Biomaterials and Clinical Application of Dental Implants in Relation to Bone Density—A Narrative Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
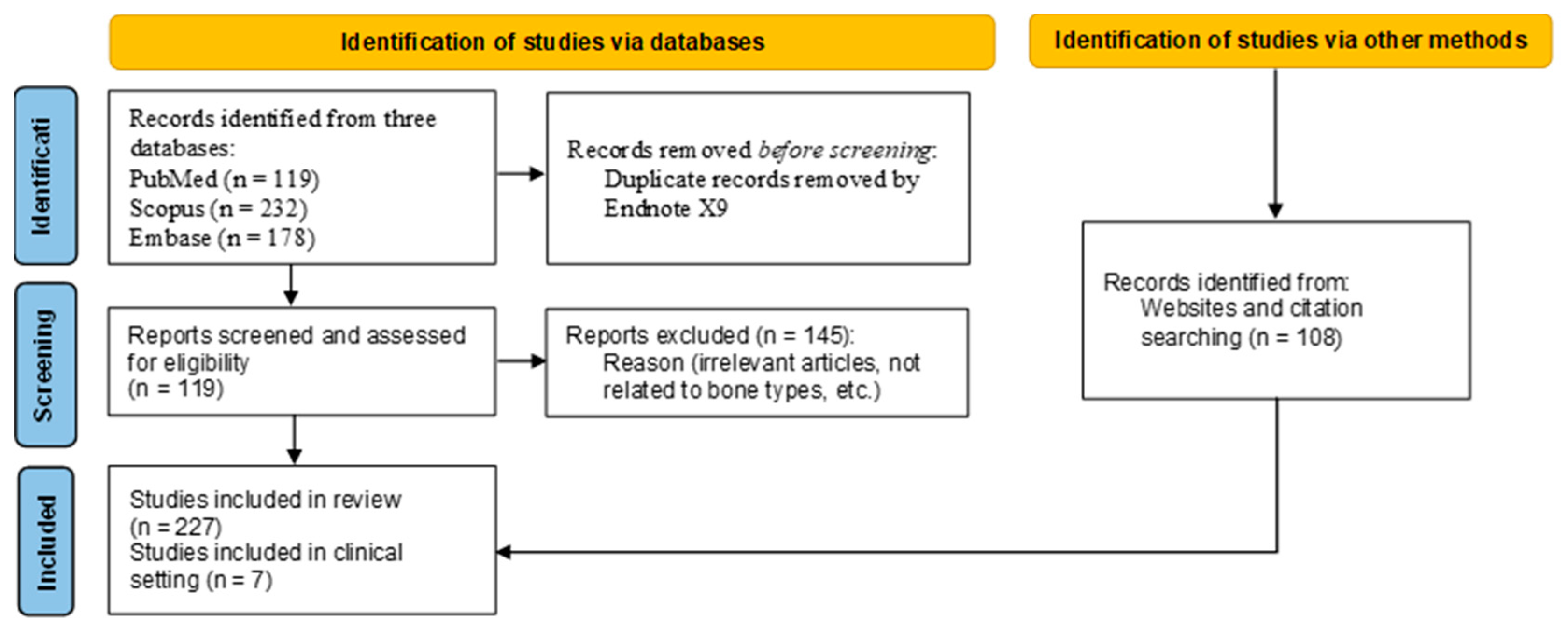
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Bone Response to Dental Implant Materials
3.1.1. Bone Density
3.1.2. Bone Remodeling and Bone Density
Peri-Implant Bone Strain
Stress Distribution in Peri-Implant Bone
Clinical Assessment Tool
Histological Assessment Tool
3.2. Material Used for Dental Implants and Their Properties
3.2.1. Biomaterial of Dental Implants
Metal and Metal Alloy
Ceramics
Polyetheretherketone (PEEK)
3.2.2. Functional Properties of Dental Implant Materials to Bone Density
Elastic Modulus, Stiffness
| Properties | Elastic Modulus (GPa) | Flexural/Tensile Strength (MPa) | Yield Strength (MPa) | Fracture Strength (N) | Surface Roughness | Thermal Conductivity | Hydrophobicity | Ref. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ti | cpTi (IV) | 104.1 | 680 | 485 | - | More than Zr and PEEK | Yes | No | [116,117] |
| TiAl6V4 | 110 | 954 | 729 | - | [118] | ||||
| Ti-Zr | 96 | 953 | - | - | [116,119] | ||||
| Ti-24Nb-4Zr-8Sn (Ti2448) | 45 | 850 | - | - | [120] | ||||
| Zr | 3Y | 210 | 900–1200 | - | 516–607 | Less | Low | No | [121] |
| ATZ | 220 | 1800–2400 | - | 1064–1734 | [121] | ||||
| PEEK | PEEK | 3–4 | 80 | - | - | Less | Low | Yes | [121,122] |
| CFR-PEEK | 18 | 120 | - | - | [121,122] | ||||
| GFR-PEEK | 12 | - | - | - | [96,121] | ||||
| Titanium Implant | Macrogeometry | Microgeometry (Thread Design) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bone Density | Implant Placement Condition | Shape | Diameter | Length | Shape | Pitch | Width | Depth |
| High | - |
| All | All (≥6 mm) |
| Standard (1.2 mm) | Standard (0.18–0.30 mm) | Standard (0.42 mm) |
| Low | - |
| Wider (≥4 mm) | Longer (9–11 mm) |
| 🡇 Lower than the standard | Standard | 🡅 Higher than the standard |
| - | Immediate |
| ≥4 mm | ≥11 mm |
| - | - | - |
Fracture Resistance
3.2.3. Biological Properties of Dental Implant Materials to Bone Density
3.3. Clinical Application of Dental Implants and Their Survival Rates
3.3.1. Survival Rate of Alternative Implant Materials
3.3.2. Survival Rate of Dental Implants Related to Bone Density
| Study/Year | Study Type | Material | Implant | Surface | Site | Geometry | Mean MBL (Mean ± SD) | Follow-Up (Month) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aldebes et al. 2022 [163] | RCTs | One-piece zirconia (Y-TZP) | 18 | Sandblasting surface | Premolar | Anatomic zirconia implant | D3/4: 0.61 ± 0.23 | 12 |
| Makary et al. 2019 [156] | CT | 16 | D1: 0.20 ± 0.27 | 12 | ||||
| Titanium | 23 | Ca2+ on the SLA-treated surface | All | Different diameters of 4, 4.5, 5, 5.5 mm with 10 mm length | D2/3: 0.11 ± 0.11 | |||
| 7 | D4: 0.33 ± 0.14 | |||||||
| Hingsammer et al. 2017 [157] | CT | 15 | D1: 0.66 ± 0.72 | 12 | ||||
| Titanium | 38 | TiUnite surface and machine neck | Posterior | Short implants | D2/3: 0.60 ± 0.77 | |||
| 21 | D4: 0.65 ± 0.68 | |||||||
| De Santis et al. 2016 [158] | CT | Titanium | 35 | TiUnite surface | All | Tapered and double-variable thread design, apical drilling blades | D2/3: 0.68 ± 0.65 | 6 |
| 109 | D4: 0.73 ± 0.46 | |||||||
| Cannizzaro et al. 2012 [159] | RCTs | Titanium | 68 | Dual etched and covered with nanoscale calcium phosphate crystal | Immediate loading site | 4 mm diameter with tapered-with external connection | D123: 0.26 ± 0.35 | 6 |
| Rossi et al. 2014 [160] | CT | Titanium | 31 | SLActive surface with moderate rough | Posterior | 6 mm length with 4.1 and 4.8 mm diameter | D123: 0.55 ± 0.80 | 12 |
| Held et al. 2013 [161] | CT | Titanium | 35 | Sandblasted and acid-etched surface | All | ELEMENT RC implants with 4, 4.5, 5 mm diameter and 8, 9.5, 11.5, 12, 14 mm length | D3/4: 1.46 ± 0.75 | 3 |
4. Conclusions
- -
- Implant material, implant design, and surgical techniques are pivotal factors affecting the success rates of dental implant placement in low-density bone.
