Graphene and Other Nanomaterial-Based Electrochemical Aptasensors
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Aptamers
3. Amperometric, Potentiometric and Impedimetric Aptasensors
3.1. Amperometric Measurements
3.2. Potentiometric Measurements

3.3. Conductimetric/Impedimetric Measurements
3.4. Field-Effect Transistors
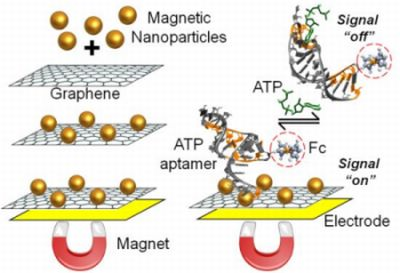
4. Graphene-Based Nanocomposites

5. Carbon Nanotubes
6. Metal Nanoparticle-Based Strategies
7. Future Prospects
References
- Soldano, C.; Mahmood, A.; Dujardin, E. Production, properties and potential of graphene. Carbon 2010, 48, 2127–2150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, P.; Zhang, J.; Li, L.; Wang, Z.; O’Neill, W.; Estrela, P. Carbon nanostructure-based field-effect transistors for label-free chemical/biological sensors. Sensors 2010, 10, 5133–5159. [Google Scholar]
- Brownson, D.A.C.; Banks, C.E. Graphene electrochemistry: An overview of potential applications. Analyst 2010, 135, 2768–2778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cash, K.J.; Ricci, F.; Plaxco, K.W. An electrochemical sensor for the detection of protein-small molecule interactions directly in serum and other complex matrices. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 6955–6957. [Google Scholar]
- Radi, A.-E.; Acero Sanchez, J.L.; Baldrich, E.; O’Sullivan, C.K. Reagentless, reusable, ultrasensitive electrochemical molecular beacon aptasensor. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 128, 117–124. [Google Scholar]
- Hianik, T.; Wang, J. Electrochemical aptasensors—Recent achievements and perspectives. Electroanalysis 2009, 21, 1223–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.S.; Lee, S.J.; Gu, M.B. Electrochemical aptamer-based biosensors. Biochip J. 2008, 2, 175–182. [Google Scholar]
- Mairal, T.; Ozalp, V.C.; Lozano Sanchez, P.; Mir, M.; Katakis, I.; O’Sullivan, C.K. Aptamers: Molecular tools for analytical applications. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2008, 390, 989–1007. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, R.E.; Zhang, Y.; Cai, J.; Cai, W.; Gao, T. Aptamer-based fluorescent biosensors. Curr. Med. Chem. 2011, 18, 4175–4184. [Google Scholar]
- Iliuk, A.B.; Hu, L.H.; Tao, W.A. Aptamer in bioanalytical applications. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 4440–4452. [Google Scholar]
- Ellington, A.D.; Szostak, J.W. In vitro selection of RNA molecules that bind specific ligands. Nature 1990, 346, 818–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuerk, C.; Gold, L. Systematic evolution of ligands by exponential enrichment: RNA ligands to bacteriophage T4 DNA polymerase. Science 1990, 249, 505–510. [Google Scholar]
- Mayer, G. The chemical biology of aptamers. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 2672–2689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drabovich, A.P.; Berezovski, M.V.; Musheev, M.U.; Krylov, S.N. Selection of smart small-molecule ligands: The proof of principle. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 490–494. [Google Scholar]
- Rockey, W.M.; Hernandez, F.J.; Huang, S.Y.; Cao, S.; Howell, C.A.; Thomas, G.S.; Liu, X.Y.; Lapteva, N.; Spencer, D.M.; McNamara, J.O.; et al. Rational truncation of an RNA aptamer to prostate-specific membrane antigen using computational structural modeling. Nucleic Acid Ther. 2011, 21, 299–314. [Google Scholar]
- Pasternak, A.; Hernandez, F.J.; Rasmussen, L.M.; Vester, B.; Wengel, J. Improved thrombin binding aptamer by incorporation of a single unlocked nucleic acid monomer. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, 1155–1164. [Google Scholar]
- Hernandez, F.J.; Kalra, N.; Wengel, J.; Vester, B. Aptamers as a model for functional evaluation of LNA and 2'-amino LNA. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2009, 19, 6585–6587. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, C.; Zhu, T.; Qi, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Xia, H.; Fu, W. Development of a quartz crystal microbalance biosensor with aptamers as bio-recognition element. Sensors 2010, 10, 5859–5871. [Google Scholar]
- Chiu, T.-C.; Huang, C.-C. Aptamer-functionalized nano-biosensors. Sensors 2009, 9, 10356–10388. [Google Scholar]
- Siqueira, J.R.; Abouzar, M.H.; Backer, M.; Zucolotto, V.; Poghossian, A.; Oliveira, O.N.; Schoning, M.J. Carbon nanotubes in nanostructured films: Potential application as amperometric and potentiometric field-effect (bio-)chemical sensors. Phys. Status Solidi A 2009, 206, 462–467. [Google Scholar]
