Response Displacement Method for Seismic Calculation of Subway Station Complex Structure of TOD Mode
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Proposition and Implementation of Improved Response Displacement Method
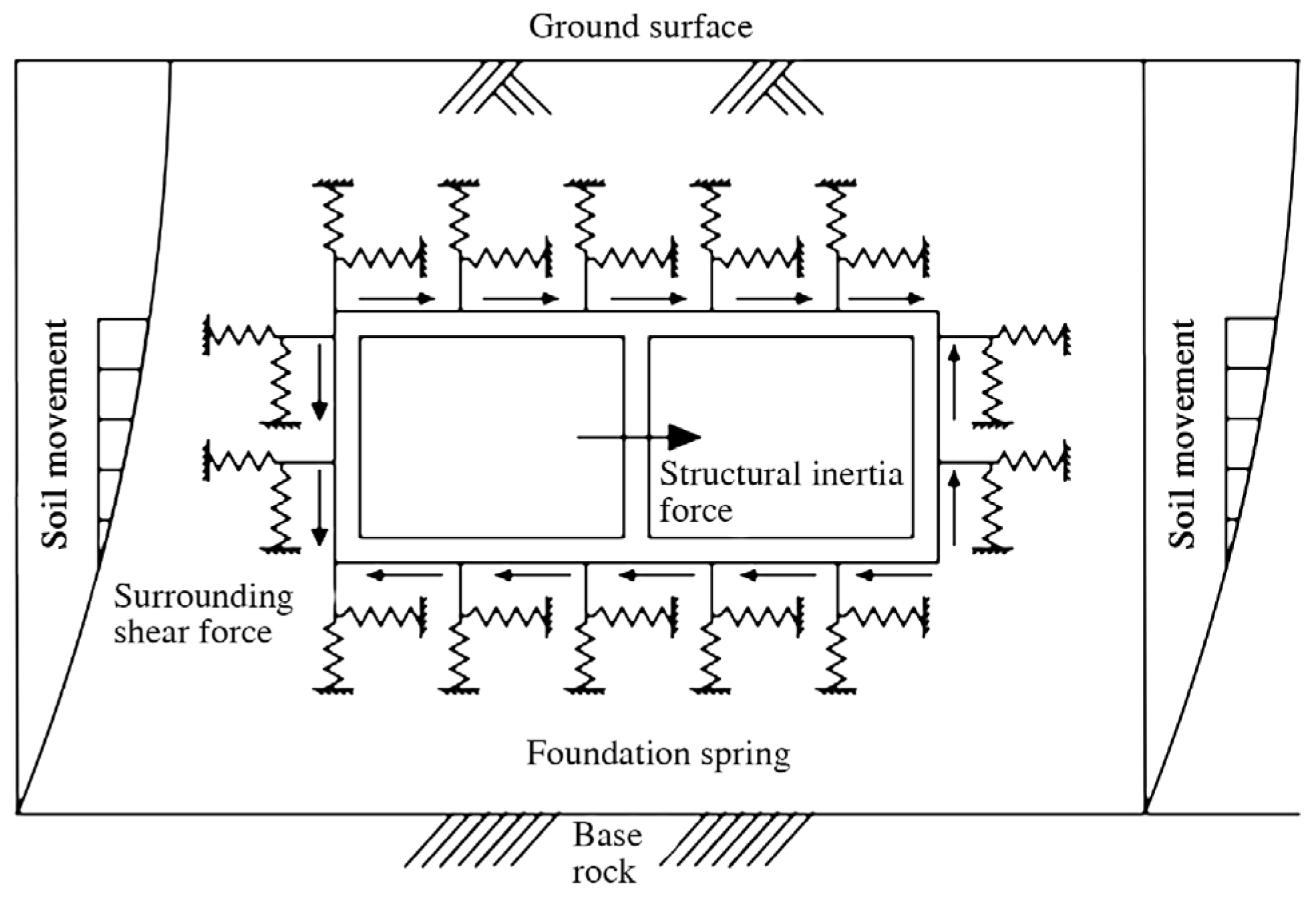
2.1. Traditional Response Displacement Method and Its Limitations
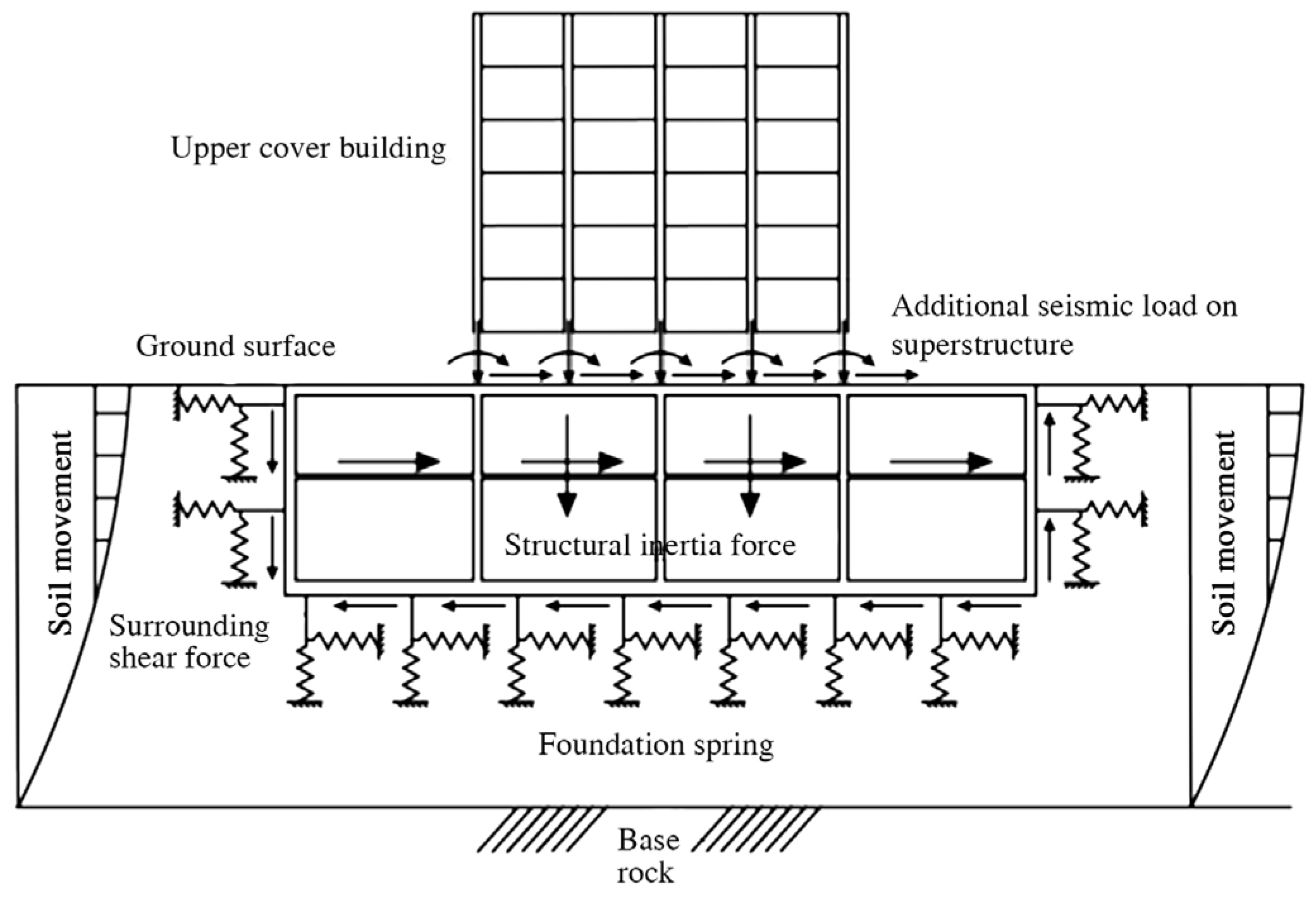
2.2. Improved Response Displacement Method
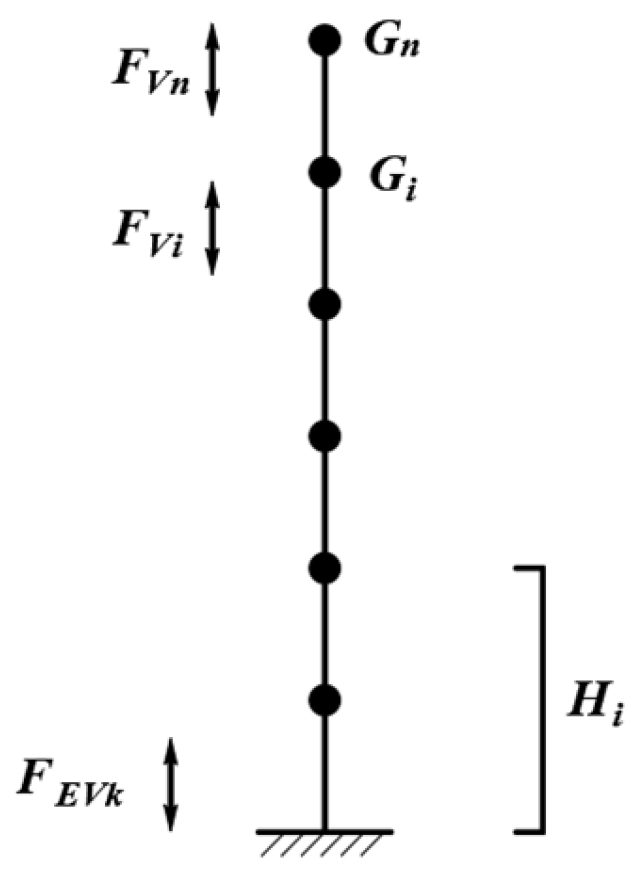
2.2.1. Additional Seismic Load of Superstructure
- (1)
- Bottom shear
- (2)
- Bottom bending moment
- (3)
- Vertical inertia force
2.2.2. Improved Response Displacement Method Implementation Steps
