Assessment of Toxicological Perturbations and Variants of Pancreatic Islet Development in the Zebrafish Model
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Fish
2.2. Chemicals
2.3. Exposures
2.4. Microscopy
2.5. Statistics
3. Results
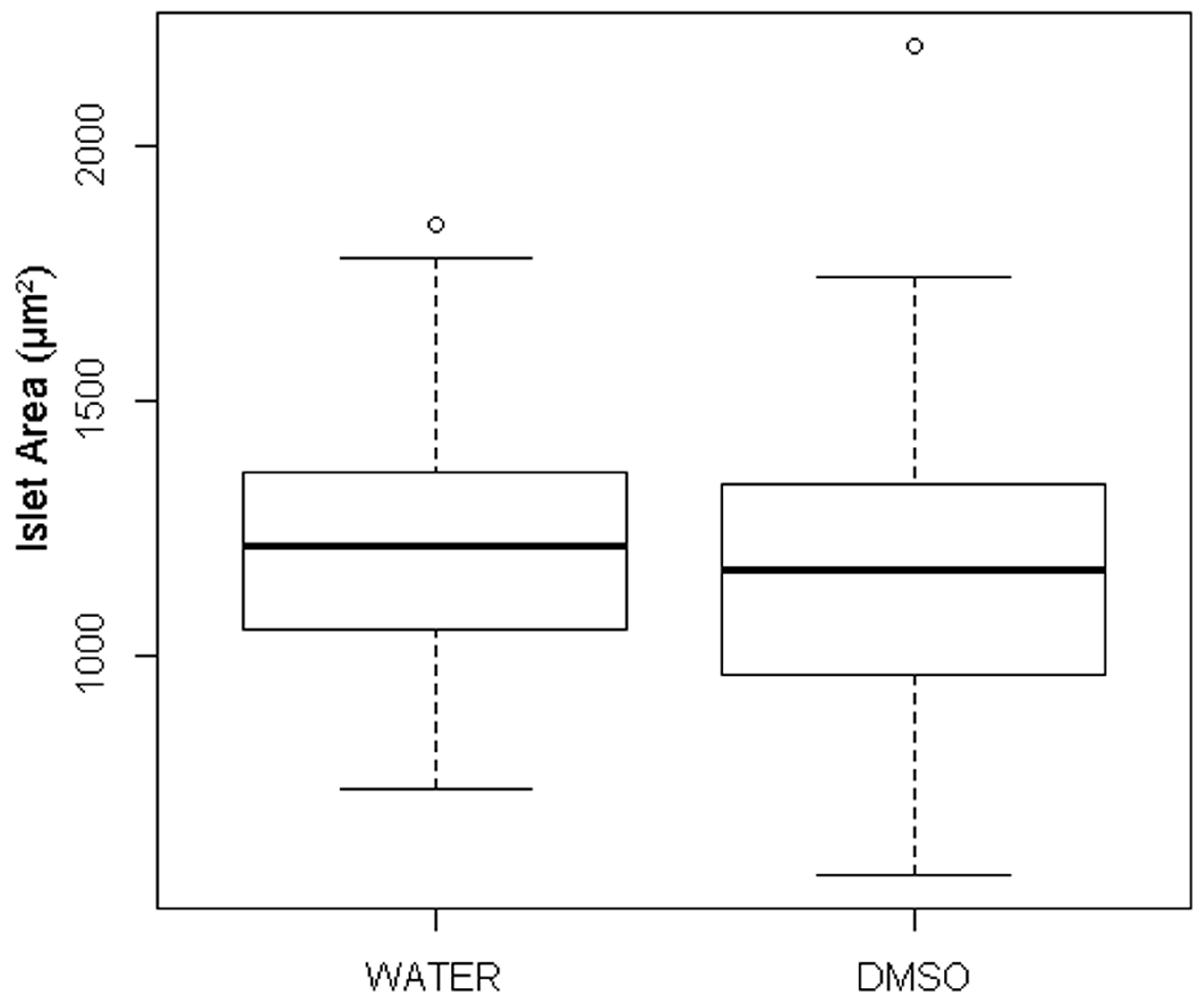
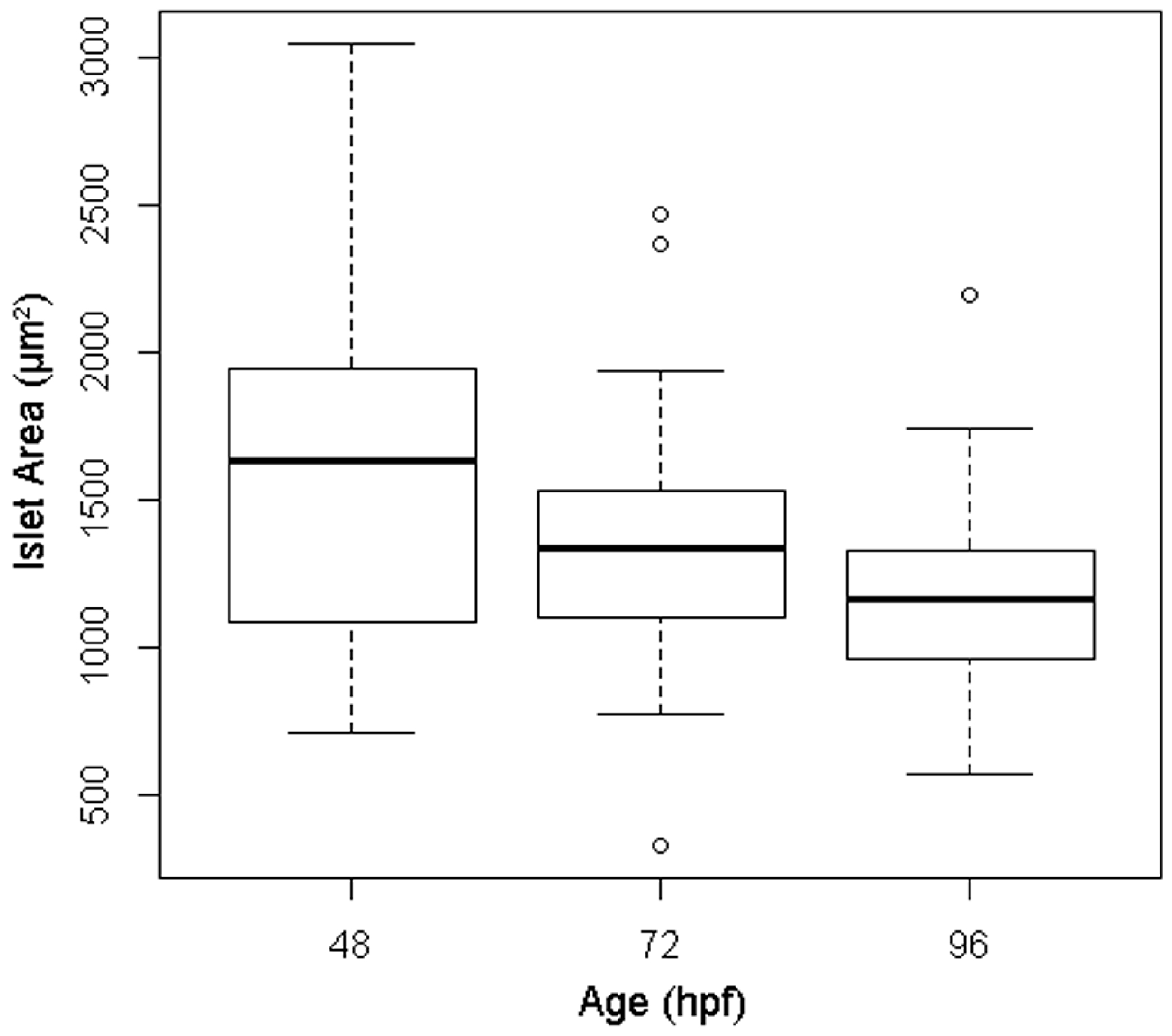
3.1. Quantification of Islet Area among Treatment Control Embryos
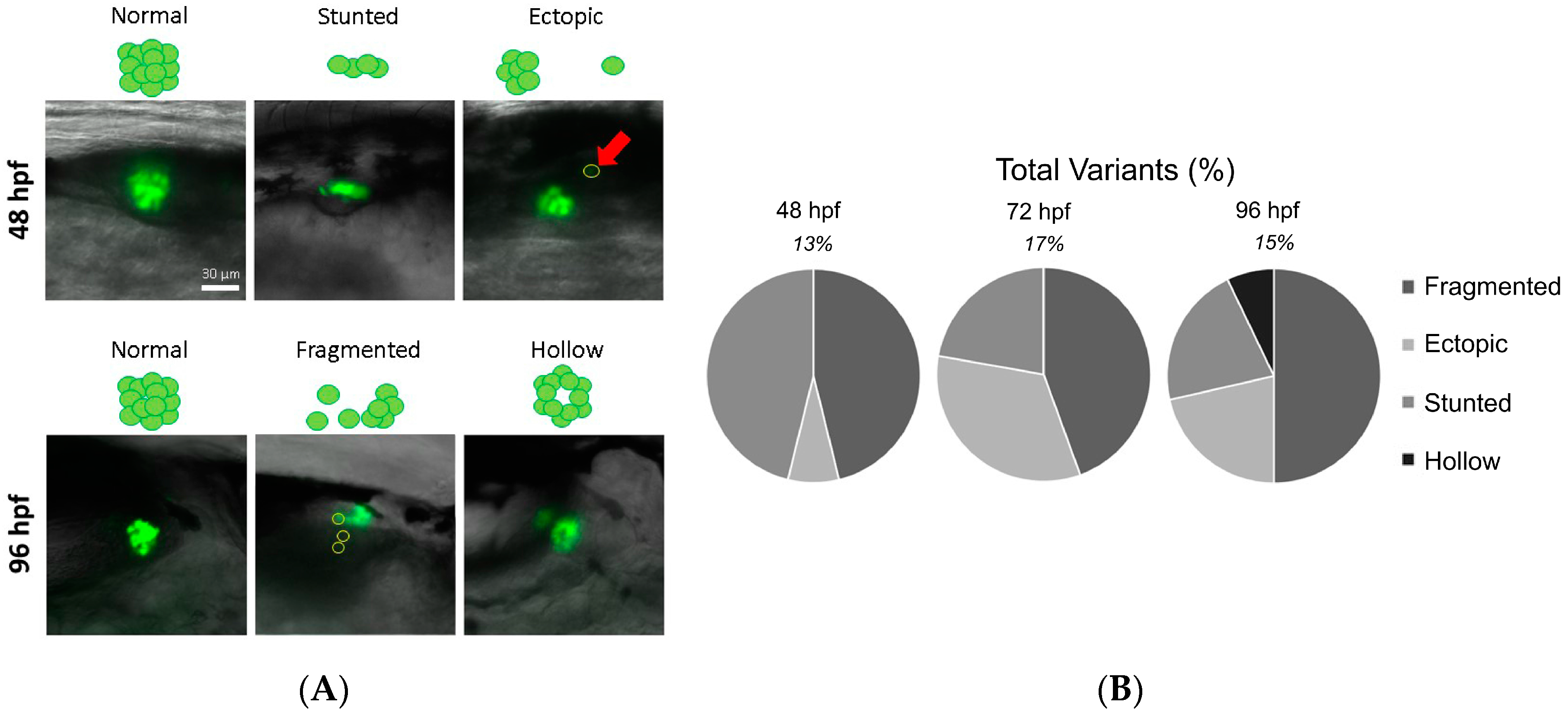
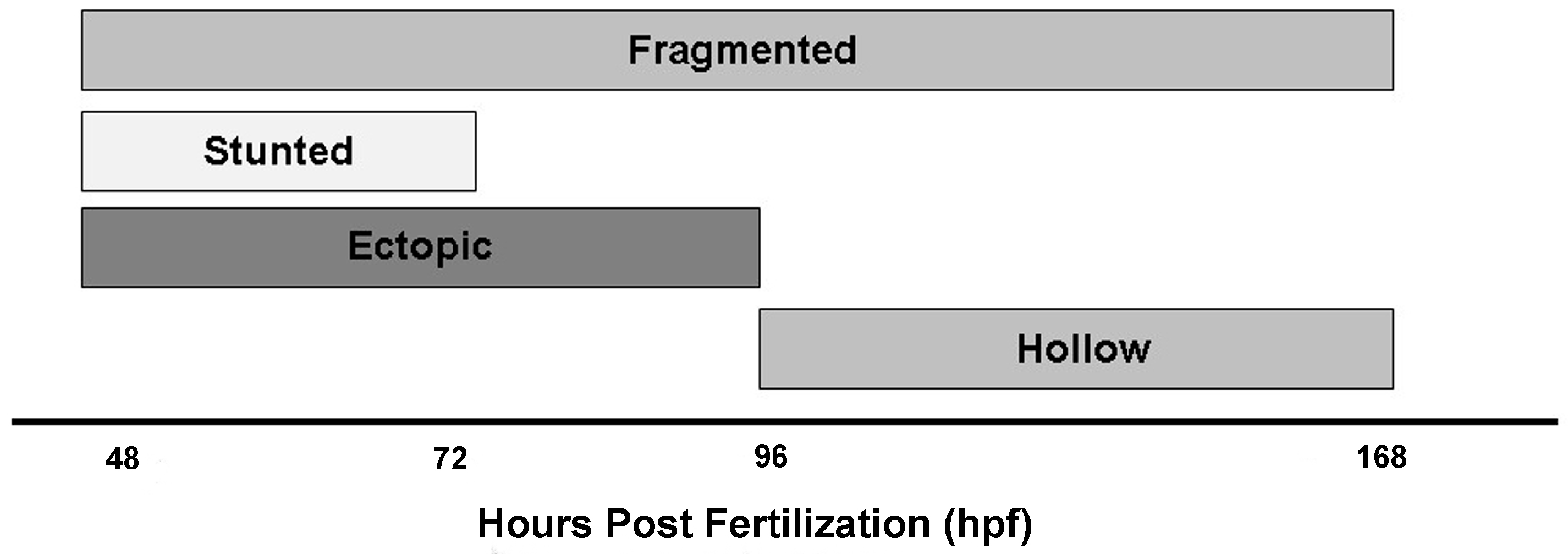
3.2. Identification of Islet Anomalies under Control Conditions
3.3. Contaminant-Induced Abnormalities of the Primary Pancreatic Islet
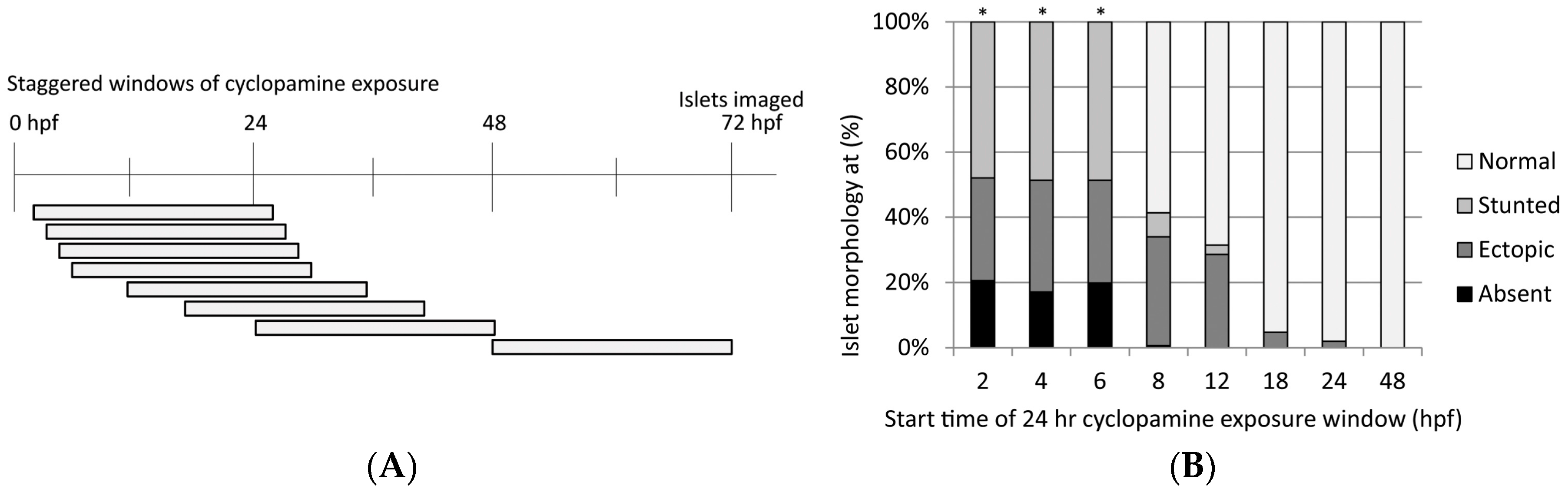
3.3.1. Cyclopamine
3.3.2. MEHP
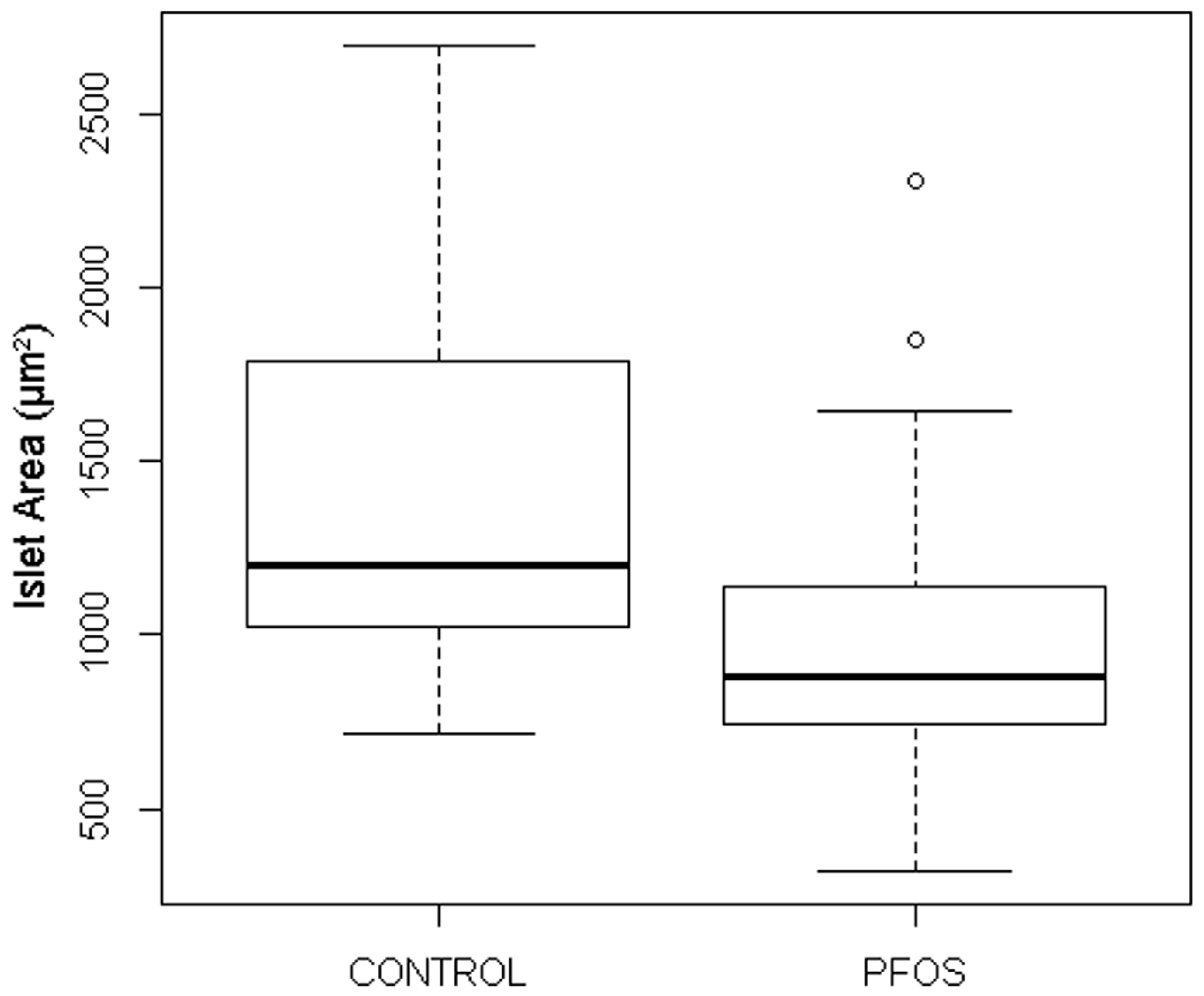
3.3.3. PFOS
3.3.4. tBOOH
4. Discussion
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hectors, T.L.; Vanparys, C.; Van, V.K.; Martens, G.A.; Jorens, P.G.; Van Gaal, L.F.; Covaci, A.; De Coen, W.; Blust, R. Environmental pollutants and type 2 diabetes: A review of mechanisms that can disrupt beta cell function. Diabetologia 2011, 54, 1273–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makaji, E.; Raha, S.; Wade, M.G.; Holloway, A.C. Effect of environmental contaminants on Beta cell function. Int. J. Toxicol. 2011, 30, 410–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barella, L.F.; Oliveira, J.C.; Mathias, P.C. Pancreatic islets and their roles in metabolic programming. Nutrition 2014, 30, 373–379. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schug, T.T.; Barouki, R.; Gluckman, P.D.; Grandjean, P.; Hanson, M.; Heindel, J.J. PPTOX III: Environmental Stressors in the Developmental Origins of Disease—Evidence and Mechanisms. Toxicol. Sci. 2013, 131, 343–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heindel, J.J.; Vandenberg, L.N. Developmental Origins of Health and Disease: A Paradigm for Understanding Disease Etiology and Prevention. Curr. Opin. Pediatr. 2015, 27, 248–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kahn, S.E. Quantifying β-cells in health and disease: The past, the present, and the need. Diabetes Care 2013, 36, 4–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gale, E.A.M. The Rise of Childhood Type 1 Diabetes in the 20th Century. Diabetes 2002, 51, 3353–3361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.-J.; Jiang, J.T.; Ma, L.; Zhang, J.; Hong, Y.; Liao, K.; Liu, Q.; Liu, G.H. Molecular and toxicologic research in newborn hypospadiac male rats following in utero exposure to di-n-butyl phthalate (DBP). Toxicology 2009, 260, 120–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.; Jie, W.; Yuan, Y.L.; Jun, C.; Zhao, Z.; Li, Q.S.; Zheng, Z.W.; Zi, Q.L.; Chen, X.; Wei, X.; et al. Developmental exposure to di(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate impairs endocrine pancreas and leads to long-term adverse effects on glucose homeostasis in the rat. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 301, E527–E538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rovira, M.; Wei, H.; Shamila, Y.; Joong, S.S.; Anthony, A.F.; Jun, O.L.; Michael, J.P. Chemical screen identifies FDA-approved drugs and target pathways that induce precocious pancreatic endocrine differentiation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 19264–19269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Audouze, K.; Brunak, S.; Grandjean, P. A computational approach to chemical etiologies of diabetes. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kuo, C.C.; Moon, K.; Thayer, K.A.; Navas-Acien, A. Environmental Chemicals and Type 2 Diabetes: An Updated Systematic Review of the Epidemiologic Evidence. Curr. Diabetes Rep. 2013, 13, 831–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Tanguay, R.L.; Tal, T.L.; Gai, Z.; Ma, X.; Bai, C.; Tilton, S.C.; Jin, D.; Yang, D.; Huang, C.; et al. Early life perfluorooctanesulphonic acid (PFOS) exposure impairs zebrafish organogenesis. Aquat. Toxicol. 2014, 150, 124–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Timme-Laragy, A.; Sant, K.E.; Rousseau, M.E.; diIorio, P.J. Deviant development of pancreatic beta cells from embryonic exposure to PCB-126 in zebrafish. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2015, 178, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- diIorio, P.J.; Moss, J.B.; Sbrogna, J.L.; Karlstrom, R.O.; Mossm, L.G. Sonic hedgehog Is Required Early in Pancreatic Islet Development. Dev. Biol. 2002, 244, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zorn, A.M.; Wells, J.M. Molecular Basis of Vertebrate Endoderm Development. In International Review of Cytology, 1st ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2007; pp. 49–111. [Google Scholar]
- Kinkel, M.D.; Prince, V.E. On the diabetic menu: Zebrafish as a model for pancreas development and function. BioEssays: News and reviews in molecular. Cell. Dev. Biol. 2009, 31, 139–152. [Google Scholar]
- Hesselson, D.; Ryan, M.A.; Marine, B.; Didier, Y.R.S. Distinct populations of quiescent and proliferative pancreatic β-cells identified by HOTcre mediated labeling. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 14896–14901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tehrani, Z.; Lin, S. Endocrine pancreas development in zebrafish. Cell Cycle 2011, 10, 3466–3472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Rovira, M.; Yusuff, S.; Parsons, M.J. Genetic inducible fate mapping in larval zebrafish reveals origins of adult insulin-producing β-cells. Development 2011, 138, 609–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Rajpurohit, S.K.; Delaspre, F.; Walker, S.L.; White, D.T.; Ceasrine, A.; Kuruvilla, R.; Li, R.J.; Shim, J.S.; Liu, J.O.; et al. First quantitative high-throughput screen in zebrafish identifies novel pathways for increasing pancreatic beta-cell mass. Elife 2015, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lenzen, S.; Drinkgern, J.; Tiedge, M. Low antioxidant enzyme gene expression in pancreatic islets compared with various other mouse tissues. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1996, 20, 463–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, M.; Yamato, E.; Toyoda, S.; Tashiro, F.; Ikegami, H.; Yodoi, J.; Miyazaki, J. Transgenic Expression of Antioxidant Protein Thioredoxin in Pancreatic β Cells Prevents Progression of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2007, 10, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hotta, M.; Tashiro, F.; Ikegami, H.; Niwa, H.; Ogihara, T.; Yodoi, J.J.; Miyazaki, J.