Remarkable Anti-Fouling Performance of TiO2-Modified TFC Membranes with Mussel-Inspired Polydopamine Binding
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Theory
Hydraulic Resistance of Polydopamine and TiO2-Modified Membranes
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Surface Modification of a Thin Film Composite (TFC) Membrane
3.2.1. Polydopamine Modification
3.2.2. Binding TiO2 Nanoparticles on TFC Membranes by Using Polydopamine
3.2.3. Binding TiO2 Nanoparticles on TFC Membranes by Self-Assembly
3.3. Characterisation of the Membrane Surfaces
3.3.1. Scanning Electron Microscopy
3.3.2. Contact Angle Measurement
3.3.3. UV-Visible Spectroscopy
3.3.4. Static BSA Surface Adhesion Measurement
3.4. Performance under Dark Conditions
3.4.1. Filtration Experiments under Dark Conditions
3.4.2. Anti-Fouling Performance under Dark Conditions
3.5. Performance under Light Conditions
3.5.1. Effect of Photocatalysis on Filtration Performance
3.5.2. Effect of Photocatalysis on Fouling Performance
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Characterisation of Membranes
4.1.1. Morphology of Unmodified and Modified Membranes
4.1.2. Hydrophilicity of Surfaces
4.1.3. Static BSA Adhesion Resistance
4.2. Performance under Dark Conditions
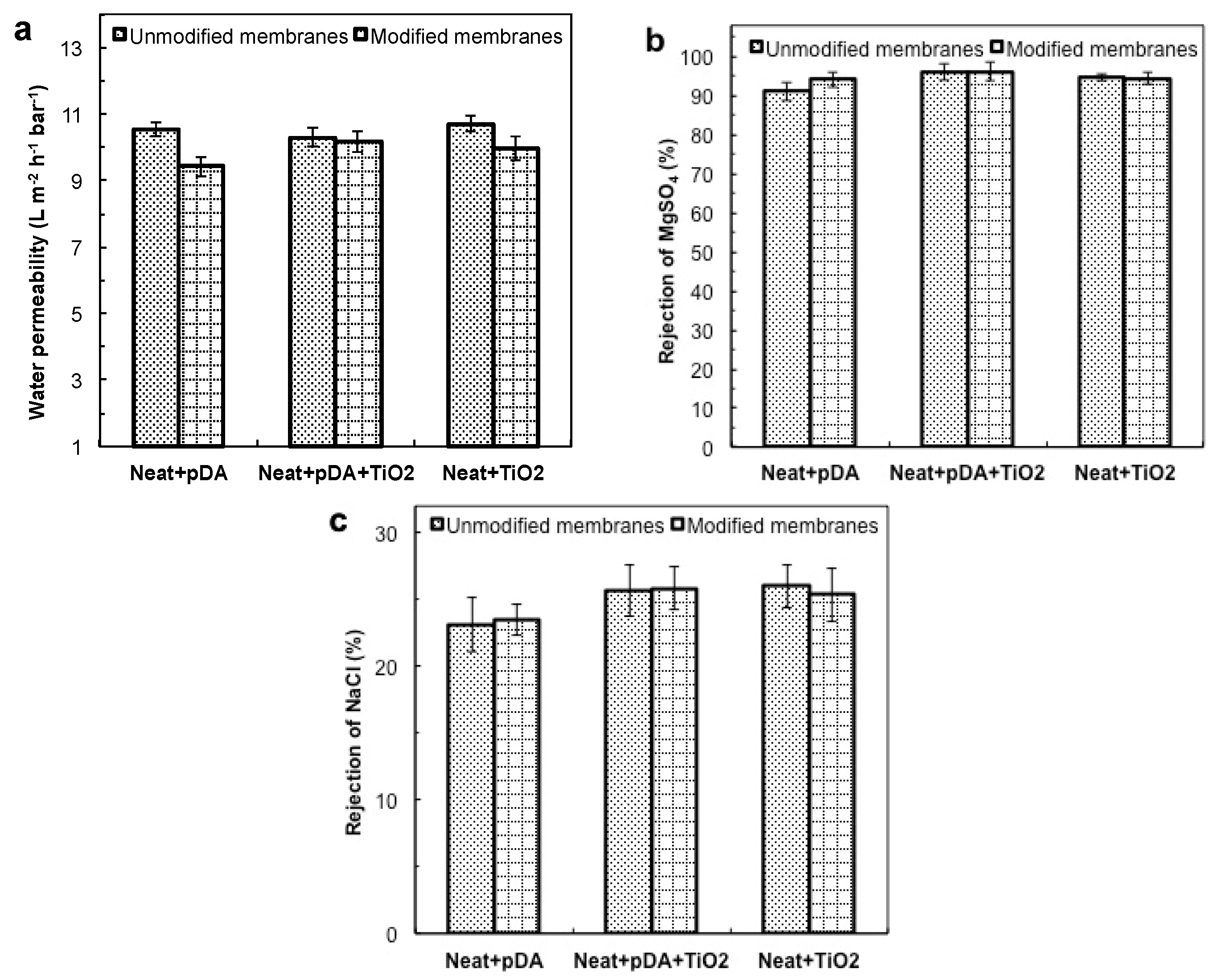
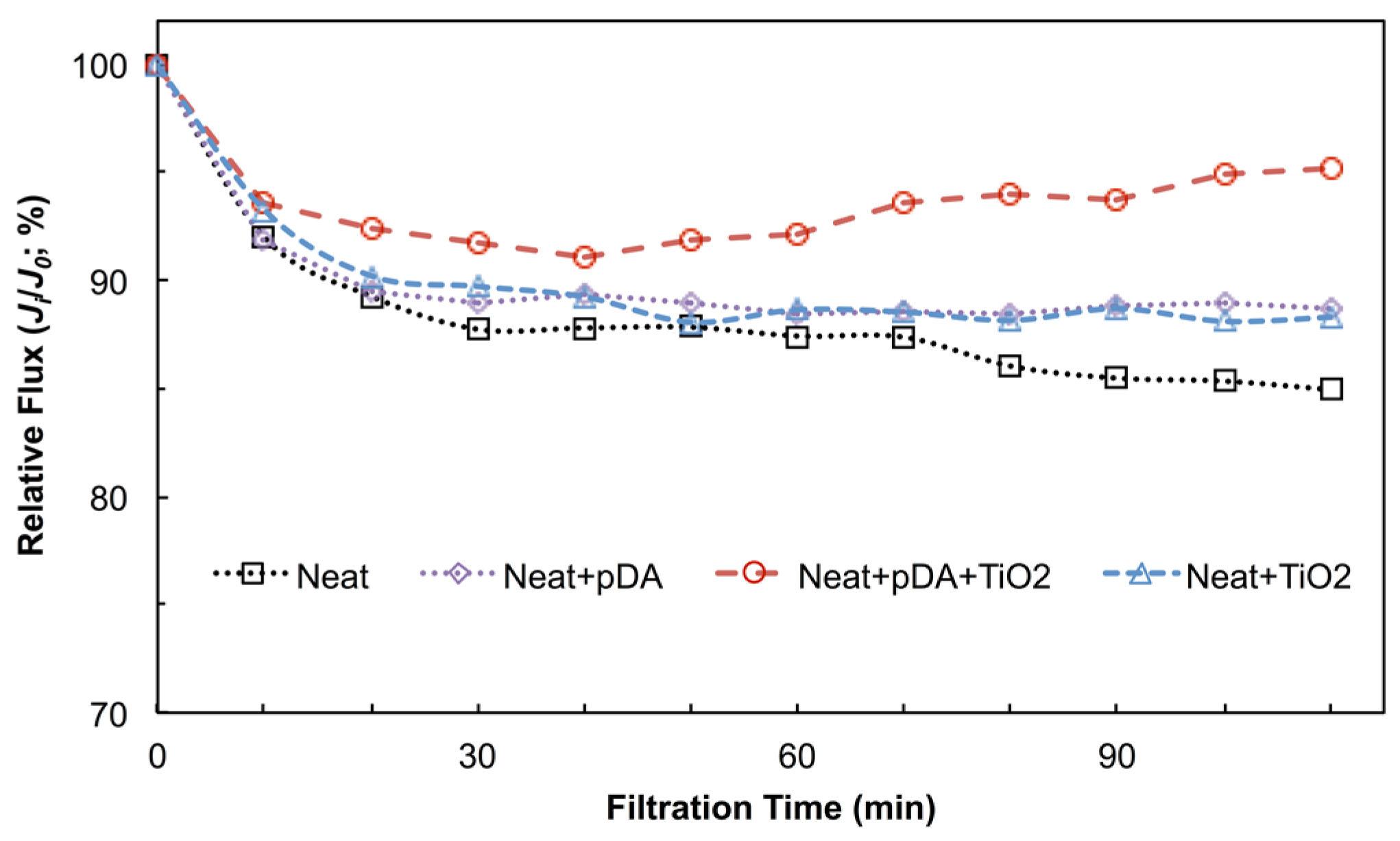
4.2.1. Filtration Performance under Dark Conditions
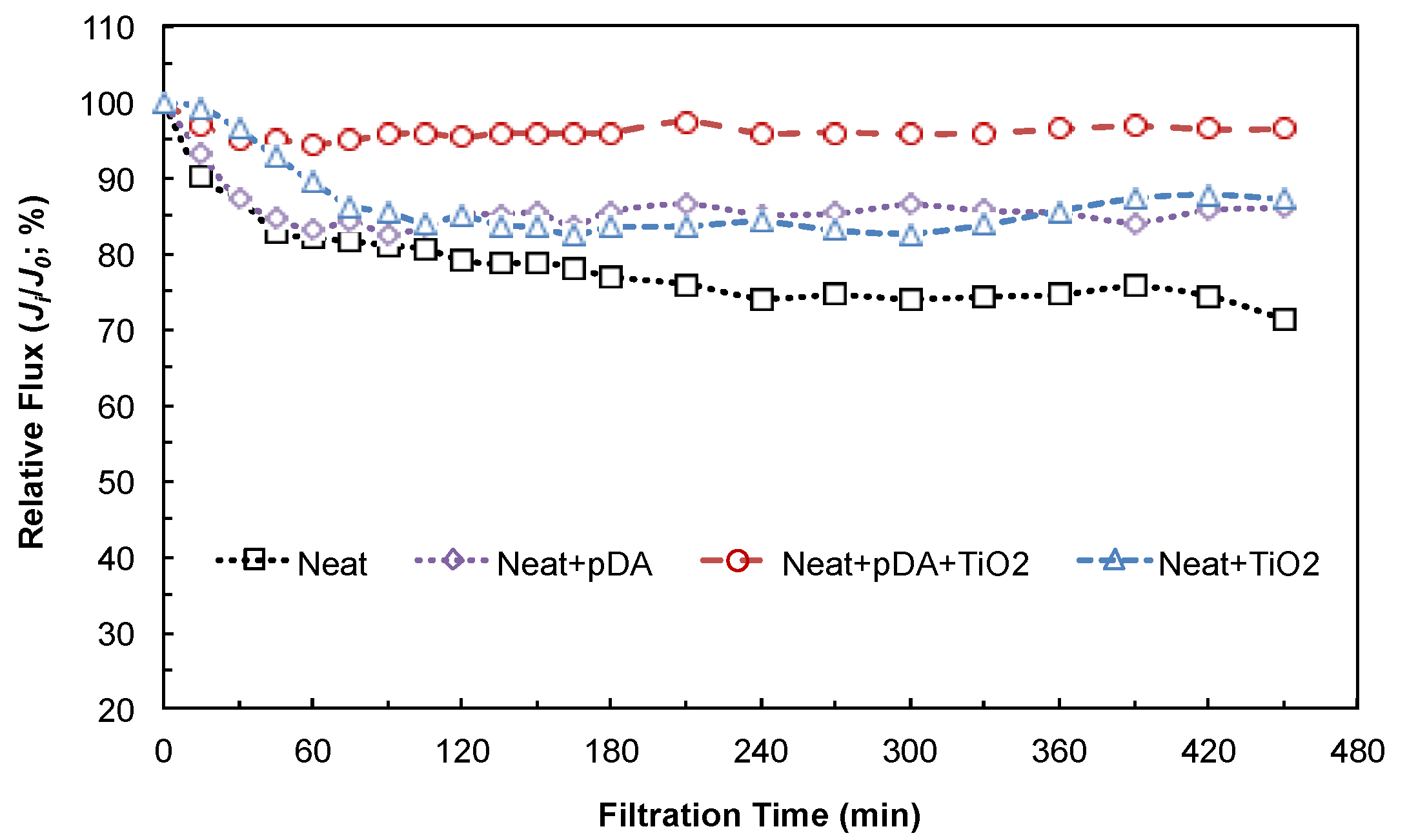
4.2.2. Anti-Fouling Performance under Dark Conditions
4.3. Performance under Light Conditions
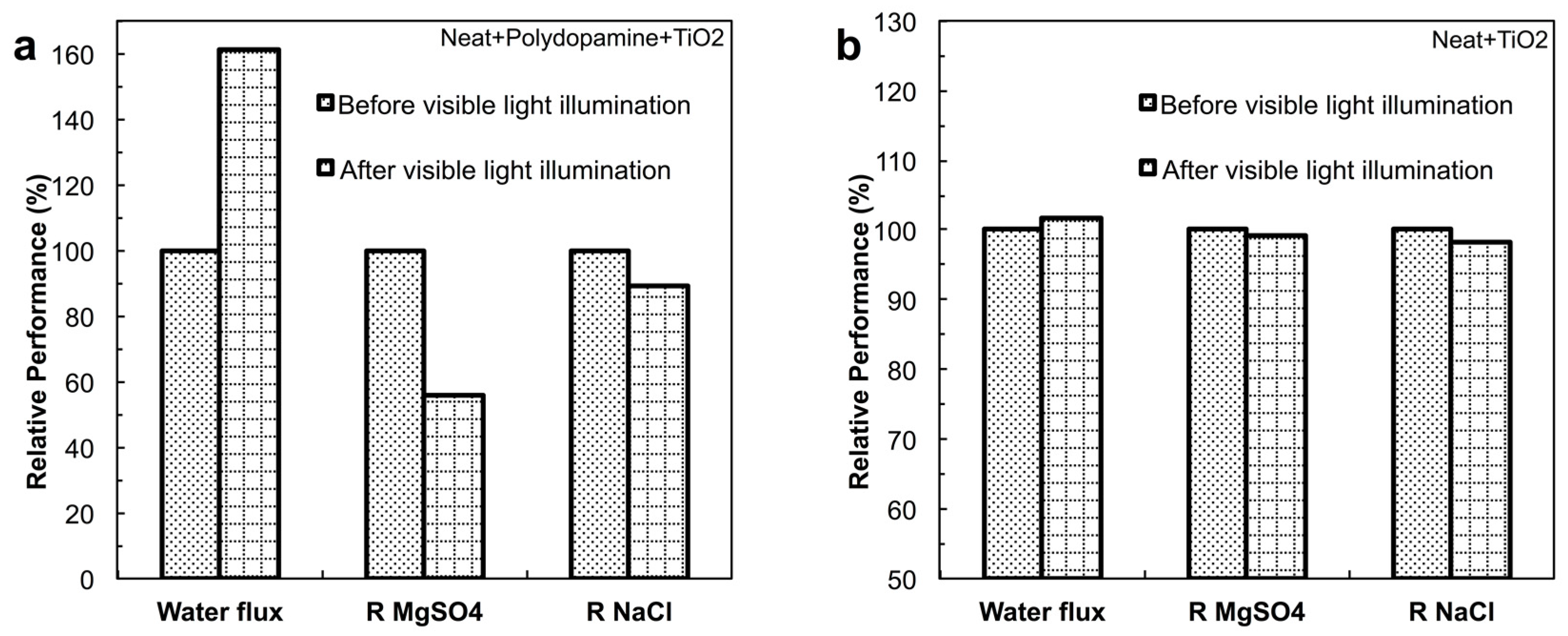
4.3.1. Effect of Photocatalysis on Filtration Performance
4.3.2. Effect of Photocatalysis on Fouling Performance
