Fabrication and Characterizations of Hot-Melt Extruded Nanocomposites Based on Zinc Sulfate Monohydrate and Soluplus
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
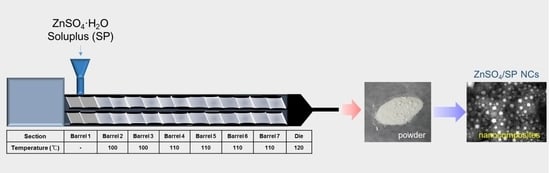
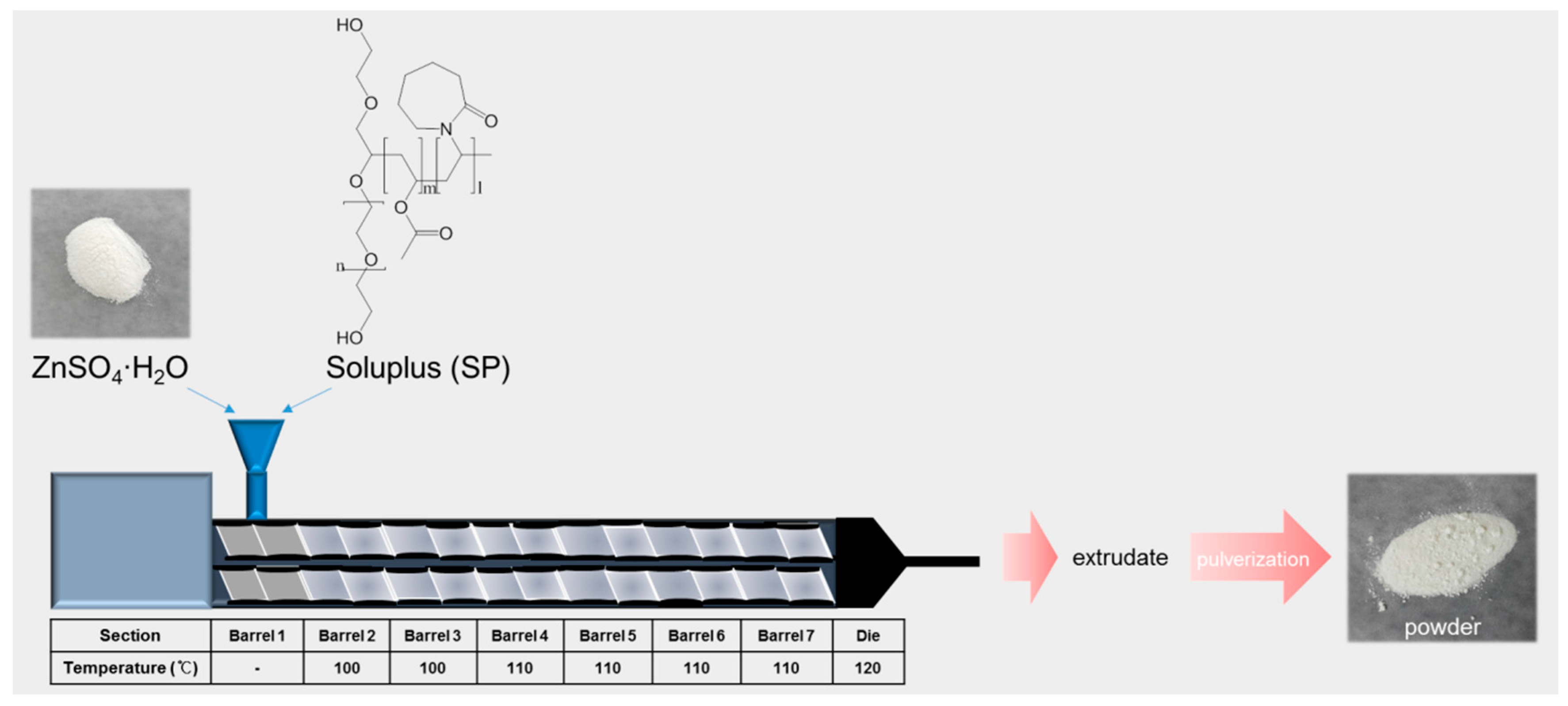
2.2. Preparation and Particle Characterizations of ZnSO4/SP NCs
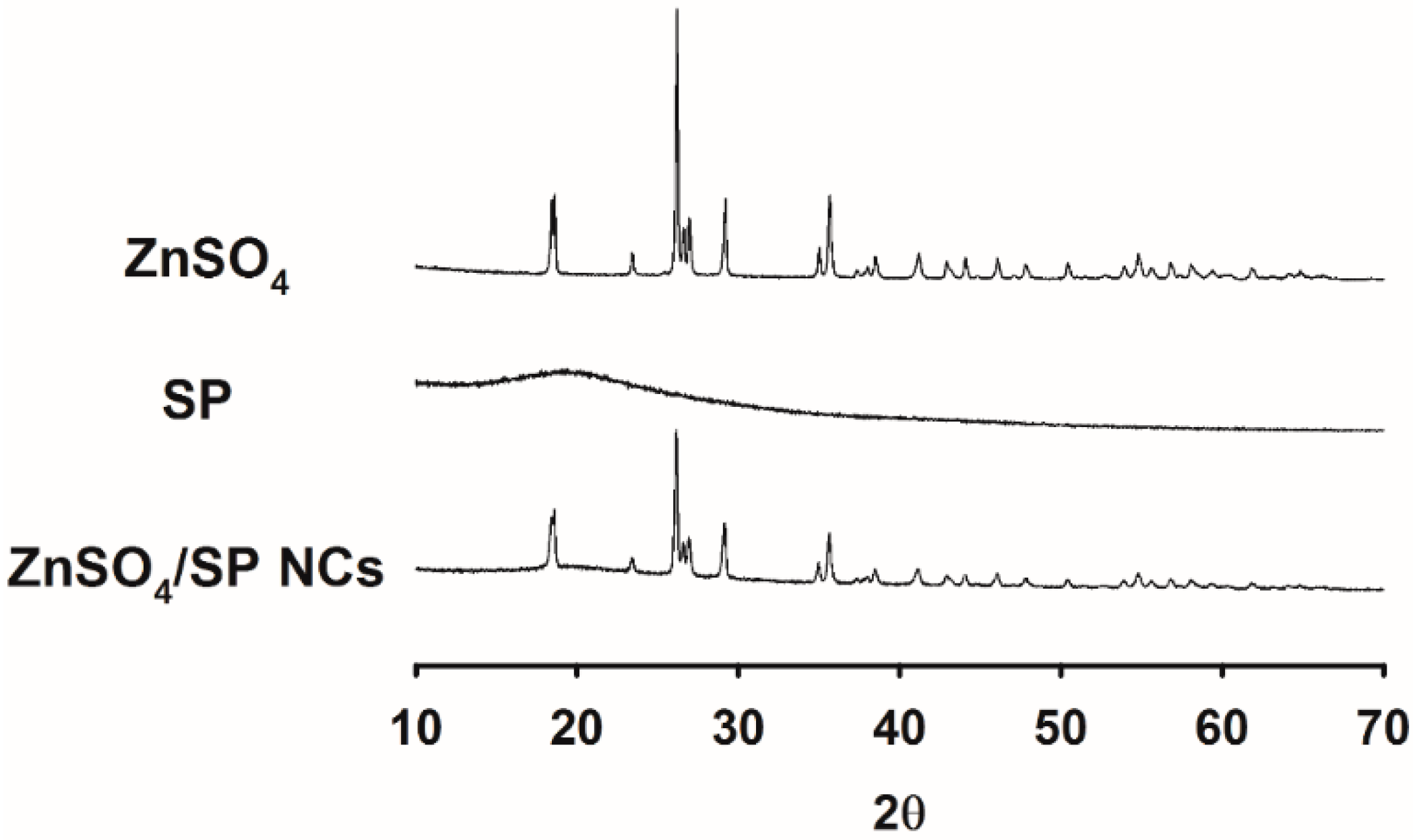
2.3. X-ray Diffractometry (XRD) Analysis
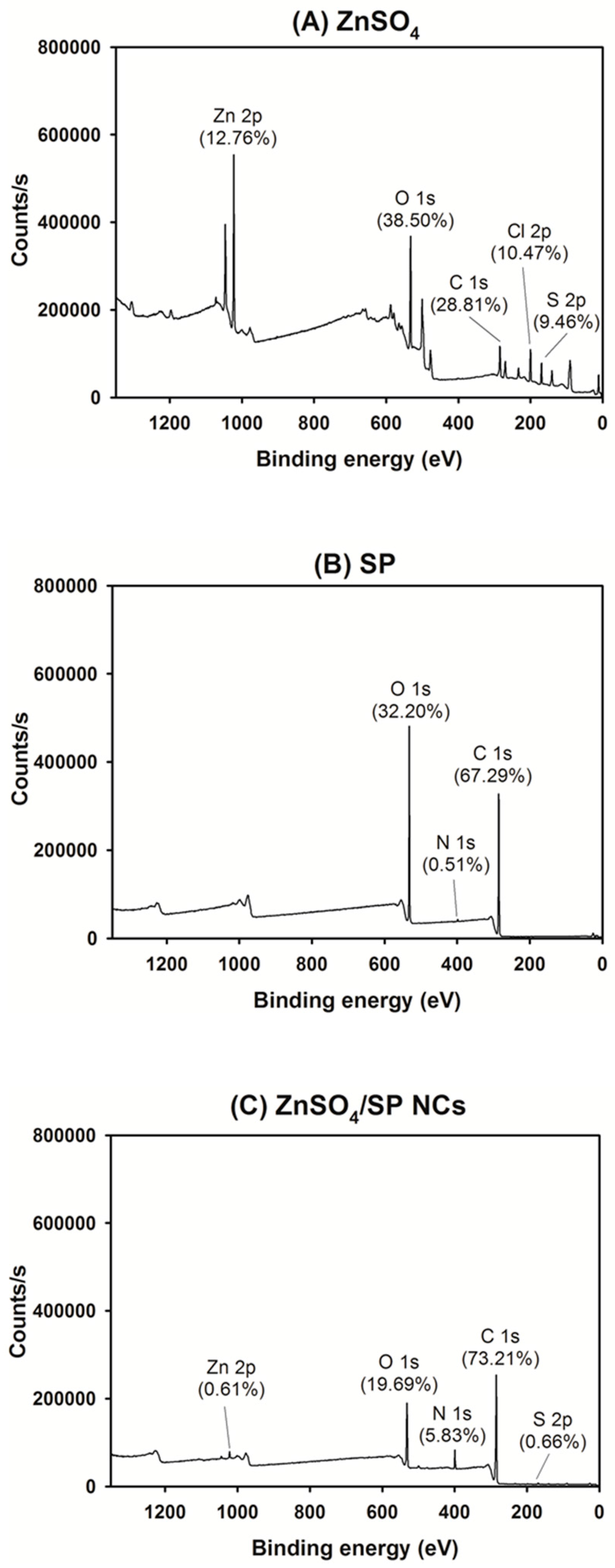
2.4. X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (XPS) Assay
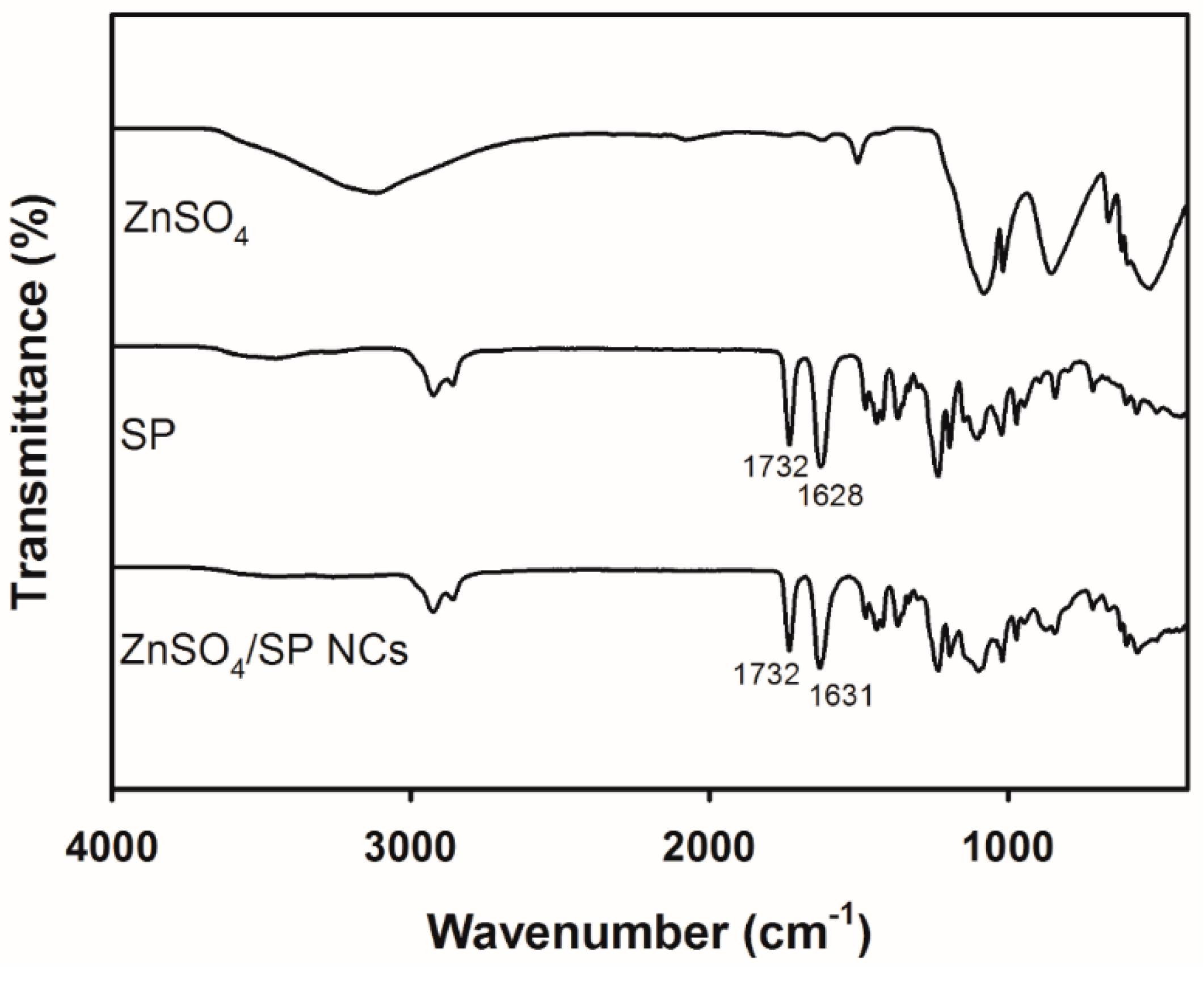
2.5. Fourier-Transform Infrared (FT-IR) Analysis
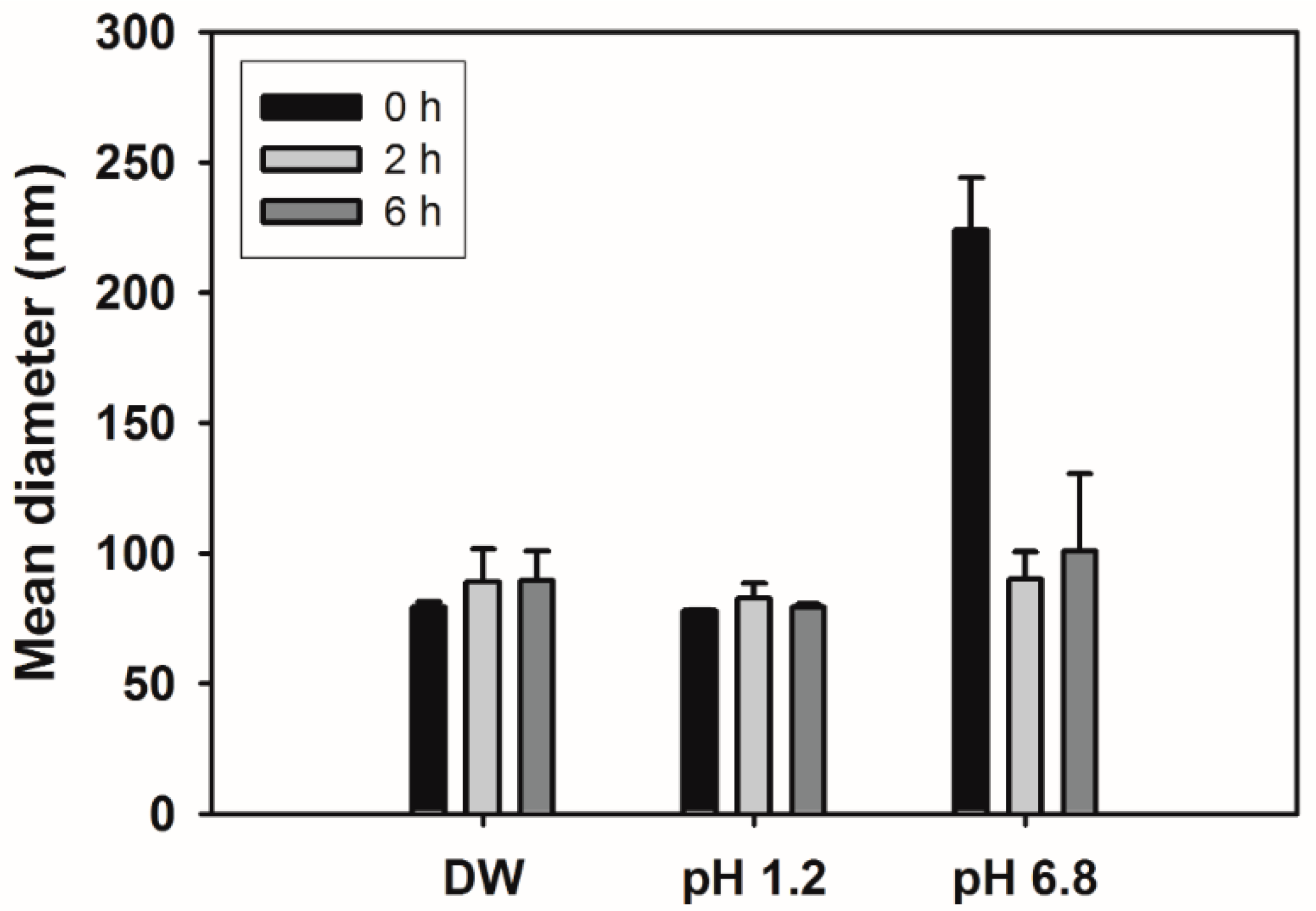
2.6. Stability Test of NCs
2.7. Toxicity Test of NCs
2.8. Data Analyses
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Preparation and Particle Characterizations of ZnSO4/SP NCs
3.2. Solid-State Studies
3.3. Stability of NCs
3.4. Intestinal Toxicity of NCs
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Livingstone, C. Zinc: Physiology, deficiency, and parenteral nutrition. Nutr. Clin. Pract. 