Abstract
This research proposes a face detection algorithm named LighterFace, which is aimed at enhancing detection speed to meet the demands of real-time community applications. Two pre-trained convolutional neural networks are combined, namely Cross Stage Partial Network (CSPNet), and ShuffleNetv2. Connecting the optimized network with Global Attention Mechanism (GAMAttention) extends the model to compensate for the accuracy loss caused by optimizing the network structure. Additionally, the learning rate of the detection model is dynamically updated using the cosine annealing method, which enhances the convergence speed of the model during training. This paper analyzes the training of the LighterFace model on the WiderFace dataset and a custom community dataset, aiming to classify faces in real-life community settings. Compared to the mainstream YOLOv5 model, LighterFace demonstrates a significant reduction in computational demands by 85.4% while achieving a 66.3% increase in detection speed and attaining a 90.6% accuracy in face detection. It is worth noting that LighterFace generates high-quality cropped face images, providing valuable inputs for subsequent face recognition models such as DeepID. Additionally, the LighterFace model is specifically designed to run on edge devices with lower computational capabilities. Its real-time performance on a Raspberry Pi 3B+ validates the results.
1. Introduction
Currently, community security is a growing concern. Communities have a large number of people coming in and out every day, and it is very common for strangers to blend into the crowd. In order to avoid them from committing illegal acts and to facilitate management, an efficient supervision system is necessary. The face detection algorithm integrated into surveillance cameras facilitates real-time identification of targeted faces. However, the development of face detection technology prompts critical considerations regarding the safeguarding of personal privacy. It is imperative to ensure that the processing of face images and associated data does not infringe upon individual privacy rights. Edge computing emerges as a viable solution to address these concerns, as it allows for the processing of face information without relying on internet connectivity, an approach which maximizes the protection of personal privacy and security. Navigating the challenge of efficiently processing image information for face detection using limited local computing resources becomes a complex task. The utilization of these constrained resources in the most effective manner requires strategic solutions to balance the imperative of accurate face detection with the need to uphold privacy rights.
Over the past decade, a great deal of research has been devoted to designing people-identification systems that are both efficient and economical. These systems aim to swiftly and accurately identify individuals, promptly alerting a remote monitoring point in the event of a potential threat, such as an unauthorized person attempting to infiltrate a neighborhood. Two primary categories of people-recognition systems have emerged in this pursuit. The first category involves what is commonly referred to as the sensory system. This system relies on sensors, such as fingerprint readers [1,2], ID card readers, or identification card readers, strategically deployed for identification purposes. However, this approach is susceptible to impersonation and spoofing, compromising the reliability of the identification process. In contrast, facial recognition devices present a more robust alternative, overcoming the limitations associated with the sensory system. Facial recognition technology enhances security measures by providing a non-intrusive and less susceptible means of identifying individuals, thereby contributing to more effective and secure people recognition systems.
Artificial intelligence-based computer vision strategies have proven to be efficient and widely deployed in numerous communities [3], particularly with high-coverage cameras [4]. However, challenges can arise due to the limited computational power of the built-in chips in these cameras, driven by economic cost considerations. Despite the advancements in face detection, especially following the release of the challenging WiderFace [5] benchmark dataset, mainstream face detection models may not be feasible for deployment under current conditions. Several algorithms have emerged to address specific challenges in face detection, showcasing innovative solutions. For instance, img2pose [6] leverages a Fast Region-based Convolutional Neural Network (R-CNN) to regress the six-degrees -of-freedom poses of faces in photos without requiring preliminary face detection. While optimized for pose estimation, it does increase computational requirements. Limb Line Free Form Deformation (LFFD) [7], on the other hand, focuses on the importance of receptive and effective receptive fields in face detection, utilizing a lightweight homemade backbone network suitable for edge computation. However, there is still room for optimizing this network structure for embedded terminals with the aim to enhance speed. RetinaFace [8] adopts a unique approach by manually labeling five facial markers in the WiderFace dataset, enriching detection features and proposing a single-phase solution with superior detection accuracy. Although well-suited for deployment in embedded terminals, further improvements in operational speed are desirable. TinaFace [9] improves face detection accuracy by enhancing the network structure based on ResNet50. This modification reflects a significant increase in accuracy, highlighting the ongoing efforts to refine and advance face detection capabilities. The algorithms mentioned above will be compared in subsequent comparative experiments, as detailed in Table 1.

Table 1.
Comparison of performance and detection speed of different detection algorithms.
