Seasonal Variation of Cistus ladanifer L. Diterpenes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
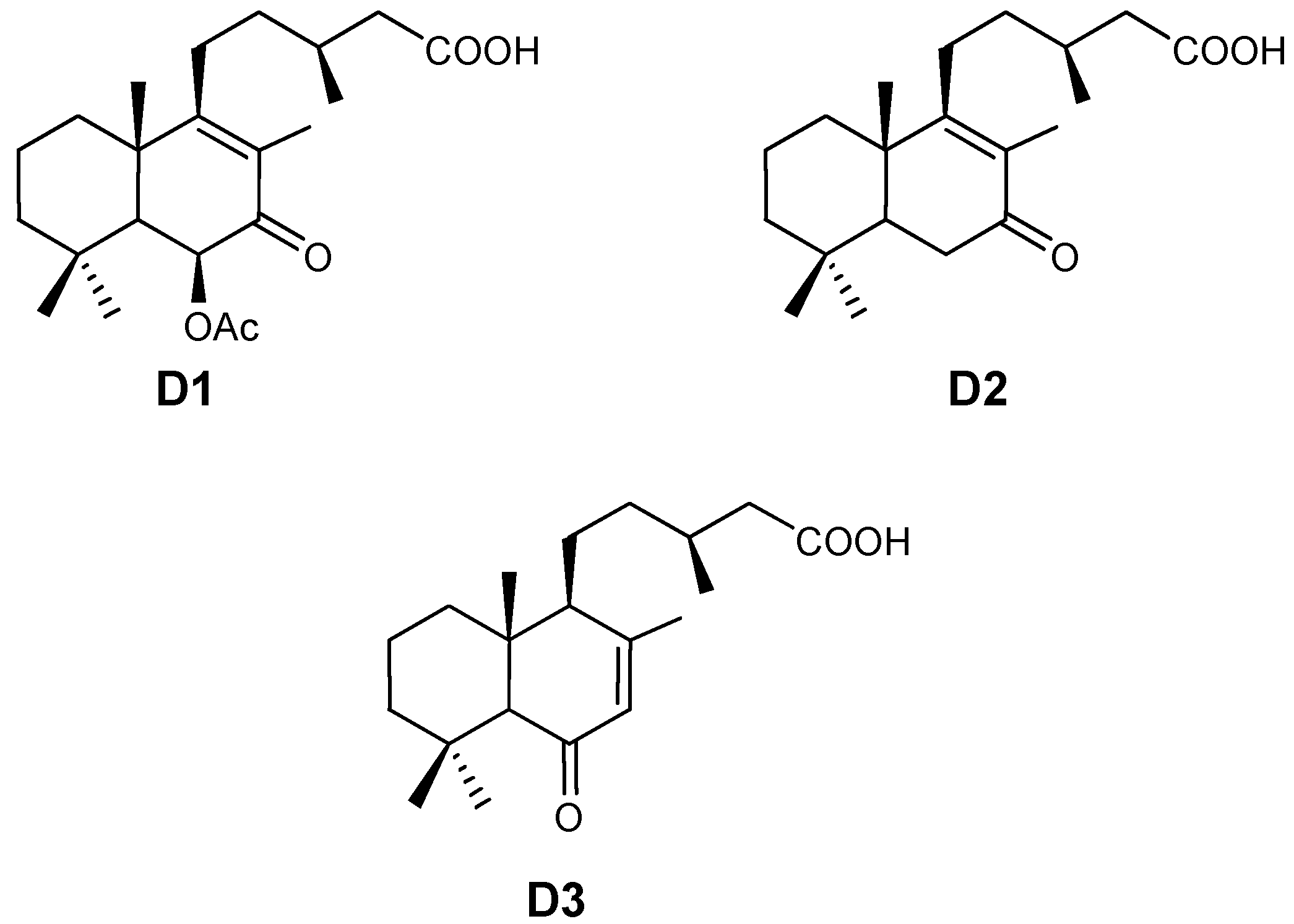
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Seasonal Variation
| Spring | Summer | Autumn | Winter | ANOVA | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Leaves | D1 | 3.50 a | 3.28 a | 3.33 a | 8.03 b | p < 0.05 |
| SD | 0.73 | 2.04 | 1.04 | 0.77 | ||
| D2 | 2.76 a | 2.03 a | 2.38 a | 4.10 b | p < 0.05 | |
| SD | 1.09 | 1.03 | 0.67 | 0.64 | ||
| D3 | 6.51 b | 3.25 a | 3.56 a | 8.79 c | p < 0.05 | |
| SD | 2.36 | 0.98 | 1.51 | 3.11 | ||
| Total diterpenes | 12.78 a | 8.57 a | 9.28 a | 20.93 b | p < 0.05 |
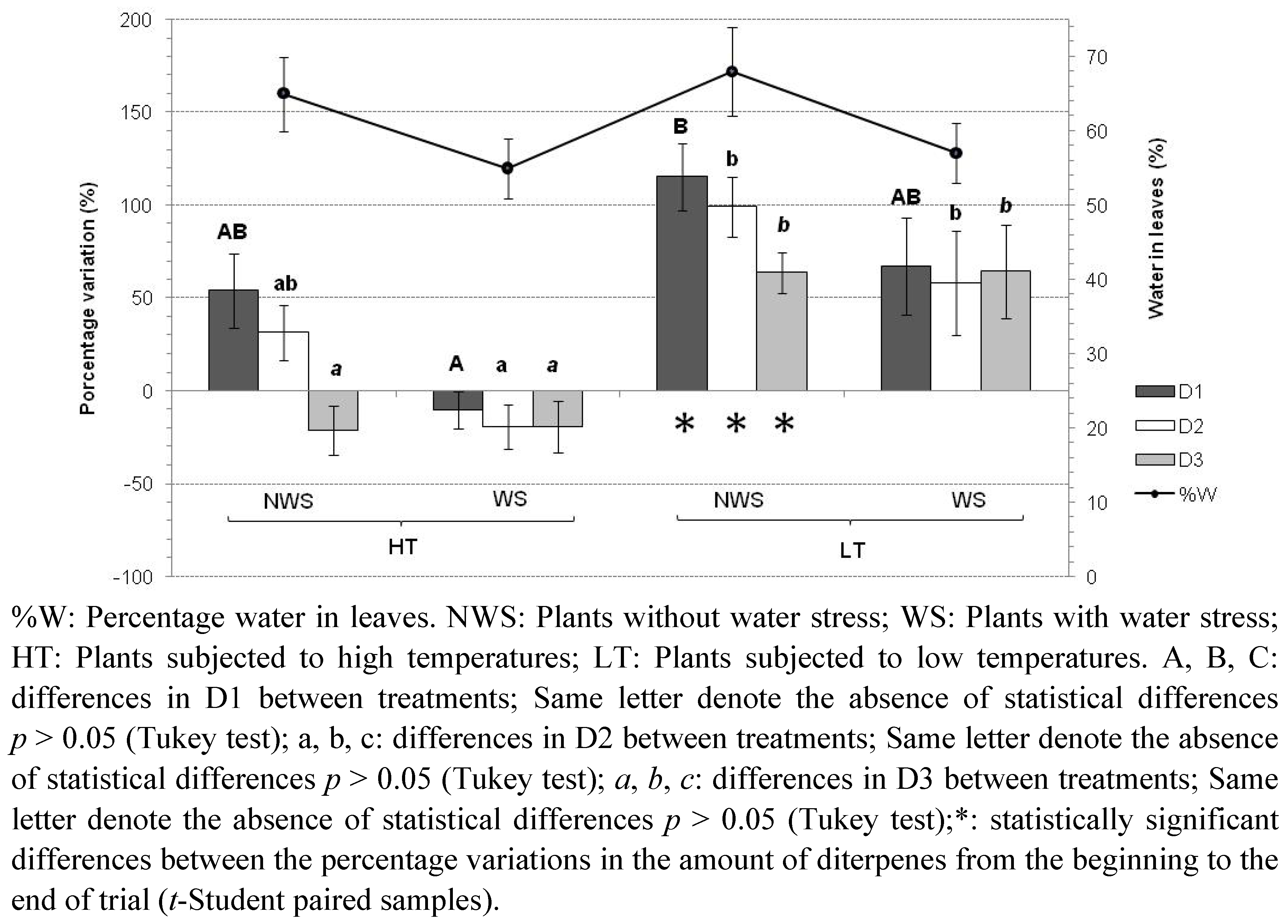
2.2. Temperature and Water Stress
| D1 | Type III Sum of Squares | df | Mean Square | F | Sig. |
| Corrected Model | 51659.677 a | 3 | 17219.892 | 3.756 | 0.025 |
| Intercept | 632425.504 | 1 | 632425.504 | 137.955 | 0.000 |
| Temperature | 31066.47 | 1 | 31066.47 | 6.777 | 0.016 |
| Stress | 20447.496 | 1 | 20447.496 | 4.46 | 0.046 |
| Temperature * Stress | 440.874 | 1 | 440.874 | 0.096 | 0.759 |
