BET Family Protein BRD4: An Emerging Actor in NFκB Signaling in Inflammation and Cancer
Abstract
:1. Introduction
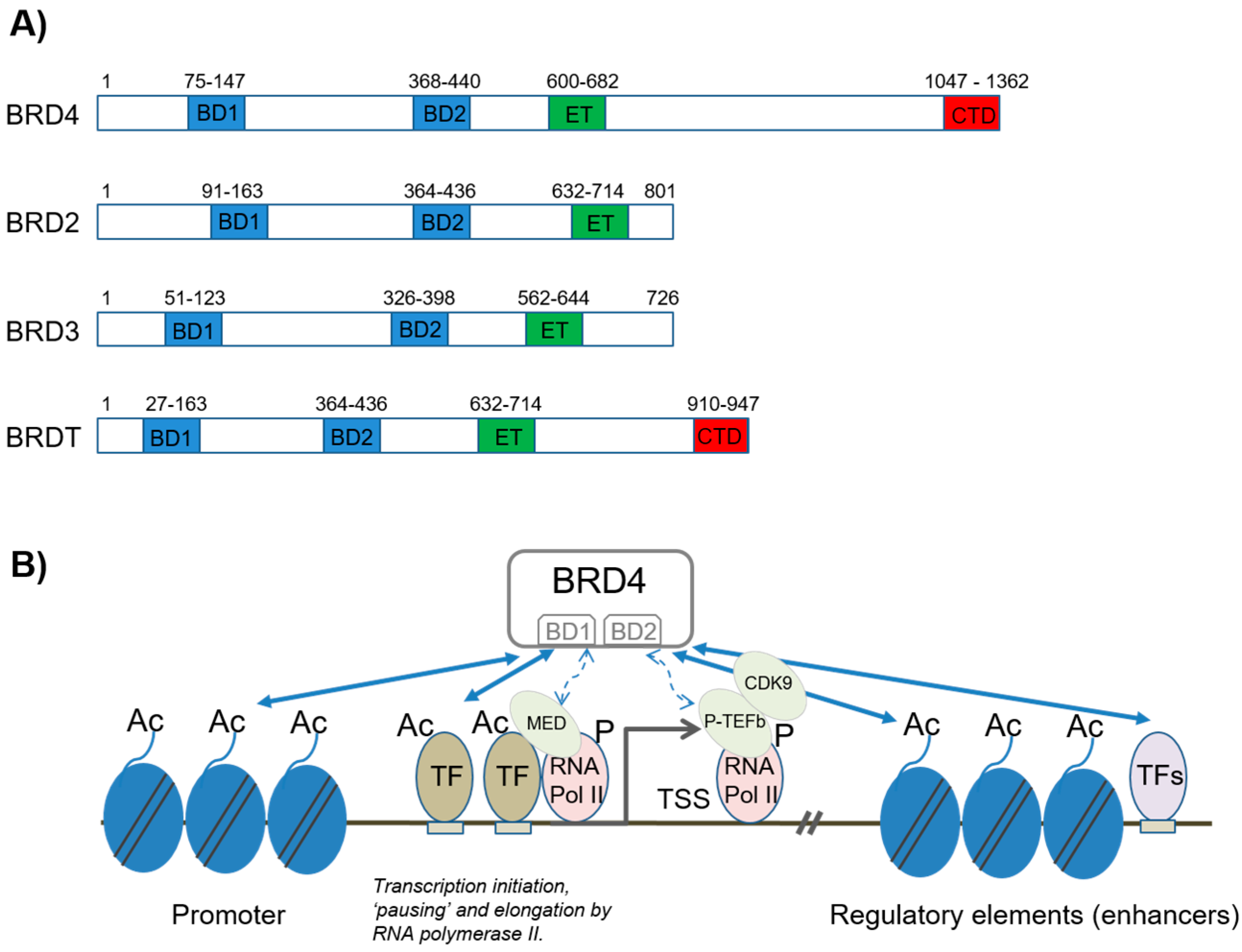
2. Structure and Function of BET Proteins
2.1. BRD4 in Transcriptional Regulation by NFκB
2.1.1. Transcription Initiation and Elongation
2.1.2. Enhancer Regulation by BRD4 and Its Role in NFκB Signaling
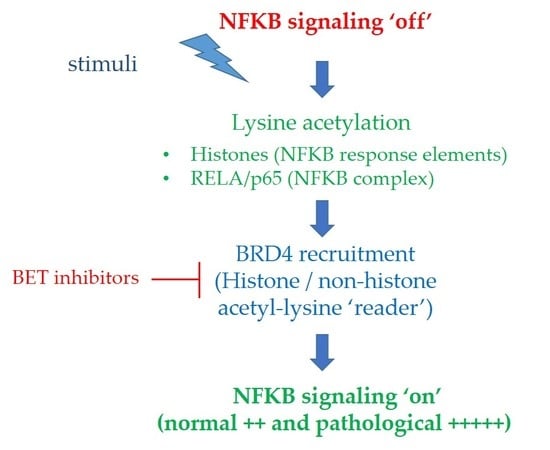
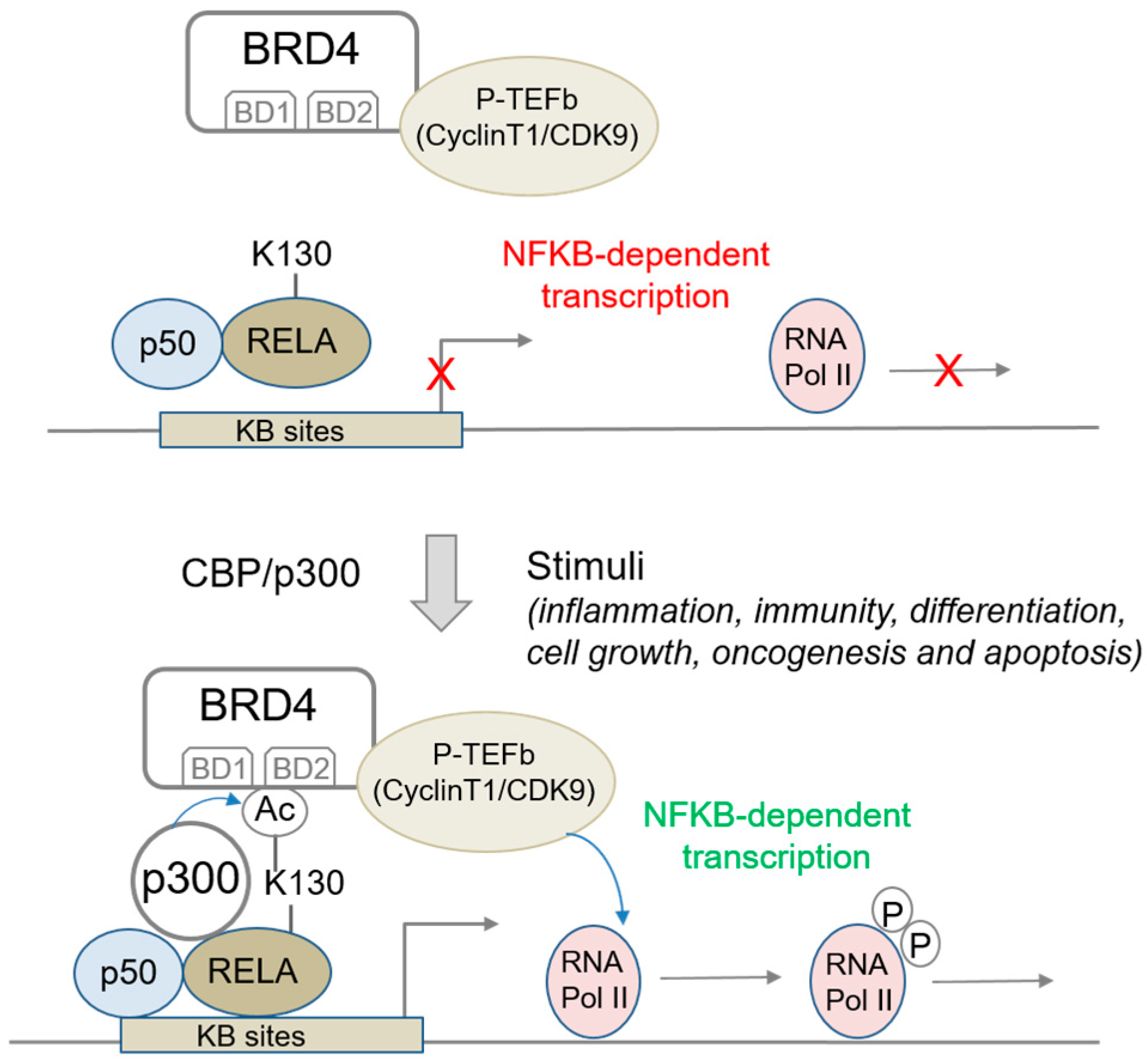
2.1.3. BRD4 Interaction with Acetylated RELA/p65; Impact on NFκB Signaling and Sensitivity to BET Inhibitors
3. BET Inhibition as an Anti-Cancer Therapy and Perspectives for Use in NFκB-Dependent Cancers
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dawson, M.A. The cancer epigenome: Concepts, challenges, and therapeutic opportunities. Science 2017, 355, 1147–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basheer, F.; Huntly, B.J. BET bromodomain inhibitors in leukemia. Exp. Hematol. 2015, 43, 718–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, J.; Vakoc, C.R. The mechanisms behind the therapeutic activity of BET bromodomain inhibition. Mol. Cell 2014, 54, 728–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhalluin, C.; Carlson, J.E.; Zeng, L.; He, C.; Aggarwal, A.K.; Zhou, M.M. Structure and ligand of a histone acetyltransferase bromodomain. Nature 1999, 399, 491–496. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Moriniere, J.; Rousseaux, S.; Steuerwald, U.; Soler-Lopez, M.; Curtet, S.; Vitte, A.L.; Govin, J.; Gaucher, J.; Sadoul, K.; Hart, D.J.; et al. Cooperative binding of two acetylation marks on a histone tail by a single bromodomain. Nature 2009, 461, 664–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filippakopoulos, P.; Knapp, S. Targeting bromodomains: Epigenetic readers of lysine acetylation. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2014, 13, 337–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smale, S.T. Hierarchies of NF-kB target-gene regulation. Nat. Immunol. 2011, 12, 689–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Q.; Li, T.; Price, D.H. RNA polymerase II elongation control. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2012, 81, 119–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Ma, Q.; Wong, K.; Li, W.; Ohgi, K.; Zhang, J.; Aggarwal, A.; Rosenfeld, M.G. Brd4 and JMJD6-associated anti-pause enhancers in regulation of transcriptional pause release. Cell 2013, 155, 1581–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, S.; Sowa, M.E.; Ottinger, M.; Smith, J.A.; Shi, Y.; Harper, J.W.; Howley, P.M. The Brd4 extraterminal domain confers transcription activation independent of pTEFb by recruiting multiple proteins, including NSD3. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2011, 31, 2641–2652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loven, J.; Hoke, H.A.; Lin, C.Y.; Lau, A.; Orlando, D.A.; Vakoc, C.R.; Bradner, J.E.; Lee, T.I.; Young, R.A. Selective inhibition of tumor oncogenes by disruption of super-enhancers. Cell 2013, 153, 320–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhagwat, A.S.; Roe, J.S.; Mok, B.Y.L.; Hohmann, A.F.; Shi, J.; Vakoc, C.R. BET Bromodomain Inhibition Releases the Mediator Complex from Select cis-Regulatory Elements. Cell Rep. 2016, 15, 519–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damm, F.; Mylonas, E.; Cosson, A.; Yoshida, K.; Della Valle, V.; Mouly, E.; Diop, M.; Scourzic, L.; Shiraishi, Y.; Chiba, K.; et al. Acquired initiating mutations in early hematopoietic cells of CLL patients. Cancer Discov. 2014, 4, 1088–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pelish, H.E.; Liau, B.B.; Nitulescu, I.I.; Tangpeerachaikul, A.; Poss, Z.C.; Da Silva, D.H.; Caruso, B.T.; Arefolov, A.; Fadeyi, O.; Christie, A.L.; et al. Mediator kinase inhibition further activates super-enhancer-associated genes in AML. Nature 2015, 526, 273–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chapuy, B.; McKeown, M.R.; Lin, C.Y.; Monti, S.; Roemer, M.G.; Qi, J.; Rahl, P.B.; Sun, H.H.; Yeda, K.T.; Doench, J.G.; et al. Discovery and characterization of super-enhancer-associated dependencies in diffuse large B cell lymphoma. Cancer Cell 2013, 24, 777–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delmore, J.E.; Issa, G.C.; Lemieux, M.E.; Rahl, P.B.; Shi, J.; Jacobs, H.M.; Kastritis, E.; Gilpatrick, T.; Paranal, R.M.; Qi, J.; et al. BET bromodomain inhibition as a therapeutic strategy to target c-Myc. Cell 2011, 146, 904–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groschel, S.; Sanders, M.A.; Hoogenboezem, R.; de Wit, E.; Bouwman, B.A.M.; Erpelinck, C.; van der Velden, V.H.J.; Havermans, M.; Avellino, R.; van Lom, K.; et al. A single oncogenic enhancer rearrangement causes concomitant EVI1 and GATA2 deregulation in leukemia. Cell 2014, 157, 369–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glodzik, D.; Morganella, S.; Davies, H.; Simpson, P.T.; Li, Y.; Zou, X.; Diez-Perez, J.; Staaf, J.; Alexandrov, L.B.; Smid, M.; et al. A somatic-mutational process recurrently duplicates germline susceptibility loci and tissue-specific super-enhancers in breast cancers. Nat. Genet. 