Face detection serves as a crucial prerequisite for effective face recognition, with the accuracy of face detection directly influencing the overall face recognition rate. While deep learning-based face detection algorithms have shown superior performance compared to traditional methods, challenges persist, particularly in accurately recognizing small-scale and heavily occluded faces. SSH (Single Shot multibox Detector with Scale Hierarchy) improves upon SSD [10], presenting a multi-branch approach within VGG-net [11] to detect multi-scale faces. This approach addresses limitations in face recognition accuracy, particularly in challenging scenarios. FDDB introduces Light-Head Faster R-CNN as a strategic enhancement for face detection performance. By incorporating multi-scale training and testing along with deformable Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN) [12], this method aims to achieve improved accuracy and efficiency within the FDDB framework. Face R-FCN [13], building upon R-FCN, employs smaller-sized location-sensitive RoI (Region of Interest) pooling kernels and additional minor anchor points. The method also integrates regular average pooling with location-sensitive average pooling, contributing to enhanced face detection accuracy. A Focusing Attention Network (FAN) introduces an attention mechanism into face detection through anchor-level attention, which is particularly beneficial for improving recall in cases of occluded faces while maintaining a low false alarm rate. PyramidBox addresses stern face detection challenges by proposing low-level feature pyramid networks [14], PyramidAnchors, and context-sensitive prediction modules. Moreover, it introduces a data anchor sampling method to augment training samples at different scales, emphasizing the importance of contextual information in face detection. These advancements collectively represent a continuous effort to refine face detection algorithms, aiming to overcome challenges and improve accuracy, especially in scenarios involving small-scale faces and occlusions.
Simplifying the face detection model to reduce the amount of computation and time is a key issue under the premise of meeting the deployment conditions of embedded terminals. It is imperative to ensure algorithmic accuracy for practical applications. Current mainstream methods for achieving lightweight models, include pruning [15], knowledge distillation [16], and optimizing neural network structure. Pruning and knowledge distillation focus on post-training optimization of the model structure, while optimizing the neural network structure involves direct training of a lightweight network. In this paper, the design approach is rooted in the notion of creating an efficient and accurate face detection model suitable for deployment on embedded terminals. Historically, the R-CNN algorithm [17] played a pivotal role in practical target detection through CNNs. Subsequent advancements, such as Fast R-CNN [18] and Faster R-CNN [19], addressed shortcomings and improved detection speed. The evolution of techniques like FCN [20] and Mask R-CNN [21] contributed to the maturation of image segmentation methods. Noteworthy lightweight algorithms, including MobileNet-SSD [22,23] and You Only Look Once (YOLO) [24,25,26,27], have simplified object detection on mobile terminals without necessitating the use of cloud servers.
Although existing algorithms have made remarkable progress in face detection, there remains a need to balance the requirement of maintaining detection accuracy while reducing computational costs. To overcome challenges posed by limited server computational power and inadequate real-time performance, our research addresses this demand by leveraging advanced deep learning techniques. By integrating state-of-the-art lightweight network ShuffleNetv2 and the excellent classification task network CSPNet, our proposed LighterFace model aims to enable real-time deployment of face detection models on edge devices. We carried out ablation and comparison experiments, and the results demonstrate that LighterFace runs on Raspberry Pi 3b+ with an accuracy of 90.6% and a speed of 1543 ms.
2. Materials and Methods
In this section, the proposed face recognition algorithm is introduced through the following two components: face detection and face recognition. CSPNet addresses the issue of redundant gradient information in the neural network backbone by integrating gradient changes into the feature maps from start to finish. This approach reduces the model’s parameter count and floating-point operations per second (FLOPS) while maintaining inference speed and accuracy, ultimately reducing the model size. ShuffleNetv2 achieves a reduction in the model’s parameter count and FLOPS by employing techniques such as Pointwise Group Convolution and channel shuffling. The face detection model LighterFace, presented in this paper, further optimizes the network structure by combining the aforementioned two networks. To compensate for the loss in detection accuracy, GAMAttention is integrated into the face detection model. As a result, the model’s structure is streamlined without sacrificing a significant amount of detection accuracy. This phase involves identifying and cropping the faces within an image or video stream. The quality of face detection significantly influences the overall accuracy of the subsequent face recognition process.
2.1. Face Detection Model
LighterFace is formulated and optimized using the Cross Stage Partial Network (CSPNet). The algorithmic model architecture is illustrated in Figure 1. The representative detection model utilized in CSPNet is YOLOv5. For comparative analysis, YOLOv5 is employed as a control group in this section to highlight the optimization advancements achieved by LighterFace more distinctly. In the network architecture of LighterFace, depicted in Figure 1, the utilization of the CBRM module occurs in the initial phase, with the feature extraction module incorporating Shuffle Block and Global Attention Mechanism (GAMAttention).
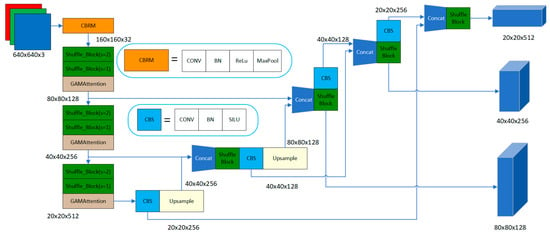
Figure 1.
LighterFace algorithm model architecture.
2.1.1. CBRM Module Structure
In the YOLO model, the original authors employ the Stem module as the initial component of the network. Its primary function is to perform a sequence of convolutional and pooling operations on the input image, extracting the initial feature representation. This facilitates subsequent layers of the network to more effectively learn and represent semantic features of the image. The structure of the Stem module is illustrated in Figure 2a.
