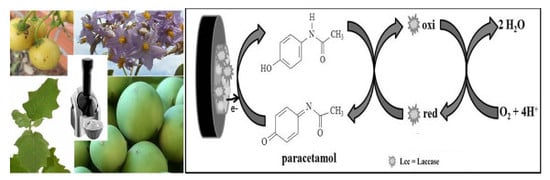
The Use of a Polyphenoloxidase Biosensor Obtained from the Fruit of Jurubeba (Solanum paniculatum L.) in the Determination of Paracetamol and Other Phenolic Drugs
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Solutions
2.2. Plant Material and Preparation of the Raw Vegetable Extract
2.3. PPO Enzymatic Activity Determination
2.4. Assay Development: Biosensor, Effect of pH, and Electrochemical Parameters
2.5. Biosensor Applicability
2.5.1. Determination of Paracetamol in Tablets
Sample Preparation
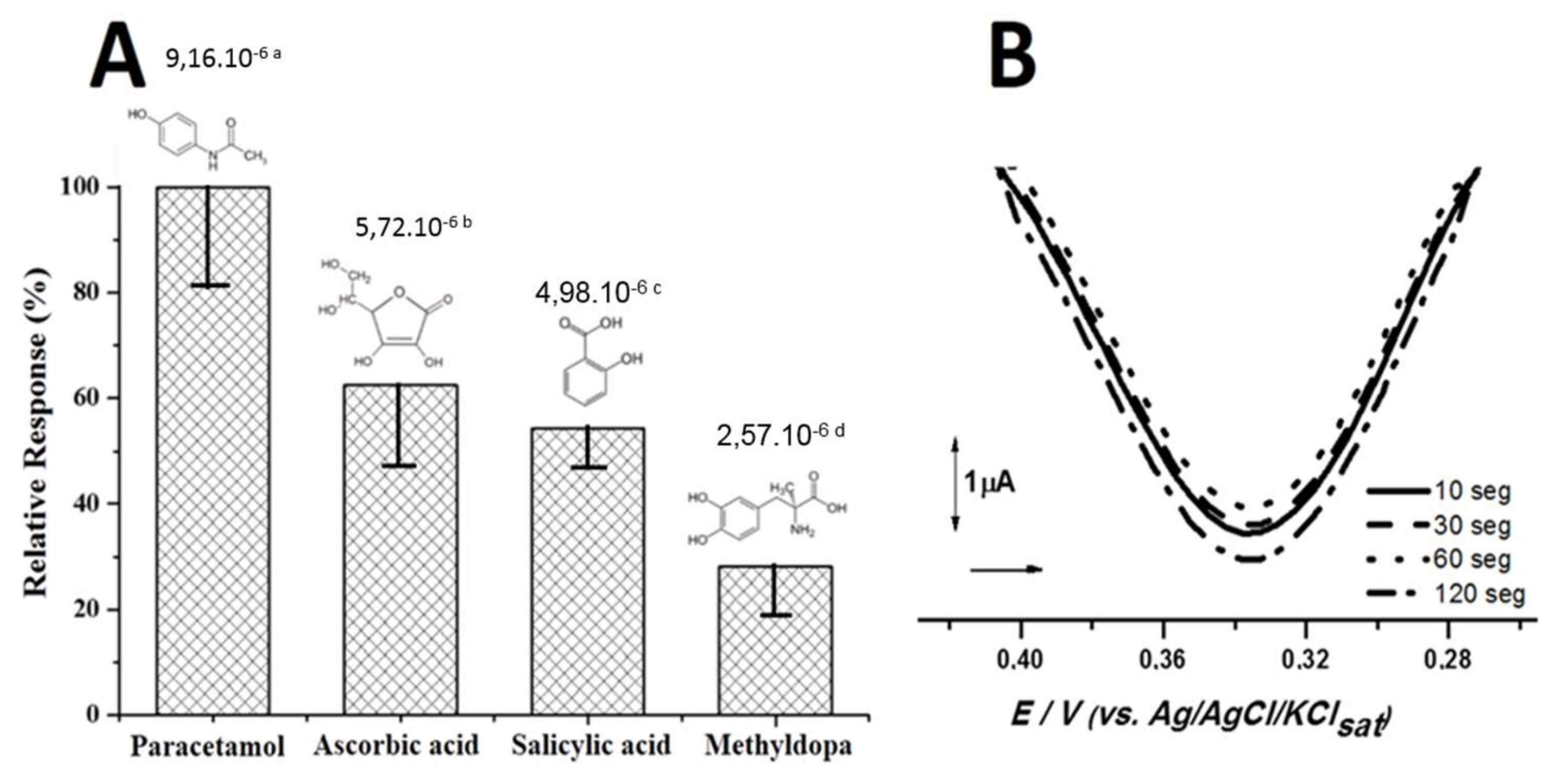
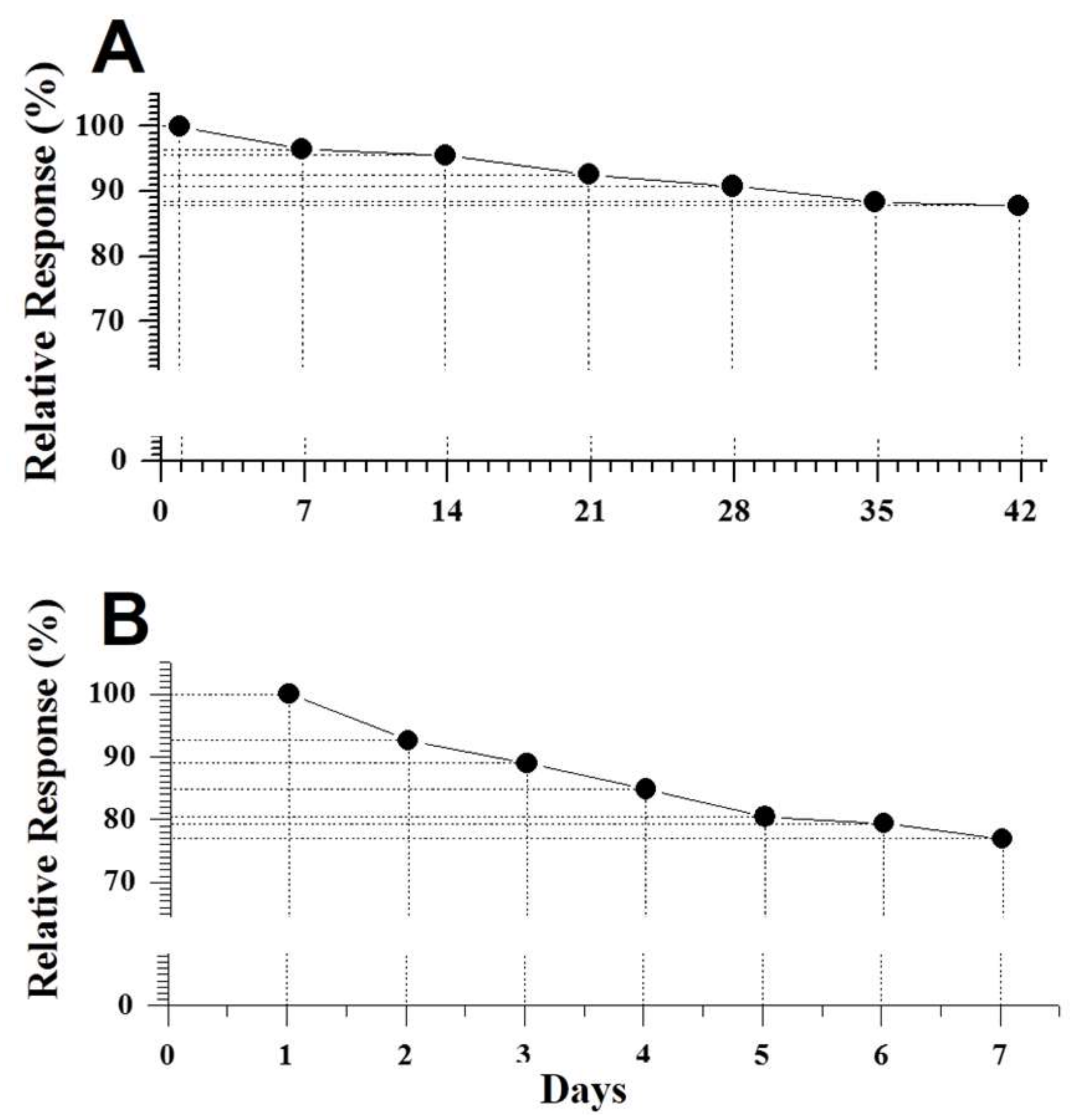
2.6. Effect of Conditioning Time and Stability (Storage and Reuse)
2.7. Analytical Features: Linearity, Repeatability, Limit of Detection (LoD), and Recovery
2.8. Electrochemical Analysis and Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. PPO Specific Activity and JEE Total Protein Activity
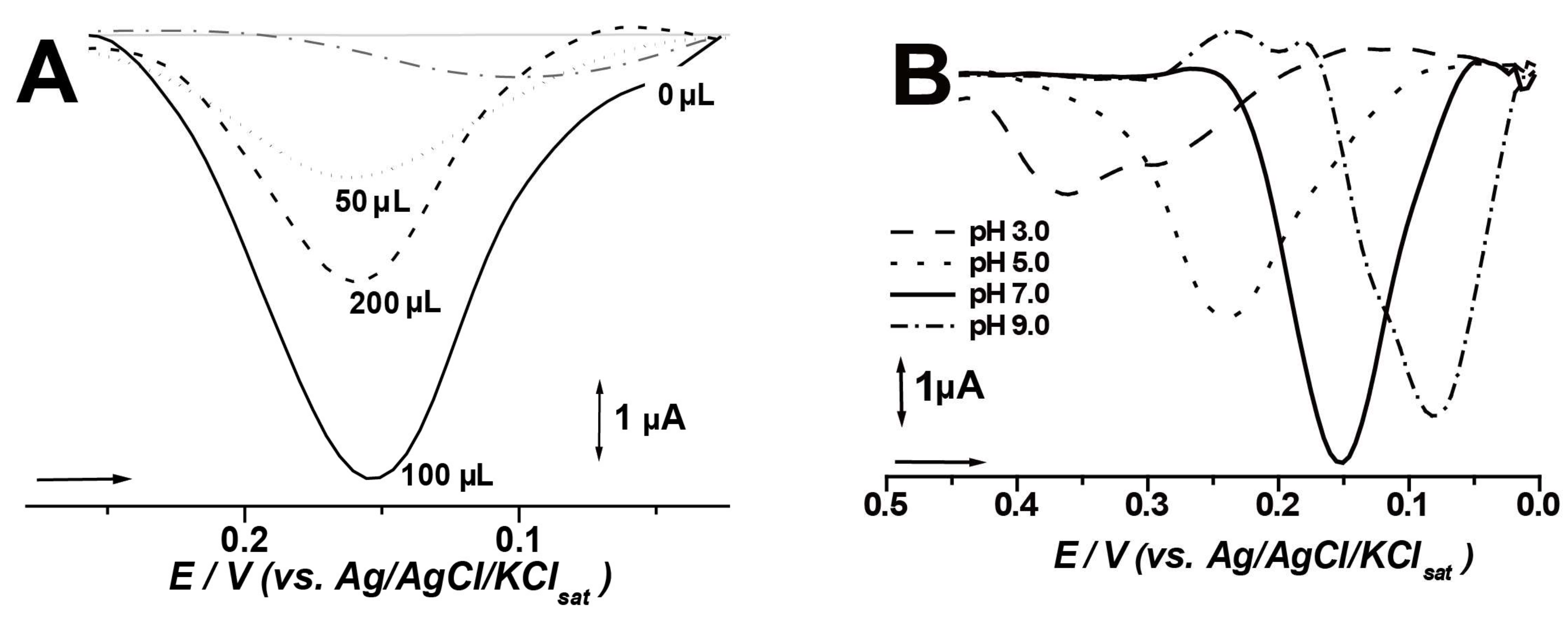
3.2. Biosensor and Assay Optimization
3.3. Biosensor Activity against Phenolic Drugs
3.4. Pharmaceutical Analysis and Recovery Assays
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Conti, R.; Guimarães, D.O.; Pupo, M.T. Aprendendo com as interações da natureza: Microrganismos simbiontes como fontes de produtos naturais bioativos. Ciênc. Cult. 2012, 64, 43–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albarello, N.; Simões-Gurgel, C.; Castro, T.C.; Gayer, C.R.M.; Coelho, M.G.P.; Moura, R.S.; Mansur, E. Anti-inflammatory and antinociceptive activity of fieldgrowth plants and tissue culture of Cleome spinosa (Jacq.) in mice. J. Med. Plants Res. 2013, 7, 1043–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatibello-Filho, O.; Lupetti, K.O.; Vieira, I.C. Chronoamperometric