Atmospheric Layers in Response to the Propagation of Gravity Waves under Nonisothermal, Wind-shear, and Dissipative Conditions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Generalized Dispersion Equation of Gravity Waves
- , ;
- , ;
- , ;
- , ;
- ,
- ;
- ,
- ,
- ;
- ,
- ;
- ,
3. Atmospheric Structure
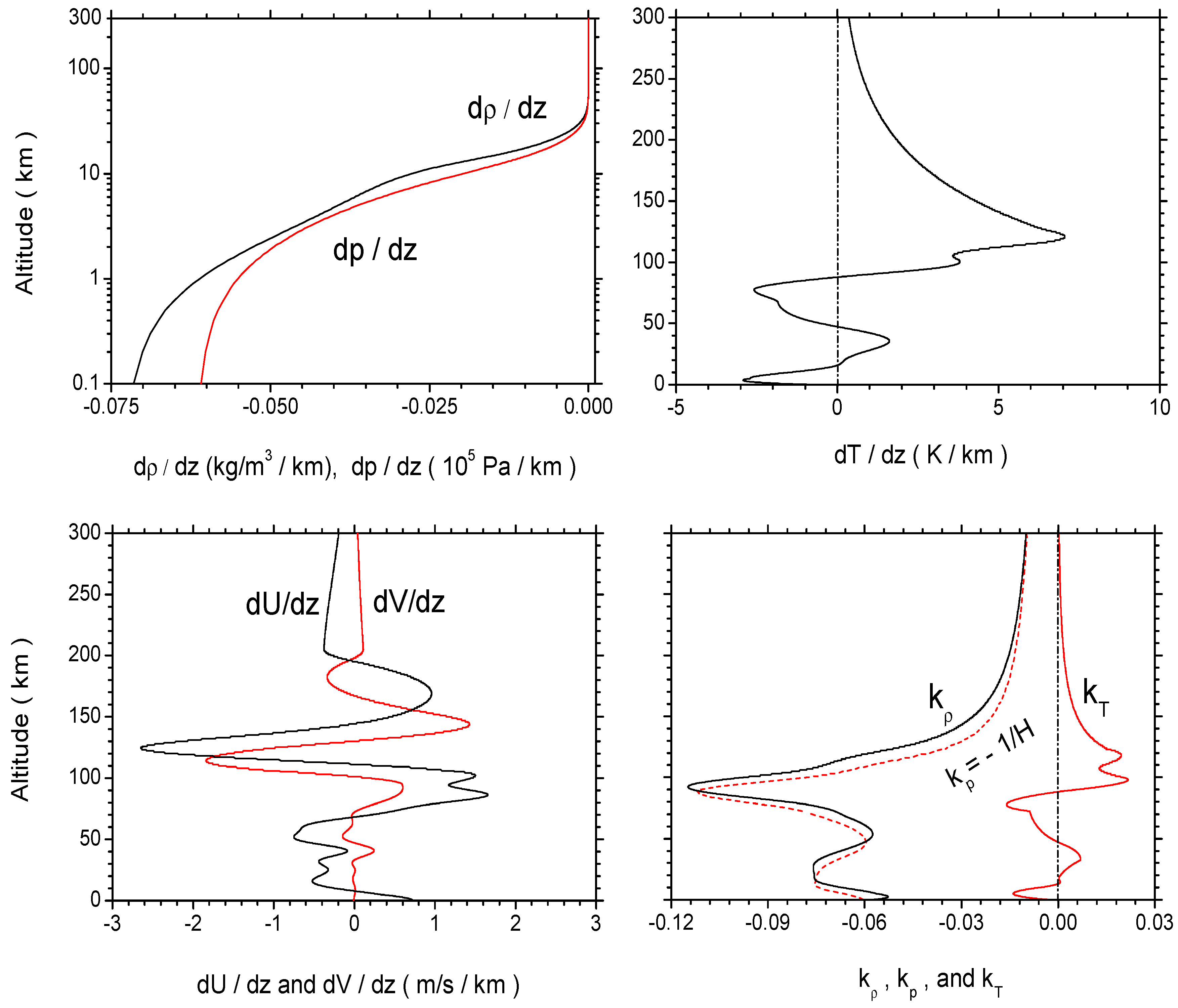
3.1. Mean-Field Properties
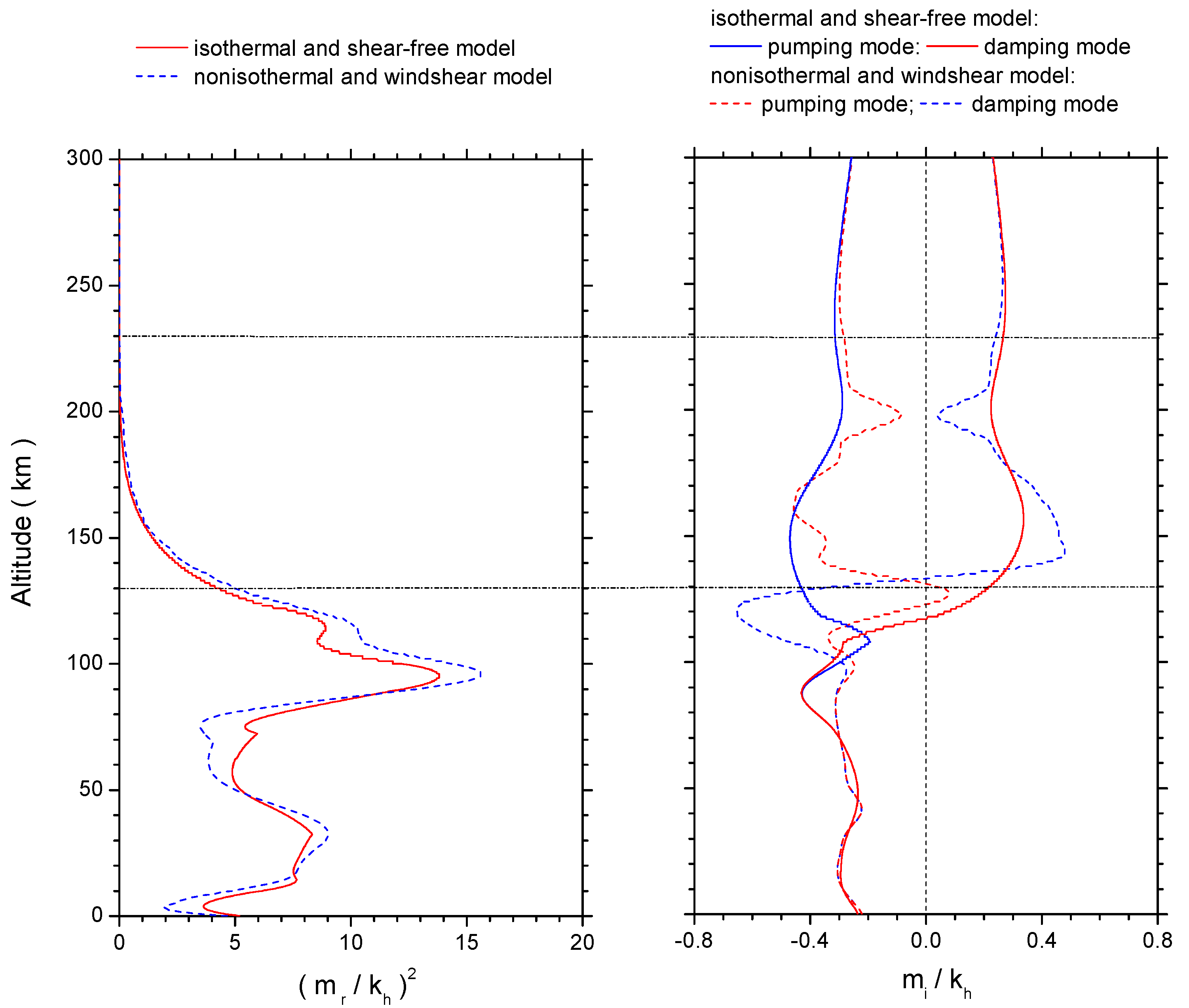
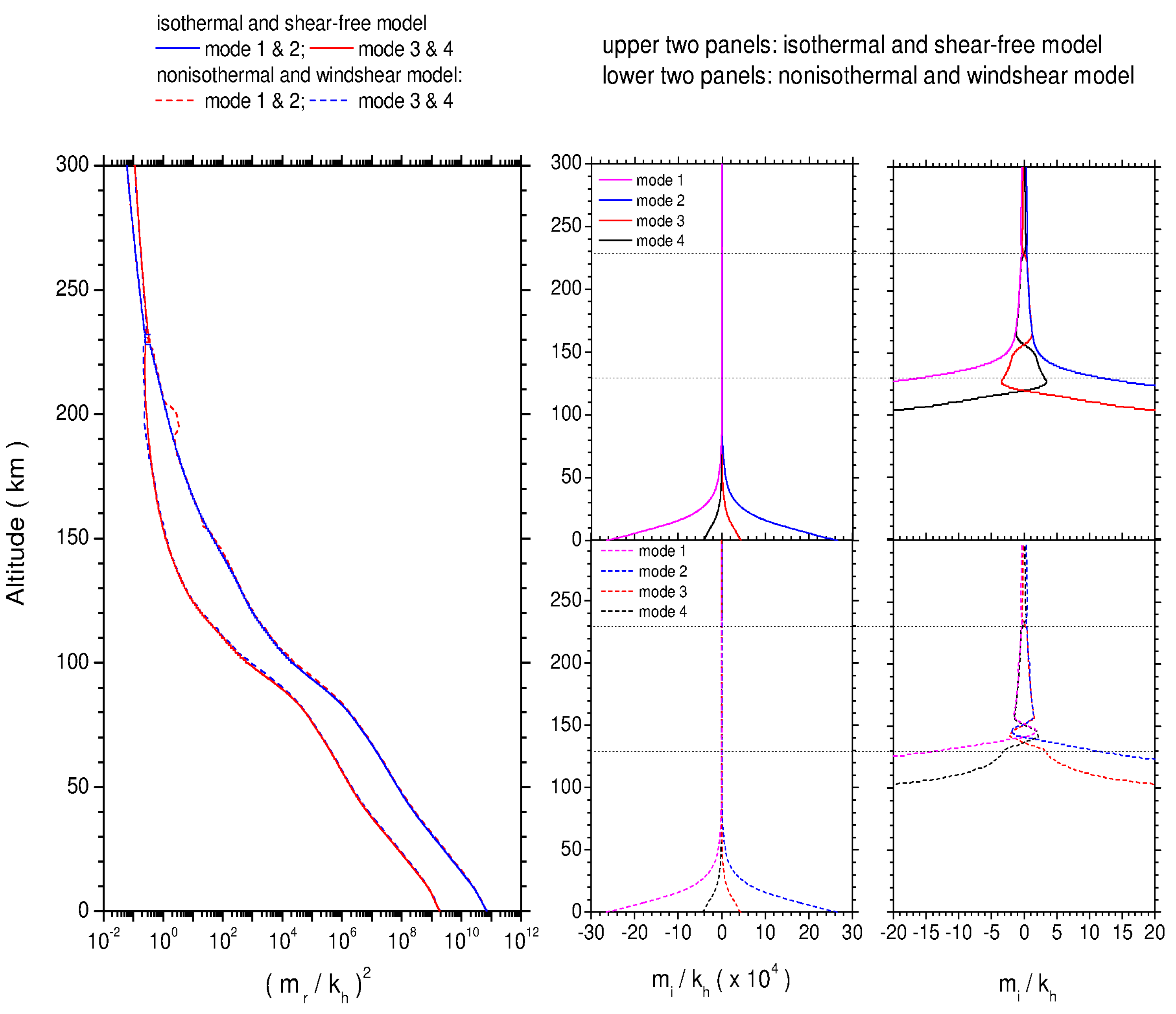
3.2. Non-Dissipative Adiabatic Layer: Existence and Fading of Hines’ Modes
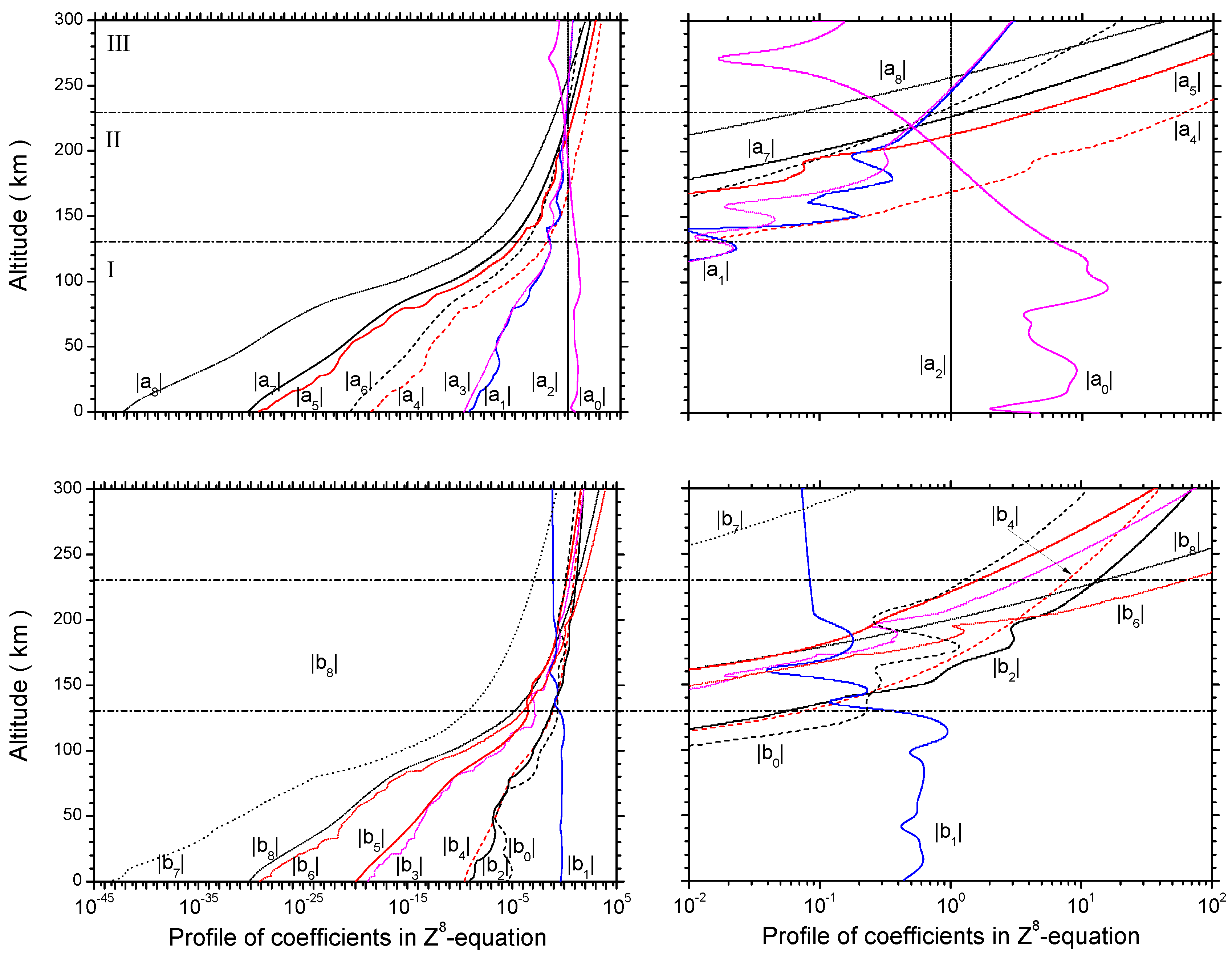
3.3. Dissipative Layer: Emergence and Development of (Extra-)Ordinary Dissipation Wave Modes