3. Example Analysis
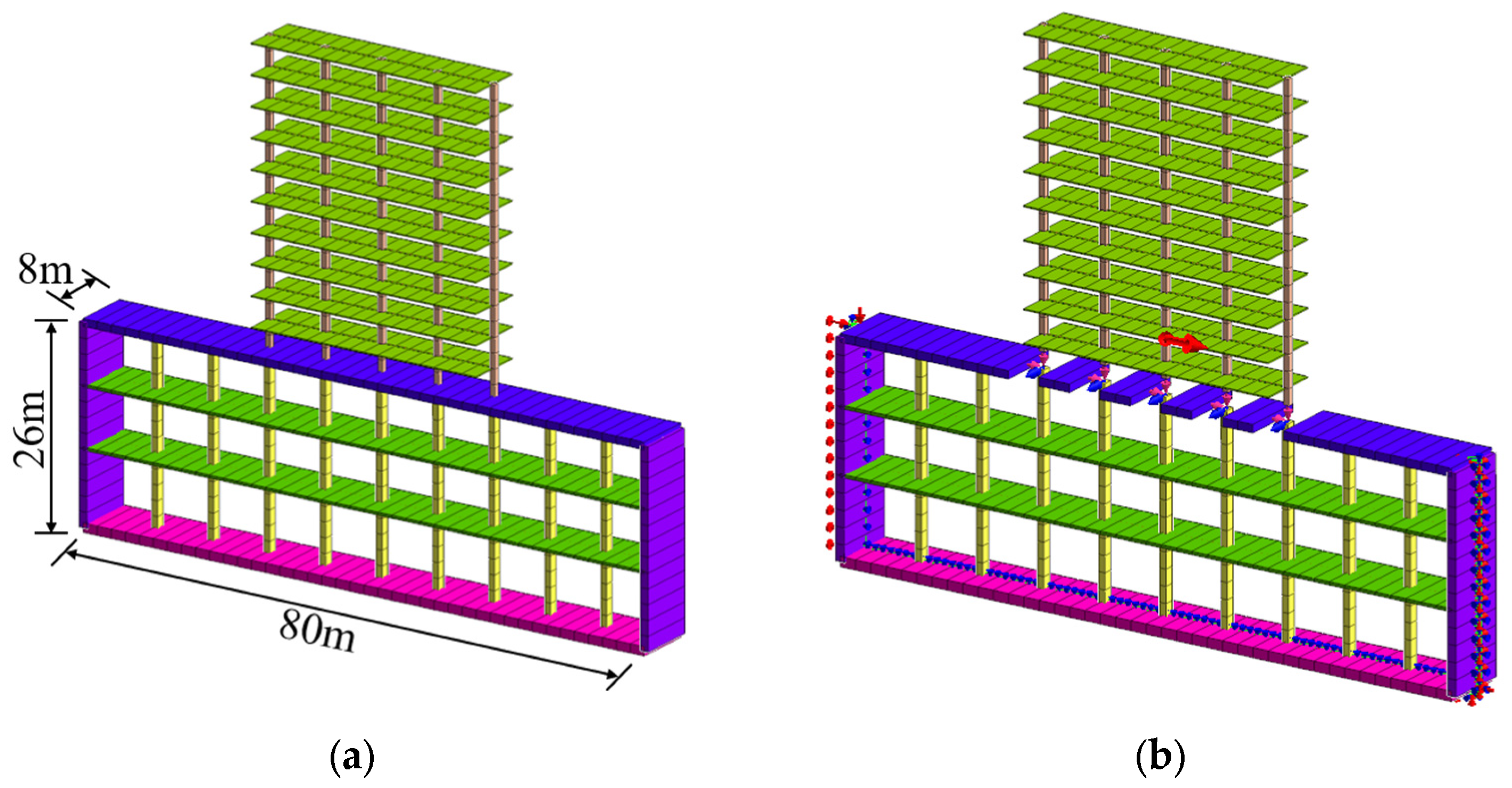
3.1. Calculation Model and Parameters
3.2. Input Ground Motion and Seismic Response of Underground Structure
4. Analysis of Calculation Results
4.1. One-Dimensional Free-Field Analysis and Bottom Shear Method Calculation Results
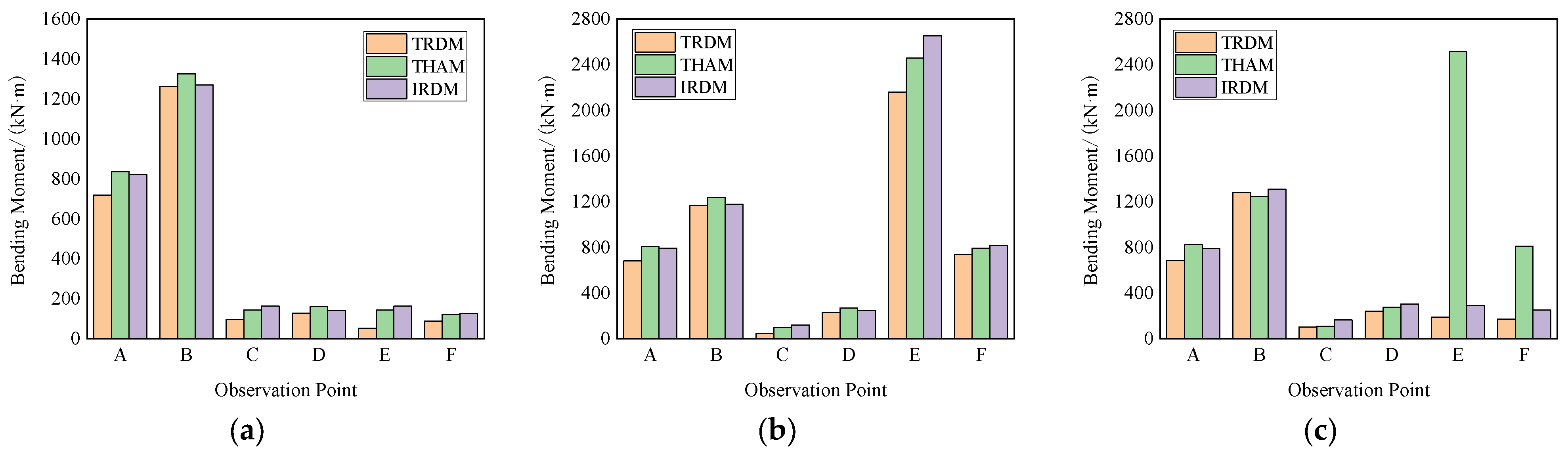
4.2. Seismic Wave Types and Different Peak Acceleration
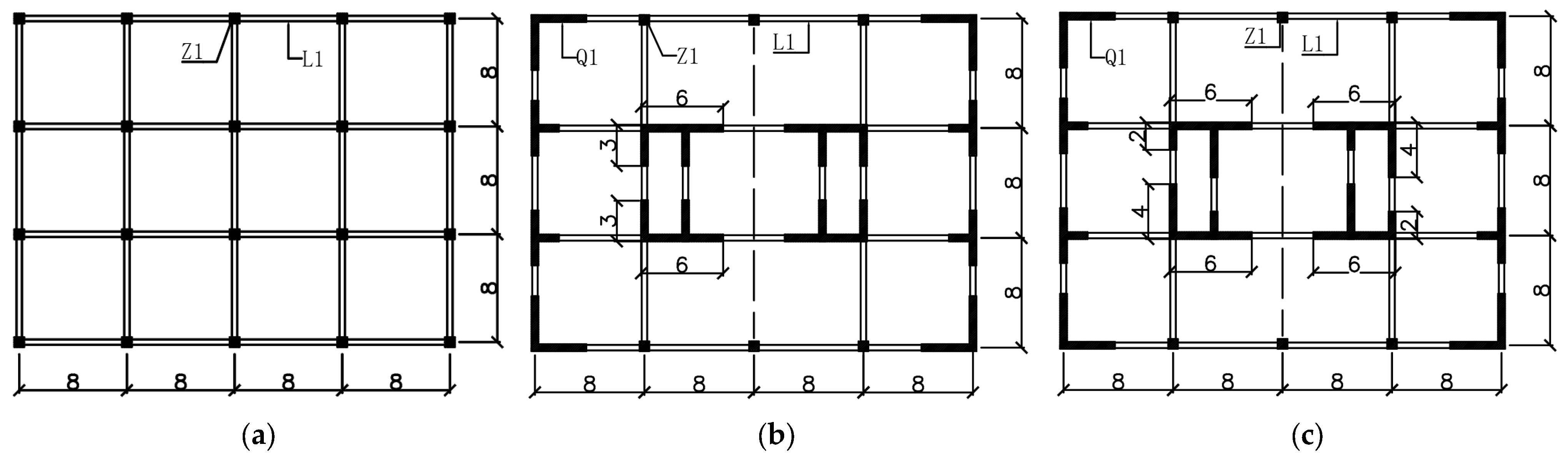
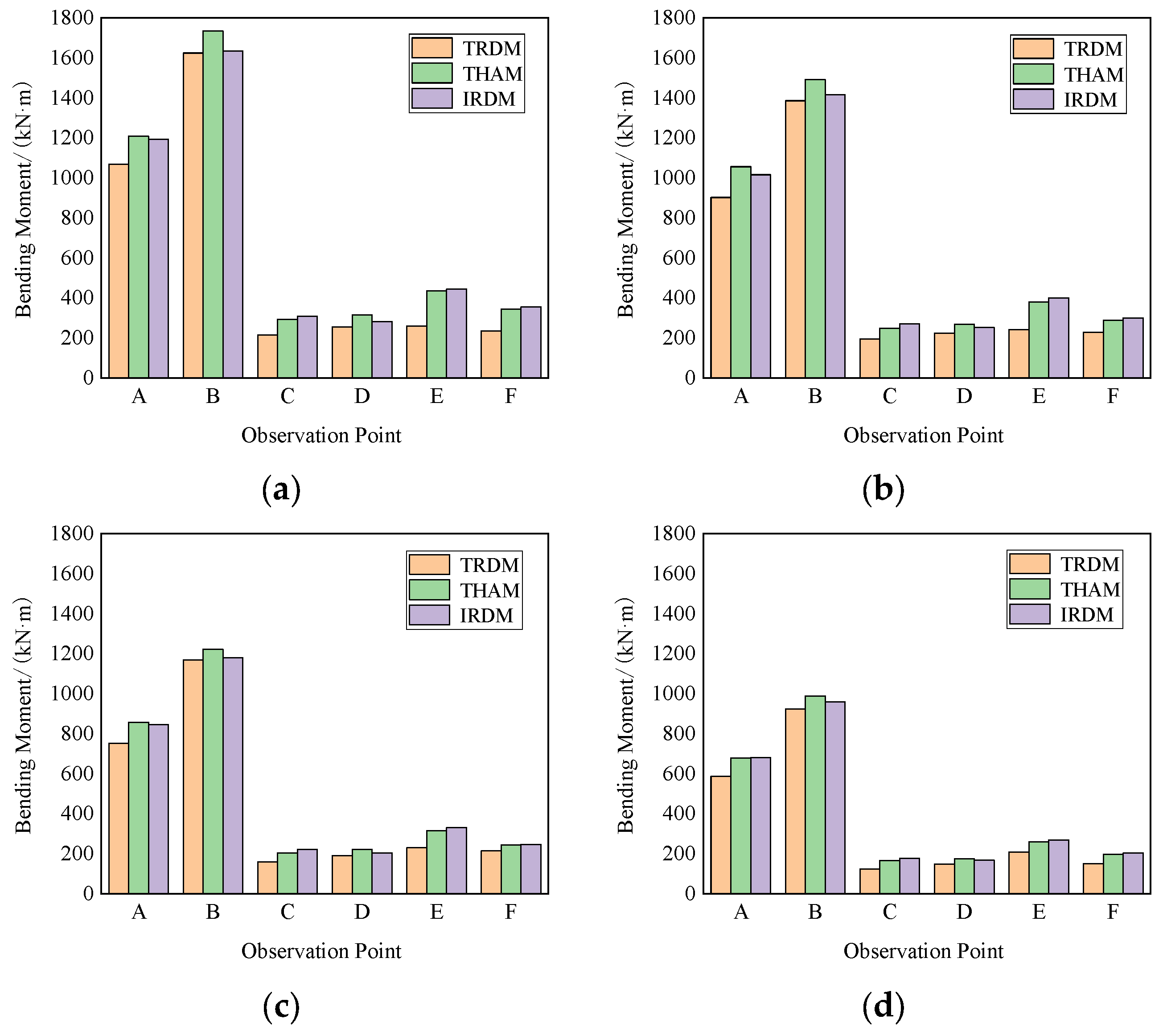
4.3. Analysis of Different Upper Cover Structure Position Forms
4.4. Different Cover Structures
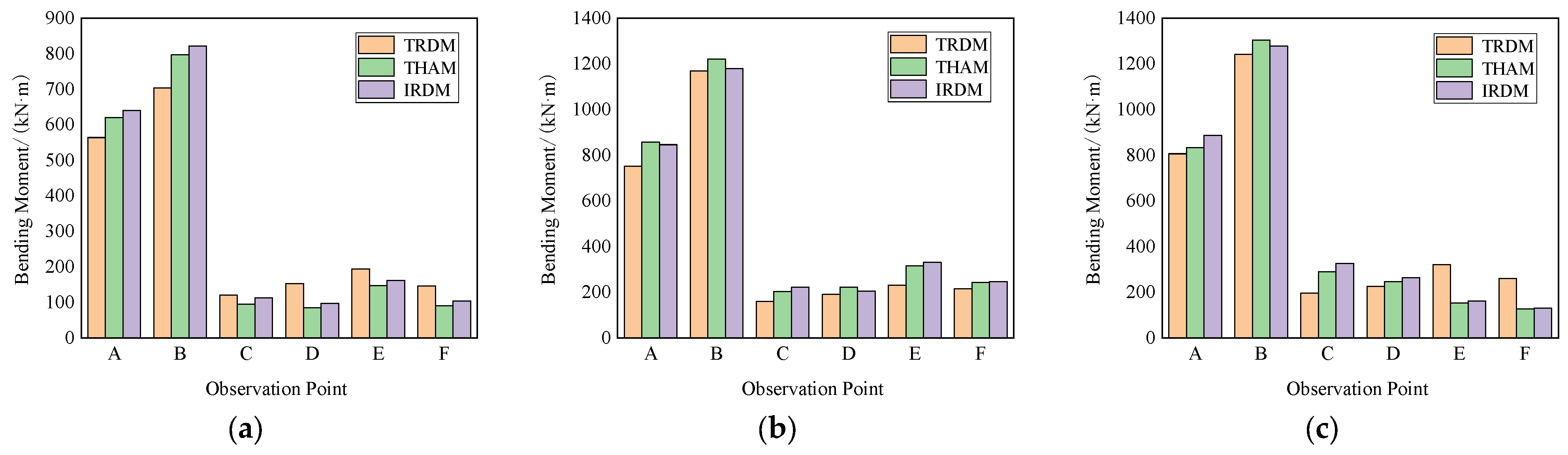
4.5. Analysis of Different Relative Positions of Underground Stations to the Ground
4.6. Different Station Complex Structure Stiffness
4.7. Different Soil Stiffness
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- For seismic calculations, both the equivalent base shear method and the mode-superposition response spectrum method are calculated assuming that the structural system is in a linear elastic state, and the structural system in the TOD mode is designed according to the elastic behavior, and the analysis of the internal forces and deformations is carried out using the linear dynamic method.