determination of paracetamol using an avocado tissue (Persea americana) biosensor. Talanta 2001, 55, 685–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Songa, E.A.; Okonkwo, J.O. Talanta Recent approaches to improving selectivity and sensitivity of enzyme-based biosensors for organophosphorus pesticides: A review. Talanta 2016, 155, 289–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia, L.F.; Benjamin, S.R.; Antunes, R.S.; Lopes, F.M.; Somerset, V.S.; Gil, E.S. Solanummelongena polyphenol oxidase biosensor for the electrochemical analysis of paracetamol. Prep. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2016, 46, 850–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antunes, R.S.; Lopes, F.M.; Brito, A.O.; Garcia, L.F.; Sousa, D.F.; Gil, E.S. Enzimas vegetais: Extração e aplicações biotecnológicas. Infarma 2017, 29, 181–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, N.F.M.; Neto, S.Y.; Luz, R.C.S.; Damos, F.S.; Yamanaka, H. Ultrasensitive Determination of Malathion Using Acetylcholinesterase Immobilized on Chitosan-Functionalized Magnetic Iron Nanoparticles. Biosensors 2018, 8, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campos, L.F.C.; Peixoto, J.V.M.; Oliveira, R.M.; Seleguini, A.; Nascimento, A.R. Propriedades físico-químicas de frutos de jurubeba de três regiões do Cerrado. Rev. Agric. Neotrop. 2015, 2, 48–54. [Google Scholar]
- Calas-Blanchard, C.; Istamboulié, G.; Bontoux, M.; Plantard, G.; Goetz, V.; Noguer, T. Biosensor-based real-time mornitoring of paracetamolphotocatalytic degradation. Chemosphere 2015, 9, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daher, D.; Gourrierec, S.L.; Pérez-Lamela, C. Effect