PSF Estimation of Space-Variant Ultra-Wide Field of View Imaging Systems
Abstract
:1. Introduction
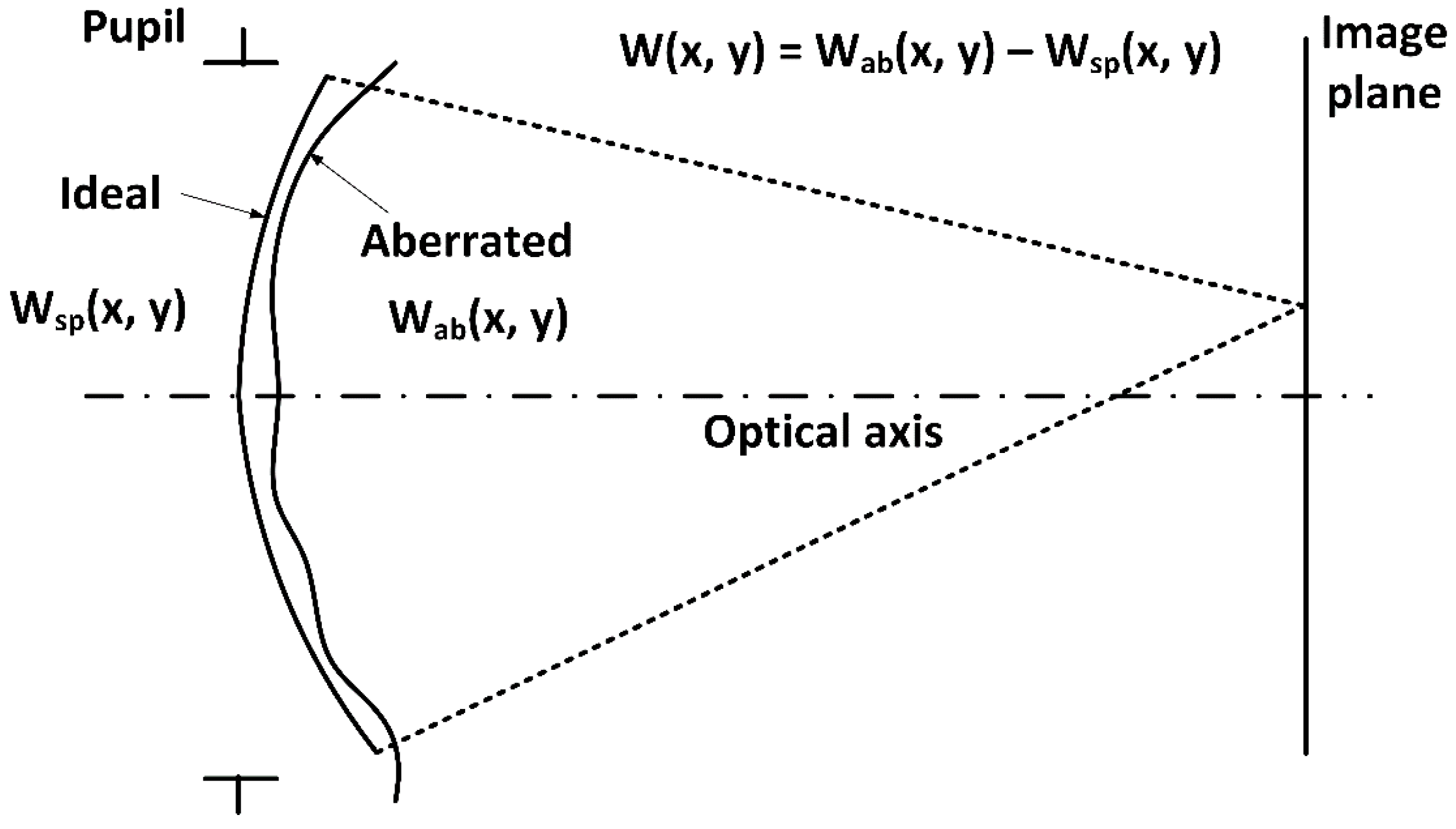
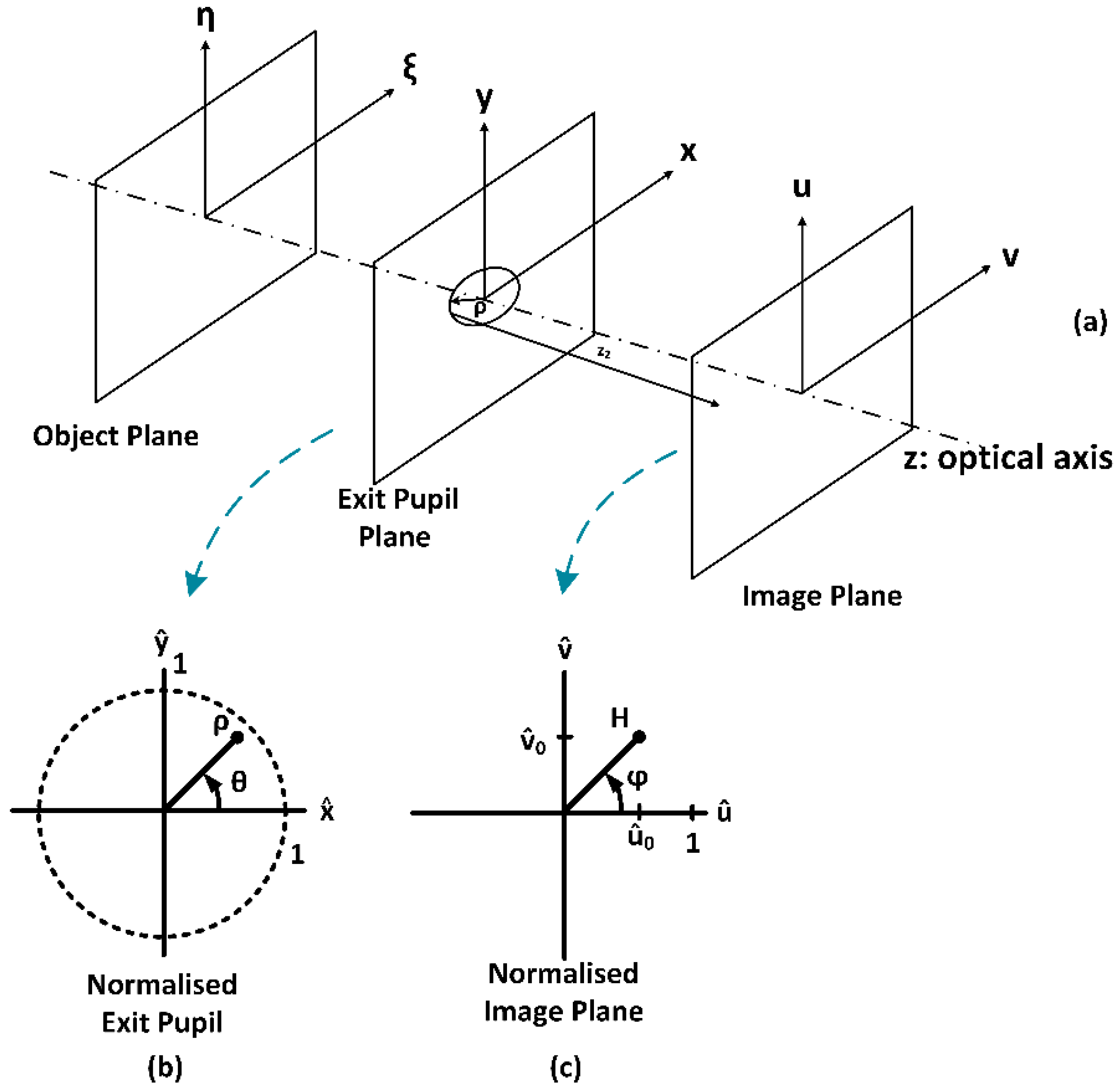
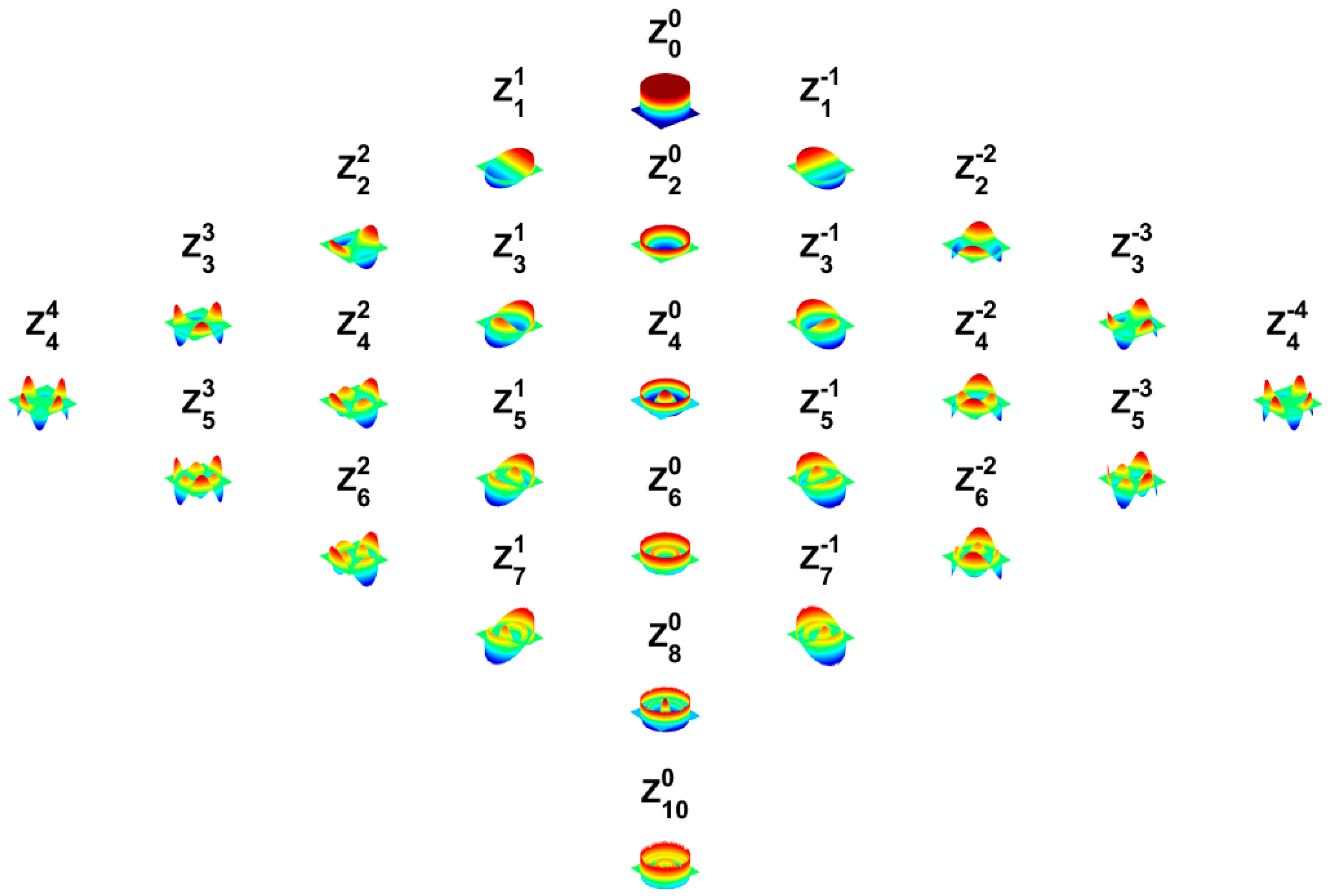
2. Wavefront Aberration Functions
3. Field Dependency of the Wavefront
4. The Space-Variant Point Spread Function
5. Proposed Method
- ●
- Select a point placed on the optical axis (this point is considered as SV aberration free).
- ○
- The optimization coefficient is based on minimizing RMSE or the MAXDIFF metrics. Then we obtain
- ○
- where is the first realization of the fit, and represent the displacement of the object point in the image plane.
- ●
- The next calibration point will be placed on the -axis and next to the first point.
- ○
- All coefficients from the first point fit will be used as start conditions in the next step of the fit.
- ●
- In the next step, we will fit all the points along the -axis by increasing distance H.
- ○
- The previous result is used as the start condition for the next point.
- ●
- Then, we can continue along the -axis by increasing distance H. This procedure gives the first view of the model.
