The Exposure to 2.45 GHz Electromagnetic Radiation Induced Different Cell Responses in Neuron-like Cells and Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture and Treatment
2.2. Blood Sample Collection and PBMC Culture
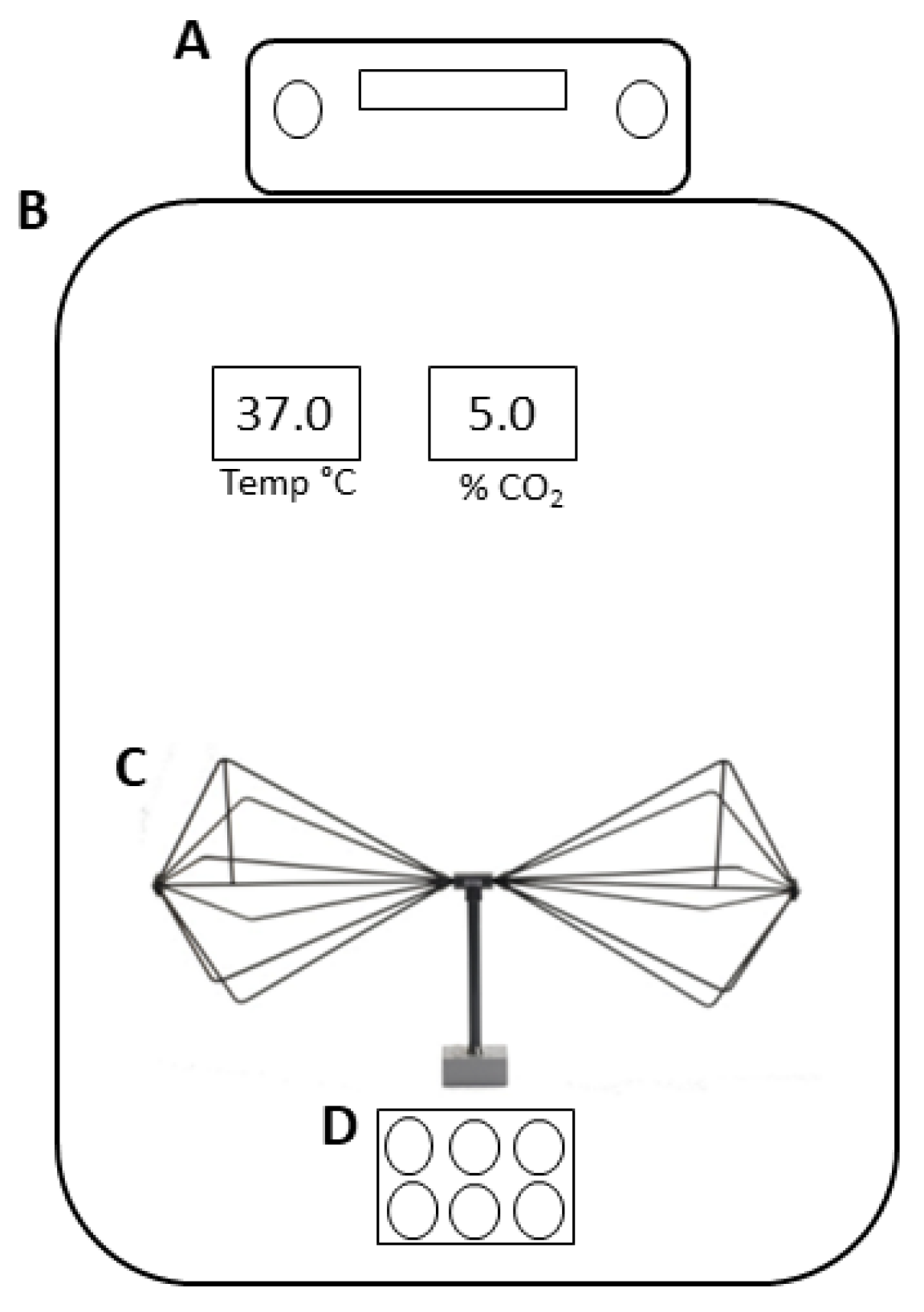
2.3. Experimental Design
- The measurement of EMF out of the incubator with the signal generator switched off;
- The measurement of EMF out of the incubator with the signal generator switched on;
- The measurement of EMF inside the incubator with the signal generator turned off and the electric field probe positioned at 20 cm from the source element antenna;
- The measurement of EMF inside the incubator with the antenna turned on and the electric field probe positioned at 20 cm from the source element antenna.
