Effect of Different Silicon Sources on Yield and Silicon Uptake of Rice Grown under Varying Phosphorus Rates
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Effect of Silicon and Phosphorus on Rice Agronomics, Phosphorus, and Silicon Uptake
2.2. Effect of Silicon and Phosporus Fertilization on Soil pH, and Soil and Plant Nutrient Composition
2.3. Evaluation of Silicon Absorption of Rice Treated with Foliar- and Soil-Applied Silicon Fertilizers
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Treatment Structure and Experimental Design
4.2. Experiment Establishment
4.3. Biomass Sampling, Harvesting, and Soil Sampling
4.4. Plant Analysis
4.5. Soil Analysis
4.6. Scanning Electron Microscopy and Energy Dispersive X-ray Analysis
4.7. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wailes, E.J.; Cramer, G.L.; Chavez, E.C.; Hansen, J.M. Arkansas Global Rice Model: International Baseline Projections for 1997–2010; Arkansas Agricultural Experiment Station Special Report; Arkansas Agricultural Experiment Station: Fayetteville, AR, USA, 1997; p. 177. [Google Scholar]
- United States Department of Agriculture-Economic Research Service. 2015. Rice Outlook/RCS-15L/December11. Available online: http://usda.mannlib.cornell.edu/usda/current/RCS/RCS-12-11-2015.pdf (accessed on 18 January 2015).
- Georgescu, M.; Lobell, D.B.; Field, C.B. Direct climate effects of perennial bioenergy crops in the United States. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 4307–4312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lobell, D.B.; Schlenker, W.; Costa-Roberts, J. Climate trends and global crop production since 1980. Science 2011, 333, 616–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdullah, M.Y. Climate Change and Food Security. 2007. Available online: http://www.undp.org.my/uploads/g_Food_security_MARDI.pdf (accessed on 3 January 2015).
- Tao, F.; Hayashi, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Sakamoto, T.; Yokozawa, M. Global warming, rice production and water use in China: Developing a probabilistic assessment. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2008, 148, 94–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masud, M.M.; Rahman, M.S.; Al-Amin, A.Q.; Kari, F.; Filho, W.L. Impact of climate change: An empirical investigation of Malaysian rice production. Mitig. Adapt. Strat. Glob. Chang. 2014, 19, 431–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruhn, P.; Goletti, F.; Yudelman, M. Integrated Nutrient Management, Soil Fertility and Sustainable Agriculture: Current Issues and Future Challenges; IFRPI/FAO Workshop: Rome, Italy, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Dobermann, A.; Fairhurst, T. Economics of fertilizer use. In Rice: Nutrient Disorders & Nutrient Management; Potash & Phosphate Institute; Potash & Phosphate Institute of Canada; International Rice Research Institute: Los Baños, Philippines, 2000; pp. 50–119. [Google Scholar]