- ○
- where is the d-th realization of the fit.
- ●
- After fitting all the on-axis points, we will start to fit all the off-axis points.
- ○
- The example in this paper uses 24 points.
- ●
- After fitting all the points, we need to evaluate the output coefficients which can describe the field dependency of our model.
- ●
- We verified experimentally that the median applied to the set of estimated coefficients provides better results of the output model than other statistical methods. Thus, we need to find the median of every coefficient over all fit realizations (the number of realizations is L) of the used points. This step will eliminate extreme values of coefficients which can occur at some positions of the PSF due to convergence issues caused by sampling of the image or overfitting effects caused by high orders polynomials. Extreme values indicate that the algorithm found some local minimum of the cost function and not the global minimum. The values of the coefficients are then significantly different from the coefficients obtained in the previous position. These variations are given by the goodness of fit.
- ●
- The output set of coefficients then consists of values verified over the field.
6. Results
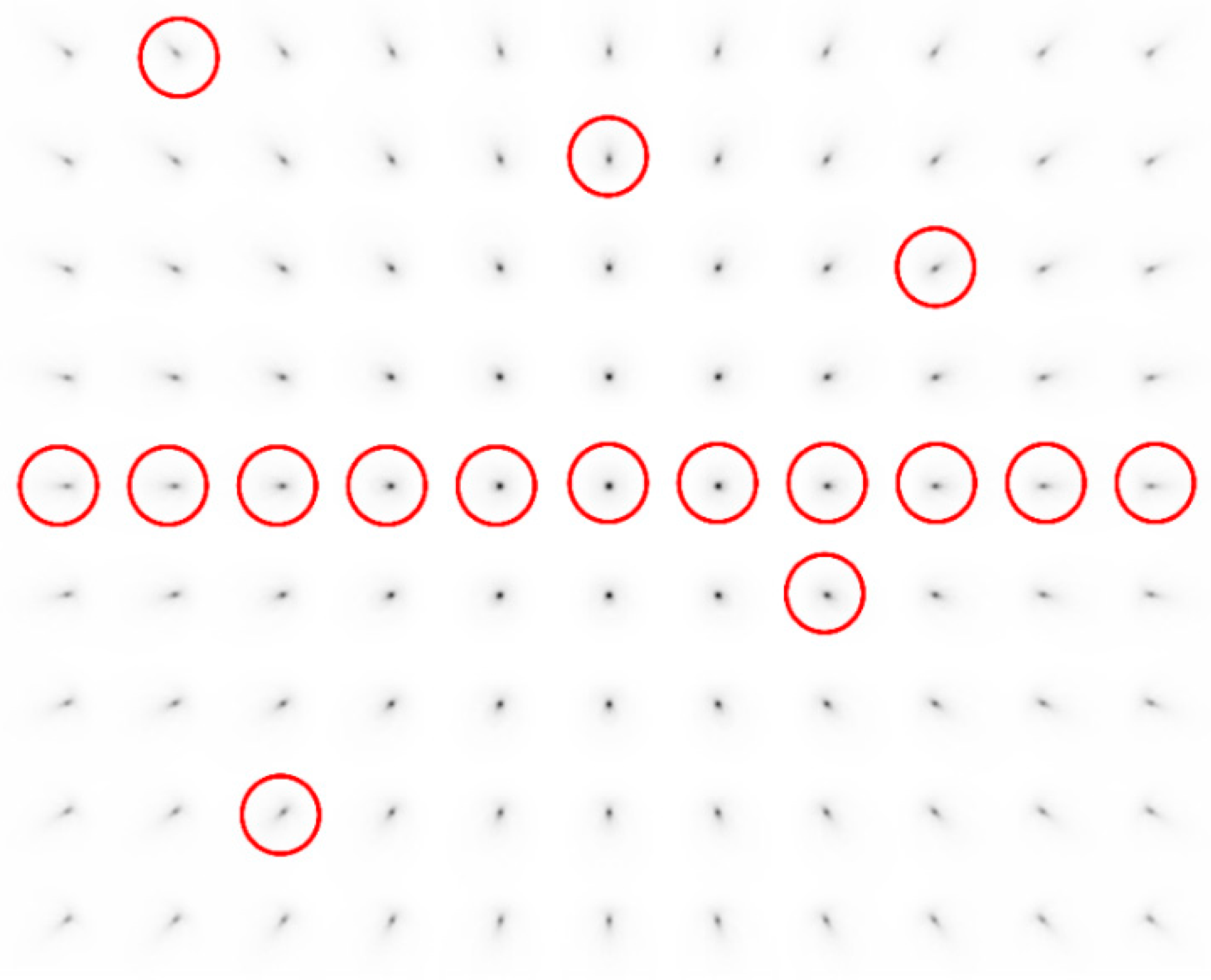
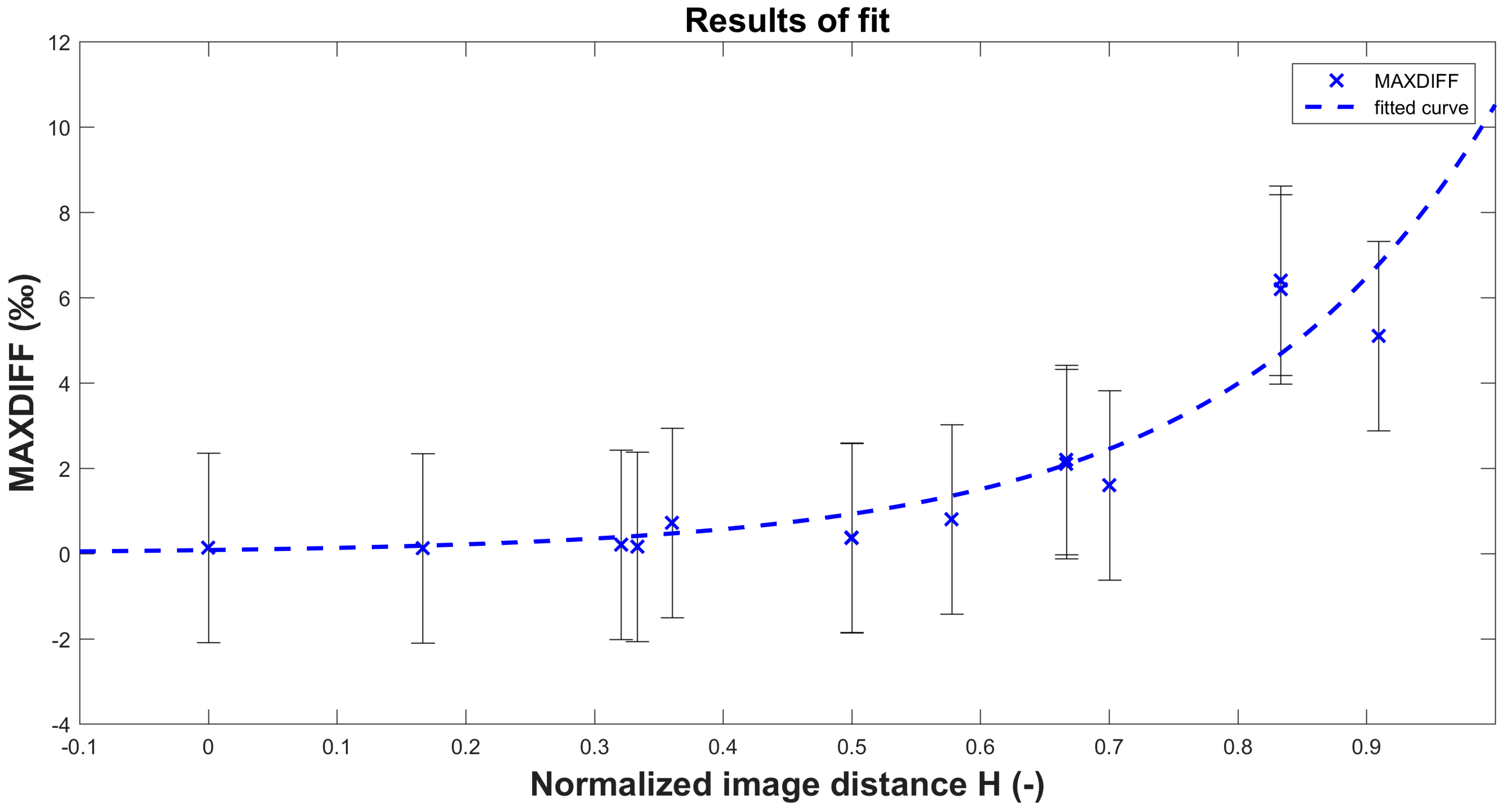
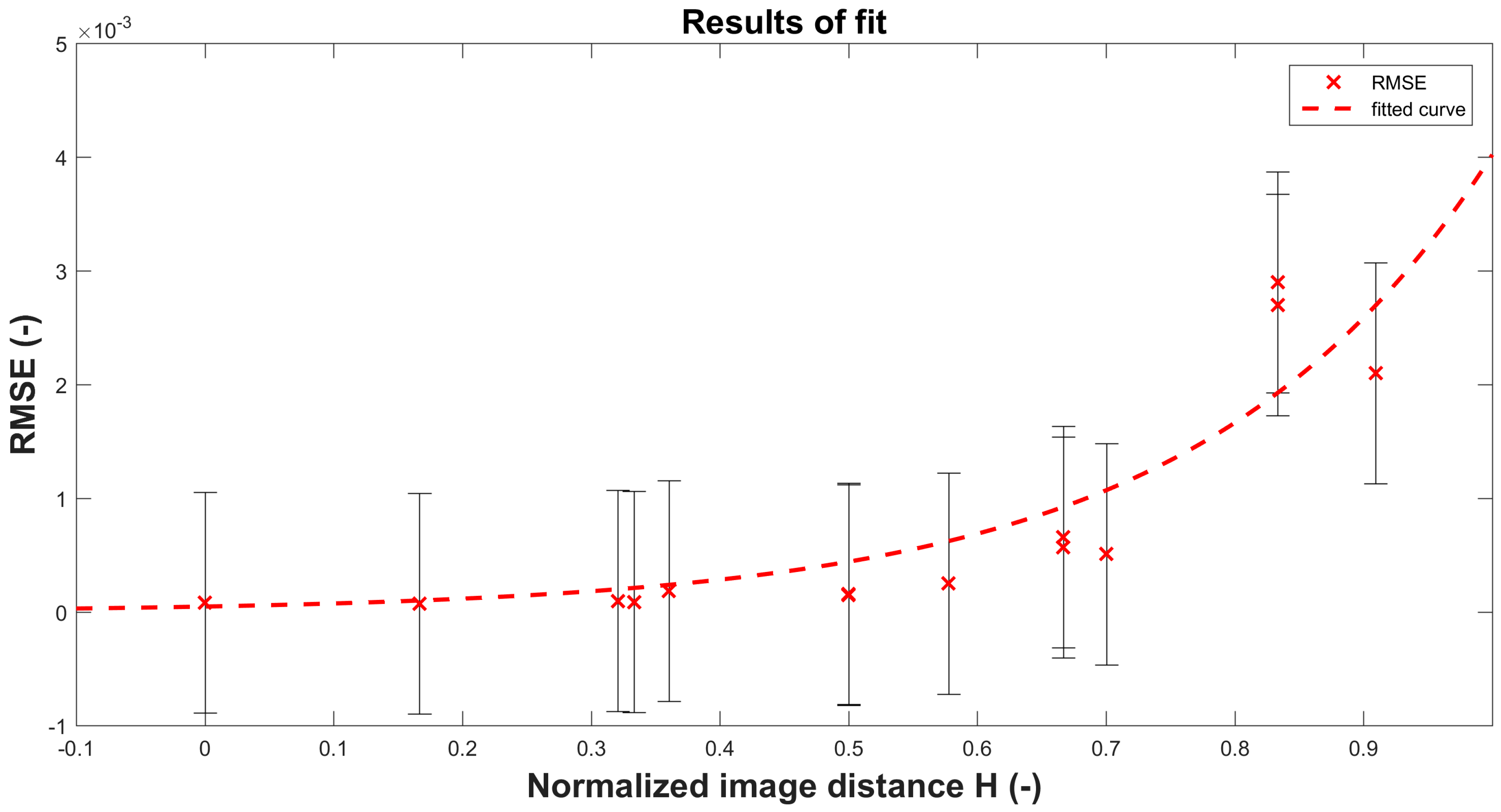
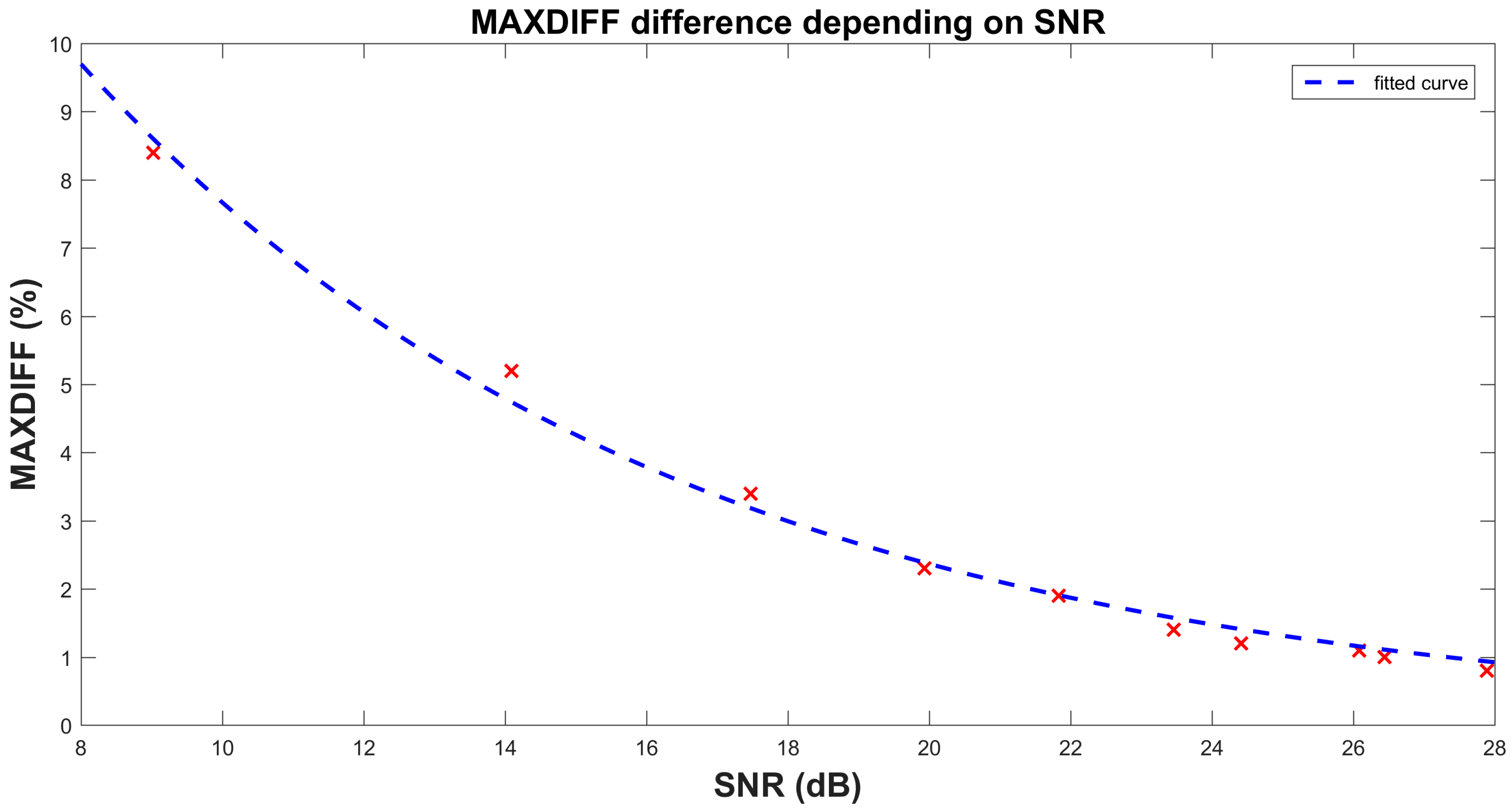
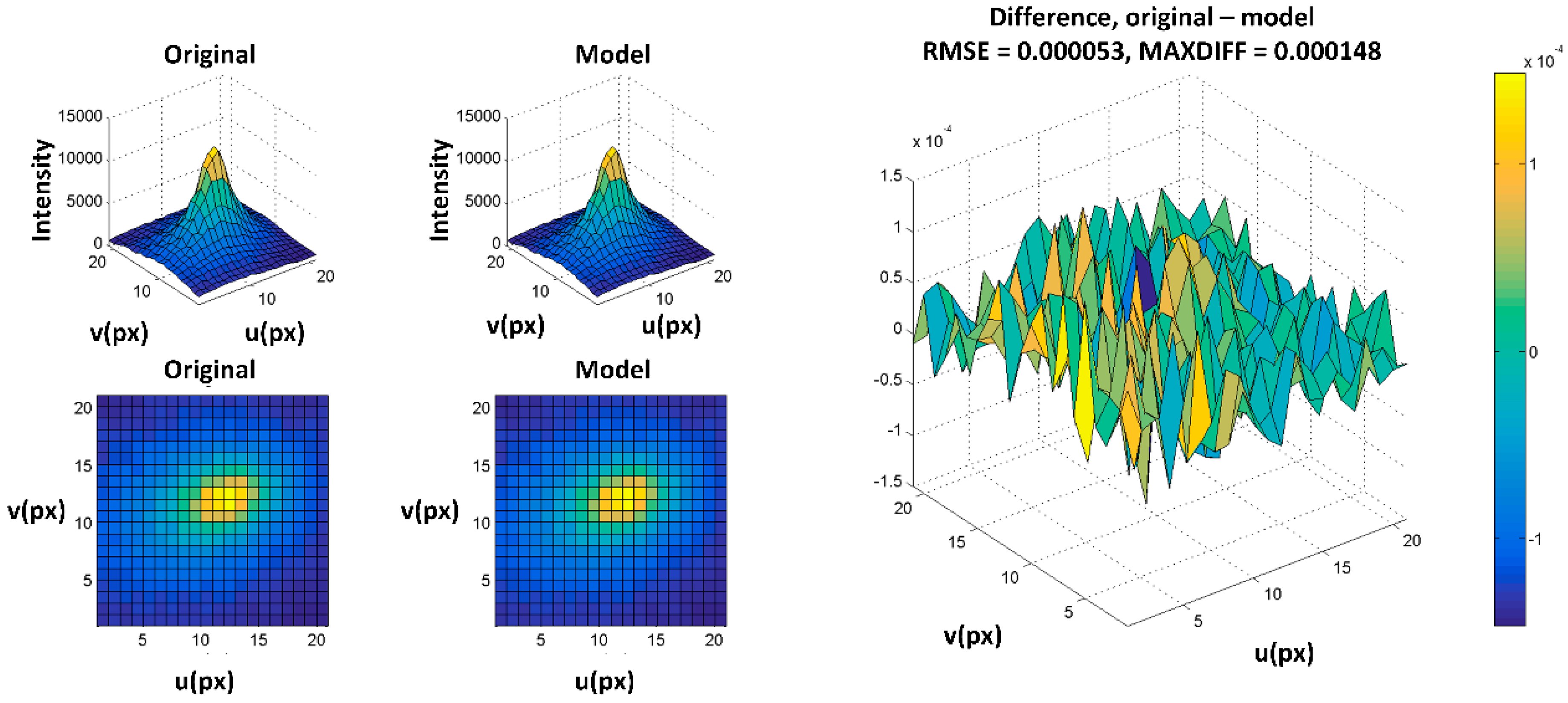
6.1. Numerical Stability Verification
6.2. Experimental Laboratory Results
7. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Expansion Coefficient Function | Name | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Piston | |||
| Tilt | |||
| Focus | |||
| Astigmatism | |||
| Coma | |||
| Spherical | |||
| Elliptical Coma | |||
| Oblique Spherical | |||
| 5th Coma | |||
| 5th Spherical | |||
| 7th Spherical | |||
| 9th Spherical |
References
- Piotrowski, L.W.; Batsch, T.; Czyrkowski, H.; Cwiok, M.; Dabrowski, R.; Kasprowicz, G.; Majcher, A.; Majczyna, A.; Malek, K.; Mankiewicz, L.; et al. PSF modelling for very wide-field CCD astronomy. Astron. Astrophys. 2013, 551, A119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, G.; Ou, X.; Horstmeyer, R.; Yang, C. Characterization of spatially varying aberrations for wide field-of-view microscopy. Opt. Express 2013, 21, 15131–15143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, G.; Horstmeyer, R.; Yang, C. Wide-field, high-resolution Fourier ptychographic microscopy. Nat. Photonics 2013, 7, 739–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lane, R.G.; Tallon, M. Wave-front reconstruction using a Shack–Hartmann sensor. Appl. Opt. 1992, 31, 6902–6908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, T.; Fujii, Y.; Ohta, N.; Saitoh, S.; Matsuura, T.; Yamamoto, T. Measurement of Space Variant PSF for Restoring Degraded Images by Security Cameras. In Proceedings of the 2016 SICE-ICASE International Joint Conference, Busan, Korea, 18–21 October 2006; pp. 2542–2545.
- Řeřábek, M.; Páta, P. Modeling of the widefield space variant security systems. In Proceedings of the 42nd Annual IEEE International Carnahan Conference on Security Technology (ICCST 2008), Prague, Czech Republic, 13–16 October 2008; pp. 121–125.
- Ito, T.; Hoshino, H.; Fujii, Y.; Ohta, N. Reconstruction of face image from security camera based on a measurement of space variant PSF. In Proceedings of the 2009 ICCAS-SICE, Fukuoka, Japan, 18–21 August 2009; pp. 2301–2304.