| a: R Squared = 329 (Adjusted R Squared = 241); *: Interaction between the two variables. | |||||
| D2 | Type III Sum of Squares | df | Mean Square | F | Sig. |
| Corrected Model | 47756.165 a | 3 | 15918.722 | 7.45 | 0.001 |
| Intercept | 523104.439 | 1 | 523104.439 | 244.799 | 0.000 |
| Temperature | 33921.278 | 1 | 33921.278 | 15.874 | 0.001 |
| Stress | 13645.168 | 1 | 13645.168 | 6.386 | 0.019 |
| Temperature * Stress | 155.981 | 1 | 155.981 | 0.073 | 0.789 |
| a: R Squared = 493 (Adjusted R Squared = 427); *: Interaction between the two variables. | |||||
| D3 | Type III Sum of Squares | df | Mean Square | F | Sig. |
| Corrected Model | 47555.955 a | 3 | 15851.985 | 9.31 | 0.000 |
| Intercept | 383756.337 | 1 | 383756.337 | 225.394 | 0.000 |
| Temperature | 45822.766 | 1 | 45822.766 | 26.913 | 0.000 |
| Stress | 8.728 | 1 | 8.728 | 0.005 | 0.944 |
| Temperature * Stress | 2.305 | 1 | 2.305 | 0.001 | 0.971 |
| a: R Squared = 548 (Adjusted R Squared = 490); *: Interaction between the two variables. | |||||
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Selection of Sampling Points and Samples Collection
