High Throughput AOTF Hyperspectral Imager for Randomly Polarized Light
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- AOTF has good spectral resolution in the visible and near-infrared region [24], and is suitable for the majority of optical imaging applications.
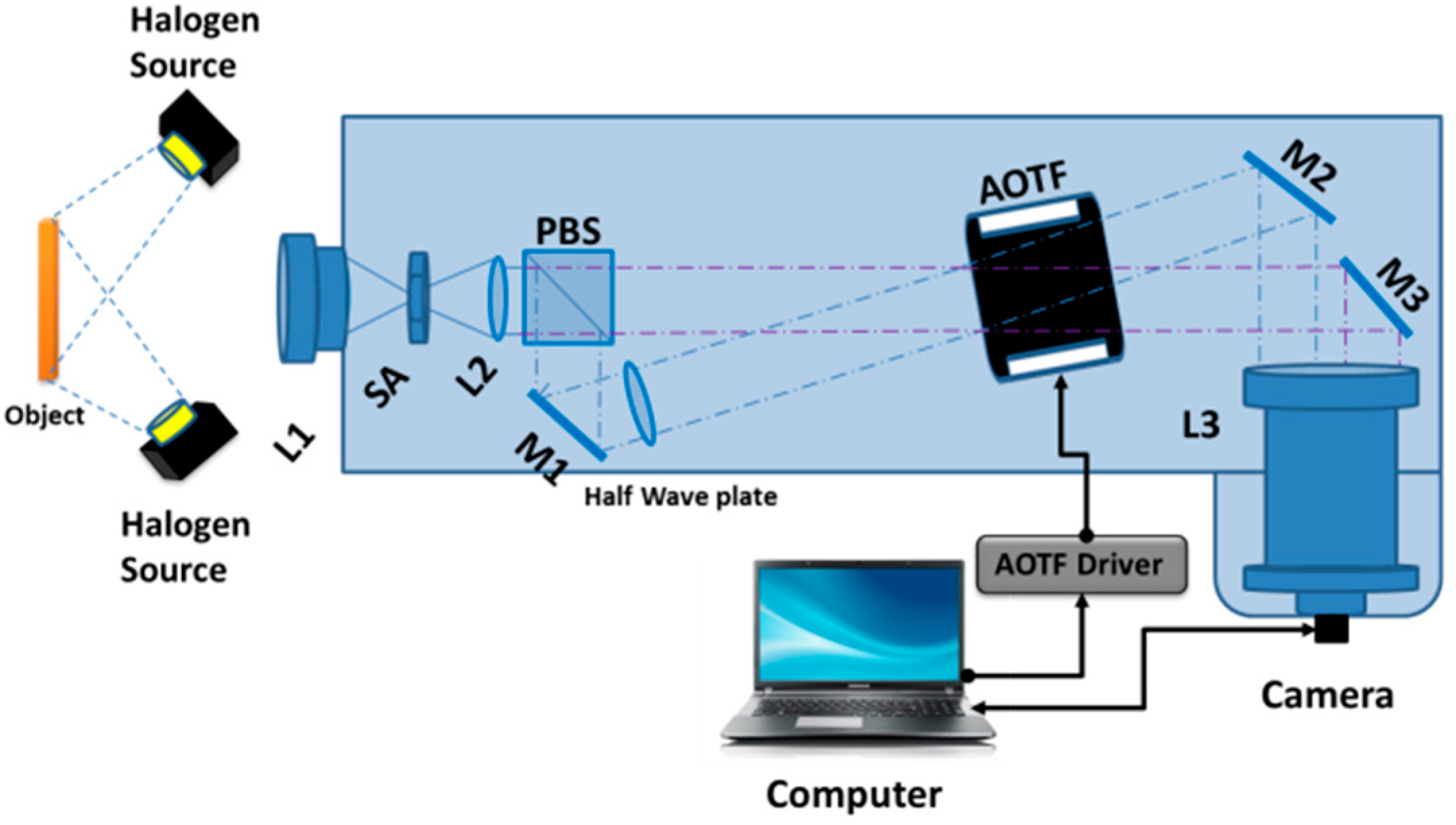
2. Materials and Methods
3. Experimental Work and Results
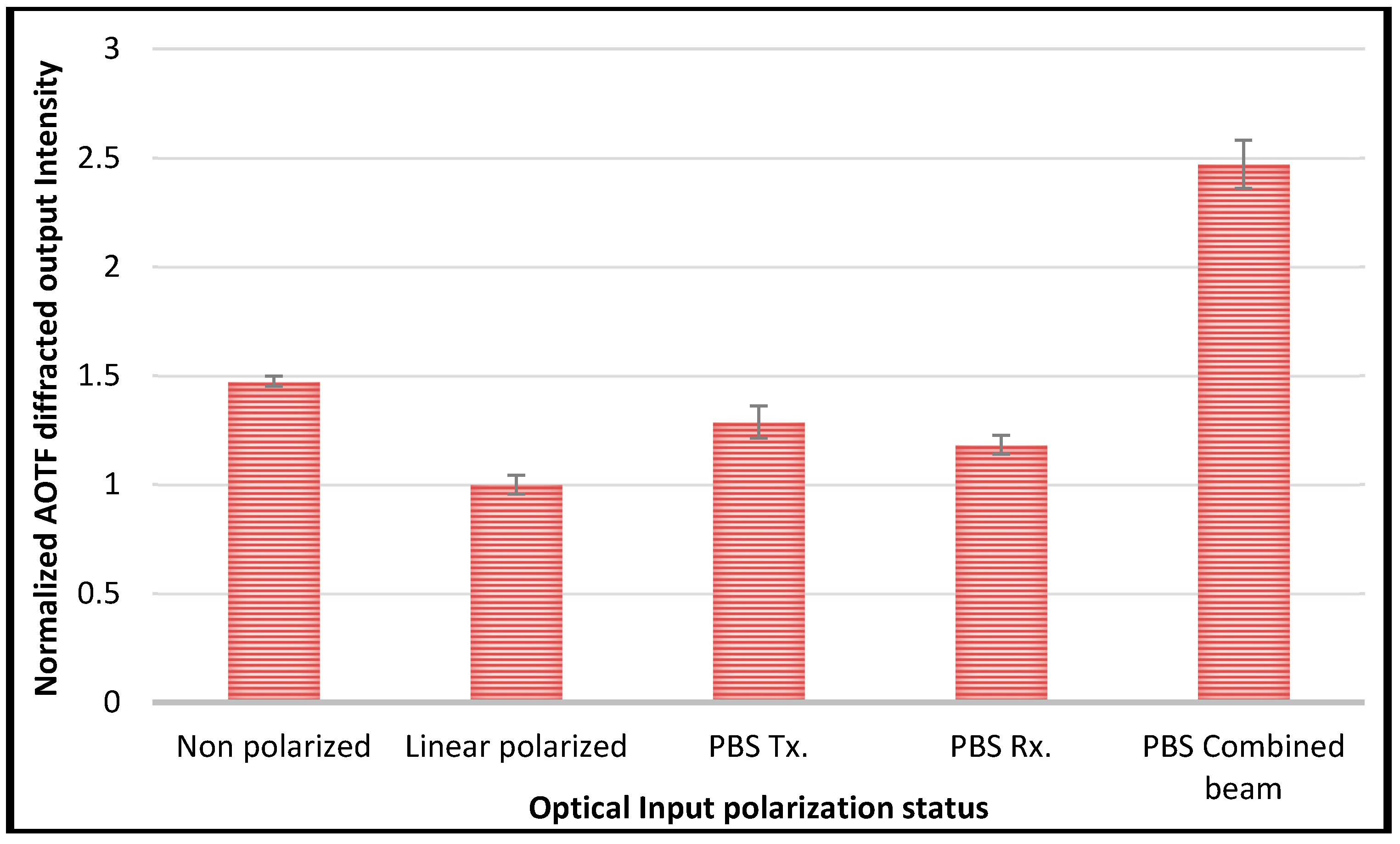
3.1. Optical Throughput Characterization
- Randomly polarized input beam with a single polarization AOTF setup (i.e., laser output directly used as an input passing the AOTF crystal);
- Single polarization AOTF setup with linearly polarized light input aligned to the optimized polarization direction of the AOTF (laser output going through a linear polarizer);
- Randomly polarized input beam going through the dual beam setup (i.e., Figure 1).
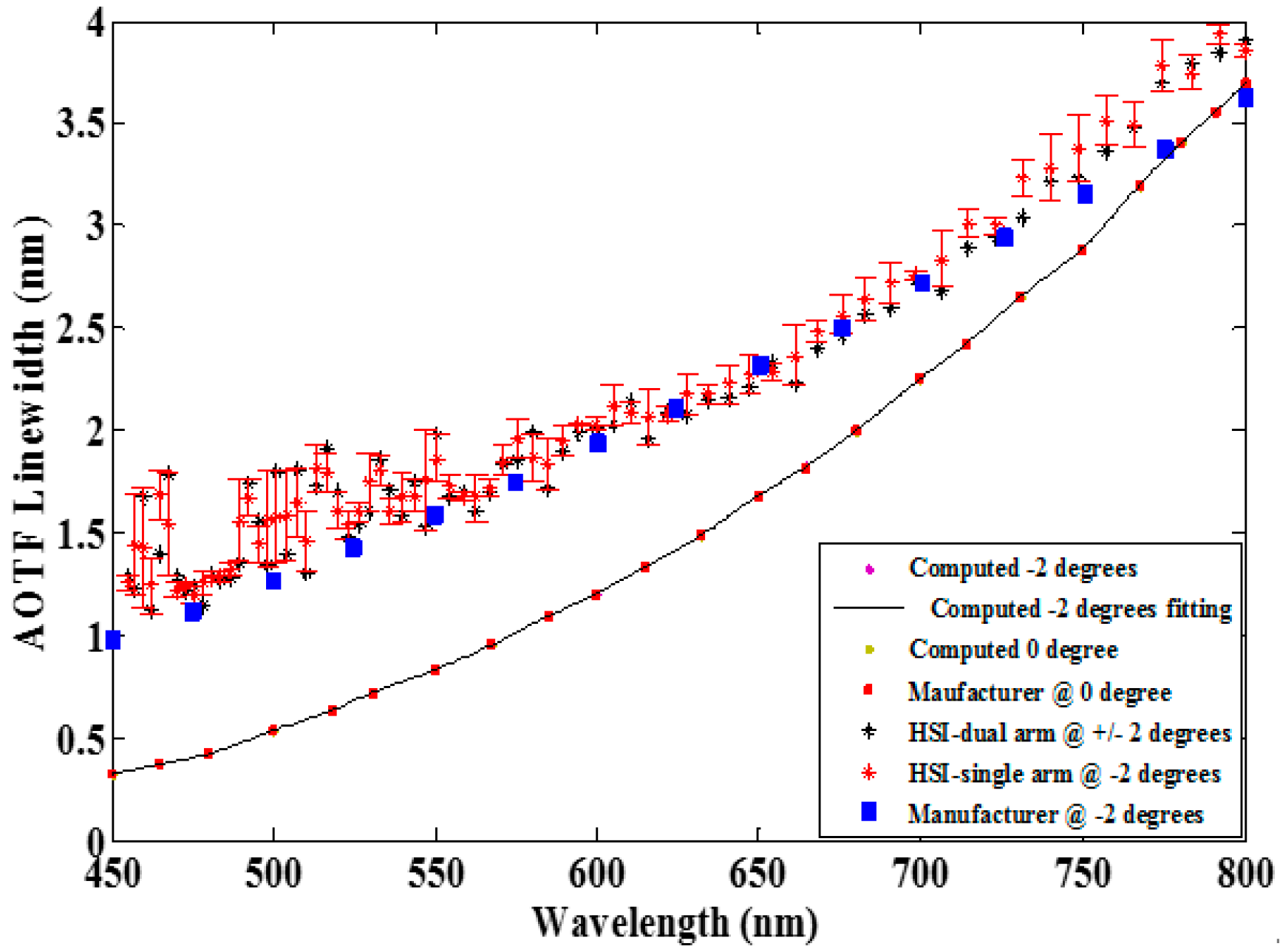
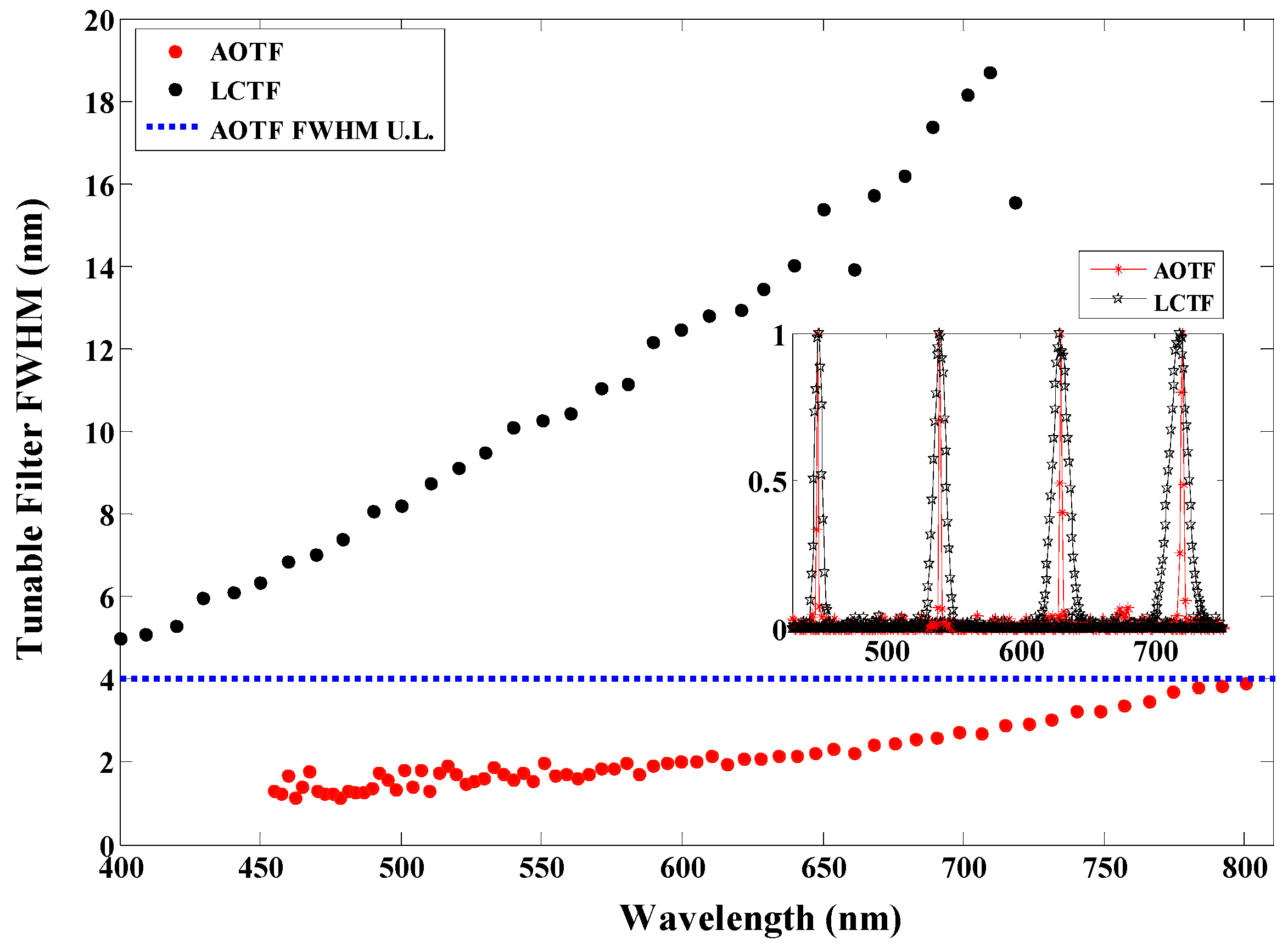
3.2. Spectral Characterization
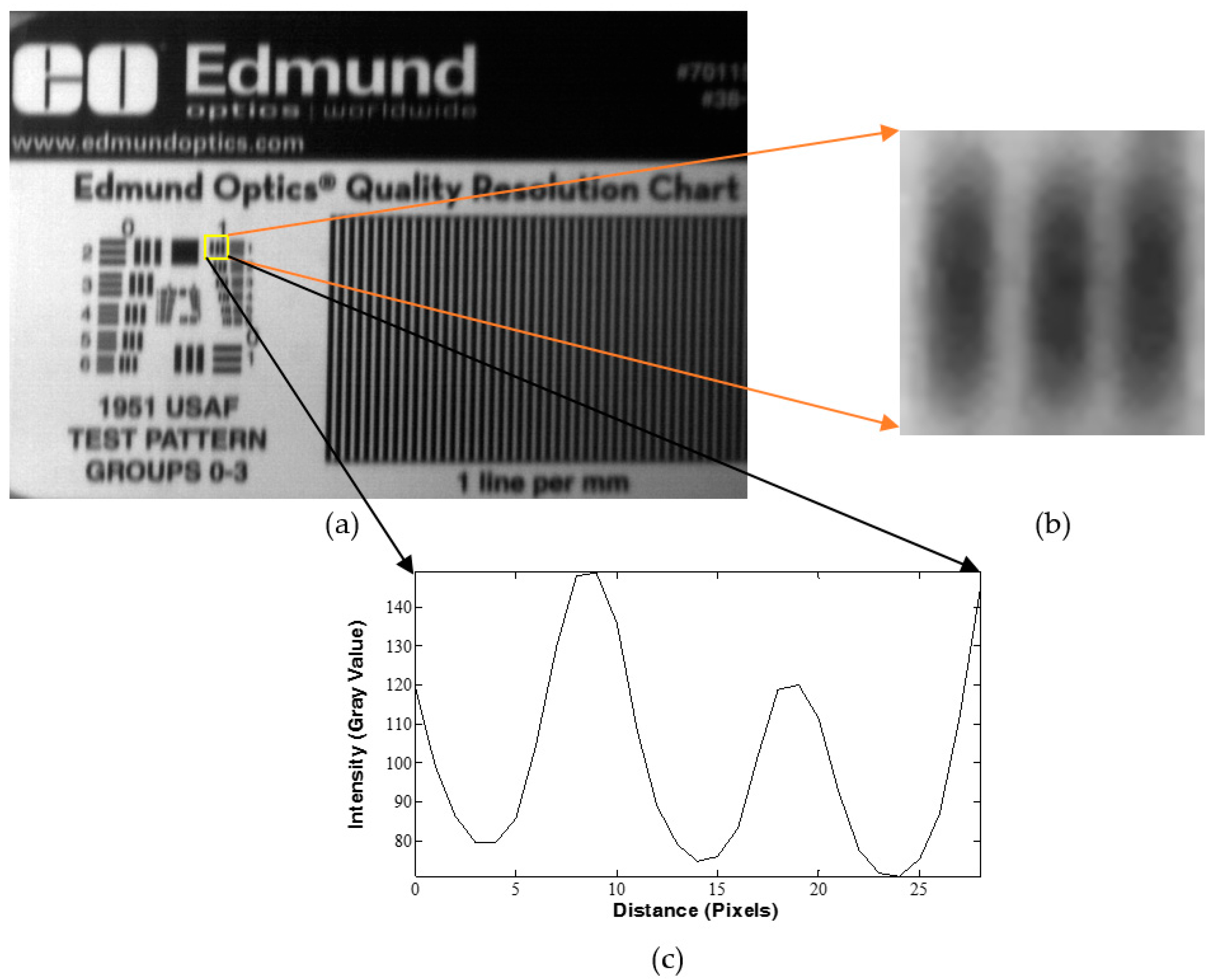
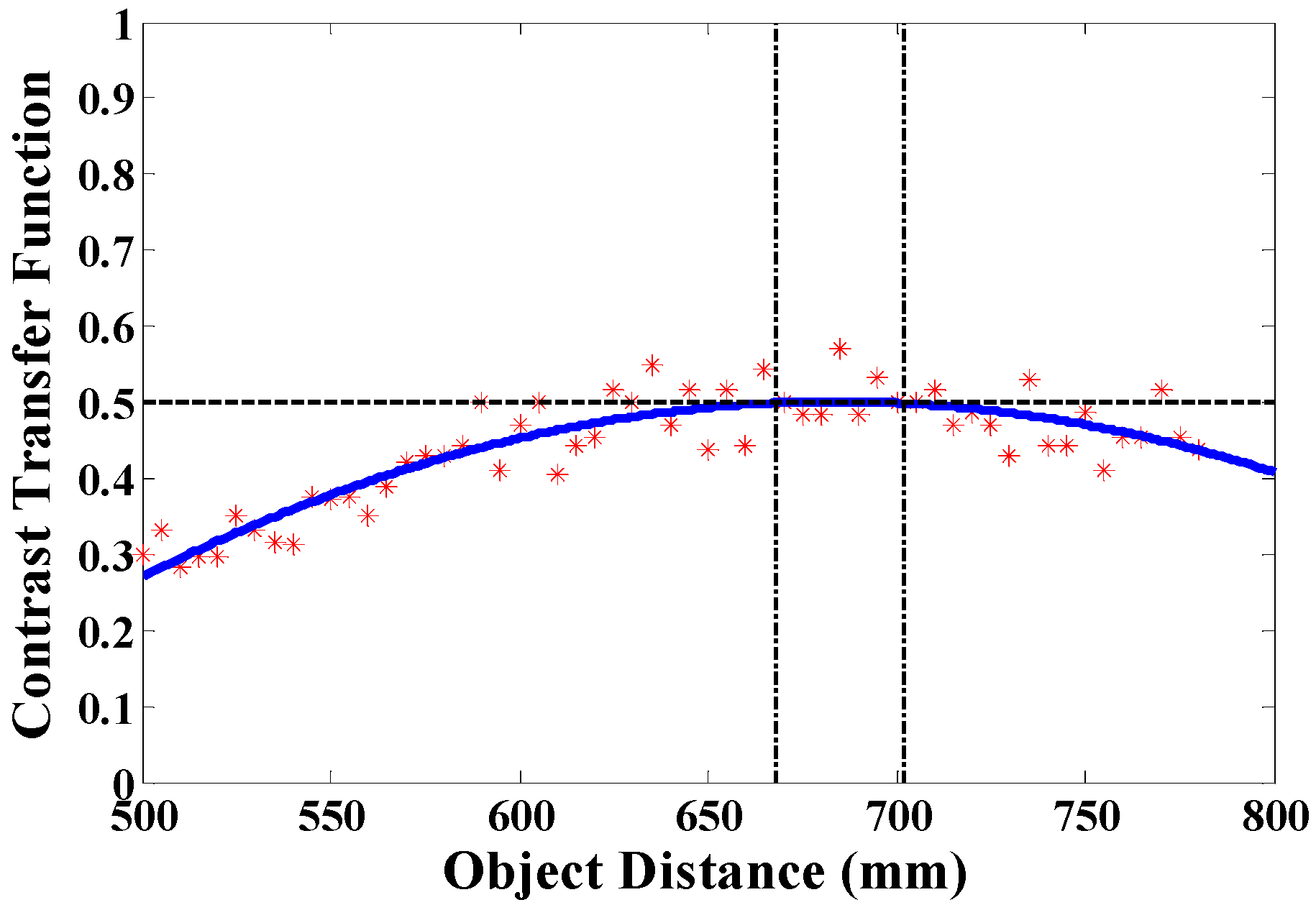
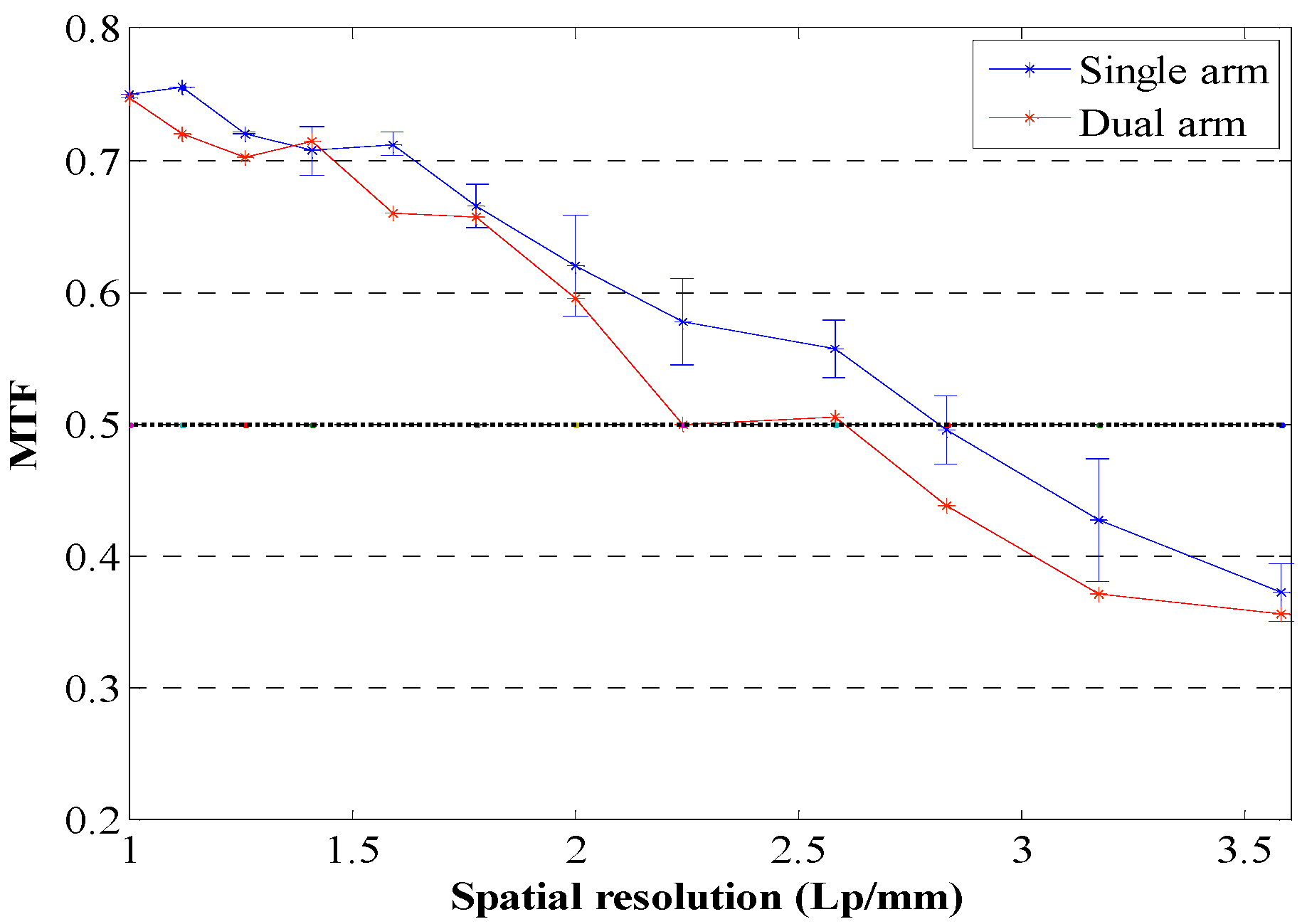
3.3. Spatial Characterization
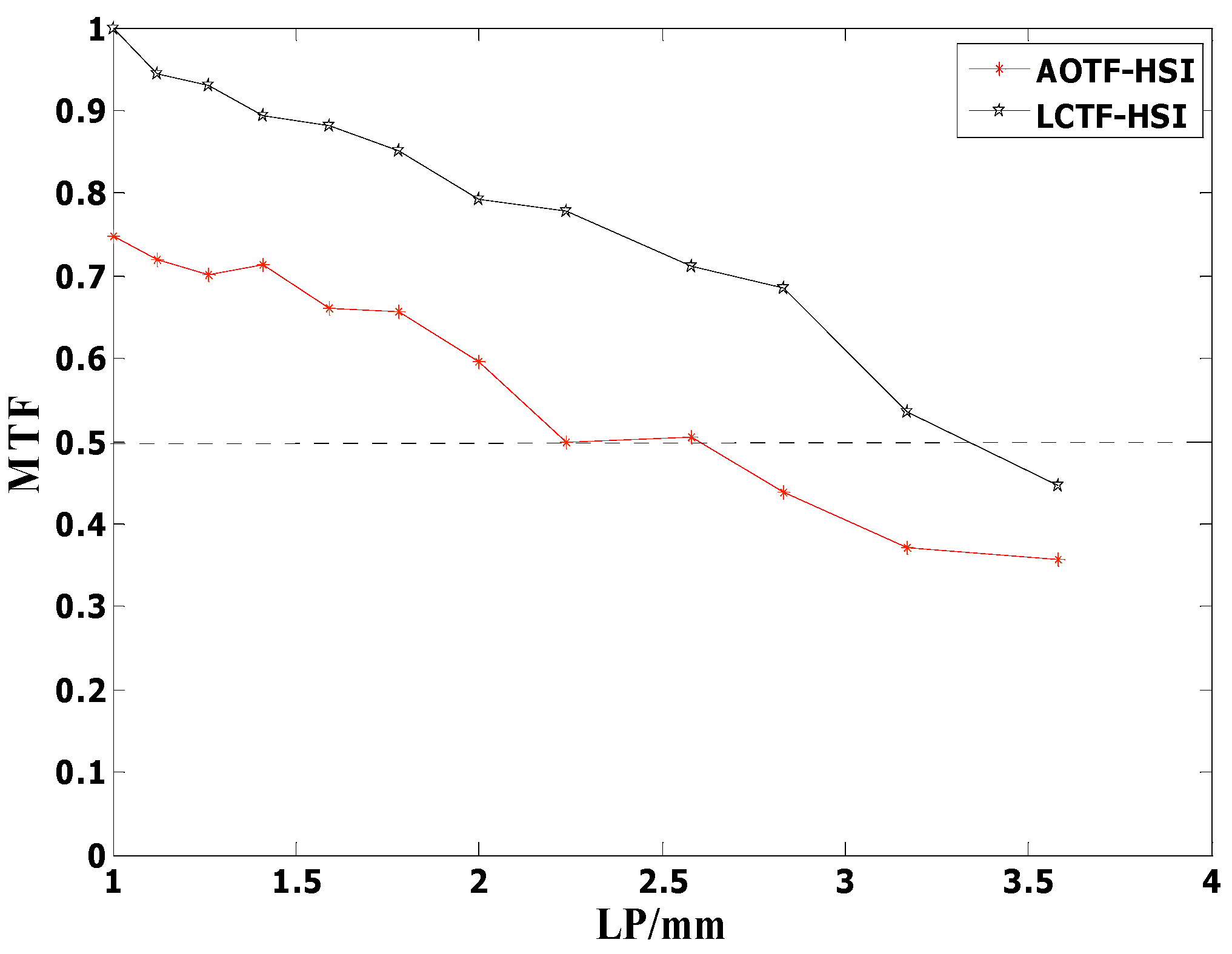
3.4. Performance Comparison to LCTF
