Global Synchronization of Multichannel EEG Based on Rényi Entropy in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. EEG Data Collection
2.3. EEG Preprocessing
2.4. EEG Data Analysis
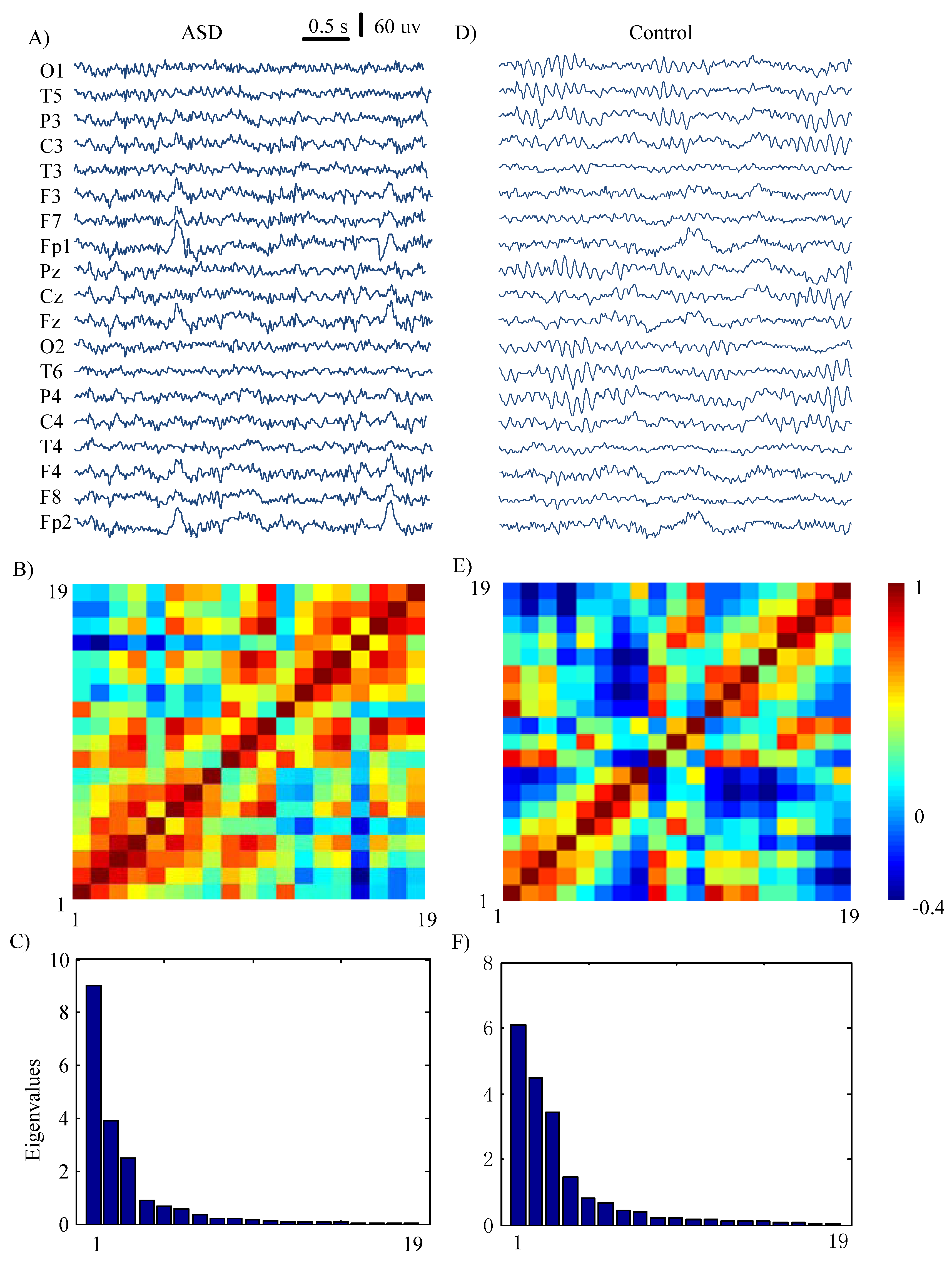
2.4.1. The Correlation Matrix Analysis and S-Estimator
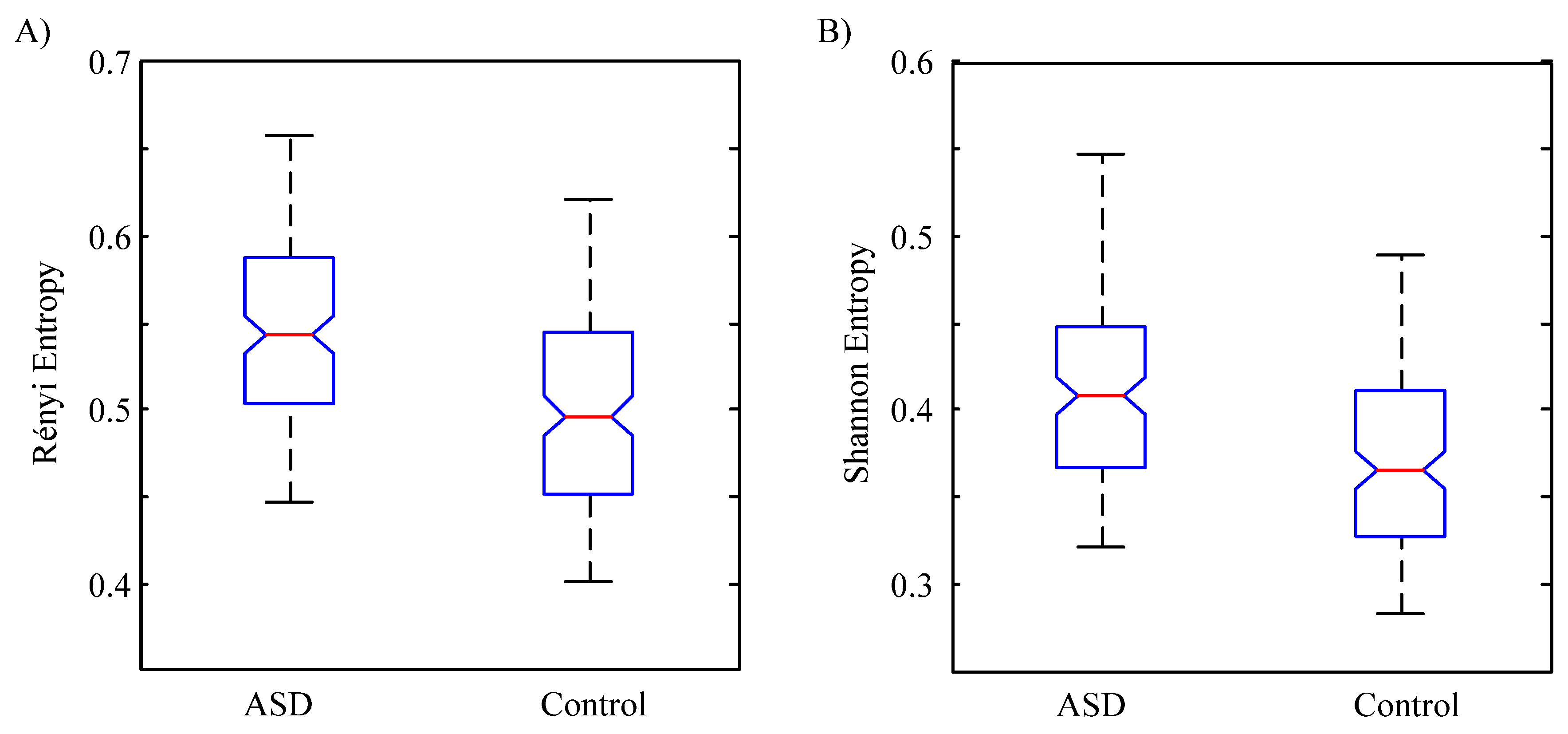
2.4.2. Rènyi Entropy and the Index
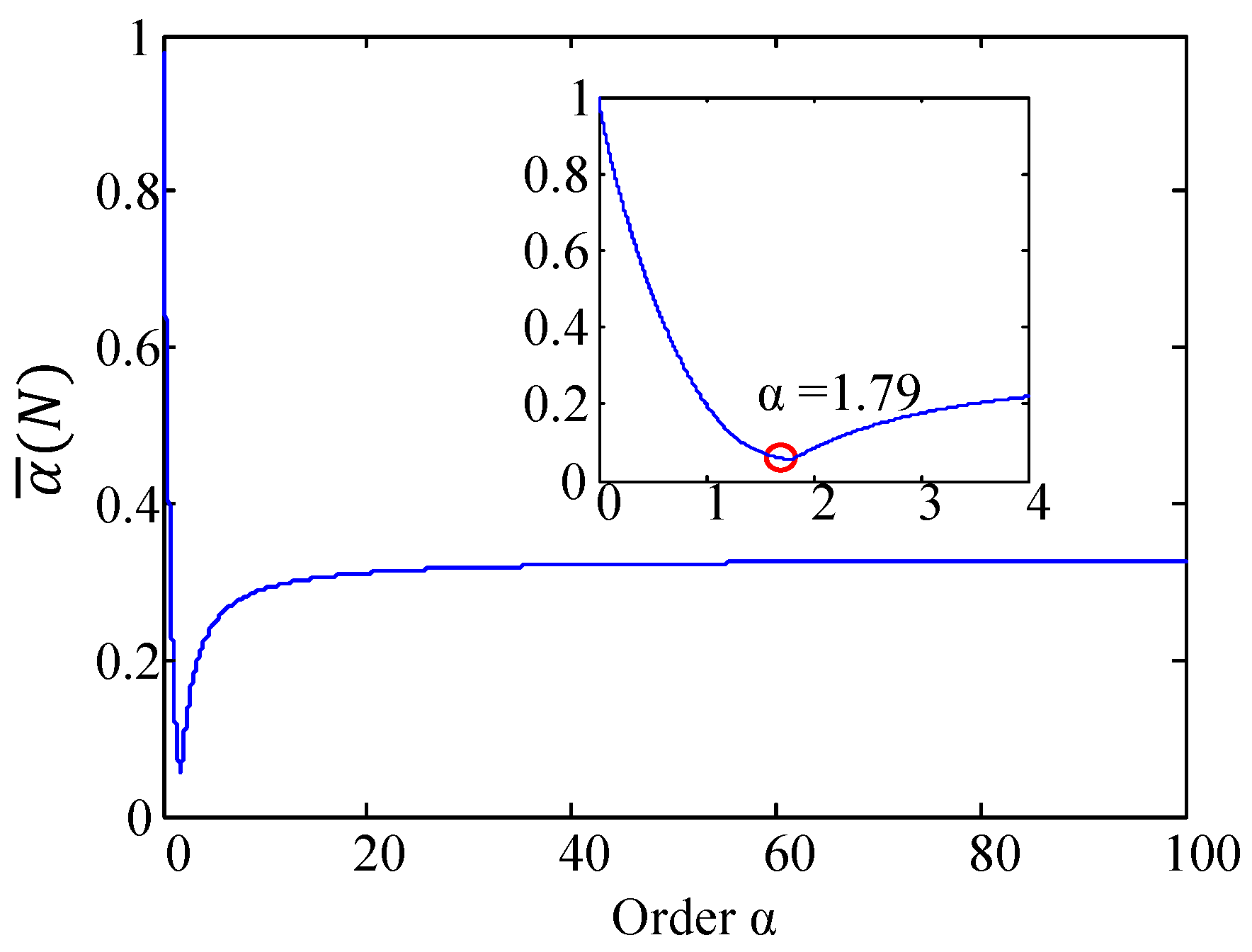
2.4.3. Optimal Order α
3. Results
4. Discussion
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Association, A.P. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 5th ed.; American Psychiatric Publishing: Arlington, VA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Braun, C.M.; Daigneault, R.; Gaudelet, S.; Guimond, A. Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders, fourth edition symptoms of mania: Which one(s) result(s) more often from right than left hemisphere lesions? Compr. Psychiatry 2008, 49, 441–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belmonte, M.K.; Allen, G.; Beckel-Mitchener, A.; Boulanger, L.M.; Carper, R.A.; Webb, S.J. Autism and abnormal development of brain connectivity. J. Neurosci. 2004, 24, 9228–9231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coben, R.; Clarke, A.R.; Hudspeth, W.; Barry, R.J. EEG power and coherence in autistic spectrum disorder. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2008, 119, 1002–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rapin, I.; Dunn, M. Update on the language disorders of individuals on the autistic spectrum. Brain Dev. 2003, 25, 166–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willyard, C. New efforts to design better tools to track autism therapy response. Nat. Med. 2016, 22, 570–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeste, S.S.; Frohlich, J.; Loo, S.K. Electrophysiological biomarkers of diagnosis and outcome in neurodevelopmental disorders. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2015, 28, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubenstein, J.L.; Merzenich, M.M. Model of autism: Increased ratio of excitation/inhibition in key neural systems. Genes Brain Behav. 2003, 2, 255–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Barstein, J.; Ethridge, L.E.; Mosconi, M.W.; Takarae, Y.; Sweeney, J.A. Resting state EEG abnormalities in autism spectrum disorders. J. Neurodev. Disord. 