| Quintana | Hornachos | Jerez de los | Cabeza | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| de la Serena | Caballeros | la Vaca | |||
| UTM coord. | 30 S 262444 | 29 S 754337 | 29 S 685866 | 29 S 728663 | |
| E 4289018 | E 4273087 | E 4238589 | E 4219514 | ||
| Spring | Tmax (°C) | 25.5 | 24.2 | 24.3 | 25.1 |
| Tmin (°C) | 11.3 | 12.2 | 11.1 | 10.9 | |
| P (mm) | 113 | 139.8 | 126 | 155 | |
| Summer | Tmax (°C) | 34.2 | 32.7 | 33.3 | 34.7 |
| Tmin (°C) | 18.1 | 16.3 | 17.4 | 18.3 | |
| P (mm) | 38 | 44 | 40 | 5 | |
| Autumn | Tmax (°C) | 16.8 | 17.8 | 15.6 | 15.2 |
| Tmin (°C) | 8.4 | 7.9 | 8.7 | 8.8 | |
| P (mm) | 156 | 219 | 300 | 309 | |
| Winter | Tmax (°C) | 14 | 13.9 | 14.4 | 13.9 |
| Tmin (°C) | 5.5 | 6.5 | 5.2 | 4.9 | |
| P (mm) | 130 | 130 | 160 | 187 | |
3.2. Laboratory Trial Conditions
- Trial A: High temperatures (30 °C light; 15 °C dark), without water stress (plants watered every day);
- Trial B: High temperatures, with water stress (plants moderately watered every 10 days);
- Trial C: Low temperatures (13 °C light; 4 °C dark), without water stress;
- Trial D: Low temperatures, with water stress.