-I. Pancreatic β Cell–specific Expression of Thioredoxin, an Antioxidative and Antiapoptotic Protein, Prevents Autoimmune and Streptozotocin-induced Diabetes. J. Exp. Med. 1998, 188, 1445–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Eberhard, D.; Kragl, M.; Lammert, E. ‘Giving and taking’: Endothelial and beta-cells in the islets of Langerhans. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2010, 21, 457–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dominguez-Munoz, J.E. Pancreatic exocrine insufficiency: Diagnosis and treatment. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2011, 26, 12–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, N.M.; Metzger, D.L.; Borowitz, S.M.; Clarke, W.L. Permanent neonatal diabetes mellitus and pancreatic exocrine insufficiency resulting from congenital pancreatic agenesis. Am. J. Dis. Child. 1993, 147, 607–609. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Agabi, J.O.; Akhigbe, A.O. Comparative sonographic evaluation of the anteroposterior dimensions of the pancreas in diabetics and nondiabetics. Niger. J. Clin. Pract. 2016, 19, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Elayat, A.A.; el-Naggar, M.M.; Tahir, M. An immunocytochemical and morphometric study of the rat pancreatic islets. J. Anat. 1995, 186, 629–637. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Misawa, R.; Zielinski, M.C.; Cowen, P.; Jo, J.; Periwal, V.; Ricordi, C.; Khan, A.; Szust, J.; Shen, J.H.; et al. Regional differences in islet distribution in the human pancreas—Preferential beta-cell loss in the head region in patients with type 2 diabetes. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e67454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wittingen, J.; Frey, C.F. Islet concentration in the head, body, tail and uncinate process of the pancreas. Ann. Surg. 1974, 179, 412–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oatis, J.E.; Brunsfeld, P.; Rushing, J.M.; Moeller, P.D.; Bearden, D.W.; Gallien, T.N.; Cooper, G. Isolation, purification, and full NMR assignments of cyclopamine from Veratrum californicum. Chem. Cent. J. 2008, 2, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Trasande, L.; Adam, J.S.; Sheela, S.; Teresa, M.A.; Jan, B. Urinary Phthalates and Increased Insulin Resistance in Adolescents. Pediatrics 2013, 132, e646–e655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sathyanarayana, S.; Calafat, A.M.; Liu, F.; Swan, S.H. Maternal and Infant Urinary Phthalate Metabolite Concentrations: Are They Related? Environ. Res. 2008, 108, 413–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez-Arguelles, D.B.; Campioli, E.; Culty, M.; Zirkin, B.R.; Papadopoulos, V. Fetal origin of endocrine dysfunction in the adult: The Phthalate Model. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2013, 137, 5–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sant, K.E.; Dolinoy, D.C.; Jilek, J.L.; Shay, B.J.; Harris, C. Mono-2-ethylhexyl phthalate (MEHP) alters histiotrophic nutrition pathways and epigenetic processes in the developing conceptus. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2016, 27, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hurst, C.H.; Waxman, D.J. Activation of PPARα and PPARγ by Environmental Phthalate Monoesters. Toxicol. Sci. 2003, 74, 297–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inoue, K.; Okada, F.; Ito, R.; Kato, S.; Sasaki, S.; Nakajima, S.; Uno, A.; Saijo, Y.; Sata, F.; Yoshimura, Y.; et al. Perfluorooctane Sulfonate (PFOS) and Related Perfluorinated Compounds in Human Maternal and Cord Blood Samples: Assessment of PFOS Exposure in a Susceptible Population during Pregnancy. Environ. Health Perspect. 2004, 112, 1204–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jensen, M.S.; Nørgaard-Pedersen, B.; Toft, G.; Hougaard, D.M.; Bonde, J.P.; Cohen, A.; Thulstrup, A.M.; Ivell, R.; Anand-Ivell, R.; Lindh, C.H.; et al. Phthalates and Perfluorooctanesulfonic Acid in Human Amniotic Fluid: Temporal Trends and Timing of Amniocentesis in Pregnancy. Environ. Health Perspect. 2012, 120, 897–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toft, G.; Jönsson, B.A.G.; Bonde, J.P.; Nørgaard-Pedersen, B.; Hougaard, D.M.; Cohen, A.; Lindh, C.H.; Ivell, R.; Anand-Ivell, R.; Lindhard, M.S. Perfluorooctane Sulfonate Concentrations in Amniotic Fluid, Biomarkers of Fetal Leydig Cell Function, and Cryptorchidism and Hypospadias in Danish Boys (1980–1996). Environ. Health Perspect. 2016, 124, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Stein, C.R.; Wolff, M.S.; Calafat, A.M.; Kato, K.; Engel, S.M. Comparison of Polyfluoroalkyl Compound Concentrations in Maternal Serum and Amniotic Fluid: A Pilot Study. Reprod. Toxicol. 2012, 34, 312–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maestri, L.; Negri, S.; Ferrari, M.; Ghittori, S.; Fabris, F.; Danesino, P.; Imbriani, M. Determination of perfluorooctanoic acid and perfluorooctanesulfonate in human tissues by liquid chromatography/single quadrupole mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2006, 20, 2728–2734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.Y.; Chen, P.C.; Lin, Y.C.; Lin, L.Y. Association among serum perfluoroalkyl chemicals, glucose homeostasis, and metabolic syndrome in adolescents and adults. Diabetes Care 2009, 32, 702–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Q.; Cornelis, M.C.; Townsend, M.K.; Tobias, D.K.; Eliassen, H.; Franke, A.A.; Hauser, R.; Hu, F.B. Association of Urinary Concentrations of Bisphenol A and Phthalate Metabolites with Risk of Type 2 Diabetes: A Prospective Investigation in the Nurses’ Health Study (NHS) and NHSII Cohorts. Environ. Health Perspect. 2014, 122, 616–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parsons, M.J.; Pisharath, H.; Yusuff, S.; Moore, J.C.; Siekmann, A.F.; Lawson, N.; Leach, S.D. Notch-responsive cells initiate the secondary transition in larval zebrafish pancreas. Mech. Dev. 2009, 126, 898–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuda, H.; Parsons, M.J.; Leach, S.D. Aldh1-Expressing Endocrine Progenitor Cells Regulate Secondary Islet Formation in Larval Zebrafish Pancreas. PLoS ONE 2013, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersson, O.; Adams, B.A.; Yoo, D.; Ellis, G.C.; Gut, P.; Anderson, R.M.; German, M.S.; Stainier, D.Y. Adenosine signaling promotes regeneration of pancreatic β-cells in vivo. Cell Metab. 