- Rodrigues, F.Á.; Datnoff, L.E. Silicon and Plant Diseases, 1st ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 67–100. [Google Scholar]
- Hunt, J.W.; Dean, A.P.; Webster, R.E. A novel mechanism by which silica defends grasses against herbivore. Ann. Bot. 2008, 102, 653–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, H.J.; Zhu, X.Y.; Chen, K.M. Silicon alleviates oxidative damage of wheat plants in pots under drought. Plant Sci. 2005, 169, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epstein, E. The anomaly of silicon in plant biology. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1991, 91, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarie, S.; Agata, W.; Kaufman, P.B. Involvement of silicon in the senescence of rice leaves. Plant Prod. Sci. 1998, 1, 104–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horiguchi, T. Mechanism of manganese toxicity and tolerance of plants. IV. Effects of silicon on alleviation of manganese toxicity of rice plants. Jpn. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 1988, 34, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savant, N.K.; Snyder, G.H.; Datnoff, L.E. Silicon management and sustainable rice production. Adv. Agron. 1997, 58, 151–199. [Google Scholar]
- Friesen, D.K.; Sanz, J.I.; Correa, F.J.; Winslow, M.D.; Okada, K.; Datnoff, L.E.; Snyder, G.H. Silicon deficiency of upland rice on highly weathered Savanna soils in Colombia. I. Evidence of a major yield constraint. In Proceedings of the IX Conferencia Internacional de arroz para America Latina e para o Caribe and V Reuniao Nacional de Pesquisa de Arroz, Castrois Park Hotel, Goiania, Goias, Brazil, 5 September 1994. [Google Scholar]
- International Rice Research Institute (IRRI). Annual Report 1965; IRRI: Los Banos, Laguna, Philippines, 1966. [Google Scholar]
- Indian Agriculture Research Institute (IARI). Annual Report 1987; IARI: New Delhi, India, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, J.F.; Takahashi, E. The effect of silicic acid on rice in a P-deficient soil. Plant Soil 1990, 126, 121–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noda, M.; Komai, Y. Effect of silicate materials on the availability of inorganic phosphate in the soil. In Studies on the Maximizing the Yield of Agricultural Products by the Application of Silicate Materials; Monbusho: Tokyo, Japan, 1958; pp. 100–115. [Google Scholar]
