The Effect of Noise on the Utilization of Fundamental Frequency and Formants for Voice Discrimination in Children and Adults
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Stimuli
2.3. Background Noise
2.4. Voice Discrimination Threshold (VDT)
2.5. Voice Discrimination Threshold in Noisy Conditions (VDTn)
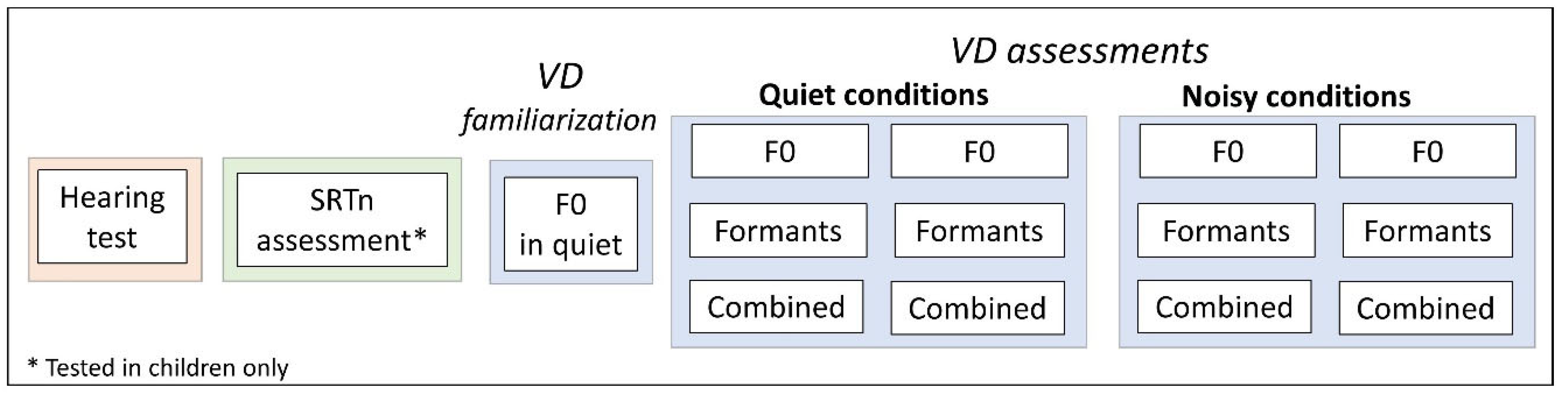
2.6. Study Design
2.7. Apparatus
2.8. Data Analysis
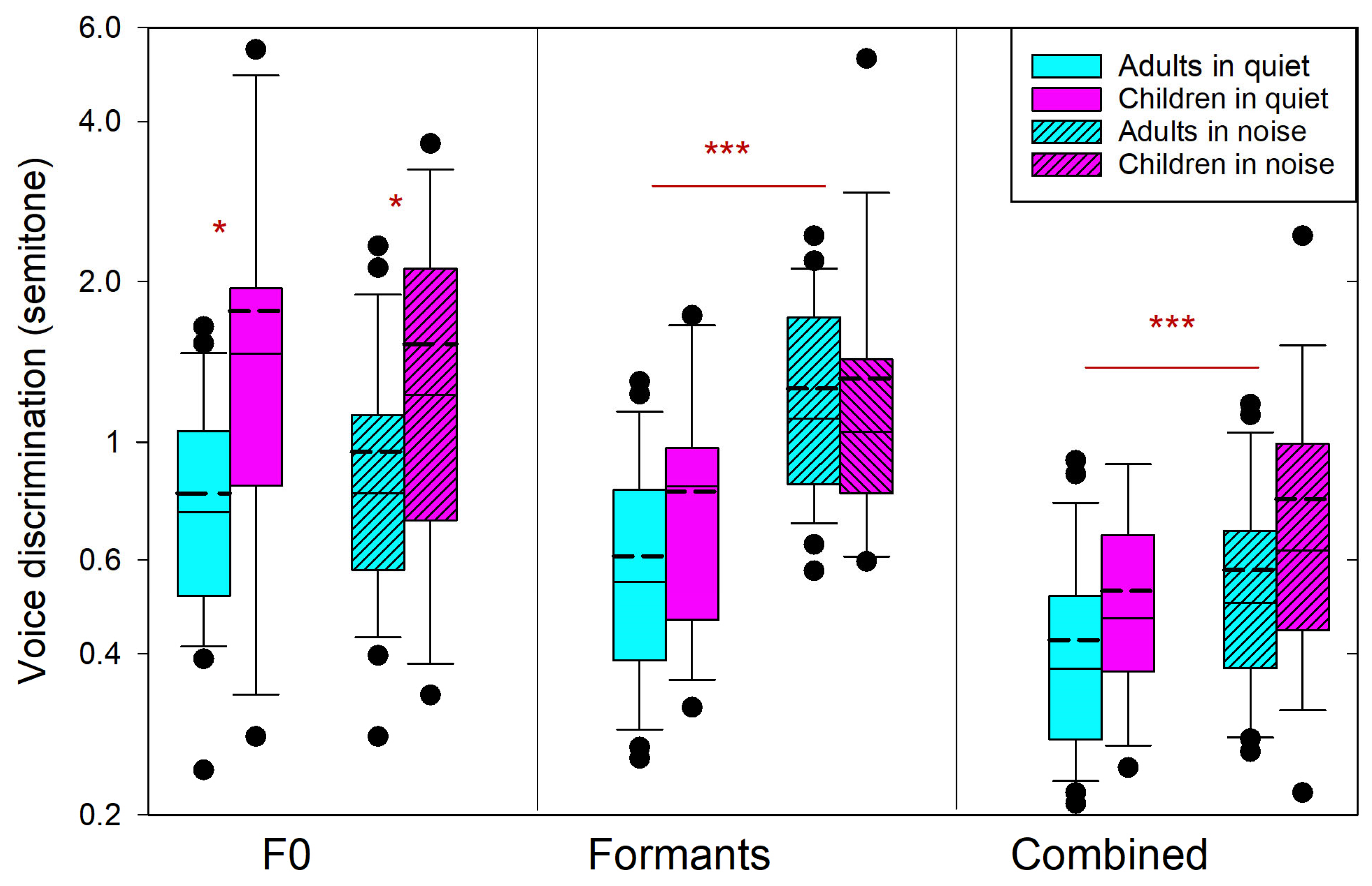
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Limitations of the Current Study and Future Directions
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brungart, D.S.; Chang, P.S.; Simpson, B.D.; Wang, D. Multitalker speech perception with ideal time-frequency segregation: Effects of voice characteristics and number of talkers. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2009, 125, 4006–4022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bronkhorst, A.W. The cocktail-party problem revisited: Early processing and selection of multi-talker speech. Atten. Percept. Psychophys. 2015, 77, 1465–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darwin, C.J.; Brungart, D.S.; Simpson, B.D. Effects of fundamental frequency and vocal-tract length changes on attention to one of two simultaneous talkers. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2003, 114, 2913–2922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drullman, R.; Bronkhorst, A.W. Speech perception and talker segregation: Effects of level, pitch, and tactile support with multiple simultaneous talkers. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2004, 116, 3090–3098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vestergaard, M.D.; Fyson, N.R.C.; Patterson, R.D. The mutual roles of temporal glimpsing and vocal characteristics in cocktail-party listening. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2011, 130, 429–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raphael, L.J.; Borden, G.J.; Harris, K.S. Speech Science Primer: Physiology, Acoustics, and Perception of Speech; LWW: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Zaltz, Y.; Goldsworthy, R.L.; Kishon-Rabin, L.; Eisenberg, L.S. Voice discrimination by adults with cochlear implants: The benefits of early implantation for vocal-tract length perception. J. Assoc. Res. Otolaryngol. 2018, 19, 193–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaltz, Y.; Goldsworthy, R.L.; Eisenberg, L.S.; Kishon-Rabin, L. Children with normal hearing are efficient users of fundamental frequency and vocal tract length cues for voice discrimination. Ear Hear. 2020, 41, 182–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaltz, Y. The effect of stimulus type and testing method on talker discrimination of school-age children. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2023, 153, 2611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuller, C.D.; Gaudrain, E.; Clarke, J.N.; Galvin, J.J.; Fu, Q.-J.; Free, R.H.; Başkent, D. Gender categorization is abnormal in cochlear implant users. J. Assoc. Res. Otolaryngol. 2014, 15, 1037–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillenbrand, J.M.; Clark, M.J. The role of f(0) and formant frequencies in distinguishing the voices of men and women. Atten. Percept. Psychophys. 2009, 71, 1150–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skuk, V.G.; Schweinberger, S.R. Gender differences in familiar voice identification. Hear. Res. 2013, 296, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meister, H.; Fürsen, K.; Streicher, B.; Lang-Roth, R.; Walger, M. The use of voice cues for speaker gender recognition in cochlear implant recipients. J. Speech Lang. Hear. Res. 2016, 59, 546–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brungart, D.S. Informational and energetic masking effects in the perception of two simultaneous talkers. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2001, 109, 1101–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ezzatian, P.; Li, L.; Pichora-Fuller, M.K.; Schneider, B.A. The effect of energetic and informational masking on the time-course of stream segregation: Evidence that streaming depends on vocal fine structure cues. Lang. Cogn. Process. 2012, 27, 1056–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Y.; Xu, L. Lexical tone recognition in noise in normal-hearing children and prelingually deafened children with cochlear implants. Int. J. Audiol. 2017, 56, S23–S30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, X. Talker variability effects on vocal emotion recognition in acoustic and simulated electric hearing. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2016, 140, EL497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corbin, N.E.; Bonino, A.Y.; Buss, E.; Leibold, L.J. Development of open-set word recognition in children: Speech-shaped noise and two-talker speech maskers. Ear Hear. 2016, 37, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wightman, F.L.; Kistler, D.J. Informational masking of speech in children: Effects of ipsilateral and contralateral distracters. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2005, 118, 3164–3176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neuman, A.C.; Wroblewski, M.; Hajicek, J.; Rubinstein, A. Combined effects of noise and reverberation on speech recognition performance of normal-hearing children and adults. Ear Hear. 2010, 31, 336–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagels, L.; Gaudrain, E.; Vickers, D.; Hendriks, P.; Başkent, D. Development of voice perception is dissociated across gender cues in school-age children. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 5074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fant, G. Acoustic Theory of Speech Production; Mouton: The Hague, The Netherlands, 1960. [Google Scholar]
- Lieberman, p.; Blumstein, S.E. Source-filter theory of speech production. In Speech Physiology, Speech Perception, and Acoustic Phonetics Cambridge Studies in Speech Science and Communication; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1988; pp. 34–50. [Google Scholar]
- Kishon-Rabin, L.; Taitelbaum, R.; Muchnik, C.; Gehtler, I.; Kronenberg, J.; Hildesheimer, M. Development of speech perception and production in children with cochlear implants. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. Suppl. 2002, 189, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlyon, R.P.; Shackleton, T.M. Comparing the fundamental frequencies of resolved and unresolved harmonics: Evidence for two pitch mechanisms? J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1994, 95, 3541–3554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oxenham, A.J. Pitch perception and auditory stream segregation: Implications for hearing loss and cochlear implants. Trends Amplif. 2008, 12, 316–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Kewley-Port, D. Formant discrimination in noise for isolated vowels. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2004, 116, 3119–3129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swanepoel, R.; Oosthuizen, D.J.J.; Hanekom, J.J. The relative importance of spectral cues for vowel recognition in severe noise. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2012, 132, 2652–2662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, S.; Kraus, N. Sensory-cognitive interaction in the neural encoding of speech in noise: A review. J. Am. Acad. Audiol. 