of high pressure processing on the microbial inactivation in fruit preparations and other vegetable based beverages. Agriculture 2017, 7, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaichi, M.J.; Ehsani, M. A novel glucose sensor based on immobilization of glucose oxidase on the chitosan-coated Fe3O4 nanoparticles and the luminol-H2O2-gold nanoparticle chemiluminescence detection system. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 223, 713–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amare, M.; Admassie, S. Polymer modified glassy carbon electrode for the electrochemical determination of caffeine in coffee. Talanta 2012, 93, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, D.; Liu, Z.; Fu, J.; Guo, Y.; Sun, X.; Yang, Q.; Wang, X. Electrochemical acetylcholinesterase biosensor based on multi-walled carbon nanotubes/dicyclohexyl phthalate modified screen-printed electrode for detection of chlorpyrifos. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2017, 801, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartwig, E.; Nogueira, D.; Mendonça, C.; Silva, J.D.F.; Alves, M.; Borges, C. Utilização das enzimas peroxidases do nabo no controle do escurecimento enzimático em maçãs minimamente processadas. Blucher Chem. Eng. Proc. 2015, 1, 2999–3004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bueno, N.G.; Pereira, A.V. Determinação espectrofotométrica de metildopa em ensaio de dissolução de comprimidos utilizando extrato de rabanete como fonte de peroxidase. Quim. Nova 2015, 38, 1107–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pundir, C.S.; Chauhan, N. Acetylcholinesterase inhibition-based biosensors for pesticide determination: A review. Anal. Biochem. 