Phosphorylation Affects DNA-Binding of the Senescence-Regulating bZIP Transcription Factor GBF1
Abstract
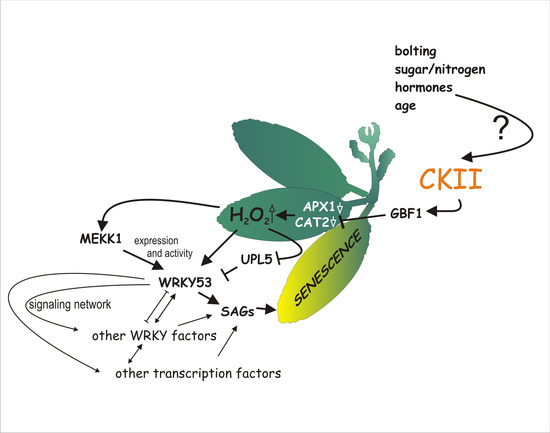
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. GBF1 Is Phosphorylated by CKII

2.2. GBF1 DNA-Binding Is Altered through Phosphorylation by CKII or Phosphorylation Mimicry


2.3. Senescence Phenotype of ckIIα Mutant Lines

3. Discussion

4. Experimental Section
4.1. Plant Material
4.2. Senescence Phenotyping
4.3. Recombinant Proteins
4.4. Western Blot Analysis and Immune Detection of 6×His-Tagged GBF1
4.5. DPI-ELISA
4.6. Site-Directed Mutagenesis
4.7. In Vitro Kinase Assay
4.8. Semi-quantitative RT PCR
| Forward Primer 5′–3′ | Reverse Primer 5′–3′ | |
|---|---|---|
| GBF1 | ggtcgaaagatggtgaagga | atccgattccaatcacgaag |
| CKIIa1 | ttgatccacaactggaagca | cattaccatcatcatcatcatcag |
| CKIIa2 | gcatttggtctcacctgagg | gaaaccggagggagtaataagaa |
| SAG12 | cccggttaatgatgagcaagc | gctttcatggcaagaccaca |
| CAT2 | caggttcgtcatgctgagaag | ttagatgcttggtctcacgtt |
| RBCS1a | attgcctacaagccaccaag | atttgtagccgcattgtcct |
| WRKY53 | gatcacaagaacaccaccattagcc | aaagttgtgtcaatctcgaccgttg |
4.9. Intracellular Hydrogen Peroxide Measurements
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Files
Supplementary File 1Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Balazadeh, S.; Riano-Pachon, D.M.; Mueller-Roeber, B. Transcription factors regulating leaf senescence in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Biol. 2008, 10, S63–S75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zentgraf, U.; Jobst, J.; Kolb, D.; Rentsch, D. Senescence-related gene expression profiles of rosette leaves of Arabidopsis thaliana: Leaf age versus plant age. Plant Biol. 2004, 6, 178–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breeze, E.; Harrison, E.; McHattie, S.; Hughes, L.; Hickman, R.; Hill, C.; Kiddle, S.; Kim, Y.S.; Penfold, C.A.; Jenkins, D.; et al. High-resolution temporal profiling of transcripts during Arabidopsis leaf senescence reveals a distinct chronology of processes and regulation. Plant Cell 2011, 23, 873–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buchanan-Wollaston, V.; Page, T.; Harrison, E.; Breeze, E.; Lim, P.O.; Nam, H.G.; Lin, J.F.; Wu, S.H.; Swidzinski, J.; Ishizaki, K.; et al. Comparative transcriptome analysis reveals significant differences in gene expression and signalling pathways between developmental and dark/starvation-induced senescence in Arabidopsis. Plant J. 2005, 42, 567–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Cai, Z.; Gan, S. Transcriptome of Arabidopsis leaf senescence. Plant Cell Environ. 2004, 27, 521–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balazadeh, S.; Siddiqui, H.; Allu, A.D.; Matallana-Ramirez, L.P.; Caldana, C.; Mehrnia, M.; Zanor, M.I.; Köhler, B.; Mueller-Roeber, B. A gene regulatory network controlled by the NAC transcription factor ANAC092/AtNAC2/ORE1 during salt-promoted senescence. Plant J. 2010, 62, 250–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balazadeh, S.; Kwasniewski, M.; Caldana, C.; Mehrnia, M.; Zanor, M.I.; Mueller-Roeber, B.; Xue, G.P. ORS1, an H2O2-responsive NAC transcription factor, controls senescence in Arabidopsis thaliana. Mol. Plant 2011, 4, 346–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zentgraf, U.; Laun, T.; Miao, Y. The complex regulation of WRKY53 during leaf senescence of Arabidopsis thaliana. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 2010, 89, 133–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Y.; Huhn, K.; Brandt, R.; Potschin, M.; Bieker, S.; Straub, D.; Doll, J.; Drechsler, T.; Zentgraf, U.; Wenkel, S. REVOLUTA and WRKY53 connect early and late leaf development in Arabidopsis. Development 2014, 141, 4772–4783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, Y.; Laun, T.; Zimmermann, P.; Zentgraf, U. Targets of the WRKY53 transcription factor and its role during leaf senescence in Arabidopsis. Plant Mol. Biol. 2004, 55, 853–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, A.; Allu, A.D.; Garapati, P.; Siddiqui, H.; Dortay, H.; Asensi-Fabado, M.A.; Munné-Bosch, S.; Zanor, M.I.; Antonio, C.; Tohge, T.; et al. JUNGBRUNNEN1, a reactive oxygen species-responsive NAC transcription factor, regulates longevity in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2012, 24, 482–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uauy, C.; Distelfeld, A.; Fahima, T.; Blechl, A.; Dubcovsky, J. A NAC gene regulating senescence improves grain protein, zinc, and iron content in wheat. Science 2006, 314, 1298–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ulker, B.; Shahid Mukhtar, M.; Somssich, I.E. The WRKY70 transcription factor of Arabidopsis influences both the plant senescence and defense signaling pathways. Planta 2007, 226, 125–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Besseau, S.; Li, J.; Palva, E.T. WRKY54 and WRKY70 co-operate as negative regulators of leaf senescence in Arabidopsis thaliana. J. Exp. Bot. 2012, 63, 2667–2679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimmermann, P.; Heinlein, C.; Orendi, G.; Zentgraf, U. Senescence-specific regulation of catalases in Arabidopsis thaliana (L.) Heynh. Plant Cell Environ. 2006, 29, 1049–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bieker, S.; Riester, L.; Stahl, M.; Franzaring, J.; Zentgraf, U. Senescence-specific alteration of hydrogen peroxide levels in Arabidopsis thaliana and oilseed rape spring variety Brassica napus L. cv. Mozart. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2012, 54, 540–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agüera, E.; Cabello, P.; de la Haba, P. Induction of leaf senescence by low nitrogen nutrition in sunflower (Helianthus annuus) plants. Physiol. Plant. 2010, 138, 256–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, Z.; Rodriguez, R.; Tran, A.; Hoang, H.; de los Santos, D.; Brown, S.; Vellanoweth, R.L. The developmental transition to flowering represses ascorbate peroxidase activity and induces enzymatic lipid peroxidation in leaf tissue in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Sci. 2000, 158, 115–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smykowski, A.; Zimmermann, P.; Zentgraf, U. G-Box binding Factor1 reduces CATALASE2 expression and regulates the onset of leaf senescence in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2010, 153, 1321–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jakoby, M.; Weisshaar, B.; Dröge-Laser, W.; Vicente-Carbajosa, J.; Tiedemann, J.; Kroj, T.; Parcy, F. bZIP transcription factors in Arabidopsis. Trends Plant Sci. 2002, 7, 106–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, R.; Izawa, T.; Chua, N.H. Plant bZIP proteins gather at ACGT elements. FASEB J. 1994, 8, 192–200. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Izawa, T.; Foster, R.; Chua, N.H. Plant bZIP protein DNA binding specificity. J. Mol. Biol. 1993, 230, 1131–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menkens, A.E.; Schindler, U.; Cashmore, A.R. The G-box: A ubiquitous regulatory DNA element in plants bound by the GBF family of bZIP proteins. Trends Biochem. Sci. 1995, 20, 506–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardtke, C.S.; Gohda, K.; Osterlund, M.T.; Oyama, T.; Okada, K.; Deng, X.W. HY5 stability and activity in Arabidopsis is regulated by phosphorylation in its COP1 binding domain. EMBO J. 2000, 19, 4997–5006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirchler, T.; Briesemeister, S.; Singer, M.; Schutze, K.; Keinath, M.; Kohlbacher, O.; Teige, M.; Vicente-Carbajosa, J.; Harter, K.; Chaban, C. The role of phosphorylatable serine residues in the DNA-binding domain of Arabidopsis bZIP transcription factors. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 2010, 89, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siberil, Y.; Doireau, P.; Gantet, P. Plant bZIP G-box binding factors. Modular structure and activation mechanisms. Eur. J. Biochem. 