Role of Pseudouridine Formation by Deg1 for Functionality of Two Glutamine Isoacceptor tRNAs
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
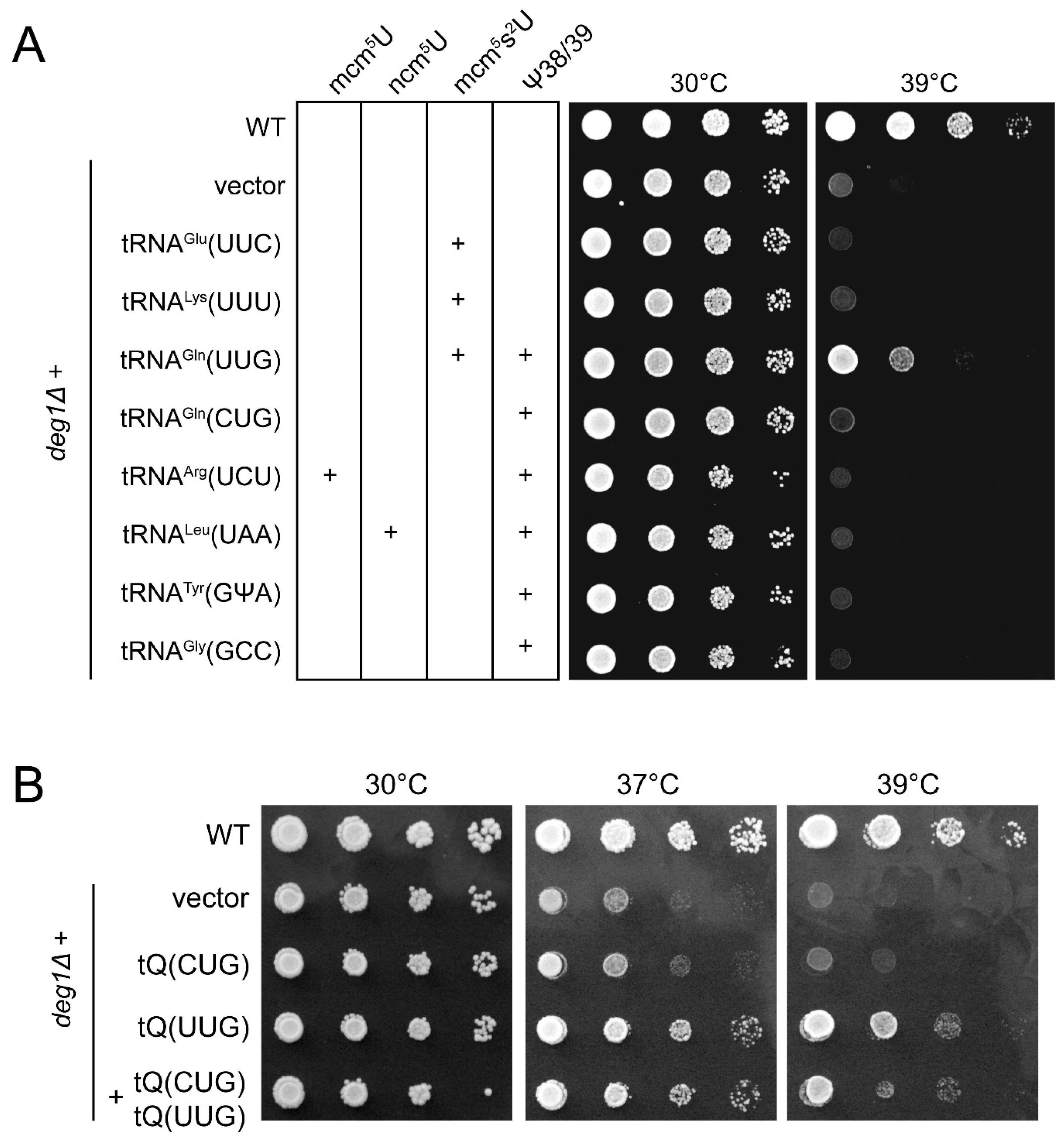
2.1. Phenotypic Rescue of deg1 Mutants by tRNA Overexpression
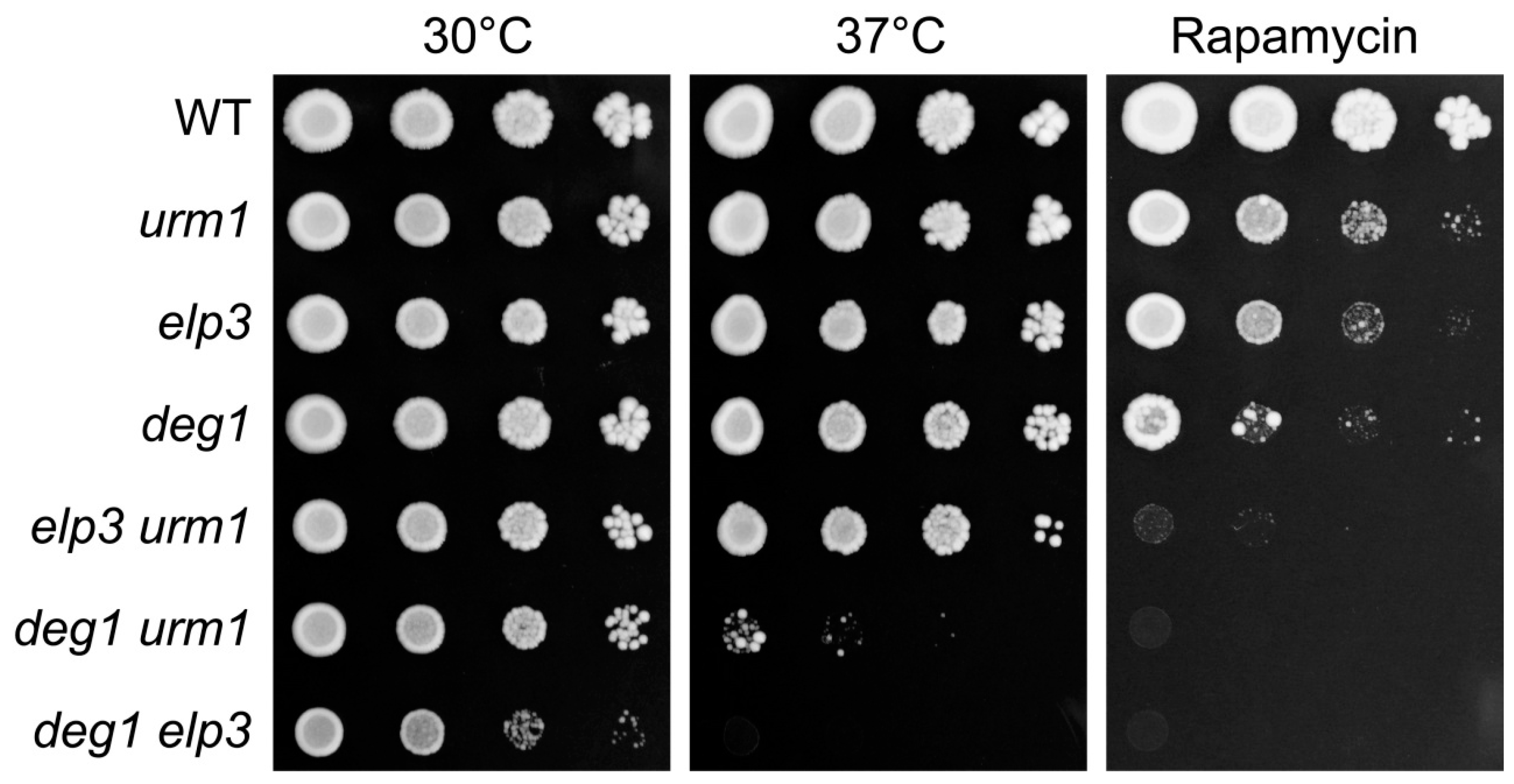
2.2. Genetic Interactions of DEG1 under TORC1 Inhibition
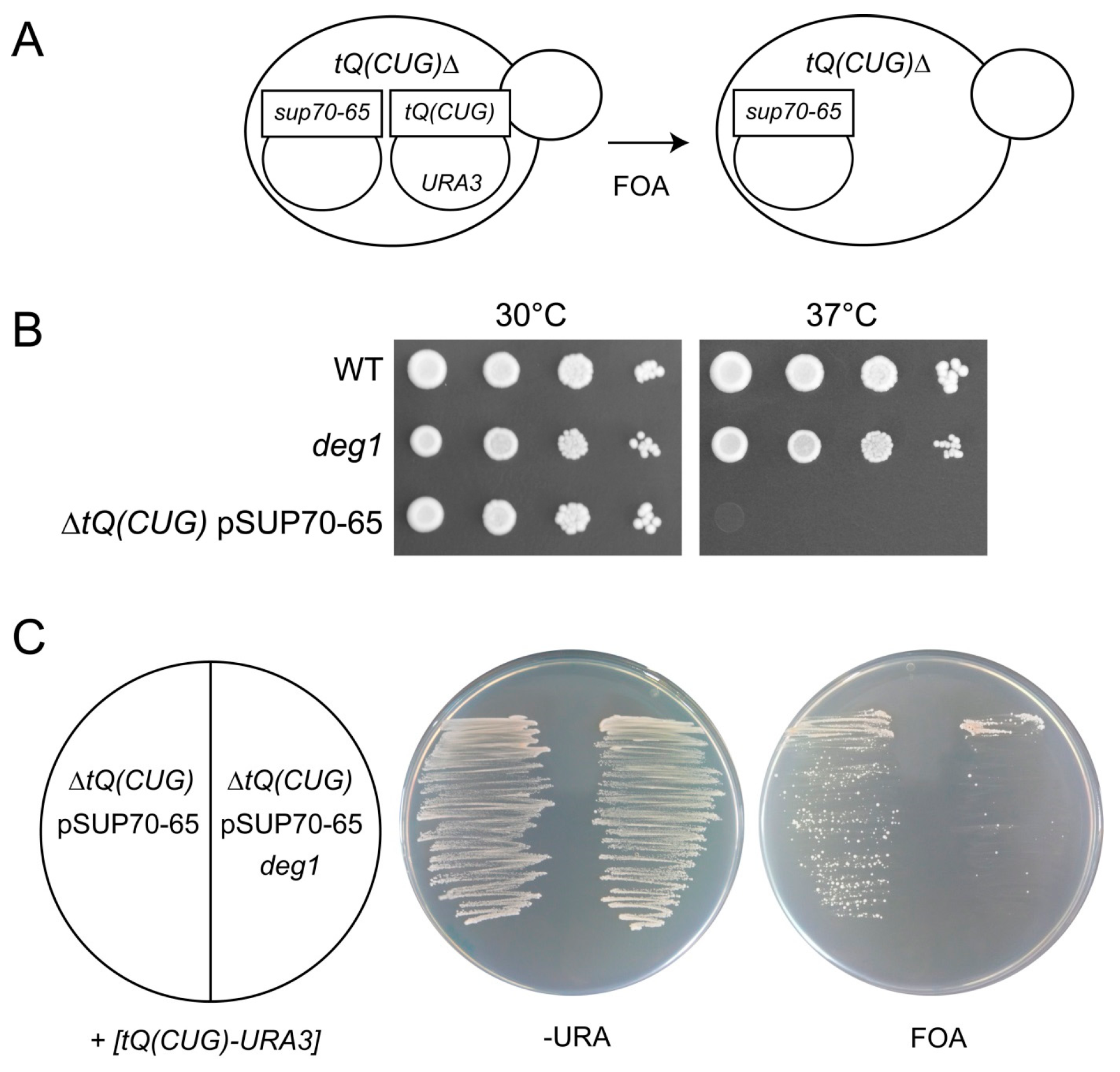
2.3. Replacement of tQ(CUG) by the sup70-65 Allele in Haploid Yeast
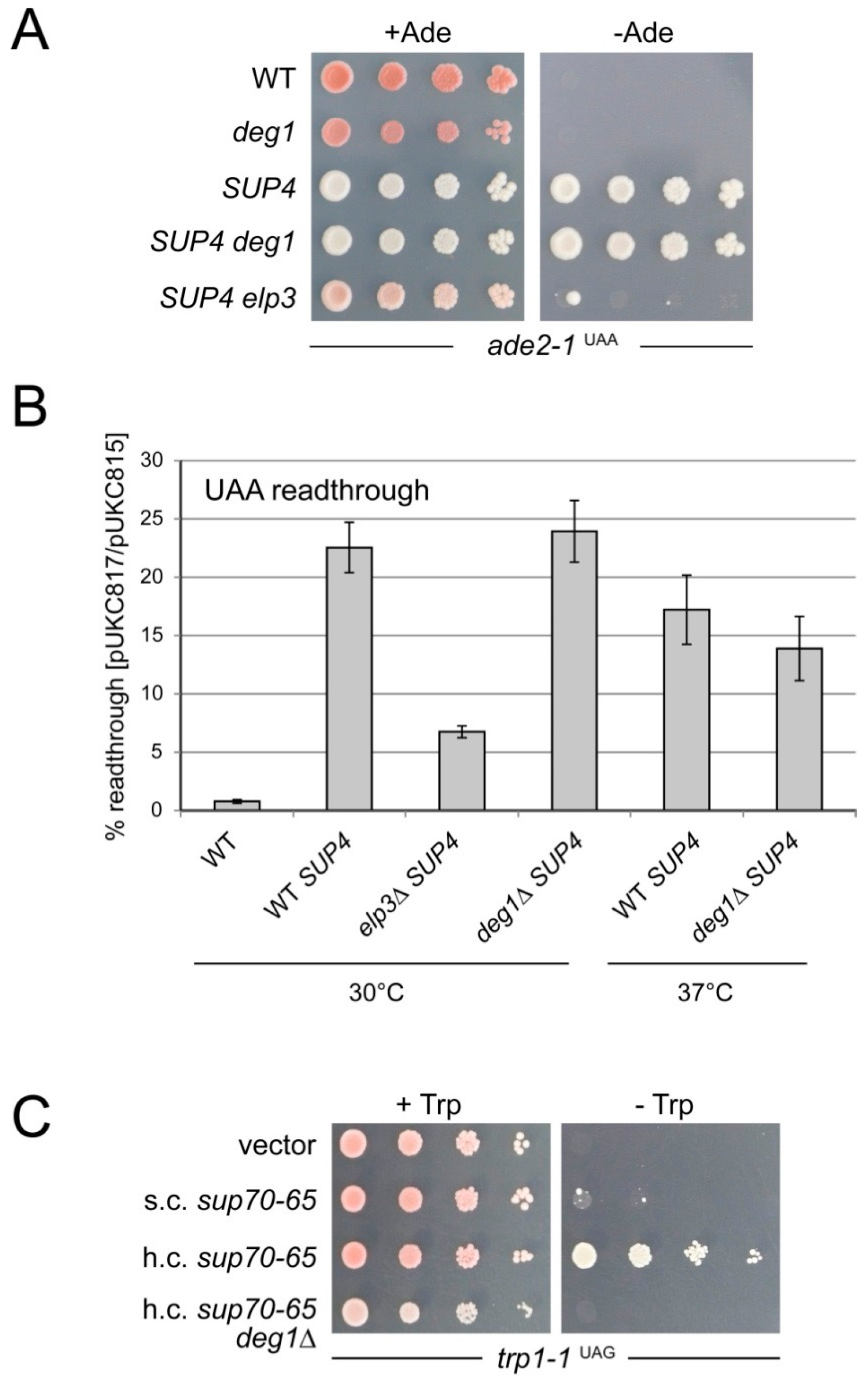
2.4. Comparison of Non-Sense Suppression by sup70-65 and SUP4 in the Presence and Absence of ψ38/39
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Strains, Plasmids and General Methods
3.2. Phenotypic Assays
3.3. Quantitative Read-through Assay
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yu, C.T.; Allen, F.W. Studies on an isomer of uridine isolated from ribonucleic acids. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1959, 32, 393–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spenkuch, F.; Motorin, Y.; Helm, M. Pseudouridine: Still mysterious, but never a fake (uridine)! RNA Biol. 2014, 11, 1540–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giaever, G.; Chu, A.M.; Ni, L.; Connelly, C.; Riles, L.; Véronneau, S.; Dow, S.; Lucau-Danila, A.; Anderson, K.; André, B.; et al. Functional profiling of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae genome. Nature 2002, 418, 387–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lecointe, F.; Simos, G.; Sauer, A.; Hurt, E.C.; Motorin, Y.; Grosjean, H. Characterization of Yeast Protein Deg1 as Pseudouridine Synthase (Pus3) Catalyzing the Formation of ψ38 and ψ39 in tRNA Anticodon Loop. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 1316–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charette, M.; Grey, M. Pseudouridine in RNA: What, where, how and why. IUBMB Life 2000, 49, 341–351. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shaheen, R.; Han, L.; Faqeih, E.; Ewida, N.; Alobeid, E.; Phizicky, E.M.; Alkuraya, F.S. A homozygous truncating mutation in PUS3 expands the role of tRNA modification in normal cognition. Hum. Genet. 2016, 135, 707–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machnicka, M.A.; Milanowska, K.; Osman Oglou, O.; Purta, E.; Kurkowska, M.; Olchowik, A.; Januszewski, W.; Kalinowski, S.; Dunin-Horkawicz, S.; Rother, K.M.; et al. MODOMICS: A database of RNA modification pathways—2013 update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D262–D267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, L.; Kon, Y.; Phizicky, E.M. Functional importance of ψ38 and ψ39 in distinct tRNAs, amplified for tRNAGln(UUG) by unexpected temperature sensitivity of the s2U modification in yeast. RNA 2015, 21, 188–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klassen, R.; Ciftci, A.; Funk, J.; Bruch, A.; Butter, F.; Schaffrath, R. tRNA anticodon loop modifications ensure protein homeostasis and cell morphogenesis in yeast. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, 10946–10959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, B.; Johansson, M.J.; Byström, A.S. An early step in wobble uridine tRNA modification requires the Elongator complex. RNA 2005, 11, 424–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, B.; Lu, J.; Byström, A.S. A genome-wide screen identifies genes required for formation of the wobble nucleoside 5-methoxycarbonylmethyl-2-thiouridine in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. RNA 2008, 14, 2183–2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalhor, H.R.; Clarke, S. Novel methyltransferase for modified uridine residues at the wobble position of tRNA. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2003, 23, 9283–9292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jablonowski, D.; Zink, S.; Mehlgarten, C.; Daum, G.; Schaffrath, R. tRNAGlu wobble uridine methylation by Trm9 identifies Elongator’s key role for zymocin-induced cell death in yeast. Mol. Microbiol. 