2012, 429, 19–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adiguzel, Y. Biosensor with UV Spectrophotometric Detection. Proceedings 2018, 2, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, R.D.; Wilund, K.R.; Cunningham, B.T.; Andrade, J.E. Comparison of Methods Study between a Photonic Crystal Biosensor and Certified ELISA to Measure Biomarkers of Iron Deficiency in Chronic Kidney Disease Patients. Sensors 2017, 17, 2203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirsch, V.; Kinnear, C.; Moniatte, M.; Rothen-Rutishauser, B.; Clift, M.J.D.; Fink, A. Surface charge of polymer coated SPIONs influences the serum protein adsorption, colloidal stability and subsequent cell interaction in vitro. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 3723–3732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The United States Pharmacopeia (USP). Rockville: United States Pharmacopeial Convention, 32nd ed.; USP: Rockville, MD, USA, 2009; 1430p. [Google Scholar]
- Farmacopeia Brasileira. Available online: http://www.anvisa.gov.br/hotsite/cd_Farmacopeia/pdf/volume2.pdf (accessed on 15 November 2017).
- Gil, E.S. Controle Físico-Químico de Qualidade de Medicamentos, 3rd ed.; Pharmabooks: São Paulo, Brazil, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Agência Nacional de Vigilância Sanitária (ANVISA). Available online: http://portal.anvisa.gov.br/documents/10181/2721567/RDC_166_2017_COMP.pdf/d5fb92b3-6c6b-4130-8670-4e3263763401 (accessed on 21 January 2018).
