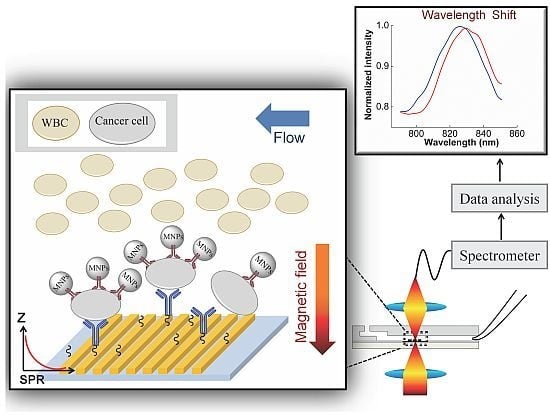
Label-Free Detection of Rare Cell in Human Blood Using Gold Nano Slit Surface Plasmon Resonance
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials
2.2. Specific Capturing and Detection of Cancer Cells—DCM

2.2.1. First Step: Isolation of Cancer Cells by Antibody I on the MNPs
2.2.1.1. Preparation of Functionalized MNPs
2.2.1.2. First Step of DCM
2.2.2. Second Step: Capture and Detection of the MNPs-Cells on the Gold Nanoslit
2.2.2.1. Immobilization of Antibody II on Gold Nanoslit
2.2.2.2. Second Step of DCM
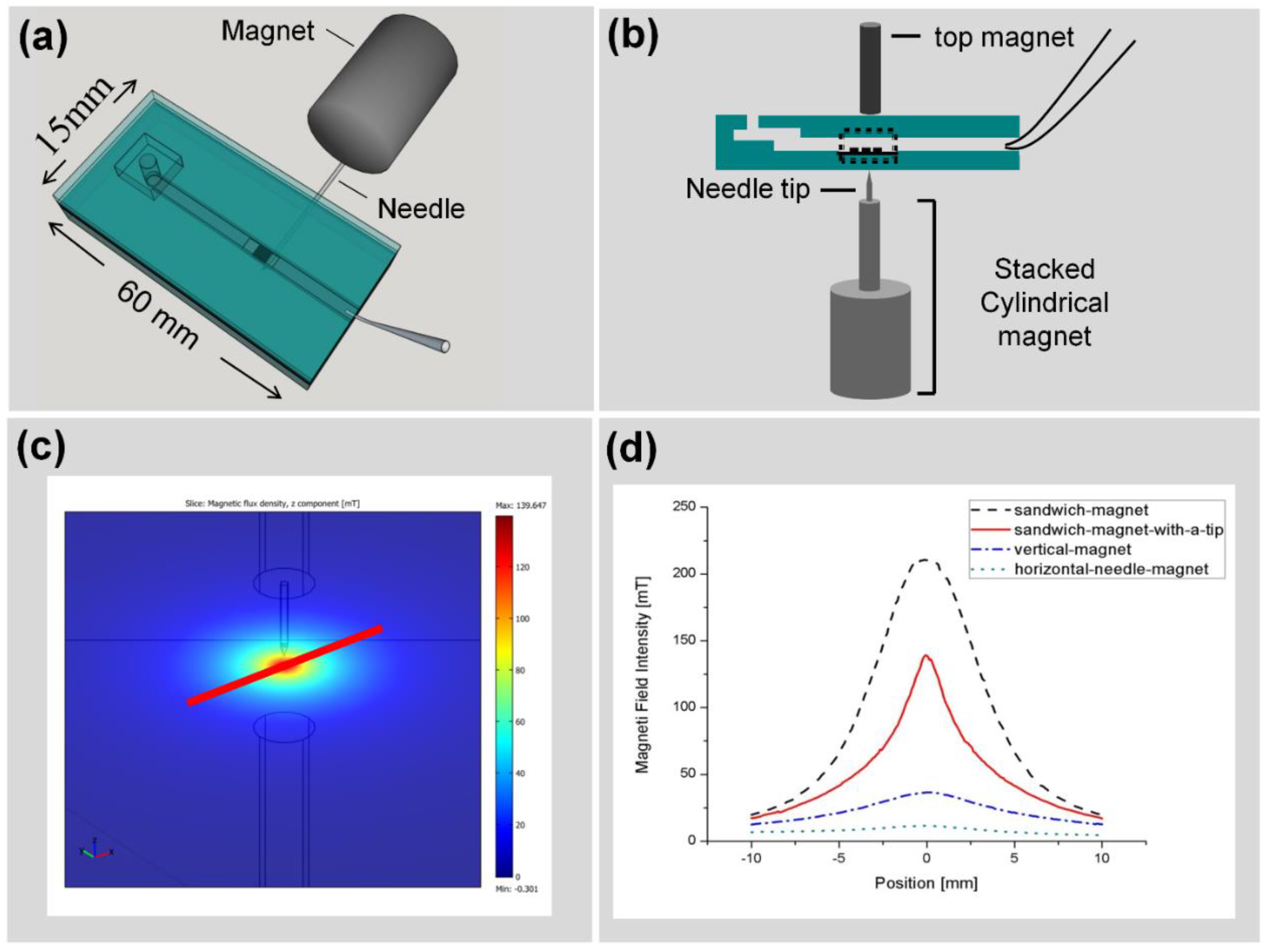
2.3. Chip Fabrication and Measurement Setup

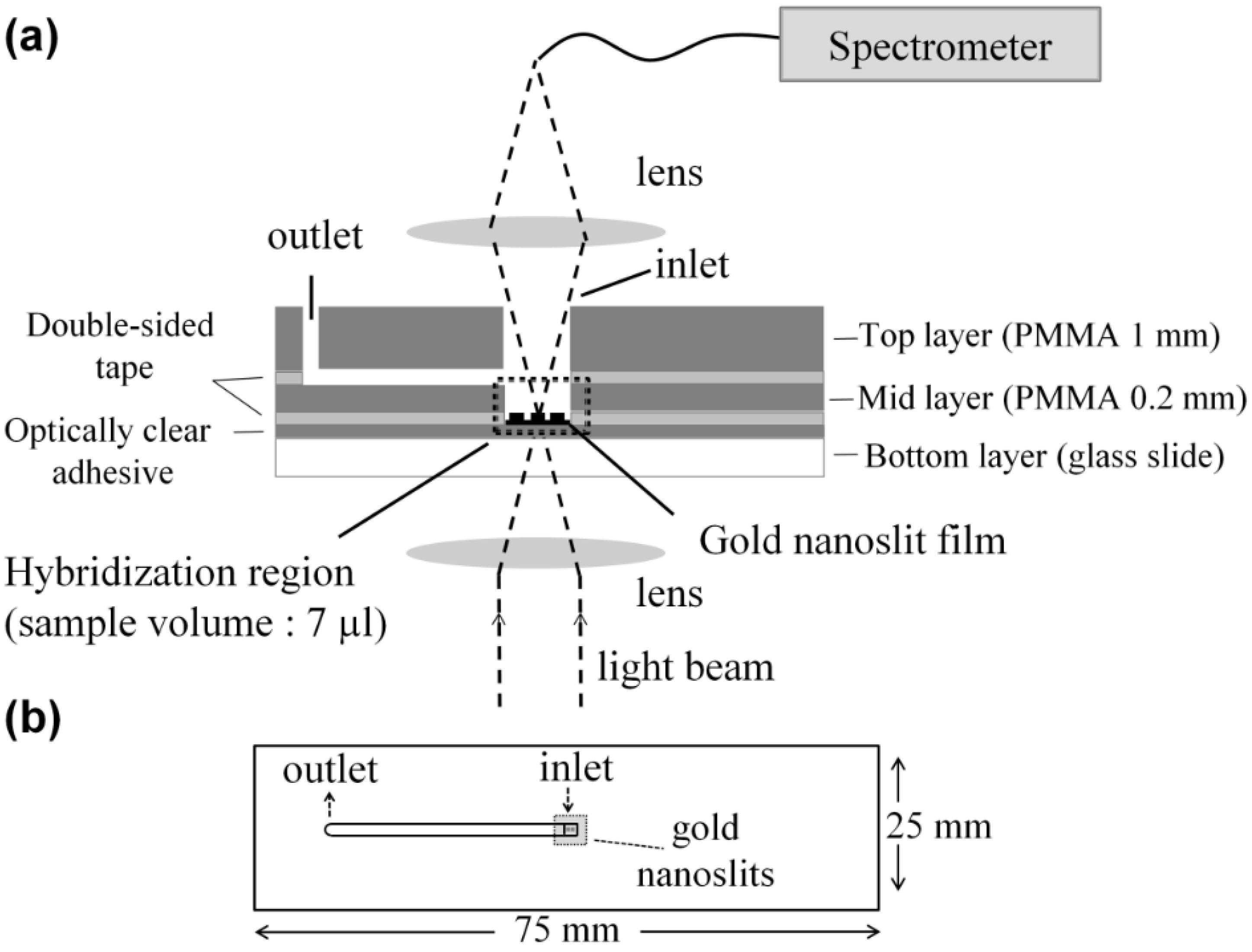
2.3.1. Microliter Volume Chip (MVC)
2.3.2. Large Volume Chip (Funnel Chip)
2.4. Cell Culture
2.5. Blood Sample Preparation
2.6. Labeling and Imaging the Cells
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. High Specificity Using Two Specific Antibodies
| Antibody on MNPs | Antibody on Gold Nanoslits | Retention Rate * (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Anti-EGFR | Anti-CD44 | 100 |
| Anti-EGFR | Anti-EphA2 (3F7) | 60 |
| Anti-EphA2 (3F7) | Anti-EGFR | 9 |
| Anti-EphA2 (3F7) | Anti-CD44 | 100 |
3.2. SPR Measurement
3.2.1. SPR to Detect Specific Cell Binding on the Sensor’s Surface

3.2.2. Capturing Cells in Blood

3.3. Improving the Sensitivity and Purity of Capturing


4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hyun, K.A.; Jung, H.I. Microfluidic Devices for the Isolation of Circulating Rare Cells: A Focus on Affinity-Based, Dielectrophoresis, and Hydrophoresis. Electrophoresis 2013, 34, 1028–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaffer, C.L.; Weinberg, R.A. A Perspective on Cancer Cell Metastasis. Science 2011, 331, 1559–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bidard, F.C.; Fehm, T.; Ignatiadis, M.; Smerage, J.B.; Alix-Panabières, C.; Janni, W.; Messina, C.; Paoletti, C.; Müller, V.; Hayes, D.F.; et al. Clinical application of circulating tumor cells in breast cancer: overview of the current interventional trials. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2013, 32, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maheswaran, S.; Haber, D.A. Circulating tumor cells: A window into cancer biology and metastasis. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2010, 20, 96–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talasaz, A.H.; Powell, A.A.; Huber, D.E.; Berbee, J.G.; Roh, K.-H.; Yud, W.; Xiao, W.Z.; Davis, M.M.; Pease, R.F.; Mindrinos, M.N.; et al. Isolating highly enriched populations of circulating epithelial cells and other rare cells from blood using a magnetic sweeper device. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 3970–3975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, A.A.; Okagbare, P.I.; Feng, J.; Hupert, M.L.; Patterson, D.; Göttert, J.; McCarley, R.L.; Nikitopoulos, D.; Murphy, M.C.; Soper, S.A. Highly efficient circulating tumor cell isolation from whole blood and label-free enumeration using polymer-based microfluidics with an integrated conductivity sensor. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 8633–8641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stott, S.L.; Hsu, C.-H.; Tsukrov, D.I.; Yu, M.; Miyamoto, D.T.; Waltman, B.A.; Rothenberg, S.M.; Shah, A.M.; Smas, M.E.; Korir, G.K.; et al. Isolation of circulating tumor cells using a microvortex-generating herringbone-chip. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 18392–18397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagrath, S.; Sequist, L.V.; Maheswaran, S.; Bell, D.W.; Irimia, D.; Ulkus, L.; Smith, M.R.; Kwak, E.L.; Digumarthy, S.; Muzikansky, A.; et al. Isolation of rare circulating tumour cells in cancer patients by microchip technology. Nature 2007, 450, 1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, S.; Lin, H.; Liu, J.-Q.; Balic, M.; Datar, R.; Cote, R.J.; Tai, Y.-C. Membrane microfilter device for selective capture, electrolysis and genomic analysis of human circulating tumor cells. J. Chromatogr. A 2007, 1162, 154–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, H.W.; Warkiani, M.E.; Khoo, B.L.; Li, Z.R.; Soo, R.A.; Tan, D.S.-W.; Lim, W.-T.; Han, J.; Bhagat, A.A.S.; Lim, C.K. Isolation and retrieval of circulating tumor cells using centrifugal forces. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hou, H.W.; Li, Q.S.; Lee, G.Y.H.; Kumar, A.P.; Ong, C.N.; Lim, C.T. Deformability study of breast cancer cells using microfluidics. Biomed. Microdevices 2009, 11, 557–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, S.J.; Yobas, L.; Lee, G.Y.H.; Ong, C.N.; Lim, C.T. Microdevice for the isolation and enumeration of cancer cells from blood. Biomed. Microdevices 2009, 11, 883–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamed, H.; Murray, M.; Turner, J.N.; Caggana, M. Isolation of tumor cells using size and deformation. J. Chromatogr. A 2009, 1216, 8289–8295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dharmasiri, U.; Balamurugan, S.; Adams, A.A.; Okagbare, P.I.; Obubuafo, A.; Soper, S.A. Highly efficient capture and enumeration of low abundance prostate cancer cells using prostate-specific membrane antigen aptamers immobilized to a polymeric microfluidic device. Electrophoresis 2009, 30, 