Hybrid Resistance and Virulence Plasmids in “High-Risk” Clones of Klebsiella pneumoniae, Including Those Carrying blaNDM-5
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gomez-Simmonds, A.; Uhlemann, A.C. Clinical implications of genomic adaptation and evolution of carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae. J. Infect. Dis. 2017, 215, S18–S27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holt, K.E.; Wertheim, H.; Zadoks, R.N.; Baker, S.; Whitehouse, C.A.; Dance, D.; Jenney, A.; Connor, T.R.; Hsu, L.Y.; Severin, J.; et al. Genomic analysis of diversity, population structure, virulence, and antimicrobial resistance in Klebsiella pneumoniae, an urgent threat to public health. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, E3574–E3581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shon, A.S.; Bajwa, R.P.; Russo, T.A. Hypervirulent (hypermucoviscous) Klebsiella pneumoniae: A new and dangerous breed. Virulence 2013, 4, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.R.; Lee, J.H.; Park, K.S.; Jeon, J.H.; Kim, Y.B.; Cha, C.J.; Jeong, B.C.; Lee, S.H. Antimicrobial resistance of hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae: Epidemiology, hypervirulence-associated determinants, and resistance mechanisms. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2017, 7, 483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roulston, K.J.; Bharucha, T.; Turton, J.F.; Hopkins, K.L.; Mack, D.J.F. A case of NDM-carbapenemase producing hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae Sequence Type 23 from the United Kingdom. JMM Case Rep. 2018, 5, e005130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, L.; Kaase, M.; Pfeifer, Y.; Fuchs, S.; Reuss, A.; von Laer, A.; Sin, M.A.; Korte-Berwanger, M.; Gatermann, S.; Werner, G. Genome-based analysis of carbapenemase-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates from German hospital patients, 2008–2014. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control. 2018, 7, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, L.N.; Vitali, L.; Gaspar, G.G.; Bellissimo-Rodrigues, F.; Martinez, R.; Darini, A.L. Expansion and evolution of a virulent, extensively drug-resistant (polymyxin B-resistant), QnrS1-, CTX-M-2-, and KPC-2-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae ST11 international high-risk clone. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2014, 52, 2530–2535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, D.; Dong, N.; Zheng, Z.; Lin, D.; Huang, M.; Wang, L.; Chan, E.W.; Shu, L.; Yu, J.; Zhang, R.; et al. A fatal outbreak of ST11 carbapenem-resistant hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae in a Chinese hospital: A molecular epidemiological study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2018, 18, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turton, J.F.; Payne, Z.; Coward, A.; Hopkins, K.L.; Turton, J.A.; Doumith, M.; Woodford, N. Virulence genes in isolates of Klebsiella pneumoniae from the UK during 2016, including among carbapenemase gene-positive hypervirulent K1-ST23 and ‘non-hypervirulent’ types ST147, ST15 and ST383. J. Med. Microbiol. 2018, 67, 118–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.H.; Chou, S.H.; Liang, S.W.; Ni, C.E.; Lin, Y.T.; Huang, Y.W.; Yang, T.C. Emergence of an XDR and carbapenemase-producing hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae strain in Taiwan. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2018, 73, 2039–2046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, M.M.C.; Wyres, K.L.; Wick, R.R.; Judd, L.M.; Fostervold, A.; Holt, K.E.; Löhr, I.H. Convergence of virulence and MDR in a single plasmid vector in MDR Klebsiella pneumoniae ST15. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2019, 74, 1218–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, N.; Lin, D.; Zhang, R.; Chan, E.W.; Chen, S. Carriage of blaKPC-2 by a virulence plasmid in hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2018, 73, 3317–3321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lery, L.M.; Frangeul, L.; Tomas, A.; Passet, V.; Almeida, A.S.; Bialek-Davenet, S.; Barbe, V.; Bengoechea, J.A.; Sansonetti, P.; Brisse, S.; et al. Comparative analysis of Klebsiella pneumoniae genomes identifies a phospholipase D family protein as a novel virulence factor. BMC Biology 2014, 12, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, M.J.; Petty, N.K.; Beatson, S.A. Easyfig: A genome comparison visualizer. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 1009–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing: Clinical Breakpoints. Available online: http://www.eucast.org/clinical_breakpoints/ (accessed on 2 September 2019).
