Severe Asthma and Biological Therapies: Now and the Future
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Definition of Severe Asthma
1.2. When a Biological Treatment Should Be Considered
2. Phenotypes and Biomarkers
2.1. Phenotypes
2.2. Biomarkers
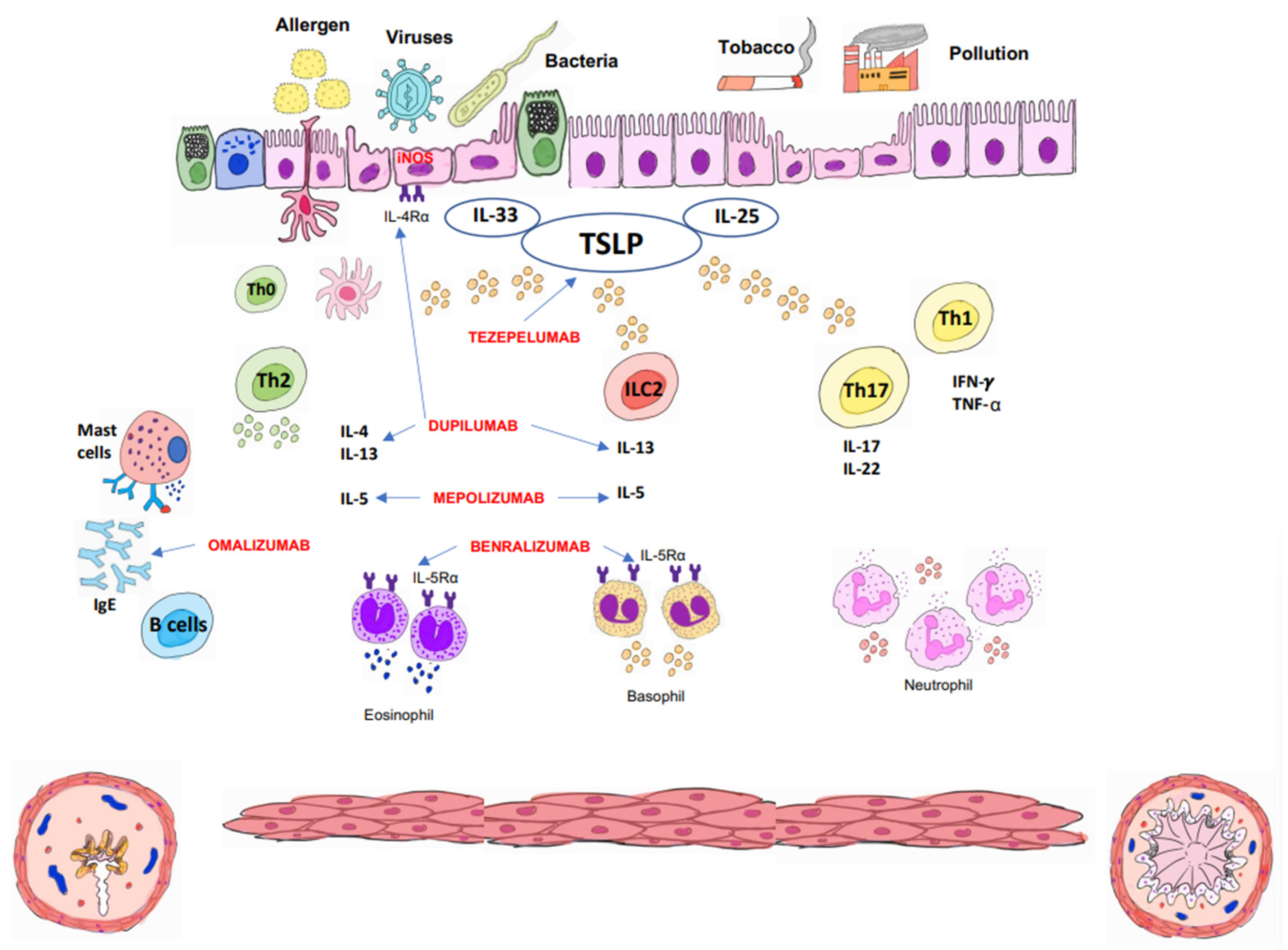
3. Biologicals Treatments
3.1. Omalizumab
3.2. Mepolizumab
3.3. Benralizumab
3.4. Dupilumab
3.5. Tezepelumab
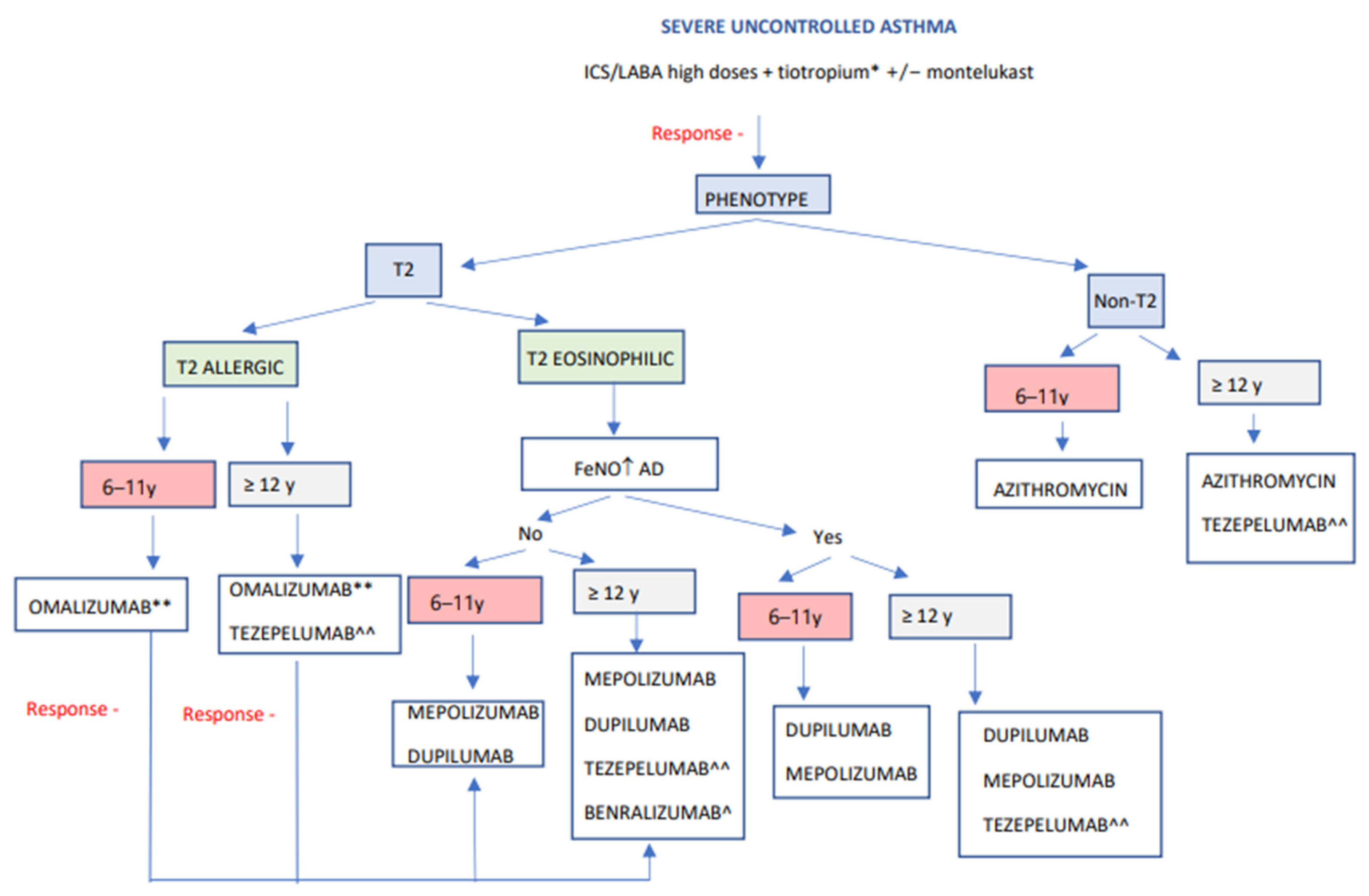
4. Personalized Treatment
5. Response Assessment
6. Future Guidelines
6.1. Pharmacogenomics
6.2. Epigenetics
6.3. Transcriptomics
6.4. Metabolomics
6.5. Microbiome
7. New Therapeutic Targets
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nordlund, B.; Melén, E.; Schultz, E.S.; Grönlund, H.; Hedlin, G.; Kull, I. Prevalence of severe childhood asthma according to the WHO. Respir. Med. 2014, 108, 1234–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lang, A.; Carlsen, K.H.; Haaland, G.; Devulapalli, C.S.; Munthe-Kaas, M.; Mowinckel, P.; Carlsen, K. Severe asthma in childhood: Assessed in 10-year-olds in a birth cohort study. Allergy 2008, 63, 1054–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rusconi, F.; Fernandes, R.M.; Pijnenburg, M.W.H.; Grigg, J.; SPACE Clinical Research Collaboration. The severe paediatric asthma collaborative in Europe (SPACE) ERS clinical research collaboration: Enhancing participation of children with asthma in therapeutic trials of new biologics and receptor blockers. Eur. Respir. J. 2018, 52, 1801665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plaza-Martín, A.M.; Vennera, M.C.; Galera, J.; Herráez, L.; PREX Study Group. Prevalence and clinical profile of difficult-to-control severe asthma in children: Results from pneumology and allergy hospital units in Spain. Allergol. Immunopathol. 2014, 42, 510–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szefler, S.J.; Zeiger, R.S.; Haselkorn, T.; Mink, D.R.; Kamath, T.V.; Fish, J.E.; Chipps, B.E. Economic burden of impairment in children with severe or difficult-to-treat asthma. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2011, 107, 110–119.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleming, M.; Fitton, C.A.; Steiner, M.F.C.; McLay, J.S.; Clark, D.; King, A.; Mackay, D.F.; Pell, J.P. Educational and health outcomes of children treated for asthma: Scotland-wide record linkage study of 683 716 children. Eur. Respir. J. 2019, 54, 1802309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montalbano, L.; Ferrante, G.; Montella, S.; Cilluffo, G.; Di Marco, A.; Bozzetto, S.; Di Palmo, E.; Licari, A.; Leonardi, L.; Caldarelli, V.; et al. Relationship between quality of life and behavioural disorders in children with persistent asthma: A multiple indicators multiple causes (MIMIC) model. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 6957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blasco Bravo, A.J.; Pérez-Yarza, E.G.; Lázaro y de Mercado, P.; Bonillo Perales, A.; Díaz Vázquez, C.A.; Moreno Galdó, A. Coste del asma en pediatría en España: Un modelo de evaluación de costes basado en la prevalencia. An Pediatr. 2011, 74, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGeachie, M.J.; Yates, K.P.; Zhou, X.; Guo, F.; Sternberg, A.L.; Van Natta, M.L.; Wise, R.A.; Szefler, S.J.; Sharma, S.; Kho, A.T.; et al. Patterns of growth and decline in lung function in persistent childhood asthma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 374, 1842–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaffin, J.M.; Petty, C.R.; Sorkness, R.L.; Denlinger, L.C.; Philips, B.R.; Ly, N.P.; Gaston, B.; Ross, K.; Fitzpatrick, A.; Bacharier, L.B.; et al. Determinants of lung function across childhood in the Severe Asthma Research Program (SARP)3. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2023, 151, 138–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tai, A.; Tran, H.; Roberts, M.; Clarke, N.; Wilson, J.; Robertson, C.F. The association between childhood asthma and adult chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Thorax 2014, 69, 805–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GINA (Global Initiative for Asthma). Global Initiative for Asthma Management and Prevention. 2023. Available online: www.ginasthma.com (accessed on 12 March 2023).
- GEMA 5.3 Guía Española del Manejo del Asma (GEMA 5.3). Available online: www.gemasma.com (accessed on 6 April 2023).
- Chung, K.F.; Wenzel, S.E.; Brozek, J.L.; Bush, A.; Castro, M.; Sterk, P.J.; Adcock, I.M.; Bateman, E.D.; Bel, E.H.; Bleecker, E.R.; et al. International ERS/ATS guidelines on definition, evaluation and treatment of severe asthma. Eur. Respir. J. 2014, 43, 343–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- BTS/SIGN British Guideline on the Management of Asthma. Available online: www.brit-thoracic.org.uk/quality-improvement/guidelines/asthma/ (accessed on 5 May 2023).
- Ahmed, H.; Turner, S. Severe asthma in children-a review of definitions, epidemiology, and treatments options in 2019. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2019, 54, 778–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bush, A.; Saglani, S. Management of severe asthma in children. Lancet 2010, 376, 814–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaillard, E.A.; Kuehni, C.E.; Turner, S.; Goutaki, M.; Holden, K.A.; de Jong, C.A.M.; Lex, C.; Lo, D.K.; Lucas, J.S.; Midulla, F.; et al. European Respiratory Society clinical practice guidelines for the diagnosis of asthma in children aged 5–6 years. Eur. Respir. J. 2021, 58, 2004173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bush, A. Which child with asthma is a candidate for biological therapies? J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pijnenburg, M.W.; Fleming, L. Advances in understanding and reducing the burden of severe asthma in children. Lancet Respir. Med. 2020, 8, 1032–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bush, A.; Filtzpatrick, A.M.; Saglani, S.; Anderson, W.C.; Szefler, S.J. Difficult-to-treat asthma management in school-age children. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2022, 10, 359–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacharier, L.B.; Jackson, D.J. Biologics in the treatment of asthma in children and adolescents. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2023, 151, 581–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bousquet, J.; Mantzouranis, E.; Cruz, A.A.; Aït-Khaled, N.; Baena-Cagnani, C.E.; Bleecker, E.R.; Brightling, C.E.; Burney, P.; Bush, A.; Busse, W.W.; et al. Uniform definition of asthma severity, control, and exacerbations: Document presented for the World Health Organization Consultation on Severe Asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2010, 126, 926–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzpatrick, A.M.; Teague, W.G.; Meyers, D.A.; Peters, S.P.; Li, X.; Li, H.; Wenzel, S.E.; Aujla, S.; Castro, M.; Bacharier, L.B.; et al. Heterogeneity of severe asthma in childhood: Confirmation by cluster analysis of children in the National Institutes of Health/National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute Severe Asthma Research Program. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2011, 127, 382–389.e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carr, T.F.; Kraft, M. Use of biomarkers to identify phenotypes and endotypes of severe asthma. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2018, 121, 414–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teague, W.G.; Phillips, B.R.; Fahy, J.V.; Wenzel, S.E.; Fitzpatrick, A.M.; Moore, W.C.; Hastie, A.T.; Bleecker, E.R.; Meyers, D.A.; Peters, S.P.; et al. Baseline features of the severe asthma research program (SARP III) cohort: Differences with age. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2018, 6, 545–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoratti, E.M.; Krouse, R.Z.; Babineau, D.C.; Pongracic, J.A.; O’Connor, G.T.; Wood, R.A.; Hershey, G.K.K.; Kercsmar, C.M.; Gruchalla, R.S.; Kattan, M.; et al. Asthma phenotypes in inner-city children. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2016, 138, 1016–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, D.J.; Bacharier, L.B.; Gergen, P.J.; Gagalis, L.; Calatroni, A.; Wellford, S.; Gill, M.A.; Stokes, J.; Liu, A.H.; Gruchalla, R.S.; et al. Mepolizumab for urban children with exacerbation-prone eosinophilic asthma in the USA (MUPPITS-2): A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group trial. Lancet 2022, 400, 502–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teach, S.J.; Gergen, P.J.; Szefler, S.J.; Mitchell, H.E.; Calatroni, A.; Wildfire, J.; Bloomberg, G.R.; Kercsmar, C.M.; Liu, A.H.; Makhija, M.M.; et al. Seasonal risk factors for asthma exacerbations among inner-city children. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2015, 135, 1465–1473.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schleich, F.; Bougard, N.; Moermans, C.; Sabbe, M.; Louis, R. Cytokine-targeted therapies for asthma and COPD. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2023, 32, 220193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, D.J.; Virnig, C.M.; Gangnon, R.E.; Evans, M.D.; Roberg, K.A.; Anderson, E.L.; Burton, R.M.; Salazar, L.P.; DaSilva, D.F.; Shanovich, K.M.; et al. Fractional exhaled nitric oxide measurements are most closely associated with allergic sensitization in school-age children. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2009, 124, 949–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rufo, J.C.; Madureira, J.; Fernandes, E.O. Volatile organic compounds in asthma diagnosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Allergy 2016, 71, 175–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bannier, M.A.G.E.; Rosias, P.P.R.; Jöbsis, Q. Exhaled breath condensate in childhood asthma: A review and current perspective. Front. Pediatr. 2019, 7, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, A.; Tan, V.Y.; Winn, J.; Svensen, M.; Bishop, C.M.; Heckerman, D.E.; Buchan, I.; Custovic, A. Beyond atopy: Multiple patterns of sensitization in relation to asthma in a birth cohort study. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2010, 181, 1200–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Licari, A.; Brambilla, I.; Sacchi, L.; Marseglia, G.; Cipranadi, G. Periostin, type 2 biomarker, is not associated with asthma control grade in asthmatic allergic children. Respir. Med. 2019, 151, 118–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buhl, R.; Bel, E.; Bourdin, A.; Davila, I.; Douglass, J.A.; FitzGerald, J.M.; Jackson, D.J.; Lugogo, N.L.; Matucci, A.; Pavord, I.D.; et al. Effective management of severe asthma with biologic medications in adult patients: A literature review and international expert opinion. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2022, 10, 422–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grunwell, J.R.; Stephenson, S.T.; Tirouvanziam, R. Children with neutrophil-predominant severe asthma have proinflammatory neutrophils with enhanced survival and impaired clearance. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2019, 7, 516–525.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konradsen, J.R.; James, A.; Nordlund, B.; Reinius, L.E.; Soderhall, C.; Melen, E.; Wheelock, Å.; Carlsen, K.C.L.; Lidegran, M.; Verhoek, M.; et al. The chitinase-like protein YKL-40: A possible biomarker of inflammation and airway remodeling in severe pediatric asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2013, 132, 328–335e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wedes, S.H.; Wu, W.; Comhair, S.A.; McDowell, K.M.; DiDonato, J.A.; Erzurum, S.C.; Hazen, S.L. Urinary bromotyrosine measures asthma control and predicts asthma exacerbations in children. J. Pediatr. 2011, 159, 248–255.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Licari, A.; Manti, S.; Castagnoli, R.; Parisi, G.F.; Salpietro, C.; Leonardi, S.; Marseglia, G.L. Targeted Therapy for Severe Asthma in Children and Adolescents: Current and Future Perspectives. Pediatr. Drugs 2019, 21, 215–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perikleous, E.P.; Steiropoulos, P.; Nena, E.; Paraskakis, E. Biologic Therapies in Pediatric Asthma. