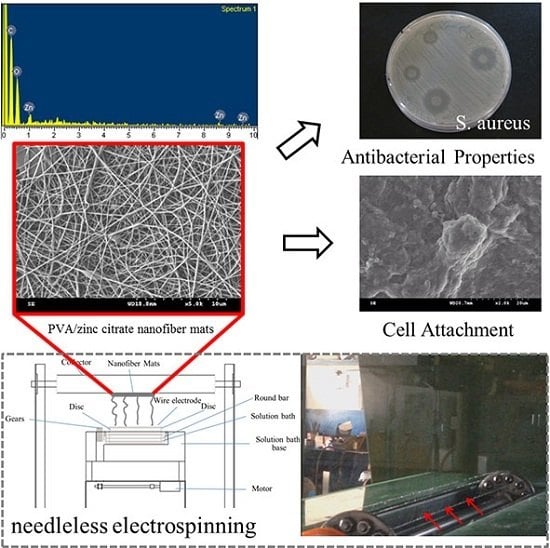
Biomedical Applications of Antibacterial Nanofiber Mats Made of Electrospinning with Wire Electrodes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Solution Preparation
2.2.2. Electrospinning


2.3. Tests
2.3.1. Viscosity
2.3.2. Conductivity
2.3.3. Scanning Electron Microscopey (SEM)
2.3.4. Diameter Analyses
2.3.5. Antibacterial Test
Disc Diffusion Assay
Broth Dilution Assay
2.3.6. Cell Attachment
2.3.7. MTT Assay
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Properties of PVA/Zinc Citrate Mixtures
| Physical Properties | Zinc Citrate Content (wt%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 wt % | 0.5 wt % | 1 wt % | 3 wt % | 5 wt % | |
| Viscosity (mPa s) | 489.9 | 708 | 920.4 | 942.4 | 992.3 |
| conductivity (μS/m) | 0.57 × 103 | 0.62 × 103 | 0.70 × 103 | 0.98 × 103 | 1.28 × 103 |
| Average diameter (nm) | 95 ± 22 | 79 ± 26 | 72 ± 18 | 75 ± 24 | 84 ± 22 |


3.2. Effects of Amount of Zinc Citrate on Morphology and Fiber Diameter of PVA/Zinc Citrate Nanofiber Mats

3.3. Element Analyses of PVA/Zinc Citrate Nanofiber Mats

| Element | Zinc Citrate Content (wt%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.5 wt % | 1 wt % | 3 wt % | 5 wt % | |
| C K | 56.23% | 55.52% | 53.85% | 52.74% |
| O K | 43.02% | 42.93% | 42.97% | 42.57% |
| Zn L | 0.74% | 1.56% | 3.18% | 4.69% |
| Totals | 100 | |||
3.4. Effects of Amount of Zinc Citrate on Antibacterial Efficacy of PVA/Zinc Citrate Nanofiber Mats

| Sample | Concentration of Zinc Citrate (wt %) | Electrospinning Voltage | Size of Inhibition Zone (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| a (control) | 0 | 80 kV | 0 |
| b | 0.5 | 80 kV | 5.0 ± 1.1 |
| c | 1 | 80 kV | 7.0 ± 0.8 |
| d | 3 | 80 kV | 11.8 ± 0.5 |
| e | 5 | 80 kV | 13.5 ± 1.0 |
3.5. Effects of Electrospinning Voltages on Morphology and Diameter of PVA/Zinc Citrate Nanofiber Mats

| Amount of Zinc Citrate (wt %) | Electrospinning Voltage (kV) | Diameter of PVA/Zinc Citrate Nanofiber Mats (nm) | Diameter of Inhibition Zone (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3 | 60 | 167 ± 39 | 8.0 ± 1.0 |
| 3 | 70 | 107 ± 22 | 9.3 ± 0.6 |
| 3 | 80 | 75 ± 24 | 11.8 ± 0.5 |
3.6. Cell Attachment and MTT Assay of PVA/Zinc Citrate Nanofiber Mats