- Lam, M.M.C.; Wyres, K.L.; Judd, L.M.; Wick, R.R.; Jenney, A.; Brisse, S.; Holt, K.E. Tracking key virulence loci encoding aerobactin and salmochelin siderophore synthesis in Klebsiella pneumoniae. Genome Med. 2018, 10, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, L.; Dong, N.; Lu, J.; Zheng, Z.; Hu, J.; Zeng, W.; Sun, Q.; Chan, E.W.; Zhou, H.; Hu, F.; et al. Emergence of OXA-232 carbapenemase-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae that carries a pLVPK-like virulence plasmid among elderly patients in China. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2019, 3, e02246-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, R.; Wang, G.; Le, S.; Wu, M.; Cheng, M.; Guo, Z.; Ji, Y.; Xi, H.; Zhao, C.; Wang, X.; et al. Three capsular polysaccharide synthesis-related glucosyltransferases, GT-1, GT-2 and WcaJ, are associated with virulence and phage sensitivity of Klebsiella pneumoniae. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H. Minimap and miniasm: Fast mapping and de novo assembly for noisy long sequences. Bioinformatics 2016, 32, 2103–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaser, R.; Sović, I.; Nagarajan, N.; Šikić, M. Fast and accurate de novo genome assembly from long uncorrected reads. Genome Res. 2017, 27, 737–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barton, B.M.; Harding, G.P.; Zuccarelli, A.J. A General Method for Detecting and Sizing Large Plasmids. Anal. Biochem. 1995, 226, 235–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zankari, E.; Hasman, H.; Cosentino, S.; Vestergaard, M.; Rasmussen, S.; Lund, O.; Aarestrup, F.M.; Larsen, M.V. Identification of acquired antimicrobial resistance genes. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2012, 67, 2640–2644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carattoli, A.; Zankari, E.; Garcia-Fernandez, A.; Voldby Larsen, M.; Lund, O.; Villa, L.; Aarestrup, F.M.; Hasman, H. PlasmidFinder and pMLST: In silico detection and typing of plasmids. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2014, 58, 3895–3903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Isolate | Virulence Plasmid | Other Virulence Factors (Chromosome) | Antibiotic Genes in Virulence Plasmid | Other Resistance Genes | Hospital (Code), Date and Source of Isolation | Clinical Manifestation | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KpvST101_OXA-48 Illumina corrected sequence | plasmid pKpvST101 CP031369 292699 bp rmpA, rmpA2, (iutA, iucABD, (iucB and iucD truncated), pcoABCDERS, silCERS terBCDE, cobW, luxR, pagO, shiF | fyuA, kfuABC, irp1, irp2, ybtAEPQSTUX, mrkABCDFHIJ, pld1 | aph(6)-Id, aph(3’)-Ib, blaTEM-1Bmph(A), sul1, sul2 and dfrA5 | Chromosome blaSHV-28, blaCTX-M-15, oqxA, oqxB, fosA plasmid CP031374 65380 bp blaOXA-48 plasmid CP031372 210661 bp armA, msr(E), mph(E) plasmid CP031373 43670 bp blaSHV-28, qnrS1 | South_East_2 (SE2) June 2018 blood | septicaemia | no iucC no terAWXYZ |