2015, 30, 371–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turnlund, J.R.; King, J.C.; Keyes, W.R.; Gong, B.; Michel, M.C. A stable isotope study of zinc absorption in young men: Effects of phytate and alpha-cellulose. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1984, 40, 1071–1077. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cousins, R.J. Absorption, transport and hepatic metabolism of copper and zinc: Special reference to metallothionein and ceruloplasmin. Physiol. Rev. 1985, 65, 238–309. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kenny, F.; Sriram, K.; Hammond, J. Clinical zinc deficiency during adequate enteral nutrition. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 1989, 8, 83–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hambidge, M.; Krebs, N.F. Interrelationships of key variables of human zinc homeostasis: Relevance to dietary zinc requirements. Ann. Rev. Nutr. 2001, 21, 429–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, C.N.R.; Matte, H.R.; Voggu, R.; Govindaraj, A. Recent progress in the synthesis of inorganic nanoparticles. Dalton Trans. 2012, 41, 5089–5120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maniruzzaman, M.; Nokhodchi, A. Continuous manufacturing via hot-melt extrusion and scale up: Regulatory matters. Drug Discov. Today 2017, 22, 340–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, I.; Kang, C.Y.; Park, J.B. Advances in hot-melt extrusion technology toward pharmaceutical objectives. J. Pharm. Investig. 2017, 47, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, H.; Tiwari, R.V.; Repka, M.A. Hot-melt extrusion: From theory to application in pharmaceutical formulation. AAPS PharmSciTech 2016, 17, 20–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piao, J.; Lee, J.Y.; Weon, J.B.; Ma, C.J.; Ko, H.J.; Kim, D.D.; Kang, W.S.; Cho, H.J. Angelica gigas Nakai and Soluplus-based solid formulations prepared by hot-melting extrusion: Oral absorption enhancing and memory ameliorating effects. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0124447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stanković, M.; Frijlink, H.W.; Hinrichs, W.L. Polymeric formulations for drug release prepared by hot melt extrusion: Application and characterization. Drug Discov. Today 2015, 20, 812–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaiswar, D.R.; Jha, D.; Amin, P.D. Preparation and characterizations of stable amorphous solid solution of azithromycin by hot melt extrusion. J. Pharm. Investig. 