- (2)
- Compared with the calculation results of the time-history analysis method, the internal force and deformation error of a subway station complex calculated via the traditional response displacement method is larger, and the overall value is smaller, so the design is dangerous. The error of internal force and deformation calculated by the improved response displacement method is small, the maximum error is only about 10%, and the variation law is basically consistent with the results in the time-history analysis method.
- (3)
- The near-field seismic wave and far-field seismic wave are selected as the input seismic bedrock motion, respectively, and compared with the calculation results of the time-history analysis method, the improved response displacement method can still provide better accuracy for different types of ground shaking.
- (4)
- The traditional response displacement method cannot consider the additional seismic load and vertical inertia force of the superstructure, some of the calculation results obtained via the traditional reaction displacement method are not in conformity with the time-range analysis, and the maximum error is 206%, which makes the calculation results obviously distorted in the process of changing the position of the superstructure frame structure. While the improved reaction displacement method in the calculation results of the underground station structure at different locations of the bending moment change rule and the time-history analysis method is basically consistent, the maximum error is 12%.
- (5)
- The deformation of the subway station complex structure under strong seismic action is shear-type deformation in the presence of a upper cover single tower frame structure, and the upper cover structure significantly increases the internal force and deformation of the columns in the underground structure connected to it. The top and bottom of the middle columns and side walls in the structure of the subway station complex of TOD mode, especially the middle column members directly connected to the upper structure, are the weak links in seismic design.
- (6)
- The internal forces and deformations of the subway station complex structure calculated via the time-history analysis method, the traditional response displacement method, and the improved response displacement method under different ground vibration intensities increase with the increase of peak acceleration of ground vibration, respectively.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lu, J.; Chen, Y. Integrated design of under-and above-ground urban space: Strategies for effective development of underground space. J. Shanghai Jiaotong Univ. 2012, 46, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Niu, B. Structural Design of Large-span Column-free subway Station Co-built with Underground Complex. Urban Rapid Rail Transit 2022, 35, 60–64. [Google Scholar]
- Li, G.; Zhang, H.; Wang, R.; Dong, Z.; Yu, D. Analysis of seismic failure and influencing factors of complex structures under seismic excitation. J. Build. Struct. 2022, 44, 188–203. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, G.B.; Yuan, M.Z.; Ma, X.F.; Wu, J. Numerical study on the seismic response of the underground subway station-surrounding soil mass-ground adjacent building system. Front. Struct. Civ. Eng. 2017, 11, 424–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Chen, Q. Seismic Response of the System of Soil and Subway Station with Upper Structure. Chin. Q. Mech. 2019, 40, 504–514. [Google Scholar]
- An, J.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, X. Seismic Response of Large Chassis Subway Station under Upper Cover Single Tower Frame Structure. China Railw. Sci. 2021, 42, 166–175. [Google Scholar]
- Han, X.; An, S.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, S. Influencing factors of seismic response of integrated transportation hub structure. J. Heilongjiang Univ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 29, 682–690. [Google Scholar]