| Kpv_ST101_SE2_2 | utg000004c (294751 bp) iutA, iucABD (iucB and iucD truncated), rmpA, rmpA2, terBCDE, pcoABCDERS, silCERS, FecA, cobW, luxR, pagO, shiF | fyuA, kfuABC, irp1, irp2, ybtAEPQSTUX, pld1, mrkABCDFHIJ | aph(6)-Id, aph(3’)-Ib, blaTEM-1B, mph(A), sul1, sul2 and dfrA5 | Chromosome blaSHV-28, blaCTX-M-15, oqxA, oqxB, fosA, utg16c; 65307 bp blaOXA-48 utg31c blaCTX-M-15, armA, msr(E), mph(E) utg27c blaSHV-28, qnrS1 | South_East_2 (SE2) May 2018 sputum | chest infection | no iucC no terAWXYZ |
| Kpv_ST101_L5 | utg00035c (267754 bp) iutA, iucABD (iucB and D truncated), rmpA, rmpA2, terBCDE, pcoABCDERS, silCERS, FecA, cobW, luxR, pagO, shiF | fyuA, irp1, irp2, kfuABC, ybtAEPQSTUX, pld1, mrkABCDFHIJ | mph(A), sul1, dfrA5 | Chromosome blaSHV-28, blaCTX-M-15, oqxA, oqxB, fosA utg000020c armA, msr(E), mph(E) utg000037c blaOXA-48 utg000108c blaSHV-28, qnrS1 | London_5 (L5) October 2018 rectal screen | screen | no iucC no terAWXYZ |
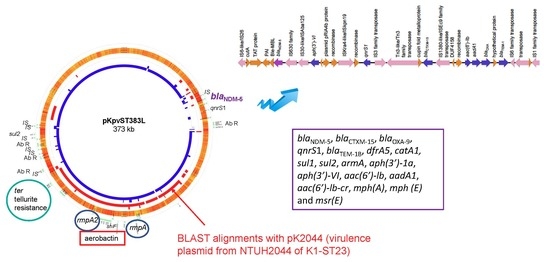
| KpvST383_NDM_OXA-48 Illumina corrected sequence | plasmid pKpvST383L CP034201 372826 bp iutA, iucABCD, rmpA/rmpA2, terABCDEWXYZ, cobW, luxR, pagO, shiF | mrkABCDFHIJ, pld1 | blaNDM-5, blaCTXM-15, blaOXA-9, qnrS1, blaTEM-1B, dfrA5, catA1, sul1, sul2, armA, aph(3′)-1a, aph(3′)-VI, aac(6′)-lb, aadA1, aac(6′)-lb-cr, mph(A), mph (E) and msr(E) | blaSHV-26, oqxA, oqxB, fosA, mph(A), catA1, tet(A) plasmid CP034202 72057 bp aph(6)-Id, aph(3’)-Ib, aph(3’)-VIb, aph(3’)-Ib, blaCTX-M-14b, blaOXA-48 | London_5 (L5) April 2018 blood | bacteraemia, sepsis, multi-organ failure and death | no yersiniabactin |
| Kpv_ST383_L2 | utg000003c (294,141) iutA, iucABCD, rmpA/rmpA2, terABCDEWZ, cobW, luxR, pagO, shiF | mrkABCDFHIJ, pld1 | aph(3’)-Ia, aadA1, sul1, tet(B) | blaSHV-26, oqxA, oqxB, fosA, sul1 utg000002c (110455 bp) rmtC, blaNDM-1 utg000011c (105957 bp) aph(’’)-Ib, aph(6)-Id, aac(6’)-Ib3, aadA1, blaOXA-48 blaCTX-M-14b, blaOXA-9, aac(6’)-Ib-cr | London_2 (L2) April 2017 blood | sepsis | Not got yersiniabactin ybt cluster, irp1,2) or terXY |