- Roy, A.C.; Ali, M.Y.; Fox, R.L.; Silva, J.A. Influence of calcium silicate on phosphate solubility and availability in Hawaiian Latosols. Proc. Int. Sympos. Soil Fertil. Eval. 1971, 1, 757–765. [Google Scholar]
- Syouji, K. Application effect of calcium silicate, rice straw and citrate on phosphorus availability in soil. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 1981, 52, 253–259. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, T.H.; Mahler, R.L. Effects of phosphorus and acidity on levels of silica extracted from a Palouse silt loam. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1987, 51, 674–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastisse, E.M. Recherches sur les conditions theoriques et practiques permettant le maintien de l'assimilabilit6 de l’acide phosphorique dans les terres latritiques. Annu. Agron. 1947, 16, 463–475. [Google Scholar]
- Reifenberg, A.; Buckwold, S. The release of silica from soils by the orthophosphate anion. J. Soil Sci. 1954, 5, 106–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, J.A. Possible mechanisms for crop response to silicate applications. Proc. Int. Sympos. Soil Fertil. Eval. 1971, 1, 805–814. [Google Scholar]
- Hingston, F.J.; Posner, A.M.; Quirk, J.P. Anion adsorption by goethite and gibbsite. The role of proton in determining adsorption envelopes. J. Soil Sci. 1972, 23, 177–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, R.; Furtini-Neto, A.E.; Santos, C.D.; Fernandes, L.A.; Curi, N.; Rodrigues, D.C. Interações silício-fósforo em solos cultivados com eucalipto em casa de vegetação. Pesq. Agropecu. Bras. 2001, 36, 557–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, C.C. Disponibilidade de fósforo para a cana-de-açúcar em solo tratado com compostos orgânicos ricos em silício. Rev. Bras. Eng. Agríc. Ambient. 2011, 15, 1222–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foy, C.D. Soil chemical factors limiting plant root growth. Adv. Soil Sci. 1992, 19, 97–149. [Google Scholar]
- Datnoff, L.E.; Snyder, G.H.; Kornodörfer, G.H. Silicon in Agriculture. Studies in Plant Science; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- International Rice Research Institute (IRRI). Annual Report 1977; IRRI: Los Banos, Laguna, Philippines, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Haynes, R.J.; Belyaeva, O.N.; Kingston, G. Evaluation of industrial wastes as sources of fertilizer silicon using chemical extractions and plant uptake. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2013, 176, 238–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, R.T.X.; Korndorfer, G.H. Slag efficacy as a lime and silicon source for rice crops through the biological method. J. Plant Nutr. 2010, 33, 1103–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guével, M.H.; Menzies, J.G.; Bélanger, R.R. Effect of root and foliar applications of soluble silicone on powdery mildew control and growth of wheat plants. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2007, 119, 429–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cacique, I.S.; Domiciano, G.P.; Moreira, W.R.; Rodrigues, F.Á.; Cruz, M.F.A.; Serra, N.S.; Català, A.B. Effect of root and leaf applications of soluble silicon on blast development in rice. Bragantia 2013, 72, 304–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowen, P.A.; Menzies, J.G.; Ehret, D.L. Soluble silicon sprays inhibit powdery mildew development on grape leaves. J. Am. Soc. Hortic. Sci. 1992, 117, 906–912. [Google Scholar]
- Menzies, J.G.; Bowen, P.A.; Ehret, D.L.; Glass, A.D.M. Foliar applications of potassium silicate reduce severity of powdery mildew on cucumber, muskmelon, and zucchini squash. J. Am. Soc. Hortic. Sci. 1992, 112, 902–905. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, Y.C.; Sun, W.C.; Si, J.; Römheld, V. Effects of foliar- and root-applied silicon on the enhancement of induced resistance to powdery mildew in Cucumis sativus. Plant Pathol. 2005, 54, 678–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crusciol, C.A.C.; Soratto, R.P.; Castro, G.S.A.; Neto, J.F.; Costa, C.H.M. Leaf application of silicic acid to upland rice and corn. Ciênc. Agrár. 2013, 34, 2803–2808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Crusciol, C.A.C.; Soratto, R.P.; Castro, G.S.A.; Costa, C.H.M.; Neto, J.F. Foliar application of stabilized silicic acid on soybean, common bean, and peanut. Rev. Ciênc. Agron. 2013, 44, 404–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamai, K.; Ma, J.F. Characterization of silicon uptake by rice roots. New Phytol. 2003, 158, 431–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.F.; Tamai1, K.; Yamaji, N.; Mitani, N.; Konishi, S.; Katsuhara, M.; Ishiguro, M.; Murata, Y.; Yano, M. A silicon transporter in rice. Nature 2006, 440, 668–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.F.; Yamaji, N.; Mitani, N. An efflux transporter of silicon in rice. Nature 2007, 448, 209–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaji, N.; Sakurai, G.; Mitani-Ueno, N.; Ma, J.F. Orchestration of three transporters and distinct vascular structures in node for intervascular transfer of silicon in rice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 11401–11406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prakash, N.B.; Chandrashekar, N.; Mahendra, C.; Patil, S.U.; Thippeshappa, G.N.; Laane, H.M. Effect of foliar spray of soluble silicic acid on growth and yield parameters of wetland rice in hilly and coastal zone soils of Karnataka, south India. J. Plant Nutr. 2011, 34, 1883–1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, K.K.; Singh, K. Effect of N and Si on growth, yields attribute and yield of rice in Alfisols. Int. Rice Res. Notes 2005, 12, 40–41. [Google Scholar]