- Han, X.; Tao, L.; Zhang, Y. Seismic damage mechanism of integrated station structure of urban rail transit hub. J. Cent. South Univ. (Sci. Technol.) 2021, 52, 925–935. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C. Seismic Performance of Integrated subway station and Upper Cover with High⁃Rise Building. J. Disaster Prev. Mitig. Eng. 2022, 42, 490–498. [Google Scholar]
- GB50909-2014; Code for Seismic Design of Urban Rail Transit Structures. China Planning Press: Beijing, China, 2014.
- Liu, J.; Wang, W.; Zhao, D.; Zhang, X. Integral response deformation method for seismic analysis of underground structure. Chin. J. Rock Mech. Eng. 2013, 32, 1618–1624. [Google Scholar]
- Du, X.; Xu, Z.; Xu, C.; Li, Y. Inertia force-displacement method for seismic analysis of shallow buried underground structures. Chin. J. Geotech. Eng. 2018, 40, 583–591. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Z.; Du, X.; Xu, C.; Han, R.; Qiao, L. Research on generalized response displacement method for seismic analysis of underground structures with complex sections. Rock Soil Mech. 2019, 40, 3247–3254. [Google Scholar]
- Du, X.; Jiang, J.; Xu, Z.; Xu, C.; Liu, S. Study on quantification of seismic performance index for rectangular frame subway station structure. China Civ. Eng. J. 2019, 52, 111–119,128. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Yu, Z. A seismic design method of subway stations affected by surrounding buildings. Rock Soil Mech. 2021, 42, 1443–1452. [Google Scholar]
- An, J.; Tao, L.; Li, J. Equivalent plane frame method for the seismic design of the cross section of underground structures. Mod. Tunn. Technol. 2016, 53, 43–50. [Google Scholar]


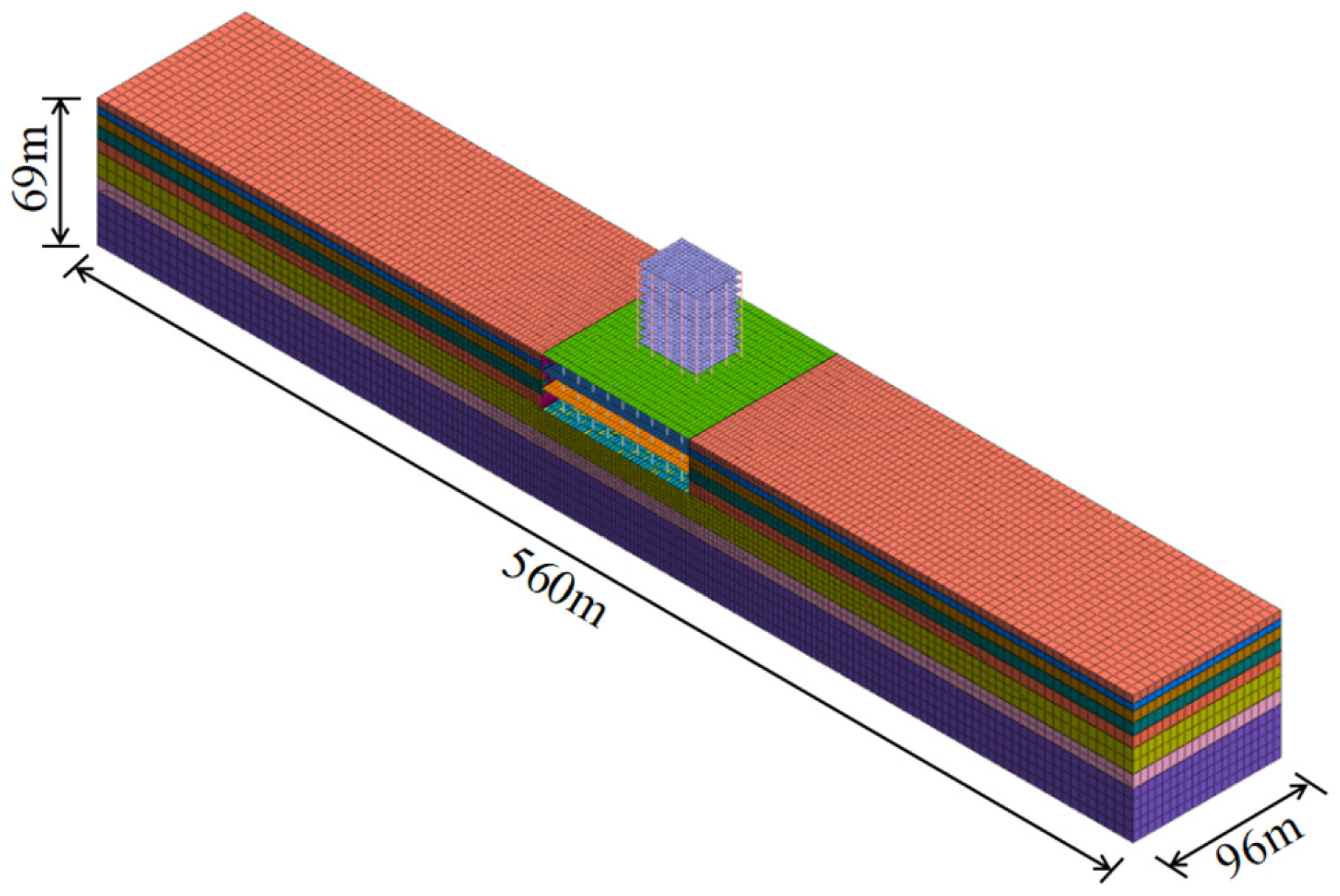


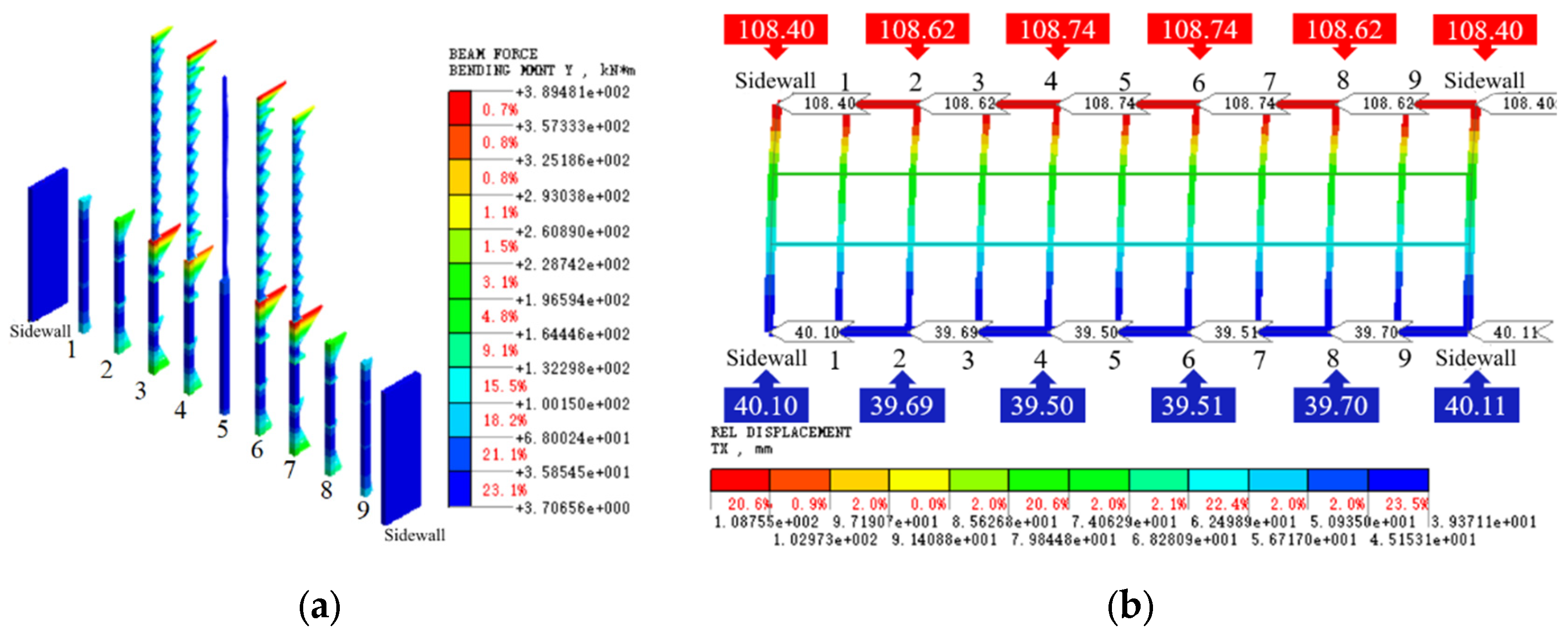
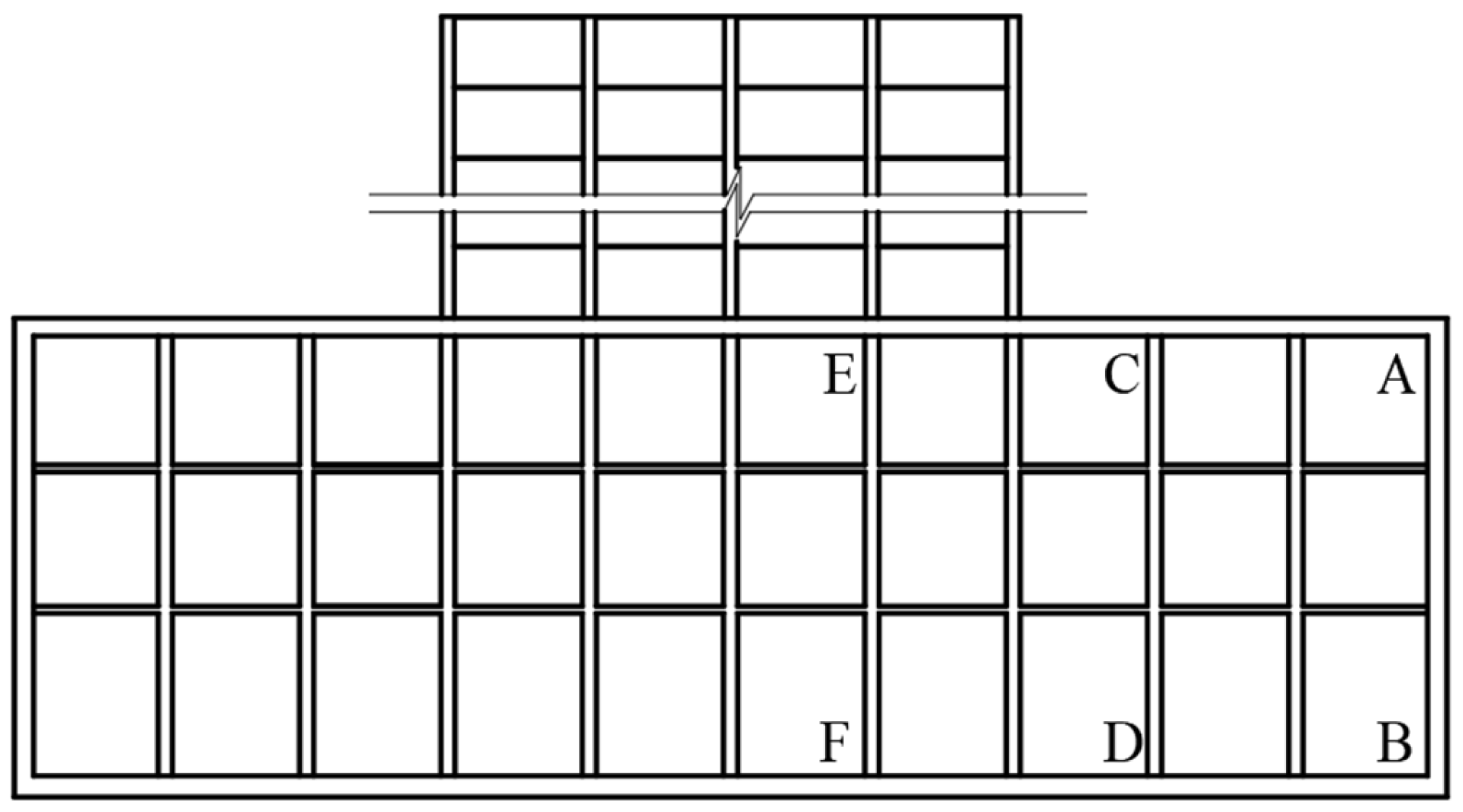
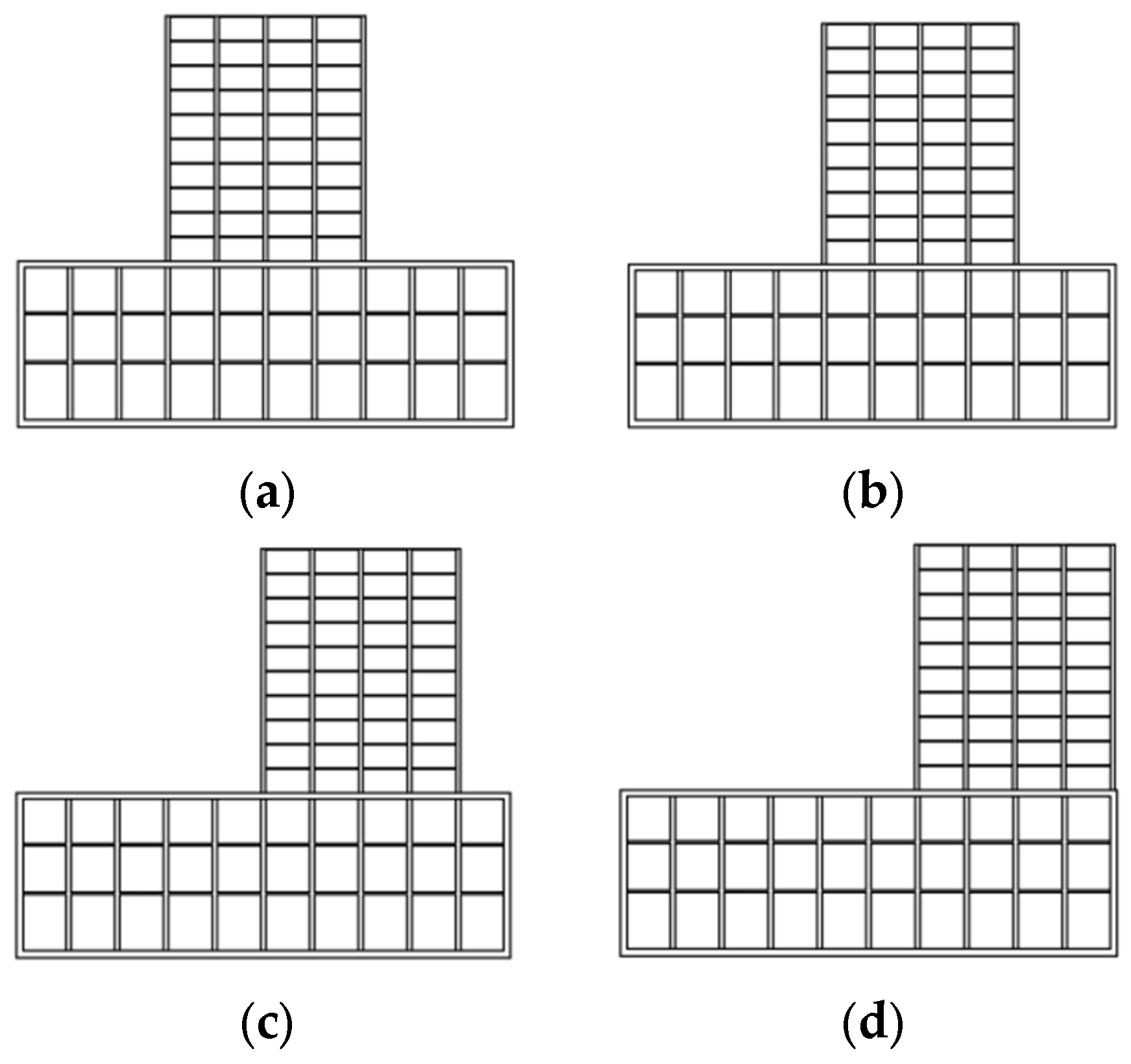
| Soil Types | Soil Thickness | Natural Density ρ (g/cm3) | Constrained Modulus E (MPa) | Poisson Ratio γ | Cohesion C (kPa) | Friction Angle φ (°) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ① Miscellaneous fill | 4.0 | 1.75 | 4.0 | 0.389 | 5 | 10 |
| ② Silty clay | 3.5 | 1.90 | 5.0 | 0.313 | 30 | 10 |
| ③ Sandy silt | 5.5 | 2.02 | 10.0 | 0.313 | 20 | 30 |
| ④ Fine sand–medium sand | 6.0 | 2.00 | 26.0 | 0.300 | 0 | 30 |
| ⑤ Silty clay | 6.0 | 1.99 | 11.0 | 0.357 | 30 | 10 |
| ⑥ Fine sand–medium sand | 12.0 | 2.02 | 55.0 | 0.300 | 0 | 32 |
| ⑦ Heavy clayey silt | 7.0 | 2.12 | 25.0 | 0.313 | 25 | 26 |
| ⑧ Pebble round gravel | 25.0 | 2.12 | 142.5 | 0.278 | 0 | 30 |
| Position | One-Dimensional Free Field Analysis | Coefficient of Soil Reaction | Additional Seismic Load | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Displacement (m) | Acceleration (g) | Shearing Force (kN) | Horizontal Direction (kN/m3) | Vertical Direction (kN/m3) | Shearing Force (kN) | Bending Moment (kN·m) | Vertical Inertia Force (kN) | |
| Top plate | 0.17 | 0.17 | - | - | - | Total shearing force 6433.48 Single column shear force 321.67 | Single column 857.79 | Total inertia force 4181.76 Single column inertia force 209.09 |
| Medium Plate 1 | 0.15 | 0.18 | 28.46 | 2563 | 2108 | |||
| Medium Plate 2 | 0.03 | 0.08 | 56.93 | 3920 | 3487 | |||
| Bedplate | 0.00 | 0.00 | 92.51 | 12,412 | 9773 | |||
| Seismic Wave | Calculating Method | Side Wall A | Side Wall B | Middle Column C | Middle Column D | Middle Column E | Middle Column F |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Beijing artificial wave | TRDM | 652.36 | 1132.68 | 170.44 | 190.28 | 230.35 | 215.14 |
| THAM | 757.08 | 1221.19 | 203.53 | 221.52 | 316.54 | 243.53 | |
| IRDM | 806.21 | 1179.35 | 211.20 | 205.37 | 330.84 | 247.25 | |
| Kobe wave | TRDM | 527.63 | 1257.64 | 92.36 | 99.22 | 110.34 | 102.61 |
| THAM | 645.38 | 1439.81 | 110.43 | 118.98 | 184.95 | 125.57 | |
| IRDM | 663.45 | 1450.48 | 100.74 | 105.83 | 210.27 | 129.58 | |