2016, 46, 655–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, B.; McGinity, J.W.; Williams, R.O. Hot-melt extrusion—Basic principles and pharmaceutical applications. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2014, 40, 1133–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.Y.; Kang, W.S.; Piao, J.; Yoon, I.S.; Kim, D.D.; Cho, H.J. Soluplus®/TPGS-based solid dispersions prepared by hot-melt extrusion equipped with twin-screw systems for enhancing oral bioavailability of valsartan. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2015, 9, 2745–2756. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, J.; Cuellar, K.; Hammer, N.I.; Jo, S.; Gryczke, A.; Kolter, K.; Langley, N.; Repka, M.A. Solid-state characterization of Felodipine-Soluplus amorphous solid dispersions. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2016, 42, 485–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thiry, J.; Kok, M.G.; Collard, L.; Frère, A.; Krier, F.; Fillet, M.; Evrard, B. Bioavailability enhancement of itraconazole-based solid dispersions produced by hot melt extrusion in the framework of the Three Rs rule. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 99, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Luo, Y.; Yao, Q.; Zhong, Y.; Tian, B.; Tang, X. Extruded Soluplus/SIM as an oral delivery system: Characterization, interactions, in vitro and in vivo evaluations. Drug Deliv. 2016, 23, 1902–1911. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Han, S.D.; Jung, S.W.; Jang, S.W.; Jung, H.J.; Son, M.; Kim, B.M.; Kang, M.J. Preparation of solid dispersion of dronedarone hydrochloride with Soluplus® by hot melt extrusion technique for enhanced drug release. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2015, 63, 295–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crowley, M.M.; Zhang, F.; Repka, M.A.; Thumma, S.; Upadhye, S.B.; Battu, S.K.; McGinity, J.W.; Martin, C. Pharmaceutical applications of hot-melt extrusion: Part I. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2007, 33, 909–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.L.; Vasoya, J.M.; Cirqueira, M.L.; Yeh, K.L.; Lee, T.; Serajuddin, A.T. Continuous preparation of 1:1 haloperidol-maleic acid salt by a novel solvent-free method using a twin screw melt extruder. Mol. Pharm. 2017, 14, 1278–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Meng, X.; Wang, Z.; Fan, A.; Wang, G.; Zhao, Y.; Tang, Y. Engineering hot-melt extruded solid dispersion for controlled release of hydrophilic drugs. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 100, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, D.S.; Tian, Y.; Li, S.; Yu, T.; Abu-Diak, O.A.; Andrews, G.P. The use of binary polymeric networks in stabilizing polyethylene oxide solid dispersions. J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 105, 3064–3072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGinity, J.W.; Zhang, F.; Koleng, J.; Repka, M. Hot-melt extrusion as a pharmaceutical process. Am. Pharm. Rev. 2001, 4, 25–37. [Google Scholar]
- Wahl, P.R.; Treffer, D.; Mohr, S.; Roblegg, E.; Koscher, G.; Khinast, J.G. Inline monitoring and a PAT strategy for pharmaceutical hot melt extrusion. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 455, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sivanesan, G.; Kolandaivel, P.; Selvasekarapandian, S. Laser Raman and FT-IR studies of pure and Zn-doped TGS. Mater. Chem. Phys. 1993, 34, 73–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Valenzano, M.C.; Mercado, J.M.; Zurbach, E.P.; Mullin, J.M. Zinc supplementation modifies tight junctions and alters barrier function of CACO-2 human intestinal epithelial layers. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2013, 58, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zödl, B.; Zeiner, M.; Sargazi, M.; Roberts, N.B.; Marktl, W.; Steffan, I.; Ekmekcioglu, C. Toxic and biochemical effects of zinc in Caco-2 cells. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2003, 97, 324–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
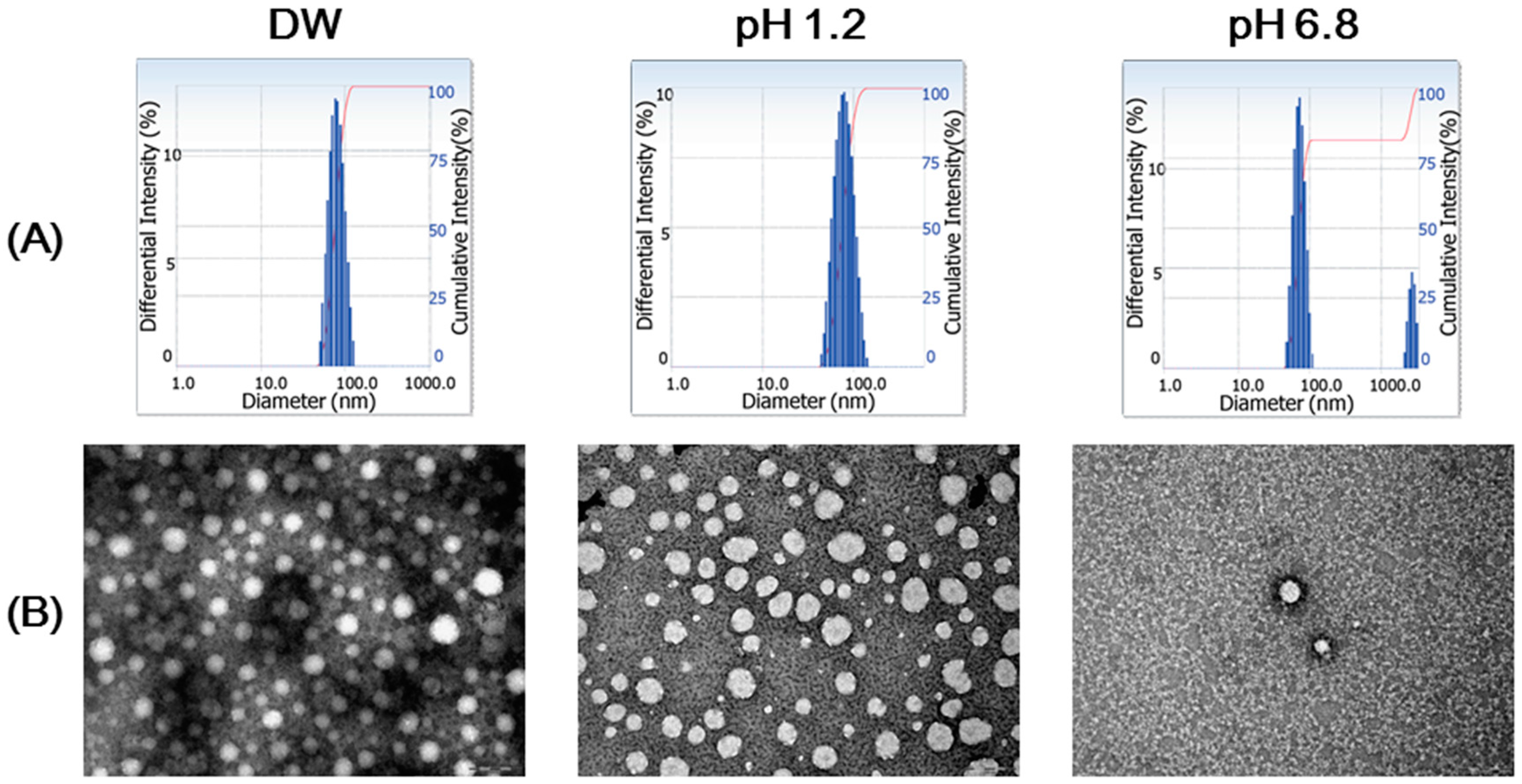

| Formulation | Mean Diameter (nm) | Polydispersity Index | Zeta Potential (mV) |
|---|---|---|---|