- Pojmanski, G. The All Sky Automated Survey. Acta Astron. 1997, 47, 467–481. [Google Scholar]
- Burd, A.; Cwiok, M.; Czyrkowski, H.; Dabrowski, R.; Dominik, W.; Grajda, M.; Husejko, M.; Jegier, M.; Kalicki, A.; Kasprowicz, G.; et al. Pi of the Sky—All-sky, real-time search for fast optical transients. New Astron. 2005, 10, 409–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickering, T.E. The MMT All-Sky Camera. In Ground-Based and Airborne Telescopes; Stepp, L.M., Ed.; Proc. SPIE: Washington, DC, USA, 2006; Volume 6267, p. 62671A-62671A-7. [Google Scholar]
- Martin, B.; Petr, P. Colour transformations and K-means segmentation for automatic cloud detection. Meteorol. Z. 2015, 24, 503–509. [Google Scholar]
- Anisimova, E.; Janout, P.; Blažek, M.; Bednář, M.; Fliegel, K.; Páta, P.; Vítek, S.; Švihlík, J. Analysis of images obtained from space-variant astronomical imaging systems. In SPIE Proceedings Vol. 8856: Applications of Digital Image Processing XXXVI; SPIE: Washington, DC, USA, 2013; p. 8856. [Google Scholar]
- Řeřábek, M. Advanced Processing of Images Obtained from Wide-field Astronomical Optical Systems. Acta Polytech. 2011, 51, 90–96. [Google Scholar]
- Řeřábek, M. Space Variant PSF Deconvolution of Wide-Field Astronomical Images. Acta Polytech. 2008, 48, 79–84. [Google Scholar]
- Trigo-Rodriguez, J.M.; Madiedo, J.M.; Gural, P.S.; Castro-Tirado, A.J.; Llorca, J.; Fabregat, J.; Vítek, S.; Pujols, P. Determination of Meteoroid Orbits and Spatial Fluxes by Using High-Resolution All-Sky CCD Cameras. Earth Moon Planet 2008, 102, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Born, M.; Wolf, E. Principles of Optics, 7th ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Zernike, F. von Beugungstheorie des schneidenver-fahrens und seiner verbesserten form, der phasenkontrastmethode. Physica 1934, 1, 689–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noll, R.J. Zernike polynomials and atmospheric turbulence. J. Opt. Soc. Am. 1976, 66, 207–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopkins, H.H. Image formation by a general optical system 1: General theory. Appl. Opt. 1985, 24, 2491–2505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasián, J. Theory of sixth-order wave aberrations. Appl. Opt. 2010, 49, 6502–6503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Gao, Z.; Wang, S.; Liu, X.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, C. Bi-Zernike polynomials for wavefront aberration function in rotationally symmetric optical systems. In Renewable Energy and the Environment, OSA Technical Digest (online); OSA: Washington, DC, USA, 2013; p. JM3A.6. [Google Scholar]
- Gray, R.W.; Dunn, C.; Thompson, K.P.; Rolland, J.P. An analytic expression for the field dependence of Zernike polynomials in rotationally symmetric optical systems. Opt. Express 2012, 20, 16436–16449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weddell, S.J.; Webb, R.Y. The restoration of extended astronomical images using the spatially-variant point spread function. In Proceedings of the 23rd International Conference on Image and Vision Computing New Zealand (IVCNZ), Christchurch, New Zealand, 26–28 November 2008; pp. 1–6.
- Janout, P.; Páta, P.; Bednář, J.; Anisimova, E.; Blažek, M.; Skala, P. Stellar objects identification using wide-field camera. In SPIE Proceedings Vol. 9450: Photonics, Devices, and Systems VI; Tománek, P., Senderáková, D., Páta, P., Eds.; SPIE: Washington, DC, USA, 2015; p. 94501I. [Google Scholar]
- Paczyński, B. Astronomy with Small Telescopes. Publ. Astron. Soc. Pac. 2006, 118, 1621–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vítek, S. Modeling of Astronomical Images. Balt. Astron. 2009, 18, 387–391. [Google Scholar]
- Hasan, S.Y.; Shaker, A.S. Study of Zernike Polynomials of an Elliptical Aperture Obscured with an Elliptical Obscuration. Available online: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23262546 (accessed on 16 March 2016).
- Thompson, K.P.; Fuerschbach, K.; Rolland, J.P. An analytic expression for the field dependence of FRINGE Zernike polynomial coefficients in optical systems that are rotationally nonsymmetric. In SPIE Proceedings Vol. 7849: Optical Design and Testing IV; Wang, Y., Bentley, J., Du, C., Tatsuno, K., Urbach, H.P., Eds.; SPIE: Washington, DC, USA, 2010; p. 784906. [Google Scholar]
- Maksimenka, R.; Nuernberger, P.; Lee, K.F.; Bonvalet, A.; Milkiewicz, J.; Barta, C.; Klima, M.; Oksenhendler, T.; Tournois, P.; Kaplan, D.; et al. Direct mid-infrared femtosecond pulse shaping with a calomel acousto-optic programmable dispersive filter. Opt. Lett. 2010, 35, 3565–3567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pata, P.; Klima, M.; Bednar, J.; Janout, P.; Barta, C.; Hasal, R.; Maresi, L.; Grabarnik, S. OFT sectorization approach to analysis of optical scattering in mercurous chloride single crystals. Opt. Express 2015, 23, 21509–21526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yokozeki, S.; Ohnishi, K. Spherical Aberration Measurement with Shearing Interferometer Using Fourier Imaging and Moiré Method. Appl. Opt. 1975, 14, 623–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sung, J.; Pitchumani, M.; Johnson, E.G. Aberration measurement of photolithographic lenses by use of hybrid diffractive photomasks. Appl. Opt. 2003, 42, 1987–1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, J.; Kim, J.; Ou, X.; Horstmeyer, R.; Yang, C. Wide field-of-view fluorescence image deconvolution with aberration-estimation from Fourier ptychography. Biomed. Opt. Express 2016, 7, 352–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, Y.L.; Cheng, Z.Y. Linear Space-Variant Model and Restoration Algorithm of Imaging System. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2014, 608–609, 559–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heide, F.; Rouf, M.; Hullin, M.B.; Labitzke, B.; Heidrich, W.; Kolb, A. High-quality Computational Imaging through Simple Lenses. ACM Trans. Graph. 2013, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shack, R.; Platt, B. Production and Use of a Lenticular Hartmann Screen. In Spring Meeting of the Optical Society of America; Chairman, D., Ed.; Optical Society of America: Washington, DC, USA, 1971. [Google Scholar]
- Navarro, R.; Arines, J.; Rivera, R. Direct and inverse discrete Zernike transform. Opt. Express 2009, 17, 24269–24281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- José, S. Introduction to Aberrations in Optical Imaging Systems; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Malacara, D. (Ed.) Optical Shop Testing, 3rd ed.; Wiley Series in Pure and Applied Optics; Wiley-Interscience: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2007.
- Mahajan, V.N.; Díaz, J.A. Imaging characteristics of Zernike and annular polynomial aberrations. Appl. Opt. 2013, 52, 2062–2074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weddell, S.J.; Webb, R.Y. Reservoir Computing for Prediction of the Spatially-Variant Point Spread Function. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Signal Process. 2008, 2, 624–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodman, J.W. Introduction to Fourier Optics; Roberts and Company Publishers: Englewood, CO, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Nelder, J.A.; Mead, R. A Simplex Method for Function Minimization. Comput. J. 1965, 7, 308–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CCD kamera G2-8300. Available online: http://www.gxccd.com/art?id=374&lang=405 (accessed on 7 July 2016).
- 10 mm F2.8 EX DC HSM Fisheye. Available online: http://www.sigmaphoto.com/10mm-f2-8-ex-dc-hsm-fisheye (accessed on 7 July 2016).