| Loma Prieta wave | TRDM | 531.45 | 1492.73 | 63.02 | 96.45 | 125.02 | 114.86 |
| THAM | 650.52 | 1594.83 | 115.10 | 132.33 | 206.01 | 137.51 | |
| IRDM | 675.34 | 1609.70 | 100.32 | 119.02 | 234.74 | 141.37 | |
| Landers wave | TRDM | 361.38 | 1029.33 | 54.60 | 97.24 | 16.11 | 81.94 |
| THAM | 554.27 | 1316.48 | 89.48 | 143.22 | 197.32 | 150.69 | |
| IRDM | 580.38 | 1331.73 | 80.95 | 131.47 | 230.59 | 155.70 |
| Seismic Wave | Calculating Method | Side Wall A | Middle Column C | Middle Column E | Deformation Error |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Beijing artificial wave | TRDM | 57.23 | 56.35 | 55.51 | 20% |
| THAM | 68.54 | 69.06 | 69.46 | - | |
| IRDM | 74.88 | 74.57 | 75.03 | 9% | |
| Kobe wave | TRDM | 60.71 | 59.82 | 58.93 | 21% |
| THAM | 74.20 | 74.62 | 74.90 | - | |
| IRDM | 82.00 | 81.52 | 82.13 | 11% | |
| Loma Prieta wave | TRDM | 51.10 | 50.54 | 49.22 | 25% |
| THAM | 66.23 | 67.77 | 68.12 | - | |
| IRDM | 74.71 | 75.24 | 75.67 | 12% | |
| Landers wave | TRDM | 65.28 | 65.61 | 64.81 | 16% |
| THAM | 76.56 | 78.21 | 78.39 | - | |
| IRDM | 85.52 | 86.08 | 86.32 | 11% |
| Different Peak Acceleration | Calculating Method | Side Wall A | Side Wall B | Middle Column C | Middle Column D | Middle Column E | Middle Column F |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.05 g | TRDM | 196.99 | 280.39 | 41.26 | 45.39 | 54.15 | 50.37 |
| THAM | 214.27 | 305.30 | 50.88 | 55.38 | 79.13 | 60.88 | |
| IRDM | 224.94 | 307.07 | 57.61 | 54.85 | 85.68 | 65.70 | |
| 0.10 g | TRDM | 380.19 | 580.41 | 83.34 | 92.15 | 112.14 | 103.25 |
| THAM | 428.54 | 610.60 | 101.76 | 110.76 | 158.27 | 121.76 | |
| IRDM | 445.37 | 611.06 | 111.76 | 106.96 | 167.94 | 126.15 | |
| 0.20 g | TRDM | 752.36 | 1168.23 | 160.44 | 190.28 | 220.35 | 215.14 |
| THAM | 857.08 | 1221.19 | 203.53 | 221.52 | 316.54 | 243.53 | |
| IRDM | 846.21 | 1179.35 | 221.28 | 205.37 | 330.84 | 247.25 | |
| 0.40 g | TRDM | 1527.29 | 2406.55 | 333.72 | 388.17 | 462.33 | 441.04 |
| THAM | 1714.16 | 2442.39 | 407.05 | 443.03 | 633.07 | 487.05 | |
| IRDM | 1699.81 | 2382.29 | 453.62 | 423.06 | 658.37 | 489.56 |
| Different Peak Acceleration | Calculating Method | Side Wall A | Middle Column C | Middle Column E | Deformation Error |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.05 g | TRDM | 14.23 | 14.01 | 13.64 | 21% |
| THAM | 17.12 | 17.26 | 17.37 | - | |
| IRDM | 18.82 | 18.46 | 18.39 | 10% | |
| 0.10 g | TRDM | 28.33 | 27.76 | 26.95 | 22% |
| THAM | 34.25 | 34.53 | 34.73 | - | |
| IRDM | 37.82 | 37.47 | 37.33 | 10% | |
| 0.20 g | TRDM | 57.23 | 56.35 | 55.51 | 20% |
| THAM | 68.54 | 69.06 | 69.46 | - | |
| IRDM | 74.88 | 74.57 | 75.03 | 9% | |
| 0.40 g | TRDM | 113.32 | 109.88 | 109.91 | 21% |
| THAM | 137.01 | 138.12 | 138.94 | - | |
| IRDM | 146.76 | 148.62 | 147.06 | 8% |
| Structural Position | Calculating Method | Side Wall A | Side Wall B | Middle Column C | Middle Column D | Middle Column E | Middle Column F |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No offset | TRDM | 752.36 | 1168.23 | 160.44 | 190.28 | 230.35 | 215.14 |
| THAM | 857.08 | 1221.19 | 203.53 | 221.52 | 316.54 | 243.53 | |
| IRDM | 846.21 | 1179.35 | 221.28 | 205.37 | 330.84 | 247.25 | |
| Offset one span | TRDM | 752.33 | 1169.25 | 170.14 | 191.36 | 228.93 | 215.68 |
| THAM | 761.95 | 1189.05 | 119.97 | 141.30 | 67.82 | 88.62 | |
| IRDM | 746.69 | 1177.83 | 136.54 | 205.66 | 88.61 | 247.53 | |
| Offset two spans | TRDM | 752.40 | 1169.88 | 175.53 | 192.47 | 227.02 | 216.53 |
| THAM | 761.13 | 1178.75 | 206.54 | 204.63 | 400.61 | 297.65 | |
| IRDM | 754.83 | 1162.06 | 220.38 | 205.91 | 362.88 | 247.76 | |
| Offset three spans | TRDM | 731.37 | 1167.41 | 177.24 | 194.37 | 226.48 | 217.58 |
| THAM | 793.40 | 1180.71 | 326.67 | 218.91 | 86.96 | 102.96 | |
| IRDM | 781.32 | 1185.24 | 205.48 | 206.17 | 98.07 | 247.69 |
