Vibration Compensation of the Frequency-Scanning-Interferometry-Based Absolute Ranging System
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Theory Background
2.1. FSI-Based Absolute Ranging System
2.2. Analysis of Vibration Effect
2.3. Method for Vibration Influence Reduction
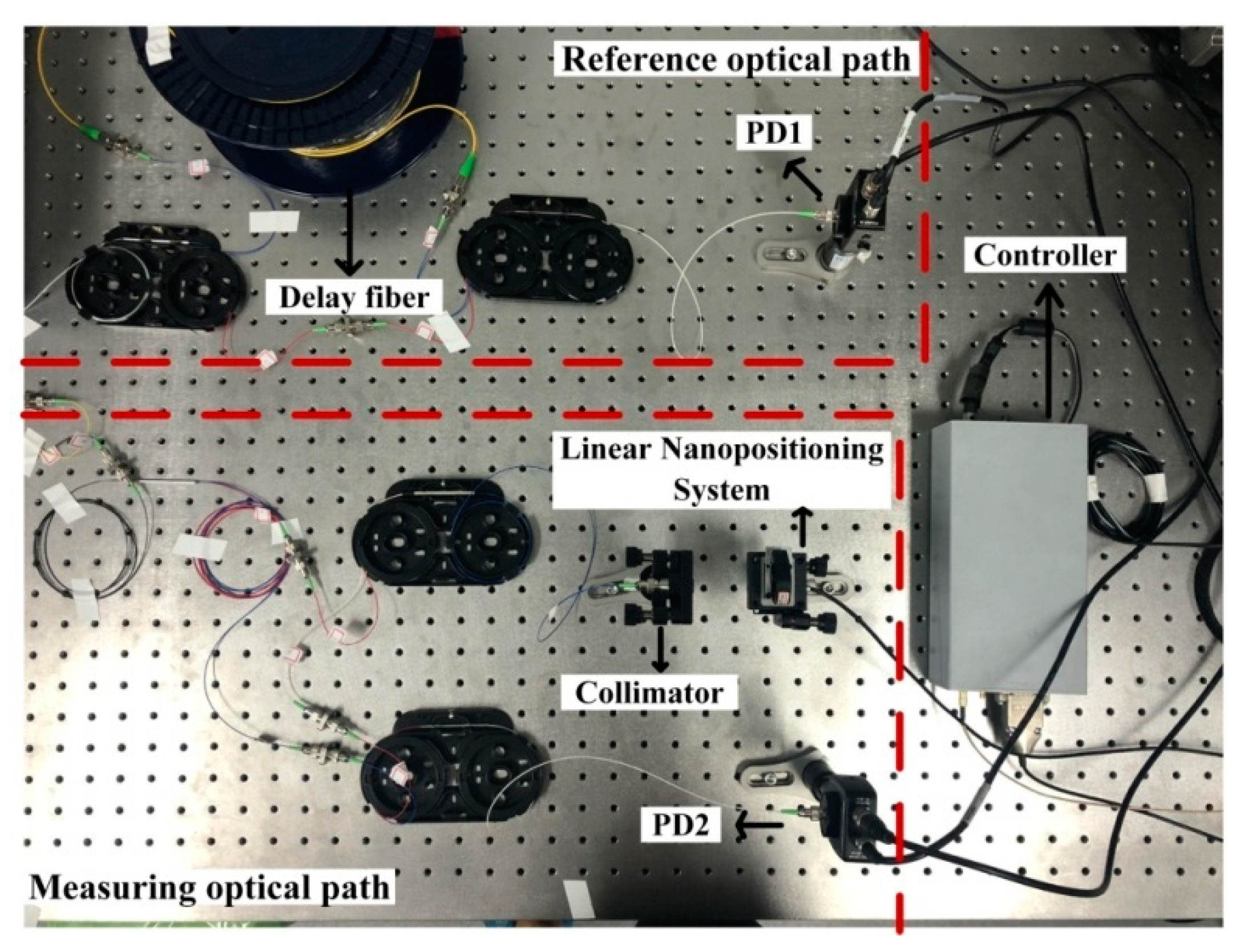
3. Experiments and Results
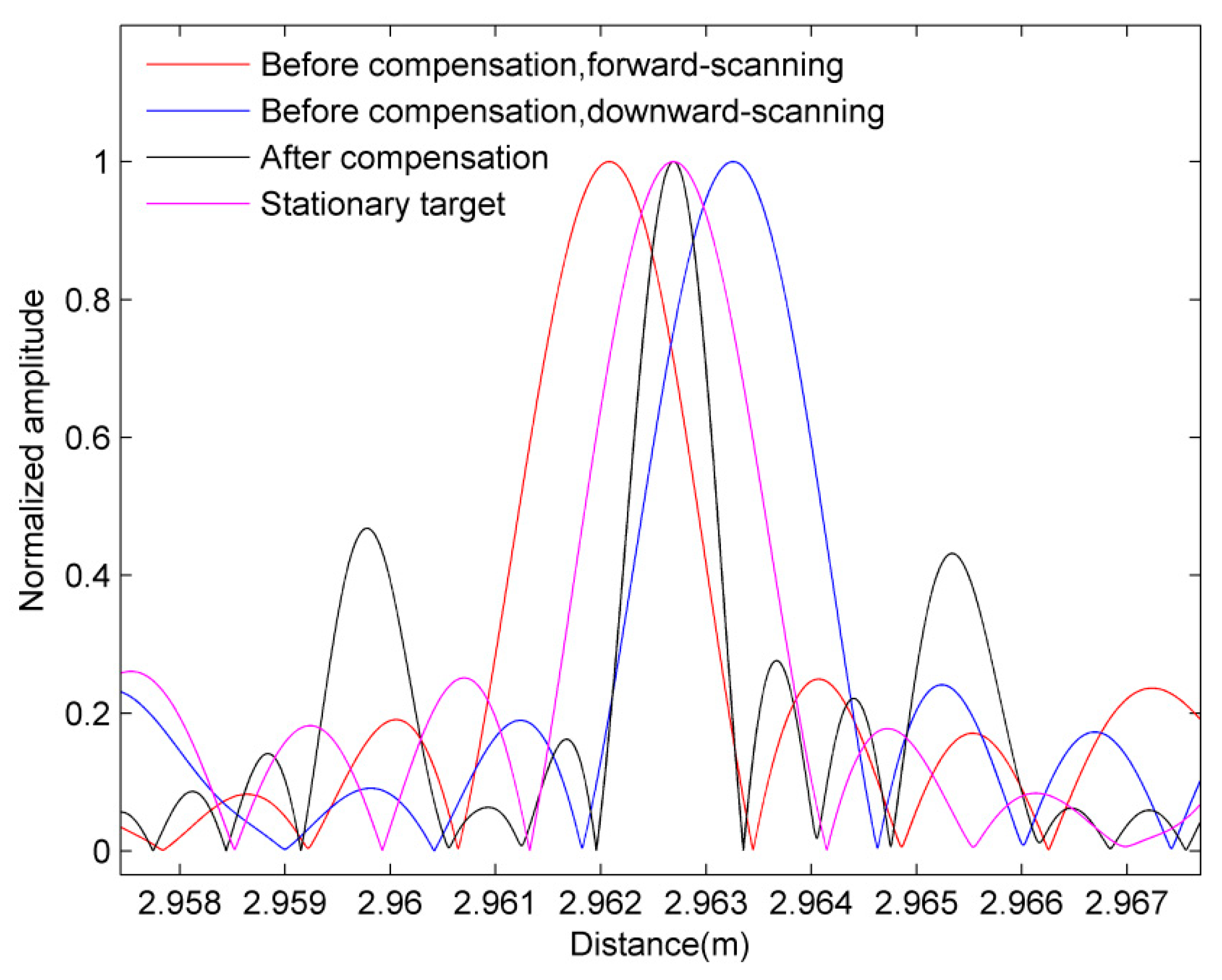
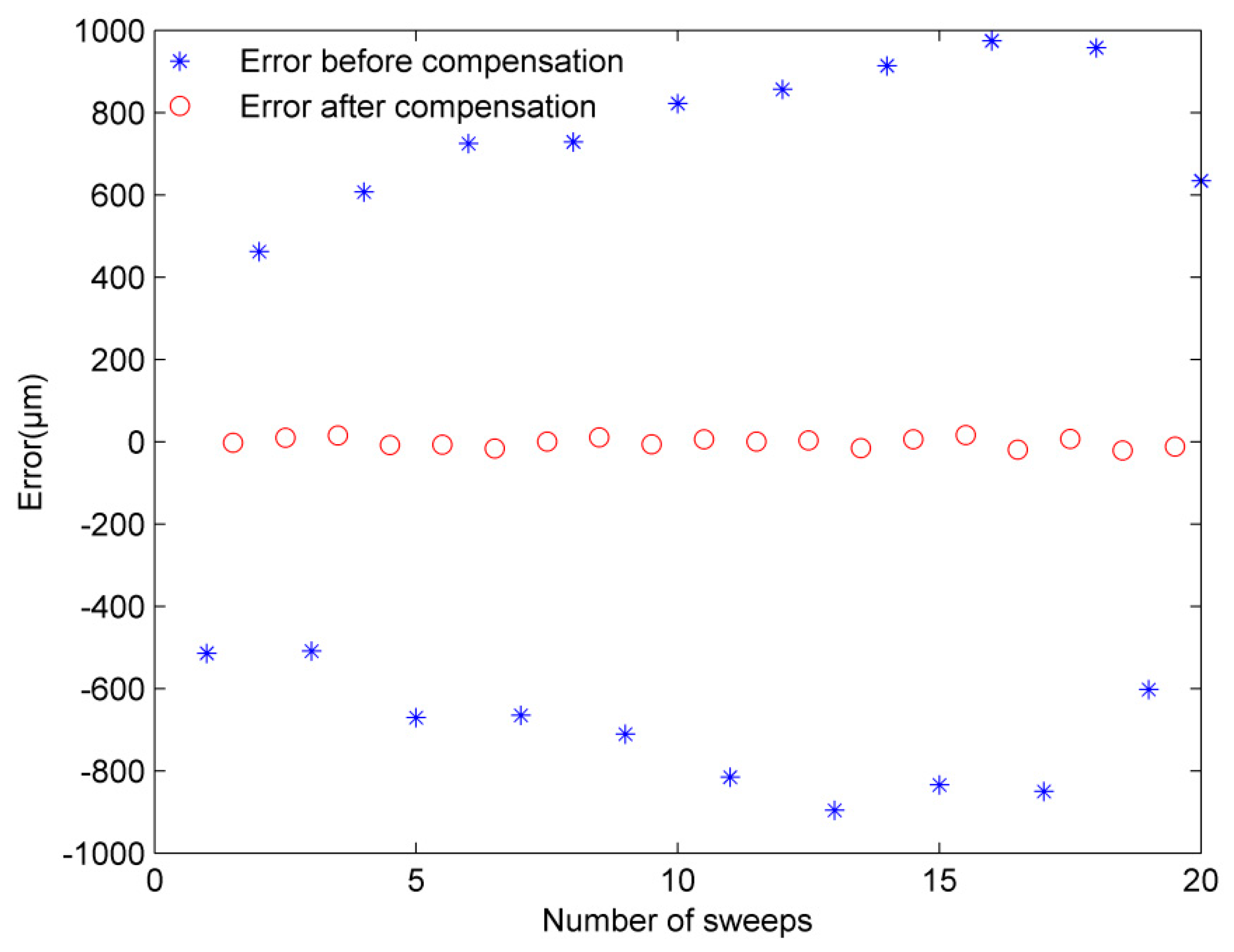
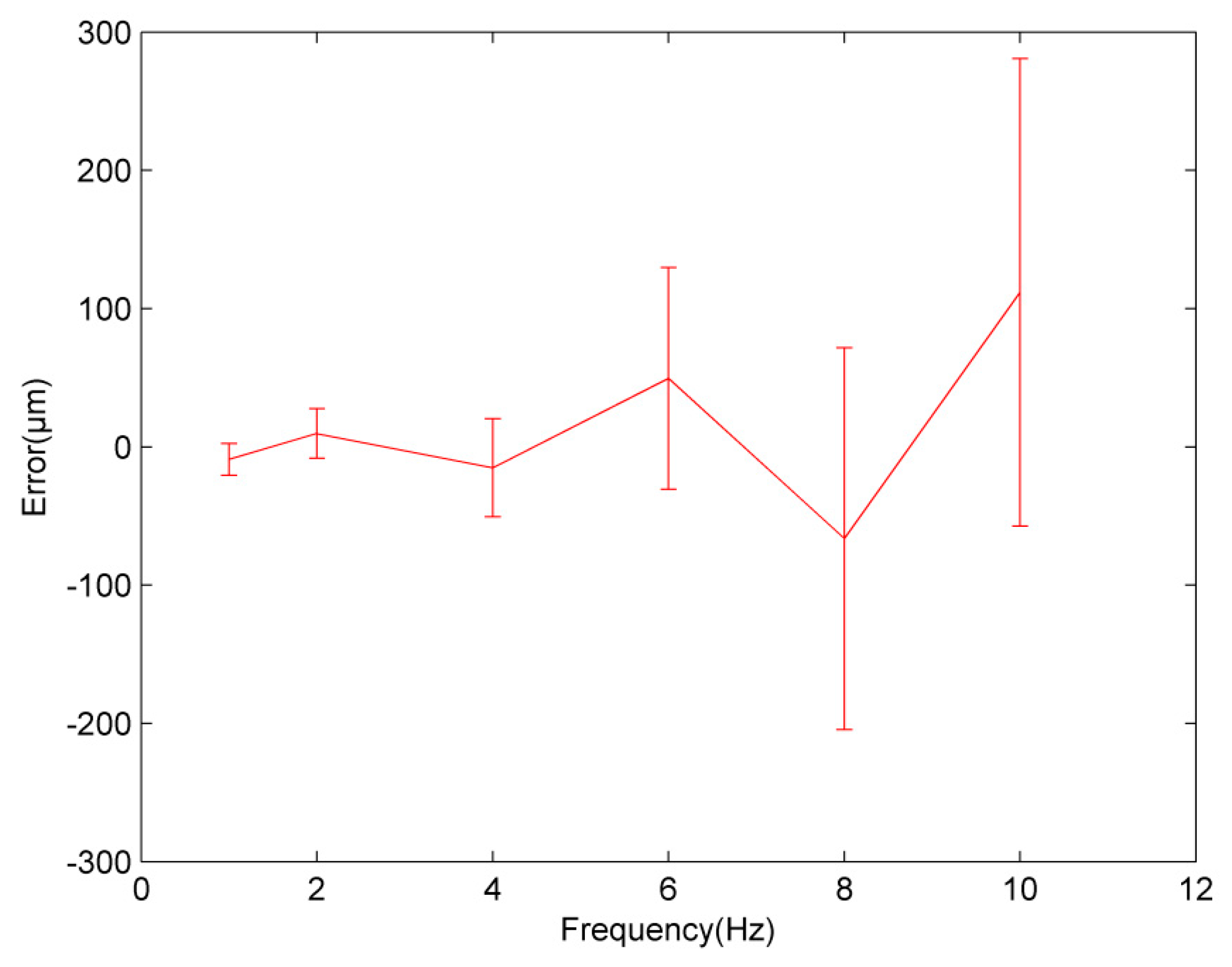
3.1. Vibration with Given Parameters
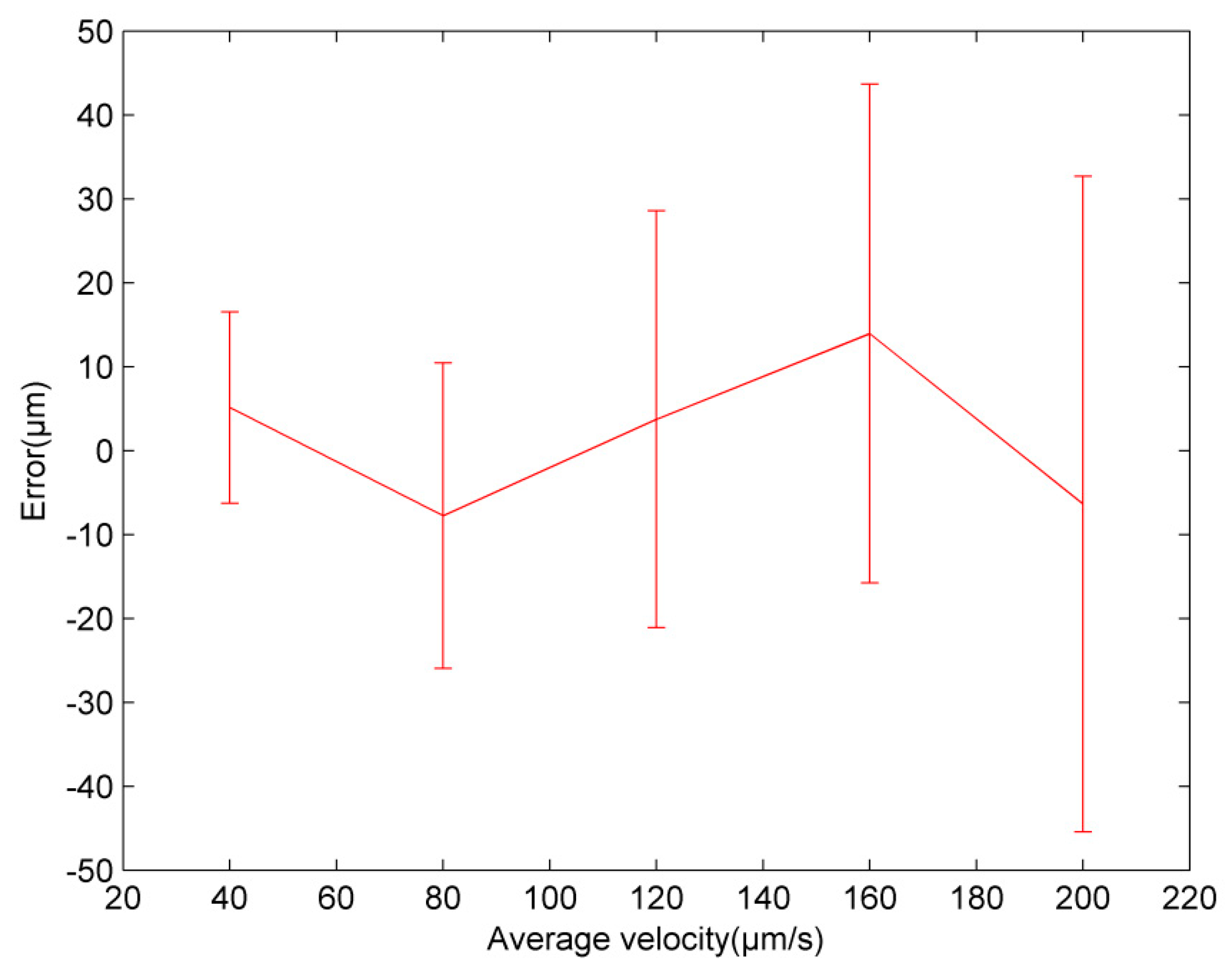
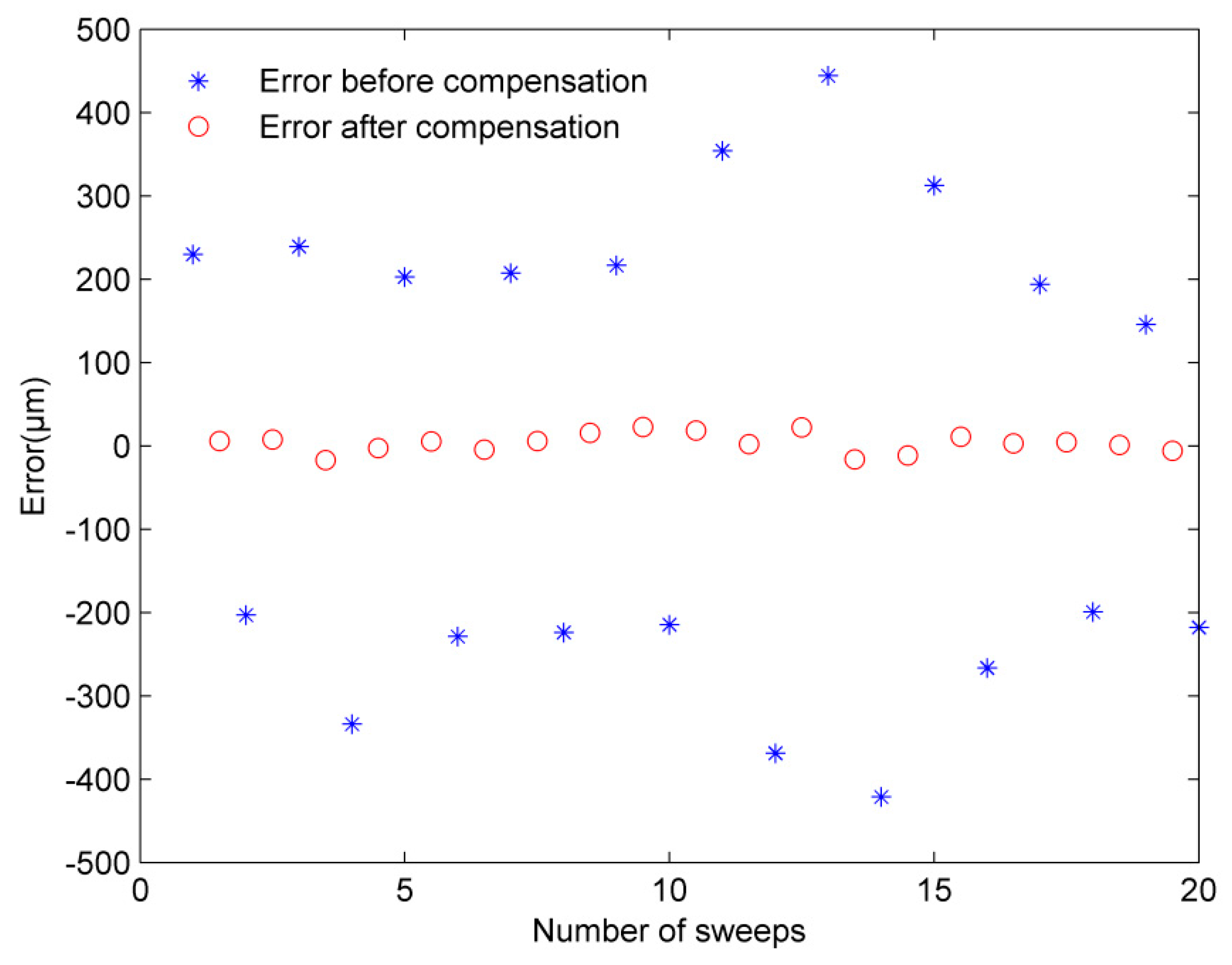
3.2. Vibration in Natural Environment
4. Analysis and Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pan, H.; Qu, X.H.; Zhang, F.M. Micron-precision measurement using a combined frequency-modulated continuous wave ladar autofocusing system at 60 meters standoff distance. Opt. Express. 2018, 26, 15186–15198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, G.; Wang, W. Single laser complex method to improve the resolution of FMCW laser ranging. J. Infrared Millim. Waves 2016, 35, 363–367. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, X.Y.; Liu, Z.G.; Deng, Z.W.; Deng, W.; Wang, Z.Y.; Zhen, Z.L. Dynamic absolute distance measurement by frequency sweeping interferometry based Doppler beat frequency tracking model. Opt. Commun. 2018, 430, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.J.; Deibel, J.; Nyberg, S.; Riles, K. High-precision absolute distance and vibration measurement with frequency scanned interferometry. Appl. Opt. 2005, 44, 3937–3944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, H.; Qu, X.H.; Shi, C.Z.; Li, Y.T.; Zhang, F.M. Precision evaluation method of measuring frequency modulated continuous wave laser distance. Acta Phys. Sin. 2018, 67, 090201. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, G.D.; Xu, X.K.; Liu, B.G.; Chen, F.D.; Hu, T.; Lu, C.; Gan, Y. A method of suppressing vibration for high precision broadband laser frequency scanning interferometry. Acta Phys. Sin. 2016, 65, 209501. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Z.Y.; Tang, L.Z.; Zhang, H.X.; Pan, S.L. Simultaneous Real-Time Ranging and Velocimetry via a Dual-Sideband Chirped Lidar. IEEE Photon. Technol. Lett. 2017, 29, 2254–2257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.J.; Wei, H.Y.; Zhang, H.Y.; Ren, L.B.; Li, Y.; Zhang, J.T. Absolute distance measurement using frequency-sweeping heterodyne interferometer calibrated by an optical frequency comb. Appl. Opt. 2013, 52, 2042–2048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.P.; Wei, H.Y.; Yang, H.L.; Wu, X.J.; Li, Y. Comb-referenced frequency-sweeping interferometry for precisely measuring large stepped structures. Appl. Opt. 2018, 57, 1247–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.J.; Wu, X.J.; Wei, H.Y.; Li, Y. Frequency comb calibrated frequency-sweeping interferometry for absolute group refractive index measurement of air. Appl. Opt. 2017, 56, 3109–3115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kakuma, S. Frequency-modulated continuous-wave laser radar using dual vertical-cavity surface-emitting laser diodes for real-time measurements of distance and radial