Remodeling Membrane Binding by Mono-Ubiquitylation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Protein Expression and Purification
2.2. In-Gel Digestion and Mass Spectrometry Analysis
2.3. Structural Modeling
2.4. PIP2-Enriched Liposome Pull-Down Assay
2.5. PIP Array Binding Assay
2.6. Live Imaging of Ent1 Derivatives
3. Results
3.1. Yeast Ent1 Undergoes Ubiquitylation
3.2. Identification of the Ent1 Ubiquitylation Sites
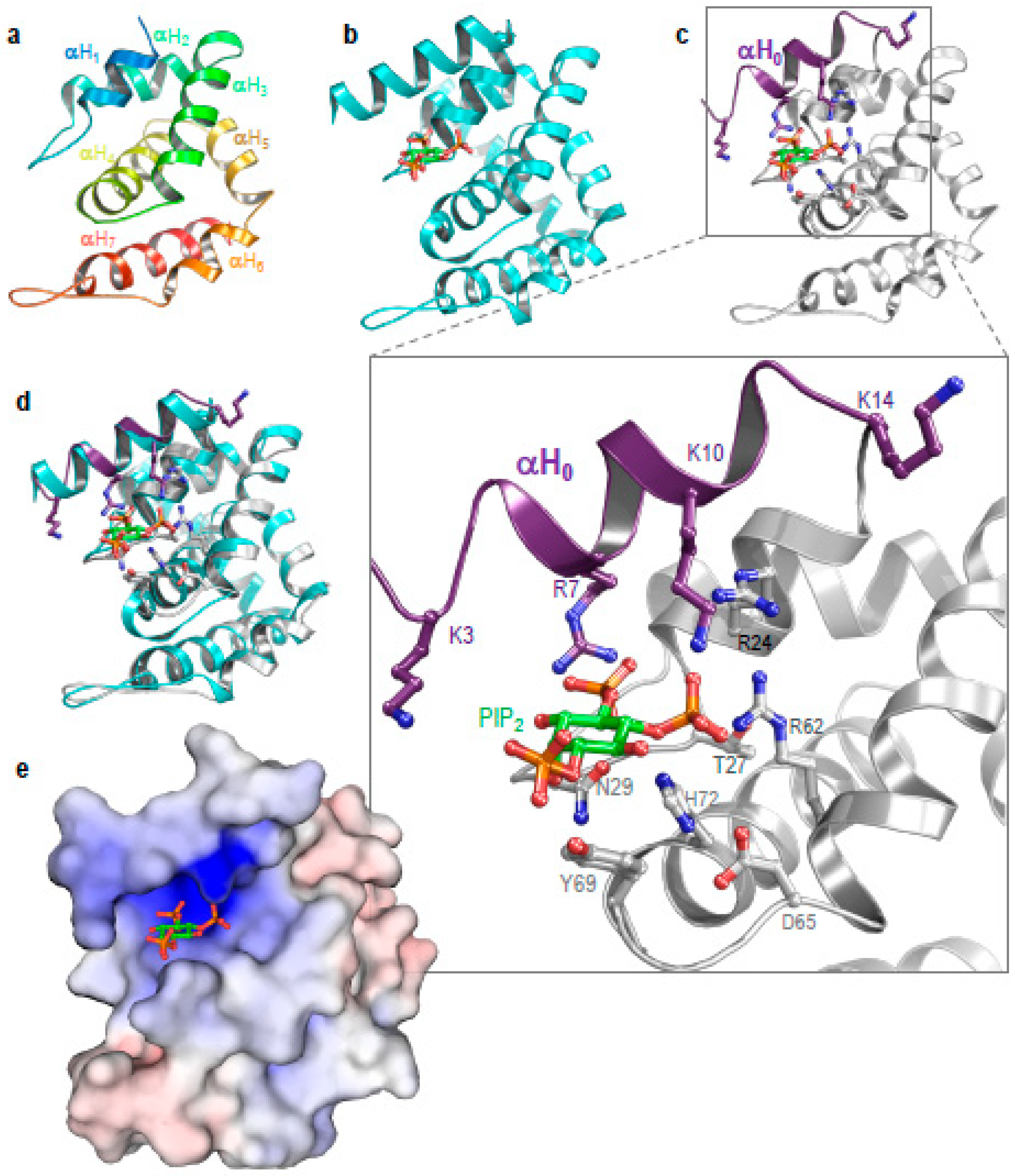
3.3. Structure of Ent1–ENTH Provides Insight into Plasma Membrane Binding
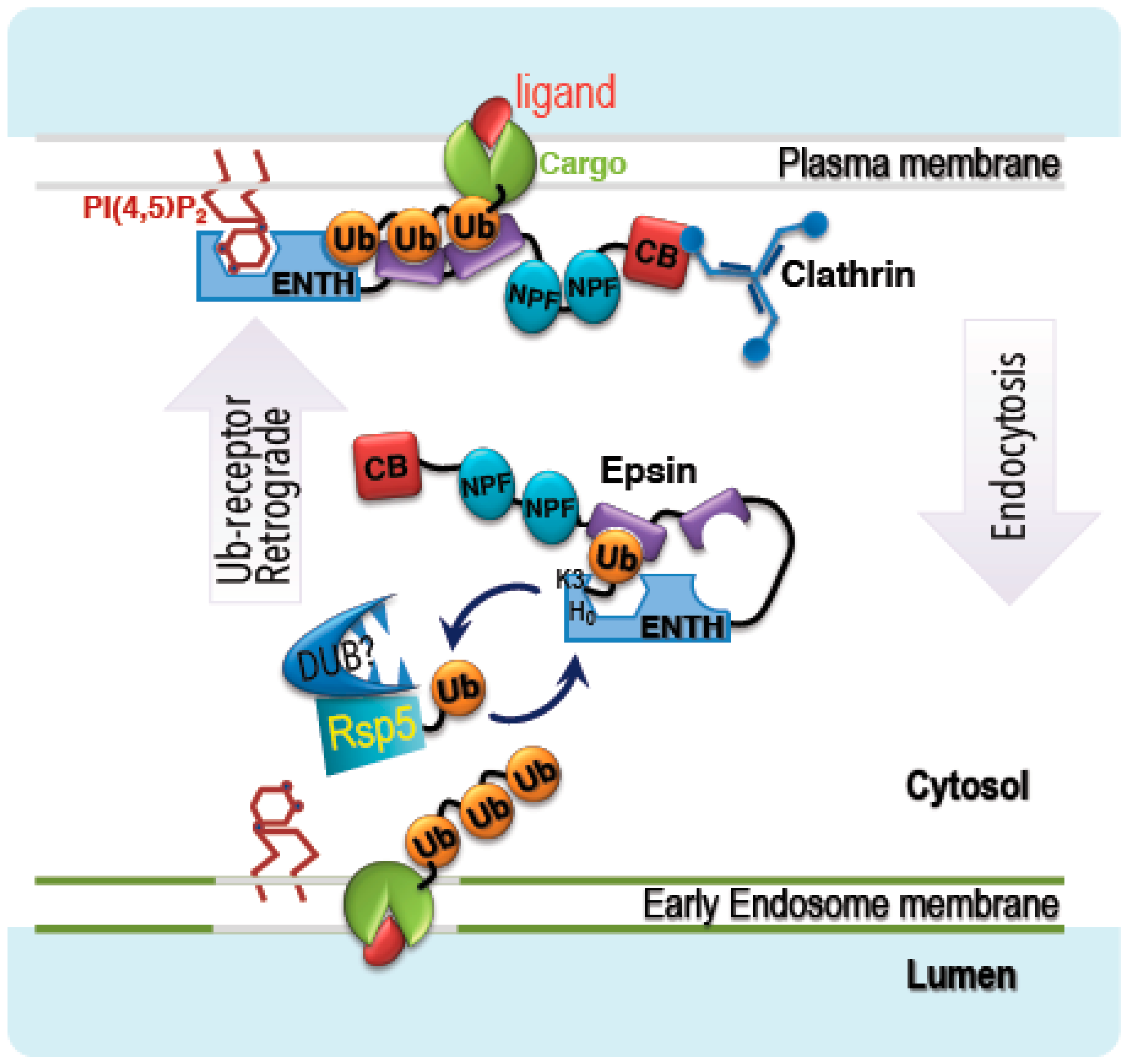
3.4. Ubiquitylation Regulates Epsin Membrane Binding In Vitro
3.5. Ubiquitylation Regulates the Plasma Membrane Association of Ent1 In Vivo
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Weissman, A.M.; Shabek, N.; Ciechanover, A. The predator becomes the prey: Regulating the ubiquitin system by ubiquitylation and degradation. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2011, 12, 605–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komander, D.; Rape, M. The ubiquitin code. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2012, 81, 203–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurley, J.H.; Lee, S.; Prag, G. Ubiquitin-binding domains. Biochem. J. 2006, 399, 361–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prag, G.; Misra, S.; Jones, E.A.; Ghirlando, R.; Davies, B.A.; Horazdovsky, B.F.; Hurley, J.H. Mechanism of ubiquitin recognition by the CUE domain of Vps9p. Cell 2003, 113, 609–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, S.C.; Prag, G.; Francis, S.A.; Sutanto, M.A.; Hurley, J.H.; Hicke, L. A ubiquitin-binding motif required for intramolecular monoubiquitylation, the CUE domain. EMBO J. 2003, 22, 1273–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mattera, R.; Bonifacino, J.S. Ubiquitin binding and conjugation regulate the recruitment of Rabex-5 to early endosomes. EMBO J. 2008, 27, 2484–2494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Keren-Kaplan, T.; Attali, I.; Motamedchaboki, K.; Davis, B.A.; Tanner, N.; Reshef, Y.; Laudon, E.; Kolot, M.; Levin-Kravets, O.; Kleifeld, O.; et al. Synthetic biology approach to reconstituting the ubiquitylation cascade in bacteria. EMBO J. 2012, 31, 378–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keren-Kaplan, T.; Zeev Peters, L.; Levin-Kravets, O.; Attali, I.; Kleifeld, O.; Shohat, N.; Artzi, S.; Zucker, O.; Pilzer, I.; Reis, N.; et al. Structure of ubiquitylated-Rpn10 provides insight into its autoregulation mechanism. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ford, M.G.; Mills, I.G.; Peter, B.J.; Vallis, Y.; Praefcke, G.J.; Evans, P.R.; Mcmahon, H.T. Curvature of clathrin-coated pits driven by epsin. Nature 2002, 419, 361–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, S.C.; Katzmann, D.J.; Schnell, J.D.; Sutanto, M.; Emr, S.D.; Hicke, L. Epsins and Vps27p/Hrs contain ubiquitin-binding domains that function in receptor endocytosis. Nat. Cell Biol. 2002, 4, 389–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar, R.C.; Watson, H.A.; Wendland, B. The yeast Epsin Ent1 is recruited to membranes through multiple independent interactions. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 10737–10743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wendland, B. Epsins: Adaptors in endocytosis? Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2002, 3, 971–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dupre, S.; Urban-Grimal, D.; Haguenauer-Tsapis, R. Ubiquitin and endocytic intemalization in yeast and animal cells. BBA Mol. Cell Res. 2004, 1695, 89–111. [Google Scholar]
- Campelo, F.; Mcmahon, H.T.; Kozlov, M.M. The hydrophobic insertion mechanism of membrane curvature generation by proteins. Biophys. J. 2008, 95, 2325–2339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boucrot, E.; Pick, A.; Camdere, G.; Liska, N.; Evergren, E.; Mcmahon, H.T.; Kozlov, M.M. Membrane Fission Is Promoted by Insertion of Amphipathic Helices and Is Restricted by Crescent BAR Domains. Cell 2012, 149, 124–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ziv, I.; Matiuhin, Y.; Kirkpatrick, D.S.; Erpapazoglou, Z.; Leon, S.; Pantazopoulou, M.; Kim, W.; Gygi, S.P.; Haguenauer-Tsapis, R.; Reis, N.; et al. A perturbed ubiquitin landscape distinguishes between ubiquitin in trafficking and in proteolysis. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2011, 10, M111-009753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, A.; Eng, J.; Zhang, N.; Li, X.J.; Aebersold, R. A uniform proteomics MS/MS analysis platform utilizing open XML file formats. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2005, 1, 2005.0017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin-Kravets, O.; Tanner, N.; Shohat, N.; Attali, I.; Keren-Kaplan, T.; Shusterman, A.; Artzi, S.; Varvak, A.; Reshef, Y.; Shi, X.; et al. A bacterial genetic selection system for ubiquitylation cascade discovery. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 945–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanner, N.; Prag, G. Purification and crystallization of yeast Ent1 ENTH domain. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. F Struct. Biol. Cryst. Commun. 2012, 68, 820–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelley, L.A.; Mezulis, S.; Yates, C.M.; Wass, M.N.; Sternberg, M.J.E. The Phyre2 web portal for protein modeling, prediction and analysis. Nat. Protoc. 