| Structural Position | Calculating Method | Side Wall A | Middle Column C | Middle Column E | Deformation Error |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No offset | TRDM | 57.23 | 56.35 | 55.51 | 20% |
| THAM | 68.54 | 69.06 | 69.46 | - | |
| IRDM | 74.88 | 74.57 | 75.03 | 9% | |
| Offset one span | TRDM | 55.00 | 54.25 | 53.26 | 22% |
| THAM | 68.22 | 68.69 | 68.13 | - | |
| IRDM | 74.82 | 75.23 | 75.63 | 11% | |
| Offset two spans | TRDM | 57.24 | 57.68 | 57.50 | 19% |
| THAM | 69.63 | 70.39 | 70.77 | - | |
| IRDM | 75.26 | 75.83 | 76.34 | 8% | |
| Offset three spans | TRDM | 57.21 | 57.70 | 57.48 | 18% |
| THAM | 69.29 | 69.76 | 70.19 | - | |
| IRDM | 74.35 | 74.63 | 74.92 | 7% |
| Structural Style | Calculating Method | Side Wall A | Side Wall B | Middle Column C | Middle Column D | Middle Column E | Middle Column F |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Frame structure | TRDM | 719.88 | 1261.52 | 97.54 | 129.47 | 53.13 | 88.02 |
| THAM | 835.07 | 1325.07 | 144.94 | 162.90 | 145.35 | 122.09 | |
| IRDM | 822.03 | 1270.68 | 164.47 | 143.52 | 163.23 | 126.55 | |
| Frame-symmetric shear wall structure | TRDM | 681.74 | 1168.65 | 49.18 | 233.73 | 2159.03 | 737.25 |
| THAM | 808.45 | 1238.56 | 101.32 | 270.50 | 2458.41 | 794.72 | |
| IRDM | 794.10 | 1178.73 | 122.80 | 249.18 | 2653.81 | 819.63 | |
| Frame-asymmetric shear wall structure | TRDM | 687.70 | 1282.86 | 104.22 | 240.72 | 192.00 | 174.57 |
| THAM | 824.87 | 1244.94 | 109.19 | 278.65 | 2515.51 | 812.40 | |
| IRDM | 791.69 | 1310.86 | 165.43 | 306.50 | 289.70 | 252.54 |
| Structural Style | Calculating Method | Side Wall A | Middle Column C | Middle Column E | Deformation Error |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Frame structure | TRDM | 49.73 | 48.53 | 47.29 | 25% |
| THAM | 64.17 | 64.79 | 65.13 | - | |
| IRDM | 72.43 | 71.98 | 72.39 | 12% | |
| Frame-symmetric shear wall structure | TRDM | 59.65 | 59.09 | 58.68 | 16% |
| THAM | 69.81 | 70.25 | 70.77 | - | |
| IRDM | 77.97 | 77.32 | 77.93 | 11% | |
| Frame-asymmetric shear wall structure | TRDM | 58.22 | 56.92 | 55.83 | 22% |
| THAM | 72.33 | 72.74 | 73.21 | - | |
| IRDM | 79.96 | 79.36 | 79.91 | 10% |
| Station and Ground | Calculating Method | Side Wall A | Side Wall B | Middle Column C | Middle Column D | Middle Column E | Middle Column F |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4 m above the ground | TRDM | 564.02 | 703.46 | 120.54 | 153.24 | 194.26 | 146.28 |
| THAM | 620.65 | 796.66 | 94.84 | 84.96 | 147.51 | 90.78 | |
| IRDM | 640.58 | 821.93 | 112.30 | 97.28 | 162.16 | 103.88 | |
| Equal to the ground | TRDM | 752.36 | 1168.23 | 160.44 | 190.28 | 230.35 | 215.14 |
| THAM | 857.08 | 1221.19 | 203.53 | 221.52 | 316.54 | 243.53 | |
| IRDM | 846.21 | 1179.35 | 221.28 | 205.37 | 330.84 | 247.25 | |
| 4 m below the ground | TRDM | 806.39 | 1241.53 | 196.57 | 226.14 | 320.54 | 260.61 |
| THAM | 833.37 | 1304.75 | 289.38 | 245.43 | 152.07 | 126.18 | |
| IRDM | 887.43 | 1277.65 | 326.13 | 264.29 | 161.23 | 129.55 |
| Station and Ground | Calculating Method | Side Wall A | Middle Column C | Middle Column E | Deformation Error |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4 m above the ground | TRDM | 55.75 | 54.88 | 54.42 | 47% |
| THAM | 101.21 | 101.56 | 101.81 | - | |
| IRDM | 95.47 | 95.01 | 96.31 | 6% | |
| Equal to the ground | TRDM | 57.23 | 56.35 | 55.51 | 20% |
| THAM | 68.54 | 69.06 | 69.46 | - | |
| IRDM | 74.88 | 74.57 | 75.03 | 9% | |
| 4 m below the ground | TRDM | 40.64 | 40.35 | 40.17 | 21% |
| THAM | 49.02 | 50.20 | 50.69 | - | |
| IRDM | 52.58 | 51.97 | 53.22 | 7% |
| Structural Stiffness | Calculating Method | Side Wall A | Side Wall B | Middle Column C | Middle Column D | Middle Column E | Middle Column F |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.50 | TRDM | 545.19 | 789.34 | 110.65 | 126.01 | 147.74 | 131.51 |
| THAM | 571.39 | 808.74 | 133.03 | 143.84 | 206.89 | 157.12 | |
| IRDM | 553.08 | 765.81 | 149.51 | 136.01 | 216.24 | 158.49 | |