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, P.A.; Brightling, C. Biologics for severe asthma—Which, when and why? Respirology 2023, 28, 709–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brusselle, G.G.; Koppelman, G.H. Biologic Therapies for Severe Asthma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 386, 157–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heymann, P.W.; Carper, H.T.; Murphy, D.D.; Platts-Mills, T.A.E.; Patrie, J.; McLaughlin, A.P.; Erwin, E.A.; Shaker, M.S.; Hellems, M.; Peerzada, J.; et al. Viral infections in relation to age, atopy, and season of admission among children hospitalized for wheezing. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2004, 114, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gill, M.A.; Liu, A.H.; Calatroni, A.; Krouse, R.Z.; Shao, B.; Schiltz, A.; Gern, J.E.; Togias, A.; Busse, W.W. Enhanced plasmacytoid dendritic cell antiviral responses after omalizumab. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2018, 141, 1735–1743.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carraro, S.; Di Palmo, E.; Licari, A.; Barni, S.; Caldarelli, V.; De Castro, G.; Di Marco, A.; Fenu, G.; Giordano, G.; Lombardi, E.; et al. Metabolomics to identify omalizumab responders among children with severe asthma: A prospective study. Allergy 2022, 77, 2852–2856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russo, D.; Di Filippo, P.; Attanasi, M.; Lizzi, M.; Di Pillo, S.; Chiarelli, F. Biologic Therapy and Severe Asthma in Children. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ficha Técnica FXOLAIR 150 MG SOLUCION INYECTABLE. Available online: https://cima.aemps.es/cima/dochtml/ft/05319008/FT_05319008.html (accessed on 10 April 2023).
- Singh, H.; Peters, J.I.; Kaur, Y.; Maselli, D.J.; Diaz, J.D. Long-term evaluation of response to omalizumab therapy in real life by a novel multimodular approach. The Real-life Effectiveness of Omalizumab Therapy (REALITY) study. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2019, 123, 476–482.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nieto García, A.; Garriga-Baraut, T.; Plaza Martín, A.M.; Nieto Cid, M.; Torres Borrego, J.; Folqué Giménez, M.M.; Blasco, J.L.; García, M.B.; Moreno-Galarraga, L.; Tortajada-Girbés, M.; et al. Omalizumab outcomes for up to 6 years in pediatric patients with severe persistent allergic asthma. Pediatr. Allergy Immunol. 2021, 32, 980–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Folqué, M.M.; Lozano, J.; Riggioni, C.; Piquer, M.; Álvaro, M.; Machinena, A.; Giner, M.; Domínguez, O.; Jiménez-Feijoo, R.; da Costa, M.D.; et al. «Real-life» experience in asthmatic children treated with omalizumab up to six-years follow-up. Allergol. Immunopathol. 2019, 47, 336–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Licari, A.; Castagnoli, R.; Denicolò, C.; Rossini, L.; Seminara, M.; Sacchi, L.; Testa, G.; De Amici, M.; Marseglia, G.L. Omalizumab in Children with Severe Allergic Asthma: The Italian Real-Life Experience. Curr. Respir. Med. Rev. 2017, 13, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deschildre, A.; Marguet, C.; Salleron, J.; Pin, I.; Rittié, J.L.; Derelle, J.; Taam, R.A.; Fayon, M.; Brouard, J.; Dubus, J.C.; et al. Add-on omalizumab in children with severe allergic asthma: A 1-year real life survey. Eur. Respir. J. 2013, 42, 1224–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarraf, H.N.; Masoud, H.H.; Zidan, M.; Wahba, B. Effectiveness and safety of omalizumab in severe, persistent IgE-mediated asthma in pediatric and adult patients: A real-world observational study in Egyptian population. J. Asthma Off. J. Assoc. Care Asthma 2020, 57, 160–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenu, G.; Tessa, A.L.; Calogero, C.; Lombardi, E. Severe pediatric asthma therapy: Omalizumab—A systematic review and meta-analysis of efficacy and safety profile. Front. Pediatr. 2023, 10, 1033511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henriksen, D.P.; Bodtger, U.; Sidenius, K.; Maltbaek, N.; Pedersen, L.; Madsen, H.; Andersson, E.A.; Norgaard, O.; Madsen, L.K.; Chawes, B.L. Efficacy of omalizumab in children, adolescents, and adults with severe allergic asthma: A systematic review, meta-analysis, and call for new trials using current guidelines for assessment of severe asthma. Allergy Asthma Clin. Immunol. 2020, 16, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Humbert, M.; Bourdin, A.; Taillé, C.; Kamar, D.; Thonnelier, C.; Lajoinie, A.; Rigault, A.; Deschildre, A.; Molimard, M. Real-life omalizumab exposure and discontinuation in a large nationwide population-based study of paediatric and adult asthma patients. Eur. Respir. J. 2022, 60, 2103130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domingo, C.; Pomares, X.; Navarro, A.; Amengual, M.J.; Montón, C.; Sogo, A.; Mirapeix, R.M. A step-down protocol for omalizumab treatment in oral corticosteroid-dependent allergic asthma patients: Omalizumab dose-decreasing protocol. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2018, 84, 339–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castagnoli, R.; De Filippo, M.; Votto, M.; Marseglia, A.; Montagna, L.; Marseglia, G.L.; Licari, A. An update on biological therapies for pediatric allergic diseases. Minerva Pediatr. 2020, 72, 364–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Z.; Xu, Y.; Cai, C. Efficacy and safety of omalizumab in children with moderate-to-severe asthma: A meta-analysis. J. Asthma 2021, 58, 1350–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abrams, E.M.; Becker, A.B.; Szefler, S.J. Current state and future of biologic therapies in the treatment of asthma in children. Pediatr. Allergy Immunol. Pulmonol. 2018, 31, 119–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phipatanakul, W.; Mauger, D.T.; Guilbert, T.W.; Bacharier, L.B.; Durrani, S.; Jackson, D.J.; Martinez, F.D.; Fitzpatrick, A.M.; Cunningham, A.; Kunselman, S.; et al. PARK Study Team. Preventing asthma in high risk kids (PARK) with omalizumab: Design, rationale, methods, lessons learned and adaptation. Contemp. Clin. Trials 2021, 100, 106228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenero, L.; Arturi, E.; Piazza, M.; Piacentini, G. Anti-IL-5 in pediatric allergic diseases. Pediatr. Allergy Immunol. 2020, 31, 14–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EMA. Nucala. European Medicines Agency. 2018. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/medicines/human/EPAR/nucala (accessed on 2 May 2023).