2015, 10, 845–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Emsley, P.; Cowtan, K. Coot: Model-building tools for molecular graphics. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2004, 60, 2126–2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murshudov, G.N.; Skubak, P.; Lebedev, A.A.; Pannu, N.S.; Steiner, R.A.; Nicholls, R.A.; Winn, M.D.; Long, F.; Vagin, A.A. REFMAC5 for the refinement of macromolecular crystal structures. Acta Crystallogr. D 2011, 67, 355–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrodinger, LLC. The PyMOL Molecular Graphics System, Version 1.8; Schrodinger LLC: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Jansen, G.; Wu, C.L.; Schade, B.; Thomas, D.Y.; Whiteway, M. Drag&Drop cloning in yeast. Gene 2005, 344, 43–51. [Google Scholar]
- Swaney, D.L.; Beltrao, P.; Starita, L.; Guo, A.; Rush, J.; Fields, S.; Krogan, N.J.; Villen, J. Global analysis of phosphorylation and ubiquitylation cross-talk in protein degradation. Nat. Methods 2013, 10, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huh, W.K.; Falvo, J.V.; Gerke, L.C.; Carroll, A.S.; Howson, R.W.; Weissman, J.S.; O’shea, E.K. Global analysis of protein localization in budding yeast. Nature 2003, 425, 686–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.Y.; Lin, Y.Y.; Qian, J.; Tao, S.C.; Zhu, J.; Pickart, C.; Zhu, H. Functional dissection of a HECT ubiquitin E3 ligase. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2008, 7, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchiki, T.; Kim, H.T.; Zhai, B.; Gygi, S.P.; Johnston, J.A.; O’bryan, J.P.; Goldberg, A.L. The ubiquitin-interacting motif protein, S5a, is ubiquitinated by all types of ubiquitin ligases by a mechanism different from typical substrate recognition. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 12622–12632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isasa, M.; Katz, E.J.; Kim, W.; Yugo, V.; Gonzalez, S.; Kirkpatrick, D.S.; Thomson, T.M.; Finley, D.; Gygi, S.P.; Crosas, B. Monoubiquitination of RPN10 regulates substrate recruitment to the proteasome. Mol. Cell 2010, 38, 733–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.; Hurley, J.H. VHS domains of ESCRT-0 cooperate in high-avidity binding to polyubiquitinated cargo. EMBO J. 2010, 29, 1045–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misra, S.; Beach, B.M.; Hurley, J.H. Structure of the VHS domain of human Tom1 (target of myb 1): Insights into interactions with proteins and membranes. Biochemistry 2000, 39, 11282–11290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, A.; Munshi, U.; Ablan, S.D.; Nagashima, K.; Freed, E.O. Functional replacement of a retroviral late domain by ubiquitin fusion. Traffic 2008, 9, 