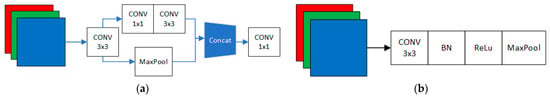
Figure 2.
(a) Stem module architecture (comparison group); (b) CBRM module architecture (LighterFace).
Stem, first through the 3 × 3 convolution of the initial extraction of image features, were sent to two branches to extract further features, with one branch through two convolutions, to extract further image features, the other branch through the MaxPool refinement of graphical features can significantly reduce the complexity of the image features. The features of the two branches are then fused and, finally, a 1 × 1 convolution of the convolution regulates the number of channels, which facilitates further extraction of image features by the subsequent backbone network.
According to the four guidelines mentioned in ShuffleNetv2 to reduce the amount of computation, as shown below, there is still room for improvement in the performance of this module [28]:
- i.
- Equal channel width minimizes Memory Access Cost (MAC);
- ii.
- Excessive group convolution increases MAC;
- iii.
- Network fragmentation reduces the degree of parallelism;
- iv.
- Element-wise operations are non-negligible.
The CBRM module is proposed based on the above four criteria, as shown in Figure 2b, which eliminates the branching structure and reduces the number of convolutional layers compared to the STEM module. The color image is divided into three monochrome layers and fed into the CBRM module, which extracts the image features directly by a 3 × 3 convolution and then connects with MaxPool in series to maximize the reduction in additional computation, which is in line with Rule ii and Rule iii.
2.1.2. ShuffleBlock
ShuffleNet is a machine-effective CNN that can be used in monolithic devices. It proposes Channel Shuffle, as shown in Figure 3, and group convolution (GConv) divides the features into three groups. After extracting the features by convolution operation, the features between different groups are not in any communication. The Channel Shuffle operator is introduced to mix the features of different groups evenly to ensure that the information can flow between different groups to improve the detection accuracy.
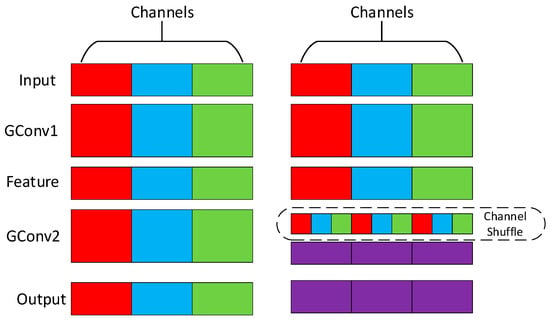
Figure 3.
The Channel Shuffle schematic (LighterFace). The data from different channels (red, blue, green) are not interconnected. Channel Shuffle can extract data from different channels and rearrange them to establish connections.
In the YOLO model, the authors use the C3 module as an essential part of the backbone network. The structure of the C3 module is shown in Figure 4. It is faster and more accurate than the CSPBottleneck, which can further extract feature information and increase the depth and width of the network for better learning of semantic features in images. However, the degree of lightweight of the multiple separated convolutions it uses could be improved. According to the Rule i criterion of ShuffleNetv2, the higher the number of channels, the more significant the gap between the number of input channels and the number of output channels, which results in the C3 module running at a less-than-optimal speed on a CPU or ARM.
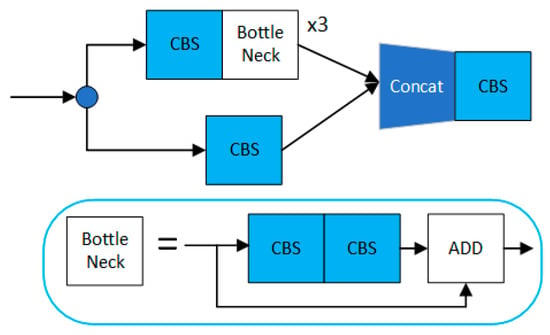
Figure 4.
The C3 modular architecture (comparison group), which consists of three standard convolutional layers and multiple Bottleneck modules.
When designing the Shuffle Block, the Shuffle Block network at stride = 1 is shown in Figure 5a. The whole does not use grouped convolutional modules, which conforms to Rule ii. The feature channel is divided into two branches before the start of the unit module, and one branch retains the original features, while the other branch uses the same input and output channels of two convolutional modules and one DepthWiseConv (DWConv) module to extract features in series. DWConv is less computationally intensive than normal Conv, which can reduce the computational complexity of the overall model, which is by Rule i and Rule iii. In order to reduce the computation time of other operations, such as Add, the features of the two branches are fused using Concat to avoid the Add, while other Element-wise operations are avoided by using Concat to fuse the features of two branches to avoid Add and other operations, which is by Rule iv. Finally, the feature information of each channel is fused by Channel Shuffle.
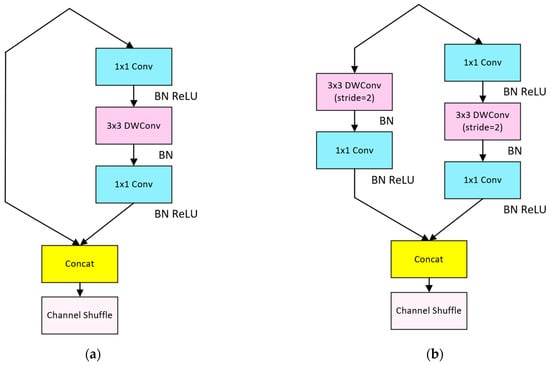
Figure 5.