4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Anton, F. Process and Apparatus for Preparing Artificial Threads. U.S. Patent 1,975,504, 2 October 1934. [Google Scholar]
- Bhardwaj, N.; Kundu, S.C. Electrospinning: A fascinating fiber fabrication technique. Biotechnol. Adv. 2010, 28, 325–347. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Koski, A.; Yim, K.; Shivkumar, S. Effect of molecular weight on fibrous pva produced by electrospinning. Mater. Lett. 2004, 58, 493–497. [Google Scholar]
- Supaphol, P.; Mit-Uppatham, C.; Nithitanakul, M. Ultrafine electrospun polyamide-6 fibers: Effect of emitting electrode polarity on morphology and average fiber diameter. J. Polym. Sci. Part B: Polym. Phys. 2005, 43, 3699–3712. [Google Scholar]
- Ki, C.S.; Baek, D.H.; Gang, K.D.; Lee, K.H.; Um, I.C.; Park, Y.H. Characterization of gelatin nanofiber prepared from gelatin-formic acid solution. Polymer 2005, 46, 5094–5102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, S.; Greiner, A.; Wendorff, J.H. Functional materials by electrospinning of polymers. Progress Polym. Sci. 2013, 38, 963–991. [Google Scholar]
- Pelipenko, J.; Kristl, J.; Janković, B.; Baumgartner, S.; Kocbek, P. The impact of relative humidity during electrospinning on the morphology and mechanical properties of nanofibers. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 456, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Holzmeister, A.; Rudisile, M.; Greiner, A.; Wendorff, J.H. Structurally and chemically heterogeneous nanofibrous nonwovens via electrospinning. Eur. Polym. J. 2007, 43, 4859–4867. [Google Scholar]
- Varesano, A.; Carletto, R.A.; Mazzuchetti, G. Experimental investigations on the multi-jet electrospinning process. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2009, 209, 5178–5185. [Google Scholar]
- Khamforoush, M.; Asgari, T. A modified electro-centrifugal spinning method to enhance the production rate of highly aligned nanofiber. Nano 2015, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahalingam, S.; Edirisinghe, M. Forming of polymer nanofibers by a pressurised gyration process. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2013, 34, 1134–1139. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.; Mahalingam, S.; Rohn, J.L.; Ren, G.; Edirisinghe, M. Physio-chemical and antibacterial characteristics of pressure spun nylon nanofibres embedded with functional silver nanoparticles. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2015, 56, 195–204. [Google Scholar]
- Yarin, A.; Zussman, E. Upward needleless electrospinning of multiple nanofibers. Polymer 2004, 45, 2977–2980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jirsak, O.; Sanetrnik, F.; Lukas, D.; Kotek, V.; Martinova, L.; Chaloupek, J. Method of nanofibres production from a polymer solution using electrostatic spinning and a device for carrying out the method. U.S. Patent 10/570,806, 8 September 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; He, J.-H.; Yu, J.-Y. Bubble-electrospinning: A novel method for making nanofibers. J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 2008, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Niu, H.; Lin, T.; Wang, X. Needleless electrospinning of nanofibers with a conical wire coil. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2009, 49, 1582–1586. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, G.; Zhang, S.; Qin, X. High throughput of quality nanofibers via one stepped pyramid-shaped spinneret. Mater. Lett. 2013, 106, 56–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cengiz-Çallıoğlu, F.; Jirsak, O.; Dayk, M. Investigation into the relationships between independent and dependent parameters in roller electrospinning of polyurethane. Textile Res. J. 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, H.; Lin, T.; Wang, X. Needleless electrospinning. I. A comparison of cylinder and disk nozzles. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2009, 114, 3524–3530. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, T.; Wang, X.; Wang, X.; Niu, H. Electrostatic spinning assembly. U.S. Patnet 13/124,742, 10 June 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Niu, H.; Lin, T. Fiber generators in needleless electrospinning. J. Nanomater. 2012, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Niu, H.; Wang, X.; Lin, T. Needleless electrospinning of uniform nanofibers using spiral coil spinnerets. J. Nanomater. 2012, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forward, K.M.; Rutledge, G.C. Free surface electrospinning from a wire electrode. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 183, 492–503. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Hu, X.; Qiu, X.; Huang, X.; Wu, D.; Sun, D. An improved tip-less electrospinning with strip-distributed solution delivery for massive production of uniform polymer nanofibers. Mater. Lett. 2013, 99, 21–23. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; He, J.-H. Bubble electrospinning for mass production of nanofibers. Int. J. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 2007, 8, 393–396. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, F.-L.; Gong, R.-H.; Porat, I. Three-jet electrospinning using a flat spinneret. J. Mater. Sci. 2009, 44, 5501–5508. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, D.; Huang, X.; Lai, X.; Sun, D.; Lin, L. High throughput tip-less electrospinning via a circular cylindrical electrode. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2010, 10, 4221–4226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.; Niu, H.; Wu, C.; Ke, Q.; Mo, X.; Lin, T. Disc-electrospun cellulose acetate butyrate nanofibers show enhanced cellular growth performances. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2013, 101, 115–122. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, R.; Li, X.; Sun, B.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, D.; Tang, Z.; Chen, X.; Wang, C. Electrospun chitosan/sericin composite nanofibers with antibacterial property as potential wound dressings. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2014, 68, 92–97. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tan, L.; Hu, J.; Zhao, H. Design of bilayered nanofibrous mats for wound dressing using an electrospinning technique. Mater. Lett. 2015, 156, 46–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.; Xue, J.; Geng, H.; Gu, H.; Chen, D.; Shi, R.; Zhang, L. Fibrous guided tissue regeneration membrane loaded with anti-inflammatory agent prepared by coaxial electrospinning for the purpose of controlled release. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 335, 121–129. [Google Scholar]
- Perez, R.A.; Kim, H.-W. Core-shell designed scaffolds for drug delivery and tissue engineering. Acta Biomater. 2015, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, R.; Ma, H.; Hsiao, B.S.; Chu, B. High-flux microfiltration filters based on electrospun polyvinylalcohol nanofibrous membranes. Polymer 2013, 54, 548–556. [Google Scholar]
- Cooper, A.; Oldinski, R.; Ma, H.; Bryers, J.D.; Zhang, M. Chitosan-based nanofibrous membranes for antibacterial filter applications. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 92, 254–259. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Liu, Y.; Ma, Y.; Liu, J.; Liu, X. Improved performance of PVdF-HFP/PI nanofiber membrane for lithium ion battery separator prepared by a bicomponent cross-electrospinning method. Mater. Lett. 2014, 133, 67–70. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Si, Y.; Wang, J.; Ding, B.; Yu, J.; Al-Deyab, S.S. A facile and highly sensitive colorimetric sensor for the detection of formaldehyde based on electro-spinning/netting nano-fiber/nets. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2012, 163, 186–193. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.; Yang, H.; Liu, X.; Mao, J.; Gu, S.; Xu, W. Electrospinning of carboxyethylchitosan/poly(vinyl alcohol)/silk fibroin nanoparticles for wound dressings. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2013, 53, 88–92. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rai, M.; Yadav, A.; Gade, A. Silver nanoparticles as a new generation of antimicrobials. Biotechnol. Adv. 2009, 27, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shalumon, K.; Anulekha, K.; Nair, S.V.; Nair, S.; Chennazhi, K.; Jayakumar, R. Sodium alginate/poly(vinyl alcohol)/nano ZnO composite nanofibers for antibacterial wound dressings. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2011, 49, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Huang, Z.-M.; Zhang, Y.-Z.; Kotaki, M.; Ramakrishna, S. A review on polymer nanofibers by electrospinning and their applications in nanocomposites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2003, 63, 2223–2253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, W.; Zhu, M.; Yang, W.; Yu, H. Experimental study on relationship between jet instability and formation of beaded fibers during electrospinning. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2005, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, O. Influence of particle size on the antibacterial activity of zinc oxide. Int. J. Inorg. Mater. 2001, 3, 643–646. [Google Scholar]
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pan, Y.-J.; Lin, J.-H.; Chiang, K.-C. Biomedical Applications of Antibacterial Nanofiber Mats Made of Electrospinning with Wire Electrodes. Appl. Sci. 2016, 6, 46. https://doi.org/10.3390/app6020046
Pan Y-J, Lin J-H, Chiang K-C. Biomedical Applications of Antibacterial Nanofiber Mats Made of Electrospinning with Wire Electrodes. Applied Sciences. 2016; 6(2):46. https://doi.org/10.3390/app6020046
Chicago/Turabian StylePan, Yi-Jun, Jia-Horng Lin, and Kun-Chien Chiang. 2016. "Biomedical Applications of Antibacterial Nanofiber Mats Made of Electrospinning with Wire Electrodes" Applied Sciences 6, no. 2: 46. https://doi.org/10.3390/app6020046
APA StylePan, Y.-J., Lin, J.-H., & Chiang, K.-C. (2016). Biomedical Applications of Antibacterial Nanofiber Mats Made of Electrospinning with Wire Electrodes. Applied Sciences, 6(2), 46. https://doi.org/10.3390/app6020046