Abstract
This paper focuses on the interfacial characteristics of dissimilar Ti6Al4V/AA6060 lap joint produced by pulsed Nd:YAG laser beam welding. The process-sensitivity analysis of welding-induced interface joining quality was performed by using the orthogonal design method. Microstructural tests such as scanning electron microscopy and energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy were used to observe the interfacial characteristics. The mechanism of interfacial crack initiation, which is an important indicator of joint property and performance, was assessed and analyzed. The preferred propagation paths of welding cracks along the interfaces of different intermetallic layers with high dislocation density were analyzed and discussed in-depth. The results indicate that discontinuous potential phases in the micro-crack tip would mitigate the mechanical resistance or performance of the welded joint, while the continuous intermetallic layer can lead to a sound jointing performance under pulsed Nd:YAG laser welding process.
1. Introduction
Dissimilar welding of lightweight alloys is attracting increasing attention in various fields because it can take advantage of specific contributions of each alloy to enhance the properties of a weld joint or bring out new functionalities. For instance, Chen et al. [] reported that Ti/Al structures have already been applied in the wing structure of airplanes. As an implication, there is a challenge for a way to use the high-level properties of dissimilar alloys such as corrosive properties and strength of titanium and lightweight and low cost of aluminum. Although considerable research has been devoted to the same or similar metal welding techniques that can supply appropriate material and mechanical performances, rather less attention has been paid to dissimilar lightweight metal welding.
To obtain good combinations of titanium with aluminum, many efforts have been made using various technologies. Friction stir welding of dissimilar alloys and the improvement of joint quality was reported by Suhuddin et al. []. The AA6061/Ti6Al4V dissimilar laminates by single-shot explosive-welding process was produced by Ege and Inal []. By using brazing, Song et al. [] and Yang et al. [] pointed out the possibility of dissimilar joining of Ti/Al and steel/Al, respectively. Wang et al. [] used ultrasonic spot-welding technology to joint dissimilar materials of DP600 steel and AA6022. Tang et al. [] indicated that the preheating treatment could improve the mechanical properties or fracture load of dissimilar joint in the welding process. The above-mentioned methods have in common that convective mixing and diffusion phenomena are suppressed or attenuated, thus bulk brittle phases in the interfacial layer do not form. Another alternative against brittle phases is the change of the chemistry of fusion zone. Sambasiva Rao et al. [] reported the dissimilar metal gas tungsten arc welding of aluminum to titanium alloy using Si-containing filler wire. Chang et al. [] used vacuum brazing method to investigate the role of additional rare-earth elements for aluminum/titanium joining performance.
One of the major problems with dissimilar metal welds is their reduced inter-metallic mechanical property. Vaidya et al. [] reported that the inter-metallic brittle phase TiAl3 formed at the weld interface between AA6065 and Ti6Al4V sheet by laser in conduction mode and affected mechanical properties: the tensile strength of the junction was found superior to the strength of aluminum alloy and the fracture happened on Al side. Chen et al. [] tried to use a specific Si-containing filler wire during the laser brazing and indicated the influence of Ti7Al5Si12 on decreasing the growth of brittle TiAl3 phase. Majumda et al. [] reported that the insert of Nb foil barrier allowed suppressing Ti/Al inter-metallic formation and enhanced tensile strength from 57 to 120 MPa. By offsetting the laser beam, different additional inter-metallic phases were observed and affected the mechanical properties. Recently, the micro-hardness, lap shear strength and fracture energy of AA2139-TiAl6V4 joints by ultrasonic welding were investigated by Zhang et al. []. They indicated that the peak load and energy of welds increased with an increase in welding time and then reached a plateau.
Recently, laser beam welding opens an attractive perspective for joining strongly dissimilar materials. One of the main advantages of laser beam welding is providing very local energy supply that allows obtaining a good quality weld. The other advantage is that laser beam welding can induce small interaction zone and high welding speed to promote high thermal gradients, which are helpful for local and potential phase content optimization. Thus, the importance of mixing and diffusion phenomena can be mitigated. Furthermore, the mismatch in thermo-physical properties of dissimilar materials is easy to accommodate by changing the laser beam to one of the substrates. Casalino et al. [] investigated the dissimilar butt joint of AA5754 and T40 by using Yb:YAG laser offset welding. Fabbro [] reported that, particularly for Nd:YAG pulsed laser welding technology, thickness of Ti/Al intermetallic layers near Ti/Al interface has been controlled to a relatively low level. Ren et al. [] showed that the interface zone of Ti/Al diffusion bonding included transition zone on Ti substrate, aluminized coating and transition zone on Al substrate. Intermetallic potential phases TiAl and TiAl3 were formed in the transition zone on Ti substrate and aluminized coating, but, in the transition zone on Al substrate, no additional intermetallic phase was found. Tomashchuk et al. [,] investigated the intermetallics in dissimilar Ti6Al4V/copper/AISI 316 L in Nd:YAG laser joints through simulation and microstructural testing methods. However, intermetallic layer in the weld joint still had high crack sensitivity, and most of the joints were fractured at Ti/Al interface under mechanical loading conditions. Therefore, it is important to investigate the mechanism and estimation of welding cracks during the thermal welding. However, up to now, few studies on the initiation mechanism and propagation paths of welding cracks produced by Nd:YAG laser welding have been published in literature.