- -
- Both titanium and zirconia implants are widely accepted materials in the market. Nonetheless, PEEK implants serve as an alternative material for specific cases, such as those involving poor bone conditions, bruxism, and esthetic concerns.
- -
- Modified implant topography, strengthened implant geometry, and a suitable surgical technique are selected and used to achieve high survival and success rates and attain superior clinical results.
- -
- In low-density conditions,
- o
- Titanium provides a better chance of achieving initial stability due to the best mechanical performance among the three materials.
- o
- Conical titanium implant design, wider diameter, longer length, reverse buttress with self-tapping, small thread pitch, and deep thread depth are recommended.
- o
- Surgical techniques, such as underpreparation, osteotome technique, and magnetodynamic surgery, play a critical role in achieving primary stability. However, piezoelectric surgery does not affect the initial stability but does affect the secondary stability.
- -
- Regardless of the material and follow-up period, low bone quality tended to have more marginal bone loss than high bone quality.
- -
- Further study is required to identify an optimal implant material in terms of the bone state in clinical settings.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Lists of Abbreviations
| Abbreviations | Explanation |
| TiO2 | Titanium oxide |
| 3Y-TZP | 3 mol% yttria–tetragonal zirconia polycrystal |
| ATZ | Alumina-toughened zirconia |
| BIC | Bone–implant interface contact |
| LTD | Low-temperature degradation |
| HUs | Hounsfield units |
| CT | Computer tomography |
| CBCT | Cone beam computed tomography |
| GVs | Gray values |
| PEEK | Polyetheretherketone |
| IT | Insertion torque |
| RFA | Resonance frequency analysis |
| ISQ | Implant stability quotient |
| RTQ | Removal torque |
| SLM | Selective laser fusion |
| EBM | Electron beam fusion |
| ZrO2 | Zirconium dioxide |
| PSZ | Partially stabilized zirconia |
| TZP | Tetragonal zirconia polycrystal |
| CFR-PEEK | Carbon fiber reinforcement polyetheretherketone |
| GFR-PEEK | Glass fiber reinforcement polyetheretherketone |
| GPa | Gigapascal |
| Ti6Al4V | Titanium–6 Aluminum–4 Vanadium |
| CpTi | Commercially pure titanium |
| HA | Hydroxyapatite |
| TPS | Titanium plasma-sprayed |
| UV | Ultraviolet |
| RCTs | Randomized Clinical Trials |
| Non-RCT | Non-Randomized Clinical Trial |
References
- Esposito, M.; Hirsch, J.M.; Lekholm, U.; Thomsen, P. Biological factors contributing to failures of osseointegrated oral implants. (I). Success criteria and epidemiology. Eur. J. Oral Sci. 1998, 106, 527–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olmedo-Gaya, M.-V.; Romero-Olid, M.-N.; Ocaña-Peinado, F.M.; Vallecillo-Rivas, M.; Vallecillo, C.; Reyes-Botella, C. Influence of different surgical techniques on primary implant stability in the posterior maxilla: A randomized controlled clinical trial. Clin. Oral Investig. 2023, 27, 3499–3508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Ahmari, N.M. Osseo-densification versus conventional surgical technique in low density jaw bone: A split mouth in vivo study. Technol. Health Care 2022, 30, 1117–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mello-Machado, R.C.; Sartoretto, S.C.; Granjeiro, J.M.; Calasans-Maia, J.A.; de Uzeda, M.J.P.G.; Mourão, C.F.A.B.; Ghiraldini, B.; Bezerra, F.J.B.; Senna, P.M.; Calasans-Maia, M.D. Osseodensification enables bone healing chambers with improved low-density bone site primary stability: An in vivo study. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 15436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javed, F.; Ahmed, H.B.; Crespi, R.; Romanos, G.E. Role of primary stability for successful osseointegration of dental implants: Factors of influence and evaluation. Interv. Med. Appl. Sci. IMAS 2013, 5, 162–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bozkaya, D.; Muftu, S.; Muftu, A. Evaluation of load transfer characteristics of five different implants in compact bone at different load levels by finite elements analysis. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2004, 92, 523–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tretto, P.H.W.; Dos Santos, M.B.F.; Spazzin, A.O.; Pereira, G.K.R.; Bacchi, A. Assessment of stress/strain in dental implants and abutments of alternative materials compared to conventional titanium alloy-3D non-linear finite element analysis. Comput. Methods Biomech. Biomed. Eng. 2020, 23, 372–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robau-Porrua, A.; Pérez-Rodríguez, Y.; Soris-Rodríguez, L.M.; Pérez-Acosta, O.; González, J.E. The effect of diameter, length and elastic modulus of a dental implant on stress and strain levels in peri-implant bone: A 3D finite element analysis. Biomed. Mater. Eng. 2020, 30, 541–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, Y.; Iyer, R.; Dommeti, V.K.; Nutu, E.; Rana, M.; Merdji, A.; Biswas, J.K.; Roy, S. Design of dental implant using design of experiment and topology optimization: A finite element analysis study. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. H 2021, 235, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Xu, W.; Chen, M.; Chen, D.; Sun, G.; Zhang, C.; Pan, Y.; Lu, J.; Guo, E.; Lu, X. Structural Design and Finite Element Simulation Analysis of Grade 3 Graded Porous Titanium Implant. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 10090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piotrowski, B.; Baptista, A.A.; Patoor, E.; Bravetti, P.; Eberhardt, A.; Laheurte, P. Interaction of bone-dental implant with new ultra low modulus alloy using a numerical approach. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2014, 38, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias Corpa Tardelli, J.; Monteiro de Barros Ciribelli Alves, B.; Lima da Costa Valente, M.; Cândido dos Reis, A. Influence of the modulus of elasticity of dental implants on the distribution of stresses in the alveolar bone by the finite element method: A systematic review. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. Med. Pathol. 2023, 35, 383–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholson, J.W. Titanium Alloys for Dental Implants: A Review. Prosthesis 2020, 2, 100–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brånemark, P.I. Osseointegration and its experimental background. J. Prosthet. Dent. 1983, 50, 399–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alghamdi, H.S.; Jansen, J.A. The development and future of dental implants. Dent. Mater. J. 2020, 39, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Chu, P.K.; Ding, C. Surface modification of titanium, titanium alloys, and related materials for biomedical applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. R Rep. 2004, 47, 49–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comisso, I.; Arias-Herrera, S.; Gupta, S. Zirconium dioxide implants as an alternative to titanium: A systematic review. J. Clin. Exp. Dent. 2021, 13, e511–e519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ban, S. Classification and Properties of Dental Zirconia as Implant Fixtures and Superstructures. Materials 2021, 14, 4879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pieralli, S.; Kohal, R.J.; Jung, R.E.; Vach, K.; Spies, B.C. Clinical Outcomes of Zirconia Dental Implants: A Systematic Review. J. Dent. Res. 2017, 96, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pieralli, S.; Kohal, R.J.; Lopez Hernandez, E.; Doerken, S.; Spies, B.C. Osseointegration of zirconia dental implants in animal investigations: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Dent. Mater. 