3.4. Nonisothermal and Wind Shear Effects on Wave Modes Below a 230-km Altitude
3.5. Pseudo-Adiabatic Layer: Extraordinary Wave Modes
4. Summary and Discussion
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hines, C.O. Gravity waves in the atmosphere. Nature 1972, 239, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peltier, W.R.; Hines, C.O. On the possible detection of tsunamis by a monitoring of the ionosphere. J. Geophys. Res. 1976, 81, 1995–2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosgrave, J. Synthesis Report: Expanded Summary. Joint Evaluation of the International Response to the Indian Ocean Tsunami; Tsunami Evaluation Coalition: London, UK, 2007; pp. 1–41. [Google Scholar]
- Artru, J.; Ducic, V.; Kanamori, H.; Lognonn´, P.; Murakami, M. Ionospheric detection of gravity waves induced by tsunamis. Geophys. J. Int. 2005, 160, 840–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Co¨sson, P.; Lognonn´, P.; Walwer, D.; Rolland, L.M. First tsunami gravity wave detection in ionospheric radio occultation data. Earth Space Sci. 2015, 2, 125–133. [Google Scholar]
- Bernard, E.N.; Robinson, A.R. Tsunamis; Harvard University Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Nappo, C.J. An Introduction to Atmospheric Gravity Waves; Academic Press: Waltham, MA, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Gossard, E.E.; Munk, W.H. On gravity waves in the atmosphere. J. Meteorol. 1954, 11, 259–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckart, C. Hydrodynamics of Oceans and Atmospheres; Pergamon: New York, NY, USA, 1960. [Google Scholar]
- Tolstoy, I. The theory of waves in stratified fluids including the effects of gravity and rotation. Rev. Mod. Phys. 1963, 35, 207–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Symposium on upper atmospheric winds, waves and ionospheric drift; Pergamon Press: Oxford, UK, 1968.
