Effect of Fly Ash on the Properties of Ceramics Prepared from Steel Slag
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Raw Materials
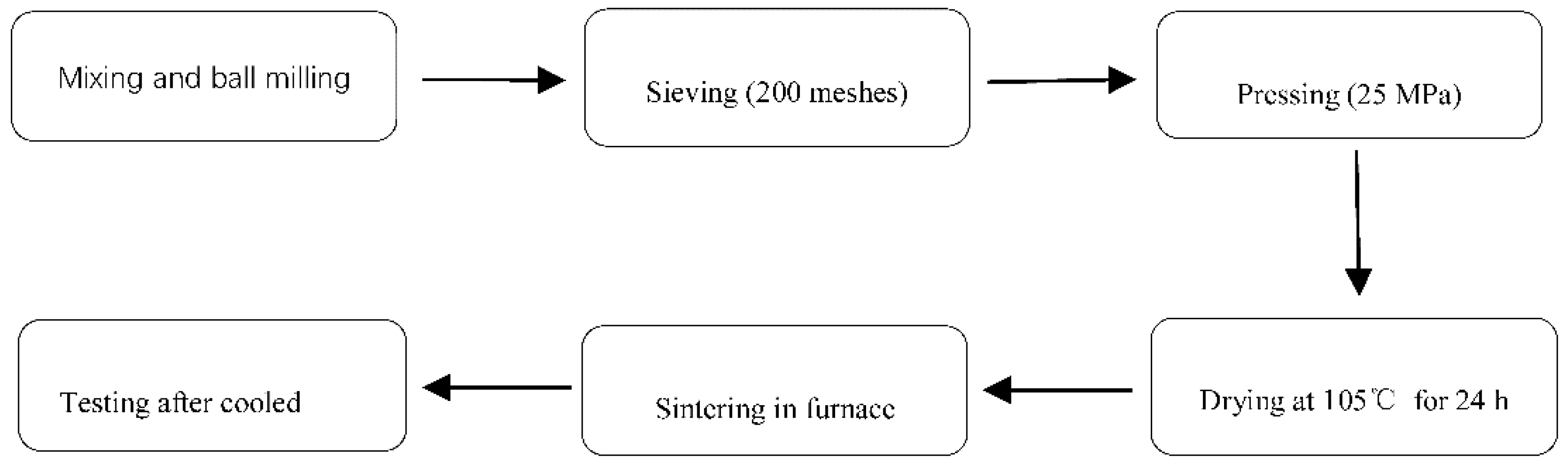
2.2. Preparation of Ceramic Samples
2.3. Characterization of Ceramic Samples
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Physical and Mechanical Properties
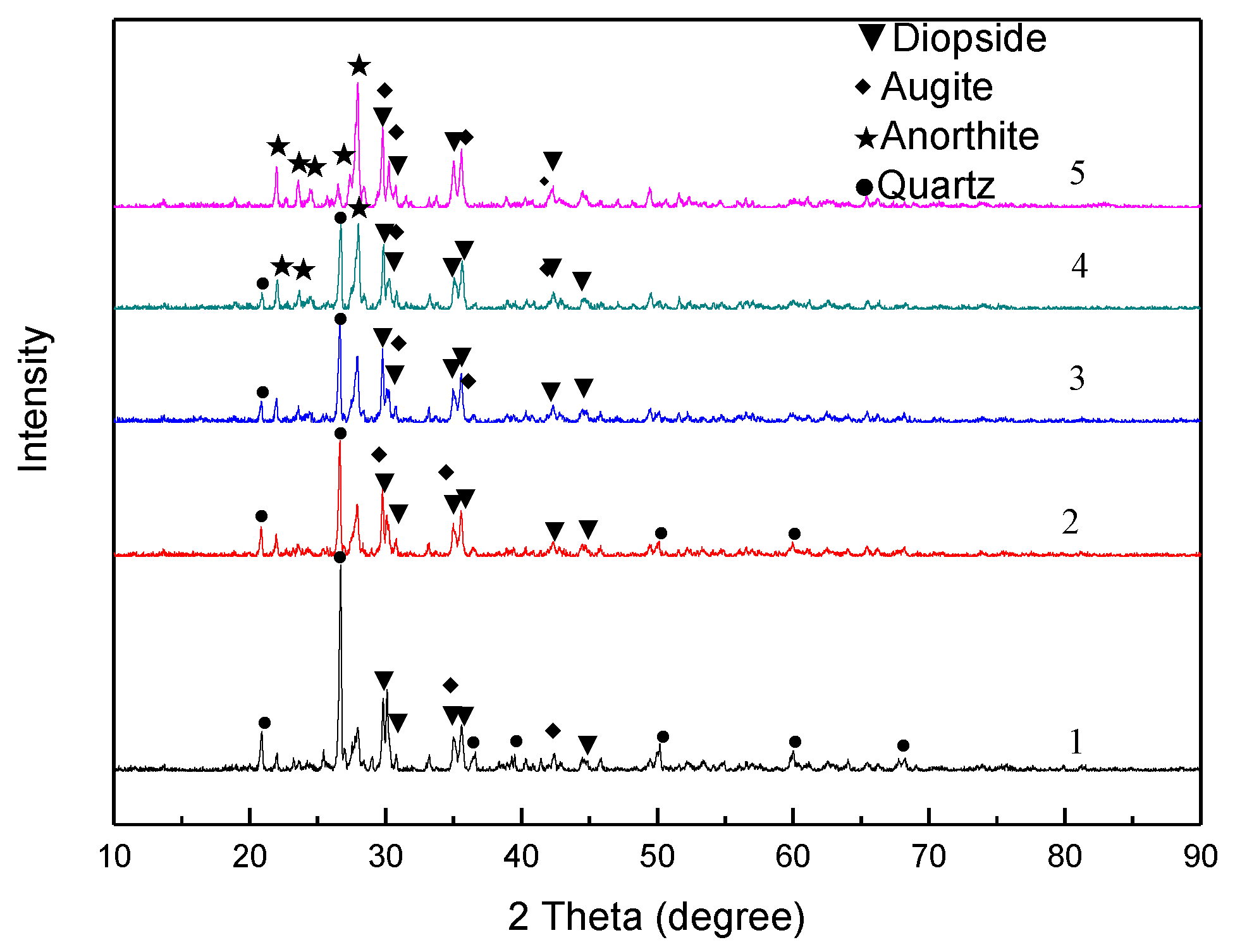
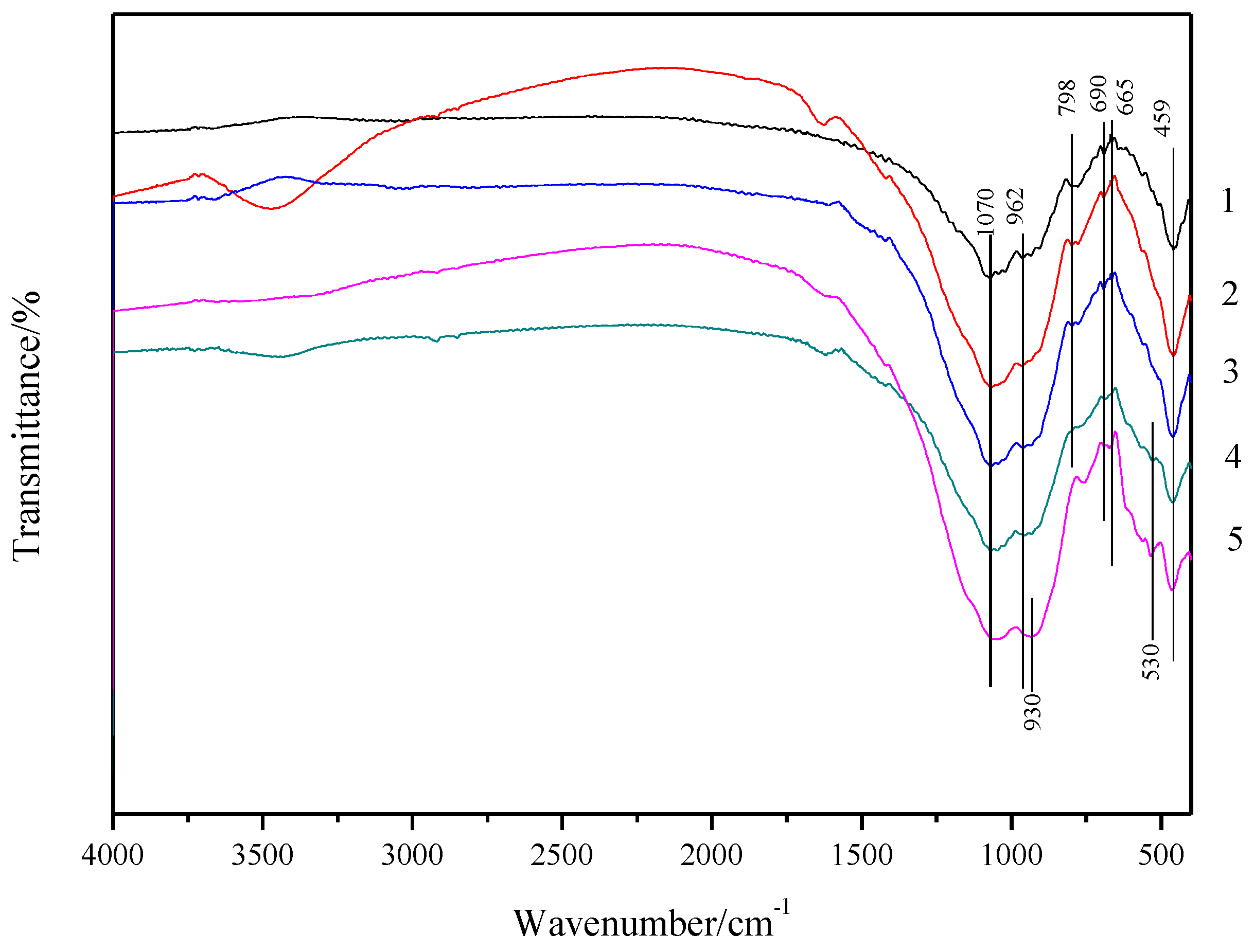
3.2. XRD and FTIR Analyses
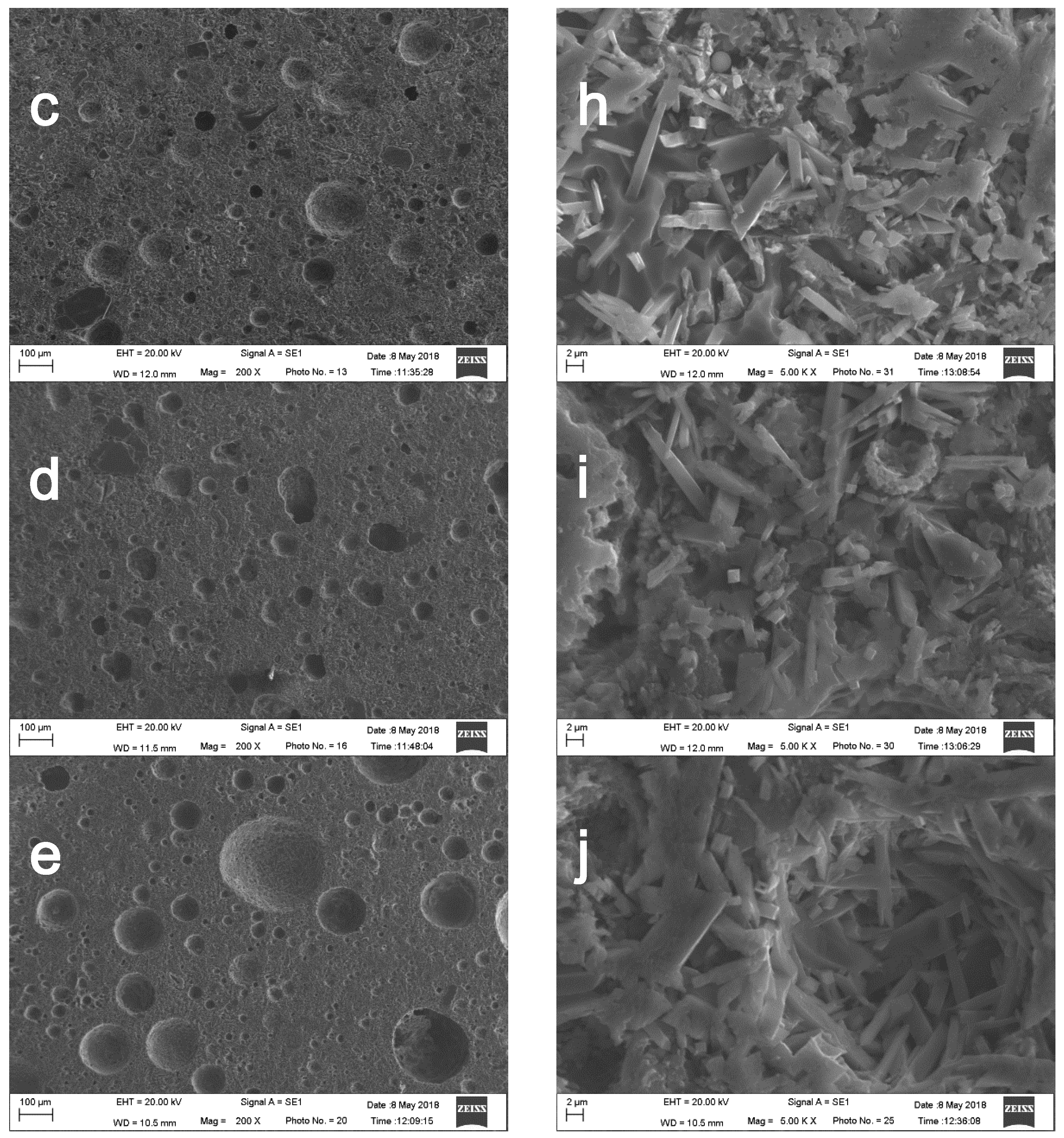
3.3. SEM Analysis
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- Based on the steel slag ceramic, fly ash was used at a maximum addition amount of 20 wt %. Sample 4 with a fly ash content of 15 wt % exhibited a sintering shrinkage of 7.36% at the optimum sintering temperature, and its bending strength and water absorption were 43.37 MPa and 0.03%, respectively, which is better than the requirements of the Chinese national standard GBT 4100-2015 for ceramic tile. The range of sintering temperature widened from 1130–1135 °C to 1135–1150 °C, allowing the addition of up to 50 wt % of solid waste.
- (2)
- With an increase in the fly ash addition amount, the diffraction peak of the quartz phase in the sintered sample gradually decreased. The main phases of the sample without added fly ash are the quartz, diopside, and augite phases. When the amount is 15 wt %, the diffraction peak of the anorthite phase increased. The main crystal phases were quartz, diopside, augite, and anorthite phases. When the addition amount increased to 20 wt %, the diffraction peak of the quartz phase disappeared.
- (3)
- The pore size of the sintered ceramic samples increased with an increase in the fly ash addition amount, which is an important factor affecting the strength of the sample, and the size of the lath-shaped crystals was roughly the same. The addition of fly ash leads to an increase in the Al2O3 content, which increased the viscosity of the liquid phase; this affected the structure of the glass phase and increased the optimal sintering temperature.