In the present work, the weldability of Ti6Al4V/AA6060 dissimilar metal alloys using Nd:YAG pulsed laser welding and the interface characteristics of lap joint were addressed. The influence of key laser welding process parameters on weld morphology, microstructure and mechanical properties were investigated by means of microstructure characterizations and experimental design approach. Initiation mechanism and estimation of interfacial crack was analyzed as well as the exploration of interfacial phase constituents.
2. Base Materials
In this study, commercially available Ti6Al4V and AA6060 with dimensions of 35 mm × 14 mm × 0.8 mm and 35 mm × 14 mm × 1.5 mm, respectively, were used as the studied base metals. The chemical compositions of two studied materials are listed in Table 1. Element Si has been demonstrated to be effective for the growth of Ti/Al brittle intermetallic []. The thermal physical properties of the received Ti6Al4V and AA6060 were provided by Titanium International Group SRL in Italy and EXTRUSAL S.A in Portugal, as listed in Table 2. Both base materials are active light metals compared to traditional steels. The detailed data information about shear strength of AA6060 can be referred to in the publication of the previous work [], and the shear strength of Ti6Al4V can be referred to in the work of He et al. []. It also can be seen that the thermal physical properties, particularly the melting point and specific heat and thermal expansion coefficient, have wide discrepancies for the two studied base metals. This means that diffusion bonding or joining of dissimilar titanium and aluminum alloys is a challenging task, and the welding parameters should play a considerable role in the weld quality.

Table 1.
Chemical composition of base materials used in the present study in wt%.

Table 2.
Thermal physical properties of the as-received Ti6Al4V and AA6060.
Microstructure morphologies of the as-received Ti6Al4V and AA6060 are shown in Figure 1. For Ti6Al4V, the α-Ti phase is shown in dark and in the form of equiaxed grains and the β-Ti phase is represented by the bright regions [,]. The microstructure contains a volume fraction of 93.9% of the α-Ti phase and 6.1% of the β-Ti phase. Aluminum alloy AA6060 heat treatable series alloys are the most widely used for the industrial applications. Louvis et al. [] reported that the amount of solid solutions such as Mg and Si is very important for the strength of the welds as well as the size and precipitate particle distributions.
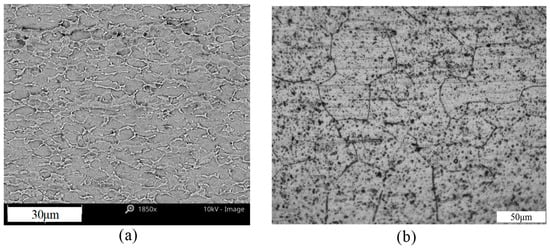
Figure 1.
Microstructure observations of base materials: (a) Ti6Al4V; and (b) AA6060.
3. Experimental Procedures
3.1. Pulsed Nd:YAG Laser Welding
In this work, pulsed Nd:YAG laser system at Department of Mechanical Engineering, University of Aveiro, i.e., SISMA SWA300, (SISMA, Vicenza, Italy) was used to perform welding experiments, as illustrated in Figure 2. The process configurations for this apparatus are listed in Table 3.

Figure 2.
Experimental apparatus of pulsed Nd:YAG laser welding.

Table 3.
Process configurations of pulsed Nd:YAG laser welding for SISMA SWA300.
To avoid an accidental movement of the welding sample, a characteristic sample fixture was developed for the stable and consistent laser welding tests. It is relatively simple and user-friendly for the fixture of sheet samples. The welding samples can be snapped into place and clamped with screws. A porthole inlet structure of assisted gas flow was designed to ensure welding samples have full gas shielding protection during the whole laser welding process. This can lead to the possibility to reduce the oxidation on the surfaces of the welding sample.