velocity. Opt. Rev. 2017, 24, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, L.; Liu, Z.G.; Zhang, W.B.; Zhou, Y.L. Frequency-scanning interferometry for dynamic absolute distance measurement using Kalman filter. Opt. Lett. 2014, 39, 6997–7000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onori, D.; Scotti, F.; Scaffardi, M.; Bogoni, A.; Laghezza, F. Coherent Interferometric Dual-Frequency Laser Radar for Precise Range/Doppler Measurement. J. Lightw. Technol. 2016, 34, 4828–4834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakuma, S.; Katase, Y. Frequency scanning interferometry immune to length drift using a pair of vertical-cavity surface-emitting laser diodes. Opt. Rev. 2012, 19, 376–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, R.; Thurmel, P.; Stockmann, M. Distance measurement of moving objects by frequency modulated laser radar. Opt. Eng. 2001, 40, 33–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swinkels, B.L.; Bhattacharya, N.; Braat, J.J.M. Correcting movement errors in frequency-sweeping interferometry. Opt. Lett. 2005, 30, 2242–2244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, Y.; Ren, D.M.; Zhao, W.J.; Qu, Y.C.; Qian, L.M.; Chen, Z.L. Heterodyne Doppler velocity measurement of moving targets by mode-locked pulse laser. Opt. Express. 2012, 20, 764–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, C.; Liu, G.D.; Liu, B.G.; Chen, F.D.; Gan, Y. Absolute distance measurement system with micron-grade measurement uncertainty and 24 m range using frequency scanning interferometry with compensation of environmental vibration. Opt. Express. 2016, 24, 30215–30224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez, J.J.; Campbell, M.A.; Warden, M.S.; Hughes, E.B.; Copner, N.J.; Lewis, A.J. Dual-Sweep Frequency Scanning Interferometry Using Four Wave Mixing. IEEE Photon. Technol. Lett. 2015, 27, 733–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, X.Y.; Liu, Z.G.; Tao, L.; Deng, Z.W. Frequency-scanning interferometry using a time-varying Kalman filter for dynamic tracking measurements. Opt. Express. 