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Koch, K.; Barthlott, W. Superhydrophobic and superhydrophilic plant surfaces: An inspiration for biomimetic materials. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2009, 367, 1487–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.; Dellatore, S.M.; Miller, W.M.; Messersmith, P.B. Mussel-inspired surface chemistry for multifunctional coatings. Science 2007, 318, 426–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, W.-H.; Lu, C.-H.; Guo, X.-C.; Chen, F.-R.; Yang, H.-H.; Wang, X.-R. Mussel-inspired molecularly imprinted polymer coating superparamagnetic nanoparticles for protein recognition. J. Mater. Chem. 2010, 20, 880–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, L.; Guo, R.; Lan, J.; Jiang, S.; Lin, S. Microwave-assisted Deposition of Silver Nanoparticles on Bamboo Pulp Fabric through Dopamine Functionalization. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 386, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, W.; Hu, Y.; Cai, K.; Liu, P.; Ding, H. Fabrication of antibacterial surface via UV-inducing dopamine polymerization combined with co-deposition Ag nanoparticles. Mater. Lett. 2016, 183, 85–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, M.-Y.; Zhou, Q.-L.; Wang, X.-Y.; Zhang, J.-X.; Xue, L.; Wang, R.; Zhang, J.-X.; Zhang, Y.-W. Immobilization of Lipase Onto Dopamine Functionalized Magnetic Nanoparticles. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. Lett. 2016, 8, 251–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Ding, Y.; Zhang, W.; Ji, L.; Zhang, X.; Yang, F. A highly sensitive sensor for simultaneous determination of ascorbic acid, dopamine and uric acid based on ultra-small Ni nanoparticles. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2016, 775, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Jiang, L. Bio-inspired self-cleaning surfaces. Annu. Rev. Mater. Res. 2012, 42, 231–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasemset, S.; Lee, A.; Miller, D.J.; Freeman, B.D.; Sharma, M.M. Effect of polydopamine deposition conditions on fouling resistance, physical properties, and permeation properties of reverse osmosis membranes in oil/water separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 425–426, 208–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCloskey, B.D.; Park, H.B.; Ju, H.; Rowe, B.W.; Miller, D.J.; Chun, B.J.; Kin, K.; Freeman, B.D. Influence of polydopamine deposition conditions on pure water flux and foulant adhesion resistance of reverse osmosis, ultrafiltration, and microfiltration membranes. Polymer 2010, 51, 3472–3485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azari, S.; Zou, L. Using zwitterionic amino acid L-DOPA to modify the surface of thin film composite polyamide reverse osmosis membranes to increase their fouling resistance. J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 401, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, D.J.; Araújo, P.A.; Correia, P.; Ramsey, M.M.; Kruithof, J.C.; van Loosdrecht, M.; Freeman, B.D.; Paul, D.R.; Whiteley, M.; Vrouwenvelder, J.S. Short-term adhesion and long-term biofouling testing of polydopamine and poly (ethylene glycol) surface modifications of membranes and feed spacers for biofouling control. Water Res. 2012, 46, 3737–3753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCloskey, B.D.; Park, H.B.; Ju, H.; Rowe, B.W.; Miller, D.J.; Freeman, B.D. A bioinspired fouling-resistant surface modification for water purification membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 413–414, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, F.; Jia, H.; Qiao, S.; Jiang, Z.; Wang, J.; Wang, B.; Zhong, Y. Bioinspired fabrication of high performance composite membranes with ultrathin defect-free skin