- Yancey, S.W.; Ortega, H.G.; Keene, O.N.; Bradford, E.S. Efficacy of add-on mepolizumab in adolescents with severe eosinophilic asthma. Allergy Asthma Clin. Immunol. 2019, 15, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lugogo, N.; Domingo, C.; Chanez, P.; Leigh, R.; Gilson, M.J.; Price, R.G.; Yancey, S.W.; Ortega, H.G. Long-term efficacy and safety of mepolizumab in patients with severe eosinophilic asthma: A multi-center, open-label, phase IIIb study. Clin. Ther. 2016, 38, 2058–2070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortega, H.G.; Yancey, S.W.; Mayer, B.; Gunsoy, N.B.; Keene, O.N.; Bleecker, E.R.; Brightling, C.E.; Pavord, I.D. Severe eosinophilic asthma treated with mepolizumab stratified by baseline eosinophil thresholds: A secondary analysis of the DREAM and MENSA studies. Lancet Respir. Med. 2016, 4, 549–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hearn, A.P.; Kavanagh, J.; d’Ancona, G.; Roxas, C.; Green, L.; Thomson, L.; Fernandes, M.; Kent, B.D.; Dhariwal, J.; Nanzer, A.M.; et al. The relationship between Feno and effectiveness of mepolizumab and benralizumab in severe eosinophilic asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2021, 9, 2093–2096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Pouliquen, I.; Austin, D.; Price, R.G.; Kempsford, R.; Steinfeld, J.; Bradford, E.S.; Yancey, S.W. Subcutaneous mepolizumab in children aged 6 to 11 years with severe eosinophilic asthma. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2019, 54, 1957–1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weir, E.; Paton, J. Mepolizumab in adolescents with severe eosinophilic asthma not eligible for omalizumab: One center’s early clinical experience. J. Asthma 2020, 57, 521–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, A.; Ikeda, M.; Geng, B.; Azmi, J.; Price, R.G.; Bradford, E.S.; Yancey, S.W.; Steinfeld, J. Long-term safety and pharmacodynamics of mepolizumab in children with severe asthma with an eosinophilic phenotype. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2019, 144, 1336–1342.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bleecker, E.R.; FitzGerald, J.M.; Chanez, P.; Papi, A.; Weinstein, S.F.; Barker, P.; Sproule, S.; Gilmartin, G.; Aurivillius, M.; Werkström, V.; et al. Efficacy and safety of benralizumab for patients with severe asthma uncontrolled with high-dosage inhaled corticosteroids and long-acting β2-agonists (SIROCCO): A randomised, multicentre, placebo-controlled phase 3 trial. Lancet 2016, 388, 2115–2127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FitzGerald, J.M.; Bleecker, E.R.; Nair, P.; Korn, S.; Ohta, K.; Lommatzsch, M.; Ferguson, G.T.; Busse, W.W.; Barker, P.; Sproule, S.; et al. Benralizumab, an anti-interleukin-5 receptor α monoclonal antibody, as add-on treatment for patients with severe, uncontrolled, eosinophilic asthma (CALIMA): A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 3 trial. Lancet 2016, 388, 2128–2141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chipps, B.E.; Newbold, P.; Hirsch, I.; Trudo, F.; Goldman, M. Benralizumab efficacy by atopy status and serum immunoglobulin E for patients with severe, uncontrolled asthma. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2018, 120, 504–511.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, D.J.; Humbert, M.; Hirsch, I.; Newbold, P.; Garcia Gil, E. Ability of Serum IgE Concentration to Predict Exacerbation Risk and Benralizumab Efficacy for Patients with Severe Eosinophilic Asthma. Adv. Ther. 2020, 37, 718–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busse, W.W.; Bleecker, E.R.; FitzGerald, J.M.; Ferguson, G.T.; Barker, P.; Sproule, S.; Olsson, R.; Martin, U.J.; Goldman, M.; Yañez, A.; et al. Long-term safety and efficacy of benralizumab in patients with severe, uncontrolled asthma: 1-year results from the BORA phase 3 extension trial. Lancet Respir. Med. 2019, 7, 46–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Busse, W.W.; Bleecker, E.R.; FitzGerald, J.M.; Ferguson, G.T.; Barker, P.; Brooks, L.; Olsson, R.F.; Martin, U.J.; Goldman, M. Benralizumab for adolescent patients with severe, eosinophilic asthma: Safety and efficacy after 3 years of treatment. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2021, 148, 266–271.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- FitzGerald, J.M.; Bleecker, E.R.; Menzies-Gow, A.; Zangrilli, J.G.; Hirsch, I.; Metcalfe, P.; Newbold, P.; Goldman, M. Predictors of enhanced response with benralizumab for patients with severe asthma: Pooled analysis of the SIROCCO and CALIMA studies. Lancet Respir. Med. 2018, 6, 51–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bleecker, E.R.; Wechsler, M.E.; FitzGerald, J.M.; Menzies-Gow, A.; Wu, Y.; Hirsch, I.; Goldman, M.; Newbold, P.; Zangrilli, J.G. Baseline patient factors impact on the clinical efficacy of benralizumab for severe asthma. Eur. Respir. J. 2018, 52, 1800936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Ma, X.; Zhou, W. Adverse events of benralizumab in moderate to severe eosinophilic asthma: A meta-analysis. Medicine 2019, 98, e15868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alpizar, S.; Megally, A.; Chen, C.; Raj, A.; Downie, J.; Colice, G. Functionality and Performance of an Accessorized Pre-Filled Syringe and an Autoinjector for At-Home Administration of Tezepelumab in Patients with Severe, Uncontrolled Asthma. J. Asthma Allergy 2021, 14, 381–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- A Multicentre, Randomised, Double-Blind, Parallel Group, Placebocontrolled, Phase 3 Efficacy and Safety Study of Benralizumab (MEDI-563) Added to Medium to High-Dose Inhaled Corticosteroid Plus Long-Acting β2 Agonist in Patients with Uncontrolled Asthma. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03186209 (accessed on 29 May 2023).
- Efficacy and Safety Study of Benralizumab Added to High-Dose Inhaled Corticosteroid Plus LABA in Patients with Uncontrolled Asthma. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01928771 (accessed on 26 June 2023).
- A Multicentre, Randomised, Double-Blind, Parallel Group, Placebo-Controlled, Time-to-First Asthma Exacerbation Phase III Efficacy and Safety Study of Benralizumab in Paediatric Patients with Severe Eosinophilic Asthma (DOMINICA) (DOMINICA). Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT05692180 (accessed on 28 June 2023).
- Le Floc’h, A.; Allinne, J.; Nagashima, K.; Scott, G.; Birchard, D.; Asrat, S.; Bai, Y.; Lim, W.K.; Martin, J.; Huang, T.; et al. Dual blockade of IL-4 and IL-13 with dupilumab, an IL-4Rα antibody, is required to broadly inhibit type 2 inflammation. Allergy 2020, 75, 1188–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ficha técnica Dupixenet 200 MG Solución Inyectable en Pluma Precargada. Available online: https://cima.aemps.es/cima/dochtml/ft/1171229014/FT_1171229014.html (accessed on 1 June 2023).
- García, H. Informe de Posicionamiento Terapéutico de Dupilumab (Dupixent®) en Dermatitis Atópica 2019. Available online: www.aemps.gob.es/medicamentosUsoHumano/informesPublicos/docs/IPT-dupilumab-Dupixent-dermatitis-atopica.pdf (accessed on 29 April 2023).
- Castro, M.; Corren, J.; Pavord, I.D.; Maspero, J.; Wenzel, S.; Rabe, K.F.; Busse, W.W.; Ford, L.; Sher, L.; Fitzgerald, J.M.; et al. Dupilumab Efficacy and Safety in Moderate-to-Severe Uncontrolled Asthma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 2486–2496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busse, W.W.; Maspero, J.F.; Rabe, K.F.; Papi, A.; Wenzel, S.E.; Ford, L.B.; Pavord, I.D.; Zhang, B.; Staudinger, H.; Pirozzi, G.; et al. Liberty Asthma QUEST: Phase 3 Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Parallel-Group Study to Evaluate Dupilumab Efficacy/Safety in Patients with Uncontrolled, Moderate-to-Severe Asthma. Adv. Ther. 2018, 35, 737–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corren, J.; Castro, M.; Chanez, P.; Fabbri, L.; Joish, V.N.; Amin, N.; Graham, N.M.; Mastey, V.; Abbé, A.; Taniou, C.; et al. Dupilumab improves symptoms, quality of life, and productivity in uncontrolled persistent asthma. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2019, 122, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, X.F.; Zhu, M.; Wu, H.X.; Fan, L.L.; Cheng, D.Y. Efficacy and safety of dupilumab for the treatment of uncontrolled asthma: A meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. Respir. Res. 2019, 20, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zayed, Y.; Kheiri, B.; Banifadel, M.; Hicks, M.; Aburahma, A.; Hamid, K.; Bachuwa, G.; Chandran, A. Dupilumab safety and efficacy in uncontrolled asthma: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. J. Asthma 2019, 56, 1110–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wenzel, S.; Castro, M.; Corren, J.; Maspero, J.; Wang, L.; Zhang, B.; Pirozzi, G.; Sutherland, E.R.; Evans, R.R.; Joish, V.N.; et al. Dupilumab efficacy and safety in adults with uncontrolled persistent asthma despite use of medium-to-high-dose inhaled corticosteroids plus a long-acting β2 agonist: A randomised double-blind placebo-controlled pivotal phase 2b dose-ranging trial. Lancet 2016, 388, 31–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maspero, J.F.; FitzGerald, J.M.; Pavord, I.D.; Rice, M.S.; Maroni, J.; Rowe, P.J.; Pirozzi, G.; Amin, N.; Ruddy, M.; Graham, N.M.H.; et al. Dupilumab efficacy in adolescents with uncontrolled, moderate-to-severe asthma: Liberty Asthma Quest. Allergy 2021, 76, 2621–2624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bacharier, L.B.; Maspero, J.F.; Katelaris, C.H.; Fiocchi, A.G.; Gagnon, R.; de Mir, I.; Jain, N.; Sher, L.D.; Mao, X.; Liu, D.; et al. Dupilumab in children with uncontrolled moderate-to-severe asthma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 2230–2240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Assessment of the Safety and Efficacy of Dupilumab in Children with Asthma (Liberty Asthma Excursion). Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03560466 (accessed on 5 June 2023).