2017, 25, 25782–25796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, X.S.; Zhang, F.M.; Qu, X.H. High precision and fast method for absolute distance measurement based on resampling technique used in FM continuous wave laser ranging. Acta Phys. Sin. 2015, 64, 2306010. [Google Scholar]
- Ahn, T.J.; Kim, D.Y. Analysis of nonlinear frequency sweep in high-speed tunable laser sources using a self-homodyne measurement and Hilbert transformation. Appl. Opt. 2007, 46, 2394–2400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, G.; Zhang, F.M.; Qu, X.H.; Meng, X.S. Absolute distance measurement by high resolution frequency modulated continuous wave laser. Acta Phys. Sin. 2014, 63, 184209. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, J. Continued analysis of optical frequency-modulated continuous-wave interference. Appl. Opt. 2005, 44, 765–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, Z.W.; Liu, Z.G.; Li, B.; Liu, Z. Precision improvement in frequency-scanning interferometry based on suppressing nonlinear optical frequency sweeping. Opt. Rev. 2015, 22, 724–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, F.-M.; Li, Y.-T.; Pan, H.; Shi, C.-Z.; Qu, X.-H. Vibration Compensation of the Frequency-Scanning-Interferometry-Based Absolute Ranging System. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 147. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9010147
Zhang F-M, Li Y-T, Pan H, Shi C-Z, Qu X-H. Vibration Compensation of the Frequency-Scanning-Interferometry-Based Absolute Ranging System. Applied Sciences. 2019; 9(1):147. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9010147
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Fu-Min, Ya-Ting Li, Hao Pan, Chun-Zhao Shi, and Xing-Hua Qu. 2019. "Vibration Compensation of the Frequency-Scanning-Interferometry-Based Absolute Ranging System" Applied Sciences 9, no. 1: 147. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9010147
APA StyleZhang, F.-M., Li, Y.-T., Pan, H., Shi, C.-Z., & Qu, X.-H. (2019). Vibration Compensation of the Frequency-Scanning-Interferometry-Based Absolute Ranging System. Applied Sciences, 9(1), 147. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9010147