3.2. Interface Characterizations
In this work, typical lap joints with dissimilar lightweight Ti6Al4V/AA6060 were produced by pulsed Nd:YAG laser welding, which is basically categorized into fusion and solid state, respectively. At the stage of the fusion bonding, the heat source induces an inhomogeneous temperature field or a nonlinear variation of thermal field. At the stage of non-uniform solidification, the microstructural variations in the fusion zone, melted area and heat-affected zone dominate the evolutions in the of interfacial joints. The present task was focused on revealing the potential interface crack initiation and micro-structural characterizations, e.g., the changes with Ti/Al intermetallic layer in the dissimilar joint. Developments of possible metallic phases in the interface as well as crack initiation were also observed by means of scanning electron microscopy (SEM), while the distribution of chemical composition across the welded joint was determined by using energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS). A comprehensive understanding of the microstructure mechanics of adhesion at the dissimilar metal interface represents the first step towards improvement of inter-metallic mechanical properties and weld quality.
Both Ti6Al4V and AA6060 are active lightweight alloys, and all sheet surfaces should be cleaned before laser welding. Oxidation films as-received on the surfaces of base materials were eliminated by polishing process. The sample was firstly cut to a suitable size using a diamond wire, and then progressive wet ground with 600–5000 grit sandpaper. Later, 2.5 µm diamond grinding cream and glue-free fabric cloth and Al2O3 polishing liquid were used for the final polish. Finally, the microstructural testing samples were cleaned by 75% alcohol solution and ultrasonic cleaning machine. After welding, typical cross-sections of the lap joints perpendicular to the welding direction were prepared for microstructure characterization near Ti/Al interface. Nova NanoSEM 230 field emission scanning electron microscopy (FE-SEM, FEI company, Hillsboro, OR, USA) and Quanta 250 energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS, Malvern Panalytical, Eindhoven, The Netherland) were used for microstructure analyses. The samples were ground and polished according to the standard metallographic methods. The surfaces of Ti6Al4V plates were cleaned in acidic solution, namely Keller reagents (1 mL HF + 1.5 mL HCl + 2.5 mL HNO3 + 95 mL H2O). Each erosion time was about 3–4 min. Then, 10% HF was used for further erosion of the sample. This persisted time is short about 5–7 s. The surfaces of AA6060 plates were cleaned in alkali liquor (NaOH 8 vol.%, H2O 92 vol.%). Finally, all plates were cleaned using an ultrasonic cleaner, and then dried through air.
3.3. Mechanical Test
To investigate the pulsed Nd:YAG laser parameters on mechanical resistance of the Ti/Al lap joints, tensile shear testing of at least three samples for each process configuration was performed, as shown in Figure 3, using a Shimadzu AG 10 kN tensile test machine (Shimadzu, Japan). The sizes of weld pieces for Ti6Al4V and AA6060 were 30 mm × 14 mm × 0.8 mm and 35 mm × 14 mm × 1.5 mm, respectively.
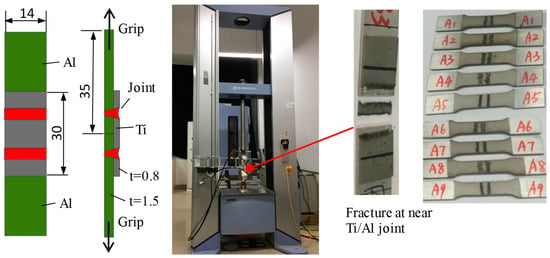
Figure 3.
Experimental apparatus and fracture sample of tensile shear test.
4. Results and Discussions
4.1. Influence of Pulsed Nd:YAG Laser Parameters on Tensile Shear Strength
Since pulsed Nd:YAG laser welding is a complex multi-physical process coupling multi-factor interactive effects, the orthogonal experimental design method was introduced to determine the roles for deciding process parameters. The design of experiment was set up as L9_4_3 orthogonal tests, considering the power percent, duration, overlap and laser beam diameter. The selected factors of the orthogonal design and the corresponding results ARE shown in Table 4. K1, K2 and K3, respectively, indicate the average of factors in each level. It should be noted that the shear strength of Ti/Al lap joint is about up to 56–78% compared to that of the single AA6060. One of the reasons may be that the tested samples with Ti/Al lap joint were not heat treated. Furthermore, there were some potential microcracks in the interface, which led to the reduction of shear strength.

Table 4.
Factors and results of L9_4_3 orthogonal tests.
To achieve exhaustive high-quality lap joint after laser beam welding, it was necessary to investigate the welding process optimization. After some “trial and error” experimental tests, it was evaluated that the suitable power for the laser welding in this case should be between 80% and 95%. Then, further optimization was carried out to analyze the influence of Ti/Al interface characteristics. According to the results of orthogonal experiments, the sensitivity of laser beam power on peak shear strength of Ti/Al lap joint was the least significant. The overlap was related to the selection of pulse duration, spot size (diameter), and traverse velocity for a specific mean power. The suitable overlap should be from 50% to 70% for the studied Ti/Al lap joint by pulsed Nd:YAG laser beam welding. Although the selected overlap hardly affected penetration, it had a significant effect on peak shear strength of Ti/Al lap joint.