2017, 49, 341–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roe, J.S.; Mercan, F.; Rivera, K.; Pappin, D.J.; Vakoc, C.R. BET Bromodomain Inhibition Suppresses the Function of Hematopoietic Transcription Factors in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Mol. Cell 2015, 58, 1028–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, J.D.; Lin, C.Y.; Duan, Q.; Griffin, G.; Federation, A.; Paranal, R.M.; Bair, S.; Newton, G.; Lichtman, A.; Kung, A.; et al. NF-κB directs dynamic super enhancer formation in inflammation and atherogenesis. Mol. Cell 2014, 56, 219–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, B.; Yang, X.D.; Zhou, M.M.; Ozato, K.; Chen, L.F. Brd4 coactivates transcriptional activation of NF-kappaB via specific binding to acetylated RelA. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2009, 29, 1375–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaikkonen, M.U.; Spann, N.J.; Heinz, S.; Romanoski, C.E.; Allison, K.A.; Stender, J.D.; Chun, H.B.; Tough, D.F.; Prinjha, R.K.; Benner, C.; et al. Remodeling of the enhancer landscape during macrophage activation is coupled to enhancer transcription. Mol. Cell 2013, 51, 310–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hah, N.; Benner, C.; Chong, L.W.; Yu, R.T.; Downes, M.; Evans, R.M. Inflammation-sensitive super enhancers form domains of coordinately regulated enhancer RNAs. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, E297–E302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicodeme, E.; Jeffrey, K.L.; Schaefer, U.; Beinke, S.; Dewell, S.; Chung, C.W.; Chandwani, R.; Marazzi, I.; Wilson, P.; Coste, H.; et al. Suppression of inflammation by a synthetic histone mimic. Nature. 2010, 468, 1119–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, Z.; Huang, B.; Wu, X.; Zhang, H.; Qi, J.; Bradner, J.; Nair, S.; Chen, L.F. Brd4 maintains constitutively active NF-κB in cancer cells by binding to acetylated RelA. Oncogene 2014, 33, 2395–2404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.; Liu, R.; Zhong, Y.; Plotnikov, A.N.; Zhang, W.; Zeng, L.; Rusinova, E.; Gerona-Nevarro, G.; Moshkina, N.; Joshua, J.; et al. Down-regulation of NFκB transcriptional activity in HIV-associated kidney disease by BRD4 inhibition. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 28840–28851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brasier, A.R.; Tian, B.; Jamaluddin, M.; Kalita, M.K.; Garofalo, R.P.; Lu, M. RelA Ser276 phosphorylation-coupled Lys310 acetylation controls transcriptional elongation of inflammatory cytokines in respiratory syncytial virus infection. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 11752–11769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.; Herrmann, A.; Deng, J.H.; Kujawski, M.; Niu, G.; Li, Z.; Forman, S.; Jove, R.; Pardoll, D.M.; Yu, H. Persistently activated Stat3 maintains constitutive NF-kappaB activity in tumors. Cancer Cell 2009, 15, 283–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levy, D.; Kuo, A.J.; Chang, Y.; Schaefer, U.; Kitson, C.; Cheung, P.; Espejo, A.; Zee, B.M.; Liu, C.L.; Tangsombatvisit, S.; et al. Lysine methylation of the NF-kB subunit RelA by SETD6 couples activity of the histone methyltransferase GLP at chromatin to tonic repression of NF-kB signaling. Nat. Immunol. 2011, 12, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagel, D.; Vincendeau, M.; Eitelhuber, A.C.; Krappmann, D. Mechanisms and consequences of constitutive NF-κB activation in B-cell lymphoid malignancies. Oncogene 2014, 33, 5655–5665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emadali, A.; Rousseaux, S.; Bruder-Costa, J.; Rome, C.; Duley, S.; Hamaidia, S.; Betton, P.; Debernardi, A.; Leroux, D.; Bernay, B.; et al. Identification of a novel BET bromodomain inhibitor-sensitive, gene regulatory circuit that controls Rituximab response and tumour growth in aggressive lymphoid cancers. EMBO Mol. Med. 2013, 5, 1180–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Emadali, A.; Hoghoughi, N.; Duley, S.; Hajmirza, A.; Verhoeyen, E.; Cosset, F.L.; Bertrand, P.; Roumier, C.; Roggy, A.; Suchaud-Martin, C.; et al. Haploinsufficiency for NR3C1, the gene encoding the glucocorticoid receptor, in blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasms. Blood 2016, 127, 3040–3053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berthon, C.; Raffoux, E.; Thomas, X.; Vey, N.; Gomez-Roca, C.; Yee, K.; Taussig, D.C.; Rezai, K.; Roumier, C.; Herait, P.; et al. Bromodomain inhibitor OTX015 in patients with acute leukaemia: A dose-escalation, phase 1 study. Lancet Haematol. 2016, 3, e186–e195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amorim, S.; Stathis, A.; Gleeson, M.; Iyengar, S.; Magarotto, V.; Leleu, X.; Morschhauser, F.; Karlin, L.; Broussais, F.; Rezai, K.; et al. Bromodomain inhibitor OTX015 in patients with lymphoma or multiple myeloma: A dose-escalation, open-label, pharmacokinetic, phase 1 study. Lancet Haematol. 2016, 3, e196–e204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baltimore, D. NF-κB is 25. Nat. Immunol. 