6Al4V (ELI) alloy: The experimental studies and the finite element simulation of the deformation and failure. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2013, 65, 1273–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, B.; Ji, H.; Huang, X.; Tang, X.; Ma, W. Effects of the cross-wedge rolling parameters on the formability of Ti–6Al–4V alloy. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2017, 92, 2217–2229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Shu, X.; Tian, D.; Xiang, W.; Wei, Y.; Han, S.; Peng, W.; Liu, C.; Wang, Y.; Niu, B. Study in shaft end forming quality of closed-open cross wedge rolling shaft using a wedge block. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2017, 93, 1095–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Shu, X.; Han, S.; Tian, D.; Wei, J. Analysis of microstructure evolution during different stages of closed-open cross wedge rolling. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2018, 95, 1975–1988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, D.; Shu, X.; Zhu, Y.; Xu, C.; Han, S.; Zhu, D.; Peng, W. Closure laws of void in the core of cross wedge rolling shaft based on the floating-pressure method. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2018, 98, 2905–2916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Dong, H.; Hu, Z. Micro-mechanism of central damage formation during cross wedge rolling. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2018, 252, 322–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egea, A.J.S.; Rojas, H.A.G.; Celentano, D.J.; Peiró, J.J. Mechanical and metallurgical changes on 308L wires drawnby electropulses. Mater. Des. 2016, 90, 1159–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egea, A.J.S.; Rojas, H.A.G.; Celentano, D.J.; Peiró, J.J.; Cao, J. Thermomechanical analysis of an electrically assisted wire drawing process. J. Manuf. Sci. Eng. 2017, 139, 111017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, M.; Zhang, Z.; Song, L.; Mo, D. High temperature compression behavior of 21-4N valve steel in hot working process. Hot Work. Technol. 