The tensile shear strength of the above tested samples was found obviously inferior to the resistance of aluminum alloy: the fracture happened at near Ti/Al welded joint. Many previous efforts [,] tried to increase the tensile strength of Ti/Al dissimilar butt joints, but the mechanical strength was still at the level of about 60–70% of aluminum alloy. The other key source of mechanical strength decrease was the thickness reduction of the intermetallic layer caused by the Si loss during the laser welding. That is why some researchers [,] attempted to use filler wire containing high silicon content for changing the intermetallic type and obtaining a beneficial effect on depressing the growth of intermetallic layer. The sensitivity order of the selected key process parameters on peak shear strength was: overlap, duration, laser beam diameter and power percent. One group of relative optimal process parameters was 90% power, 9 ms duration, 50% overlap and 1.0 mm laser beam diameter. However, under this optimal process configuration, there were still some welding defects, e.g., crack initiation, surface oxidation and splash, as shown in Figure 4. This is because the impact of laser welding affects the physical properties of the welded dissimilar materials. In other words, the aluminum base material encompasses inherent characteristics including oxide surface films, low absorptivity to laser beam, low boiling point elements and a tendency to form low melting constituents []. Therefore, it was essential to further investigate the interface characteristics associated with the microstructural evolution.
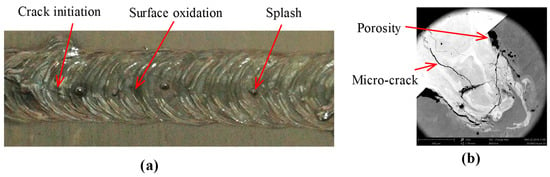
Figure 4.
Welding-induced defects on Ti/Al lap joint by pulsed Nd: YAG laser welding: (a) macro-defects; and (b) micro-defects.
4.2. Estimation of Interfacial Crack Initiation of Dissimilar Ti6Al4V/AA6060 Lap Joint
The major problem with dissimilar welds originated from the different thermal expansion and contraction, leading to the reduction of the jointing properties after welding. The microstructure mechanics of adhesion (e.g., chemical potential) at the dissimilar metal interface and the non-homogeneous crack initiation under different process conditions were not ensured. Ti/Al hybrid structures have advantage in comparison to single material for both performance and lightweight requirements. Since titanium and aluminum have low inter-solubility and brittle intermetallic, they easily form interface crack during thermal welding, which would seriously degrade properties of the Ti/Al joint. Thus, it is vital to produce sound Ti/Al weld joints without defects.
Typical cross-section of the lap joint with almost full penetration is illustrated in Figure 5. Numerous cracks crossing interface are visible. It can be supposed that they generated or formed immediately after the solidification of the weld as a result of local accumulation of residual stress. In other words, the shrinkage of the melt served as the initiator of interface cracks. Microstructures of weld zone near Ti/Al interface at different locations are marked as A–D zones. Because pulsed Nd:YAG laser welding process has high temperature gradient in the thickness direction, weld thermal cycle suffered at Ti/Al interface as top/side and bottom/root of the lap joint were different. Due to direct heating by laser beam, titanium material was fully melted and partially mixed with base aluminum in the interface. Since the Ti/Al intermetallic layers have intrinsic brittleness, cracks could initiate easily with welding-induced residual stress. Eventually, formation of brittle interfacial phases would affect properties of the lap joint for having an evident crack sensitivity. In the side areas, Zones A and C, peak temperature at Ti/Al interface was too high, and titanium as fully melted. A thick serrate reaction layer was generated. In the root area, Zone B, due to insufficient reactions between titanium and mixed aluminum, a thin serrate reaction layer was observed. In the center area, Zone D, because titanium was not directly combined with aluminum, there are almost no obvious reaction layers.
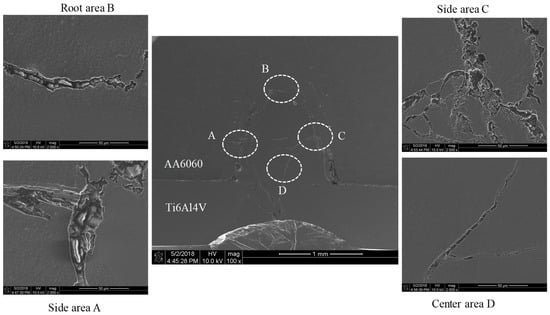
Figure 5.