2.4. Cell Viability Assay
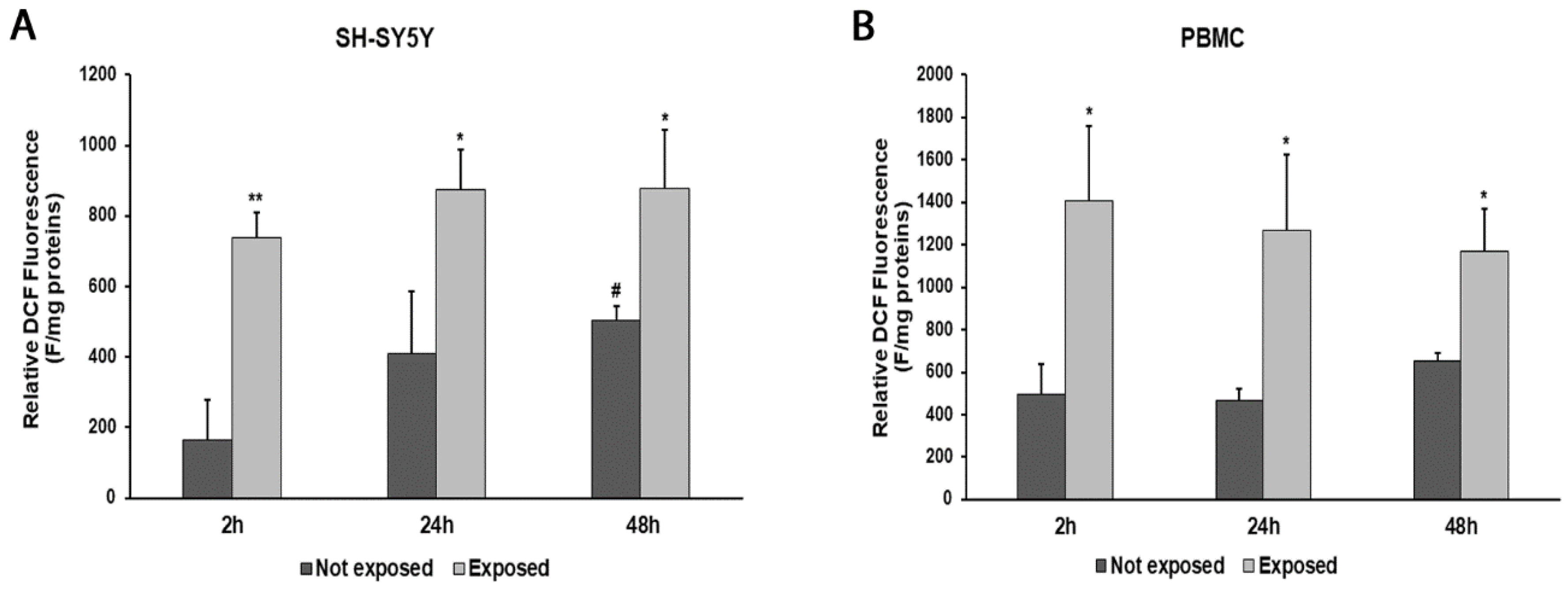
2.5. Measurement of Intracellular Reactive Oxygen Species
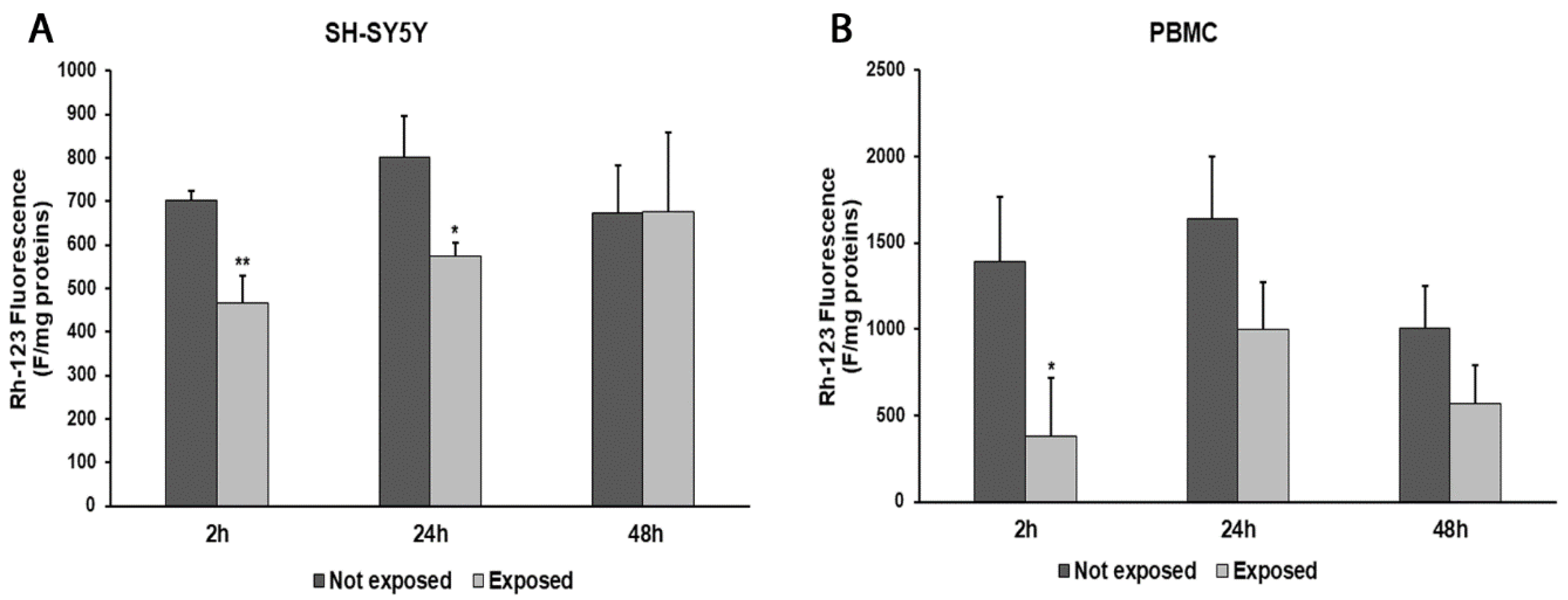
2.6. Measurement of Mitochondrial Transmembrane Potential (ΔΨm)
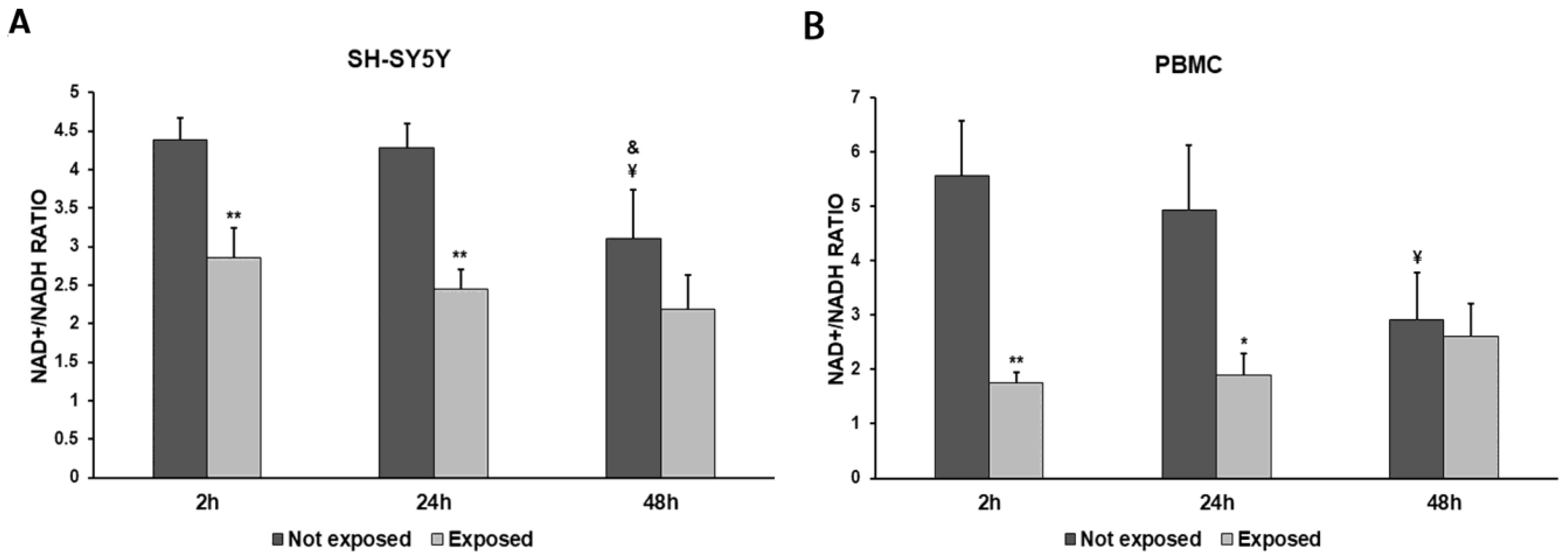
2.7. Measurement of NAD+/NADH Ratio
2.8. Real-Time PCR
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shahbazi-Gahrouei, D.; Hashemi-Beni, B.; Ahmadi, Z. Effects of RF-EMF Exposure from GSM Mobile Phones on Proliferation Rate of Human Adipose-derived Stem Cells: An In-vitro Study. J. Biomed. Phys. Eng. 2016, 6, 243–252. [Google Scholar]
- Shahin, S.; Mishra, V.; Singh, S.P.; Chaturvedi, C.M. 2.45-GHz microwave irradiation adversely affects reproductive function in male mouse, Mus musculus by inducing oxidative and nitrosative stress. Free Radic. Res. 2014, 48, 511–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Iuliis, G.N.; Newey, R.J.; King, B.V.; Aitken, R.J. Mobile phone radiation induces reactive oxygen species production and DNA damage in human spermatozoa in vitro. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e6446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulati, S.; Kosik, P.; Durdik, M.; Skorvaga, M.; Jakl, L.; Markova, E.; Belyaev, I. Effects of different mobile phone UMTS signals on DNA, apoptosis and oxidative stress in human lymphocytes. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 267, 115632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardell, L.; Sage, C. Biological effects from electromagnetic field exposure and public exposure standards. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2008, 62, 104–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundi, M.; Mild, K.; Hardell, L.; Mattsson, M.O. Mobile telephones and cancer—A review of epidemiological evidence. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health B Crit. Rev. 2004, 7, 351–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lerchl, A.; Kruger, H.; Niehaus, M.; Streckert, J.R.; Bitz, A.K.; Hansen, V. Effects of mobile phone electromagnetic fields at nonthermal SAR values on melatonin and body weight of Djungarian hamsters (Phodopus sungorus). J. Pineal Res. 2008, 44, 267–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragy, M.M. Effect of exposure and withdrawal of 900-MHz-electromagnetic waves on brain, kidney and liver oxidative stress and some biochemical parameters in male rats. Electromagn. Biol. Med. 2015, 34, 279–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panagopoulos, D.J.; Margaritis, L.H. The effect of exposure duration on the biological activity of mobile telephony radiation. Mutat. Res. 2010, 699, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, H.; Sharma, R.S.; Singh, R. Immunotoxicity of radiofrequency radiation. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 309, 119793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeni, O.; Di Pietro, R.; d’Ambrosio, G.; Massa, R.; Capri, M.; Naarala, J.; Juutilainen, J.; Scarfi, M.R. Formation of reactive oxygen species in L929 cells after exposure to 900 MHz RF radiation with and without co-exposure to 3-chloro-4-(dichloromethyl)-5-hydroxy-2(5H)-furanone. Radiat. Res. 2007, 167, 306–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasdag, S.; Akdag, M.Z.; Ulukaya, E.; Uzunlar, A.K.; Yegin, D. Mobile phone exposure does not induce apoptosis on spermatogenesis in rats. Arch. Med. Res. 2008, 39, 40–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokolovic, D.; Djindjic, B.; Nikolic, J.; Bjelakovic, G.; Pavlovic, D.; Kocic, G.; Krstic, D.; Cvetkovic, T.; Pavlovic, V. Melatonin reduces oxidative stress induced by chronic exposure of microwave radiation from mobile phones in rat brain. J. Radiat. Res. 2008, 49, 579–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stankiewicz, W.; Dabrowski, M.P.; Kubacki, R.; Sobiczewska, E.; Szmigielski, S. Immunotropic influence of 900 MHz microwave GSM signal on human blood immune cells activated in vitro. Electromagn. Biol. Med. 2006, 25, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossmann, K.A.; Hermann, D.M. Effects of electromagnetic radiation of mobile phones on the central nervous system. Bioelectromagnetics 2003, 24, 49–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulraj, R.; Behari, J. Single strand DNA breaks in rat brain cells exposed to microwave radiation. Mutat. Res. 2006, 596, 76–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curcio, G.; Ferrara, M.; Moroni, F.; D’Inzeo, G.; Bertini, M.; De Gennaro, L. Is the brain influenced by a phone call? An EEG study of resting wakefulness. Neurosci. Res. 2005, 53, 265–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamblin, D.L.; Wood, A.W.; Croft, R.J.; Stough, C. Examining the effects of electromagnetic fields emitted by GSM mobile phones on human event-related potentials and performance during an auditory task. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2004, 115, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinrichs, H.; Heinze, H.J. Effects of GSM electromagnetic field on the MEG during an encoding-retrieval task. Neuroreport 2004, 15, 1191–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Zuo, H.; Li, Y. Effects of Radiofrequency Electromagnetic Radiation on Neurotransmitters in the Brain. Front. Public Health 2021, 9, 691880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, R.; Treyer, V.; Schuderer, J.; Berthold, T.; Buck, A.; Kuster, N.; Landolt, H.P.; Achermann, P. Exposure to pulse-modulated radio frequency electromagnetic fields affects regional cerebral blood flow. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2005, 21, 1000–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inskip, P.D.; Tarone, R.E.; Hatch, E.E.; Wilcosky, T.C.; Shapiro, W.R.; Selker, R.G.; Fine, H.A.; Black, P.M.; Loeffler, J.S.; Linet, M.S. Cellular-telephone use and brain tumors. N. Engl. J. Med. 2001, 344, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shipley, M.M.; Mangold, C.A.; Szpara, M.L. Differentiation of the SH-SY5Y Human Neuroblastoma Cell Line. J. Vis. Exp. 2016, e53193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashevich, M.; Folkman, D.; Kesar, A.; Barbul, A.; Korenstein, R.; Jerby, E.; Avivi, L. Exposure of human peripheral blood lymphocytes to electromagnetic fields associated with cellular phones leads to chromosomal instability. Bioelectromagnetics 2003, 24, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandhi, G.; Kaur, G.; Nisar, U. A cross-sectional case control study on genetic damage in individuals residing in the vicinity of a mobile phone base station. Electromagn. Biol. Med. 2015, 34, 344–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Condello, S.; Calabro, E.; Caccamo, D.; Curro, M.; Ferlazzo, N.; Satriano, J.; Magazu, S.; Ientile, R. Protective effects of agmatine in rotenone-induced damage of human SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells: Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy analysis in a model of Parkinson’s disease. Amino Acids 2012, 42, 775–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, S.; Singh, N.N.; Sreedhar, G.; Mukherjee, S. Analysis of the Genotoxic Effects of Mobile Phone Radiation using Buccal Micronucleus Assay: A Comparative Evaluation. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2016, 10, ZC82–ZC85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celik, O.; Kahya, M.C.; Naziroglu, M. Oxidative stress of brain and liver is increased by Wi-Fi (2.45 GHz) exposure of rats during pregnancy and the development of newborns. J. Chem. Neuroanat. 2016, 75, 134–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baan, R.; Grosse, Y.; Lauby-Secretan, B.; El Ghissassi, F.; Bouvard, V.; Benbrahim-Tallaa, L.; Guha, N.; Islami, F.; Galichet, L.; Straif, K.; et al. Carcinogenicity of radiofrequency electromagnetic fields. Lancet Oncol. 