2010, 21, 575–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erickson, L.C.; Newman, R.S. Influences of background noise on infants and children. Curr. Dir. Psychol. Sci. 2017, 26, 451–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, L.L.; Connors, S.; Kille, E.; Levin, S.; Ball, K.; Katz, D. Children’s understanding of monosyllabic nouns in quiet and in noise. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1979, 66, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaltz, Y.; Bugannim, Y.; Zechoval, D.; Kishon-Rabin, L.; Perez, R. Listening in noise remains a significant challenge for cochlear implant users: Evidence from early deafened and those with progressive hearing loss compared to peers with normal hearing. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doyle, A.B. Listening to distraction: A developmental study of selective attention. J. Exp. Child Psychol. 1973, 15, 100–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coch, D.; Sanders, L.D.; Neville, H.J. An event-related potential study of selective auditory attention in children and adults. J. Cogn. Neurosci. 2005, 17, 605–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonino, A.Y.; Leibold, L.J.; Buss, E. Release from perceptual masking for children and adults: Benefit of a carrier phrase. Ear Hear. 2013, 34, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leibold, L.J.; Buss, E. Children’s Identification of Consonants in a Speech-Shaped Noise or a Two-Talker Masker. J. Speech Lang. Hear. Res. 2013, 56, 1144–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, J.K.; Linthicum, F.H. The human auditory system: A timeline of development. Int. J. Audiol. 2007, 46, 460–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, D.R.; Cowan, J.A.; Riley, A.; Edmondson-Jones, A.M.; Ferguson, M.A. Development of auditory processing in 6- to 11-yr-old children. Ear Hear. 2011, 32, 269–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buss, E.; Flaherty, M.M.; Leibold, L.J. Development of frequency discrimination at 250 Hz is similar for tone and /ba/ stimuli. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2017, 142, EL150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flaherty, M.M.; Buss, E.; Leibold, L.J. Developmental effects in children’s ability to benefit from F0 differences between target and masker speech. Ear Hear. 2019, 40, 927–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisenberg, L.S.; Shannon, R.V.; Martinez, A.S.; Wygonski, J.; Boothroyd, A. Speech recognition with reduced spectral cues as a function of age. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2000, 107, 2704–2710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mlot, S.; Buss, E.; Hall, J.W. Spectral integration and bandwidth effects on speech recognition in school-aged children and adults. Ear Hear. 2010, 31, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishi, K.; Lewis, D.E.; Hoover, B.M.; Choi, S.; Stelmachowicz, P.G. Children’s recognition of American English consonants in noise. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2010, 127, 3177–3188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, J.W.; Grose, J.H. Development of temporal resolution in children as measured by the temporal modulation transfer function. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1994, 96, 150–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaltz, Y.; Ari-Even Roth, D.; Karni, A.; Kishon-Rabin, L. Long-term training-induced gains of an auditory skill in school-age children as compared with adults. Trends Hear. 2018, 22, 2331216518790902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halliday, L.F.; Taylor, J.L.; Edmondson-Jones, A.M.; Moore, D.R. Frequency discrimination learning in children. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2008, 123, 4393–4402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagels, L.; Gaudrain, E.; Vickers, D.; Matos Lopes, M.; Hendriks, P.; Başkent, D. Development of vocal emotion recognition in school-age children: The EmoHI test for hearing-impaired populations. PeerJ 2020, 8, e8773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ANSI/ASA S3.6-2018—Specification for Audiometers. Available online: https://webstore.ansi.org/standards/asa/ansiasas32018 (accessed on 19 August 2023).