- Menzies-Gow, A.; Corren, J.; Bourdin, A.; Chupp, G.; Israel, E.; Wechsler, M.E.; Brightling, C.E.; Griffiths, J.M.; Hellqvist, Å.; Bowen, K.; et al. Tezepelumab in Adults and Adolescents with Severe, Uncontrolled Asthma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 1800–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korn, S.; Cook, B.; Simpson, L.J.; Llanos, J.P.; Ambrose, C.S. Efficacy of Biologics in Severe, Uncontrolled Asthma Stratified by Blood Eosinophil Count: A Systematic Review. Adv. Ther. 2023; Online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menzies-Gow, A.; Wechsler, M.E.; Brightling, C.E.; Korn, S.; Corren, J.; Israel, E.; Chupp, G.; Bednarczyk, A.; Ponnarambil, S.; Caveney, S.; et al. Long-term safety and efficacy of tezepelumab in people with severe, uncontrolled asthma (DESTINATION): A randomised, placebo-controlled extension study. Lancet Respir. Med. 2023, 11, 425–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoy, S.M. Tezepelumab: First Approval. Drugs 2022, 82, 461–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Study to Evaluate the Pharmacokinetics of Tezepelumab in Children with Asthma (TRAILHEAD). Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04673630 (accessed on 12 June 2023).
- Santos-Valente, E.; Buntrock-Döpke, H.; Abou Taam, R.; Arasi, S.; Bakirtas, A.; Lozano Blasco, J.; Bønnelykke, K.; Craiu, M.; Cutrera, R.; Deschildre, A.; et al. Biologicals in childhood severe asthma: The European PERMEABLE survey on the status quo. ERJ Open Res. 2021, 7, 00143–02021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agache, I.; Akdis, C.A.; Akdis, M.; Canonica, G.W.; Casale, T.; Civato, T.; Corren, J.; Chu, D.K.; Del Giacco, S.; Eiwegger, T.; et al. EAACI Biological guidelines-recommendations for severe asthma. Allergy 2021, 76, 14–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxena, S.; Rosas-Salazar, C.; Fitzpatrick, A.; Bacharier, L.B. Biologics and severe asthma in children. Curr. Opin. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2023, 23, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porsbjerg, C.; Melén, E.; Lehtimäki, L.; Shaw, D. Asthma. Lancet 2023, 401, 858–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denton, E.; Price, D.B.; Tran, T.N.; Canonica, G.W.; Menzies-Gow, A.; FitzGerald, J.M.; Sadatsafavi, M.; de Llano, L.P.; Christoff, G.; Quinton, A.; et al. Cluster Analysis of Inflammatory Biomarker Expression inthe International Severe Asthma Registry. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2021, 9, 2680–2688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oppenheimer, J.; Hoyte, F.C.L.; Phipatanakul, W.; Silver, J.; Howarth, P.; Lugogo, N.L. Allergic and eosinophilic asthma in the era of biomarkers and biologics: Similarities, differences and misconceptions. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2022, 129, 169–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, N.M.; Carlsen, K.C.L.; Cunningham, S.; Fenu, G.; Fleming, L.J.; Gappa, M.; Karadag, B.; Midulla, F.; Petrarca, L.; Pijnenburg, M.W.; et al. First analysis of the Severe Paediatric Asthma Collaborative in Europe registry. ERJ Open Res. 2020, 6, 00566–02020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bossley, C.J.; Fleming, L.; Gupta, A.; Regamey, N.; Frith, R.; Oates, T.; Tsartsali, L.; Lloyd, C.M.; Bush, A.; Saglani, S. Pediatric severe asthma is characterized by eosinophilia and remodeling without TH2 cytokines. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2012, 129, 974–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saglani, S.; Lloyd, C.M. Eosinophils in the pathogenesis of paediatric severe asthma. Curr. Opin. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2014, 14, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teague, W.G.; Lawrence, M.G.; Shirley, D.A.T.; Garrod, A.S.; Earley, S.V.; Payne, J.B.; Wisniewski, J.A.; Heymann, P.W.; Daniero, J.J.; Steinke, J.W.; et al. Lung lavage granulocyte patterns and clinical phenotypes in children with severe asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2019, 7, 1803–1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullman, N.; Boosley, C.J.; Fleming, L.; Silvestri, M.; Bush, A.; Saglani, S. Blood eosinophil counts rarely reflect airway eosinophilia in children with severe asthma. Allergy 2013, 68, 402–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holguin, F.; Cardet, J.C.; Fan Chung, K.; Diver, S.; Ferreira, D.S.; Fitzpatrick, A.; Gaga, M.; Kellermeyer, L.; Khurana, S.; Knight, S.; et al. Management of severe asthma: A European Respiratory Society/American Thoracic Society guideline. Eur. Respir. J. 2020, 55, 1900588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agache, I.; Beltran, J.; Akdis, C.; Akdis, M.; Canelo-Aybar, C.; Walter Canonica, G.; Casale, T.; Chivato, T.; Corren, J.; Del Giacco, S.; et al. Efficacy and safety of treatment with biologicals (benralizumab, dupilumab, mepolizumab, omalizumab and reslizumab) for severe eosinophilic asthma. A systematic review for the EAACI Guidelines–Recommendations on the use of biologicals in severe asthma. Allergy 2020, 75, 1023–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Mir Messa, I.; López Neyra, A.; Valverde Molina, J. Asma grave: Del asma difícil de tratar al asma resistente al tratamiento. In Tratado de Neumología Pediátrica SENP-SEPAR, 1st ed.; Andrés-Martín, A., Valverde-Molina, J., Eds.; EIOSALUD: Lima, Peru, 2021; ISBN 978-84-124442-1-6. Available online: https://tienda.separ.es/producto/tratado-de-neumologia-pediatrica/ (accessed on 24 August 2023).
- Porsbjerg, C.M.; Sverrild, A.; Lloyd, C.M.; Menzies-Gow, A.N.; Bel, E.H. Anti-alarmins in asthma: Targeting the airway epithelium with next-generation biologics. Eur. Respir. J. 2020, 56, 2000260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corren, J.; Pham, T.-H.; Garcia Gil, E.; Sałapa, K.; Ren, P.; Parnes, J.R.; Colice, G.; Griffiths, J.M. Baseline type 2 biomarker levels and response to tezepelumab in severe asthma. Allergy 2022, 77, 1786–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Undela, K.; Goldsmith, L.; Kew, K.M.; Ferrara, G. Macrolides versus placebo for chronic asthma. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2021, 11, CD002997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, S.L.; Ivey, K.L.; Gibson, P.G.; Simpson, J.L.; Rogers, G.B. Airway abundance of Haemophilus influenzae predicts response to azithromycin in adults with persistent uncontrolled asthma. Eur. Respir. J. 2020, 56, 2000194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elwyn, G.; Frosch, D.; Thomson, R.; Joseph-Williams, N.; Lloyd, A.; Kinnersley, P.; Cording, E.; Tomson, D.; Dodd, C.; Rollnick, S.; et al. Shared decision making: A model for clinical practice. J. Gen. Intern. Med. 2012, 27, 1361–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buhl, R.; Humbert, M.; Bjermer, L.; Chanez, P.; Heaney, L.G.; Pavord, I.; Quirce, S.; Virchow, J.C.; Holgate, S. Severe eosinophilic asthma: A roadmap to consensus. Eur. Respir. J. 2017, 49, 1700634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Upham, J.W.; Le Lievre, C.; Jackson, D.J.; Masoli, M.; Wechsler, M.E.; Price, D.B.; Mansur, A.; Detoraki, A.; Altraja, A.; James, A.; et al. Defining a Severe Asthma Super-Responder: Findings from a Delphi Process. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2021, 9, 3997–4004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaleva, E.; Rattu, A.; Brightling, C.; Bush, A.; Bourdin, A.; Bossios, A.; Chung, K.F.; Chaudhuri, R.; Coleman, C.; Djukanovic, R.; et al. Definitions of non-response and response to biological therapy for severe asthma: A systematic review. ERJ Open Res. 2023, 9, 00444–02022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaleva, E.; Rattu, A.; Brightling, C.; Bush, A.; Bossios, A.; Bourdin, A.; Chung, K.F.; Chaudhuri, R.; Coleman, C.; Dahlén, S.-E.; et al. Development of Core Outcome Measures sets for paediatric and adult Severe Asthma (COMSA). Eur. Respir. J. 2023, 61, 2200606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Votto, M.; De Filippo, M.; Marseglia, A.; Brambilla, I.; Marseglia, G.L.; Licari, A. Applying a new set of core outcome measures for severe pediatric asthma in real-life: A single-center experience. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2023; ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroes, J.A.; Zielhius, S.W.; van Roon, E.N.; ten Brinke, A. Prediction of response to biological treatment with monoclonal antibodies in severe asthma. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2020, 179, 113978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez de Llano, L.; Cisneros, C.; Domínguez Ortega, J.; Martínez Moragon, E.; Olaguibel, J.M.; Plaza, V.; Quirce, S.; Dávila, I. Response to monoclonal antibodies in asthma: Definitions, potential reasons for faliure, and therapeutic options for suboptimal response. J. Investig. Allergol. Clin. Immunol. 2023, 33, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menzies-Gow, A.; Bafadhel, M.; Busse, W.W.; Casale, T.B.; Kocks, J.W.H.; Pavord, I.D.; Szefler, S.J.; Woodruff, P.G.; de Giorgio-Miller, A.; Trudo, F.; et al. An expert consensus framework for asthma remission as a treatment goal. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2020, 145, 757–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, D.; McDonald, V.M.; Pavord, I.D.; Gibson, P.G. Asthma remission: What is it and how can it be achieved? Eur. Respir. J. 2022, 60, 2102583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varricchi, G.; Ferri, S.; Pepys, J.; Poto, R.; Spadaro, G.; Nappi, E.; Paoletti, G.; Virchow, J.C.; Heffler, E.; Canonica, W.G. Biologics and airway remodeling in severe asthma. Allergy 2022, 77, 3538–3552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tyler, S.R.; Bunyavanich, S. Leveraging-omics for asthma endotyping. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2019, 144, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Licari, A.; Castagnoli, R.; Brambilla, I.; Marseglia, A.; Tosca, M.A.; Marseglia, G.L.; Ciprandi, G. Asthma Endotyping and Biomarkers in Childhood Asthma. Pediatr. Allergy Immunol. Pulmonol. 2018, 31, 44–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijverberg, S.J.; Brinkman, P.; Rutjes, N.W.; Der Zee, A.H.M.-V. Precision medicine in severe pediatric asthma. Curr. Opin. Pulm. Med. 2020, 26, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Aziz, M.I.; Neerincx, A.H.; Vijverberg, S.J.H.; Hashimoto, S.; Brinkman, P.; Gorenjak, M.; Toncheva, A.A.; Harner, S.; Brandstetter, S.; Wolff, C.; et al. A System Pharmacology Multi-Omics Approach toward Uncontrolled Pediatric Asthma. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Q.; Liu, N.; Forno, E.; Canino, G.; Celedón, J.C.; Chen, W. An Integrative Association Method for Omics Data Based on a Modified Fisher’s Method with Application to Childhood Asthma. PLoS Genet 2019, 15, e1008142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee-Sarwar, K.A.; Kelly, R.S.; Lasky-Su, J.; Zeiger, R.S.; O’Connor, G.T.; Sandel, M.T.; Bacharier, L.B.; Beigelman, A.; Laranjo, N.; Gold, D.R.; et al. Integrative Analysis of the Intestinal Metabolome of Childhood Asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2019, 144, 442–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera-Luis, E.; Hernandez-Pacheco, N.; Vijverberg, S.J.; Flores, C.; Pino-Yanes, M. Role of Genomics in Asthma Exacerbations. Curr. Opin. Pulm. Med. 2019, 25, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Menaya, J.M.; Cordobés-Durán, C.; García-Martín, E.; Agúndez, J.A.G. Pharmacogenetic Factors Affecting Asthma Treatment Response. Potential Implic. Drug Ther. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farzan, N.; Vijverberg, S.J.; Kabesch, M.; Sterk, P.J.; Maitland-van der Zee, A.H. The use of pharmacogenomics, epigenomics, and transcriptomics to improve childhood asthma management: Where do we stand? Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2018, 53, 836–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernandez-Pacheco, N.; Pino-Yanes, M.; Flores, C. Genomic Predictors of Asthma Phenotypes and Treatment Response. Front. Pediatr. 2019, 7, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slob, E.M.A.; Vijverberg, S.J.H.; Palmer, C.A.N.; Zazuli, Z.; Farzan, N.; Oliveri, N.M.B.; Pijnenburg, M.W.; Koppelman, G.H.; der Zee, A.H.M.-V. Pharmacogenetics of Inhaled Long-Acting Beta2-Agonists in Asthma: A Systematic Review. Pediatr. Allergy Immunol. 2018, 29, 705–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keskin, O.; Farzan, N.; Birben, E.; Akel, H.; Karaaslan, C.; Maitland-Van Der Zee, A.H.; Wechsler, M.E.; Vijverberg, S.J.; Kalayci, O. Genetic Associations of the Response to Inhaled Corticosteroids in Asthma: A Systematic Review. Clin. Transl. Allergy 2019, 9, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Aziz, M.I.; Neerincx, A.H.; Vijverberg, S.J.; Kraneveld, A.D.; Der Zee, A.H.M.-V. Omics for the future in asthma. Semin. Immunopathol. 2020, 42, 111–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleming, L.; Murray, C.; Bansal, A.T.; Hashimoto, S.; Bisgaard, H.; Bush, A.; Frey, U.; Hedlin, G.; Singer, F.; van Aalderen, W.M.; et al. The burden of severe asthma in childhood and adolescence: Results from the paediatric U-BIOPRED cohorts. Eur. Respir. J. 2015, 46, 1322–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzpatrick, A.M.; Higgins, M.; Holguin, F.; Brown, L.A.S.; Teague, W.G. The molecular phenotype of severe asthma in children. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2010, 125, 851–857.e18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visscher, P.M.; Wray, N.R.; Zhang, Q.; Sklar, P.; McCarthy, M.I.; Brown, M.A.; Yang, J. 10 Years of GWAS Discovery: Biology, Function, and Translation. Am. J. Hum. Genet 2017, 101, 5–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petersen, B.S.; Fredrich, B.; Hoeppner, M.P.; Ellinghaus, D.; Franke, A. Opportunities and Challenges of Whole-Genome and -Exome Sequencing. BMC Genet 2017, 18, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernandez-Pacheco, N.; Flores, C.; Oh, S.S.; Burchard, E.G.; Pino-Yanes, M. What Ancestry Can Tell Us About the Genetic Origins of Inter-Ethnic Differences in Asthma Expression. Curr. Allergy Asthma Rep. 2016, 16, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spear, M.L.; Hu, D.; Pino-Yanes, M.; Huntsman, S.; Eng, C.; Levin, A.M.; Ortega, V.E.; White, M.J.; McGarry, M.E.; Thakur, N.; et al. A Genome-Wide Association and Admixture Mapping Study of Bronchodilator Drug Response in African Americans with Asthma. Pharmacogenom. J. 2019, 19, 249–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernandez-Pacheco, N.; Farzan, N.; Francis, B.; Karimi, L.; Repnik, K.; Vijverberg, S.J.; Soares, P.; Schieck, M.; Gorenjak, M.; Forno, E.; et al. Genome-wide association study of inhaled corticosteroid Response in Admixed Children with Asthma. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2019, 49, 789–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-García, J.; Herrera-Luis, E.; Lorenzo-Díaz, F.; González, M.; Sardón, O.; Villar, J.; Pino-Yanes, M. Precision Medicine in Childhood Asthma: Omic Studies of Treatment Response. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ricciardolo, F.L.M. Multiple Roles of Nitric Oxide in the Airways. Thorax 2003, 58, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kichaev, G.; Bhatia, G.; Loh, P.R.; Gazal, S.; Burch, K.; Freund, M.K.; Schoech, A.; Pasaniuc, B.; Price, A.L. Leveraging Polygenic Functional Enrichment to Improve GWAS Power. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2019, 104, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lutz, S.M.; Cho, M.H.; Young, K.; Hersh, C.P.; Castaldi, P.J.; McDonald, M.L.; Regan, E.; Mattheisen, M.; DeMeo, D.L.; Parker, M.; et al. A Genome-Wide Association Study Identifies Risk Loci for Spirometric Measures among Smokers of European and African Ancestry. BMC Genet 2015, 16, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera-Luis, E.; Espuela-Ortiz, A.; Lorenzo-Diaz, F.; Keys, K.L.; Mak, A.C.Y.; Eng, C.; Huntsman, S.; Villar, J.; Rodriguez-Santana, J.R.; Burchard, E.G.; et al. Genome-wide association study reveals a novel locus for asthma with severe exacerbations in diverse populations. Pediatr. Allergy Immunol. 2021, 32, 106–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera-Luis, E.; Mak, A.C.Y.; Perez-Garcia, J.; Martin-Gonzalez, E.; Eng, C.; Beckman, K.B.; Huntsman, S.; Hu, D.; González-Pérez, R.; Hernández-Pérez, J.M.; et al. Admixture mapping of severe asthma exacerbations in Hispanic/Latino childen and youth. Thorax 2023, 78, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farzan, N.; Vijverberg, S.J.; Hernandez-Pacheco, N.; Bel, E.H.D.; Berce, V.; Bønnelykke, K.; Bisgaard, H.; Burchard, E.G.; Canino, G.; Celedón, J.C.; et al. 17q21 variant increases the risk of exacerbations in asthmatic children despite inhaled corticosteroids use. Allergy 2018, 73, 2083–2088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernandez-Pacheco, N.; Vijverberg, S.J.; Herrera-Luis, E.; Li, J.; Sio, Y.Y.; Granell, R.; Corrales, A.; Maroteau, C.; Lethem, R.; Perez-Garcia, J.; et al. Genome-wide association study of asthma exacerbations despite inhaled corticosteroid use. Eur. Respir. J. 2021, 57, 2003388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The ENCODE Project Consortium. An integrated encyclopedia of DNA elements in the human genome. Nature 2012, 489, 57–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GTEx Consortium. The Genotype-Tissue Expression (GTEx) project. Nat. Genet 2013, 45, 580–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrine, N.; Portelli, M.A.; John, C.; Soler Artigas, M.; Bennett, N.; Hall, R.; Lewis, J.; Henry, A.P.; Billington, C.K.; Ahmad, A.; et al. Moderate-to-severe asthma in individuals of European ancestry: A genome-wide association study. Lancet Respir. Med. 2019, 7, 20–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, F.D. Gene-environment interactions in asthma. With apologies to William of Ockham. Proc. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2007, 4, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forno, E.; Celedón, J.C. Epigenomics and Transcriptomics in the Prediction and Diagnosis of Childhood Asthma: Are We There Yet? Front. Pediatr. 2019, 7, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.L.; Gruzieva, O.; Qiu, W.; Kebede Merid, S.; Celedón, J.C.; Raby, B.A.; Söderhäll, C.; DeMeo, D.L.; Weiss, S.T.; Melén, E.; et al. DNA Methylation Is Associated with Inhaled Corticosteroid Response in Persistent Childhood Asthmatics. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2019, 49, 1225–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.L.; Qiu, W.; Demeo, D.L.; Raby, B.A.; Weiss, S.T.; Tantisira, K.G. DNA Methylation Is Associated with Improvement in Lung Function on Inhaled Corticosteroids in Pediatric Asthmatics. Pharmacogenet. Genom. 