- Tefere, N.S.; Delon, A.; Buckow, R.; Versteeg, C. Blueberry polyphenol oxidase: Characterization and the kinetics of thermal and high pressure activation and inactivation. Food Chem. 2015, 188, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradford, M. Um método rápido e sensível para a quantificação de micrograma quantidades de proteínas, utilizando o princípio da proteína corantes vinculação. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polesel, D.N.; Sinhorini, A.L.C.; Perone, C.A.S. Caracterização cinética da enzima catecolase (Polifenoloxidase) em extratos brutos da polpa e da casca de berinjela (Solanum melongena L.). J. Health Sci. Inst. 2010, 28, 175–180. [Google Scholar]
- Mishra, B.B.; Gautam, S.; Sharma, A. Purification and characterization of polyphenol oxidase (PPO) from eggplant. Food Chem. 2012, 34, 1855–1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganesh, H.V.S.; Noroozifar, M.; Kerman, K. EpigallocatechinGallate-Modified Graphite Paste Electrode for Simultaneous Detection of Redox-Active Biomolecules. Sensors 2018, 18, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narang, J. A nylon membrane based amperometric biosensor for polyphenol determination. J. Mol. Catal. B: Enzym. 2011, 72, 276–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, I.C.; Lupetti, K.O.; Fatibello-Filho, O. Determination of paracetamol in pharmaceutical products using a carbon paste biosensor modified with crude extract of zucchini (Cucurbita pepo). Quím. Nova 2003, 26, 39–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
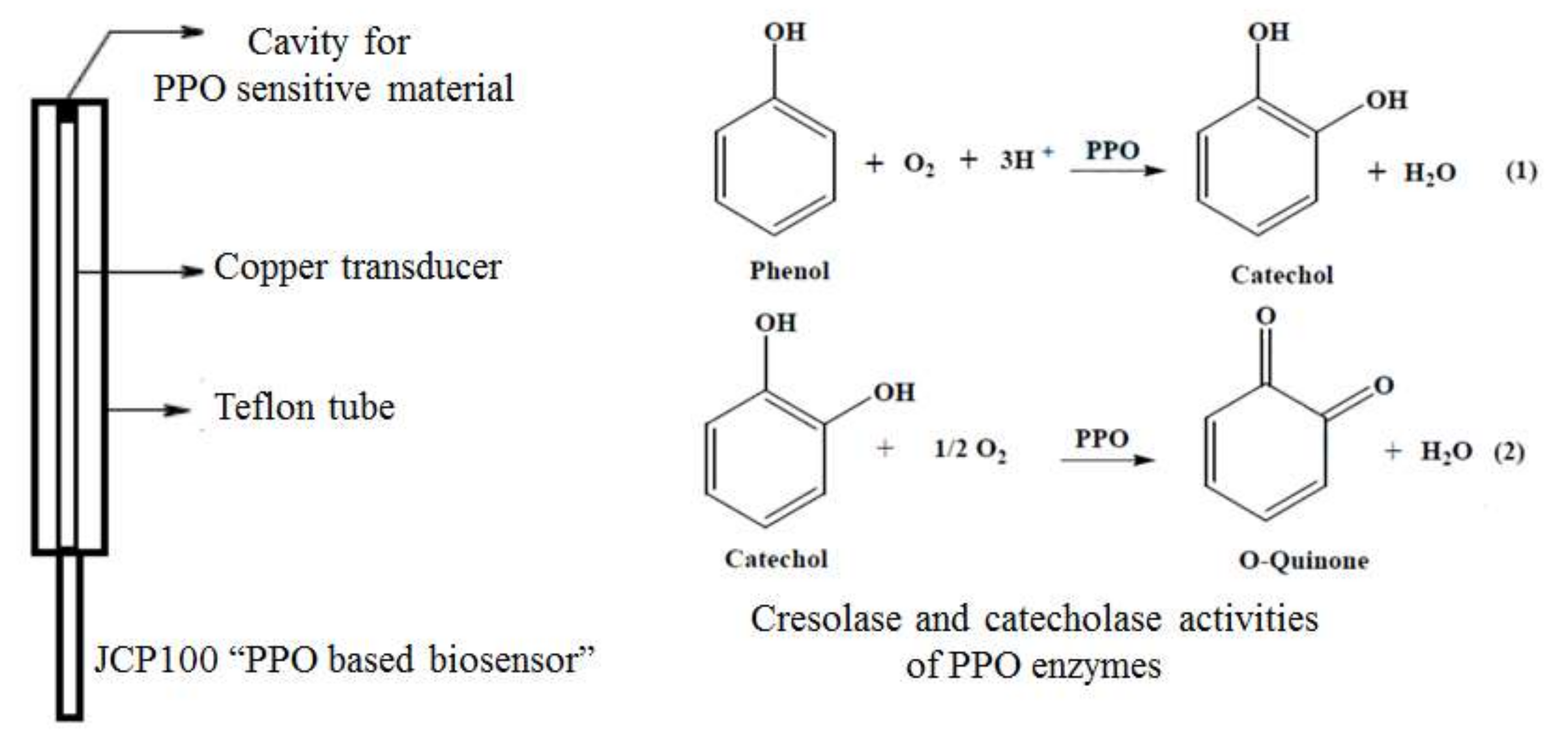


| Biosensor | Graphite Powder (mg) | Vegetable Extract (μL) | Mineral Oil (mg) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CP | 100 | - | 30 |
| JCP50 | 100 | 50 | 30 |
| JCP100 | 100 | 100 | 30 |
| JCP200 | 100 | 200 | 30 |
| Samples | Tablets |