- Trujillo, I.; Aguerri, A.; Cepa, J.; Gutierrez, C.M. The effects of seeing on Sersic profiles. II. The Moffat PSF. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2001, 328, 977–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vítek, S.; Blažek, M. Notes on DSLR Photometry. Astron. Soc. India Conf. Ser. 2012, 7, 231. [Google Scholar]
- Lukeš, T.; Křížek, P.; Švindrych, Z.; Benda, J.; Ovesný, M.; Fliegel, K.; Klíma, M.; Hagen, G.M. Three-dimensional super-resolution structured illumination microscopy with maximum a posteriori probability image estimation. Opt. Express 2014, 22, 29805–29817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lukeš, T.; Hagen, G.M.; Křížek, P.; Švindrych, Z.; Fliegel, K.; Klíma, M. Comparison of Image Reconstruction Methods for Structured Illumination Microscopy. In SPIE Proceedings Vol. 9129: Biophotonics—Photonic Solutions for Better Health Care IV; Popp, J., Tuchin, V.V., Matthews, D.L., Pavone, F.S., Garside, P., Eds.; SPIE: Washington, DC, USA, 2014; p. 91293J. [Google Scholar]
- Fliegel, K.; Janout, P.; Bednář, J.; Krasula, L.; Vítek, S.; Švihlík, J.; Páta, P. Performance Evaluation of Image Deconvolution Techniques in Space-Variant Astronomical Imaging Systems with Nonlinearities. In SPIE Proceedings Vol. 9599: Applications of Digital Image Processing XXXVIII; Tescher, A.G., Ed.; SPIE: Washington, DC, USA, 2015; p. 959927. [Google Scholar]