2019, 29, 65–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin-Almeida, M.; Perez-Garcia, J.; Herrera-Luis, E.; Rosa-Baez, C.; Gorenjak, M.; Neerincx, A.H.; Sardón-Prado, O.; Toncheva, A.A.; Harner, S.; Wolff, C.; et al. Epigenome-Wide Association Studies of the Fractional Exhaled Nitric Oxide and Bronchodilator Drug Response in Moderate-to-Severe Pediatric Asthma. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kho, A.T.; McGeachie, M.J.; Moore, K.G.; Sylvia, J.M.; Weiss, S.T.; Tantisira, K.G. Circulating MicroRNAs and Prediction of Asthma Exacerbation in Childhood Asthma. Respir. Res. 2018, 19, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, Y.L.; Su, M.W.; Chiang, B.L.; Yang, Y.H.; Tsai, C.H.; Lee, Y.L. Genetic Profiles of Transcriptomic Clusters of Childhood Asthma Determine Specific Severe Subtype. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2018, 48, 1164–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, W.; Guo, F.; Glass, K.; Yuan, G.C.; Quackenbush, J.; Zhou, X.; Tantisira, K.G. Differential Connectivity of Gene Regulatory Networks Distinguishes Corticosteroid Response in Asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2018, 141, 1250–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGeachie, M.J.; Clemmer, G.L.; Hayete, B.; Xing, H.; Runge, K.; Wu, A.C.; Jiang, X.; Lu, Q.; Church, B.; Khalil, I.; et al. Systems Biology and in Vitro Validation Identifies Family with Sequence Similarity 129 Member A (FAM129A) as an Asthma Steroid Response Modulator. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2018, 142, 1479–1488.e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.; Wang, J.; Liu, J.; Huang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, S.; Zhang, W.; Yang, M.; Zhang, H. Niban Protein Regulates Apoptosis in HK-2 Cells via Caspase-Dependent Pathway. Ren. Fail. 2019, 41, 455–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katayama, S.; Stenberg Hammar, K.; Krjutškov, K.; Einarsdottir, E.; Hedlin, G.; Kere, J.; Söderhäll, C. Acute wheeze-specific gene module shows correlation with vitamin D and asthma medication. Eur. Respir. J. 2020, 55, 1901330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, Q.; Sun, B. Interferons Command Trim22 to Fight against Viruses. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2017, 14, 794–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neerincx, A.H.; Vijverberg, S.J.H.; Bos, L.D.J.; Brinkman, P.; van der Schee, M.P.; de Vries, R.; Sterk, P.J.; Maitland-van Der Zee, A.-H. Breathomics from exhaled volatile organic compounds in pediatric asthma. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2017, 52, 1616–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pité, H.; Morais-Almeida, M.; Rocha, S.M. Metabolomics in Asthma: Where Do We Stand? Curr. Opin. Pulm. Med. 2018, 24, 94–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, R.S.; Sordillo, J.E.; Lutz, S.M.; Avila, L.; Soto-Quiros, M.; Celedón, J.C.; McGeachie, M.J.; Dahlin, A.; Tantisira, K.; Huang, M.; et al. Pharmacometabolomics of Bronchodilator Response in Asthma and the Role of Age-Metabolite Interactions. Metabolites 2019, 9, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, R.S.; Chawes, B.L.; Blighe, K.; Virkud, Y.V.; Croteau-Chonka, D.C.; McGeachie, M.J.; Clish, C.B.; Bullock, K.; Celedón, J.C.; Weiss, S.T.; et al. An Integrative Transcriptomic and Metabolomic Study of Lung Function in Children With Asthma. Chest 2018, 154, 335–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toncheva, A.A.; Potaczek, D.P.; Schedel, M.; Gersting, S.W.; Michel, S.; Krajnov, N.; Gaertner, V.D.; Klingbeil, J.M.; Illig, T.; Franke, A.; et al. Childhood asthma is associated with mutations and gene expression differences of ORMDL genes that can interact. Allergy 2015, 70, 1288–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, I.V.; Lozupone, C.A.; Schwartz, D.A. The environment, epigenome, and asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2017, 140, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivaska, L.E.; Hanif, T.; Ahmad, F.; Tan, G.; Altunbulakli, C.; Mikola, E.; Silvoniemi, A.; Puhakka, T.; Akdis, C.A.; Toppila-Salmi, S.; et al. Tonsillar microbial diversity, abundance, and interrelations in atopic and non-atopic individuals. Allergy 2020, 75, 2133–2135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valverde-Molina, J.; García-Marcos, L. Microbiome and Asthma: Microbial Dysbiosis and the Origins, Phenotypes, Persistence, and Severity of Asthma. Nutrients 2023, 15, 486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.J.; Porsche, C.; Kozik, A.J.; Lynch, S.V. Microbiome-Immune Interactions in Allergy and Asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2022, 10, 2244–2251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ver Heul, A.; Planer, J.; Kau, A.L. The Human Microbiota and Asthma. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2019, 57, 350–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sverrild, A.; Kiilerich, P.; Brejnrod, A.; Pedersen, R.; Porsbjerg, C.; Bergqvist, A.; Erjefält, J.S.; Kristiansen, K.; Backer, V. Eosinophilic airway inflammation in asthmatic patients is associated with an altered airway microbiome. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2017, 140, 407–417.e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barcik, W.; Boutin, R.C.T.; Sokolowska, M.; Finlay, B.B. The Role of Lung and Gut Microbiota in the Pathology of Asthma. Immunity 2020, 52, 241–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Jackson, D.; Bacharier, L.B.; Mauger, D.; Boushey, H.; Castro, M.; Durack, J.; Huang, Y.; Robert, F.L., Jr.; Storch, G.A.; et al. The upper-airway microbiota and loss of asthma control among asthmatic children. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 5714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durack, J.; Huang, Y.J.; Nariya, S.; Christian, L.S.; Ansel, K.M.; Beigelman, A.; Castro, M.; Dyer, A.-M.; Israel, E.; Kraft, M.; et al. Bacterial biogeography of adult airways in atopic asthma. Microbiome 2018, 6, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Depner, M.; Ege, M.J.; Cox, M.J.; Dwyer, S.; Walker, A.W.; Birzele, L.T.; Genuneit, J.; Horak, E.; Braun-Fahrländer, C.; Danielewicz, H.; et al. Bacterial microbiota of the upper respiratory tract and childhood asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2017, 139, 826–834.e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-García, J.; Hernández-Pérez, J.M.; González-Pérez, R.; Sardón, O.; Martin-Gonzalez, E.; Espuela-Ortiz, A.; Mederos-Luis, E.; Callero, A.; Herrera-Luis, E.; Corcuera, P.; et al. The Genomics and Metagenomics of Asthma Severity (GEMAS) Study: Rationale and Design. J. Pers. Med. 2020, 10, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-García, J.; González-Carracedo, M.; Espuela-Ortiz, A.; Hernández-Pérez, J.M.; González-Pérez, R.; Sardón-Prado, O.; Martin-Gonzalez, E.; Mederos-Luis, E.; Poza-Guedes, P.; Corcuera-Elosegui, P.; et al. The upper-airway microbiome as a biomarker of asthma exacerbations despite inhaled corticosteroid treatment. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2023, 151, 706–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Nimwegen, F.A.; Penders, J.; Stobberingh, E.E.; Postma, D.S.; Koppelman, G.H.; Kerkhof, M.; Reijmerink, N.E.; Dompeling, E.; Brandt, P.A.v.D.; Ferreira, I.; et al. Mode and place of delivery, gastrointestinal microbiota, and their influence on asthma and atopy. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2011, 128, 948–955.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrahamsson, T.R.; Jakobsson, H.E.; Andersson, A.F.; Björkstén, B.; Engstrand, L.; Jenmalm, M.C. Low gut microbiota diversity in early infancy precedes asthma at school age. Clin. Exp. Allergy. 2014, 44, 842–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrieta, M.C.; Stiemsma, L.T.; Dimitriu, P.A.; Thorson, L.; Russell, S.; Yurist-Doutsch, S.; Kuzeljevic, B.; Gold, M.J.; Britton, H.M.; Lefebvre, D.L.; et al. Early infancy microbial and metabolic alterations affect risk of childhood asthma. Sci. Transl. Med. 2015, 7, 307ra152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blankestijn, J.M.; López-Rincón, A.; Neerincx, A.H.; Vijverberg, S.J.H.; Hashimoto, S.; Gorenjak, M.; Prado, O.S.; Corcuera-Elosegui, P.; Korta-Murua, J.; Pino-Yanes, M.; et al. Classifying asthma control using salivary and fecal bacterial microbiome in children with moderate-to-severe asthma. Pediatr. Allergy Immunol. 2023, 34, e13919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Ciaccio, C.E.; Casale, T.B. Potential new targets for drug development in severe asthma. World Allergy Organ. J. 2018, 11, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelsen, S.G.; Agache, I.O.; Soong, W.; Israel, E.; Chupp, G.L.; Cheung, D.S.; Theess, W.; Yang, X.; Staton, T.L.; Choy, D.F.; et al. Astegolimab (anti-ST2) efficacy and safety in adults with severe asthma: A randomized clinical trial. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2021, 148, 790–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wechsler, M.E.; Ruddy, M.K.; Pavord, I.D.; Israel, E.; Rabe, K.F.; Ford, L.B.; Maspero, J.F.; Abdulai, R.M.; Hu, C.-C.; Martincova, R.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Itepekimab in Patients with Moderate-to-Severe Asthma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 1656–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efficacy and Safety of Tozorakimab in Symptomatic Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease with a History of Exacerbations (OBERON). Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT05166889 (accessed on 25 May 2023).