2001, 268, 5655–5666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terzaghi, W.B.; Bertekap, R.L., Jr.; Cashmore, A.R. Intracellular localization of GBF proteins and blue light-induced import of GBF2 fusion proteins into the nucleus of cultured Arabidopsis and soybean cells. Plant J. 1997, 11, 967–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klimczak, L.J.; Schindler, U.; Cashmore, A.R. DNA binding activity of the Arabidopsis G-box binding factor GBF1 is stimulated by phosphorylation by casein kinase II from broccoli. Plant Cell 1992, 4, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Droge-Laser, W.; Kaiser, A.; Lindsay, W.P.; Halkier, B.A.; Loake, G.J.; Doerner, P.; Dixon, R.A.; Lamb, C. Rapid stimulation of a soybean protein-serine kinase that phosphorylates a novel bZIP DNA-binding protein, G/HBF-1, during the induction of early transcription-dependent defenses. EMBO J. 1997, 16, 726–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciceri, P.; Gianazza, E.; Lazzari, B.; Lippoli, G.; Genga, A.; Hoscheck, G.; Schmidt, R.J.; Viotti, A. Phosphorylation of Opaque2 changes diurnally and impacts its DNA binding activity. Plant Cell 1997, 9, 97–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meshi, T.; Moda, I.; Minami, M.; Okanami, M.; Iwabuchi, M. Conserved Ser residues in the basic region of the bZIP-type transcription factor HBP-1a(17): Importance in DNA binding and possible targets for phosphorylation. Plant Mol. Biol. 1998, 36, 125–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, W.H.; Gigot, C. Protein complexes binding to cis elements of the plant histone gene promoters: Multiplicity, phosphorylation and cell cycle alteration. Plant Mol. Biol. 1997, 33, 367–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulekar, J.J.; Bu, Q.; Chen, F.; Huq, E. Casein kinase II α subunits affect multiple developmental and stress-responsive pathways in Arabidopsis. Plant J. 2012, 69, 343–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreno-Romero, J.; Espunya, C.; Platara, M.; Arino, J.; Martinez, M.C. A role for protein kinase CK2 in plant development: Evidence obtained using a dominant-negative mutant. Plant J. 2008, 55, 118–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulekar, J.J.; Huq, E. Expanding roles of protein kinase CK2 in regulating plant growth and development. J. Exp. Bot. 2014, 65, 2883–2893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salinas, P.; Fuentes, D.; Vidal, E.; Jordana, X.; Echeverria, M.; Holuigue, L. An extensive survey of CK2 alpha and beta subunits in Arabidopsis: Multiple isoforms exhibit differential subcellular localization. Plant Cell Physiol. 2006, 47, 1295–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schweer, J.; Türkeri, H.; Link, B.; Link, G. AtSIG6, a plastid sigma factor from Arabidopsis, reveals functional impact of cpCK2 phosphorylation. Plant J. 2010, 62, 192–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, H.-G.; Klessig, D.F. Salicylic acid-inducible Arabidopsis CK2-like activity phosphorylates TGA2. Plant Mol. Biol. 2005, 57, 541–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nieva, C.; Busk, P.K.; Domínguez-Puigjaner, E.; Lumbreras, V.; Testillano, P.S.; Risueño, M.-C.; Pagès, M. Isolation and functional characterisation of two new bZIP maize regulators of the ABA responsive gene rab28. Plant Mol. Biol. 2005, 58, 899–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collinge, M.A.; Walker, J.C. Isolation of an Arabidopsis thaliana casein kinase II beta subunit by complementation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Plant Mol. Biol. 1994, 25, 649–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobrowolska, G.; Meggio, F.; Szczegielniak, J.; Muszynska, G.; Pinna, L.A. Purification and characterization of maize seedling casein kinase IIB, a monomeric enzyme immunologically related to the alpha subunit of animal casein kinase-2. Eur. J. Biochem. 