- Georges, T.M. Acoustic-Gravity Waves in the Atmosphere; U.S. Government Printing Office: Washinton, DC, USA, 1968. [Google Scholar]
- AGARD. Effects of Atmospheric Acoustic Gravity Waves on Electromagnetic Wave Propagation; Harford House: London, UK, 1972. [Google Scholar]
- Francis, S.H. Global propagation of atmospheric gravity waves: A review. J. Atmos. Terr. Phys. 1975, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritts, D.C. Gravity wave saturation in the middle atmosphere: A review of theory and observations. Rev. Geophys. Space Phys. 1984, 22, 275–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritts, D.C. A review of gravity wave saturation processes, effects, and variability in the middle atmosphere. Pure Appl. Geophys. 1989, 130, 343–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hocke, K.; Schlegel, K. A review of atmospheric gravity waves and travelling ionospheric disturbances: 1982–1995. Ann. Geophys. 1996, 14, 917–940. [Google Scholar]
- Fritts, D.C.; Alexander, M.J. Gravity wave dynamics and effects in the middle atmosphere. Rev. Geophys. 2003, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritts, D.C.; Lund, T.S. Gravity wave influences in the thermosphere and ionosphere: Observations and recent modeling. In Aeronomy of the Earth’s Atmosphere and Ionosphere; Abdu, M.A., Pancheva, D., Bhattacharyya, A., Eds.; Springer: Houten, The Netherlands, 2011; pp. 109–130. [Google Scholar]
- Pitteway, M.L.V.; Hines, C.O. The viscous damping of atmospheric gravity waves. Can. J. Phys. 1963, 41, 1935–1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Midgley, J.E.; Liemohn, H.B. Gravity waves in a realistic atmosphere. J. Geophys. Res. 1966, 71, 3729–3748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanowitch, M. Effect of viscosity on vertical oscillations of an isothermal atmosphere. Can. J. Phys. 1967, 45, 2003–2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanowitch, M. Effect of viscosity on gravity waves and the upper boundary conditions. J. Fluid. Mech. 1967, 29, 209–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindzen, R.S. Vertically propagating waves in an atmosphere with inversely proportional to density. Can. J. Phys. 1968, 46, 1835–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindzen, R.S. Internal gravity waves in atmospheres with realistic dissipation and tempeature (Part I). Geophys. Fluid Dyn. 1970, 1, 303–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hines, C.O. Generalization of the Richardson criterion for the onset of atmospheric turbulence. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1971, 97, 429–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyon, P.; Yanowitch, M. Vertical oscillations in a viscous and thermally conducting isothermal atmosphere. J. Fluid Mech. 1974, 66, 273–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, L.M.C. On viscous and resistive dissipation of hydrodynamic and hydromagnetic waves in atmospheres. J. Mec. Theor. Appl. 1983, 2, 861–891. [Google Scholar]
- Alkahby, H.Y.; Yanowitch, M. The effects of Newtonian cooling on the reflection of vertically propagating acoustic waves in an isothermal atmosphere. Wave Motion 1989, 11, 419–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanowitch, M. Vertically propagating hydromagnetic waves in an isothermal atmosphere with a horizontal magnetic field. Wave Motion 1979, 1, 123–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhugzhda, Y.D.; Dzihalilov, N.S. Magneto-acoustic gravity waves in a horizontal magnetic field. Geophys. Fluid Dyn. 1986, 35, 131–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkahby, H.Y.; Yanowitch, M. Reflection of vertically propagating waves in a thermally conducting isothermal atmosphere with a horizontal magnetic field. Geophys. Astrophys. Fluid Dyn. 1991, 56, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkahby, H.Y. Acoustic-gravity waves in a viscous and thermally conducting isothermal atmosphere. Int. J. Math. Math. Sci. 1995, 18, 371–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkahby, H.Y. Acoustic-gravity waves in a viscous and thermally conducting isothermal atmosphere (part II: For small Prandtl number). Int. J. Math. Math. Sci. 1995, 18, 579–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkahby, H.Y. Acoustic-gravity waves in a viscous and thermally conducting isothermal atmosphere (part III: for arbitrary Prandtl number). Int. J. Math. Math. Sci. 1997, 20, 367–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruce, C.H.; Peaceman, D.W.; Rachford, H.H.; Rice, J.P. Calculations of unsteady-state gas flow through porous media. J. Pet. Technol. 