- Janout, P.; Páta, P.; Skala, P.; Fliegel, K.; Vítek, S.; Bednář, J. Application of Field Dependent Polynomial Model. In SPIE Proceedings Vol. 9971: Applications of Digital Image Processing XXXIX; Tescher, A.G., Ed.; SPIE: Washington, DC, USA, 2016; p. 99710F. [Google Scholar]

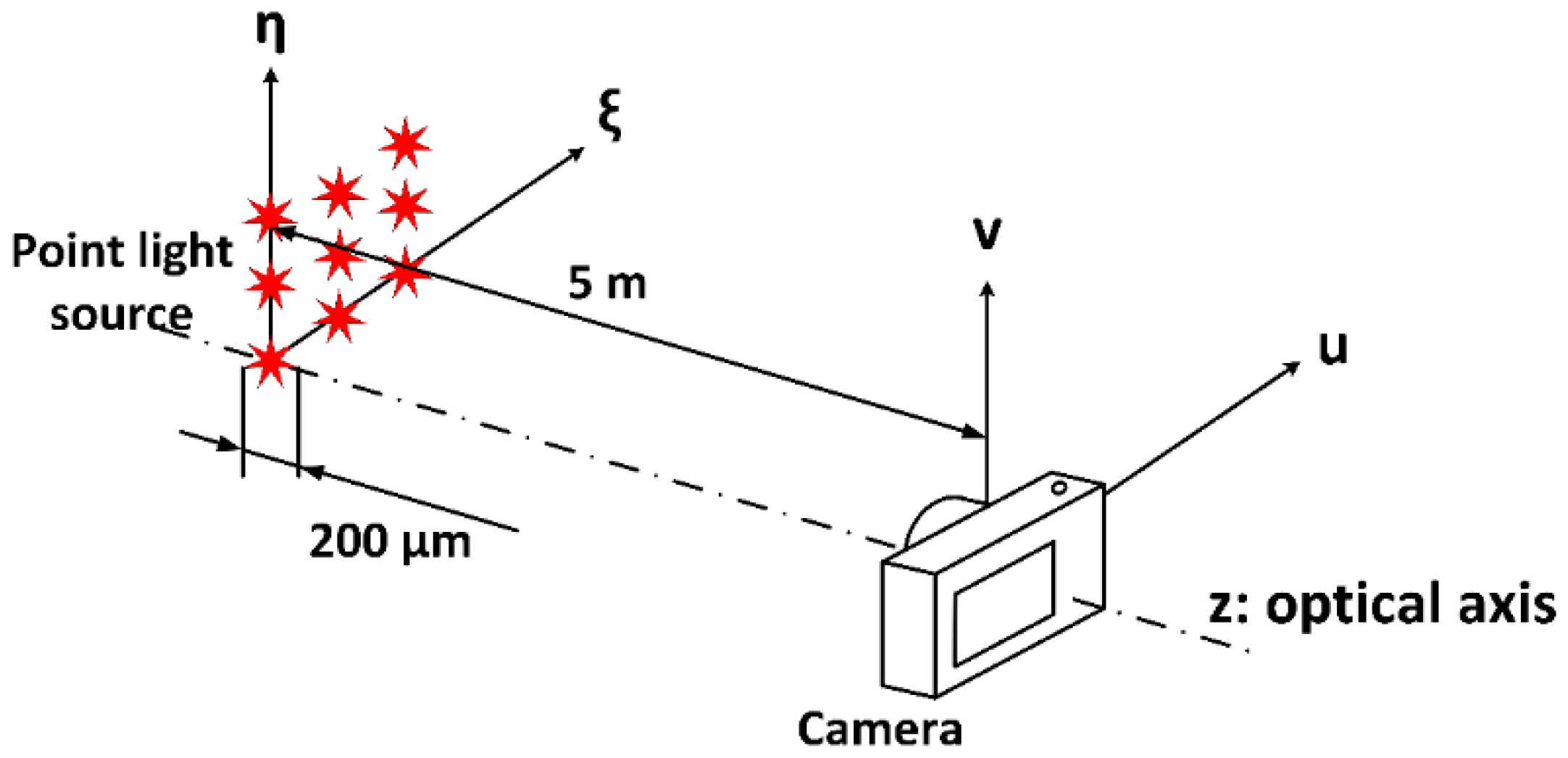
| Resolution | 3358 × 2536 px |
| Sensor size | 18.1 × 13.7 mm |
| Pixel size | 5.39 µm |
| Lens focus distance | 10 mm |
| FOV | 110° |
| Metrics | Normalized Image Distance H (-) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0.17 | 0.33 | 0.50 | 0.67 | 0.83 | |
| RMSE (10−5) | 8.2 | 7.3 | 8.8 | 16 | 57 | 270 |
| MAXDIFF (‰) | 0.14 | 0.13 | 0.16 | 0.36 | 2.1 | 6.4 |
| Resolution | 3358 × 2536 px |
| Sensor size | 18.1 × 13.7 mm |
| Pixel size | 5.39 µm |
| Lens focus distance | 10 mm |
| FOV | 110° |
| Metrics | Normalized Image Distance H (-) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0.17 | 0.33 | 0.50 | 0.67 | 0.83 | |
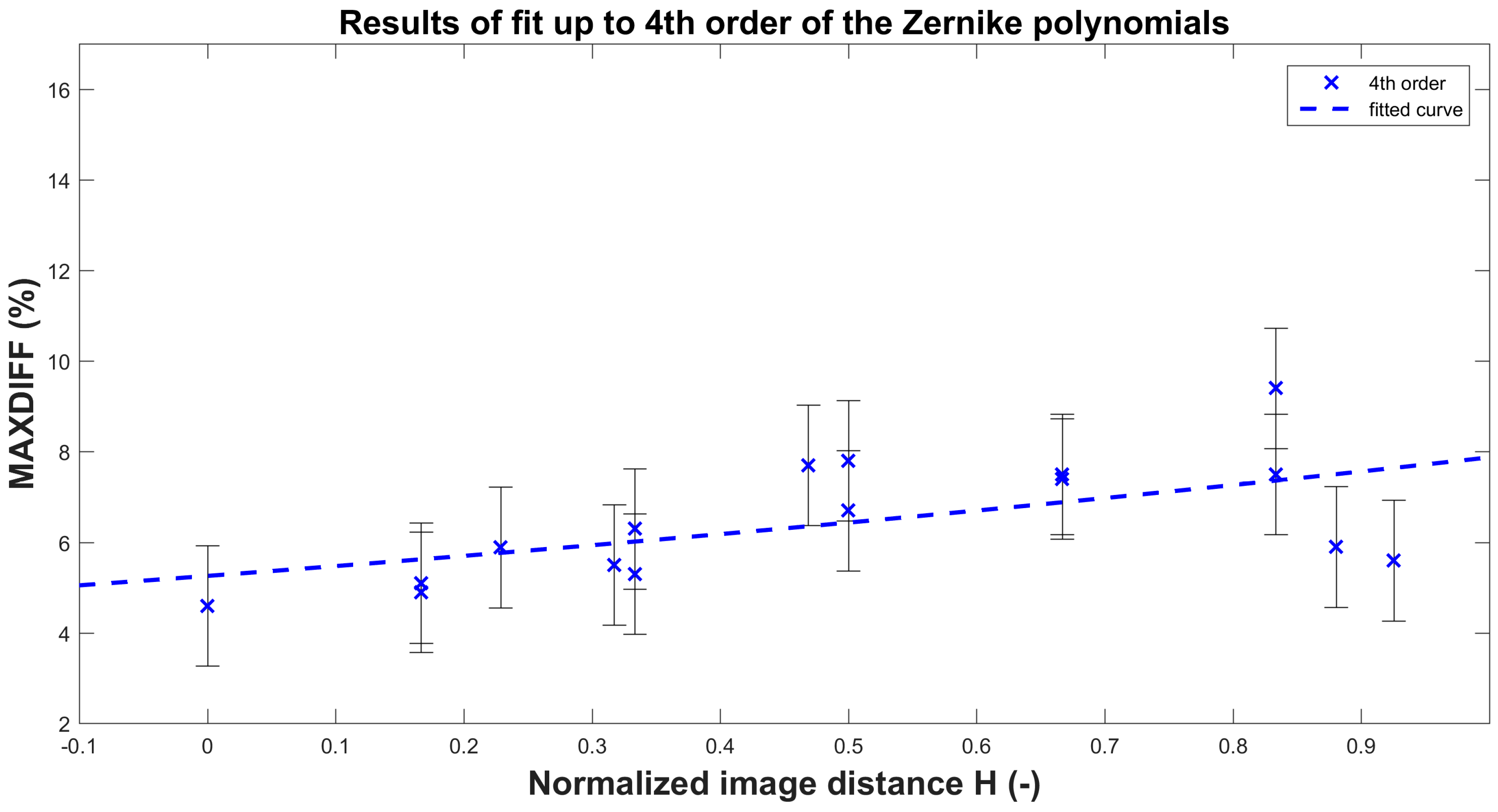
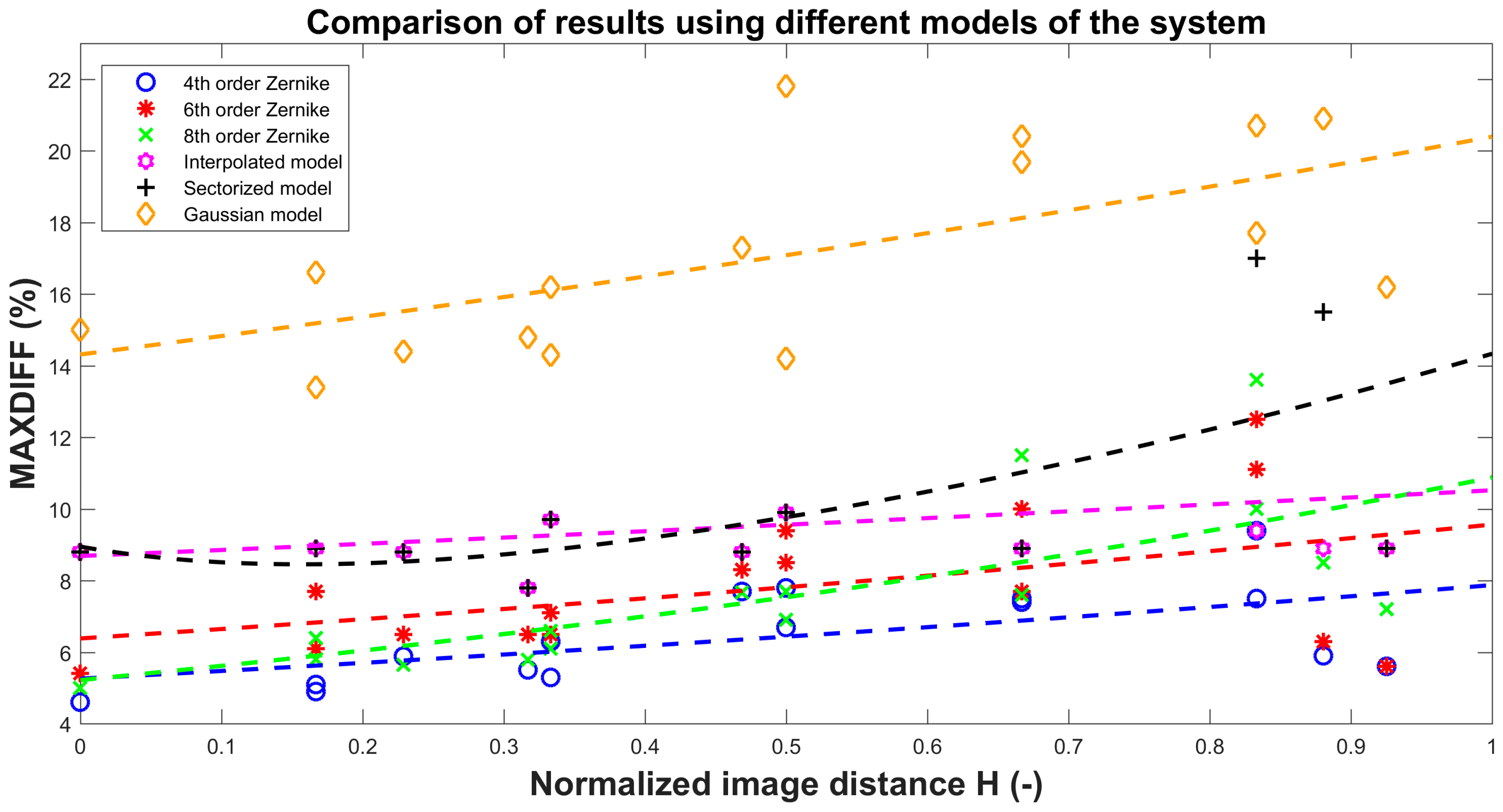
| 4th order | 4.6 | 5.1 | 5.3 | 7.8 | 7.5 | 9.4 |