Morphology and microstructure of dissimilar Ti/Al lap joint: interface at different areas.
The lap joint was cut from the Ti/Al interface, and then analyzed the interface microstructure by using SEM and XRD. The test results are shown in Figure 6. The potential phases TiAl, TiAl2, and TiAl3 were observed near the Ti/Al interface. Near the layer interface, there are two main zones: Al-rich and Ti-rich. Figure 6 shows that Al dominates on interface of Ti/Al lap joint. This means that phase change is situated mainly in Al-rich melted zone. However, sometimes it crosses interface and even touches Ti-rich melted zone as some quantities of intermetallic phase also present. For example, brittle TiAl3 phase was found in low quantities, as shown in Figure 7. The combination of relatively fast flash speed and large laser power enables performing laser welding in capillary mode with short time.
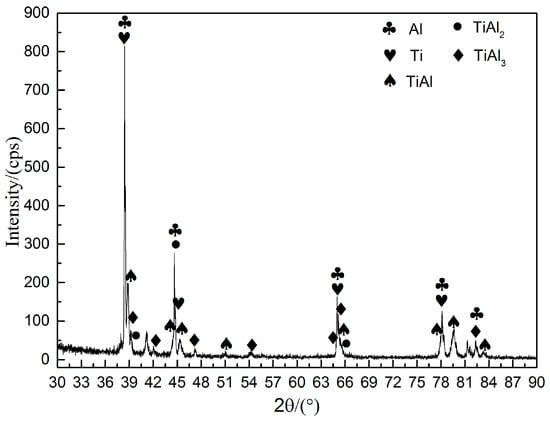
Figure 6.
X-ray diffraction profiles of the Ti/Al lap joint interface.
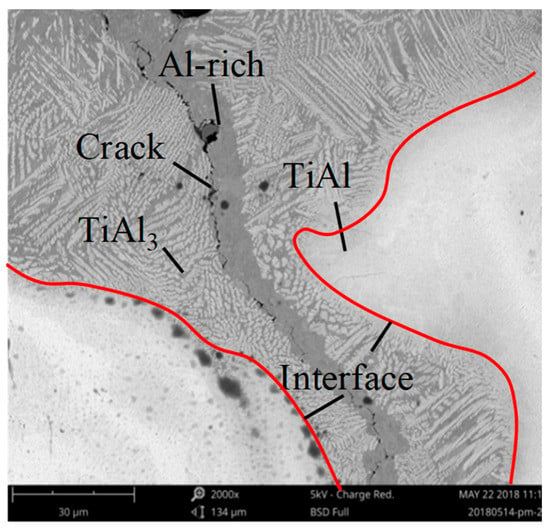
Figure 7.
Propagation paths of potential phase distribution in the Ti/Al interface.
The propagation path of phase change in the Ti/Al interface can be explained by mismatch in thermo-physical properties and by thermodynamic factor. As the Ti6Al4V has much higher fusion temperature than AA6060 (Table 2), the volume of melted aluminum was much larger than volume of melted titanium. Due to the high solidification rates proper to laser welding, the main solidification process was the local equilibrium at solid–liquid interface and the convective mixture between melted materials is poor. The previous study indicates that the solidification associated with thermodynamic properties of Al-Ti system begins from solid solutions and β-Ti phase. Besides the coexisting Al-rich liquids, the key change of Al in Ti-rich melted zone was dependent on lower Gibbs energy of (β-Ti) formation. In addition, diffusion coefficient of aluminum in liquid titanium overestimates that of titanium in liquid aluminum. Thus, compared to the concentration of Ti in Al-rich zone, Al in Ti-rich zone was more active during the separation of the materials through the contact interface. As for the stage of solidification, Ti-rich melted zone was relatively slowly depleted in Ti. Then, some (β-Ti) solid solutions having high Al content were formed. Consequently, in Ti-rich zone, these (β-Ti) solutions could be transformed into α-Ti and/or Ti3Al at the further cooling stage, which should be depending on Al content.
Based on the above analysis, it can be indicated that the rapid rate with respect to cooling or solidification rate seriously affected the crack initiation. It should be noticed that the time available for the residual liquid to refill and heal the initiated cracks may be mitigated by high cooling rates. Kanazawa [] showed that the higher susceptibility of hot tearing and porosity could be obtained at lower duty cycles through pulsed Nd:YAG laser welding. In other words, the shorter is the average beam interaction time, the higher is the average temperature gradient of the interface and the faster is the cooling rate. Thus, it is generally recommended to shorten the off-time of the pulse or to use high duty cycle to reduce the solidification time of the molten pool. For the pulsed laser welding, some defects such as crack may be prevented if the next pulse occurs before the initiation of solidification cracking caused by the previous pulse. Another control strategy to reduce interfacial crack is to apply preheating to the work-piece because of an influence on cooling rate. For example, Ion [] indicated that preheating to 500 °C could reduce solidification cracking in a series of aluminum alloys by reducing the cooling rate. It may be explained as it allows voids to heal before solidification is complete. Nowadays, the preheating control strategy is widely adopted during industrial applications.