layer. J. Membr. Sci. 2009, 341, 279–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.; Li, S.; Zhao, W.; Wei, Q.; Nie, S.; Sun, S.; Zhao, C. The hydrodynamic permeability and surface property of polyethersulfone ultrafiltration membranes with mussel-inspired polydopamine coatings. J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 417–418, 228–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, K.; Grimm, M.; Meyers, J.; Dietrich, C.; Gläser, R.; Schulze, A. Photoactive microfiltration membranes via directed synthesis of TiO2 nanoparticles on the polymer surface for removal of drugs from water. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 478, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngo, T.H.A.; Nguyen, D.T.; Do, K.D.; Nguyen, T.T.M.; Mori, S.; Tran, D.T. Surface modification of polyamide thin film composite membrane by coating of titanium dioxide nanoparticles. J. Sci. Adv. Mater. Devices 2016, 1, 468–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarado, C.; Farris, K.; Kilduff, J. Membrane Fouling, Modelling and Recent Developments for Mitigation. Emerg. Membr. Technol. Sustain. Water Treat. 2016, 433–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.; Zhang, T.; Gutierrez, L.; Ma, J.; Croue, J.-P. Influence of surface properties of filtration-layer metal oxide on ceramic membrane fouling during ultrafiltration of oil/water emulsion. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 4668–4674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Ding, L.; Luo, J.; Jaffrin, M.Y.; Tang, B. Membrane fouling in photocatalytic membrane reactors (PMRs) for water and wastewater treatment: A critical review. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 302, 446–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.H.; Kwak, S.-Y.; Sohn, B.