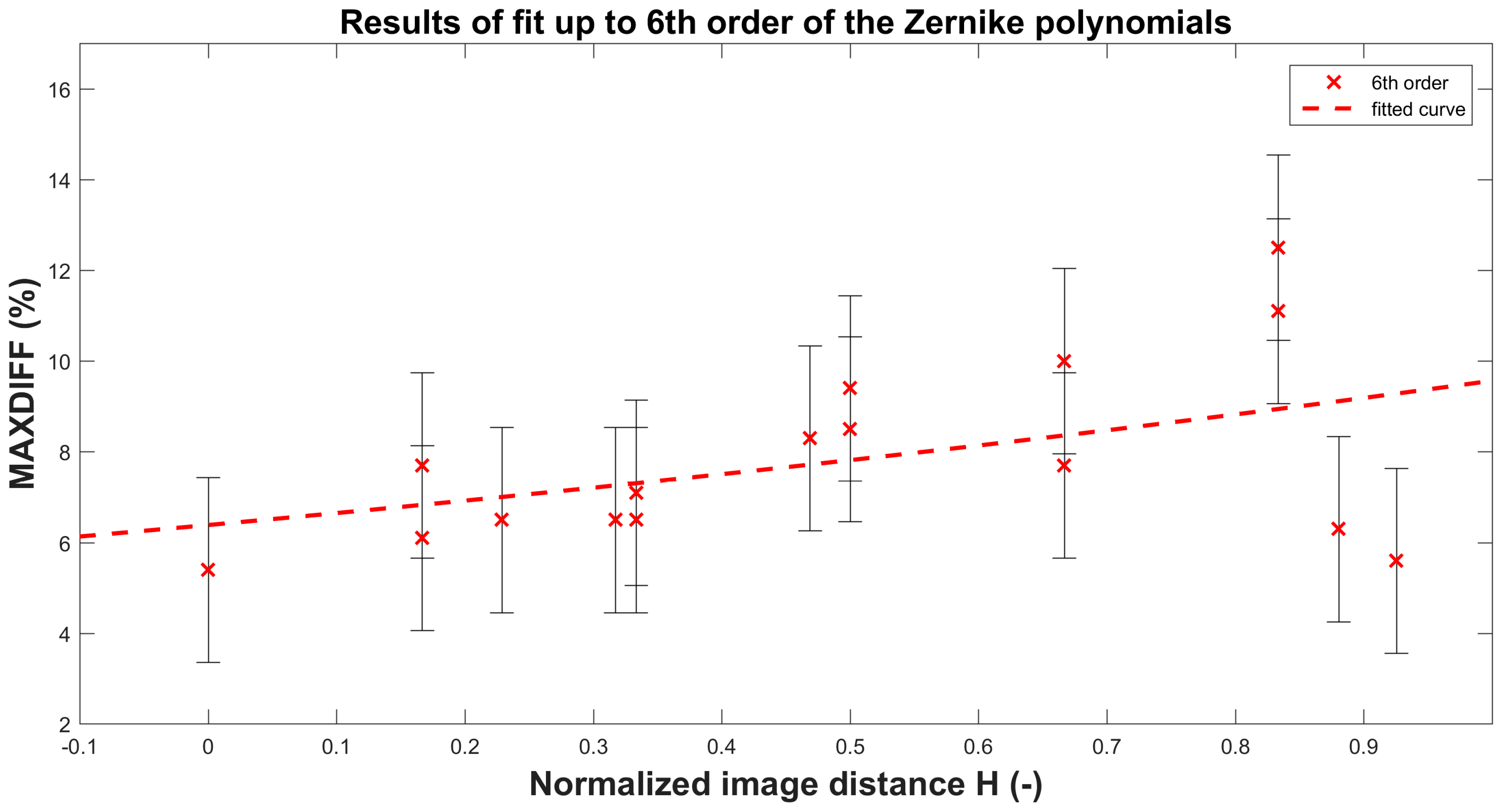
| 6th order | 5.4 | 7.7 | 6.5 | 9.4 | 7.7 | 12.5 |
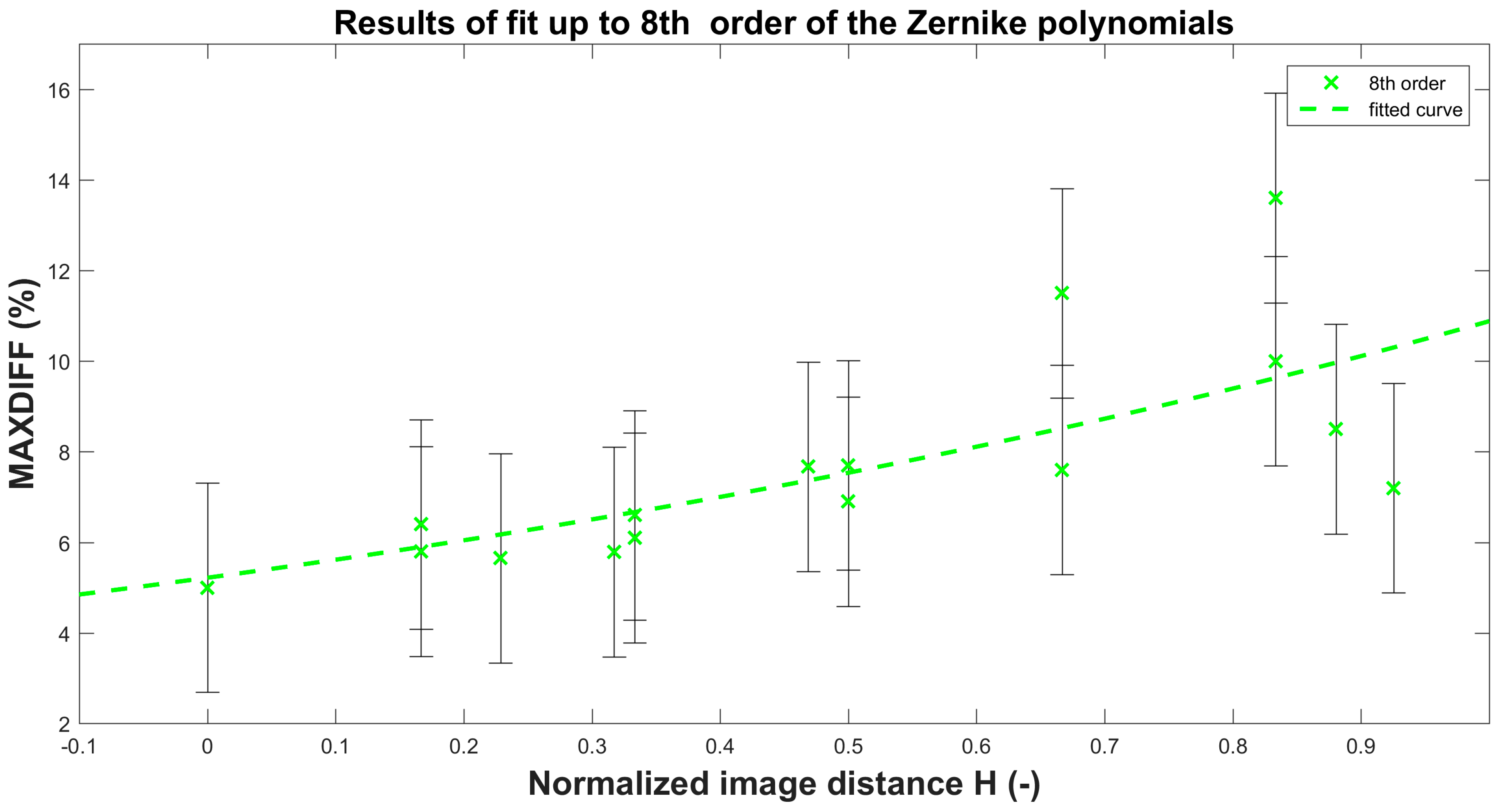
| 8th order | 5 | 6.4 | 6.1 | 7.7 | 7.6 | 10 |
| Metrics | 4th Order | 6th Order | 8th Order |
|---|---|---|---|
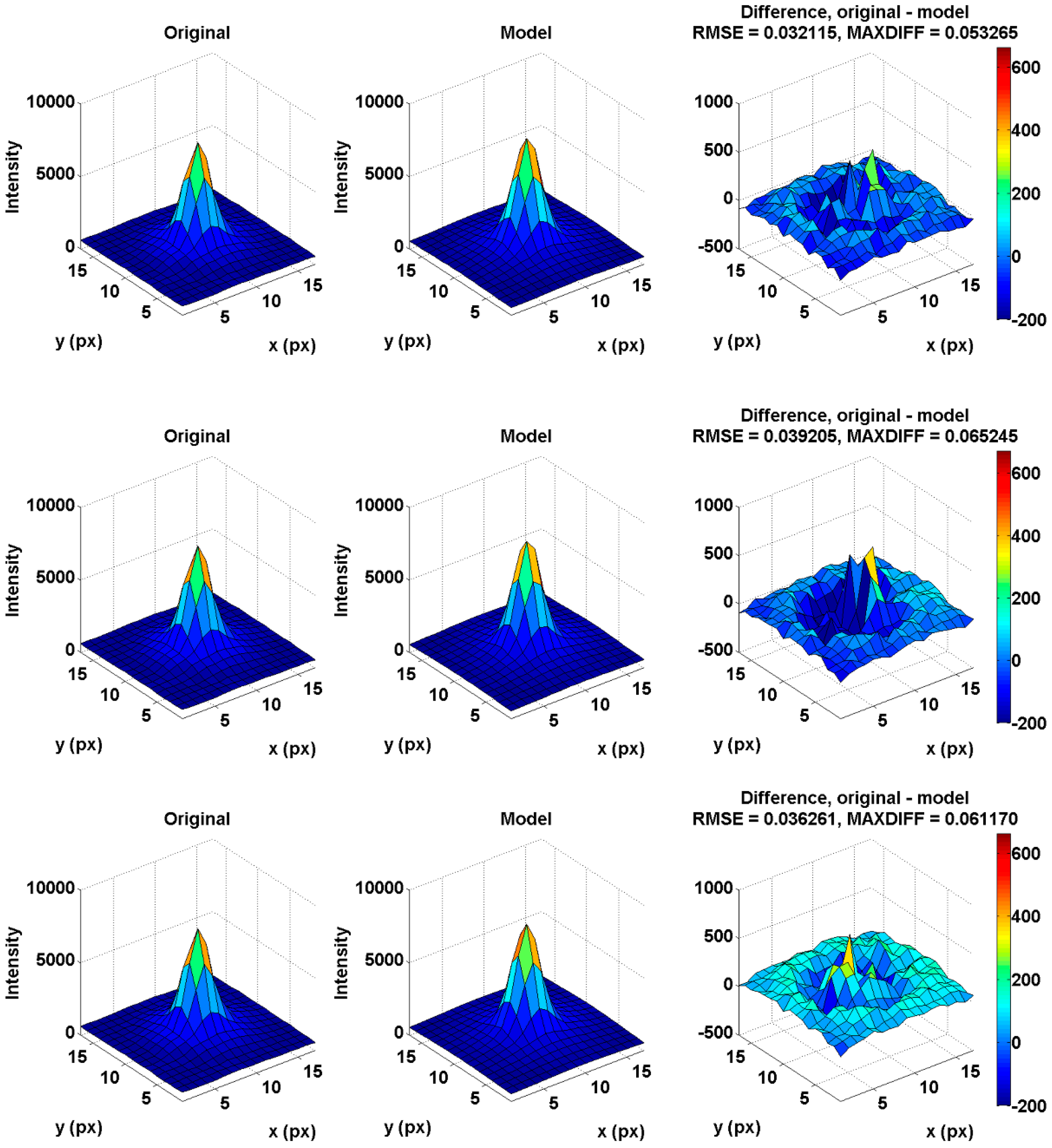
| RMSE (-) | 0.032 | 0.039 | 0.036 |
| MAXDIFF (%) | 5.3 | 6.5 | 6.1 |
| Total flux difference (‰) | 0.31 | 0.35 | 0.37 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Janout, P.; Páta, P.; Skala, P.; Bednář, J. PSF Estimation of Space-Variant Ultra-Wide Field of View Imaging Systems. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 151. https://doi.org/10.3390/app7020151
Janout P, Páta P, Skala P, Bednář J. PSF Estimation of Space-Variant Ultra-Wide Field of View Imaging Systems. Applied Sciences. 2017; 7(2):151. https://doi.org/10.3390/app7020151
Chicago/Turabian StyleJanout, Petr, Petr Páta, Petr Skala, and Jan Bednář. 2017. "PSF Estimation of Space-Variant Ultra-Wide Field of View Imaging Systems" Applied Sciences 7, no. 2: 151. https://doi.org/10.3390/app7020151
APA StyleJanout, P., Páta, P., Skala, P., & Bednář, J. (2017). PSF Estimation of Space-Variant Ultra-Wide Field of View Imaging Systems. Applied Sciences, 7(2), 151. https://doi.org/10.3390/app7020151