2012, 41, 46–48. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Z.; Zhang, K.; Wang, B.; Shu, X.; Yang, C. Technology and Numerical Simulation of Parts Forming by Cross Wedge Rolling; Metallurgical Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Pater, Z. Theoretical method for estimation of mean pressure on contact area between rolling tools and workpiece in cross wedge rolling processes. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 1997, 39, 233–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, W.; Jiao, S.; Shu, X.; Zhang, K. Feasibility of cross wedge rolling asymmetric shaft parts. J. Cent. South Univ. (Sci. Technol.) 2012, 43, 4280–4285. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, X.P.; Dean, T.A. Past developments, current applications and trends in the cross wedge rolling process. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 1993, 33, 367–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, F.; Yang, C.; Zhang, K.; Hu, Z. Effect of alternating times on the internal rarefaction of cross wedge rolling. Forg. Stamp. Technol. 2005, 30, 39–41. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, J.; Yu, Y.; Zeng, Q. Analysis and experimental of internal voids in multi-wedge cross wedge rolling stepped shaft. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2014, 72, 1559–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pater, Z. Preliminary analysis of a rotary compression test. Adv. Sci. Technol. Res. J. 2018, 12, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Hu, F.; Hu, F.; Hu, Z. Experimental research on rolling radius of formed parts for cross wedge rolling. J. Mech. Eng. 2010, 46, 22–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
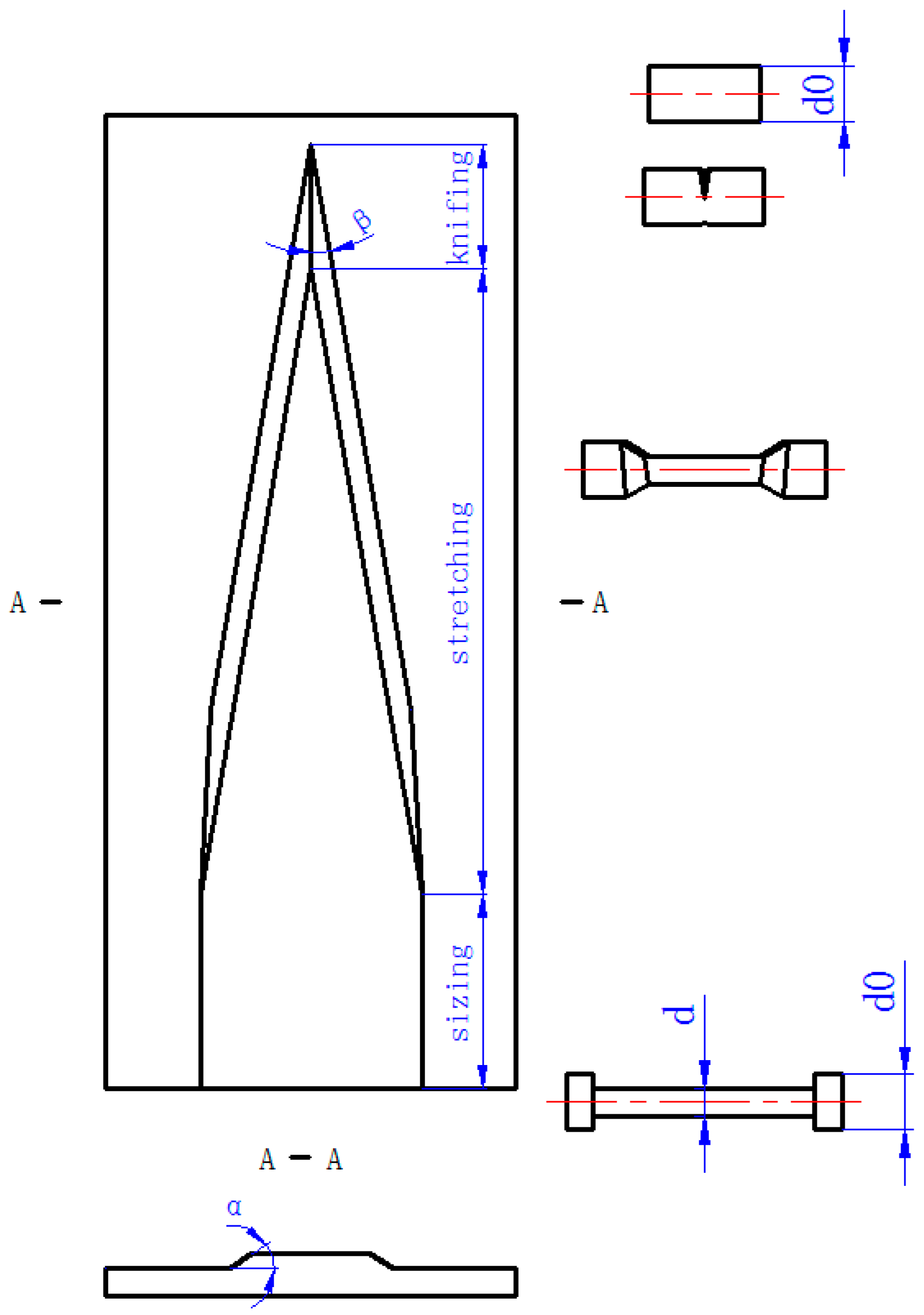


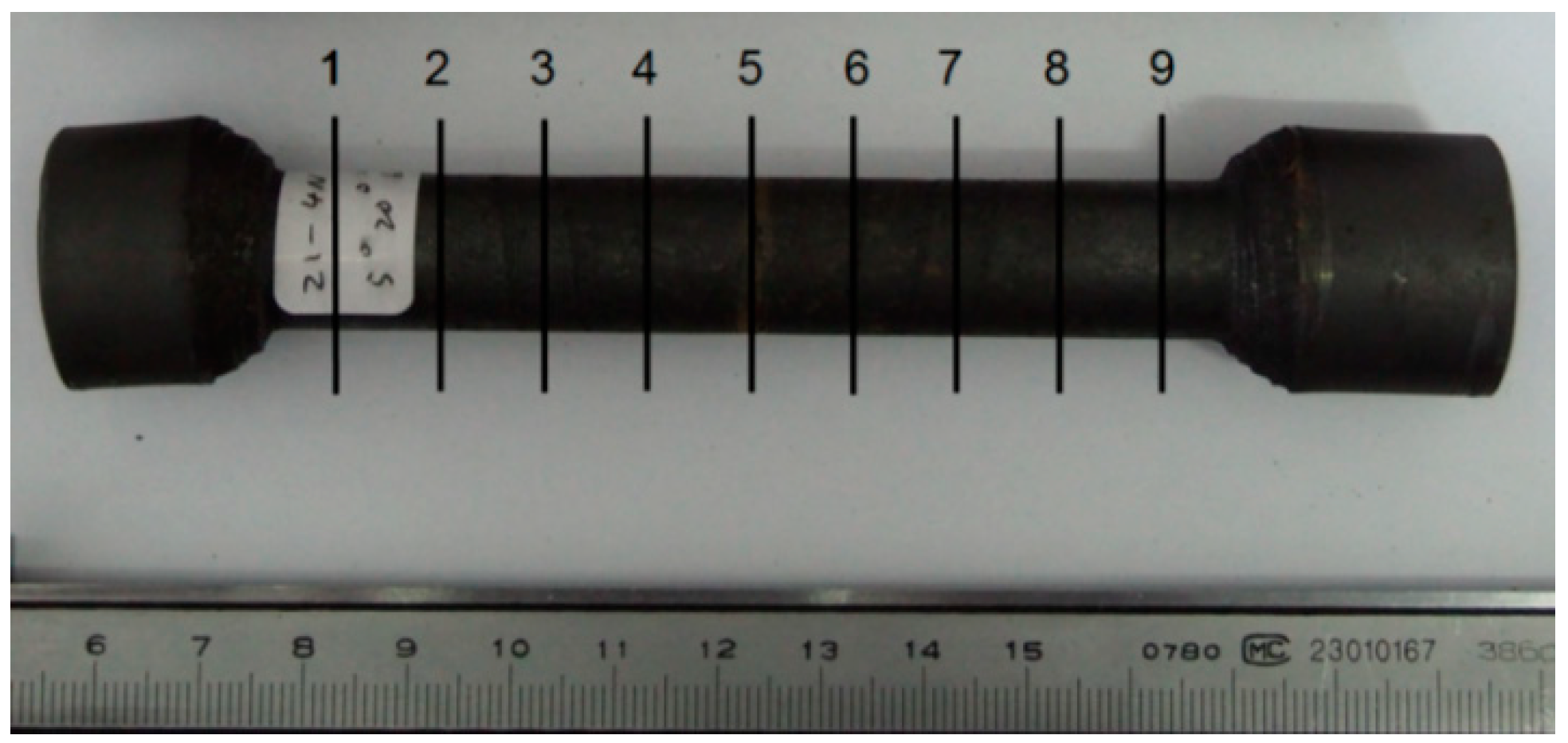



| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Motor power (KW) | 30 |
| Roller diameter (mm) | 500 |
| Max rolling diameter (mm) | 40 |