-H.; Park, T.H. Design of TiO2 nanoparticle self-assembled aromatic polyamide thin-film-composite (TFC) membrane as an approach to solve biofouling problem. J. Membr. Sci. 2003, 211, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madaeni, S.; Ghaemi, N. Characterization of self-cleaning RO membranes coated with TiO2 particles under UV irradiation. J. Membr. Sci. 2007, 303, 221–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, S.-Y.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, S.S. Hybrid organic/inorganic reverse osmosis (RO) membrane for bactericidal anti-fouling. 1. Preparation and characterization of TiO2 nanoparticle self-assembled aromatic polyamide thin-film-composite (TFC) membrane. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2001, 35, 2388–2394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.S.; Im, S.J.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, J.P.; Min, B.R. Polyamide thin-film nanofiltration membranes containing TiO2 nanoparticles. Desalination 2008, 219, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansourpanah, Y.; Madaeni, S.; Rahimpour, A.; Farhadian, A.; Taheri, A. Formation of appropriate sites on nanofiltration membrane surface for binding TiO2 photo-catalyst: Performance, characterization and fouling-resistant capability. J. Membr. Sci. 2009, 330, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, J.; Son, S.H.; Jegal, J.; Kim, J.; Lee, Y.H. Preparation and characterization of polyamide nanofiltration composite membranes with TiO2 layers chemically connected to the membrane surface. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2007, 105, 1267–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajh, T.; Dimitrijevic, N.M.; Rozhkova, E.A. Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles in Advanced Imaging and Nanotherapeutics. In Biomedical Nanotechnology; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2011; pp. 63–75. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, R.-X.; Braeken, L.; Luis, P.; Wang, X.-L.; Van der Bruggen, B. Novel binding procedure of TiO2 nanoparticles to thin film composite membranes via self-polymerized polydopamine. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 437, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitrijevic, N.M.; Rozhkova, E.; Rajh, T. Dynamics of localized charges in dopamine-modified TiO2 and their effect on the formation of reactive oxygen species. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 2893–2899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Shao, B.; Yang, F. Polydopamine coating–surface modification of polyester filter and fouling reduction. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2013, 118, 226–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, T.; Tan, G.-X.; Ning, C.-Y.; Rong, X.-C.; Yu, Z.; Lei, Z. Bioinspired polydopamine functionalization of titanium surface for silver nanoparticles immobilization with antibacterial property. J. Inorg. Mater. 2014, 29, 1320–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; ho Shin, C.; Park, S.; Cui, L.; Kim, D.; Park, J.-S.; Ryu, M. Enhanced antibacterial activity of silver-coated kapok fibers through dopamine functionalization. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2015, 226, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Jiang, L. Design and creation of superwetting/antiwetting surfaces. Adv. Mater. 2006, 18, 3063–3078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, S.H.; Ingole, P.G.; Kim, K.H.; Choi, W.K.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, H.K. Properties and performances of polymer composite membranes correlated with monomer and polydopamine for flue gas dehydration by water vapor permeation. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 258, 348–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhushan, B. Bioinspired structured surfaces. Langmuir 2012, 28, 1698–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cassie, A.; Baxter, S. Wettability of porous surfaces. Trans. Faraday Soc. 1944, 40, 546–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, L.; Wang, Z.X.; Zhang, Y.L.; Jiang, Z.X.; Liu, Y.Y. A facile strategy to enhance PVDF ultrafiltration membrane performance via self-polymerized polydopamine followed by hydrolysis of ammonium fluotitanate. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 461, 10–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, G.; Zhang, S.; Li, X.; Widjojo, N.; Chung, T.-S. Thin film composite forward osmosis membranes based on polydopamine modified polysulfone substrates with enhancements in both water flux and salt rejection. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2012, 80, 219–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, A.; Thompson, M. Hydrodynamic structure of bovine serum albumin determined by transient electric birefringence. Biophys. J. 1975, 15, 137–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, S.; Dong, S.; Tian, X.; Xu, Z.; Ma, D.; Cui, B.; Ren, N.; Rittmann, B.E. Role of self-assembly coated Er3+: YAlO3/TiO2 in intimate coupling of visible-light-responsive photocatalysis and biodegradation reactions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 302, 386–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drelich, J.; Chibowski, E.; Meng, D.D.; Terpilowski, K. Hydrophilic and superhydrophilic surfaces and materials. Soft Matter 2011, 7, 9804–9828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


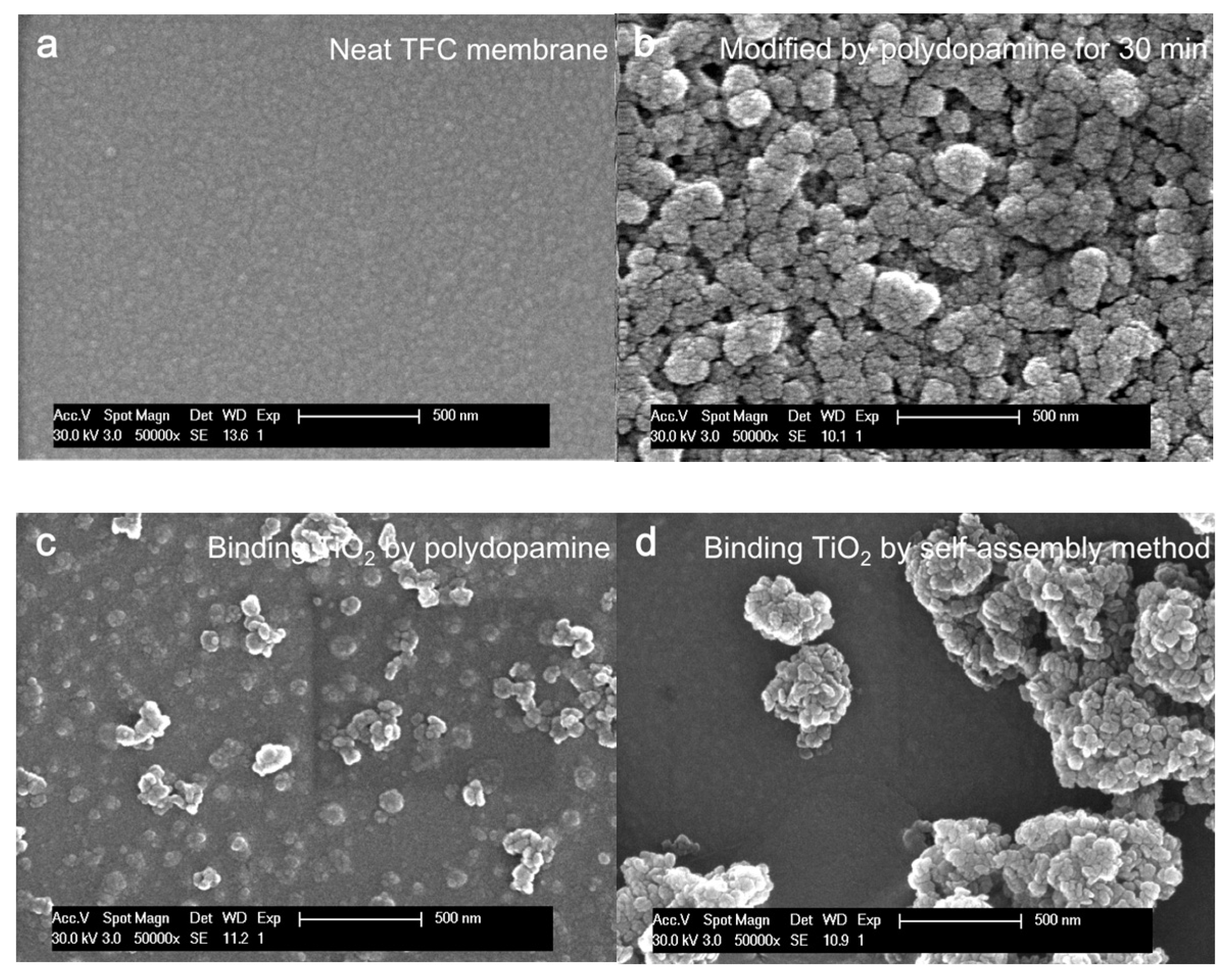