2006, 59, 677–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fichtner, L.; Frohloff, F.; Bürkner, K.; Larsen, M.; Breunig, K.D.; Schaffrath, R. Molecular analysis of KTI12/TOT4, a Saccharomyces cerevisiae gene required for Kluyveromyces lactis zymocin action. Mol. Microbiol. 2002, 43, 783–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bär, C.; Zabel, R.; Liu, S.; Stark, M.J.; Schaffrath, R. A versatile partner of eukaryotic protein complexes that is involved in multiple biological processes: Kti11/Dph3. Mol. Microbiol. 2008, 69, 1221–1233. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zabel, R.; Bär, C.; Mehlgarten, C.; Schaffrath, R. Yeast α-tubulin suppressor Ats1/Kti13 relates to the Elongator complex and interacts with Elongator partner protein Kti11. Mol. Microbiol. 2008, 69, 175–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehlgarten, C.; Jablonowski, D.; Breunig, K.D.; Stark, M.J.; Schaffrath, R. Elongator function depends on antagonistic regulation by casein kinase Hrr25 and protein phosphatase Sit4. Mol. Microbiol. 2009, 73, 869–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel-Fattah, W.; Jablonowski, D.; di Santo, R.; Scheidt, V.; Hammermeister, A.; ten Have, S.M.; Thüring, K.L.; Helm, M.; Schaffrath, R.; Stark, M.J.R. Phosphorylation of Elp1 by Hrr25 is required for Elongator-dependent tRNA modification in yeast. PLoS Genet. 2015, 11, e1004931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaffrath, R.; Leidel, S.A. Wobble uridine modifications—A reason to live, a reason to die?! RNA Biol. 2016. accepted. [Google Scholar]