2018, 34, 171–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Monzavi, M.; Li, M.; Čokić, S.; Manesh, A.; Nowzari, H.; Vleugels, J.; Van Meerbeek, B. Fracture analysis of one/two-piece clinically failed zirconia dental implants. Dent. Mater. 2022, 38, 1633–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heimes, D.; Becker, P.; Pabst, A.; Smeets, R.; Kraus, A.; Hartmann, A.; Sagheb, K.; Kämmerer, P.W. How does dental implant macrogeometry affect primary implant stability? A narrative review. Int. J. Implant Dent. 2023, 9, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stacchi, C.; Troiano, G.; Montaruli, G.; Mozzati, M.; Lamazza, L.; Antonelli, A.; Giudice, A.; Lombardi, T. Changes in implant stability using different site preparation techniques: Osseodensification drills versus piezoelectric surgery. A multi-center prospective randomized controlled clinical trial. Clin. Implant Dent. Relat. Res. 2022, 25, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giudice, A.; Bennardo, F.; Antonelli, A.; Barone, S.; Wagner, F.; Fortunato, L.; Traxler, H. Influence of clinician’s skill on primary implant stability with conventional and piezoelectric preparation techniques: An ex-vivo study. J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents 2020, 34, 739–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, U.; Joos, U.; Mythili, J.; Stamm, T.; Hohoff, A.; Fillies, T.; Stratmann, U.; Wiesmann, H.P. Ultrastructural characterization of the implant/bone interface of immediately loaded dental implants. Biomaterials 2004, 25, 1959–1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferguson, S.J.; Langhoff, J.D.; Voelter, K.; von Rechenberg, B.; Scharnweber, D.; Bierbaum, S.; Schnabelrauch, M.; Kautz, A.R.; Frauchiger, V.M.; Mueller, T.L.; et al. Biomechanical comparison of different surface modifications for dental implants. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant 2008, 23, 1037–1046. [Google Scholar]
- Piattelli, A. Bone Response to Dental Implant Materials; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Elsayed, M. Biomechanical factors that influence the bone-implant-interface. Res. Rep. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2019, 3, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Misch, C.E. Density of bone: Effect on treatment plans, surgical approach, healing, and progressive boen loading. Int. J. Oral Implantol. 1990, 6, 23–31. [Google Scholar]
- Misch, C. Available bone influences prosthodontic treatment. Dent. Today 1988, 7, 44–75. [Google Scholar]
- Lekholm, U. Patient selection and preparation. In Tissue Integrated Prostheses: Osseointegration in Clinical Dentistry; Branemark, P.I., Zarb, G.A., Albrektsson, T., Eds.; Quintessence Publishing Company: Chicago, IL, USA, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Misch, C. Bone character: Second vital implant criterion. Dent. Today 1988, 7, 39. [Google Scholar]
- Roy, S.; Das, M.; Chakraborty, P.; Biswas, J.K.; Chatterjee, S.; Khutia, N.; Saha, S.; Chowdhury, A.R. Optimal selection of dental implant for different bone conditions based on the mechanical response. Acta Bioeng. Biomech. 2017, 19, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Turkyilmaz, I.; McGlumphy, E.A. Influence of bone density on implant stability parameters and implant success: A retrospective clinical study. BMC Oral Health 2008, 8, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Misch, C.E. Density of bone: Effect on surgical approach, and healing. In Contemporary Implant Dentistry; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc.: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1999; pp. 371–384. [Google Scholar]
- Eguren, M.; Holguin, A.; Diaz, K.; Vidalon, J.; Linan, C.; Pacheco-Pereira, C.; Lagravere Vich, M.O. Can gray values be converted to Hounsfield units? A systematic review. Dentomaxillofacial Radiol. 2022, 51, 20210140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patrick, S.; Birur, N.P.; Gurushanth, K.; Raghavan, A.S.; Gurudath, S. Comparison of gray values of cone-beam computed tomography with hounsfield units of multislice computed tomography: An in vitro study. Indian J. Dent. Res. 2017, 28, 66. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lim Fat, D.; Kennedy, J.; Galvin, R.; O’Brien, F.; Mc Grath, F.; Mullett, H. The Hounsfield value for cortical bone geometry in the proximal humerus—An in vitro study. Skelet. Radiol. 2012, 41, 557–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aamodt, A.; Kvistad, K.A.; Andersen, E.; Lund-Larsen, J.; Eine, J.; Benum, P.; Husby, O.S. Determination of the Hounsfield value for CT-based design of custom femoral stems. J. Bone Jt. Surgery. Br. Vol. 1999, 81, 143–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.; Ikram, Y.; Qureshi, F.; Sharjeel, M.; Khan, Z.A.; Ataullah, K. Assessment of Jaw Bone Density in Terms of Hounsfield Units Using Cone Beam Computed Tomography for Dental Implant Treatment Planning. Pak. Armed Forces Med. J. 2021, 71, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frost, H.M. Wolff’s Law and bone’s structural adaptations to mechanical usage: An overview for clinicians. Angle Orthod 1994, 64, 175–188. [Google Scholar]
- Frost, H.M. From Wolff’s law to the Utah paradigm: Insights about bone physiology and its clinical applications. Anat. Rec. 2001, 262, 398–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demenko, V.; Linetsky, I.; Nesvit, V.; Linetska, L.; Shevchenko, A. FE study of bone quality effect on load-carrying ability of dental implants. Comput. Methods Biomech. Biomed. Eng. 2014, 17, 1751–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leblebicioğlu Kurtuluş, I.; Kilic, K.; Bal, B.; Kilavuz, A. Finite Element Analysis of the Stress Distribution Associated With Different Implant Designs for Different Bone Densities. J. Prosthodont. 2022, 31, 614–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rungsiyakull, P.; Rungsiyakull, C.; Monstaporn, M.; Sae-Lee, D.; Elsaka, S. Effects of bone type and occlusal loading pattern on bone remodeling in implant-supported single crown: A finite element study. J. Prosthodont. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yalçın, M.; Kaya, B.; Laçin, N.; Arı, E. Three-Dimensional Finite Element Analysis of the Effect of Endosteal Implants with Different Macro Designs on Stress Distribution in Different Bone Qualities. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant 2019, 34, e43–e50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Jansen, J.A.; Walboomers, X.F.; van den Beucken, J.J. Mechanical aspects of dental implants and osseointegration: A narrative review. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2020, 103, 103574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Mortadi, N.; Bataineh, K.; Albakri, I. A Three–Dimensional Finite Element Analysis of Polyetheretherketone PEEK in Dental Implant Prosthesis: A Novel Implant System. Open Dent. J. 2022, 16, e187421062203040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.T.; Koak, J.Y.; Lim, Y.J.; Kim, S.K.; Kwon, H.B.; Kim, M.J. Stress shielding and fatigue limits of poly-ether-ether-ketone dental implants. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2012, 100, 1044–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friberg, B.; Sennerby, L.; Gröndahl, K.; Bergström, C.; Bäck, T.; Lekholm, U. On cutting torque measurements during implant placement: A 3-year clinical prospective study. Clin. Implant Dent. Relat. Res. 1999, 1, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esposito, M.; Grusovin, M.G.; Willings, M.; Coulthard, P.; Worthington, H.V. The effectiveness of immediate, early, and conventional loading of dental implants: A Cochrane systematic review of randomized controlled clinical trials. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant 2007, 22, 893–904. [Google Scholar]