3.3. Exudate Extraction
3.4. Sample Analysis; Linear Calibration
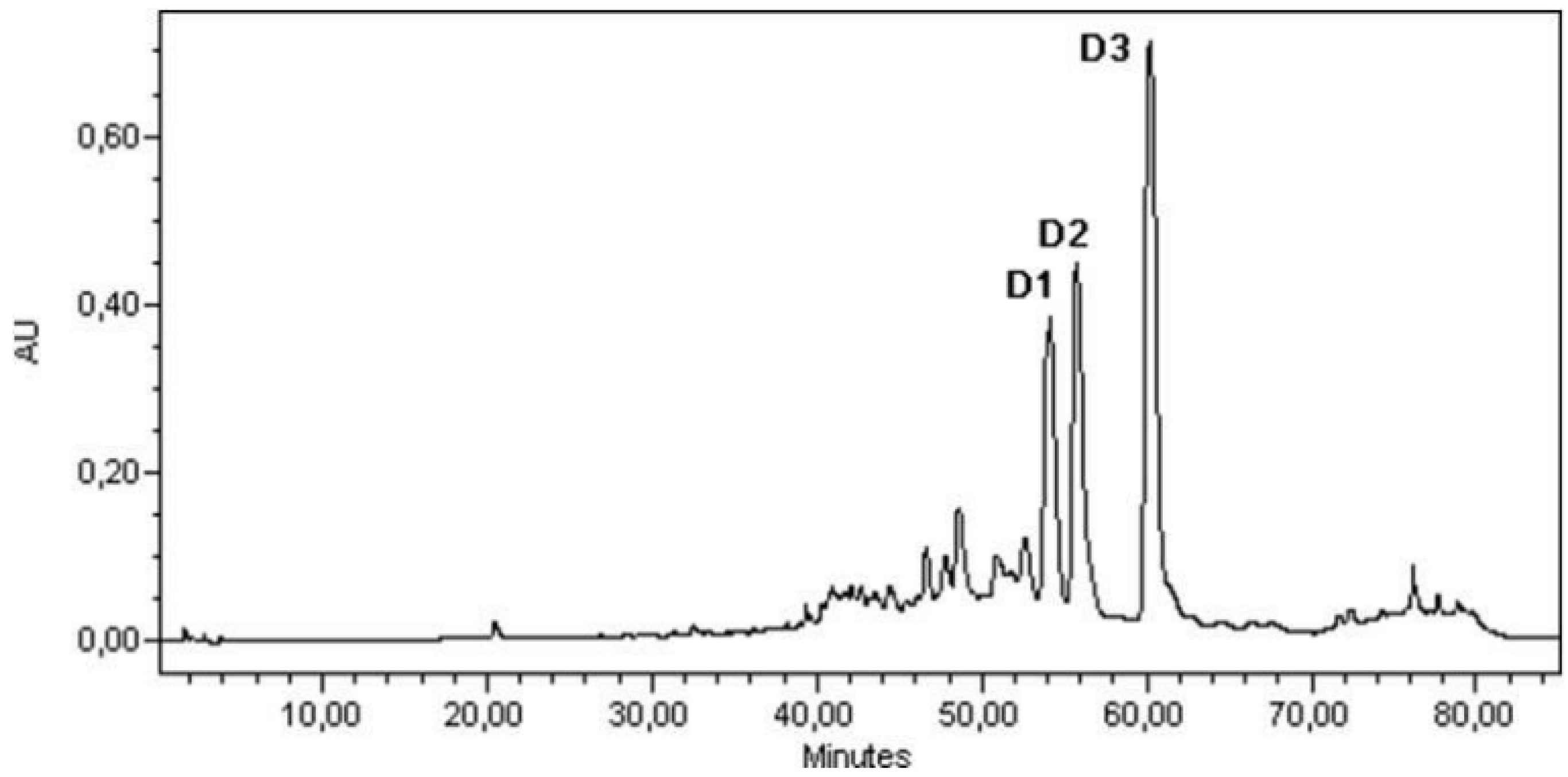
- D1 linear calibration equation: y = 1.1186x; r2 = 0.988;
- D2 linear calibration equation: y = 0.9307x; r2 =0 .998;
- D3 linear calibration equation: y = 1.3238x; r2 = 0.992.