1953, 5, 79–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindzen, R.S.; Kuo, H.L. A reliable method for the numerical integration of a large class of ordinary and partial differential equations. Mon. Weather Rev. 1969, 97, 732–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volland, H. The upper atmosphere as a multiple refractive medium for neutral air motions. J. Atmos. Terr. Phys. 1969, 31, 491–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klostermeyer, J. Numerical calculation of gravity wave propagation in a realistic thermosphere. J. Atmos. Terr. Phys. 1972, 34, 765–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klostermeyer, J. Comparison between observed and numerically calculated atmospheric gravity waves in the F-region. J. Atmos. Terr. Phys. 1972, 34, 1393–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klostermeyer, J. Influence of viscosity, thermal conduction, and ion drag on the propagation of atmospheric gravity waves in the thermosphere. Z. Geophys. 1972, 38, 881–890. [Google Scholar]
- Hickey, M.P.; Walterscheid, R.L.; Taylor, M.J.; Ward, W.; Schubert, G.; Zhou, Q.; Garcia, F.; Kelley, M.C.; Shepherd, G.G. Numerical simulations of gravity waves imaged over Arecibo during the 10-day January 1993 campaign. J. Geophys. Res. 1997, 102, 11475–11489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hickey, M.P.; Taylor, M.J.; Gardner, C.S.; Gibbons, C.R. Full-wave modeling of small-scale gravity waves using Airborne Lidar and Observations of the Hawaiian Airglow (ALOHA-93) O(1S) images and coincident Na wind/temperature LiDAR measurements. J. Geophys. Res. 1998, 103, 6439–6453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hickey, M.P.; Walterscheid, R.L.; Schubert, G. Gravity wave heating and cooling in Jupiter’s thermosphere. Icarus 2000, 148, 266–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hickey, M.P.; Schubert, G.; Walterscheid, R.L. Acoustic wave heating of the thermosphere. J. Geophys. Res. 2001, 106, 21543–21548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hickey, M.P.; Walterscheid, R.L.; Schubert, G. A full-wave model for a binary gas thermosphere: Effects of thermal conductivity and viscosity. J. Geophys. Res. 2015, 120, 3074–3083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walterscheid, R.L.; Hickey, M.P. One-gas models with height-dependent mean molecular weight: Effects on gravity wave propagation. J. Geophys. Res. 2001, 106, 28831–28839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schubert, G.; Hickey, M.P.; Walterscheid, R.L. Physical processes in acoustic wave heating of the thermosphere. J. Geophys. Res. 2005, 110, D07106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hickey, M.P. Effects of eddy viscosity and thermal conduction and Coriolis force in the dynamics of gravity wave driven fluctuations in the OH nightglow. J. Geophys. Res. 1988, 93, 4077–4088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hickey, M.P.; Schubert, G.; Walterscheid, R.L. Propagation of tsunami-driven gravity waves into the thermosphere and ionosphere. J. Geophys. Res. 2009, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hickey, M.P. Atmospheric gravity waves and effects in the upper atmosphere associated with tsunamis. In The Tsunami Threat—Research and Technology; MA˜rner, N.-A., Ed.; In Tech: Rijeka, Croatia; Shanghai, China, 2011; pp. 667–690. [Google Scholar]
- Vadas, S.L. Horizontal and vertical propagation and dissipation of gravity waves in the thermosphere from lower atmospheric and thermospheric sources. J. Geophys. Res. 2007, 112, A06305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vadas, S.L.; Makela, J.J.; Nicolls, M.J.; Milliff, R.F. Excitation of gravity waves by ocean surface wave packets: Upward propagation and reconstruction of the thermospheric gravity wave field. J. Geophys. Res. 2015, 120, 9748–9780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vadas, S.L.; Nicolls, M.J. The phases and amplitudes of gravity waves propagating and dissipating in the thermosphere: Theory. J. Geophys. Res. 2012, 117, A05322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Morton, Y.T. Gravity wave propagation in a nonisothermal atmosphere with height varying background wind. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34, L23803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, K.C.; Liu, C.H. Acoustic-gravity waves in the upper atmosphere. Rev. Geophys. 