- Bugannim, Y.; Roth, D.A.-E.; Zechoval, D.; Kishon-Rabin, L. Training of speech perception in noise in pre-lingual hearing-impaired adults with cochlear implants compared with normal hearing adults. Otol. Neurotol. 2019, 40, e316–e325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaltz, Y.; Kishon-Rabin, L. Difficulties experienced by older listeners in utilizing voice cues for speaker discrimination. Front. Psychol. 2022, 13, 797422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moulines, E.; Charpentier, F. Pitch-synchronous waveform processing techniques for text-to-speech synthesis using diphones. Speech Commun. 1990, 9, 453–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitch, W.T.; Giedd, J. Morphology and development of the human vocal tract: A study using magnetic resonance imaging. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1999, 106, 1511–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lammert, A.C.; Narayanan, S.S. On short-time estimation of vocal tract length from formant frequencies. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0132193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kollmeier, B.; Warzybok, A.; Hochmuth, S.; Zokoll, M.A.; Uslar, V.; Brand, T.; Wagener, K.C. The multilingual matrix test: Principles, applications, and comparison across languages: A review. Int. J. Audiol. 2015, 54 (Suppl. S2), 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, L.L. Performance of children aged 9 to 17 years on a test of speech intelligibility in noise using sentence material with controlled word predictability. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1979, 66, 651–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, J.W.; Grose, J.H.; Buss, E.; Dev, M.B. Spondee recognition in a two-talker masker and a speech-shaped noise masker in adults and children. Ear Hear. 2002, 23, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niesen, M.; Bourguignon, M.; Bertels, J.; Vander Ghinst, M.; Wens, V.; Goldman, S.; De Tiège, X. Cortical tracking of lexical speech units in a multi-talker background is immature in school-aged children. Neuroimage 2023, 265, 119770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levitt, H. Transformed up-down methods in psychoacoustics. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1971, 49 (Suppl. S2), 467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobon, K.A.; Taleb, N.M.; Buss, E.; Grose, J.H.; Calandruccio, L. Psychometric function slope for speech-in-noise and speech-in-speech: Effects of development and aging. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2019, 145, EL284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Latif, K.H.A.; Meister, H. Speech Recognition and Listening Effort in Cochlear Implant Recipients and Normal-Hearing Listeners. Front. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 725412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubno, J.R.; Dirks, D.D. Evaluation of hearing-impaired listeners using a Nonsense-Syllable Test. I. Test reliability. J. Speech Hear. Res. 1982, 25, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stelmachowicz, P.G.; Lewis, D.E.; Kelly, W.J.; Jesteadt, W. Speech perception in low-pass filtered noise for normal and hearing-impaired listeners. J. Speech Hear. Res. 1990, 33, 290–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gockel, H.; Moore, B.C.J.; Plack, C.J.; Carlyon, R.P. Effect of noise on the detectability and fundamental frequency discrimination of complex tones. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2006, 120, 957–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitrijevic, A.; Pratt, H.; Starr, A. Auditory cortical activity in normal hearing subjects to consonant vowels presented in quiet and in noise. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2013, 124, 1204–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.-H.; Lee, J.; Lee, H.-J. Noise-induced change of cortical temporal processing in cochlear implant users. Clin. Exp. Otorhinolaryngol. 2020, 13, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Best, V.; Gallun, F.J.; Carlile, S.; Shinn-Cunningham, B.G. Binaural interference and auditory grouping. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2007, 121, 1070–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heinrich, A.; Schneider, B.A.; Craik, F.I.M. Investigating the influence of continuous babble on auditory short-term memory performance. Q. J. Exp. Psychol. 2008, 61, 735–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, J.A.; Zatorre, R.J. Attention to simultaneous unrelated auditory and visual events: Behavioral and neural correlates. Cereb. Cortex 2005, 15, 1609–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Başkent, D.; Gaudrain, E. Musician advantage for speech-on-speech perception. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2016, 139, EL51–EL56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vestergaard, M.D.; Fyson, N.R.C.; Patterson, R.D. The interaction of vocal characteristics and audibility in the recognition of concurrent syllables. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2009, 125, 1114–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Quiet | Noise | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adults | Children | Adults | Children | |
| F0 1 | 0.88 | 1.66 | 0.99 | 1.78 |
| (0.12) | (0.38) | (0.12) | (0.45) | |
| F0 2 | 0.72 | 1.86 | 0.93 | 1.28 |
| (0.08) | (0.38) | (0.11) | (0.32) | |
| Formant 1 | 0.62 | 0.85 | 1.32 | 1.39 |
| (0.07) | (0.14) | (0.13) | (0.35) | |
| Formant 2 | 0.60 | 0.76 | 1.20 | 1.25 |
| (0.07) | (0.12) | (0.13) | (0.31) | |
| Combined 1 | 0.42 | 0.59 | 0.57 | 0.76 |
| (0.03) | (0.07) | (0.07) | (0.19) | |
| Combined 2 | 0.43 | 0.46 | 0.58 | 0.80 |
| (0.06) | (0.06) | (0.06) | (0.20) | |
| F0 | Formants | Combined | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Adults and children | Noise = quiet | Noise > quiet *** | Noise > quiet *** |
| Quiet and noise | Children > adults * | Children = adults | Children = adults |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kishon-Rabin, L.; Zaltz, Y. The Effect of Noise on the Utilization of Fundamental Frequency and Formants for Voice Discrimination in Children and Adults. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 10752. https://doi.org/10.3390/app131910752
Kishon-Rabin L, Zaltz Y. The Effect of Noise on the Utilization of Fundamental Frequency and Formants for Voice Discrimination in Children and Adults. Applied Sciences. 2023; 13(19):10752. https://doi.org/10.3390/app131910752
Chicago/Turabian StyleKishon-Rabin, Liat, and Yael Zaltz. 2023. "The Effect of Noise on the Utilization of Fundamental Frequency and Formants for Voice Discrimination in Children and Adults" Applied Sciences 13, no. 19: 10752. https://doi.org/10.3390/app131910752
APA StyleKishon-Rabin, L., & Zaltz, Y. (2023). The Effect of Noise on the Utilization of Fundamental Frequency and Formants for Voice Discrimination in Children and Adults. Applied Sciences, 13(19), 10752. https://doi.org/10.3390/app131910752