(a) The Shuffle Block network at stride = 1 (LighterFace); (b) The Shuffle Block network at stride = 2 (LighterFace).
2.1.3. GAMAttention
This module [29] serves to mitigate information loss and enhance global dimensional interaction features. The overall process is defined by
where is input to the GAM, the intermediate state is obtained by channel attention module and spatial attention module and element by element multiplication, and the output is shown in Figure 6.
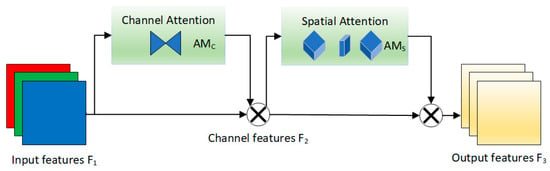
Figure 6.
GAMAttention module architecture. GAMAttention achieves this by performing element-wise multiplication with both the Channel Attention Module and the Spatial Attention Module.
The channel attention module employs a 3D arrangement to preserve information across three dimensions. Subsequently, it enhances the spatial dependence of the cross-dimensional channels by employing a two-layer multilayer perceptron (MLP). The structure of the channel attention module is visually represented in Figure 7.
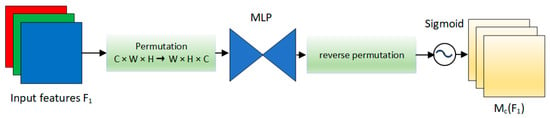
Figure 7.
The schematic diagram of channel attention module, which uses 3D permutation to retain information across three dimensions.
In the spatial attention module, to incorporate spatial information, this paper chooses not to use max-pooling for spatial information extraction. Instead, it employs two convolutional layers to extract the output of the channel attention module, aligning with Rule iv in ShuffleNet. The influence factor is utilized in this paper to configure the weight of the channel and spatial attention modules, preventing dispersion in the training results. The structure of the spatial attention module is depicted in Figure 8.
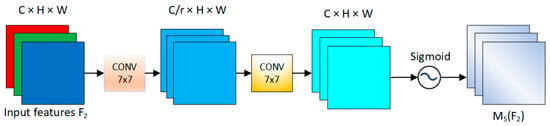
Figure 8.
The schematic diagram of the spatial attention module. To focus on spatial information, we use two convolutional layers for spatial information fusion.
2.1.4. Loss Function
This paper uses the loss function, as shown, to improve the stability of training and convergence speed.
where the ratio of overlapping area of the predicted and labeled boxes is (), S1 is the overlapping area of the two boxes, and S2 is the total area. The similarity of the width-to-height ratios of the two boxes are considered from multiple perspectives ().
As shown in Figure 9, the loss function in this not only takes into account the distance between the detection frame and the labeling frame but also considers the relative proportion of the two rectangular frames. This approach contributes to a more efficient convergence speed in the training process and overall performance, leading to an enhanced detection effect.
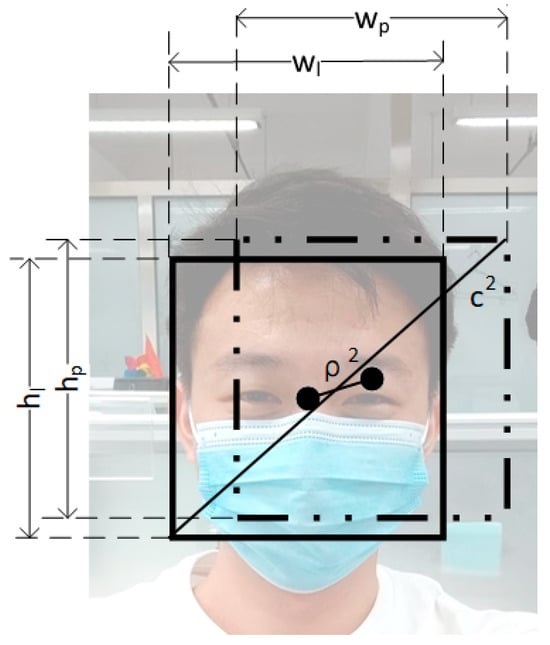
Figure 9.
Schematic diagram of loss function parameters. Where the width (Wl) and height (Hl) of the labeling box and the width (Wp) and height (Hp) of the prediction box, the distance between the centroids (), the diagonal length of the minimum enclosing matrix of the two boxes (), the derivation of the formula is shown.
2.2. Face Feature Extraction DeepID
High-accuracy face detection is crucial for the overall face recognition system, providing multiple advantages that enhance the effectiveness and reliability of face recognition technology. LighterFace contributes to expediting the face recognition process by swiftly identifying and localizing faces in images or video streams. By reducing the computational load in subsequent stages of the face recognition pipeline, LighterFace enhances overall efficiency. Building on this foundation, we further DeepID for face detection, with the goal of enhancing both the accuracy and speed of the face recognition system. This integration aims to optimize the detection capabilities, contributing to an overall improvement in the performance of the face recognition system.