3289–3300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yashunsky, V.; Lirtsman, V.; Golosovsky, M.; Davidov, D.; Aroeti, B. Real-Time Monitoring of Epithelial Cell-Cell and Cell-Substrate Interactions by Infrared Surface Plasmon Spectroscopy. Biophys. J. 2010, 99, 4028–4036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yashunsky, V.; Lirtsman, V.; Zilbershtein, A.; Bein, A.; Schwartz, B.; Aroeti, B.; Golosovsky, M.; Davidov, D. Surface plasmon-based infrared spectroscopy for cell biosensing. J. Biomed. Opt. 2012, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice, J.M.; Stern, L.J.; Guignon, E.F.; Lawrence, D.A.; Lynes, M.A. Antigen-specific T cell phenotyping microarrays using grating coupled surface plasmon resonance imaging and surface plasmon coupled emission. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2012, 31, 264–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hiragun, T.; Yanase, Y.; Kose, K.; Kawaguchi, T.; Uchida, K.; Tanaka, S.; Hide, M. Surface plasmon resonance-biosensor detects the diversity of responses against epidermal growth factor in various carcinoma cell lines. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2012, 32, 202–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.-H.; Hsieh, S.-Y.; Lee, K.-L.; Weng, R.-H.; Chiou, A.; Wei, P.-K. Cell viability monitoring using Fano resonance in gold nanoslit array. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2013, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Liu, K.; Liu, J.; Yu, Z.T.-F.; Xu, X.; Zhao, L.; Lee, T.; Lee, E.K.; Reiss, J.; Lee, Y.-K.; et al. Highly efficient capture of circulating tumor cells by using nanostructured silicon substrates with integrated chaotic micromixers. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 3084–3088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.-L.; Lee, C.-W.; Wang, W.-S.; Wei, P.-K. Sensitive biosensor array using surface plasmon resonance on metallic nanoslits. J. Biomed. Opt. 2007, 12. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.L.; Wang, W.S.; Wei, P.K. Sensitive label-free biosensors by using gap plasmons in gold nanoslits. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2008, 24, 210–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.L.; Wang, W.S.; Wei, P.K. Comparisons of Surface Plasmon Sensitivities in Periodic Gold Nanostructures. Plasmonics 2008, 3, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.-L.; Chen, P.-W.; Wu, S.-H.; Huang, J.-B.; Yang, S.-Y.; Wei, P.-K. Enhancing Surface Plasmon Detection Using Template-Stripped Gold Nanoslit Arrays on Plastic Films. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 2931–2939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brolo, A.G.; Gordon, R.; Leathem, B.; Kavanagh, K.L. Surface plasmon sensor based on the enhanced light transmission through arrays of nanoholes in gold films. Langmuir 2004, 20, 4813–4815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tetz, K.A.; Pang, L.; Fainman, Y. High-resolution surface plasmon resonance sensor based on linewidth-optimized nanohole array transmittance. Opt. Lett. 2006, 31, 1528–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lesuffleur, A.; Im, H.; Lindquist, N.C.; Oh, S.-H. Periodic nanohole arrays with shape-enhanced plasmon resonance as real-time biosensors. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2007, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Leebeeck, A.; Kumar, L.K.S.; de Lange, V.; Sinton, D.; Gordon, R.; Brolo, A.G. On-chip surface-based detection with nanohole arrays. Anal. Chem. 2007, 79, 4094–4100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, L.; Hwang, G.M.; Slutsky, B.; Fainman, Y. Spectral sensitivity of two-dimensional nanohole array surface plasmon polariton resonance sensor. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2007, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebbesen, T.W.; Lezec, H.J.; Ghaemi, H.F.; Thio, T.; Wolff, P.A. Extraordinary optical transmission through sub-wavelength hole arrays. Nature 1998, 391, 667–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Lee, J.; Lee, S.J.; Lee, H.J. Ultra-sensitive detection of IgE using biofunctionalized nanoparticle-enhanced SPR. Talanta 2010, 81, 1755–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teramura, Y.; Arima, Y.; Iwata, H. Surface plasmon resonance-based highly sensitive immunosensing for brain natriuretic peptide using nanobeads for signal amplification. Anal. Biochem. 2006, 357, 208–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mousavi, M.Z.; Chen, H.-Y.; Wu, S.-H.; Peng, S.-W.; Lee, K.-L.; Wei, P.-K.; Cheng, J.-Y. Magnetic nanoparticle-enhanced SPR on gold nanoslits for ultra-sensitive, label-free detection of nucleic acid biomarkers. Analyst 2013, 138, 2740–2748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiewlich, D.; Zhang, J.; Gross, C.; Xia, W.; Larsen, B.; Cobb, R.R.; Biroc, S.; Gu, J.-M.; Sato, T.; Light, D.R.; et al. Anti-EphA2 antibodies decrease EphA2 protein levels in murine CT26 colorectal and human MDA-231 breast tumors but do not inhibit tumor growth. Neoplasia 2006, 8, 18–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, J.-Y.; Wei, C.-W.; Hsu, K.-H.; Young, T.-H. Direct-write laser micromachining and universal surface modification of PMMA for device development. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2004, 99, 186–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.-Y.; Yen, M.-H.; Kuo, C.-T.; Young, T.-H. A transparent cell-culture microchamber with a variably controlled concentration gradient generator and flow field rectifier. Biomicrofluidics 2008, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, Y.-W.; Yang, P.-C.; Yang, S.-C.; Shyu, Y.-C.; Hendrix, M.J.C.; Wu, R.; Wu, C.-W. Selection of invasive and metastatic subpopulations from a human lung adenocarcinoma cell line. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 1997, 17, 353–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shih, J.-Y.; Yang, S.-C.; Hong, T.-M.; Yuan, A.; Chen, J.J.W.; Yu, C.-J.; Chang, Y.-L.; Lee, Y.-C.; Peck, K.; Wu, C.-W.; et al. Collapsin response mediator protein-1 and the invasion and metastasis of cancer cells. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2001, 93, 1392–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, H.-F.; Huang, C.-W.; Chang, H.-F.; Chen, J.J.W.; Lee, C.-H.; Cheng, J.Y. Evaluation of EGFR and RTK signaling in the electrotaxis of lung adenocarcinoma cells under direct-current electric field stimulation. PLoS ONE 2013, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.-W.; Chen, H.-Y.; Yen, M.-H.; Chen, J.J.W.; Young, T.-H.; Cheng, J.-Y. Gene expression of human lung cancer cell line CL1-5 in response to a direct current electric field. PLoS ONE 2011, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brannan, J.M.; Sen, B.; Saigal, B.; Prudkin, L.; Behrens, C.; Solis, L.; Dong, W.; Bekele, B.N.; Wistuba, I.; Johnson, F.M. EphA2 in the Early pathogenesis and progression of non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Prev. Res. 2009, 2, 1039–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, M.; Miyahara, R.; Sonobe, M.; Horiuchi, M.; Mennju, T.; Nakayama, E.; Kobayashi, M.; Kikuchi, R.; Kitamura, J.; Imamura, N.; et al. Higher expression of EphA2 and ephrin-A1 is related to favorable clinicopathological features in pathological stage I non-small cell lung carcinoma. Lung Cancer 2012, 76, 431–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, P.; Maiti, A.; Brown, K.L.; Li, R. A role for the cell adhesion molecule CD44 and sulfation in leukocyte-endothelial cell adhesion during an inflammatory response? Biochem. Pharmacol. 2000, 59, 455–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graham, V.A.; Marzo, A.L.; Tough, D.F. A role for CD44 in T cell development and function during direct competition between CD44(+) and CD44(-) cells. Eur. J. Immunol. 