- Norton, M. Primary stability versus viable constraint—A need to redefine. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant 2013, 28, 19–21. [Google Scholar]
- Stocchero, M. On Influence of Undersized Implant Site On Implant Stability and Osseointegration; Faculty of Odontology, Malmö University: Malmö, Sweden, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Toia, M.; Stocchero, M.; Cecchinato, F.; Corrà, E.; Jimbo, R.; Cecchinato, D. Clinical Considerations of Adapted Drilling Protocol by Bone Quality Perception. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant 2017, 32, 1288–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turkyilmaz, I.; Sennerby, L.; Yilmaz, B.; Bilecenoglu, B.; Ozbek, E.N. Influence of defect depth on resonance frequency analysis and insertion torque values for implants placed in fresh extraction sockets: A human cadaver study. Clin. Implant Dent. Relat. Res. 2009, 11, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersson, P.; Pagliani, L.; Verrocchi, D.; Volpe, S.; Sahlin, H.; Sennerby, L. Factors Influencing Resonance Frequency Analysis (RFA) Measurements and 5-Year Survival of Neoss Dental Implants. Int. J. Dent. 2019, 2019, 3209872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atsumi, M.; Park, S.H.; Wang, H.L. Methods used to assess implant stability: Current status. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant 2007, 22, 743–754. [Google Scholar]
- Johansson, C.; Albrektsson, T. Integration of screw implants in the rabbit: A 1-year follow-up of removal torque of titanium implants. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant 1987, 2, 69–75. [Google Scholar]
- Mathieu, V.; Vayron, R.; Soffer, E.; Anagnostou, F.; Haïat, G. Influence of healing time on the ultrasonic response of the bone-implant interface. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2012, 38, 611–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masuda, T.; Yliheikkilä, P.K.; Felton, D.A.; Cooper, L.F. Generalizations regarding the process and phenomenon of osseointegration. Part I. In vivo studies. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant 1998, 13, 17–29. [Google Scholar]
- Albrektsson, T.; Eriksson, A.R.; Friberg, B.; Lekholm, U.; Lindahl, L.; Nevins, M.; Oikarinen, V.; Roos, J.; Sennerby, L.; Astrand, P. Histologic investigations on 33 retrieved Nobelpharma implants. Clin. Mater. 1993, 12, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.; Chowdhary, R. PEEK materials as an alternative to titanium in dental implants: A systematic review. Clin. Implant Dent. Relat. Res. 2019, 21, 208–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Mao, S.S. Titanium dioxide nanomaterials: Synthesis, properties, modifications, and applications. Chem. Rev. 2007, 107, 2891–2959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osman, R.B.; Swain, M.V. A Critical Review of Dental Implant Materials with an Emphasis on Titanium versus Zirconia. Materials 2015, 8, 932–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morais, L.S.; Serra, G.G.; Muller, C.A.; Andrade, L.R.; Palermo, E.F.A.; Elias, C.N.; Meyers, M. Titanium alloy mini-implants for orthodontic anchorage: Immediate loading and metal ion release. Acta Biomater. 2007, 3, 331–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, R.C.S.; Agrelli, A.; Andrade, A.N.; Mendes-Marques, C.L.; Arruda, I.R.S.; Santos, L.R.L.; Vasconcelos, N.F.; Machado, G. Titanium Dental Implants: An Overview of Applied Nanobiotechnology to Improve Biocompatibility and Prevent Infections. Materials 2022, 15, 3150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grandin, H.M.; Berner, S.; Dard, M. A Review of Titanium Zirconium (TiZr) Alloys for Use in Endosseous Dental Implants. Materials 2012, 5, 1348–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiapasco, M.; Casentini, P.; Zaniboni, M.; Corsi, E.; Anello, T. Titanium-zirconium alloy narrow-diameter implants (Straumann Roxolid(®)) for the rehabilitation of horizontally deficient edentulous ridges: Prospective study on 18 consecutive patients. Clin. Oral Implant Res. 2012, 23, 1136–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, T.T.; Reis, A.C. Fabrication of dental implants by the additive manufacturing method: A systematic review. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2019, 122, 270–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, A.A. Bioceramics for implant coatings. Mater. Today 2003, 6, 26–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohal, R.J.; Att, W.; Bächle, M.; Butz, F. Ceramic abutments and ceramic oral implants. An update. Periodontology 2000 2008, 47, 224–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neacşu, I.A.; Nicoară, A.I.; Vasile, O.R.; Vasile, B.Ş. Chapter 9—Inorganic micro- and nanostructured implants for tissue engineering. In Nanobiomaterials in Hard Tissue Engineering; Grumezescu, A.M., Ed.; William Andrew Publishing: Norwich, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 271–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jitwirachot, K.; Rungsiyakull, P.; Holloway, J.A.; Jia-mahasap, W. Wear Behavior of Different Generations of Zirconia: Present Literature. Int. J. Dent. 2022, 2022, 9341616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz, L.; Readey, M.J. Effect of Heat Treatment on Grain Size, Phase Assemblage, and Mechanical Properties of 3 mol% Y-TZP. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1996, 79, 2331–2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia-mahasap, W.; Jitwirachot, K.; Holloway, J.A.; Rangsri, W.; Rungsiyakull, P. Wear of various restorative materials against 5Y-ZP zirconia. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2022, 128, 814.e1–814.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorusso, F.; Noumbissi, S.; Francesco, I.; Rapone, B.; Khater, A.G.A.; Scarano, A. Scientific Trends in Clinical Research on Zirconia Dental Implants: A Bibliometric Review. Materials 2020, 13, 5534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chevalier, J.; Loh, J.; Gremillard, L.; Meille, S.; Adolfson, E. Low-temperature degradation in zirconia with a porous surface. Acta Biomater. 