- Deren, C.W.; Datnoff, L.E.; Snyder, G.H.; Martin, F.G. Silicon concentration, disease response, and yield components of rice genotypes grown on flooded organic histosols. Crop Sci. 1994, 34, 733–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.C.; Ma, T.S.; Li, F.J.; Feng, Y.J. Silicon availability and response of rice and wheat to silicon in calcareous soils. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 1994, 25, 2285–2297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korndorfer, G.H.; Arantes, V.A.; Correa, G.F.; Snyder, G.H. Effect of calcium silicate on silicon content and grain yield of upland rice. Rev. Bras. Cienc. Solo 1999, 23, 635–641. [Google Scholar]
- Crusciol, C.A.C.; Pulz, A.L.; Lemos, L.B.; Soratto, R.P.; Lima, G.P.P. Effects of silicon and drought stress on tuber yield and leaf biochemical characteristics in Potato. Crop Sci. 2009, 49, 949–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanayakkara, U.N.; Uddin, W.; Datnoff, L.E. Application of silicon sources increases silicon accumulation in perennial ryegrass turf on two soil types. Plant Soil 2008, 303, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steenbjerg, F.; Jakobsen, S.T. Plant nutrition and yield curves. Soil Sci. 1962, 95, 69–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, E.; Naidu, R.; Alston, A.M. Effect of phophorus, sodium, and calcium on arsenic sorption. J. Environ. Qual. 2002, 31, 557–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferguson, J.F.; Jenkins, D.; Eastman, J. Calcium phosphate precipitation at slightly alkaline pH values. Water Pollut. Control Fed. 1973, 45, 620–631. [Google Scholar]
- Tubaña, B.S.; Mascagni, H., Jr.; Wang, J. Soil phosphorus buffer coefficient can improve soil test-based phosphorus recommendation. La. Agric. 2013, 56, 20–21. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, D.E.; Vlamis, J. The effect of silicon on yield and manganese uptake and distribution in the leaves of barley plants grown in culture solutions. Plant Physiol. 1957, 32, 404–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okuda, A.; Takahashi, E. Effect of silicon supply on the injuries due to excessive amounts of Fe, Mn, Cu, As, Al, Co of barley and rice plant. Jpn. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 1962, 33, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Rogalla, H.; Romheld, V. Role of leaf apoplast in silicon-mediated manganese tolerance of Cucumis sativus L. Plant Cell Environ. 