| Kpv_ST383_S1 | utg000038c (374430 bp) (pKpvST383_S1) iutA, iucABCD, rmpA, rmpA2, terABCDEWXYZ, cobW, pagO, shiF, luxR | mrkABCDFHIJ, pld1 | aadA1, aac(6’)-Ib aph(3’)-Ia, armA, aph(3’)-VI, blaTEM-1B, blaOXA-9, blaCTX-M-15, blaNDM-5, aac(6’)-Ib-cr, qnrS1, msr(E), mph(E), mph(A), catA1, sul1, sul2, dfrA5 | blaSHV-26, oqxA, oqxB, fosA, mph(A), catA1, tet(A) utg000039c (72122 bp) aph(3’)-Ib, aph(3’)-VIb, aph(3’)-Ib, aph(6)-Id, blaOXA-48, blaCTX-M-14b | Scotland1 (S1) Feb 2016 rectal swab | No information; screening swab | terXY present, no ybt irp1,2 cluster Ex Egypt (in hospital in Cairo) |
| KpvST147L_NDM previously described [9]; Illumina corrected | plasmid pKpvST147L CM007852.1 343,282 bp iutA, iucABCD, rmpA, rmpA2, terABCDEWXYZ, cobW, luxR, pagO, shiF | mrkABCDFHIJ | sul1, sul2, armA, dfrA5, mph(A), msr(E), mph(E), aph(3’)-Ia | blaNDM-1, aph(3’)-Ia. aac(6’)-Ib, aadA1 blaTEM-1A, blaOXA-9, blaCTX-M-15, blaSHV-67, qnrS1, aac(6’)-Ib-cr, oqxA, oqxB, fosA | London_5 (L5) January 2016 rectal swab | screening swab | |
| KpvST147B_SE1_1_NDM Illumina corrected sequence | plasmid pKpvST147B CP040726 (339117 bp) iutA, iucABCD, rmpA, rmpA2, terABCDEWXYZ, cobW, luxR, pagO, shiF | fyuA, mrkABCDFHIJ, irp1, irp2, ybtAEPQSTUX | sul1, sul2, armA, dfrA5, mph(A), msr(E), mph(E) blaCTX-M-15 | aac(6’)-Ib, aadA1, blaSHV-67, blaOXA-9, blaTEM-1A, oqxA oqxB, aac(6’)-Ib-cr fosA plasmid CP040728 53950 bp aac(6’)-Ib-cr, aph(3’)-VI, blaOXA-1, blaCTX-M-15, blaNDM-1, qnrS1, catB3, ARR-3, sul1 | South_East_1 (SE1) January 2019 rectal swab | no information, screening swab | |
| Kpv_ST147_SE1_2 Illumina corrected sequence | utg000005c (338588 bp) iutA, iucABCD, rmpA, rmpA2, terABCDEWXYZ, cobW, luxR, pagO, shiF | fyuA, mrkABCDFHIJ, irp1, irp2, ybtAEPQSTUX | armA, mphA, sul1, sul2, dfrA5, blaCTX-M-15, mph(E), msr(E) | Chromosome oqxA, oqxB, fosA, blaSHV-67 utg000020c; 53949 bp, blaNDM-1, sul1, aph(3’)-VI, catB3, ARR-3, qnrS1, aac(6’)-Ib-cr, blaOXA-1 utg000007c 39671 bp aadA1, aac(6’)-Ib, blaTEM-1A, blaOXA-9, aac(6’)-Ib-cr | South_East_1 (SE1) December 2018 urine | patient died | |
| Kpv_ST147_L3 | utg000005c (339641 bp) iutA, iucABCD, rmpA, rmpA2, terABCDEWXYZ, cobW, luxR, pagO, shiF | fyuA, mrkABCDFHIJ, irp1, irp2, ybtAEPQSTUX | armA, aph(3’)-Ia, blaCTX-M-15, mph(A), mph(E), msr(E), sul1, sul2, dfrA5 | Chromosome blaSHV-67, oqxA, oqxB, fosA utg000004c; 53895 bp blaNDM-1, aac(6’)-Ib-cr, aph(3’)-VI, blaOXA-1, blaCTX-M-15, aac(6’)-Ib-cr, qnrS1, catB3, ARR-3, sul1 | London_3 (L3) January 2019 not given | No information | |
| Kpv_ST15_NDM (L6) Illumina corrected sequence | plasmid pKpvST15 CP040595 277162 bp iutA, iucABCD, rmpA, rmpA2, pbrABCR, pcoABCDERS, silCERS, cobW, shiF | fyuA, irp1, irp2, ybtAEPQSTUX, kfuABC, mrkA(B), | aac(6’)-Ib3, rmtC, blaCMY-6, aac(6’)-Ib-cr, sul1 | blaCTX-M-15, blaSHV-28, oqxA, oqxB, fosA, plasmid CP040598 106597 bp blaNDM-1, sul1 | London_6 (L6) 19.12.16 Throat swab | screen | mrkB truncated (17% only), no mrkCDFHIJ, no tellurite resistance genes, pagO or luxR |