1972–1983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donaldson, K.M.; Yin, H.; Gekakis, N.; Supek, F.; Joazeiro, C.A. Ubiquitin signals protein trafficking via interaction with a novel ubiquitin binding domain in the membrane fusion regulator, Vps9p. Curr. Biol. 2003, 13, 258–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindsten, K.; Menendez-Benito, V.; Masucci, M.G.; Dantuma, N.P. A transgenic mouse model of the ubiquitin/proteasome system. Nat. Biotechnol. 2003, 21, 897–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghaemmaghami, S.; Huh, W.K.; Bower, K.; Howson, R.W.; Belle, A.; Dephoure, N.; O’shea, E.K.; Weissman, J.S. Global analysis of protein expression in yeast. Nature 2003, 425, 737–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Alai, M.M.; Heidemann, J.; Skruzny, M.; Gieras, A.; Mertens, H.D.T.; Svergun, D.I.; Kaksonen, M.; Uetrecht, C.; Meijers, R. Epsin and Sla2 form assemblies through phospholipid interfaces. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aguilar, R.C.; Longhi, S.A.; Shaw, J.D.; Yeh, L.Y.; Kim, S.; Schon, A.; Freire, E.; Hsu, A.; Mccormick, W.K.; Watson, H.A.; et al. Epsin N-terminal homology domains perform an essential function regulating Cdc42 through binding Cdc42 GTPase-activating proteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 4116–4121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mosesson, Y.; Chetrit, D.; Schley, L.; Berghoff, J.; Ziv, T.; Carvalho, S.; Milanezi, F.; Admon, A.; Schmitt, F.; Ehrlich, M.; et al. Monoubiquitinylation regulates endosomal localization of Lst2, a negative regulator of EGF receptor signaling. Dev. Cell 2009, 16, 687–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woelk, T.; Oldrini, B.; Maspero, E.; Confalonieri, S.; Cavallaro, E.; Di Fiore, P.P.; Polo, S. Molecular mechanisms of coupled monoubiquitination. Nat. Cell Biol. 2006, 8, 1246–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tanner, N.; Kleifeld, O.; Nachman, I.; Prag, G. Remodeling Membrane Binding by Mono-Ubiquitylation. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 325. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom9080325
Tanner N, Kleifeld O, Nachman I, Prag G. Remodeling Membrane Binding by Mono-Ubiquitylation. Biomolecules. 2019; 9(8):325. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom9080325
Chicago/Turabian StyleTanner, Neta, Oded Kleifeld, Iftach Nachman, and Gali Prag. 2019. "Remodeling Membrane Binding by Mono-Ubiquitylation" Biomolecules 9, no. 8: 325. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom9080325
APA StyleTanner, N., Kleifeld, O., Nachman, I., & Prag, G. (2019). Remodeling Membrane Binding by Mono-Ubiquitylation. Biomolecules, 9(8), 325. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom9080325