2011, 7, 2986–2993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chevalier, J.; Gremillard, L.; Virkar, A.V.; Clarke, D.R. The Tetragonal-Monoclinic Transformation in Zirconia: Lessons Learned and Future Trends. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2009, 92, 1901–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmero, P.; Fornabaio, M.; Montanaro, L.; Reveron, H.; Esnouf, C.; Chevalier, J. Towards long lasting zirconia-based composites for dental implants. Part I: Innovative synthesis, microstructural characterization and in vitro stability. Biomaterials 2015, 50, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altmann, B.; Karygianni, L.; Al-Ahmad, A.; Butz, F.; Bächle, M.; Adolfsson, E.; Fürderer, T.; Courtois, N.; Palmero, P.; Follo, M.; et al. Assessment of Novel Long-Lasting Ceria-Stabilized Zirconia-Based Ceramics with Different Surface Topographies as Implant Materials. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2017, 27, 1702512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burkhardt, F.; Harlass, M.; Adolfsson, E.; Vach, K.; Spies, B.C.; Kohal, R.-J. A Novel Zirconia-Based Composite Presents an Aging Resistant Material for Narrow-Diameter Ceramic Implants. Materials 2021, 14, 2151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pabst, W.; Havrda, J.; Gregorová, E.; Krcmova, B. Alumina toughened zirconia made by room temperature extrusion of ceramic pastes. Ceram.-Silikáty 2000, 44, 41–47. [Google Scholar]
- Schwitalla, A.D.; Spintig, T.; Kallage, I.; Müller, W.D. Flexural behavior of PEEK materials for dental application. Dent. Mater. 2015, 31, 1377–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmitasari, F.; Ishida, Y.; Kurahashi, K.; Matsuda, T.; Watanabe, M.; Ichikawa, T. PEEK with Reinforced Materials and Modifications for Dental Implant Applications. Dent. J. 2017, 5, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wegst, U.G.; Bai, H.; Saiz, E.; Tomsia, A.P.; Ritchie, R.O. Bioinspired structural materials. Nat. Mater. 2015, 14, 23–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anusavice, K.J.; Shen, C.; Rawls, H.R. Phillips’ Science of Dental Materials; Elsevier Health Sciences: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Campo, E.A. 2—Mechanical Properties of Polymeric Materials. In Selection of Polymeric Materials; Campo, E.A., Ed.; William Andrew Publishing: Norwich, NY, USA, 2008; pp. 41–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiskott, H.A.; Belser, U.C. Lack of integration of smooth titanium surfaces: A working hypothesis based on strains generated in the surrounding bone. Clin. Oral Implant Res. 1999, 10, 429–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitamura, E.; Stegaroiu, R.; Nomura, S.; Miyakawa, O. Influence of marginal bone resorption on stress around an implant--a three-dimensional finite element analysis. J. Oral Rehabil. 2005, 32, 279–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozlovsky, A.; Tal, H.; Laufer, B.Z.; Leshem, R.; Rohrer, M.D.; Weinreb, M.; Artzi, Z. Impact of implant overloading on the peri-implant bone in inflamed and non-inflamed peri-implant mucosa. Clin. Oral Implant Res. 2007, 18, 601–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niinomi, M. Recent Research and Development in Titanium Alloys for Biomedical Applications and Healthcare Goods. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2003, 4, 445–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.J.; Ueno, T.; Nomura, N.; Wakabayashi, N.; Hanawa, T. Titanium-Zirconium Binary Alloy as Dental Implant Material: Analysis of the Influence of Compositional Change on Mechanical Properties and In Vitro Biologic Response. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant 2016, 31, 547–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Chen, D.; Cheng, M.; Lu, W.; Wang, L.; Zhang, X. The bone tissue compatibility of a new Ti35Nb2Ta3Zr alloy with a low Young’s modulus. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2013, 31, 689–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmquist, A.; Snis, A.; Emanuelsson, L.; Browne, M.; Thomsen, P. Long-term biocompatibility and osseointegration of electron beam melted, free-form-fabricated solid and porous titanium alloy: Experimental studies in sheep. J. Biomater. Appl. 2013, 27, 1003–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Pevida, E.; Brizuela-Velasco, A.; Chávarri-Prado, D.; Jiménez-Garrudo, A.; Sánchez-Lasheras, F.; Solaberrieta-Méndez, E.; Diéguez-Pereira, M.; Fernández-González, F.J.; Dehesa-Ibarra, B.; Monticelli, F. Biomechanical Consequences of the Elastic Properties of Dental Implant Alloys on the Supporting Bone: Finite Element Analysis. BioMed Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 1850401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najeeb, S.; Zafar, M.S.; Khurshid, Z.; Siddiqui, F. Applications of polyetheretherketone (PEEK) in oral implantology and prosthodontics. J. Prosthodont. Res. 2016, 60, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Chen, C.; Zhang, S.; Ren, L.; Zhao, Y.; Guo, W. Mediation of mechanically adapted TiCu/TiCuN/CFR-PEEK implants in vascular regeneration to promote bone repair in vitro and in vivo. J. Orthop. Transl. 2022, 33, 107–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, J.C.M.; Pinho, S.S.; Braz, M.P.; Silva, F.S.; Henriques, B. Carbon fiber-reinforced PEEK in implant dentistry: A scoping review on the finite element method. Comput. Methods Biomech. Biomed. Eng. 2021, 24, 1355–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.; Ren, M.; Shi, Y.; Liu, X.; Wei, H. State-of-the-art polyetheretherketone three-dimensional printing and multifunctional modification for dental implants. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2023, 11, 1271629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Anwar, M.I.; El-Zawahry, M.M.; Ibraheem, E.M.; Nassani, M.Z.; ElGabry, H. New dental implant selection criterion based on implant design. Eur. J. Dent. 2017, 11, 186–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.M.; Kim, S.J.; Han, I.; Shin, S.W.; Ryu, J.J. A comparison of the implant stability among various implant systems: Clinical study. J. Adv. Prosthodont. 2009, 1, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Righesso, L.; Blatt, S.; Kwon, Y.-D.; Al-Nawas, B. Primärstabilität dentaler Implantate—Eine Übersichtsarbeit. Implantologie 2016, 24, 261–268. [Google Scholar]