2011, 12, 683–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Compound | Company | Indications | Phases | Completion Date | NCT Number |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FT-1101 | Forma Therapeutics, Inc. (Watertown, MA, USA) | Acute Myeloid Leukemia/Acute Myelogenous Leukemia/Myelodysplastic Syndrome | Phase 1 | August 2018 | NCT02543879 |
| RO6870810 * | Hoffmann-La Roche (Basel, Switzerland) | Multiple Myeloma | Phase 1 | 15 January 2020 | NCT03068351 |
| CPI-0610 | Constellation Pharmaceuticals (Cambridge, MA, USA) | Lymphoma | Phase 1 | July 2018 | NCT01949883 |
| Multiple Myeloma | Phase 1 | March 2019 | NCT02157636 | ||
| Acute Myeloid Leukemia/Myelodysplastic Syndrome (MDS)/ Myelodysplastic/Myeloproliferative Neoplasm, Unclassifiable/Myelofibrosis | Phase 1 | January 2019 | NCT02158858 | ||
| Peripheral Nerve Tumors | Phase 2 | March 2020 | NCT02986919 | ||
| GSK525762 | GSK (Brentford, UK) | Cancer | Phase 1 | 24 February 2020 | NCT01943851 |
| Carcinoma, Midline | Phase 1 | 9 September 2019 | NCT01587703 | ||
| ZEN003694 ** | Zenith Epigenetics (San Francisco, CA, USA) | Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer | Phase 1 | April 2018 | NCT02711956 |
| BMS-986158 | Bristol-Myers Squibb (New York, NY, USA) | Multiple Indications Cancer | Phase 1/Phase 2 | 17 December 2018 | NCT02419417 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hajmirza, A.; Emadali, A.; Gauthier, A.; Casasnovas, O.; Gressin, R.; Callanan, M.B. BET Family Protein BRD4: An Emerging Actor in NFκB Signaling in Inflammation and Cancer. Biomedicines 2018, 6, 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines6010016
Hajmirza A, Emadali A, Gauthier A, Casasnovas O, Gressin R, Callanan MB. BET Family Protein BRD4: An Emerging Actor in NFκB Signaling in Inflammation and Cancer. Biomedicines. 2018; 6(1):16. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines6010016
Chicago/Turabian StyleHajmirza, Azadeh, Anouk Emadali, Arnaud Gauthier, Olivier Casasnovas, Rémy Gressin, and Mary B. Callanan. 2018. "BET Family Protein BRD4: An Emerging Actor in NFκB Signaling in Inflammation and Cancer" Biomedicines 6, no. 1: 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines6010016
APA StyleHajmirza, A., Emadali, A., Gauthier, A., Casasnovas, O., Gressin, R., & Callanan, M. B. (2018). BET Family Protein BRD4: An Emerging Actor in NFκB Signaling in Inflammation and Cancer. Biomedicines, 6(1), 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines6010016