2013, 5, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghanbari, Y.; Bloy, L.; Christopher Edgar, J.; Blaskey, L.; Verma, R.; Roberts, T.P. Joint analysis of band-specific functional connectivity and signal complexity in autism. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2015, 45, 444–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murias, M.; Webb, S.J.; Greenson, J.; Dawson, G. Resting state cortical connectivity reflected in EEG coherence in individuals with autism. Biol. Psychiatry 2007, 62, 270–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daoust, A.M.; Limoges, E.; Bolduc, C.; Mottron, L.; Godbout, R. EEG spectral analysis of wakefulness and rem sleep in high functioning autistic spectrum disorders. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2004, 115, 1368–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buzsaki, G. Large-scale recording of neuronal ensembles. Nat. Neurosci. 2004, 7, 446–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, D.; Liu, X.; Wan, Y.; Li, X. Estimation of genuine and random synchronization in multivariate neural series. Neural Netw. 2010, 23, 698–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouyang, G.; Wang, Y.; Yang, Z.; Li, X. Global synchronization of multichannel EEG in patients with electrical status epilepticus in sleep. Clin. EEG Neurosci. 2015, 46, 357–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhat, S.; Acharya, U.R.; Dadmehr, N.; Adeli, H. Clinical neurophysiological and automated EEG-based diagnosis of the alzheimer’s disease. Eur. Neurol. 2015, 74, 202–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Courchesne, E.; Karns, C.M.; Davis, H.R.; Ziccardi, R.; Carper, R.A.; Tigue, Z.D.; Chisum, H.J.; Moses, P.; Pierce, K.; Lord, C.; et al. Unusual brain growth patterns in early life in patients with autistic disorder: An mri study. Neurology 2001, 57, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hazlett, H.C.; Poe, M.; Gerig, G.; Smith, R.G.; Provenzale, J.; Ross, A.; Gilmore, J.; Piven, J. Magnetic resonance imaging and head circumference study of brain size in autism: Birth through age 2 years. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 2005, 62, 1366–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lainhart, J.E.; Bigler, E.D.; Bocian, M.; Coon, H.; Dinh, E.; Dawson, G.; Deutsch, C.K.; Dunn, M.; Estes, A.; Tager-Flusberg, H.; et al. Head circumference and height in autism: A study by the collaborative program of excellence in autism. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 2006, 140, 2257–2274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patidar, S.; Pachori, R.B.; Upadhyay, A.; Rajendra Acharya, U. An integrated alcoholic index using tunable-q wavelet transform based features extracted from EEG signals for diagnosis of alcoholism. Appl. Soft Comput. 2017, 50, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, K.; Yan, J.; Wang, Y.; Sik, A.; Ouyang, G.; Li, X. Automatic detection of absence seizures with compressive sensing EEG. Neurocomputing 2016, 171, 497–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pecora, L.M.; Carroll, T.L. Synchronization of chaotic systems. Chaos 2015, 25, 097611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.W.; Bakardjian, H.; Cichocki, A.; Principe, J.C. A new nonlinear similarity measure for multichannel signals. Neural Netw. 2008, 21, 222–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, J.; Wang, Y.; Ouyang, G.; Yu, T.; Li, X. Using max entropy ratio of recurrence plot to measure electrocorticogram changes in epilepsy patients. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2016, 443, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Righero, M. A cooperation index based on the rényi entropy of correlation matrix spectrum. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 2012, 17, 2960–2968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Lowe, H.J. A novel hybrid approach to automated negation detection in clinical radiology reports. J. Am. Med. Inform. Assoc. JAMIA 2007, 14, 304–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Humeau-Heurtier, A. Multivariate generalized multiscale entropy analysis. Entropy 2016, 18, 411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCrimmon, A.W.S.; Amanda, D. Wechsler abbreviated scale of intelligence, 2nd edition (WASI-II). J. Psychoneurotic Assess. 2013, 31, 337–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamal, W.; Das, S.; Oprescu, I.-A.; Maharatna, K.; Apicella, F.; Sicca, F. Classification of autism spectrum disorder using supervised learning of brain connectivity measures extracted from synchrostates. J. Neural Eng. 2014, 11, 046019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durka, P.J.; Klekowicz, H.; Blinowska, K.J.; Szelenberger, W.; Niemcewicz, S. A simple system for detection of EEG artifacts in polysomnographic