- Staedt, H.; Kämmerer, P.W.; Goetze, E.; Thiem, D.G.E.; Al-Nawas, B.; Heimes, D. Implant primary stability depending on protocol and insertion mode—An ex vivo study. Int. J. Implant Dent. 2020, 6, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steigenga, J.T.; al-Shammari, K.F.; Nociti, F.H.; Misch, C.E.; Wang, H.L. Dental implant design and its relationship to long-term implant success. Implant Dent. 2003, 12, 306–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soto-Peñaloza, D.; Caneva, M.; Viña-Almunia, J.; Martin-de-Llano, J.J.; García-Mira, B.; Peñarrocha-Oltra, D.; Botticelli, D.; Peñarrocha-Diago, M. Effect on osseointegration of two implant macro-designs:A histomorphometric analysis of bicortically installed implants in different topographic sites of rabbit’s tibiae. Med. Oral Patol. Oral Cir. Bucal. 2019, 24, e502–e510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chun, H.J.; Cheong, S.Y.; Han, J.H.; Heo, S.J.; Chung, J.P.; Rhyu, I.C.; Choi, Y.C.; Baik, H.K.; Ku, Y.; Kim, M.H. Evaluation of design parameters of osseointegrated dental implants using finite element analysis. J. Oral Rehabil. 2002, 29, 565–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.Y.; Kim, S.J.; An, H.W.; Kim, H.S.; Ha, D.G.; Ryo, K.H.; Park, K.B. The effect of the thread depth on the mechanical properties of the dental implant. J. Adv. Prosthodont. 2015, 7, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abuhussein, H.; Pagni, G.; Rebaudi, A.; Wang, H.L. The effect of thread pattern upon implant osseointegration. Clin. Oral Implant Res. 2010, 21, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tumedei, M.; Petrini, M.; Pietropaoli, D.; Cipollina, A.; La Torre, C.; Di Carmine, M.S.; Piattelli, A.; Iezzi, G. The Influence of the Implant Macrogeometry on Insertion Torque, Removal Torque, and Periotest Implant Primary Stability: A Mechanical Simulation on High-Density Artificial Bone. Symmetry 2021, 13, 776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadkhodazadeh, M.; Safi, Y.; Moeintaghavi, A.; Amid, R.; Baghani, M.T.; Shidfar, S. Marginal Bone Loss Around One-Piece Implants: A 10-Year Radiological and Clinical Follow-up Evaluation. Implant Dent. 2019, 28, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, A.Y.; Hsu, J.T.; Chee, W.; Lin, Y.T.; Fuh, L.J.; Huang, H.L. Biomechanical evaluation of one-piece and two-piece small-diameter dental implants: In-vitro experimental and three-dimensional finite element analyses. J. Formos. Med. Assoc. 2016, 115, 794–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.M.; Lee, J.B.; Um, H.S.; Chang, B.S.; Lee, J.K. Long-term effect of implant-abutment connection type on marginal bone loss and survival of dental implants. J. Periodontal. Implant Sci. 2022, 52, 496–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, J. Safety and sagacious use of remdesivir: Paramount focus on contemporary perspectives. Ann. Afr. Med. 2019, 18, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shadid, R.M.; Sadaqah, N.R.; Othman, S.A. Does the Implant Surgical Technique Affect the Primary and/or Secondary Stability of Dental Implants? A Systematic Review. Int. J. Dent. 2014, 2014, 204838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antonelli, A.; Barone, S.; Attanasio, F.; Salviati, M.; Cerra, M.G.; Calabria, E.; Bennardo, F.; Giudice, A. Effect of Implant Macro-Design and Magnetodynamic Surgical Preparation on Primary Implant Stability: An In Vitro Investigation. Dent. J. 2023, 11, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernhard, N.; Berner, S.; de Wild, M.; Wieland, M. The binary TiZr Alloy—A newly developed Ti alloy for use in dental implants. Forum Implantol. 2009, 5, 30–39. [Google Scholar]
- Sarraf, M.; Rezvani Ghomi, E.; Alipour, S.; Ramakrishna, S.; Liana Sukiman, N. A state-of-the-art review of the fabrication and characteristics of titanium and its alloys for biomedical applications. Bio-Des. Manuf. 2022, 5, 371–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- May, Y. Ceramic vs. Titanium Implants | Zirconia or Titanium Implants | Dental Implant Materials. Available online: https://naturaldentistrycenter.com/zirconiaimplants/implants/ (accessed on 1 August 2023).
- Sharma, A.; Waddell, J.N.; Li, K.C.; Sharma, L.A.; Prior, D.J.; Duncan, W.J. Is titanium-zirconium alloy a better alternative to pure titanium for oral implant? Composition, mechanical properties, and microstructure analysis. Saudi Dent. J. 2021, 33, 546–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Li, S.J.; Hao, Y.L.; Huang, H.H.; Bai, Y.; Hao, Y.Q.; Guo, Z.; Xue, J.Q.; Yang, R. Electrochemical and surface analyses of nanostructured Ti–24Nb–4Zr–8Sn alloys in simulated body solution. Acta Biomater. 2014, 10, 2866–2875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khurshid, Z.; Hafeji, S.; Tekin, S.; Habib, S.R.; Ullah, R.; Sefat, F.; Zafar, M.S. 2—Titanium, zirconia, and polyetheretherketone (PEEK) as a dental implant material. In Dental Implants; Zafar, M.S., Khurshid, Z., Khan, A.S., Najeeb, S., Sefat, F., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2020; pp. 5–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandler, J.; Werner, P.; Shaffer, M.S.P.; Demchuk, V.; Altstädt, V.; Windle, A.H. Carbon-nanofibre-reinforced poly(ether ether ketone) composites. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2002, 33, 1033–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 14801:2016; Dentistry-Implants-Dynamic loading test for endosseous dental implants. Vernier: Geneva, Switzerland, 2016.
- Jung, R.E.; Zembic, A.; Pjetursson, B.E.; Zwahlen, M.; Thoma, D.S. Systematic review of the survival rate and the incidence of biological, technical, and aesthetic complications of single crowns on implants reported in longitudinal studies with a mean follow-up of 5 years. Clin. Oral Implant Res. 2012, 23 (Suppl. S6), 2–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiménez-Melendo, M.; Llena-Blasco, O.; Bruguera, A.; Llena-Blasco, J.; Yáñez-Vico, R.M.; García-Calderón, M.; Vaquero-Aguilar, C.; Velázquez-Cayón, R.; Gutiérrez-Pérez, J.L.; Torres-Lagares, D. Mechanical behavior of single-layer ceramized zirconia abutments for dental implant prosthetic rehabilitation. J. Clin. Exp. Dent. 2014, 6, e485–e490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agustín-Panadero, R.; Serra-Pastor, B.; Roig-Vanaclocha, A.; Fons-Font, A.; Solá-Ruiz, M.F. Fracture resistance and the mode of failure produced in metal-free crowns cemented onto zirconia abutments in dental implants. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0220551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Holanda Cavalcanti Pereira, A.K.; de Oliveira Limirio, J.P.J.; Cavalcanti do Egito Vasconcelos, B.; Pellizzer, E.P.; Dantas de Moraes, S.L. Mechanical behavior of titanium and zirconia abutments at the implant-abutment interface: A systematic review. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohal, R.J.; Wolkewitz, M.; Mueller, C. Alumina-reinforced zirconia implants: Survival rate and fracture strength in a masticatory simulation trial. Clin. Oral Implant Res. 2010, 21, 1345–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanes, B.; Feitosa, S.; Phasuk, K.; Levon, J.A.; Morton, D.; Lin, W.S. Fracture Resistance Behaviors of Titanium-Zirconium and Zirconia Implants. J. Prosthodont. 2022, 31, 441–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bethke, A.; Pieralli, S.; Kohal, R.J.; Burkhardt, F.; von Stein-Lausnitz, M.; Vach, K.; Spies, B.C. Fracture Resistance of Zirconia Oral Implants In Vitro: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Materials 2020, 13, 562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spies, B.C.; Fross, A.; Adolfsson, E.; Bagegni, A.; Doerken, S.; Kohal, R.J. Stability and aging resistance of a zirconia oral implant using a carbon fiber-reinforced screw for implant-abutment connection. Dent. Mater. 