| 1.00 | TRDM | 752.36 | 1168.23 | 160.44 | 190.28 | 230.35 | 215.14 |
| THAM | 857.08 | 1221.19 | 203.53 | 221.52 | 316.54 | 243.53 | |
| IRDM | 846.21 | 1179.35 | 221.28 | 205.37 | 330.84 | 247.25 | |
| 2.00 | TRDM | 1068.35 | 1670.57 | 232.64 | 268.29 | 278.49 | 255.50 |
| THAM | 1259.91 | 1856.21 | 311.40 | 347.79 | 484.31 | 375.04 | |
| IRDM | 1269.32 | 1792.61 | 338.56 | 310.11 | 509.49 | 378.29 | |
| 4.00 | TRDM | 1715.38 | 2675.25 | 364.20 | 430.03 | 505.58 | 486.22 |
| THAM | 1997.00 | 2820.95 | 476.26 | 513.93 | 731.21 | 560.12 | |
| IRDM | 1963.21 | 2759.68 | 511.16 | 476.46 | 764.24 | 578.57 |
| Structural Stiffness | Calculating Method | Side Wall A | Middle Column C | Middle Column E | Deformation Error |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.50 | TRDM | 66.16 | 65.37 | 64.39 | 23% |
| THAM | 82.25 | 82.87 | 83.35 | - | |
| IRDM | 91.35 | 89.48 | 90.04 | 11% | |
| 1.00 | TRDM | 57.23 | 56.35 | 55.51 | 20% |
| THAM | 68.54 | 69.06 | 69.46 | - | |
| IRDM | 74.88 | 74.57 | 75.03 | 9% | |
| 2.00 | TRDM | 47.30 | 46.57 | 46.65 | 19% |
| THAM | 56.64 | 57.07 | 57.40 | - | |
| IRDM | 61.38 | 61.63 | 62.01 | 8% | |
| 4.00 | TRDM | 43.03 | 42.37 | 41.74 | 20% |
| THAM | 51.53 | 51.92 | 52.23 | - | |
| IRDM | 54.66 | 54.04 | 55.17 | 6% |
| Soil Stiffness | Calculating Method | Side Wall A | Side Wall B | Middle Column C | Middle Column D | Middle Column E | Middle Column F |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1/4 | TRDM | 1068.35 | 1623.84 | 216.59 | 254.98 | 260.38 | 236.14 |
| THAM | 1208.48 | 1734.09 | 293.08 | 314.56 | 436.83 | 343.38 | |
| IRDM | 1193.16 | 1633.40 | 308.91 | 283.21 | 443.82 | 354.83 | |
| 1/2 | TRDM | 901.33 | 1385.87 | 194.77 | 223.58 | 241.45 | 228.17 |
| THAM | 1055.07 | 1491.07 | 248.31 | 270.03 | 379.21 | 289.07 | |
| IRDM | 1015.45 | 1415.22 | 270.85 | 252.81 | 400.98 | 300.16 | |
| 1 | TRDM | 752.36 | 1168.23 | 160.44 | 190.28 | 230.35 | 215.14 |
| THAM | 857.08 | 1221.19 | 203.53 | 221.52 | 316.54 | 243.53 | |
| IRDM | 846.21 | 1179.35 | 221.28 | 205.37 | 330.84 | 247.25 | |
| 2 | TRDM | 586.84 | 922.90 | 123.38 | 149.37 | 209.25 | 151.25 |
| THAM | 679.66 | 989.16 | 166.89 | 176.33 | 259.56 | 198.48 | |
| IRDM | 681.20 | 959.99 | 177.69 | 168.61 | 267.98 | 203.24 |
| Soil Stiffness | Calculating Method | Side Wall A | Middle Column C | Middle Column E | Deformation Error |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1/4 | TRDM | 86.42 | 84.33 | 83.26 | 26% |
| THAM | 102.81 | 109.11 | 112.53 | - | |
| IRDM | 110.26 | 110.92 | 111.63 | 7% | |
| 1/2 | TRDM | 74.40 | 73.26 | 72.16 | 24% |
| THAM | 89.79 | 87.71 | 95.16 | - | |
| IRDM | 97.34 | 95.45 | 97.16 | 10% | |
| 1 | TRDM | 57.23 | 56.35 | 55.51 | 20% |
| THAM | 68.54 | 69.06 | 69.46 | - | |
| IRDM | 74.88 | 74.57 | 75.03 | 9% | |
| 2 | TRDM | 45.78 | 45.64 | 46.07 | 19% |
| THAM | 54.83 | 56.63 | 55.57 | - | |
| IRDM | 59.90 | 59.66 | 59.27 | 7% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
An, J.; Feng, F.; Zhang, Y.; Li, M. Response Displacement Method for Seismic Calculation of Subway Station Complex Structure of TOD Mode. Buildings 2023, 13, 2987. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings13122987
An J, Feng F, Zhang Y, Li M. Response Displacement Method for Seismic Calculation of Subway Station Complex Structure of TOD Mode. Buildings. 2023; 13(12):2987. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings13122987
Chicago/Turabian StyleAn, Junhai, Fuqiang Feng, Yanhua Zhang, and Ming Li. 2023. "Response Displacement Method for Seismic Calculation of Subway Station Complex Structure of TOD Mode" Buildings 13, no. 12: 2987. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings13122987
APA StyleAn, J., Feng, F., Zhang, Y., & Li, M. (2023). Response Displacement Method for Seismic Calculation of Subway Station Complex Structure of TOD Mode. Buildings, 13(12), 2987. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings13122987