recordings. IEEE Trans. Bio-Med. Eng. 2003, 50, 526–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carmeli, C.; Knyazeva, M.G.; Innocenti, G.M.; De Feo, O. Assessment of EEG synchronization based on state-space analysis. NeuroImage 2005, 25, 339–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mammone, N.; Duun-Henriksen, J.; Kjaer, T.; Morabito, F. Differentiating interictal and ictal states in childhood absence epilepsy through permutation rényi entropy. Entropy 2015, 17, 4627–4643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mammone, N.; Inuso, G.; La Foresta, F.; Versaci, M.; Morabito, F.C. Clustering of entropy topography in epileptic electroencephalography. Neural Comput. Appl. 2011, 20, 825–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apolloni, B.; Bassis, S.; Marinaro, M. New Directions in Neural Networks: 18th Italian Workshop on Neural Networks Wirn 2008—Volume 193 Frontiers in Artificial Intelligence and Applications; IOS Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2009; p. 270. [Google Scholar]
- Apolloni, B. Multiresolution Minimization of Renyi’s Mutual Information for Fetal-ECG Extraction, New Directions in Neural Networks: 18th Italian Workshop on Neural Networks: WIRN 2008; IOS Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2009; p. 50. [Google Scholar]
- Teipel, S.J.; Pogarell, O.; Meindl, T.; Dietrich, O.; Sydykova, D.; Hunklinger, U.; Georgii, B.; Mulert, C.; Reiser, M.F.; Moller, H.J.; et al. Regional networks underlying interhemispheric connectivity: An EEG and dti study in healthy ageing and amnestic mild cognitive impairment. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2009, 30, 2098–2119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mak-Fan, K.M.; Morris, D.; Vidal, J.; Anagnostou, E.; Roberts, W.; Taylor, M.J. White matter and development in children with an autism spectrum disorder. Autism Int. J. Res. Pract. 2013, 17, 541–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, L.; Gozzi, M.; Lenroot, R.; Thurm, A.; Behseta, B.; Swedo, S.; Pierpaoli, C. Diffusion tensor imaging in young children with autism: Biological effects and potential confounds. Biol. Psychiatry 2012, 72, 1043–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, A.S.; Han, Y.M.Y.; Sze, S.L.; Cheung, M.-C.; Leung, W.W.-M.; Chan, R.C.K.; To, C.Y. Disordered connectivity associated with memory deficits in children with autism spectrum disorders. Res. Autism Spect. Disord. 