| Membranes | Neat | Neat + pDA | Neat + pDA + TiO2 | Neat + TiO2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Contact angle | 50.4 ± 2.3 | 59.3 ± 1.3 | 27.2 ± 2.9 | 24.5 ± 2.9 |
| Solutions | Original BSA Solution | Neat | Neat + pDA | Neat + pDA + TiO2 | Neat + TiO2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UV absorption percentage (%) | 32.4 ± 0.7 | 19.3 ± 1.0 | 21.6 ± 1.2 | 29.7 ± 1.0 | 26.7 ± 1.4 |
| Membranes | pDA Modified RpDA | pDA + TiO2 Modified RTiO2_pDA | TiO2 Modified RTiO2_self-assembly |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hydraulic Resistance (×1010 m−1) | 40.28 | 4.47 | 25.27 |
© 2017 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, R.-X.; Braeken, L.; Liu, T.-Y.; Luis, P.; Wang, X.-L.; Van der Bruggen, B. Remarkable Anti-Fouling Performance of TiO2-Modified TFC Membranes with Mussel-Inspired Polydopamine Binding. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 81. https://doi.org/10.3390/app7010081
Zhang R-X, Braeken L, Liu T-Y, Luis P, Wang X-L, Van der Bruggen B. Remarkable Anti-Fouling Performance of TiO2-Modified TFC Membranes with Mussel-Inspired Polydopamine Binding. Applied Sciences. 2017; 7(1):81. https://doi.org/10.3390/app7010081
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Rui-Xin, Leen Braeken, Tian-Yin Liu, Patricia Luis, Xiao-Lin Wang, and Bart Van der Bruggen. 2017. "Remarkable Anti-Fouling Performance of TiO2-Modified TFC Membranes with Mussel-Inspired Polydopamine Binding" Applied Sciences 7, no. 1: 81. https://doi.org/10.3390/app7010081
APA StyleZhang, R.-X., Braeken, L., Liu, T.-Y., Luis, P., Wang, X.-L., & Van der Bruggen, B. (2017). Remarkable Anti-Fouling Performance of TiO2-Modified TFC Membranes with Mussel-Inspired Polydopamine Binding. Applied Sciences, 7(1), 81. https://doi.org/10.3390/app7010081