2012, 15, 885–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuji, N.; Ninov, N.; Delawary, M.; Osman, S.; Roh, A.S.; Gut, P.; Didier, Y.R.; Stainier, D.Y.R. Whole Organism High Content Screening Identifies Stimulators of Pancreatic Beta-Cell Proliferation. PLoS ONE 2014, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ninov, N.; Hesselson, D.; Gut, P.; Zhou, A.; Fidelin, K.; Stainier, D.Y. Metabolic regulation of cellular plasticity in the pancreas. Curr. Biol. CB 2013, 23, 1242–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maddison, L.A.; Chen, W. Nutrient Excess Stimulates β-Cell Neogenesis in Zebrafish. Diabetes 2012, 61, 2517–2524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wicksteed, B.; Brissova, M.; Yan, W.; Opland, D.M.; Plank, J.L.; Reinert, R.B.; Dickson, L.M.; Tamarina, N.A.; Philipson, L.H.; Shostak, A.; et al. Conditional Gene Targeting in Mouse Pancreatic β-Cells: Analysis of Ectopic Cre Transgene Expression in the Brain. Diabetes 2010, 59, 3090–3098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, J.W.; Biankin, A.V.; Horb, M.E.; Ghosh, B.; Prasad, N.B.; Yee, N.S.; Pack, M.A.; Leach, S.D. Differential requirement for ptf1a in endocrine and exocrine lineages of developing zebrafish pancreas. Dev. Biol. 2004, 274, 491–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Godinho, L.; Mumm, J.S.; Williams, P.R.; Schroeter, E.H.; Koerber, A.; Park, S.W.; Leach, S.D.; Wong, R.O. Targeting of amacrine cell neurites to appropriate synaptic laminae in the developing zebrafish retina. Development 2005, 132, 5069–5079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Westerfield, M. The Zebrafish Book. A Guide for the Laboratory Use of Zebrafish (Danio Rerio); University of Oregon Press: Eugene, OR, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Varshney, S.; Johnson, C.D. Pancreas divisum. Int. J. Pancreatol. 1999, 25, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaughn, D.D.; Jabra, A.A.; Fishman, E.K. Pancreatic disease in children and young adults: Evaluation with CT. Radiographics 1998, 18, 1171–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prasad, T.R.; Gupta, S.D.; Bhatnagar, V. Ectopic pancreas associated with a choledochal cyst and extrahepatic biliary atresia. Pediatr. Surg. Int. 2001, 17, 552–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alonso-Magdalena, P.; Quesada, I.; Nadal, A. Endocrine disruptors in the etiology of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2011, 7, 346–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chevalier, N.; Fenichel, P. Endocrine disruptors: New players in the pathophysiology of type 2 diabetes? Diabetes Metab. 2015, 41, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodman, M.; Narayan, K.M.; Flanders, D.; Chang, E.T.; Adami, H.O.; Boffetta, P.; Mandel, J.S. Dose-Response Relationship Between Serum 2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-Dioxin and Diabetes Mellitus: A Meta-Analysis. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2015, 181, 374–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaacks, L.M.; Staimez, L.R. Association of persistent organic pollutants and non-persistent pesticides with diabetes and diabetes-related health outcomes in Asia: A systematic review. Environ. Int. 2015, 76, 57–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sung, T.-C.; Huang, J.-W.; Guo, H.-R. Association between Arsenic Exposure and Diabetes: A Meta-Analysis. Biomed. Res. Int. 2015, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, C.J.; Ryckman, K.K. Epigenetic and developmental influences on the risk of obesity, diabetes, and metabolic syndrome. Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity. Targets Ther. 2015, 8, 295–302. [Google Scholar]