- Nakai, Y.; Nakai, M.; Hayashi, H. Thio-modification of yeast cytosolic tRNA requires a ubiquitin-related system that resembles bacterial sulfur transfer systems. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 27469–27476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noma, A.; Sakaguchi, Y.; Suzuki, T. Mechanistic characterization of the sulfur-relay system for eukaryotic 2-thiouridine biogenesis at tRNA wobble positions. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, 1335–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leidel, S.; Pedrioli, P.G.; Bucher, T.; Brost, R.; Costanzo, M.; Schmidt, A.; Aebersold, R.; Boone, C.; Hofmann, K.; Peter, M. Ubiquitin-related modifier Urm1 acts as a sulphur carrier in thiolation of eukaryotic transfer RNA. Nature 2009, 458, 228–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goehring, A.S.; Rivers, D.M.; Sprague, G.F., Jr. Urmylation: A ubiquitin-like pathway that functions during invasive growth and budding in yeast. Mol. Biol. Cell 2003, 14, 4329–4341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jüdes, A.; Ebert, F.; Bär, C.; Thüring, K.L.; Harrer, A.; Klassen, R.; Helm, M.; Stark, M.J.R.; Schaffrath, R. Urmylation and tRNA thiolation functions of ubiquitin-like Uba4•Urm1 systems are conserved from yeast to man. FEBS Lett. 2015, 589, 904–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jüdes, A.; Bruch, A.; Klassen, R.; Helm, M.; Schaffrath, R. Sulfur transfer and activation by ubiquitin-like modifier system Uba4•Urm1 link protein urmylation and tRNA thiolation in yeast. Microb. Cell 2016, 3, 423–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frohloff, F.; Fichtner, L.; Jablonowski, D.; Breunig, K.D.; Schaffrath, R. Saccharomyces cerevisiae Elongator mutations confer resistance to the Kluyveromyces lactis zymocin. EMBO J. 2001, 20, 1993–2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esberg, A.; Huang, B.; Johansson, M.J.O.; Byström, A.S. Elevated levels of two tRNA species bypass the requirement for elongator complex in transcription and exocytosis. Mol. Cell 2006, 24, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rezgui, V.A.; Tyagi, K.; Ranjan, N.; Konevega, A.L.; Mittelstaet, J.; Rodnina, M.V.; Peter, M.; Pedrioli, P.G. tRNA tKUUU, tQUUG, and tEUUC wobble position modifications fine-tune protein translation by promoting ribosome A-site binding. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 12289–12294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tükenmez, H.; Xu, H.; Esberg, A.; Byström, A.S. The role of wobble uridine modifications in +1 translational frameshifting in eukaryotes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, 9489–9499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nedialkova, D.D.; Leidel, S.A. Optimization of Codon Translation Rates via tRNA Modifications Maintains Proteome Integrity. Cell 2015, 161, 1606–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klassen, R.; Grunewald, P.; Thüring, K.L.; Eichler, C.; Helm, M.; Schaffrath, R. Loss of Anticodon Wobble Uridine Modifications Affects tRNALys Function and Protein Levels in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0119261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klassen, R.; Bruch, A.; Schaffrath, R. Independent suppression of ribosomal +1 frameshifts by different tRNA anticodon loop modifications. RNA Biol. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johansson, M.J.; Esberg, A.; Huang, B.; Björk, G.R.; Byström, A.S. Eukaryotic wobble uridine modifications promote a functionally redundant decoding system. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2008, 28, 3301–3312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lecointe, F.; Namy, O.; Hatin, I.; Simos, G.; Rousset, J.P.; Grosjean, H. Lack of pseudouridine 38/39 in the anticodon arm of yeast cytoplasmic tRNA decreases in vivo recoding efficiency. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 30445–30453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damon, J.R.; Pincus, D.; Ploegh, H.L. tRNA thiolation links translation to stress responses in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol. Biol. Cell 2015, 26, 270–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alings, F.; Sarin, L.P.; Fufezan, C.; Drexler, H.C.; Leidel, S.A. An evolutionary approach uncovers a diverse response of tRNA 2-thiolation to elevated temperatures in yeast. RNA 2015, 21, 202–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tyagi, K.; Pedrioli, P.G. Protein degradation and dynamic tRNA thiolation fine-tune translation at elevated temperatures. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, 4701–4712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheidt, V.; Jüdes, A.; Bär, C.; Klassen, R.; Schaffrath, R. Loss of wobble uridine modification in tRNA anticodons interferes with TOR pathway signaling. Microb. Cell 2014, 1, 416–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, L.E.; Rowley, N.; Dawes, I.W.; Johnston, G.C.; Singer, R.A. A yeast glutamine tRNA signals nitrogen status for regulation of dimorphic growth and sporulation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 8619–8624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kemp, A.J.; Betney, R.; Ciandrini, L.; Schwenger, A.C.; Romano, M.C.; Stansfield, I. A yeast tRNA mutant that causes pseudohyphal growth exhibits reduced rates of CAG codon translation. Mol. Microbiol. 2013, 87, 284–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorgoni, B.; Ciandrini, L.; McFarland, M.R.; Romano, M.C.; Stansfield, I. Identification of the mRNA targets of tRNA-specific regulation using genome-wide simulation of translation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, 9231–9244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stansfield, I.; Akhmaloka; Tuite, M.F. A mutant allele of the SUP45 (SAL4) gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae shows temperature-dependent allosuppressor and omnipotent suppressor phenotypes. Curr. Genet. 