3.5. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
References
- Herrera, C.M. Tipos morfológicos y funcionales en plantas del matorral mediterráneo del sur de España. Stvdia Oecologica 1984, 5, 7–34. [Google Scholar]
- Chaves, N.; Escudero, J.C.; Gutierrez-Merino, C. Seasonal variation of exudate of Cistus ladanifer L. J. Chem. Ecol. 1993, 19, 2577–2591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaves, N.; Ríos, J.L.; Gutiérrez, C.; Escudero, J.C.; Alías, J.M. Analysis of secreted flavonoids of Cistus ladanifer L. by high-performance liquid chromatography-particle beam mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. 1998, 799, 111–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascual, T.; Urones, J.G.; Basage, P.; Marcos, I.S.; Montaña, A. Nuevo estudio sobre componentes de Cistus ladanifer L. Stud. Chem. Univ. Salamanca 1984, 9, 31–47. [Google Scholar]
- Bell, E.A. The possible significance of secondary compounds in plants. In Secundary Plant Products; Bell, E.A., Charlwood, B.V., Eds.; Springer-Verlag: New York, NY, USA, 1980; pp. 11–21. [Google Scholar]
- Larcher, W. Temperature stress and survival ability of Mediterranean sclerophyllous plants. Plant Biosyst. 2000, 134, 279–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cen, Y.P.; Bornman, J.F. The effect of exposure to enhanced UV-B radiation on the penetration of monochromatic and polychromatic UV-B radiation in leaves of Brassica napus. Physiol. Plantarum 1993, 87, 249–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaves, N.; Escudero, J.C.; Gutiérrez-Merino, C. Role of ecological variables in the seasonal variation of flavonoid content of Cistus ladanifer L. exudate. J. Chem. Ecol. 1997, 23, 579–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaves, N.; Sosa, T.; Alías, J.C.; Escudero, J.C. Identification and effects of the interaction of phytotoxic compounds from exudate of Cistus ladanifer L. leaves. J. Chem. Ecol. 2001, 27, 611–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sosa, T.; Chaves, N.; Alías, J.C.; Escudero, J.C.; Henao, F.; Gutiérrez-Merino, C. Inhibition of mouth skeletal muscle relaxation by flavonoids of Cistus ladanifer L.: A plant defense mechanism against herbivores. J. Chem. Ecol. 2004, 30, 1087–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaves, N.; Escudero, J.C. Allelopathic effect of Cistus ladanifer L. on seed germination. Funct. Ecol. 1997, 11, 432–440. [Google Scholar]
- Alías, J.C. Influencia de los factores climáticos en la síntesis y actividad de compuestos fitotóxicos secretados por Cistus ladanifer L. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Extremadura, Badajoz, Spain, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Pascual, T.; Urones, J.G.; Gonzalez, M. Terpenoides monohidroxilados de la gomorresina de Cistus ladaniferus L. An. Quím. 1977, 73, 1024–1028. [Google Scholar]
- Pascual, T.; Urones, J.G.; Basabe, P.; Aubanell, F.H. Componentes minoritarios de Cistus ladaniferus L.: Lactosas. An. Quím. 1979, 75, 335–340. [Google Scholar]
- Pascual, T.; Bellido, I.S.; Basabe, P.; Urones, J.G. Labdane diterpenoids from Cistus ladaniferus L. Phytochemistry 1982, 21, 899–901. [Google Scholar]
- Alías, J.C.; Simonet, A.M.; Torres, A.; Sosa, T.; Chaves, N.; Macías, F.A. Determination of the allelopathic activity of diterpenes of the exudate of Cistus ladanifer L. In Proceeding of the IV Congress on Allelopathy: Establishing the scientific bases, Wagga-wagga, Australia, 21–26 August 2005; Harper, J.D.I., An, M., Wu, H., Kent, J.H., Eds.; International Allelopathy Society: Wagga-wagga, Australia, 2005; pp. 396–398. [Google Scholar]
- Sosa, T.; Alías, J.C.; Escudero, J.C.; Chaves, N. Oxocativic acid: The diterpene possible responsible for the allelopathic activity of Cistus ladanifer L. In Proceeding of the IV Congress on Allelopathy: Establishing the scientific bases, Wagga-wagga, Australia, 21–26 August 2005; Harper, J.D.I., An, M., Wu, H., Kent, J.H., Eds.; International Allelopathy Society: Wagga-wagga, Australia, 2005; pp. 410–412. [Google Scholar]
- Lerdau, M.; Peñuelas, J. Los terpenos en la atmosfera: Vínculos entre la biosfera y la atmósfera. Mundo Científico 1993, 131, 60–63. [Google Scholar]