|---|---|
| 1 | Reference 750 mg |
| 2 | Generic 750 mg |
| 3 | Similar 750 mg |
| 4 | Reference 500 mg |
| 5 | Generic 500 mg |
| 6 | Similar 500 mg |
| PPO Plant Source | Enzymatic Activity of PPO (U/mg Protein) | Linear Range (μM) | LoD (μM) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Persea americana | 375 | 1200–53,000 | 880 | [3] |
| Cucurbita pepo | 137 | 1200–53,000 | 690 | [30] |
| Solanum melongena | 552.60 | 20–200 | 5 | [5] |
| Solanum paniculatum L. | 616 | 5–245 | 3 | This work |
| Medicines Category | Labeled Value (mg) | Official Method (mg) | Proposed Method (mg) | Relative Error * (%) | Relative Error ** (%) | Relative Error *** (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reference 1 | 750 | 773.76 ± 1.20 | 769.74 ± 0.77 | +3.16 | +2.63 | −0.51 |
| Generic 2 | 750 | 752.94 ± 0.77 | 747.06 ± 0.36 | +2.94 | −0.39 | −0.78 |
| Similar 3 | 750 | 753.86 ± 0.59 | 751.84 ± 0.65 | +0.51 | +0.24 | −0.26 |
| Reference 4 | 500 | 510.38 ± 0.46 | 507.18 ± 0.40 | +2.07 | +1.43 | −0.62 |
| Generic 5 | 500 | 497.36 ± 0.34 | 495.38 ± 0.37 | −0.52 | −0.92 | −0.39 |
| Similar 6 | 500 | 505.60 ± 0.38 | 491.46 ± 0.58 | +1.12 | −1.70 | −2.79 |
| Paracetamol Concentration (μM) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tablet | Incorporated | Found | RSD (%) | Recovery (%) |
| Reference | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 |
| 10 | 9.76 ± 0.13 | 2.40 | 97.60 | |
| 20 | 19.71 ± 0.67 | 1.45 | 98.55 | |
| 30 | 29.56 ± 0.88 | 1.46 | 98.53 | |
| 40 | 40.06 ± 0.91 | 0.15 | 100.15 | |
| Generic | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 |
| 10 | 10.12 ± 0.23 | 1.20 | 101.20 | |
| 20 | 20.03 ± 0.97 | 0.15 | 100.15 | |