2002, 25, 549–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.F. Role of silicon in enhancing the resistance of plants to biotic and abiotic stresses. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2004, 50, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Zhu, Y.G.; Liu, W.J.; Liang, Y.C.; Geng, C.N.; Wang, S.G. Is the effect of silicon on rice uptake of arsenate (AsV) related to internal silicon concentrations, iron plaque and phosphate nutrition. Environ. Pollut. 2007, 148, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.F.; Yamaji, N.; Mitani, N.; Xu, X.Y.; Su, Y.H.; McGrath, S.P.; Zhao, F.J. Transporters of arsenite in rice and their role in arsenic accumulation in rice grain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 9931–9935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rezende, D.C.; Rodrigues, F.A.; Carre-Missio, V.; Schurt, D.A.; Kawamura, K.; Korndorfer, G.H. Effect of root and foliar applications of silicon on brown spot development in rice. Aust. Plant Pathol. 2009, 38, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, J.V.; Rodrigues, C.R.; Luz, J.M.Q.; Carvalho, P.C.; Rodrigues, T.M.; Brito, C.H. Silicato de potássio via foliar no milho: Fotossíntese, crescimento e produtividade. Biosci. J. 2010, 26, 502–513. [Google Scholar]
- Kanto, T.; Miyoshi, A.; Ogawa, T.; Maekawa, K.; Aino, M. Suppressive effect of potassium silicate on powdery mildew of strawberry in hydroponics. J. Gen. Plant Pathol. 2004, 70, 207–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanto, T.; Miyoshi, A.; Ogawa, T.; Maekawa, K.; Aino, M. Suppressive effect of liquid potassium silicate on powdery mildew of strawberry in soil. J. Gen. Plant Pathol. 2006, 72, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallmark, C.T.; Wilding, L.P.; Smeck, N.E. Silicon. In Methods of Soil Analysis, Part 2; Page, A.L., Miller, R.H., Keeney, D.R., Eds.; American Society of Agronomy: Madison, WI, USA, 1982; pp. 263–273. [Google Scholar]
- Kraska, J.E.; Breitenbeck, G.A. Survey the silicon status of flooded rice in Louisiana. Agron. J. 2010, 102, 523–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, J.B.; Wolf, B.; Mills, H.A. Plant Analysis Handbook; Micro-Macro Publishing: Athens, GA, USA, 1991; pp. 23–26. [Google Scholar]
- Korndorfer, G.H.; Snyder, G.H.; Ulloa, M.; Powell, G.; Datnoff, L.E. Calibration of soil and plant silicon for rice production. J. Plant Nutr. 2001, 24, 1071–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehlich, A. Mehlich-3 soil test extractant: A modification of Mehlich-2 extractant. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 1984, 15, 1409–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMullan, D. Scanning electron microscopy. Scanning 2006, 17, 175–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