4.3. Interface Microstructural Characterizations of Dissimilar Ti6Al4V/AA6060 Lap Joint
The distribution order of intermetallic in the selected reaction layers near Ti/Al interface was determined using EDS. The selected interface without micro-cracks, as illustrated in Figure 8, is helpful for the analyses of phase change and chemical potential. Chemical compositions of the selected locations marked P1–P5 on the interface were analyszd. As shown in Figure 9, the atomic ratio of Ti to Al at Point 1 was about 2:1. The layer was supposed to contain α-Ti solution and to some extent TiAl. Atomic percent of Ti at Point 2 was nearly equal to Al, thus the layer was mainly composed of intermetallic TiAl. At Point 3, atomic ratio of Ti to Al was about 1:2. The layer was mainly composed of intermetallic TiAl2. At Point 4, atomic ratio of Ti to Al was about 1:4. The layer was composed of intermetallic TiAl3 and α-Ti. The atomic percentages of Ti and Al at Point 5 were 94.71% and 5.01%, respectively. The results suggest the layer is α-Ti solution. Some other potential phases, e.g., Ti5Si3, might exist in the interface. Because TiAl/TiAl3 is prone to be eutectic mixture structure with the potential Ti5Si3, it should be further investigated using nanoparticle observation. However, the authors think the amount of Ti5Si3 would be scant if it existed in the interface.

Figure 8.
The selected Ti/Al interface without micro-crack for EDS observation.
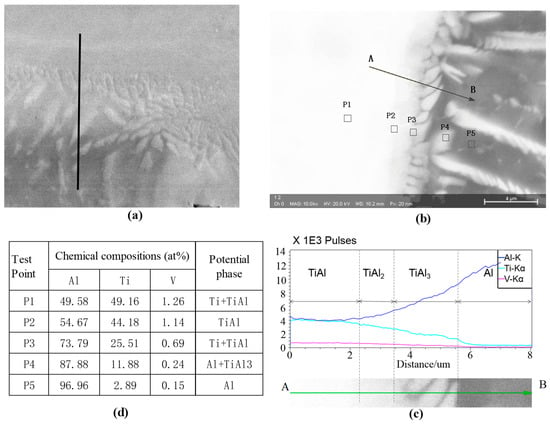
Figure 9.
EDS element analysis at selected points in the interface: (a) the selected interfacial area; (b) the selected points in the interface; (c) chemical compositions of the selected points; and (d) EDS element distribution along the selected interface.
Owing to different physical performance, including the coefficient of linear expansion and lattice structure, the Ti/Al intermetallic layers have different solidification processes. The divergence of two dissimilar base materials resulted in high edge dislocation density near interfaces of the Ti/Al multi-layers. Due to welding-induced residual stress [,], dislocations migrated and accumulated to the interface, and some micro-crack sources formed along the interface, as shown in Figure 10. Once welding micro-crack initiates in the melted zone, propagation tendency of welding micro-cracks would be along the interface with high dislocations density. Welding cracks mainly propagate along the longitudinal direction of the interface between TiAl layer and TiAl3 layer. It should be noted that there are still some potential phase and discontinuous distribution in the micro-crack tip. It might be Ti5Si3 or other brittle phases, which would mitigate the mechanical strength or performance of the welded joint.

Figure 10.
Welding micro-crack initiation in the Ti/Al interface.
It should be noted that the effect of the thickness of intermetallic layer on the mechanical strength or other properties of the Ti/Al joint is considerable. Although microstructures in the laser beam Ti/Al dissimilar joint by using silicon filler wire and the effect of intermetallic layer morphology in the fracture behavior of the joint were demonstrated by Chen et al. [,], the authors preferred to focus on the laser welding of dissimilar Ti/Al alloys without the addition of filler wire. This is because the formation of dissimilar Ti/Al alloys without additional fillers is prone to industrial applications. Of particular interest was continuous distribution of potential phase in the Ti/Al interface, as shown in Figure 11. It is not common but generated in the TA8 sample in this study. The sample was obtained under the following laser welding parameters: 95% power percent, 9 ms duration, 50% overlap and 1.0 mm laser beam diameter. It was found that the mechanical resistance of the Ti/Al lap joint is prominent compared to the other welding configurations. The continuous intermetallic layer can lead to a sound jointing performance under Nd:YAG laser welding process.