| 30 | 29.97 ± 0.33 | 0.10 | 99.90 | |
| 40 | 41.03 ± 42 | 2.57 | 102.57 | |
| Similar | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 |
| 10 | 9.96 ± 1.14 | 0.40 | 99.60 | |
| 20 | 20.14 ± 0.31 | 0.70 | 100.70 | |
| 30 | 30.02 ± 0.98 | 0.06 | 100.06 | |
| 40 | 39.91 ± 0.77 | 0.22 | 99.77 | |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Antunes, R.S.; Garcia, L.F.; Somerset, V.S.; Gil, E.D.S.; Lopes, F.M. The Use of a Polyphenoloxidase Biosensor Obtained from the Fruit of Jurubeba (Solanum paniculatum L.) in the Determination of Paracetamol and Other Phenolic Drugs. Biosensors 2018, 8, 36. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios8020036
Antunes RS, Garcia LF, Somerset VS, Gil EDS, Lopes FM. The Use of a Polyphenoloxidase Biosensor Obtained from the Fruit of Jurubeba (Solanum paniculatum L.) in the Determination of Paracetamol and Other Phenolic Drugs. Biosensors. 2018; 8(2):36. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios8020036
Chicago/Turabian StyleAntunes, Rafael Souza, Luane Ferreira Garcia, Vernon Sydwill Somerset, Eric De Souza Gil, and Flavio Marques Lopes. 2018. "The Use of a Polyphenoloxidase Biosensor Obtained from the Fruit of Jurubeba (Solanum paniculatum L.) in the Determination of Paracetamol and Other Phenolic Drugs" Biosensors 8, no. 2: 36. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios8020036
APA StyleAntunes, R. S., Garcia, L. F., Somerset, V. S., Gil, E. D. S., & Lopes, F. M. (2018). The Use of a Polyphenoloxidase Biosensor Obtained from the Fruit of Jurubeba (Solanum paniculatum L.) in the Determination of Paracetamol and Other Phenolic Drugs. Biosensors, 8(2), 36. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios8020036