- Bodin, J.; Stene, L.C.; Nygaard, U.C. Can Exposure to Environmental Chemicals Increase the Risk of Diabetes Type 1 Development? Biomed. Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 208947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Xie, Z.T.; Lin, Y.; Zhang, D.F. Association of inorganic arsenic exposure with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A meta-analysis. J. Epidemiol. Community Health 2014, 68, 176–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janghorbani, M.; Momeni, F.; Mansourian, M. Systematic review and metaanalysis of air pollution exposure and risk of diabetes. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2014, 29, 231–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navas-Acien, A.; Silbergeld, E.K.; Streeter, R.A.; Clark, J.M.; Burke, T.A.; Guallar, E. Arsenic Exposure and Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review of the Experimental and Epidemiologic Evidence. Environ. Health Perspect. 2006, 114, 641–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitehead, R.; Guan, H.; Arany, E.; Cernea, M.; Yang, K. Prenatal exposure to bisphenol A alters mouse fetal pancreatic morphology and islet composition. Horm. Mol. Biol. Clin. Investig. 2016, 25, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trevino, S.; Waalkes, M.P.; Flores, H.J.A.; León-Chavez, B.A.; Aguilar-Alonso, P.; Brambila, E. Chronic cadmium exposure in rats produces pancreatic impairment and insulin resistance in multiple peripheral tissues. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2015, 583, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Wu, T.; Chen, M.; Guo, Z.; Yang, Z.; Zuo, Z.; Wang, C. Chronic Exposure to Aroclor 1254 Disrupts Glucose Homeostasis in Male Mice via Inhibition of the Insulin Receptor Signal Pathway. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 10084–10092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alonso-Magdalena, P.; García-Arévalo, M.; Quesada, I.; Nadal, Á. Bisphenol-A treatment during pregnancy in mice: A new window of susceptibility for the development of diabetes in mothers later in life. Endocrinology 2015, 156, 1659–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lasram, M.M.; Bouzid, K.; Douib, I.B.; Annabi, A.; Elj, N.; Fazaa, S.; Abdelmoula, J.; Gharbi, N. Lipid metabolism disturbances contribute to insulin resistance and decrease insulin sensitivity by malathion exposure in Wistar rat. Drug Chem. Toxicol. 