2011, 12, 624–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayalaxmi. Cytogenetic studies in human blood lymphocytes exposed in vitro to 2.45 GHz or 8.2 GHz radiofrequency radiation. Radiat. Res. 2006, 166, 532–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuermann, D.; Mevissen, M. Manmade Electromagnetic Fields and Oxidative Stress-Biological Effects and Consequences for Health. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cadet, J.; Davies, K.J.A.; Medeiros, M.H.; Di Mascio, P.; Wagner, J.R. Formation and repair of oxidatively generated damage in cellular DNA. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2017, 107, 13–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marnett, L.J. Oxyradicals and DNA damage. Carcinogenesis 2000, 21, 361–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chou, C.K. Controversy in Electromagnetic Safety. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 16942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozgur, E.; Guler, G.; Kismali, G.; Seyhan, N. Mobile phone radiation alters proliferation of hepatocarcinoma cells. Cell Biochem. Biophys. 2014, 70, 983–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esmekaya, M.A.; Aytekin, E.; Ozgur, E.; Guler, G.; Ergun, M.A.; Omeroglu, S.; Seyhan, N. Mutagenic and morphologic impacts of 1.8 GHz radiofrequency radiation on human peripheral blood lymphocytes (hPBLs) and possible protective role of pre-treatment with Ginkgo biloba (EGb 761). Sci. Total Environ. 2011, 410–411, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manna, D.; Ghosh, R. Effect of radiofrequency radiation in cultured mammalian cells: A review. Electromagn. Biol. Med. 2016, 35, 265–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgiou, C.D.; Margaritis, L.H. Oxidative Stress and NADPH Oxidase: Connecting Electromagnetic Fields, Cation Channels and Biological Effects. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 10041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saliev, T.; Begimbetova, D.; Masoud, A.R.; Matkarimov, B. Biological effects of non-ionizing electromagnetic fields: Two sides of a coin. Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 2019, 141, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakymenko, I.; Tsybulin, O.; Sidorik, E.; Henshel, D.; Kyrylenko, O.; Kyrylenko, S. Oxidative mechanisms of biological activity of low-intensity radiofrequency radiation. Electromagn. Biol. Med. 2016, 35, 186–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durdik, M.; Kosik, P.; Markova, E.; Somsedikova, A.; Gajdosechova, B.; Nikitina, E.; Horvathova, E.; Kozics, K.; Davis, D.; Belyaev, I. Microwaves from mobile phone induce reactive oxygen species but not DNA damage, preleukemic fusion genes and apoptosis in hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 16182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marjanovic, A.M.; Pavicic, I.; Trosic, I. Cell oxidation-reduction imbalance after modulated radiofrequency radiation. Electromagn. Biol. Med. 2015, 34, 381–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santini, S.J.; Cordone, V.; Falone, S.; Mijit, M.; Tatone, C.; Amicarelli, F.; Di Emidio, G. Role of Mitochondria in the Oxidative Stress Induced by Electromagnetic Fields: Focus on Reproductive Systems. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2018, 2018, 5076271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rimal, S.; Tantray, I.; Li, Y.; Pal Khaket, T.; Li, Y.; Bhurtel, S.; Li, W.; Zeng, C.; Lu, B. Reverse electron transfer is activated during aging and contributes to aging and age-related disease. EMBO Rep. 2023, 24, e55548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Sauve, A.A. NAD+ metabolism: Bioenergetics, signaling and manipulation for therapy. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2016, 1864, 1787–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campisi, A.; Gulino, M.; Acquaviva, R.; Bellia, P.; Raciti, G.; Grasso, R.; Musumeci, F.; Vanella, A.; Triglia, A. Reactive oxygen species levels and DNA fragmentation on astrocytes in primary culture after acute exposure to low intensity microwave electromagnetic field. Neurosci. Lett. 2010, 473, 52–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marjanovic Cermak, A.M.; Pavicic, I.; Trosic, I. Oxidative stress response in SH-SY5Y cells exposed to short-term 1800 MHz radiofrequency radiation. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A Tox. Hazard. Subst. Environ. Eng. 2018, 53, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, S.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, W.; Lai, K.; Yao, K. Study of oxidative stress in human lens epithelial cells exposed to 1.8 GHz radiofrequency fields. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e72370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, K.; Wu, W.; Wang, K.; Ni, S.; Ye, P.; Yu, Y.; Ye, J.; Sun, L. Electromagnetic noise inhibits radiofrequency radiation-induced DNA damage and reactive oxygen species increase in human lens epithelial cells. Mol. Vis. 2008, 14, 964–969. [Google Scholar]