- Maehashi, K.; Matsumoto, K. Label-free electrical detection using carbon nanotube-based biosensors. Sensors 2009, 9, 5368–5378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.J.; Wei, W.L.; Qu, X.G. Colorimetric biosensing using smart materials. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, 4215–4236. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, Z.; Mallikaratchy, P.; Yang, R.; Kim, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Wang, H.; Tan, W. Aptamer switch probe based on intramolecular displacement. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 11268–11269. [Google Scholar]
- Song, K.M.; Cho, M.; Jo, H.; Min, K.; Jeon, S.H.; Kim, T.; Han, M.S.; Ku, J.K.; Ban, C. Gold nanoparticle-based colorimetric detection of kanamycin using a DNA aptamer. Anal. Biochem. 2011, 415, 175–181. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, D.L.; Chan, D.S.H.; Man, B.Y.W.; Leung, C.H. Oligonucleotide-based luminescent detection of metal ions. Chem. Asian J. 2011, 6, 986–1003. [Google Scholar]
- Ozalp, V.C. Acoustic quantification of ATP using a quartz crystal microbalance with dissipation. Analyst 2011, 136, 5046–5050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozalp, V.C. Dual-polarization interferometry for quantification of small molecules using aptamers. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2011, 402, 799–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelossof, G.; Tel-Vered, R.; Liu, X.Q.; Willner, I. Amplified surface plasmon resonance based DNA biosensors, aptasensors, and Hg(2+) sensors using hemin/G-quadruplexes and Au nanoparticles. Chem. Eur. J. 2011, 17, 8904–8912. [Google Scholar]
- Hernandez, F.J.; Dondapati, S.K.; Ozalp, V.C.; Pinto, A.; O’Sullivan, C.K.; Klar, T.A.; Katakis, I. Label free optical sensor for Avidin based on single gold nanoparticles functionalized with aptamers. J. Biophotonics 2009, 2, 227–231. [Google Scholar]
- Han, K.; Liang, Z.; Zhou, N. Design strategies for aptamer-based biosensors. Sensors 2010, 10, 4541–4557. [Google Scholar]
- Chumbimuni-Torres, K.Y.; Rubinova, N.; Radu, A.; Kubota, L.T.; Bakker, E. Solid contact potentiometric sensors for trace level measurements. Anal. Chem. 2006, 78, 1318–1322. [Google Scholar]
- Numnuam, A.; Chumbimuni-Torres, K.Y.; Xiang, Y.; Bash, R.; Thavarungkul, P.; Kanatharana, P.; Pretsch, E.; Wang, J.; Bakker, E. Aptamer-based potentiometric measurements of proteins using ion-selective microelectrodes. Anal. Chem. 2008, 80, 707–712. [Google Scholar]
- Sassolas, A.; Blum, L.J.; Leca-Bouvier, B.D. Electrochemical aptasensors. Electroanalysis 2009, 21, 1237–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindholm-Sethson, B.; Nystrom, J.; Malmsten, M.; Ringstad, L.; Nelson, A.; Geladi, P. Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy in label-free biosensor applications: Multivariate data analysis for an objective interpretation. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2010, 398, 2341–2349. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, C.-S.; Kim, S.; Kim, M. Ion-sensitive field-effect transistor for biological sensing. Sensors 2009, 9, 7111–7131. [Google Scholar]
- Maehashi, K.; Katsura, T.; Kerman, K.; Takamura, Y.; Matsumoto, K.; Tamiya, E. Label-free protein biosensor based on aptamer-modified carbon nanotube field-effect transistors. Anal. Chem. 2007, 79, 782–787. [Google Scholar]
- An, T.; Kim, K.S.; Hahn, S.K.; Lim, G. Real-time, step-wise, electrical detection of protein molecules using dielectrophoretically aligned SWNT-film FET aptasensors. Lab Chip 2010, 10, 2052–2056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohno, Y.; Maehashi, K.; Matsumoto, K. Label-free biosensors based on aptamer-modified graphene field-effect transistors. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 18012–18013. [Google Scholar]