2.2.1. Network Infrastructure
DeepID is an efficient approach for extracting face features using the deep convolutional network. Figure 10 shows the feature extraction process. The convolutional network learns to classify all the faces available for training based on their identity and activates corresponding features through neurons in a hidden layer. Each convolutional network takes the face features from the previous layer as input and extracts local low-level features at the bottom. The number of features decreases progressively along the feature extraction cascade, while increasingly global and high-level features are formed at the top layer. A highly compact 160-dimensional face feature vector is obtained at the end of the cascade, which contains rich identity information and directly predicts a more significant number of identity classes.
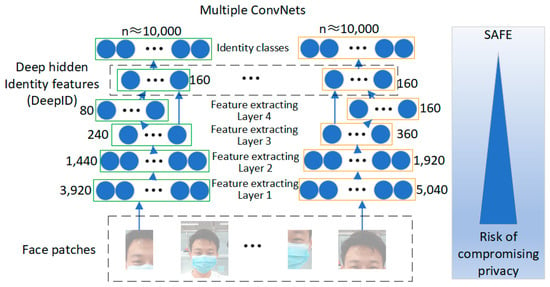
Figure 10.
DeepID algorithm model architecture.
2.2.2. Face Privacy Protection
Amid growing public concerns about the privacy of face datasets, ensuring the protection of face privacy has become an essential consideration in the field of face recognition technology. In this paper, facial images undergo a transformation into 160-dimensional face feature vectors using DeepID, which are then stored in the database. Notably, these feature vectors are associated with the names of individuals in the community rather than being directly linked to the original face images and names. This strategic approach ensures that the feature vectors cannot be reversed or inverted back to reveal the original images, thereby significantly minimizing the risk of privacy leakage for residents in the community.
3. Experiment and Discussion
The overall network framework is implemented, and train using Pytorch 1.10.0 + cu102 version is also implemented and trained on a server configured with an Intel Xeon Silver 4210R processor and an NVIDIA Quadro RTX 5000 graphics card. The edge device used in real-world community applications is the Raspberry Pi 3B+, which is also the ARM configuration mentioned in the experimental section later in the paper.
The research results in this paper are mainly based on two aspects: (1) model accuracy (2) model running speed. The evaluation indexes of AP@0.5, the number of model parameters, the amount of model computation and the average speed of detecting test set images are chosen as the evaluation indexes of the detection module with the following formulas:
where TP is the number of samples that were correctly classified as positive by the model. FP is the number of samples that were incorrectly classified as positive by the model. TN is the number of samples that were correctly classified as negative by the model. FN is the number of samples that were incorrectly classified as negative by the model. IOU determines the positive and negative classes in re-image detection. In this paper, when IOU > 0.5, it is judged as a positive class and vice versa as a negative class.
3.1. Datasets
The two datasets used to train the model in this study are WiderFace and the homemade dataset.
In this paper, the face detection benchmark dataset WiderFace dataset (WF) is used, in which the images are selected from the publicly available WiderFace dataset, with a total of 32,203 images labeled with 393,703 faces. The training, validation and test sets are differentiated in the ratio of 4:1:5. This ratio is set according to the official instructions provided by WiderFace.
This research creates a face detection dataset for testing Community Face (CF). The dataset is shown in Figure 11. This dataset is used to prove that the model of this paper also keeps the leading performance in different datasets, in which the images come from the web and real community photos. In the WiderFace dataset, there is a lack of data on Asian faces. To address this gap, we specifically selected individuals entering and leaving communities in real-life projects, focusing solely on Asians. We annotated only real faces, excluding images containing distractions, such as faces on billboards or packaging boxes. There are 9240 images labeled 11,962 faces. The ratio of the training set, verification set, and test set is set to 6:2:2. Due to weather, light, and occlusion, faces become blurred in the images. In order to ensure that the trained model has better detection ability for blurred faces as well, there are a total of 902 images in the dataset that were taken in rainy and night-time conditions.

Figure 11.
Community face dataset (CF), A mosaic has been created for the community.
3.2. Experimental Setup and Technical Details
In order to facilitate the comparison, this paper reproduces several mainstream face recognition algorithms, the original YOLOv5 and the improved algorithm based on ShuffleNet.
The batch size affects both the optimization degree and the speed of the model, while also impacting the memory usage of the CPU or GPU. Given the relatively standard training configuration, the batch size is set to eight to reduce memory usage. Setting the number of epochs to 100 is a common fixed value chosen by many models, as it allows the model to be thoroughly trained to reach its optimal and most stable state. In order to avoid the local optimum point to find the global optimum point, the cosine annealing algorithm is used to set the dynamic learning rate, and the formula is as follows:
where lr is the new learning rate, is the initial learning rate, is the minimum learning rate, is the value corresponding to the current training to a particular epoch, is the total number of epochs trained. In the deep learning network, mainly through the gradient descent method to find a set of parameters that can minimize the structural risk, and the learning rate in the training process of deep learning is a very important hyperparameter, guiding the model on how to adjust the hyperparameters of the network weights through the gradient of the loss function. The lower the learning rate, the slower the rate of change in the loss function. While using a low learning rate ensures that the algorithmic model will not miss any local minima, it also means that the algorithmic model will take longer to converge. The higher the learning rate, the faster the loss function changes, but it tends to miss local minima. The cosine annealing algorithm avoids falling into local minima during training by stepping out of the local minima and leading to a path to find the global optimal solution.