| ZnSO4/SP NCs | 75 ± 2 | 0.10 ± 0.01 | −1.0 ± 1.3 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, S.Y.; Nam, S.; Choi, Y.; Kim, M.; Koo, J.S.; Chae, B.-J.; Kang, W.-S.; Cho, H.-J. Fabrication and Characterizations of Hot-Melt Extruded Nanocomposites Based on Zinc Sulfate Monohydrate and Soluplus. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 902. https://doi.org/10.3390/app7090902
Lee SY, Nam S, Choi Y, Kim M, Koo JS, Chae B-J, Kang W-S, Cho H-J. Fabrication and Characterizations of Hot-Melt Extruded Nanocomposites Based on Zinc Sulfate Monohydrate and Soluplus. Applied Sciences. 2017; 7(9):902. https://doi.org/10.3390/app7090902
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Song Yi, Suyeong Nam, Yohan Choi, Minju Kim, Ja Seong Koo, Byung-Jo Chae, Wie-Soo Kang, and Hyun-Jong Cho. 2017. "Fabrication and Characterizations of Hot-Melt Extruded Nanocomposites Based on Zinc Sulfate Monohydrate and Soluplus" Applied Sciences 7, no. 9: 902. https://doi.org/10.3390/app7090902
APA StyleLee, S. Y., Nam, S., Choi, Y., Kim, M., Koo, J. S., Chae, B.-J., Kang, W.-S., & Cho, H.-J. (2017). Fabrication and Characterizations of Hot-Melt Extruded Nanocomposites Based on Zinc Sulfate Monohydrate and Soluplus. Applied Sciences, 7(9), 902. https://doi.org/10.3390/app7090902