- Kazemi, E.; Mortazavi, S.M.; Ali-Ghanbari, A.; Sharifzadeh, S.; Ranjbaran, R.; Mostafavi-Pour, Z.; Zal, F.; Haghani, M. Effect of 900 MHz Electromagnetic Radiation on the Induction of ROS in Human Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells. J. Biomed. Phys. Eng. 2015, 5, 105–114. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Y.S.; Huang, B.T.; Huang, Y.X. Reactive oxygen species formation and apoptosis in human peripheral blood mononuclear cell induced by 900 MHz mobile phone radiation. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2012, 2012, 740280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Zong, L.; Gao, Z.; Zhu, S.; Tong, J.; Cao, Y. Mitochondrial DNA damage and oxidative damage in HL-60 cells exposed to 900 MHz radiofrequency fields. Mutat. Res. 2017, 797–799, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, S.; Zhou, Z.; Zhang, L.; Yu, Z.; Zhang, W.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Li, M.; Chen, Y.; Chen, C.; et al. Exposure to 1800 MHz radiofrequency radiation induces oxidative damage to mitochondrial DNA in primary cultured neurons. Brain Res. 2010, 1311, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asl, J.F.; Goudarzi, M.; Shoghi, H. The radio-protective effect of rosmarinic acid against mobile phone and Wi-Fi radiation-induced oxidative stress in the brains of rats. Pharmacol. Rep. 2020, 72, 857–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Target | Primer Sequence 5′ > 3′ | Length of Expected Product (bp) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Forward | Reverse | ||
| β-actin | TTGTTACAGGAAGTCCCTTGCC | ATGCTATCACCTCCCCTGTGTG | 100 |
| mtTFA | TCATCTGTCTTGGCAAGTTGTC | AGTCCGCCCTATAAGCATCT | 192 |
| SOD1 | GGTGTGGCCGATGTGTCTATT | CTGCTTTTTCATGGACCACCA | 73 |
| LC3 | CGGTGATAATAGAACGATACAAG | CTGAGATTGGTGTGGAGAC | 186 |
| BAX | GGACGAACTGGACAGTAACATGG | GCAAAGTAGAAAAGGGCGACAAC | 127 |
| BCL2 | ATCGCCCTGTGGATGACTGAG | CAGCCAGGAGAAATCAAACAGAGG | 105 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bertuccio, M.P.; Acri, G.; Ientile, R.; Caccamo, D.; Currò, M. The Exposure to 2.45 GHz Electromagnetic Radiation Induced Different Cell Responses in Neuron-like Cells and Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 3129. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11123129
Bertuccio MP, Acri G, Ientile R, Caccamo D, Currò M. The Exposure to 2.45 GHz Electromagnetic Radiation Induced Different Cell Responses in Neuron-like Cells and Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells. Biomedicines. 2023; 11(12):3129. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11123129
Chicago/Turabian StyleBertuccio, Maria Paola, Giuseppe Acri, Riccardo Ientile, Daniela Caccamo, and Monica Currò. 2023. "The Exposure to 2.45 GHz Electromagnetic Radiation Induced Different Cell Responses in Neuron-like Cells and Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells" Biomedicines 11, no. 12: 3129. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11123129