1974, 12, 193–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindzen, R.S. Turbulence and stress owing to gravity wave and tidal breakdown. J. Geophys. Res. 1981, 86, 9707–9714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hines, C.O. The saturation of gravity waves in the middle atmosphere (part II): Development of Doppler-spread theory. J. Atmos. Sci. 1991, 48, 1360–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuda, T.; Kato, S.; Nakamura, T.; Vincent, R.A.; Manson, A.H.; Meek, C.E.; Wilson, R.L. Variations of the gravity wave characteristics with height, season and latitude revealed by comparative observations. J. Atmos. Sol. Terr. Phys. 1994, 56, 555–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vadas, S.L.; Fritts, D.C. Gravity wave radiation and mean responses to local body forces in the atmosphere. J. Atmos. Sci. 2001, 58, 2249–2279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vadas, S.L.; Fritts, D.C. Thermospheric responses to gravity waves arising from mesoscale convective complexes. J. Atmos. Sol. Terr. Phys. 2004, 66, 781–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vadas, S.L.; Fritts, D.C. Thermospheric responses to gravity waves: Influences of increasing viscosity and thermal diffusivity. J. Geophys. Res. 2005, 110, D15103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vadas, S.L.; Fritts, D.C. Reconstruction of the gravity wave field from convective plumes via ray tracing. Ann. Geophys. 2009, 27, 147–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.D.; Yi, F. A numerical study of propagation characteristics of gravity wave packets propagating in a dissipative atmosphere. J. Geophys. Res. 2002, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vadas, S.L.; Crowley, G. Sources of the traveling ionospheric disturbances observed by the ionospheric TIDDBIT sounder near Wallops Island on 30 October 2007. J. Geophys. Res. 2010, 115, A07324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broutman, D.; Eckermann, S.D. Analysis of a ray-tracing model for gravity waves generated by tropospheric convection. J. Geophys. Res. 2012, 117, D05132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hines, C.O. Internal atmospheric gravity waves at ionospheric heights. Can. J. Phys. 1960, 38, 1441–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vadas, S.L.; Fritts, D.C. Influence of solar variability on gravity wave structure and dissipation in the thermosphere from tropospheric convection. J. Geophys. Res. 2006, 111, A10S12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritts, D.C.; Vadas, S.L. Gravity wave penetration into the thermosphere: Sensitivity to solar cycle variations and mean winds. Ann. Geophys. 2008, 26, 3841–3861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vadas, S.; Yue, J.; Nakamura, T. Mesospheric concentric gravity waves generated by multiple convective storms over the North American Great Plain. J. Geophys. Res. 2012, 117, D07113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vadas, S.L.; Liu, H.-L.; Lieberman, R.S. Numerical modeling of the global changes to the thermosphere and ionosphere from the dissipation of gravity waves from deep convection. J. Geophys. Res. 2014, 119, 7762–7793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gossard, E.E.; Hooke, W.H. Waves in the Atmosphere; Elsevier: New York, NY, USA, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Del Genio, A.D.; Schubert, G. Gravity wave propagation in a diffusively separated atmosphere with height-dependent collision frequencies. J. Geophys. Res. 1979, 84, 4371–4378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hickey, M.P.; Cole, K.D. A quartic dispersion equation for internal gravity waves in the thermosphere. J. Atmos. Terr. Phys. 1987, 49, 889–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DalGarno, A.; Smith, F.J. The thermal conductivity and viscosity of atomic oxygen. Planet. Space Sci. 1962, 9, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Wan, W.; Ding, F.; Mao, T. Gravity wave propagation in the realistic atmosphere based on a three-dimensional transfer function model. Ann. Geophys. 2007, 25, 1979–1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picone, J.M.; Hedin, A.E.; Drob, D.P.; Aikin, A.C. NRLMSISE-00 empirical model of the atmosphere: Statistical comparisons and scientific issues. J. Geophys. Res. 2002, 107, 1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedin, A.E.; Fleming, E.L.; Manson, A.H.; Schmidlin, F.J.; Avery, S.K.; Clark, R.R.; Franke, S.J.; Fraser, G.J.; Tsuda, T.; Vial, F.; et al. Empirical wind model for the upper, middle and lower atmosphere. J. Atmos. Terr. Phys. 1996, 58, 1421–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vadas, S.; NWRA, Boulder, CO, USA. Personal communication, 2015.