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Goetz, A.F.H. Three decades of hyperspectral remote sensing of the Earth: A personal view. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, S5–S16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, Q.; Zhang, B.; Zheng, L. Hyperspectral remote sensing technology and applications in china. In Proceedings of the 2nd CHRIS/Proba Work. ESA/ESRIN, Frascati, Italy, 28–30 April 2004; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Gat, N. Imaging Spectroscopy Using Tunable Filters: A Review. In Proceedings of the SPIE, Orlando, FL, USA, 5 April 2000; Volume 4056, pp. 50–64. [Google Scholar]
- Gowen, A.; Odonnell, C.; Cullen, P.; Downey, G.; Frias, J. Hyperspectral imaging—An emerging process analytical tool for food quality and safety control. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2007, 18, 590–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Liu, L.; Ngadi, M.O. Recent developments in hyperspectral imaging for assessment of food quality and safety. Sensors 2014, 14, 7248–7276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, H. Advances in multispectral and hyperspectral imaging for archaeology and art conservation. Appl. Phys. A 2011, 106, 309–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edelman, G.J.; Gaston, E.; van Leeuwen, T.G.; Cullen, P.J.; Aalders, M.C.G. Hyperspectral imaging for non-contact analysis of forensic traces. Forensic Sci. Int. 2012, 223, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zalevsky, Z.; Ilovitsh, A.; Beiderman, Y. Usage of cornea and sclera back reflected images captured in security cameras for forensic and card games applications. In Optics and Photonics for Counterterrorism, Crime Fighting and Defence IX; and Optical Materials and Biomaterials in Security and Defence Systems Technology, Proceedings of the SPIE, Dresden, Germany, 31 October 2013; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2013; Volume 8901, p. 89010I. [Google Scholar]
- Yuen, P.W.; Richardson, M. An introduction to hyperspectral imaging and its application for security, surveillance and target acquisition. Imaging Sci. J. 2010, 58, 241–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, T.-H.; Cheng, L.-J.; Yu, J.; Reyes, G. Acousto-Optic Tunable Filter Imaging Spectrometers. In Proceedings of the 11th Annual International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Espoo, Finland, 3–6 June 1991; Volume 1, pp. 585–588. [Google Scholar]
- Glenar, D.A.; Hillman, J.J.; Saif, B.; Bergstralh, J. Acousto-optic imaging spectropolarimetry for remote sensing. Appl. Opt. 1994, 33, 7412–7424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, F.; Yan, L. Hull vector-based incremental learning of hyperspectral remote sensing images. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2015, 9, 96022. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, G.; Fei, B. Medical hyperspectral imaging: A review. J. Biomed. Opt. 2014, 19, 10901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mordant, D.J.; Al-Abboud, I.; Muyo, G.; Gorman, A.; Sallam, A.; Ritchie, P.; Harvey, A.R.; McNaught, A.I. Spectral imaging of the retina. Eye 2011, 25, 309–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiyotoki, S.; Nishikawa, J.; Okamoto, T.; Hamabe, K.; Saito, M.; Goto, A.; Fujita, Y.; Hamamoto, Y.; Takeuchi, Y.; Satori, S.; et al. New method for detection of gastric cancer by hyperspectral imaging: A pilot study. J. Biomed. Opt. 2013, 18, 26010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Wang, H.; Li, Q. Tongue tumor detection in medical hyperspectral images. Sensors 2012, 12, 162–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panasyuk, S.V.; Yang, S.; Faller, D.V.; Ngo, D.; Lew, R.A.; Freeman, J.E.; Rogers, A.E. Medical hyperspectral imaging to facilitate residual tumor identification during surgery. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2007, 6, 439–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Beule, P.A.; Dunsby, C.; Galletly, N.P.; Stamp, G.W.; Chu, A.C.; Anand, U.; Anand, P.; Benham, C.D.; Naylor, A.; French, P.M. A hyperspectral fluorescence lifetime probe for skin cancer diagnosis. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2007, 78, 123101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Q.; Zhegalova, N.G.; Wang, S.T.; Akers, W.J.; Berezin, M.Y. Multispectral imaging in the extended near-infrared window based on endogenous chromophores. J. Biomed. Opt. 2013, 18, 101318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballabriga, R.; Campbell, M.; Heijne, E.H.M.; Llopart, X.; Tlustos, L. The Medipix3 Prototype, a Pixel Readout Chip Working in Single Photon Counting Mode with Improved Spectrometric Performance. IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 2007, 54, 1824–1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, M.; Chen, D.; Cheng, A.; Wei, H.; Stanley, D. Change detection from remotely sensed images: From pixel-based to object-based approaches. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2013, 80, 91–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, Z.; An, R.; Hayward, J.E.; Farrell, T.J.; Fang, Q. Hyperspectral fluorescence lifetime imaging for optical biopsy. J. Biomed. Opt. 2013, 18, 096001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Wang, H. The narrow band AOTF based hyperspectral microscopic imaging on the rat skin stratum configuration. J. Eur. Opt. Soc. 2014, 9, 14034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Peng, H.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Guo, F. Coexpression of CdSe and CdSe/CdS quantum dots in live cells using molecular hyperspectral imaging technology. J. Biomed. Opt. 2015, 20, 110504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, L.; Kester, R.T.; Tkaczyk, T.S. Compact Image Slicing Spectrometer (ISS) for hyperspectral fluorescence microscopy. Opt. Express 2009, 17, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jolivot, R.; Vabres, P.; Marzani, F. Reconstruction of hyperspectral cutaneous data from an artificial neural network-based multispectral imaging system. Comput. Med. Imaging Graph. 2011, 35, 85–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagen, N.; Kudenov, M.W. Review of snapshot spectral imaging technologies. Opt. Eng. 2013, 52, 90901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Hwang, J.-Y.; Krishnanmoorthy, M.; Ning, J.; Zhang, Y.; Ye, K.; Wang, R.-C.; Deen, M.J.; Fang, Q. High throughput AOTF-Based Time-resolved fluorescence spectrometer for optical biopsy. Opt. Lett. 2009, 34, 1132–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nouri, D.; Lucas, Y.; Treuillet, S. Calibration