| Kpv_ST15_NW1 | utg000104c (340,126 bp): iutA, iucABCD, rmpA, rmpA2, terABCDEWXYZ, cobW, luxR, pagO, shiF 2nd plasmid: utg000031c 222308 bp: pcoABCDERS, silCERS | irp1, irp2, mrkABCDFHIJ, ybtAEPQSTUX, kfuABC | armA, aph(3’)-Ia, msr(E), mph(E), mph(A), sul1, sul2, dfrA5 utg000031c: blaSHV-1, tet(D) | aph(3’)-VI, blaNDM-1, blaSHV-28, qnrS1 (utg000030l), oqxA, oqxB (utg000001l), | North_West_1 (NW1) September 2018 urine | No information | pcoABCDERS, silCERS, tet(D) in 2nd plasmid |
| Kpv_ST48_NDM Illumina corrected sequence | plasmid pKpvST48_1 CM016731 302,220 bp iutA, iucABCD, rmpA, rmpA2, cobW, luxR, pagO, shiF 2nd plasmid KpvST48_2 CM016732 226800 bp pcoABCDERS, silCERS, FecA | mrkABCDFHIJ, irp1, irp2, ybtAEPQSTUX, fyuA | CM016731: aph(3’)-Ia aph(3’)-VI aac(6’)-Ib aadA1, blaNDM-5, blaCTX-M-15, blaOXA-9, blaTEM-1B, qnrS1, aac(6’)-Ib-cr, catA1 CM016732: tet(D) | aadA2, aph(3’)-Ia, blaSHV-172, blaCTX-M-14b, oqxA, oqxB, fosA, mph(A), sul1, dfrA12 | London_5 (L5) October 2018 rectal screen | No information; screening swab | pcoABCDERS, silCERS, FecA, tet(D) in CM016732, no tellurite resistance genes, patient ex Egypt |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Turton, J.; Davies, F.; Turton, J.; Perry, C.; Payne, Z.; Pike, R. Hybrid Resistance and Virulence Plasmids in “High-Risk” Clones of Klebsiella pneumoniae, Including Those Carrying blaNDM-5. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 326. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms7090326
Turton J, Davies F, Turton J, Perry C, Payne Z, Pike R. Hybrid Resistance and Virulence Plasmids in “High-Risk” Clones of Klebsiella pneumoniae, Including Those Carrying blaNDM-5. Microorganisms. 2019; 7(9):326. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms7090326
Chicago/Turabian StyleTurton, Jane, Frances Davies, Jack Turton, Claire Perry, Zoë Payne, and Rachel Pike. 2019. "Hybrid Resistance and Virulence Plasmids in “High-Risk” Clones of Klebsiella pneumoniae, Including Those Carrying blaNDM-5" Microorganisms 7, no. 9: 326. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms7090326
APA StyleTurton, J., Davies, F., Turton, J., Perry, C., Payne, Z., & Pike, R. (2019). Hybrid Resistance and Virulence Plasmids in “High-Risk” Clones of Klebsiella pneumoniae, Including Those Carrying blaNDM-5. Microorganisms, 7(9), 326. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms7090326