The learning rate was configured using the cosine annealing method and manually set to 0.1 for comparison. The experimental results are depicted in Figure 12. The red line represents the loss curve of training for 100 epochs with a learning rate set to 0.1, while the blue line utilizes CosineAnnealingLR. Loss is one of the crucial metrics for assessing model performance; smaller loss values indicate a smaller discrepancy between the model’s predictions and the true labels. From the graph, it is evident that the training results with CosineAnnealingLR are superior. When the learning rate is fixed, the model may become trapped in the local minima. Using a fixed learning rate for loss prediction yields worse results compared to using CosineAnnealingLR for training.
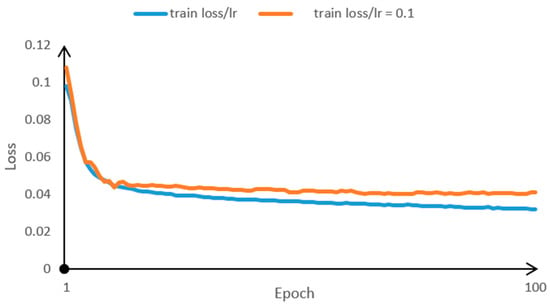
Figure 12.
Loss comparison of fixed learning rate and cosine annealing algorithms.
3.3. Face Detection Accuracy and Speed
Face detection is a crucial prerequisite for the stable execution of face recognition. The face detection algorithm LighterFace proposed in this paper is compared with other recent face detection algorithms, including TinaFace, Retina-Face, LFFD, and YoloV5; the comparison results are shown in Table 1. The dataset used is the WiderFace dataset, which is more widely recognized. For a better comparison, this paper uses AP@0.5 and the detection speed of the model on CPU and ARM to form Table 2.

Table 2.
Comparison of detection speed of different feature extraction modules with the same architecture.
By optimizing the network structure of the feature extraction module, the detection speed of LighterFace is very much improved. This paper uses CSPNet as the backbone, which has less computational complexity than ResNet and LFFDNet. This paper’s final model accuracy and detection speed are better than YoloV5 when using the same backbone.
3.4. Ablation Experiment
In this subsection, in order to better represent the improvements in LighterFace, we conducted ablation experiments to demonstrate the performance of Shuffle Block, CBAM, and GAMAttenion. In addition to using the standard evaluation metric of average accuracy at IoU = 0.5 (AP@0.5) in the WiderFace dataset, this paper utilizes the more stringent IoU = 0.5:0.05:0.95 average accuracy (AP@0.5:0.95), where different evaluation metrics allow for multi-latitudinal reviewing of model performance. This paper evaluates the performance of several different settings on the WiderFace validation set and self-made data set, focusing on their AP and running speed. The experimental results are shown in Table 3, speed and convergence speed comparison (Figure 13 and Table 2).

Table 3.
Comparison of detection performance of different feature extraction modules with the same architecture.
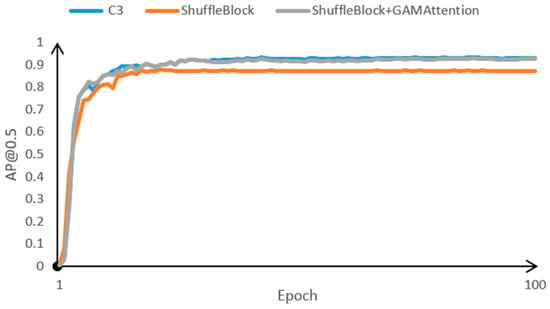
Figure 13.
Comparison of accuracy convergence speed for different extracted features.
Shuffle Block replaces CSPNet with Shuffle Block. After that, the computational complexity and model size are significantly reduced, the amount of parameters is reduced by 87.9%, GLOPs are reduced by 88.6%, accuracy is reduced by 4.5%, and detection speed is accelerated by 46.7%. The architectures of both networks are the same. LighterFace adds the attention module interspersed in ShuffleNet, and all other settings remain unchanged.
After the addition of GAMAttention, the number of parameters is reduced by 81.1%, GLOPs are reduced by 85.4% compared to CSPNet, the accuracy is improved by 2.4%, and the speed is slowed down by 5.3% compared to ShuffleNet.
3.5. Community Detection Scenarios
The objective of the experiment is to underscore the importance of face detection and recognition in preventing unauthorized individuals from invading or damaging public equipment. Additionally, the experiment aims to identify and mark specific areas within the natural community as potentially dangerous zones. These areas include the community entrance, the community exit, the entrance of residential buildings, and the vicinity of the electric box. The overall layout of the experimental environment is visually represented in Figure 14.