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guzel, G.; Deveci, H. Properties of polymer composites based on bisphenol a epoxy resins with original/modified steel slag. Polym. Compos. 2018, 39, 513–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Xu, J. The Status and Development of Steel Slag Hot Stew Method. Ind. Heat. 2016, 4, 68–70. [Google Scholar]
- Ning, D.; Liang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Xiao, J.; Duan, A. Impacts of steel-slag-based silicate fertilizer on soil acidity and silicon availability and metals-immobilization in a paddy soil. PLOS ONE 2016, 11, e168163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Yang, M.; Xiu, P.; Zhao, X.; Bai, H.; Li, H. Characteristics of nitrate removal from aqueous solution by modified steel slag. Water 2017, 9, 757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, M.; Zeng, G.; Huang, D.; Lai, C.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, C.; Wang, R.; Qin, L.; Xue, W.; Song, B.; et al. High adsorption of methylene blue by salicylic acid–methanol modified steel converter slag and evaluation of its mechanism. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 515, 232–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, H.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, B.; Zhu, J.; Liu, D. Dynamics Study on Vanadium Extraction Technology from Chloride Leaching Steel Slag. Rare Met. Mater. Eng. 2013, 42, 696–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsakiridis, P.E.; Papadimitriou, G.D.; Tsivilis, S.; Koroneos, C. Utilization of steel slag for Portland cement clinker production. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 152, 805–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortega, J.M.; Sánchez, I.; Antón, C.; de Vera, G. Influence of Environment on Durability of Fly Ash Cement Mortars. ACI Mater. J. 2012, 109, 647. [Google Scholar]