2018, 34, 1585–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivaraman, K.; Chopra, A.; Narayan, A.I.; Balakrishnan, D. Is zirconia a viable alternative to titanium for oral implant? A critical review. J. Prosthodont. Res. 2018, 62, 121–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berglundh, T.; Abrahamsson, I.; Lang, N.P.; Lindhe, J. De novo alveolar bone formation adjacent to endosseous implants. Clin. Oral Implant Res. 2003, 14, 251–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terheyden, H.; Lang, N.P.; Bierbaum, S.; Stadlinger, B. Osseointegration--communication of cells. Clin. Oral Implant Res. 2012, 23, 1127–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perrotti, V.; Iaculli, F.; Fontana, A.; Piattelli, A.; Iezzi, G. 1—Introduction to bone response to dental implant materials. In Bone Response to Dental Implant Materials; Piattelli, A., Ed.; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2017; pp. 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, F.P.; Weng, D.; Krämer, S.; Biesterfeld, S.; Jahn-Eimermacher, A.; Wagner, W. Osseointegration of one-piece zirconia implants compared with a titanium implant of identical design: A histomorphometric study in the dog. Clin. Oral Implant Res. 2010, 21, 350–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadid-Zadeh, R.; Willis, J.; Forgo, G.; Haraszthy, V. Comparative analysis of biofilm formation on materials used for the fabrication of implant-supported prostheses. Braz. Dent. J. 2020, 31, 380–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Najeeb, S.; Mali, M.; Syed, A.U.Y.; Zafar, M.S.; Khurshid, Z.; Alwadaani, A.; Matinlinna, J.P. 21—Dental implants materials and surface treatments. In Advanced Dental Biomaterials; Khurshid, Z., Najeeb, S., Zafar, M.S., Sefat, F., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2019; pp. 581–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chokaree, P.; Poovarodom, P.; Chaijareenont, P.; Yavirach, A.; Rungsiyakull, P. Biomaterials and Clinical Applications of Customized Healing Abutment—A Narrative Review. J. Funct. Biomater. 2022, 13, 291. [Google Scholar]
- Wennerberg, A.; Albrektsson, T. Effects of titanium surface topography on bone integration: A systematic review. Clin. Oral Implant Res. 2009, 20 (Suppl. S4), 172–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shalabi, M.M.; Gortemaker, A.; Van’t Hof, M.A.; Jansen, J.A.; Creugers, N.H. Implant surface roughness and bone healing: A systematic review. J. Dent. Res. 2006, 85, 496–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albrektsson, T.; Wennerberg, A. Oral implant surfaces: Part 1—Review focusing on topographic and chemical properties of different surfaces and in vivo responses to them. Int. J. Prosthodont. 2004, 17, 536–543. [Google Scholar]
- Rohr, N.; Hoda, B.; Fischer, J. Surface Structure of Zirconia Implants: An Integrative Review Comparing Clinical Results with Preclinical and In Vitro Data. Materials 2022, 15, 3664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurup, A.; Dhatrak, P.; Khasnis, N. Surface modification techniques of titanium and titanium alloys for biomedical dental applications: A review. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 39, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhatrak, P.; Shirsat, U.; Deshmukh, V. Fatigue life prediction of commercial dental implants based on biomechanical parameters: A review. IJSEIMS 2015, 3, 221–226. [Google Scholar]
- Granato, R.; Bonfante, E.A.; Castellano, A.; Khan, R.; Jimbo, R.; Marin, C.; Morsi, S.; Witek, L.; Coelho, P.G. Osteointegrative and microgeometric comparison between micro-blasted and alumina blasting/acid etching on grade II and V titanium alloys (Ti-6Al-4V). J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2019, 97, 288–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Souza, J.C.M.; Sordi, M.B.; Kanazawa, M.; Ravindran, S.; Henriques, B.; Silva, F.S.; Aparicio, C.; Cooper, L.F. Nano-scale modification of titanium implant surfaces to enhance osseointegration. Acta Biomater. 2019, 94, 112–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadav, A.; Yadav, R.; Gupta, A.; Baranwal, A.; Bhatnagar, A.; Singh, V. Effect of Ultraviolet Irradiation on the Osseointegration of a Titanium Alloy with Bone. Contemp. Clin. Dent. 2017, 8, 571–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lang, N.P.; Karring, T. Proceedings of the First European Workshop on Periodontology; 1983 February 1–4; Quintessence: Thurgau, Switzerland; Enfield, UK, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Buser, D.; Janner, S.F.M.; Wittneben, J.-G.; Brägger, U.; Ramseier, C.A.; Salvi, G.E. 10-Year Survival and Success Rates of 511 Titanium Implants with a Sandblasted and Acid-Etched Surface: A Retrospective Study in 303 Partially Edentulous Patients. Clin. Implant Dent. Relat. Res. 2012, 14, 839–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borges, H.; Correia, A.R.M.; Castilho, R.M.; de Oliveira Fernandes, G.V. Zirconia Implants and Marginal Bone Loss: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Clinical Studies. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant 2020, 35, 707–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haro Adánez, M.; Nishihara, H.; Att, W. A systematic review and meta-analysis on the clinical outcome of zirconia implant–restoration complex. J. Prosthodont. Res. 2018, 62, 397–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allum, S.R.; Tomlinson, R.A.; Joshi, R. The impact of loads on standard diameter, small diameter and mini implants: A comparative laboratory study. Clin. Oral Implant Res. 2008, 19, 553–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barter, S.; Stone, P.; Brägger, U. A pilot study to evaluate the success and survival rate of titanium-zirconium implants in partially edentulous patients: Results after 24 months of follow-up. Clin. Oral Implant Res. 2012, 23, 873–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altuna, P.; Lucas-Taulé, E.; Gargallo-Albiol, J.; Figueras-Álvarez, O.; Hernández-Alfaro, F.; Nart, J. Clinical evidence on titanium-zirconium dental implants: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2016, 45, 842–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makary, C.; Menhall, A.; Zammarie, C.; Lombardi, T.; Lee, S.Y.; Stacchi, C.; Park, K.B. Primary Stability Optimization by Using Fixtures with Different Thread Depth According To Bone Density: A Clinical Prospective Study on Early Loaded Implants. Materials 2019, 12, 2398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hingsammer, L.; Watzek, G.; Pommer, B. The influence of crown-to-implant ratio on marginal bone levels around splinted short dental implants: A radiological and clincial short term analysis. Clin. Implant Dent Relat. Res. 2017, 19, 1090–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Santis, D.; Cucchi, A.; Rigoni, G.; Longhi, C.; Nocini, P.F. Relationship Between Primary Stability and Crestal Bone Loss of Implants Placed with High Insertion Torque: A 3-Year Prospective Study. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant 2016, 31, 1126–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cannizzaro, G.; Leone, M.; Ferri, V.; Viola, P.; Gelpi, F.; Esposito, M. Immediate loading of single implants inserted flapless with medium or high insertion torque: A 6-month follow-up of a split-mouth randomised controlled trial. Eur. J. Oral. Implant 2012, 5, 333–342. [Google Scholar]