2002, 27, 417–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherman, F. Getting started with yeast. Methods Enzymol. 2002, 350, 3–41. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gueldener, U.; Heinisch, J.; Koehler, G.J.; Voss, D.; Hegemann, J.H. A second set of loxP marker cassettes for Cre-mediated multiple gene knockouts in budding yeast. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002, 30, e23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gietz, D.; Schiestl, R.H. High-efficiency yeast transformation using the LiAc/SS carrier DNA/PEG method. Nat. Protocols 2007, 2, 31–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klassen, R.; Paluszynski, J.P.; Wemhoff, S.; Pfeiffer, A.; Fricke, J.; Meinhardt, F. The primary target of the killer toxin from Pichia acaciae is tRNAGln. Mol. Microbiol. 2008, 69, 681–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiorentini, P.; Huang, K.N.; Tishkoff, D.X.; Kolodner, R.D.; Symington, L.S. Exonuclease I of Saccharomyces cerevisiae Functions in Mitotic Recombination In Vivo and In Vitro. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1997, 17, 2764–2773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, J.H. Experiments in Molecular Genetics; Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press: New York, NY, USA, 1972. [Google Scholar]
- Laten, H.M. Antisuppression of class I suppressors in an isopentenylated-transfer RNA deficient mutant of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Curr. Genet. 1984, 8, 29–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Strain | Genotype | Reference/Source |
|---|---|---|
| Saccharomyces cerevisiae BY4741 | MATa, his3Δ, leu2Δ, met15Δ, ura3Δ | Euroscarf, Frankfurt |
| S. cerevisiae elp3 | BY4741 elp3ΔKanMX4 | Euroscarf, Frankfurt |
| S. cerevisiae urm1 | BY4741 urm1ΔKanMX4 | Euroscarf, Frankfurt |