and test of a hyperspectral imaging prototype for intra-operative surgical assistance. In Proceedings of the SPIE, Medical Imaging 2013: Digital Pathology, Orlando, FL, USA, 9 February 2013; Volume 11, p. 86760P. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Kashti, T.; Kella, D.; Frank, T.; Shaked, D.; Ulichney, R.; Fischer, M.; Allebach, J.P. Measuring the modulation transfer function of image capture devices: What do the numbers really mean? In Proceedings of the SPIE, Image Quality and System Performance IX, Burlingame, CA, USA, 25 January 2012; Volume 8293, p. 829307. [Google Scholar]
- Morris, H.R.; Hoyt, C.C. Imaging Spectrometers for Fluorescence and Raman Microscopy: Acousto-Optics and Liquid Crystal Tunable Filters. Appl. Spectrosc. 1994, 48, 847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stratis, D.N.; Eland, K.L.; Carter, J.C.; Angel, S.M.; Tomlinson, S.J. Comparison of Acousto-optic and Liquid Crystal Tunable Filters for Laser-Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy. Appl. Spectrosc. 2001, 55, 999–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, P.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, Y.; Li, C. Accurate optical design of an acousto-optic tunable filter imaging spectrometer. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE International Conference on Imaging Systems and Techniques (IST), Manchester, UK, 16–17 July 2012; pp. 249–253. [Google Scholar]
- Sengul, O.; Turkmenoglu, M.; Yalciner, L.B. MTF Measurements for the Imaging System Quality Analysis. Gazi Univ. J. Sci. 2012, 25, 19–28. [Google Scholar]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abdlaty, R.; Orepoulos, J.; Sinclair, P.; Berman, R.; Fang, Q. High Throughput AOTF Hyperspectral Imager for Randomly Polarized Light. Photonics 2018, 5, 3. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics5010003
Abdlaty R, Orepoulos J, Sinclair P, Berman R, Fang Q. High Throughput AOTF Hyperspectral Imager for Randomly Polarized Light. Photonics. 2018; 5(1):3. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics5010003
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbdlaty, Ramy, John Orepoulos, Peter Sinclair, Richard Berman, and Qiyin Fang. 2018. "High Throughput AOTF Hyperspectral Imager for Randomly Polarized Light" Photonics 5, no. 1: 3. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics5010003
APA StyleAbdlaty, R., Orepoulos, J., Sinclair, P., Berman, R., & Fang, Q. (2018). High Throughput AOTF Hyperspectral Imager for Randomly Polarized Light. Photonics, 5(1), 3. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics5010003