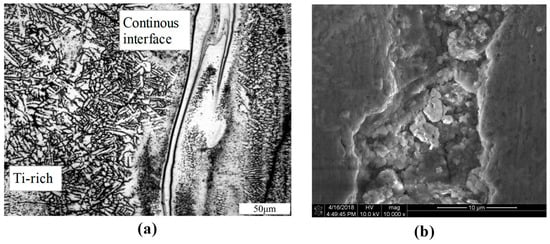
Figure 11.
Continuous distribution of potential phase in the Ti/Al interface: (a) continuous intermetallic layer; and (b) potential continuous phases in the interfacial layer.
5. Conclusions
The interfacial characteristics of dissimilar Ti6Al4V/AA6060 lap joint produced by pulsed Nd:YAG laser beam welding was addressed. To better understand the interaction relationship of interfacial characteristics and process parameters, the corresponding experimental optimization design and microstructural observations were performed as well as the sensitivity analysis of welding-induced interfacial joining quality. The main conclusions can be drawn as follows:
- (1)
- By using the orthogonal experimental design method, the sensitivity order of the selected key process parameters on peak shear strength was: overlap, duration, laser beam diameter and power percent. One group of relatively optimal process parameters was: 90% power, 9 ms duration, 50% overlap and 1.0 mm laser beam diameter.
- (2)
- The potential phases TiAl, TiAl2, and TiAl3 were observed near the Ti/Al interface. The phase change was situated mainly in Al-rich melted zone. However, sometimes it crosses interface and even touches Ti-rich melted zone as some quantities of intermetallic phase were also present. The estimation of interfacial crack initiation was analyzed and discussed in detail.
- (3)
- The discontinuous potential phases in the micro-crack tip can lead to mitigating the mechanical strength or performance of the welded joint, and a better jointing performance under pulsed Nd:YAG laser welding process may be obtained with the formation of continuous intermetallic layer.
Author Contributions
Methodology. X.X., A.P. and J.L.; investigation, X.X., A.P., and G.V.; data curation, X.X. and X.W.; writing—original draft preparation, X.X. and J.L.; writing—review and editing, A.P. and G.V.; supervision, A.P. and G.V.; project administration, A.P. and G.V.; and funding acquisition, X.X., A.P., G.V. and J.L.
Funding
This research was funded by the Portuguese Foundation of Science and Technology (SFRH/BPD/114823/2016 and UID/EMS/00481/2013-FCT), project CENTRO-01-0145-FEDER-022083, National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51705080 and No. 51805087), and Natural Science Foundation of Fujian Province (No. 2018J01761 and No. 2018J01764).
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank Rafael Gomes at the Department of Mechanical Engineering, University of Aveiro for the assistance with some dissimilar welding experiments.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Chen, S.; Li, L.; Chen, Y.; Huang, J. Improving interfacial reaction nonhomogeneity during laser welding-brazing aluminum to titanium. Mater. Des. 2011, 32, 3913–3919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suhuddin, U.F.H.; Fischer, V.; Kostka, A.; Santos, J.F. Microstructure evolution in refill friction stir spot weld of a dissimilar Al–Mg alloy to Zn-coated steel. Sci. Technol. Weld. Join. 2017, 22, 658–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ege, E.S.; Inal, O.T. Stability of interfaces in explosively welded aluminium titanium laminates. J. Mater. Sci. Lett. 2000, 19, 1533–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.; Nakata, K.; Wu, A.; Liao, J. Interfacial microstructure and mechanical property of Ti6Al4V/AA6061 dissimilar joint by direct laser brazing without filler metal and groove. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2013, 560, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Yu, Z.S.; Li, Y.L.; Zhang, H.; Guo, W.; Zhou, N. Influence of alloy elements on microstructure and mechanical properties of Al/steel dissimilar joint by laser welding/brazing. Weld. World 2018, 62, 427–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.H.; Shivakant, S.; Frank, M.; Mishra, R.S. Evolution of bond formation and fracture process of ultrasonic spot welded dissimilar materials. Sci. Technol. Weld. J. 2019, 24, 171–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.M.; Shen, Y.F. Effects of preheating treatment on temperature distribution and material flow of aluminum alloy and steel friction stir welds. J. Manuf. Process. 2017, 29, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sambasiva Rao, A.; Madhusudhan Reddy, G.; Satya Prasad, K. Microstructure and tensile properties of dissimilar metal gas tungsten arc welding of aluminium to titanium alloy. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2011, 27, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.Y.; Tsao, L.C.; Lei, Y.H.; Mao, S.M.; Huang, C.H. Brazing of 6061aluminum alloy/Ti6Al4V using Al–Si–Cu–Ge filler metals. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2012, 212, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaidya, W.V.; Horstmann, M.; Ventzke, V.; Pertovski, B.; Kocak, M.; Kocik, R.; Tempus, G. Improving interfacial properties of a laser beam welded dissimilar joint of aluminum AA6056 and titanium Ti6Al4V for aeronautical applications. J. Mater. Sci. 2010, 45, 6242–6254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Li, L.; Chen, Y.; Huang, J. Joining mechanism of Ti/Al dissimilar alloys during laser welding-brazing process. J. Alloys Compd. 2011, 509, 891–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majumda, B.; Galun, R.; Weisheit, A.; Mordike, B.L. Formation of crack-free joint between Ti-alloy and Al alloy by using a high-power CO2 laser. J. Mater. Sci. 1997, 32, 6191–6200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.Q.; Robson, J.D.; Prangnell, P.B. Dissimilar ultrasonic spot welding of aerospace aluminum alloy AA2139 to titanium alloy TiAl6V4. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2016, 231, 382–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casalino, G.; Mortello, M.; Peyre, P. Yb–YAG laser offset welding of AA5754 and T40 butt joint. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2015, 223, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabbro, R. Developments in Nd–Yag laser welding. In Handbook of Laser Welding Technologies; Katayama, S., Ed.; Woodhead Publishing Limited: Oxford, UK, 2013; pp. 47–72. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, J.W.; Li, Y.J.; Feng, T. Microstructure characteristics in the interface zone of Ti/Al diffusion bonding. Mater. Lett. 2002, 56, 647–652. [Google Scholar]
- Tomashchuk, I.; Sallamand, P.; Jouvard, J.M.; Grevey, D. The simulation of morphology of dissimilar copper–steel electron beam welds using level set method. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2010, 48, 827–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomashchuk, I.; Sallamand, P.; Andrzejewski, H.; Grevey, D. The formation of intermetallics in dissimilar Ti6Al4V/copper/AISI 316 L electron beam and Nd:YAG laser joints. Intermetallics 2011, 19, 1466–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, A.C.; Moreira, A.F.R.; Mello, C.B.; Riva, R.; Oliveira, R.M. Influence of Si coating on interfacial microstructure of laser joining of titanium and aluminium alloys. Mater. Res. 2018, 21, e20161109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, X.; Liao, J.; Vincze, G.; Pereira, A.B. Control strategy of twist springback for aluminium alloy hybrid thin-walled tube after mandrel-rotary draw bending. Int. J. Mater. Form. 2018, 11, 311–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, P.G.; Chen, K.; Yu, B.; Yue, C.Y.; Yang, J.L. Surface microstructures and epoxy bonded shear strength of Ti6Al4V alloy anodized at various temperatures. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2013, 82, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Squillace, A.; Prisco, U.; Ciliberto, S.; Astarita, A. Effect of welding parameters on morphology and mechanical properties of Ti6Al4V laser beam welded butt joints. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2012, 212, 427–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaithilingam, J.; Goodridge, R.D.; Richard, J.M.; Hague, R.J.M.; Christie, S.D.R.; Edmondson, S. The effect of laser remelting on the surface chemistry of Ti6Al4V components fabricated by selective laser melting. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2016, 232, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louvis, E.; Fox, P.; Christopher, J.; Sutcliffe, C.J. Selective laser melting of aluminium components. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2011, 211, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moller, F.; Grden, M.; Thomy, C.; Vollertsen, F. Combined laser beam welding and brazing process for aluminium titanium hybrid structures. Phys. Procedia 2011, 12, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saida, K.; Ohnishi, H.; Nishimoto, K. Laser brazing of TiAl intermetallic compound using precious brazing filler metals. Weld. World 2015, 59, 9–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cam, G.; Koçak, M. Progress in joining of advanced materials Part 2: Joining of metal matrix composites and joining of other advanced materials. Sci. Technol. Weld. Join. 1998, 3, 159–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanazawa, H. Welding performance of high power YAG lasers in aluminium alloys. J. Light Met. Weld. Constr. 1997, 35, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ion, J.C. Laser beam welding of wrought aluminium alloys. Sci. Technol. Weld. Join. 2013, 5, 265–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisazadeh, H.; Bunn, J.; Coules, H.E.; Achuthan, A.; Goldak, J.; Aidun, D.K. A residual stress study in similar and dissimilar welds. Weld. J. 2016, 95, 111–119. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, F.; Liu, Y.; Wu, Y.C. Effect of lattice matching degree and intermetallic compound on the properties of Mg/Al dissimilar material welded joints. Sci. Technol. Weld. Join. 2017, 22, 719–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).