- Ohno, Y.; Maehashi, K.; Inoue, K.; Matsumoto, K. Label-free aptamer-based immunoglobulin sensors using graphene field-effect transistors. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, H.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, N.; Kim, B.G.; Jang, J. A novel sensor platform based on aptamer-conjugated polypyrrole nanotubes for label-free electrochemical protein detection. ChemBioChem 2008, 9, 634–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.S.; Kim, K.S.; Kim, C.J.; Hahn, S.K.; Jo, M.H. Electrical detection of VEGFs for cancer diagnoses using anti-vascular endotherial growth factor aptamer-modified Si nanowire FETs. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2009, 24, 1801–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.; Luo, S.C.; Yu, H.H. Electric-field-assisted growth of functionalized poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) nanowires for label-free protein detection. Small 2009, 5, 2611–2617. [Google Scholar]
- Kwon, O.S.; Park, S.J.; Jang, J. A high-performance VEGF aptamer functionalized polypyrrole nanotube biosensor. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 4740–4747. [Google Scholar]
- Shao, Y.; Wang, J.; Wu, H.; Liu, J.; Aksay, I.A.; Lin, Y. Graphene based electrochemical sensors and biosensors: A review. Electroanalysis 2010, 22, 1027–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enoki, T.; Kobayashi, Y.; Fukui, K.I. Electronic structures of graphene edges and nanographene. Int. Rev. Phys. Chem. 2007, 26, 609–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro Neto, A.H.; Guinea, F.; Peres, N.M.R.; Novoselov, K.S.; Geim, A.K. The electronic properties of graphene. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2009, 81, 109–162. [Google Scholar]
- Geim, A.K.; Novoselov, K.S. The rise of graphene. Nat. Mater. 2007, 6, 183–191. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, Y.; Gou, X.; Yuan, R.; Chai, Y.; Zhuo, Y.; Ye, X.; Gan, X. Graphene-promoted 3,4,9,10-perylenetetracarboxylic acid nanocomposite as redox probe in label-free electrochemical aptasensor. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2011, 30, 123–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.Y.; Chen, Y.; Ren, J.S.; Qu, X.G. A graphene functionalized electrochemical aptasensor for selective label-free detection of cancer cells. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 2930–2937. [Google Scholar]
- Li, T.; Shi, L.; Wang, E.; Dong, S. Multifunctional G-quadruplex aptamers and their application to protein detection. Chem. Eur. J. 2009, 15, 1036–1042. [Google Scholar]
- Hao, C.; Ding, L.; Zhang, X.; Ju, H. Biocompatible conductive architecture of carbon nanofiber-doped chitosan prepared with controllable electrodeposition for cytosensing. Anal. Chem. 2007, 79, 4442–4447. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, W.; Ding, L.; Lei, J.; Ding, S.; Ju, H. Effective cell capture with tetrapeptide-functionalized carbon nanotubes and dual signal amplification for cytosensing and evaluation of cell surface carbohydrate. Anal. Chem. 2008, 80, 3867–3872. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, J.F.; Chen, Z.B.; Guo, L.; Li, L.D. Electrochemical sensing of L-histidine based on structure-switching DNAzymes and gold nanoparticle-graphene nanosheet composites. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 5476–5478. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Zhu, C.; Han, L.; Jin, L.; Zhou, M.; Dong, S. Label-free, regenerative and sensitive surface plasmon resonance and electrochemical aptasensors based on graphene. Chem. Common. 2011, 47, 7794–7796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Chen, G.; Zhu, L.; Li, G. Graphene quantum dots-based platform for the fabrication of electrochemical biosensors. Electrochem. Commun. 2011, 13, 31–33. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, D.P.; Tang, J.; Li, Q.F.; Liu, B.Q.; Yang, H.H.; Chen, G.N. Target-induced biomolecular release for sensitive aptamer-based electrochemical detection of small molecules from magnetic graphene. RSC Adv. 2011, 1, 40–43. [Google Scholar]
- Willner, I.; Katz, E. Magnetic control of electrocatalytic and bioelectrocatalytic processes. Angew. Chem. Int. Edit. 2003, 42, 4576–4588. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, S.; Du, Y.; Yang, X.; Dong, S.; Wang, E. Solid-state label-free integrated aptasensor based on graphene-mesoporous silica-gold nanoparticle hybrids and silver microspheres. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 8035–8040. [Google Scholar]
- Ahammad, A.J.S.; Lee, J.-J.; Rahman, M.A. Electrochemical sensors based on carbon nanotubes. Sensors 2009, 9, 2289–2319. [Google Scholar]
- Szabo, A.; Perri, C.; Csato, A.; Giordano, G.; Vuono, D.; Nagy, J.B. Synthesis methods of carbon nanotubes and related materials. Materials 2010, 3, 3092–3140. [Google Scholar]