- Study to Assess the Efficacy and Safety of MEDI3506 in Adults with Uncontrolled Moderate-to-Severe Asthma (FRONTIER-3). Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04570657 (accessed on 20 June 2023).
- Brightling, C.E.; Nair, P.; Cousins, D.J.; Louis, R.; Singh, D. Risankizumab in Severe Asthma–A Phase 2a, Placebo-Controlled Trial. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 1669–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, A.W.; Poulton, L.; Shim, D.; Mabon, D.; Butt, D.; Pollard, M.; Pande, V.; Husten, J.; Lyons, J.; Tian, C.; et al. An anti-TL1A antibody for the treatment of asthma and inflammatory bowel disease. MAbs 2018, 10, 664–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A 16-Week, Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Parallel-Group, Proof-of-Concept Study to Evaluate the Efficacy and Safety of TEV-48574 in Adults with T2-low/Non-T2 Severe Uncontrolled Asthma. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04545385 (accessed on 18 May 2023).
- A Randomized, Placebo Controlled, Double Blind Phase IIa Study to Evaluate the Safety, Tolerability, Pharmacokinetics, and Clinical Activity of Multiple Intravenous Doses of FB704A in Adults with Severe Asthma. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT05018299 (accessed on 25 April 2023).
- Gauvreau, G.M.; Hohlfeld, J.M.; FitzGerald, J.M.; Boulet, L.P.; Cockcroft, D.W.; Davis, B.E.; Korn, S.; Kornmann, O.; Leigh, R.; Mayers, I.; et al. Inhaled anti-TSLP antibody fragment, ecleralimab, blocks responses to allergen in mild asthma. Eur. Respir. J. 2023, 61, 2201193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Name | Target | Mechanism of Action | Authorized (Age) | Indication | Dosage S.Q. | Comorbidities Treatable | Predictors Response | Clinical Outcomes | Adverse Effects | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FDA | EMA | E | C | P.F. | QoL | OCS | ||||||||
| OMALIZUMAB | IgE | Circulating IgE binding preventing receptor binding FcεR.I. in mast cells, basophils, and dendritic plasmacytoid cells; FcεRII in dendritic plasmacytoid cells and Eos. Reduction of free IgE and downregulation of receptor expression. | ≥6 | ≥6 | Uncontrolled allergic SA with sensitization to perennial pneumoallergens and in range according to weight and IgE. | By weight and total IgE: FDA: 75–375 mg IgE (KU/L): 6–11 y: 30–1300 mg. : 30–700 mg. EMA: 75–600 mg IgE (KU/L): ≥6 y: 30–1300 mg/2–4 w. Prefilled syringe. Home administration. | Idiopathic chronic urticaria. Nasal polyposis. | Eos ≥ 260/μL FeNO > 20 ppb | ↓ | ↑ | =↑ | ↑ | ↓ | Local reaction. Headache. Fever (6–12 years). Anaphylaxis (very rare). |
| MEPOLIZUMAB | IL-5 | Circulating IL-5 binding prevents binding to the α-receptor. Eos reduction. | ≥6 | ≥6 | SA uncontrolled and Eos ≥ 150/μL or ≥300/μL in the last year. | 6–11 y: 40 mg. ≥12 y: 100 mg/4 w. Prefilled syringe or autoinjector (pen). Home administration. | Nasal polyposis. EGPA. HES. | ↑ Eos ↑ E Nasal polyposis OCS | ↓ | ↑ | ↑ | ↑ | ↓ | Local reaction. Headache. Nasal congestion. Anaphylaxis (very rare). |
| BENRALIZUMAB | IL-5Rα | Binding to IL-5Rα Rapid apoptosis of Eos by cytotoxicity mechanism. | ≥12 | No | SA uncontrolled and Eos ≥ 150/μL or ≥300/μL in the last year. | 30 mg/8 w (first 3 doses every four w). Prefilled syringe or autoinjector (pen). Home administration. | ↑ Eos ↑ E Nasal polyposis OCS ↓ PF | ↓ | ↑ | ↑ | ↑ | ↓ | Local reaction. Headache. Pharyngitis. Anaphylaxis (very rare). | |
| DUPILUMAB | IL-4Rα | Binding to IL-4Rα blocking IL-4/IL-13 signaling. T2 inflammatory pathway downregulation. Prevent Eos extravasation to tissues. | ≥6 | ≥12 | SA uncontrolled and Eos ≥ 150/μL and ≤1500/μL and/or FeNO ≥ 25 ppb and/or need for OCS. | FDA: 6–11 y ≤ 30 kg:100 mg/2 w or 300 mg/4 w. 6–11 y > 30 kg: 200 mg/2 w or 300 mg/4 w. FDA and EMA ≥ 12 y: 200 mg/2 w (first dose 400 mg). Prefilled syringe or autoinjector (pen). Home administration. | AD. Nasal polyposis. EEo. | ↑ Eos ↑ FeNO | ↓ | ↑ | ↑ | ↑ | ↓ | Local reaction. Transient elevation of eosinophilia. EGPA (very rare). Anaphylaxis (very rare). |
| TEZEPELUMAB | TSLP | Binding to circulating TSLP prevents receptor binding. Acts at high levels of the inflammatory cascade. | ≥12 | ≥12 | SA T2 or non-T2 with exacerbations. | 210 mg/4 w. Prefilled syringe or autoinjector (pen). | ↑ Eos ↑ FeNO T2 low | ↓ | ↑ | ↑ | ↑ | = | Local reaction. Pharyngitis. Arthralgias. Lumbar pain. Nasal congestion. Anaphylaxis (very rare). | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sardon-Prado, O.; Diaz-Garcia, C.; Corcuera-Elosegui, P.; Korta-Murua, J.; Valverde-Molina, J.; Sanchez-Solis, M. Severe Asthma and Biological Therapies: Now and the Future. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 5846. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12185846
Sardon-Prado O, Diaz-Garcia C, Corcuera-Elosegui P, Korta-Murua J, Valverde-Molina J, Sanchez-Solis M. Severe Asthma and Biological Therapies: Now and the Future. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(18):5846. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12185846
Chicago/Turabian StyleSardon-Prado, Olaia, Carolina Diaz-Garcia, Paula Corcuera-Elosegui, Javier Korta-Murua, Jose Valverde-Molina, and Manuel Sanchez-Solis. 2023. "Severe Asthma and Biological Therapies: Now and the Future" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 18: 5846. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12185846