- Ma, J.Z.G. Modulation of atmospheric nonisothermality and wind shears on the propagation of seismic tsunami-excited gravity waves. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2016, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.Z.G.; Hickey, M.P.; Komjathy, A. Ionospheric electron density perturbations driven by seismic tsunami-excited gravity waves: Effect of dynamo electric field. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2015, 3, 1194–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, A.Z.; Hocking, W.K.; Franke, S.J.; Thayaparan, T. Comparison of Na LiDAR and meteor radar wind measurements at starfire optical range, NM, USA. J. Atmos. Terr. Phys. 2002, 64, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritts, D.C.; Williams, B.P.; She, C.Y.; Vance, J.D.; Rapp, M.; L¨bken, F.-J.; M¨llemann, A.; Schmidlin, F.J.; Goldberg, R.A. Observations of extreme temperature and wind gradients near the summer mesopause during the MaCWAVE/MIDAS rocket campaign. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2004, 31, L24S06. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franke, S.J.; Chu, X.; Liu, A.Z.; Hocking, W.K. Comparison of meteor radar and Na Doppler LiDAR measurements of winds in the mesopause region above Maui, HI. J. Geophys. Res. 2005, 110, D09S02. [Google Scholar]
- She, C.Y.; Williams, B.P.; Hoffmann, P.; Latteck, R.; Baumgarten, G.; Vance, J.D.; Fiedler, J.; Acott, P.; Fritts, D.C.; Luebken, F.-J. Observation of anti-correlation between sodium atoms and PMSE/NLC in summer mesopause at ALOMAR, Norway (69 N, 12 E). J. Atmos. Sol. Terr. Phys. 2006, 68, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- She, C.Y.; Krueger, D.A.; Akmaev, R.; Schmidt, H.; Talaat, E.; Yee, S. Long-term variability in mesopause region temperatures over Fort Collins, Colorado (41∘ N, 105∘ W) based on LiDAR observations from 1990 through 2007. J. Terr. Sol. Atmos. Phys. 2009, 71, 1558–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marks, C.J.; Eckermann, S.D. A three-dimensional nonhydrostatic ray-tracing model for gravity waves: Formulation and preliminary results for the middle atmosphere. J. Atmos. Sci. 1995, 52, 1959–1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Occhipinti, G.; Lognonn´, P.; Kherani, E.A.; H´bert, H. Three dimensional waveform modeling of ionospheric signature induced by the 2004 Sumatra tsunami. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33, L20104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godin, O.A.; Zabotin, N.A.; Bullett, T.W. Acoustic-gravity waves in the atmosphere generated by infragravity waves in the ocean. Earth Planets Space 2015, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- H´bert, H.; Sladen, A.; Schindel´, F. Numerical modeling of the great 2004 Indian Ocean tsunami: Focus on the Mascarene Islands. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 2007, 97, S208–S222. [Google Scholar]
- Erkaev, N.V.; Semenov, V.S.; Kubyshkin, I.V.; Kubyshkina, M.V.; Biernat, H.K. MHD model of the flapping motions in the magnetotail current sheet. J. Geophys. Res. 2009, 114, A03206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.Z.G.; Hirose, A. Formation and evolution of flapping and ballooning waves in magnetospheric plasma sheet. Plasma Phys. Rep. 2016, 42. in press. [Google Scholar]





© 2016 by the author; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, J.Z.G. Atmospheric Layers in Response to the Propagation of Gravity Waves under Nonisothermal, Wind-shear, and Dissipative Conditions. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2016, 4, 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse4010025
Ma JZG. Atmospheric Layers in Response to the Propagation of Gravity Waves under Nonisothermal, Wind-shear, and Dissipative Conditions. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2016; 4(1):25. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse4010025
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, John Z. G. 2016. "Atmospheric Layers in Response to the Propagation of Gravity Waves under Nonisothermal, Wind-shear, and Dissipative Conditions" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 4, no. 1: 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse4010025
APA StyleMa, J. Z. G. (2016). Atmospheric Layers in Response to the Propagation of Gravity Waves under Nonisothermal, Wind-shear, and Dissipative Conditions. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 4(1), 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse4010025