- Baughman, R.H.; Zakhidov, A.A.; de Heer, W.A. Carbon nanotubes—The route toward applications. Science 2002, 297, 787–792. [Google Scholar]
- Gruner, G. Carbon nanotube transistors for biosensing applications. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2006, 384, 322–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.N.; Rusling, J.F.; Papadimitrakopoulos, F. Carbon nanotubes for electronic and electrochemical detection of biomolecules. Adv. Mater. 2007, 19, 3214–3228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, L.J.; Yuan, R.; Chai, Y.Q.; Yuan, Y.L.; Mao, L.; Wang, Y. Platinum-gold alloy nanoparticles and horseradish peroxidase functionalized nanocomposite as a trace label for ultrasensitive electrochemical detection of thrombin. Anal. Chim. Acta 2011, 698, 14–19. [Google Scholar]
- Das, B.K.; Tlili, C.; Badhulika, S.; Cella, L.N.; Chen, W.; Mulchandani, A. Single-walled carbon nanotubes chemiresistor aptasensors for small molecules: Picomolar level detection of adenosine triphosphate. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 3793–3795. [Google Scholar]
- Xiang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Qian, X.; Chai, Y.; Wang, J.; Yuan, R. Ultrasensitive aptamer-based protein detection via a dual amplified biocatalytic strategy. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2010, 25, 2539–2542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Li, Y.; Zheng, J.; Zhang, J.; Sheng, Q. Carbon nanotube-enhanced electrochemical aptasensor for the detection of thrombin. Talanta 2010, 81, 1619–1624. [Google Scholar]
- Porfireva, A.V.; Evtugyn, G.A.; Ivanov, A.N.; Hianik, T. Impedimetric aptasensors based on carbon nanotubes—poly(methylene blue) composite. Electroanalysis 2010, 22, 2187–2195. [Google Scholar]
- Tran, L.D.; Nguyen, D.T.; Nguyen, B.H.; Do, Q.P.; Nguyen, H.L. Development of interdigitated arrays coated with functional polyaniline/MWCNT for electrochemical biodetection: Application for human papilloma virus. Talanta 2011, 85, 1560–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.H.; Yuan, R.; Chai, Y.Q.; Zhuo, Y.; Yuan, Y.L.; Bai, L.J.; Mao, L.; Yuan, S.R. In situ produced ascorbic acid as coreactant for an ultrasensitive solid-state tris(2,2'-bipyridyl) ruthenium(II) electrochemiluminescence aptasensor. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2011, 26, 4815–4818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, F.; Jia, L.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, B.; Qi, H.; Gao, Q.; Zhang, C. Electrogenerated chemiluminescence aptasensor for thrombin incorporating poly(pyrrole-co-pyrrole propylic acid) nanoparticles loaded with aptamer and ruthenium complex. Sci. China Chem. 2011, 54, 1357–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.F.; Han, M.; Bai, H.Y.; Wu, Y.; Dai, Z.H.; Bao, J.C. A sensitive electrochemical aptasensor based on water soluble CdSe quantum dots (QDs) for thrombin determination. Electrochim. Acta 2011, 56, 7058–7063. [Google Scholar]
- Bonel, L.; Vidal, J.C.; Duato, P.; Castillo, J.R. An electrochemical competitive biosensor for ochratoxin A based on a DNA biotinylated aptamer. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2011, 26, 3254–3259. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.D.; Zhao, H.T.; Chen, Z.B.; Mu, X.J.; Guo, L. Aptamer biosensor for label-free impedance spectroscopy detection of thrombin based on gold nanoparticles. Sens. Actuat. B 2011, 157, 189–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2012 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Hernandez, F.J.; Ozalp, V.C. Graphene and Other Nanomaterial-Based Electrochemical Aptasensors. Biosensors 2012, 2, 1-14. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios2010001
Hernandez FJ, Ozalp VC. Graphene and Other Nanomaterial-Based Electrochemical Aptasensors. Biosensors. 2012; 2(1):1-14. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios2010001
Chicago/Turabian StyleHernandez, Frank J., and Veli Cengiz Ozalp. 2012. "Graphene and Other Nanomaterial-Based Electrochemical Aptasensors" Biosensors 2, no. 1: 1-14. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios2010001
APA StyleHernandez, F. J., & Ozalp, V. C. (2012). Graphene and Other Nanomaterial-Based Electrochemical Aptasensors. Biosensors, 2(1), 1-14. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios2010001