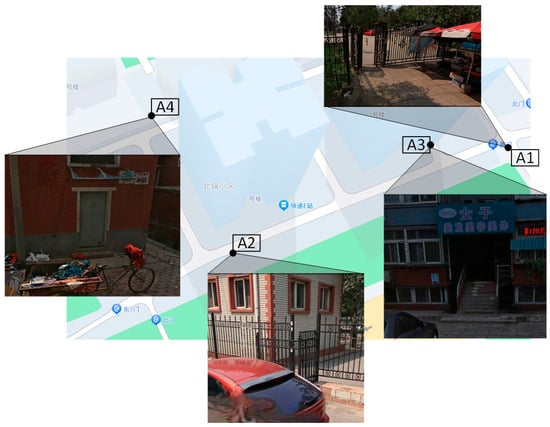
Figure 14.
Community monitoring area.
Upon the appearance of a face in the surveillance area, a face detection program is activated. The identified face is then utilized to extract face feature vectors through DeepID, subsequently undergoing a comparison with the facial data stored in the database. This comparison aims to ascertain whether the individual is a stranger. These detection and identification processes are crucially time-sensitive, demanding real-time execution to avoid missing the optimal warning window. Upon detecting a stranger, an immediate warning is transmitted to community managers, enabling them to proactively monitor potential intruders. This proactive strategy is strategically designed to thwart incidents such as burglary and vandalism, ensuring that community managers possess ample time to remain vigilant to potential threats and respond promptly and appropriately.
The experiment was conducted over four rounds, encompassing various activities, as outlined in Table 4. In the initial phase of the experiment, the algorithm’s performance was tested, with LighterFace being compared against current mainstream face detection methods.

Table 4.
Definitions of the 4 identified activities during the test.
3.6. LighterFace in the Monitoring Area
After clearly defining the community detection scene, we conducted comparative experiments to employ YoloV5s, LFFD, YoloV5n, and LighterFace to assess their face detection accuracy and speed in the context of four identified activities. The primary objective is to verify and compare the performance of these models. Subsequently, 100 registered faces from each identified activity were selected for testing. The face detection mechanism is applied to crop face images, and these images are utilized to extract face feature vectors using DeepID. The resulting feature vectors are then compared with the facial data stored in the face database to evaluate the efficacy of the face recognition function.
Table 5 presents the average time and accuracy results for face detection across all algorithms, along with the accuracy of face recognition for the three datasets. Notably, LighterFace exhibits the capability to achieve face detection within 1700 ms in real application scenarios, utilizing a low-computing chip. The detection accuracy is consistently maintained at approximately 90%. This high level of detection accuracy establishes a robust foundation for subsequent face recognition. Consequently, the correct rate of the face recognition function is also sustained at around 90%.

Table 5.
LighterFace application in the monitoring area.
4. Conclusions
In this paper, we have proposed a real-time monitoring system for tracking people entering and exiting a community using a face detection model. The objective was to prevent strangers from intruding into the community, thereby enhancing overall security performance. The key innovation lies in developing a lightweight model with reduced computational complexity, enabling deployment on computationally inefficient embedded devices while maintaining commendable detection accuracy and speed. LighterFace incorporates a customized ShuffleBlock as the primary feature extraction module within the CSPNet network. Through structural adjustments, the FLOPs were reduced from 15.8 to 2.3, and we achieved an 85.4% reduction in computational workload. When performing face detection on the CPU platform, the detection speed improved from taking 69.66 ms per frame to 39.5 ms per frame, achieving a 43.3% increase in detection speed. When conducting face detection on the ARM platform, the detection speed improved from taking 4578 ms per frame to 1543 ms per frame, resulting in a 66.3% increase in detection speed. Evaluation on the WiderFace dataset and a community face dataset ensures that LighterFace maintained high detection accuracy (AP@0.5) while prioritizing speed performance. To validate real-world applicability, various models were deployed on a Raspberry Pi 3B+ for testing. Results demonstrate that LighterFace can effectively support face detection on ARM chips with low computational power. Furthermore, its compatibility with mainstream older cameras facilitates software iterative upgrading, confirming LighterFace’s performance in terms of speed under practical conditions.