- Joshaghani, A.; Balapour, M.; Ramezanianpour, A.A. Effect of controlled environmental conditions on mechanical, microstructural and durability properties of cement mortar. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 164, 134–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, M.; Ortega, J.M.; Sánchez, I.; Isidro, S.; Marta, C. Non-destructive study of the microstructural effects of sodium and magnesium sulphate attack on mortars containing silica fume using impedance spectroscopy. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramezanianpour, A.A.; Malhotra, V.M. Effect of curing on the compressive strength, resistance to chloride-ion penetration and porosity of concretes incorporating slag, fly ash or silica fume. Cement Concr. Compos. 1995, 17, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dana, K.; Dey, J.; Das, S.K. Synergistic effect of fly ash and blast furnace slag on the mechanical strength of traditional porcelain tiles. Ceram. Int. 2005, 31, 147–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, R.; Zhang, Z.; Yan, C.; Zhu, M.; Li, Z. Preparation of novel ceramic tiles with high Al2O3 content derived from coal fly ash. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 114, 888–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karamanova, E.; Avdeev, G.; Karamanov, A. Ceramics from blast furnace slag, kaolin and quartz. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2011, 31, 989–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, D.; Li, Y.; Cang, D. Na+ -solidification behavior of SiO2–Al2O3–CaO–MgO (10 wt %) ceramics prepared from red mud. Ceram. Int. 2017, 43, 16936–16942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Li, Y.; Cang, D. Effect of Al2O3 on the Sintering Properties of Pyroxene Ceramics. J. Synth. Cryst. 2015, 11, 3346–3349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Li, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Cang, D. Preparation of novel ceramics with high CaO content from steel slag. Mater. Des. 2014, 64, 608–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, X.B.; Li, Y.; Gu, X.M.; Cang, D.Q. Development of ceramic based on steel slag with different magnesium content. Adv. Appl. Ceram. 