1992, 204, 299–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schindler, U.; Menkens, A.E.; Beckmann, H.; Ecker, J.R.; Cashmore, A.R. Heterodimerization between light-regulated and ubiquitously expressed Arabidopsis GBF bZIP proteins. EMBO J. 1992, 11, 1261–1273. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Meggio, F.; Pinna, L.A. One-thousand-and-one substrates of protein kinase CK2? FASEB J. 2003, 17, 349–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klimczak, L.J.; Collinge, M.A.; Farini, D.; Giuliano, G.; Walker, J.C.; Cashmore, A.R. Reconstitution of Arabidopsis casein kinase II from recombinant subunits and phosphorylation of transcription factor GBF1. Plant Cell 1995, 7, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berberich, S.J.; Cole, M.D. Casein kinase II inhibits the DNA-binding activity of Max homodimers but not Myc/Max heterodimers. Genes Dev. 1992, 6, 166–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellenberger, T.E.; Brandl, C.J.; Struhl, K.; Harrison, S.C. The GCN4 basic region leucine zipper binds DNA as a dimer of uninterrupted alpha helices: Crystal structure of the protein-DNA complex. Cell 1992, 71, 1223–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohler, J.J.; Metallo, S.J.; Schneider, T.L.; Schepartz, A. DNA specificity enhanced by sequential binding of protein monomers. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 11735–11739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Metallo, S.J.; Schepartz, A. Certain bZIP peptides bind DNA sequentially as monomers and dimerize on the DNA. Nat. Struct. Biol. 1997, 4, 115–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreno-Romero, J.; Armengot, L.; Marquès-Bueno, M.M.; Cadavid-Ordóñez, M.; Martínez, M.C. About the role of CK2 in plant signal transduction. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2011, 356, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armengot, L.; Marquès-Bueno, M.M.; Soria-Garcia, A.; Müller, M.; Munné-Bosch, S.; Martínez, M.C. Functional interplay between protein kinase CK2 and salicylic acid sustains PIN transcriptional expression and root development. Plant J. 2014, 78, 411–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Chang, H.; Hu, S.; Lu, X.; Yuan, C.; Zhang, C.; Wang, P.; Xiao, W.; Xiao, L.; Xue, G.P.; et al. Plastid casein kinase 2 knockout reduces abscisic acid (ABA) sensitivity, thermotolerance, and expression of ABA- and heat-stress-responsive nuclear genes. J. Exp. Bot. 2014, 65, 4159–4175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zentgraf, U.; Zimmermann, P.; Smykowski, A. Role of intracellular hydrogen peroxide as signaling molecule for plant senescence. In Senescence; Nagata, T., Ed.; In-tech Open Access Publishing: Rijeka, Croatia, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Panchuk, I.I.; Zentgraf, U.; Volkov, R.A. Expression of the APX gene family during leaf senescence of Arabidopsis thaliana. Planta 2005, 222, 926–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Smykowski, A.; Fischer, S.M.; Zentgraf, U. Phosphorylation Affects DNA-Binding of the Senescence-Regulating bZIP Transcription Factor GBF1. Plants 2015, 4, 691-709. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants4030691
Smykowski A, Fischer SM, Zentgraf U. Phosphorylation Affects DNA-Binding of the Senescence-Regulating bZIP Transcription Factor GBF1. Plants. 2015; 4(3):691-709. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants4030691
Chicago/Turabian StyleSmykowski, Anja, Stefan M. Fischer, and Ulrike Zentgraf. 2015. "Phosphorylation Affects DNA-Binding of the Senescence-Regulating bZIP Transcription Factor GBF1" Plants 4, no. 3: 691-709. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants4030691
APA StyleSmykowski, A., Fischer, S. M., & Zentgraf, U. (2015). Phosphorylation Affects DNA-Binding of the Senescence-Regulating bZIP Transcription Factor GBF1. Plants, 4(3), 691-709. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants4030691