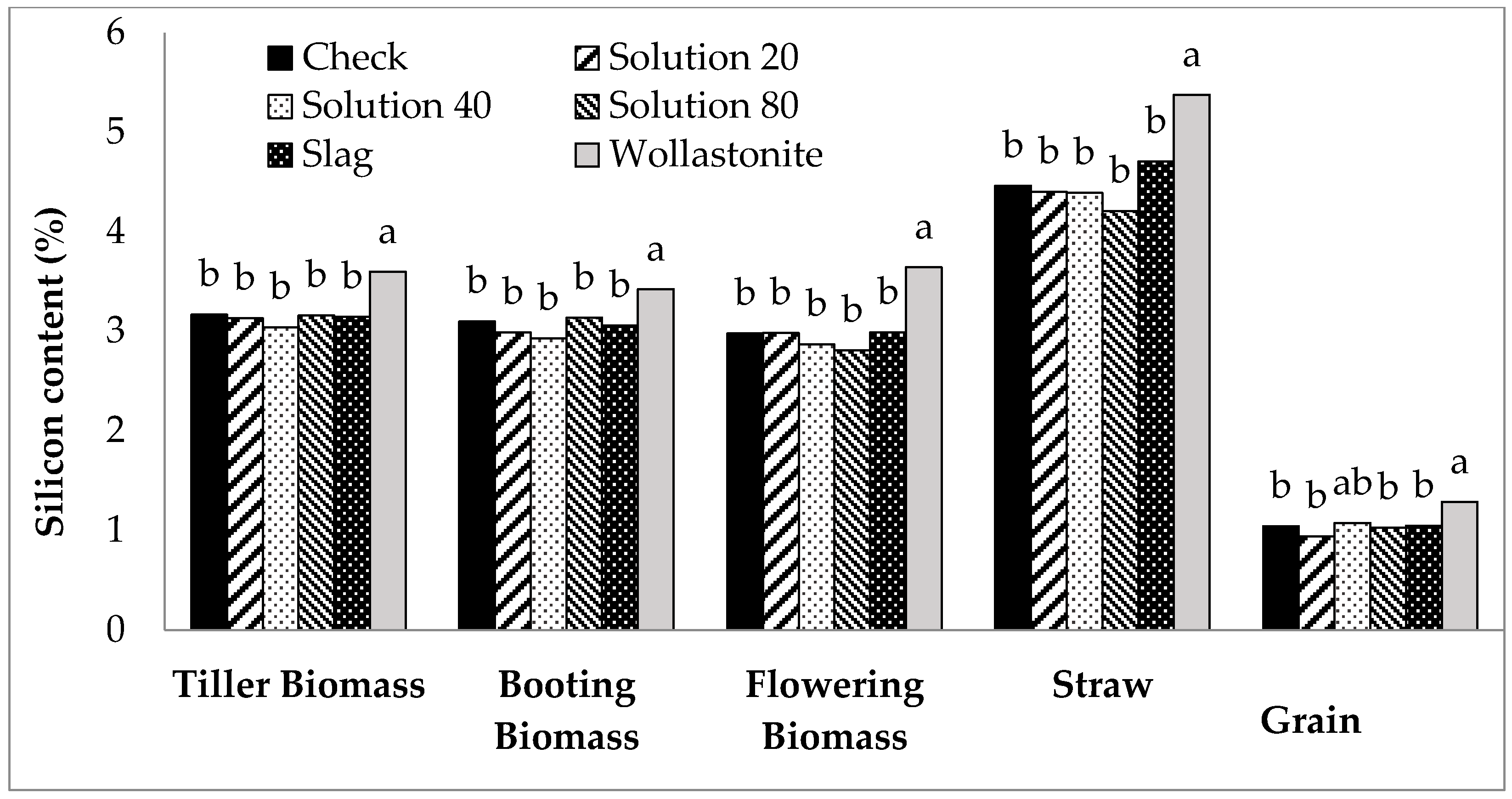
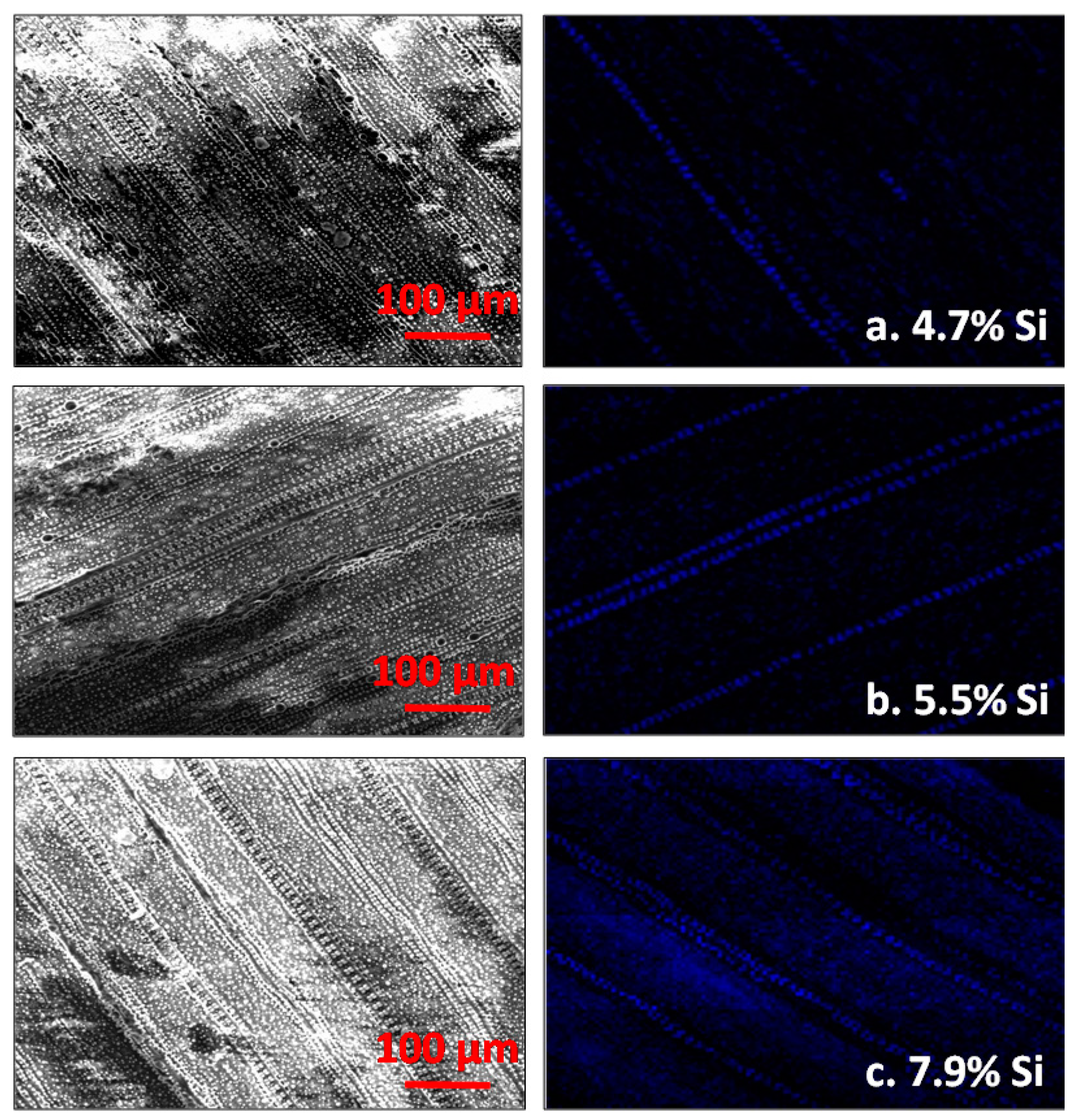

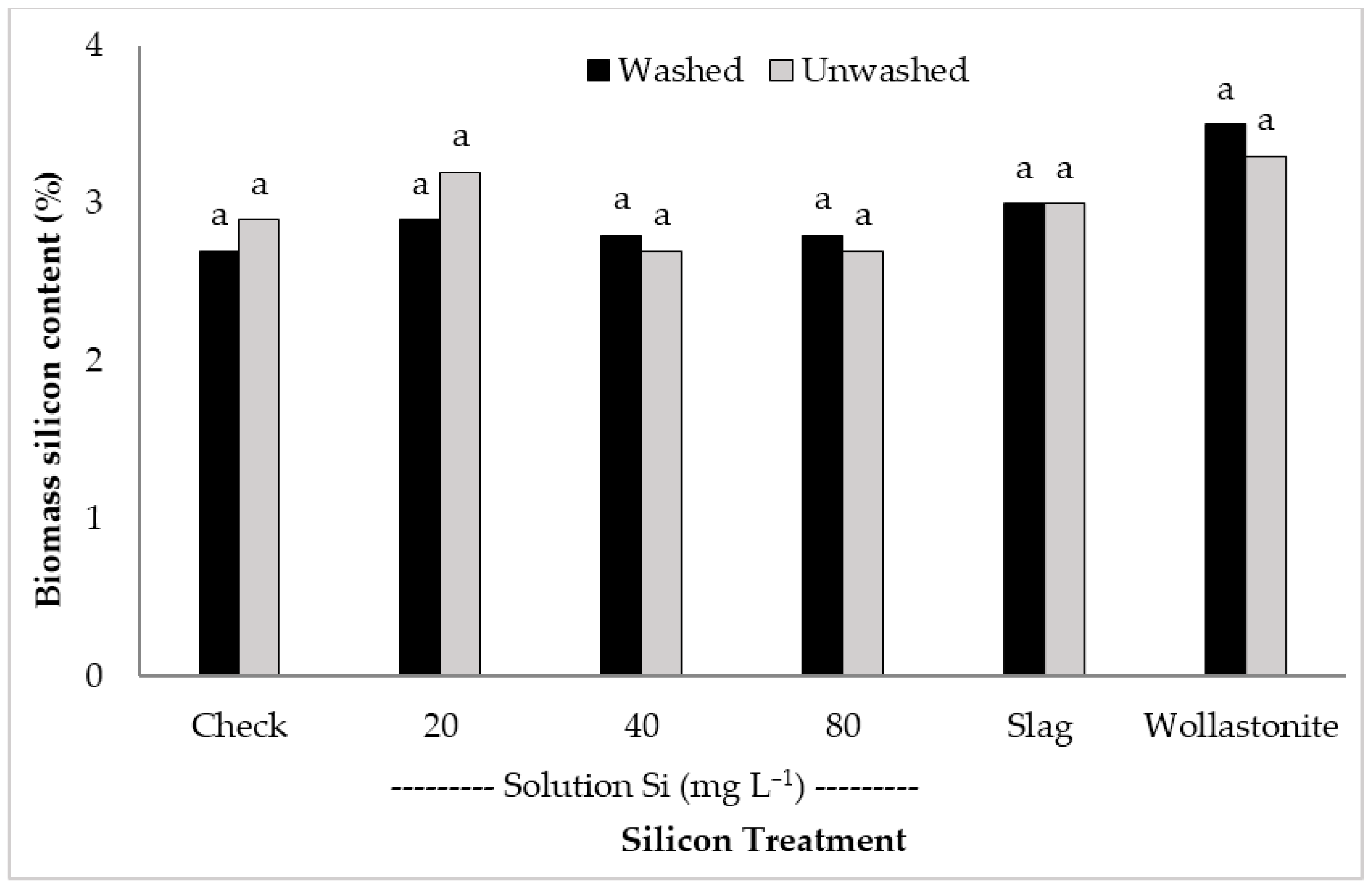
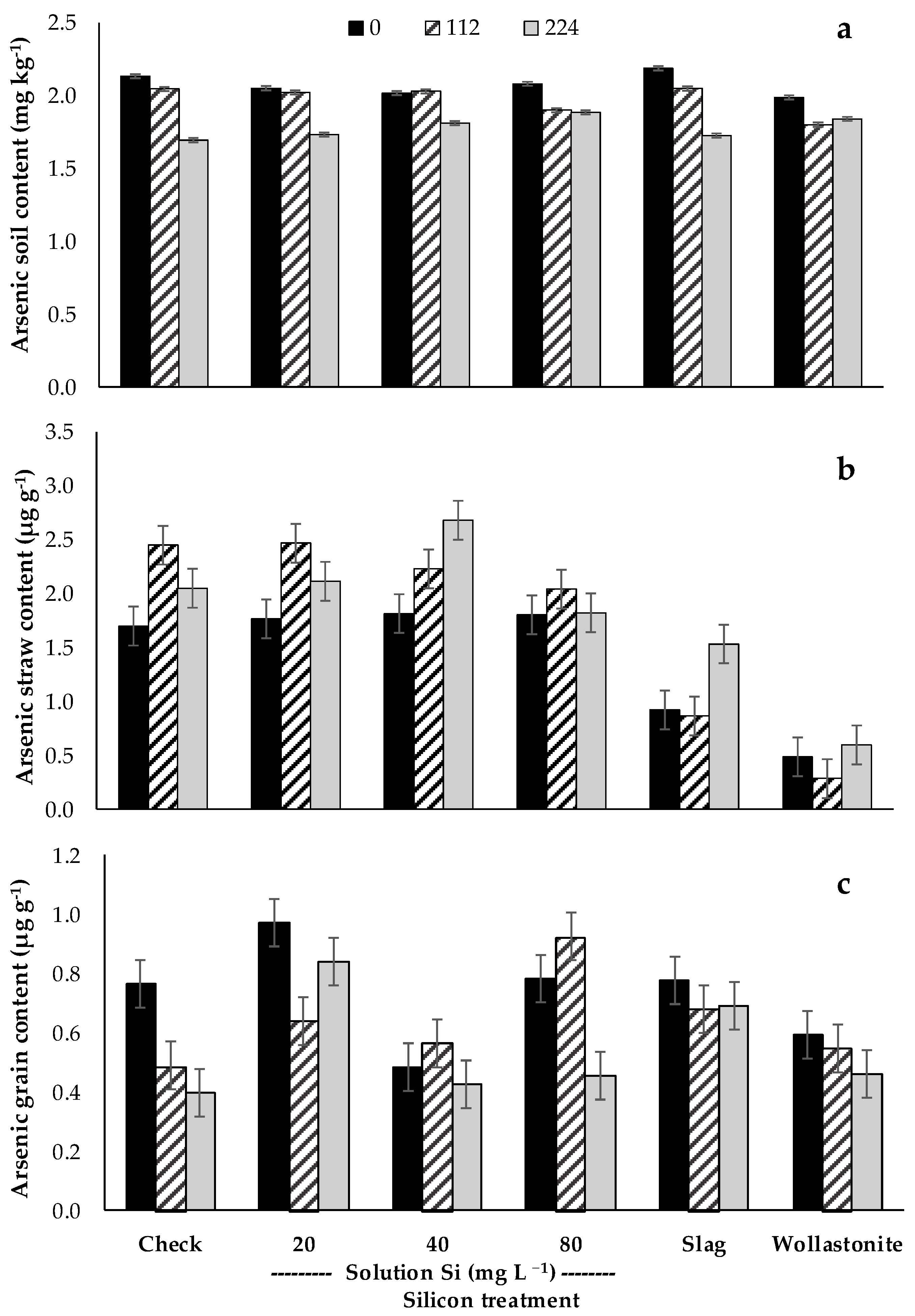
| Treatments | Booting | Flowering | Harvest | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tiller | Biomass | Tiller | Biomass | Tiller | Biomass | Grain | |
| count pot−1 | g pot−1 | count pot−1 | g pot−1 | count pot−1 | g pot−1 | g pot−1 | |
| P rate (P), kg ha−1 | |||||||
| 0 | 9.3 | 17.3 | 6.3 | 19.1 | 17.1 | 73.9 | 42.8 |
| 112 | 8.5 | 17.2 | 5.8 | 18.2 | 17.1 | 71.6 | 41.6 |
| 224 | 8.8 | 19.0 | 6.3 | 19.3 | 17.0 | 73.0 | 42.4 |
| P-value | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS |
| Si treatment (Si) | |||||||
| Check | 7.7 e | 17.2 ab | 6.0 ab | 17.5 ab | 17.4 | 74.6 ab | 43.2 ab |
| Solution, 20 mg L−1 | 9.1 bc | 19.5 ab | 6.7 ab | 21.0 a | 16.8 | 73.6 ab | 42.8 ab |
| Solution, 40 mg L−1 | 9.9 a | 20.9 a | 5.9 ab | 19.0 ab | 17.6 | 74.6 ab | 43.6 ab |
| Solution, 80 mg L−1 | 8.3 de | 16.9 ab | 7.0 a | 21.0 a | 18.1 | 79.4 a | 45.8 a |
| Slag | 9.4 ab | 17.3 ab | 5.9 ab | 19.0 ab | 16.3 | 64.6 b | 37.2 b |
| Wollastonite | 8.8 cd | 15.3 b | 5.3 b | 14.8 b | 16.1 | 70.2 ab | 40.7 ab |
| P-value | NS | NS | <0.05 | <0.05 | NS | <0.05 | <0.05 |
| P × Si | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS |
| Treatments | Soil | Straw | Grains | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | Si | P | Al | Mn | Fe | As | P | Mg | Mn | As | P | Fe | Mn | As | |
| mg kg−1 | % | mg kg−1 | % | mg kg−1 | |||||||||||
| P rate (P), kg ha−1 | |||||||||||||||
| 0 | 7.33 | 57 | 24 c | 643 a | 149 a | 905 a | 0.424 | 0.049 | 0.086 | 417 a | 1.415 | 0.254 | 147 a | 36.9 | 0.728 |
| 112 | 7.35 | 53 | 39 b | 605 b | 134 b | 877 ab | 0.399 | 0.048 | 0.087 | 416 a | 1.723 | 0.244 | 122 ab | 36.3 | 0.640 |
| 224 | 7.28 | 58 | 59 a | 575 b | 130 b | 847 b | 0.385 | 0.050 | 0.081 | 358 b | 1.799 | 0.250 | 114 b | 35.5 | 0.544 |
| P-value | NS | NS | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.01 | NS | NS | <0.01 | NS | <0.05 | NS | |||
| Si treatment (Si) | |||||||||||||||
| Check | 6.97 b | 39 c | 37 b | 651 a | 140 | 894 | 0.398 | 0.052 | 0.074 bc | 423 a | 2.066 | 0.234 | 121 | 38 a | 0.050 |
| Solution, 20 mg L−1 | 7.01 b | 36 c | 38 ab | 634 a | 126 | 860 | 0.399 | 0.052 | 0.089 b | 442 a | 2.116 | 0.263 | 128 | 38 a | 0.817 |
| Solution, 40 mg L−1 | 7.13 b | 37 c | 38 ab | 637 a | 133 | 903 | 0.406 | 0.050 | 0.079 bc | 403 a | 2.242 | 0.263 | 106 | 40 a | 0.491 |
| Solution, 80 mg L−1 | 7.08 b | 37 c | 45 ab | 631 a | 142 | 873 | 0.411 | 0.053 | 0.082 bc | 426 a | 1.889 | 0.239 | 126 | 40 a | 0.720 |