2013, 112, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Li, Y.; Zhang, L.; Cang, D. Effects of CaO and Fe2O3 on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of SiO2–CaO–MgO–Fe2O3 Ceramics from Steel Slag. ISIJ Int. 2017, 57, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogami, M.; Ogawa, S.; Nagasak, K. Preparation of cordierite glass by the sol-gel process. J. Mater. Sci. 1989, 24, 4339–4342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agathopoulos, S.; Tulyaganov, D.U.; Ventura, J.M.G.; Kannan, S.; Karakassides, M.A.; Ferreira, J.M.F. Formation of hydroxyapatite onto glasses of the CaO–MgO–SiO2, system with B2O3, Na2O, CaF2, and P2O5, additives. Biomaterials 2006, 27, 1832–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agathopoulos, S.; Tulyaganova, D.U.; Ventura, J.M.G.; Kannan, S.; Saranti, A.; Karakassides, M.A.; Ferreira, J.M.F. Structural analysis and devitrification of glasses based on the CaO–MgO–SiO2, system with B2O3, Na2O, CaF2, and P2O5, additives. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2006, 352, 322–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.S.; Yeo, W.J. Thermal properties of CaMgSi2O6 glass–ceramics with Al2O3. Ceram. Int. 2012, 38, S547–S550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, X.-B.; Bai, H.; Zhao, L.; Cang, D.-Q.; Tang, Q. Thermodynamic analysis and formula optimization of steel slag-based ceramic materials by FACTsage software. Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater. 2013, 20, 379–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badiee, H.; Maghsoudipour, A.; Raissi Dehkordi, B. Use of Iranian steel slag for production of ceramic floor tiles. Adv. Appl. Ceram. 2008, 107, 111–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Wei, W.; Bai, H.; Zhang, X.; Cang, D.-Q. Synthesis of steel slag ceramics: chemical composition and crystalline phases of raw materials. Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater. 2015, 22, 325–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Feng, L.; Xiangdong, L.; Xuezhi, J. Effect of CaO on Crystallization Ability of Glass Ceramics Made from Ash Fly. China Ceram. 2014, 10, 81–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, F.; Li, Y.; Zhao, L.; Cang, D. Novel ceramics prepared from inferior clay rich in CaO and Fe2O3: Properties, crystalline phases evolution and densification process. Appl. Clay Sci. 2017, 143, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Zong, Y.; Hou, J. Preparation of slag glass ceramic from electric arc furnace slag, quartz sand and talc under various MgO/Al2O3 ratios. Br. Ceram. Trans. 2015, 115, 144–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.; Drummond, I.C.H.; Wang, J. Incorporation of Chromium (III) and Chromium (VI) Oxides in a Simulated Basaltic, Industrial Waste Glass-ceramic. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2010, 87, 2047–2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caurant, D.; Loiseau, P.; Bardez, I.; Gervais, C. Effect of Al2O3, concentration on zirconolite (Ca (Zr, Hf) Ti2O7) crystallization in (TiO2, ZrO2, HfO2)-rich SiO2-Al2O3-CaO-Na2O glasses. J. Mater. Sci. 2007, 42, 8558–8570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, G.; Song, Y.; Zhang, C.; Xia, Y.; Zhang, H.; Chui, P. Diopside-based glass-ceramics from MSW fly ash and bottom ash. Waste Manag. 2006, 26, 1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Zong, Y.; Ma, H.; Dai, W.; Cang, D. Influence of Al2O3 content on microstructure and properties of different binary basicity slag glass ceramics. Adv. Appl. Ceram. 2014, 113, 394–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Content (wt %) | SiO2 | CaO | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | MgO | K2O | Na2O | TiO2 | MnO2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steel slag | 11.65 | 52.69 | 2.07 | 21.89 | 4.18 | 0.10 | 0.14 | 1.05 | 2.78 |