With the proposed approach, the community can deploy the model in cameras that come with low-computing power chips, which is expected to help reduce potential community security risks.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.S., W.G. and H.Z.; methodology, M.Z., J.L., S.L., Y.D. and H.Z.; software, H.Z. and J.L; validation, J.L., S.L. and H.Z.; formal analysis, Y.S. and H.Z.; investigation, H.Z.; resources, H.Z., W.G. and H.Z.; data curation, W.G. and H.Z.; writing—original draft preparation, M.Z. and H.Z.; writing—review and editing, S.L. and H.Z.; visualization, H.Z.; supervision, H.Z.; project administration, Y.S. and H.Z.; funding acquisition, Y.S. and M.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was sponsored by National Key R&D Program of China [2023YFC3306400], the National Natural Science Foundation of China (62273007).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The results/data/figures in this manuscript have not been published elsewhere, nor are they under consideration (from you or one of your Contributing Authors) by another publisher.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Nakamura, K.; Koike, Y.; Sato, Y.; Yanagitani, T. Giga-hertz ultrasonic reflectometry for fingerprint imaging using epitaxial PbTiO3 transducers. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2022, 121, 172903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saguy, M.; Almog, J.; Cohn, D.; Champod, C. Proactive forensic science in biometrics: Novel materials for fingerprint spoofing. J. Forensic Sci. 2022, 67, 534–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayoudh, K.; Knani, R.; Hamdaoui, F.; Mtibaa, A. A survey on deep multimodal learning for computer vision: Advances, trends, applications, and datasets. Vis. Comput. 2022, 38, 2939–2970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marasinghe, R.; Yigitcanlar, T.; Mayere, S.; Washington, T.; Limb, M. Computer vision applications for urban planning: A systematic review of opportunities and constraints. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2023, 100, 105047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Luo, P.; Loy, C.C.; Tang, X.O. Wider Face: A Face Detection Benchmark. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 5525–5533. [Google Scholar]
- Albiero, V.; Chen, X.; Yin, X.; Pang, G.; Hassner, T. Img2pose: Face Alignment and Detection Via 6dof, Face Pose Estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 7617–7627. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, D.; Wu, L.; He, Y.; Zhao, Q. OS-LFFD: A Light and Fast Face Detector with Ommateum Structure. Multimed Tools Appl. 2021, 80, 34153–34172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Guo, J.; Ververas, E.; Kotsia, I.; Zafeiriou, S. Retinaface: Single-Shot Multi-Level Face Localisation in The Wild. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Srattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 5203–5212. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Y.; Cai, H.; Zhang, S.H.; Wang, C.H.; Xiong, Y.C. Tinaface: Strong but Simple Baseline for Face Detection. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2011.13183. [Google Scholar]
- Najibi, M.; Samangouei, P.; Chellappa, R.; Davis, L.S. SSH: Single Stage Headless Face Detector. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 4875–4884. [Google Scholar]
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Very Deep Convolutional Networks for Large-Scale Image Recognition. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1409.1556. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Xu, X.; Tu, D. Face Detection Using Improved Faster RCNN. Neurocomputing 2018, 299, 42–50. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Yuan, Y.; Yu, G. Face Attention Network: An Effective Face Detector for The Occluded Faces. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1711.07246. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, X.; Du, D.K.; He, Z.; Liu, J. Pyramidbox: A Context-Assisted Single Shot Face Detector. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 812–828. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Li, J.G.; Shen, Z.Q.; Huang, G.; Yan, S.M.; Zhang, C.S. Learning Efficient Convolutional Networks through Network Slimming. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 2736–2744. [Google Scholar]
- Hinton, G.; Vinyals, O.; Dean, J. Distilling the Knowledge in A Neural Network. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1503.02531. [Google Scholar]
- Girshick, R.; Donahue, J.; Darrell, T.; Malik, J. Rich Feature Hierarchies for Accurate Object Detection and Semantic Segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Columbus, OH, USA, 23–28 June 2014; pp. 580–587. [Google Scholar]
- Girshick, R. Fast R-CNN. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (CVPR), Santiago, Chile, 7–13 December 2015; pp. 1440–1448. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, S.; He, K.; Girshick, R.; Sun, J. Faster R-CNN: Towards Real-Time Object Detection with Region Proposal Networks. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2018, 13, 1137–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shelhamer, E.; Long, J.; Darrell, T. Fully Convolutional Networks for Semantic Segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (CVPR), Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 640–651. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Gkioxari, G.; Dollar, P.; Girshick, R. Mask R-CNN. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 386–397. [Google Scholar]
- Howard, A.G.; Zhu, M.; Chen, B.; Kalenichenko, D.; Wang, W.; Weyand, T.; Andreetto, M.; Adam, H. Mobilenets: Efficient Convolutional Neural Networks for Mobile Vision Applications. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1704.04861. [Google Scholar]
- Sandler, M.; Howard, A.; Zhu, M.; Zhmoginov, A.; Chen, L.C. Mobilenetv2: Inverted Residuals and Linear Bottlenecks. In Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 4510–4520. [Google Scholar]
- Redmon, J.; Divvala, S.K.; Girshick, R.; Farhadi, A. You Only Look Once: Unified, Real-Time Object Detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 779–788. [Google Scholar]
- Redmon, J.; Farhadi, A. YOLO9000: Better, faster, stronger. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 6517–6525. [Google Scholar]
- Redmon, J.; Farhadi, A. Yolov3: An Incremental Improvement. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1804.02767. [Google Scholar]
- Bochkovskiy, A.; Wang, C.; Liao, H.M. Yolov4: Optimal Speed and Accuracy of Object Detection. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2004.10934. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, N.; Zhang, X.; Zheng, H.T.; Sun, J. Shufflenet V2: Practical Guidelines for Efficient CNN Architecture Design. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 116–131. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.C.; Shao, Z.R.; Hoffmann, N. Global Attention Mechanism: Retain Information to Enhance Channel-Spatial Interactions. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2112.05561. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).