- Rossi, F.; Lang, N.P.; Ricci, E.; Ferraioli, L.; Marchetti, C.; Botticelli, D. Early loading of 6-mm-short implants with a moderately rough surface supporting single crowns—A prospective 5-year cohort study. Clin. Oral Implant Res. 2015, 26, 471–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Held, U.; Rohner, D.; Rothamel, D. Early loading of hydrophilic titanium implants inserted in low-mineralized (D3 and D4) bone: One year results of a prospective clinical trial. Head. Face Med. 2013, 9, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goiato, M.C.; dos Santos, D.M.; Santiago, J.F., Jr.; Moreno, A.; Pellizzer, E.P. Longevity of dental implants in type IV bone: A systematic review. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2014, 43, 1108–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldebes, A.; Al-Khanati, N.M.; Abou Nassar, J.; Kharboutly, N.A.D.; Aldamman, F. Effect of restoration material on marginal bone resorption around modified anatomic zirconia dental implants: A randomised controlled trial. Ann. Med. Surg. 2022, 80, 104313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Databases | Search Strategy |
|---|---|
| PubMed/Medline | MeSH terms: (Dental Implants) AND ((Osseointegration) OR (bone–implant interface) OR (survival rate)) Text words: ((Titanium) OR (titanium implant) OR (zirconia) OR (zirconium oxide) OR (yttria-stabilized tetragonal zirconia) OR (zirconia implant) OR (ceramic implant) OR (PEEK) OR (Polyetheretherketone)) AND ((bone density) OR (bone mineral) OR (bone condition)) AND ((success rate) OR (marginal bone loss) OR (bone–implant contact) OR (removal torque) OR (osteoblasts) OR (cell proliferation) OR (bone remodeling)) |
| Scopus | (Dental implants) AND ((titanium) OR (titanium implant) OR (zirconia) OR (zirconium oxide) OR (yttria-stabilized tetragonal zirconia) OR (zirconia implant) OR (ceramic implant) OR (PEEK) OR (Polyetheretherketone)) AND ((bone density) OR (bone mineral) OR (bone condition)) AND ((osseointegration) OR (bone–implant-interface) OR (survival rate) OR (success rate) OR (marginal bone loss) OR (bone–implant contact) OR (removal torque) OR (osteoblasts) OR (cell proliferation) OR (bone remodeling)) |
| Embase | (Dental implants) AND ((titanium) OR (titanium implant) OR (zirconia) OR (zirconium oxide) OR (yttria-stabilized tetragonal zirconia) OR (zirconia implant) OR (ceramic implant) OR (PEEK) OR (Polyetheretherketone)) AND ((bone density) OR (bone mineral) OR (bone condition)) AND ((osseointegration) OR (bone–implant-interface) OR (survival rate) OR (success rate) OR (marginal bone loss) OR (bone–implant contact) OR (removal torque) OR (osteoblasts) OR (cell proliferation) OR (bone remodeling)) |
| Type | Anterior Maxilla (%) | Posterior Maxilla (%) | Anterior Mandible (%) | Posterior Mandible (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| D1 | 0 | 0 | 6 | 3 |
| D2 | 25 | 10 | 66 | 50 |
| D3 | 65 | 50 | 25 | 46 |
| D4 | 10 | 40 | 3 | 1 |
| Substance | Hounsfield Units | |
|---|---|---|
| Air | −1000 | |
| Water | 0 | |
| Bone | Cancellous | +300 to +400 [37] |
| Cortical | +500 to +1900 [37,38,39] | |
| Anterior maxilla | +600 to +700 [34,40] | |
| Posterior maxilla | +300 to +400 [34,40] | |
| Anterior mandible | +800 to +1100 [34,40] | |
| Posterior mandible | +500 to +600 [34,40] | |
| Substances | Elastic Modulus (GPa) |
|---|---|
| Zirconia Oxide | 210 |
| TiAl6V4 | 110 |
| CpTi (Grade IV) | 104.1 |
| PEEK | 3.6 |
| Carbon-reinforced PEEK | 18 |
| Cortical | 15.85 ± 2.10 |
| Trabecular | 7.95 ± 2.10 |
| Properties | Titanium | Zirconia | PEEK | Citation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Esthetics | Acceptable | Superior to Ti | Superior to Ti | [117,121] |
| Tissue adhesion | Acceptable | Superior to Ti | Lesser or similar to Ti and Zr | [117,121,136,139] |
| Biocompatibility | Acceptable | Superior to Ti | Superior to Ti | [117,121,139] |
| Bacterial formation | Moderate | Lesser or similar to Ti | Least | [117,121,139] |
| Cytotoxicity | Moderate | Lower than Ti | Least | [121] |
| Osseointegration | High | Similar to Ti (after surface treatment) | Lesser than Ti and Zr | [96,121,136] |
| Titanium | Zirconia | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Subtractive | Additive | Subtractive | Additive |
| Electropolishing | HA and other calcium phosphate coatings | Sandblasting | Additive sintering and slurrying |
| Mechanical polishing | TPS surfaces | Sandblasting followed by acid etching | Injection molding |
| Blasting | Ion deposition | Laser ablation | Additionally heat-treated |
| Etching | |||
| Oxidation | |||
| UV light | |||
| Clinical Settings | Titanium | Zirconia | PEEK |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bone density | |||
| Yes | Yes | Maybe |
| Yes | No (low osseointegration) | Questionable (yes, mechanical aspect) (no, biological aspect) |
| Occlusal force | Normal to high | Normal | High (bruxism) |
| Esthetic benefits | Maybe | Yes | Yes |
| Allergy | Maybe | Low | Low |
| Study/Year | Material | Marginal Bone Loss | Survival Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Borges et al. 2020 [151] | Zirconia | 0.80 mm (95% CI: 0.60 to 1.00) at a 1-year post-loading. | 71.2% at 1 year to 100% at 7.8 years. |
| 1.01 mm (95% CI: 0.72 to 1.29) at a 2-year post-loading | |||
| Adanez et al. 2018 [152] | Zirconia | 0.89 mm (95% CI: 0.60 to 1.18) at a 1-year post-loading period. | 76% to 100% after observation periods between 1 and 7 years. |
| The mean survival rate was 95% after an observation period between 1 and 7 years (one-piece zirconia: 95%, two-piece zirconia: 94%). | |||
| Borges et al. 2020 [151] | Titanium–zirconia alloy | 0.36 ± 0.06 mm after 1 year. | 98.4% at 1 year after implant placement. |
| 0.41 ± 0.09 mm after 2 years. | 97.7% at 2 years after implant placement. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khaohoen, A.; Sornsuwan, T.; Chaijareenont, P.; Poovarodom, P.; Rungsiyakull, C.; Rungsiyakull, P. Biomaterials and Clinical Application of Dental Implants in Relation to Bone Density—A Narrative Review. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 6924. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12216924
Khaohoen A, Sornsuwan T, Chaijareenont P, Poovarodom P, Rungsiyakull C, Rungsiyakull P. Biomaterials and Clinical Application of Dental Implants in Relation to Bone Density—A Narrative Review. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(21):6924. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12216924
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhaohoen, Angkoon, Tanapon Sornsuwan, Pisaisit Chaijareenont, Pongsakorn Poovarodom, Chaiy Rungsiyakull, and Pimduen Rungsiyakull. 2023. "Biomaterials and Clinical Application of Dental Implants in Relation to Bone Density—A Narrative Review" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 21: 6924. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12216924
APA StyleKhaohoen, A., Sornsuwan, T., Chaijareenont, P., Poovarodom, P., Rungsiyakull, C., & Rungsiyakull, P. (2023). Biomaterials and Clinical Application of Dental Implants in Relation to Bone Density—A Narrative Review. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(21), 6924. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12216924