| Slag | 7.79 a | 77 b | 39 ab | 635 a | 143 | 877 | 0.433 | 0.046 | 0.113 a | 393 a | 1.106 | 0.250 | 139 | 31 b | 0.715 |
| Wollastonite | 7.94 a | 106 a | 48 ab | 460 b | 140 | 851 | 0.370 | 0.042 | 0.070 c | 300 b | 0.455 | 0.250 | 148 | 31 b | 0.532 |
| P-value | <0.05 | <0.001 | <0.05 | <0.001 | NS | NS | NS | <0.001 | <0.001 | NS | NS | <0.001 | |||
| P × Si | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | <0.01 | NS | NS | NS | <0.05 | NS | NS | NS | <0.01 |
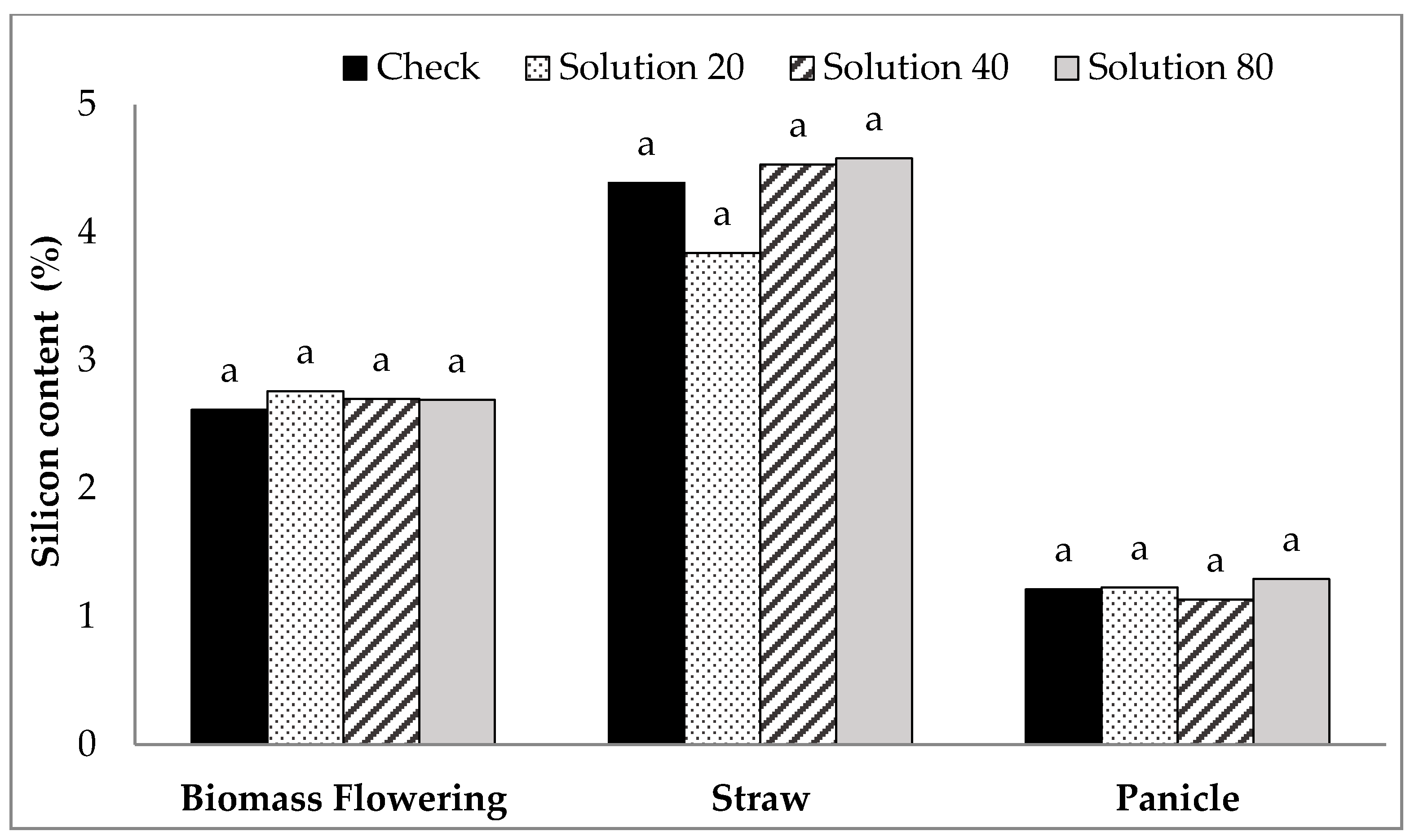
| Treatment | Biomass Si at Flowering (%) | Straw Si (%) | Panicle Si (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tiller with foliar Si | 2.97 | 4.27 | 1.17 |
| Tiller without foliar Si | 2.92 | 4.57 | 1.16 |
| P-value | NS | NS | NS |
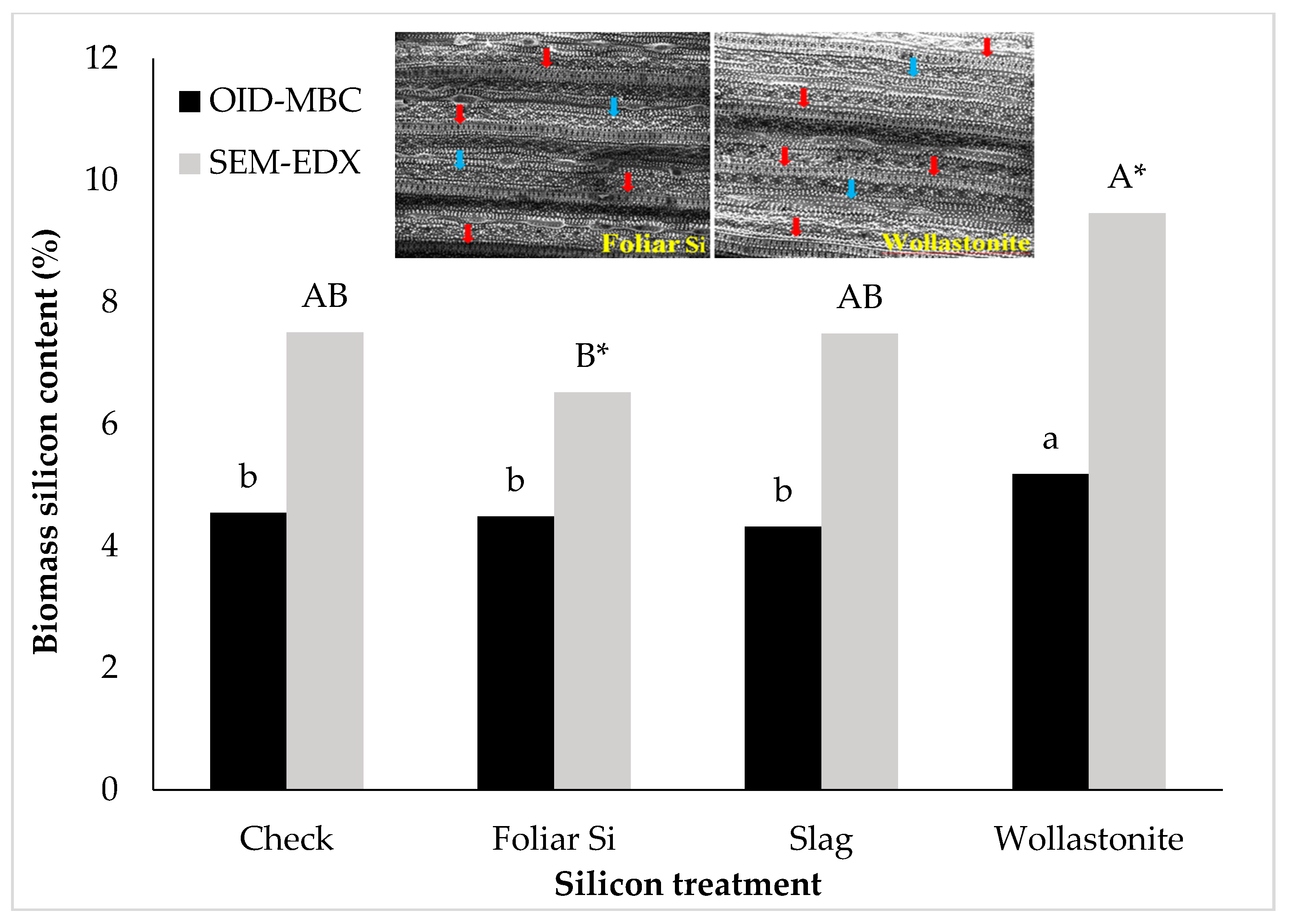
| Variable | Washing Solution | Silicon treatments | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Check | Foliar Si | Slag | Wollastonite | ||
| Silicon in plant biomass (%) | DI water | 4.55 | 4.48 | 4.67 | 5.09 |
| 2% HNO3 | 4.68 | 4.29 | 3.62 | 5.02 | |
| P-value | NS | NS | NS | NS | |
| Silicon in washing solution (µg mL−1) | DI water | 0.01 b | 1.14 b | ND | 0.17 b |
| 2% HNO3 | 0.16 a | 1.63 a | 0.85 | 1.28 a | |
| P-value | <0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 | ||
| Texture | pH (1:1 Water) | Sum of Bases (cmolc dm−3) | CEC (cmolc kg−1) | Extractable Nutrients (mg kg−1) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Si | P | K | Ca | Mg | Na | S | Cu | Zn | ||||
| Silt Loam | 6.14 | 5 | 12 | 37 | 16 | 39 | 756 | 112 | 20 | 14 | 1 | 2 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Agostinho, F.B.; Tubana, B.S.; Martins, M.S.; Datnoff, L.E. Effect of Different Silicon Sources on Yield and Silicon Uptake of Rice Grown under Varying Phosphorus Rates. Plants 2017, 6, 35. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants6030035
Agostinho FB, Tubana BS, Martins MS, Datnoff LE. Effect of Different Silicon Sources on Yield and Silicon Uptake of Rice Grown under Varying Phosphorus Rates. Plants. 2017; 6(3):35. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants6030035
Chicago/Turabian StyleAgostinho, Flavia B., Brenda S. Tubana, Murilo S. Martins, and Lawrence E. Datnoff. 2017. "Effect of Different Silicon Sources on Yield and Silicon Uptake of Rice Grown under Varying Phosphorus Rates" Plants 6, no. 3: 35. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants6030035
APA StyleAgostinho, F. B., Tubana, B. S., Martins, M. S., & Datnoff, L. E. (2017). Effect of Different Silicon Sources on Yield and Silicon Uptake of Rice Grown under Varying Phosphorus Rates. Plants, 6(3), 35. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants6030035