2015, 38, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajesh, P.; Balasubramanian, K. Gestational exposure to di(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate (DEHP) impairs pancreatic β-cell function in F1 rat offspring. Toxicol. Lett. 2015, 232, 46–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eriksson, J.G.; Forsén, T.; Tuomilehto, J.; Winter, P.D.; Osmond, C.; Barker, D.J.P. Catch-up growth in childhood and death from coronary heart disease: Longitudinal study. BMJ Br. Med. J. 1999, 318, 427–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dulloo, A.G.; Jacquet, J.; Seydoux, J.; Montani, J.P. The thrifty ‘catch-up fat’ phenotype: Its impact on insulin sensitivity during growth trajectories to obesity and metabolic syndrome. Int J. Obes. 2006, 30, S23–S35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hermann, G.M.; Miller, R.L.; Erkonen, G.E.; Dallas, L.M.; Hsu, E.; Zhu, V.; Roghair, R.D. Neonatal Catch-Up Growth Increases Diabetes Susceptibility But Improves Behavioral and Cardiovascular Outcomes of Low Birth Weight Male Mice. Pediatr. Res. 2009, 66, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiso, N.; Moro, E.; Argenton, F. Zebrafish pancreas development. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2009, 312, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Field, H.A.; Donga, S.P.D.; Beisa, D.; Stainier, D.Y.R. Formation of the digestive system in zebrafish. II. pancreas morphogenesis. Dev. Biol. 2003, 261, 197–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biemar, F.; Argenton, F.; Schmidtke, R.; Epperlein, S.; Peers, B.; Driever, W. Pancreas Development in Zebrafish: Early Dispersed Appearance of Endocrine Hormone Expressing Cells and Their Convergence to Form the Definitive Islet. Dev. Biol. 2001, 230, 189–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.; Vogel, S.S.; Liu, N.; Melton, D.A.; Lin, S. Analysis of pancreatic development in living transgenic zebrafish embryos. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2001, 177, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadokoro, H.; Takase, M.; Nobukawa, B. Development and congenital anomalies of the pancreas. Anat. Res. Int. 2011, 2011, 351217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bento, A.; Baptista, H.; Oliveira, F. Congenital pancreas malformations: A clinical case report. Rev. Assoc. Med. Bras. 2013, 59, 35–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nijs, E.; Callahan, M.J.; Taylor, G.A. Disorders of the pediatric pancreas: Imaging features. Pediatr. Radiol. 2005, 35, 358–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poki, H.O.; Holland, A.J.; Pitkin, J. Double bubble, double trouble. Pediatr. Surg. Int. 2005, 21, 428–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balakrishnan, V.; Narayanan, V.A.; Siyad, I.; Radhakrishnan, L.; Nair, P. Agenesis of the dorsal pancreas with chronic calcific pancreatitis. Case report, review of the literature and genetic basis. JOP 2006, 7, 651–659. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shoji, F.; Takeo, S.; Shikada, Y.; Katsura, M. Anterior mediastinal gastroenteric cyst containing pancreatic tissue influenced the diabetes mellitus status. Interact. Cardiovasc. Thorac. Surg. 2013, 16, 413–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lainakis, N.; Antypas, S.; Panagidis, A.; Alexandrou, I.; Kambouri, K.; Kyriazis, C.; Dolatzas, T. Annular pancreas in two consecutive siblings: An extremely rare case. Eur. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2005, 15, 364–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Concepcion, J.P.; Reh, C.S.; Daniels, M.; Liu, X.; Paz, V.P.; Ye, H.; Highland, H.M.; Hanis, C.L.; Greeley, S.A. Neonatal Diabetes, Gallbladder Agenesis, Duodenal Atresia, and Intestinal Malrotation Caused by a Novel Homozygous Mutation in RFX6. Pediatr. Diabetes 2014, 15, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gentile, M.; Fiorente, P. Esophageal, duodenal, rectoanal and biliary atresia, intestinal malrotation, malformed/hypoplastic pancreas, and hypospadias: Further evidence of a new distinct syndrome. Am. J. Med. Genet. 1999, 87, 82–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilinsky, N.H.; Lewis, J.W.; Flueck, J.A.; Fried, A.M. Annular pancreas associated with diffuse chronic pancreatitis. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 1987, 82, 681–684. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mitchell, J.; Punthakee, Z.; Lo, B.; Bernard, C.; Chong, K.; Newman, C.; Cartier, L.; Desilets, V.; Cutz, E.; Hansen, I.L.; et al. Neonatal diabetes, with hypoplastic pancreas, intestinal atresia and gall bladder hypoplasia: Search for the aetiology of a new autosomal recessive syndrome. Diabetologia 2004, 47, 2160–2167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moss, L.G.; Caplan, T.V.; Moss, J.B. Imaging beta cell regeneration and interactions with islet vasculature in transparent adult zebrafish. Zebrafish 2013, 10, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
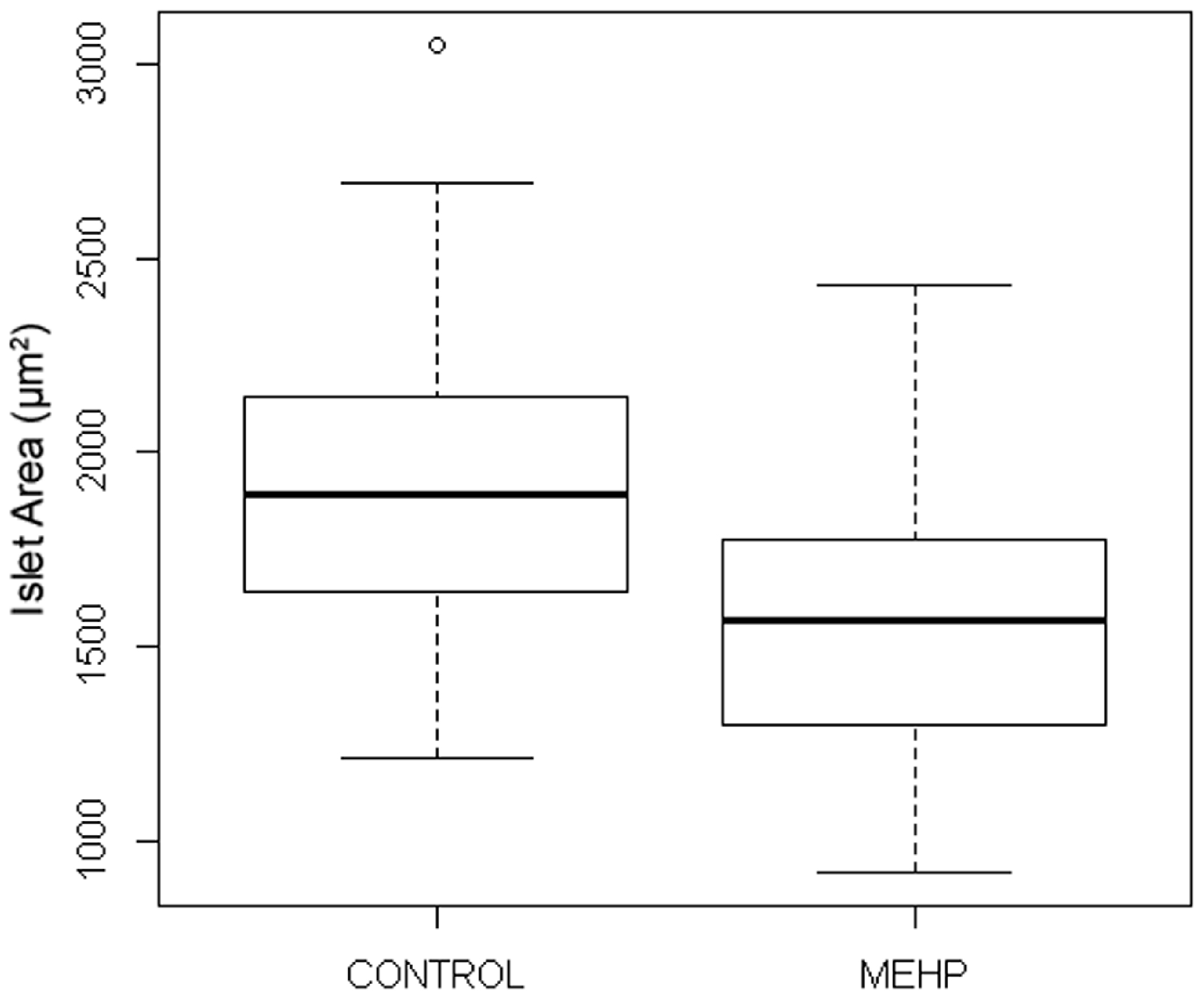

| Variant Phenotype | Control (DMSO 1) | MEHP 2 (0.7 µM) |
|---|---|---|
| Fragmented Islets | 5/29 (17%) | 4/27 (15%) |
| Ectopic Beta Cells | 0/29 (0%) | 3/27 (11%) |
| Total Variants | 5/29 (17%) | 7/27 (26%) |
| Variant Phenotype | Control (DMSO) | PFOS 1 (32 µM) |
|---|---|---|
| Fragmented Islets | 1/37 (3%) | 3/39 (18%) |
| Ectopic Beta Cells | 1/37 (3%) | 1/39 (3%) |
| Stunted Islets | 1/37 (3%) | 11/39 (28%) |
| Total Variants | 3/37 (8%) | 15/39 (38%) |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sant, K.E.; Jacobs, H.M.; Xu, J.; Borofski, K.A.; Moss, L.G.; Moss, J.B.; Timme-Laragy, A.R. Assessment of Toxicological Perturbations and Variants of Pancreatic Islet Development in the Zebrafish Model. Toxics 2016, 4, 20. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics4030020
Sant KE, Jacobs HM, Xu J, Borofski KA, Moss LG, Moss JB, Timme-Laragy AR. Assessment of Toxicological Perturbations and Variants of Pancreatic Islet Development in the Zebrafish Model. Toxics. 2016; 4(3):20. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics4030020
Chicago/Turabian StyleSant, Karilyn E., Haydee M. Jacobs, Jiali Xu, Katrina A. Borofski, Larry G. Moss, Jennifer B. Moss, and Alicia R. Timme-Laragy. 2016. "Assessment of Toxicological Perturbations and Variants of Pancreatic Islet Development in the Zebrafish Model" Toxics 4, no. 3: 20. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics4030020
APA StyleSant, K. E., Jacobs, H. M., Xu, J., Borofski, K. A., Moss, L. G., Moss, J. B., & Timme-Laragy, A. R. (2016). Assessment of Toxicological Perturbations and Variants of Pancreatic Islet Development in the Zebrafish Model. Toxics, 4(3), 20. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics4030020