2007, 37, 925–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, G.; Nogalski, M.T.; Yurochko, A.D. Activation of EGFR on monocytes is required for human cytomegalovirus entry and mediates cellular motility. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 22369–22374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.-H.; Lee, K.-L.; Weng, R.-H.; Zheng, Z.-X.; Chiou, A.; Wei, P.-K. Dynamic monitoring of mechano-sensing of cells by gold nanoslit surface plasmon resonance sensor. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e89522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Homola, J. Present and future of surface plasmon resonance biosensors. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2003, 377, 528–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.J.; Wong, G.; de Heer, A.-M.; Xia, W.L.; Bourguignon, L.Y.W. CD44 Variant Isoforms in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma Progression. Laryngoscope 2009, 119, 1518–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bourguignon, L.Y.W.; Gilad, E.; Brightman, A.; Diedrich, F.; Singleton, P. Hyaluronan-CD44 interaction with leukemia-associated RhoGEF and epidermal growth factor receptor promotes Rho/Ras co-activation, phospholipase C epsilon-Ca2+ signaling, and cytoskeleton modification in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 14026–14040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Appendix


Identification of Captured Cells

© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mousavi, M.Z.; Chen, H.-Y.; Hou, H.-S.; Chang, C.-Y.-Y.; Roffler, S.; Wei, P.-K.; Cheng, J.-Y. Label-Free Detection of Rare Cell in Human Blood Using Gold Nano Slit Surface Plasmon Resonance. Biosensors 2015, 5, 98-117. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios5010098
Mousavi MZ, Chen H-Y, Hou H-S, Chang C-Y-Y, Roffler S, Wei P-K, Cheng J-Y. Label-Free Detection of Rare Cell in Human Blood Using Gold Nano Slit Surface Plasmon Resonance. Biosensors. 2015; 5(1):98-117. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios5010098
Chicago/Turabian StyleMousavi, Mansoureh Z., Huai-Yi Chen, Hsien-San Hou, Chou-Yuan-Yuan Chang, Steve Roffler, Pei-Kuen Wei, and Ji-Yen Cheng. 2015. "Label-Free Detection of Rare Cell in Human Blood Using Gold Nano Slit Surface Plasmon Resonance" Biosensors 5, no. 1: 98-117. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios5010098
APA StyleMousavi, M. Z., Chen, H.-Y., Hou, H.-S., Chang, C.-Y.-Y., Roffler, S., Wei, P.-K., & Cheng, J.-Y. (2015). Label-Free Detection of Rare Cell in Human Blood Using Gold Nano Slit Surface Plasmon Resonance. Biosensors, 5(1), 98-117. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios5010098