| Clay | 64.28 | 0.98 | 20.38 | 8.99 | 0.71 | 3.25 | 0.16 | 0.96 | - |
| Quartz | 96.5 | 0.09 | 1.85 | 0.83 | 0.11 | 0.51 | - | - | - |
| Feldspar | 65.61 | 5.98 | 15.26 | 1.33 | 0.43 | 8.65 | 2.18 | 0.18 | 0.08 |
| Talc | 61.77 | 3.57 | 0.25 | 0.23 | 34 | 0.02 | - | - | - |
| Fly ash | 47.72 | 3.57 | 41.63 | 2.89 | 0.41 | 0.62 | 0.18 | 1.82 | - |
| Sample | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steel slag | 35 | 35 | 35 | 35 | 35 |
| Clay | 25 | 25 | 25 | 25 | 25 |
| Quartz | 15 | 12.5 | 10 | 7.5 | 5 |
| Feldspar | 15 | 12.5 | 10 | 7.5 | 5 |
| Talc | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 |
| Fly ash | 0 | 5 | 10 | 15 | 20 |
| Sample | Sintering Temperature, °C | Sintering Shrinkage, % | Water Absorption, % | Flexural Strength, MPa |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1130 | 8.18 | 0.26 | 62.2 |
| 2 | 1130 | 8.28 | 0.48 | 52.89 |
| 3 | 1135 | 7.96 | 0.04 | 51.12 |
| 4 | 1145 | 8.42 | 0.03 | 43.37 |
| 5 | 1160 | 7.94 | 0.26 | 35.58 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zong, Y.; Zhang, X.; Mukiza, E.; Xu, X.; Li, F. Effect of Fly Ash on the Properties of Ceramics Prepared from Steel Slag. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 1187. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8071187
Zong Y, Zhang X, Mukiza E, Xu X, Li F. Effect of Fly Ash on the Properties of Ceramics Prepared from Steel Slag. Applied Sciences. 2018; 8(7):1187. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8071187
Chicago/Turabian StyleZong, Yanbing, Xuedong Zhang, Emile Mukiza, Xiaoxiong Xu, and Fei Li. 2018. "Effect of Fly Ash on the Properties of Ceramics Prepared from Steel Slag" Applied Sciences 8, no. 7: 1187. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8071187
APA StyleZong, Y., Zhang, X., Mukiza, E., Xu, X., & Li, F. (2018). Effect of Fly Ash on the Properties of Ceramics Prepared from Steel Slag. Applied Sciences, 8(7), 1187. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8071187