| Max rolling width (mm) | 400 |
| Max rolling speed (rpm) | 8.45 |
| C | Si | Mn | P | S | Cr | Ni | Cu | Mo | W |
| 0.52 | 0.14 | 8.98 | 0.028 | 0.002 | 21.30 | 3.67 | 0.30 | 0.05 | 0.03 |
| V | Ti | Al | B | Nb | Pb | Sn | Co | N | Fe |
| 0.08 | 0.01 | 0.003 | 0.001 | 0.03 | 0.001 | 0.005 | 0.09 | 0.43 | Bal. |
| Item | Temperature (℃) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 25 | 500 | 550 | 600 | 650 | 700 | 750 | 800 | |
| Tensile Strength, Ultimate (MPa) | 950 | 650 | 600 | 550 | 500 | 450 | 370 | 300 |
| Tensile Strength, Yield (MPa) | 580 | 350 | 330 | 300 | 270 | 250 | 230 | 200 |
| Item | Stretching Angle (°) | Forming Angle (°) | Surface Quality | Central Quality | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Max Diameter Difference | Surface Appearance | ||||
| 1 | 3 | 20 | 1.46 mm, slight necking | spiral | cavity |
| 2 | 25 | 1.48 mm, slight necking | spiral | cavity | |
| 3 | 30 | failed, tension fracture | - | - | |
| 4 | 35 | failed, tension fracture | - | - | |
| 5 | 5 | 20 | 0.24 mm | slight spiral | cavity |
| 6 | 25 | 0.44 mm | spiral | slight cavity | |
| 7 | 30 | 2.38 mm, slight necking | spiral | good | |
| 8 | 35 | 5.2 mm, necking | spiral | good | |
| 9 | 7 | 20 | 0.08 mm | good | cavity |
| 10 | 25 | 0.1 mm | good | cavity | |
| 11 | 30 | 0.36 mm | spiral | good | |
| 12 | 35 | 1.02 mm, slight necking | spiral | good | |
© 2019 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zheng, Z. Experimental Study on Cross Wedge Rolling of 21-4N Heat Resistant Steel. Metals 2019, 9, 39. https://doi.org/10.3390/met9010039
Zheng Z. Experimental Study on Cross Wedge Rolling of 21-4N Heat Resistant Steel. Metals. 2019; 9(1):39. https://doi.org/10.3390/met9010039
Chicago/Turabian StyleZheng, Zhenhua. 2019. "Experimental Study on Cross Wedge Rolling of 21-4N Heat Resistant Steel" Metals 9, no. 1: 39. https://doi.org/10.3390/met9010039
APA StyleZheng, Z. (2019). Experimental Study on Cross Wedge Rolling of 21-4N Heat Resistant Steel. Metals, 9(1), 39. https://doi.org/10.3390/met9010039