2011, 5, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vissers, M.E.; Cohen, M.X.; Geurts, H.M. Brain connectivity and high functioning autism: A promising path of research that needs refined models, methodological convergence, and stronger behavioral links. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2012, 36, 604–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zikopoulos, B.; Barbas, H. Altered neural connectivity in excitatory and inhibitory cortical circuits in autism. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2013, 7, 609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagherzadeh, S.; Sheikhani, A.; Behnam, H. Evaluation of EEG synchronization in autistic children using cross-sample entropy and cross-approximate entropy. Open Sci. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2015, 2, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Carper, R.A.; Moses, P.; Tigue, Z.D.; Courchesne, E. Cerebral lobes in autism: Early hyperplasia and abnormal age effects. NeuroImage 2002, 16, 1038–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geschwind, D.H.; Levitt, P. Autism spectrum disorders: Developmental disconnection syndromes. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2007, 17, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Han, J.; Li, Y.; Kang, J.; Cai, E.; Tong, Z.; Ouyang, G.; Li, X. Global Synchronization of Multichannel EEG Based on Rényi Entropy in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 257. https://doi.org/10.3390/app7030257
Han J, Li Y, Kang J, Cai E, Tong Z, Ouyang G, Li X. Global Synchronization of Multichannel EEG Based on Rényi Entropy in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder. Applied Sciences. 2017; 7(3):257. https://doi.org/10.3390/app7030257
Chicago/Turabian StyleHan, Junxia, Yanzhu Li, Jiannan Kang, Erjuan Cai, Zhen Tong, Gaoxiang Ouyang, and Xiaoli Li. 2017. "Global Synchronization of Multichannel EEG Based on Rényi Entropy in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder" Applied Sciences 7, no. 3: 257. https://doi.org/10.3390/app7030257
APA StyleHan, J., Li, Y., Kang, J., Cai, E., Tong, Z., Ouyang, G., & Li, X. (2017). Global Synchronization of Multichannel EEG Based on Rényi Entropy in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder. Applied Sciences, 7(3), 257. https://doi.org/10.3390/app7030257