| S. cerevisiae deg1 | BY4741 deg1ΔKanMX4 | Euroscarf, Frankfurt |
| S. cerevisiae elp3 urm1 | BY4741 elp3ΔKanMX4 urm1ΔHIS3 | [31] |
| S. cerevisiae deg1 urm1 | BY4741 urm1ΔKanMX4 deg1ΔSpHIS5 | [9] |
| S. cerevisiae deg1 elp3 | BY4741 elp3ΔKanMX4 deg1ΔSpHIS5 | [9] |
| S. cerevisiae sup70 | BY4741 pAK01 tQ(CUG)ΔKlLEU2 | [31] |
| S. cerevisiae sup70-65-pAK01 | BY4741 pAK01 tQ(CUG)ΔKlLEU2 pSUP70-65-CEN | this work |
| S. cerevisiae sup70-65 | BY4741 tQ(CUG)ΔKlLEU2 pSUP70-65 CEN | this work |
| S. cerevisiae sup70-65-pAK01 | BY4741 pAK01 tQ(CUG)ΔKlLEU2 deg1ΔKanMX4 pSUP70-65-CEN | this work |
| S. cerevisiae W303-1B | MATα leu2-3,112 trp1-1 can1-100 ura3-1 ade2-1 his3-11,15 | [47] |
| S. cerevisiae RK207 | W303-1B deg1ΔSpHIS5 | this work |
| S. cerevisiae RK273 | W303-1B deg1ΔloxP | this work |
| S. cerevisiae UMY2893 | MATα SUP4 leu2-3,112 trp1-1 can1-100 ura3-1 ade2-1 his3-11,15 | [10] |
| S. cerevisiae UMY2916 | UMY2893 elp3∆KanMX4 | [10] |
| S. cerevisiae RK208 | UMY2893 deg1ΔSpHIS5 | this work |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Klassen, R.; Schaffrath, R. Role of Pseudouridine Formation by Deg1 for Functionality of Two Glutamine Isoacceptor tRNAs. Biomolecules 2017, 7, 8. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom7010008
Klassen R, Schaffrath R. Role of Pseudouridine Formation by Deg1 for Functionality of Two Glutamine Isoacceptor tRNAs. Biomolecules. 2017; 7(1):8. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom7010008
Chicago/Turabian StyleKlassen, Roland, and Raffael Schaffrath. 2017. "Role of Pseudouridine Formation by Deg1 for Functionality of Two Glutamine Isoacceptor tRNAs" Biomolecules 7, no. 1: 8. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom7010008
APA StyleKlassen, R., & Schaffrath, R. (2017). Role of Pseudouridine Formation by Deg1 for Functionality of Two Glutamine Isoacceptor tRNAs. Biomolecules, 7(1), 8. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom7010008