- Gershenzon, J. Metabolic cost of terpenoid accumulation in higher plants. J. Chem. Ecol. 1994, 20, 1281–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owena, S.M.; Harleyb, P.; Guentherb, A.; Hewitta, C.N. Light dependency of VOC emissions from selected Mediterranean plant species. Atmos. Environ. 2002, 36, 3147–3159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivoal, A.; Fernandez, C.; Lavoir, A.-V.; Olivier, R.; Lecareux, C.; Greff, S.; Roche, P.; Vila, B. Environmental control of terpene emissions from Cistus monspeliensis L. in natural Mediterranean shrublands. Chemosphere 2010, 78, 942–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Munné-Bosch, S.; Alegre, L.; Schwarz, K. The formation of phenolic diterpenes in Rosmarinus officinalis L. under Mediterranean climate. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2000, 210, 263–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levinsohn, E.; Gijzen, M.; Muzika, R.M.; Barton, K.; Croteau, R. Oleoresinosis in grand fir (Abies grandis) saplings and mature trees: Modulation of this wound response by light and water stresses. Plant Physiol. 1993, 101, 1021–1028. [Google Scholar]
- Llusià, J.; Peñuelas, J.; Alessio, G.A.; Estiarte, M. Seasonal contrasting changes of foliar concentrations of terpenes and other volatile organic compound in tour dominant species of a Mediterranean shrubland submitted to a field experimental drought and warming. Physiol. Plant. 2006, 127, 632–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanch, J.S.; Peñuelas, J.; Sardans, J.; Llusià, J. Drought, warming and soil fertilization effects on leaf volatile terpene concentrations in Pinus halepensis and Quercus ilex. Acta Physiol. Plant 2009, 31, 207–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sosa, T.; Alías, J.C.; Escudero, J.C.; Chaves, N. Interpopulational variation in flavonoid composition of Cistus ladanifer L. exudate. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2005, 33, 353–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paiva, N.L. An introduction to the biosynthesis of chemicals used in plant microbe communication. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2000, 19, 131–143. [Google Scholar]
- Chaves, N.; Sosa, T.; Alías, J.C.; Escudero, J.C. Germination inhibition of herbs in Cistus ladanifer L. soils: Possible involvement of allelochemiclas. Allelopathy J. 2003, 11, 31–42. [Google Scholar]
- Alías, J.C.; Sosa, T.; Escudero, J.; Chaves, N. Autotoxicity against germination and seedling emergence in Cistus ladanifer L. Plant Soil 2006, 282, 327–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabezas, J.; Núñez, E.; Escudero, J.C. Distribución espacial y temporal de las precipitaciones en la provincia de Badajoz y cuantificación de los volúmenes de agua precipitada por planimetría, 1st ed; Consejería de Agricultura y Comercio, Junta de Extremadura: Badajoz, Spain, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Valares, C.; Alías, J.C.; Sosa, T.; Chaves, N. Estudio sobre las posibles vías de incorporación de sustancias alelopáticas al suelo. Cuad. Soc. Esp. Cienc. For. 2008, 25, 425–430. [Google Scholar]
- Cabezas, J.; Escudero, J.C. Estudio termométrico de la provincia de Badajoz, 1st ed; Dirección General de Investigación, Extensión y Capacitación Agrarias: Badajoz, Spain, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Vogt, T.; Gülz, P.G. Isocratic column liquid chromatographic separation of a complex mixture of epicuticular flavonoid aglycones and intracellelar flavonol glycosides from Cistus laurifolius L. J. Chromatogr. 1991, 537, 453–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2012 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Alías, J.C.; Sosa, T.; Valares, C.; Escudero, J.C.; Chaves, N. Seasonal Variation of Cistus ladanifer L. Diterpenes. Plants 2012, 1, 6-15. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants1010006
Alías JC, Sosa T, Valares C, Escudero JC, Chaves N. Seasonal Variation of Cistus ladanifer L. Diterpenes. Plants. 2012; 1(1):6-15. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants1010006
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlías, Juan Carlos, Teresa Sosa, Cristina Valares, José Carlos Escudero, and Natividad Chaves. 2012. "Seasonal Variation of Cistus ladanifer L. Diterpenes" Plants 1, no. 1: 6-15. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants1010006
APA StyleAlías, J. C., Sosa, T., Valares, C., Escudero, J. C., & Chaves, N. (2012). Seasonal Variation of Cistus ladanifer L. Diterpenes. Plants, 1(1), 6-15. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants1010006






