Development of Highly Efficient Universal Pneumocystis Primers and Their Application in Investigating the Prevalence and Genetic Diversity of Pneumocystis in Wild Hares and Rabbits
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Source and DNA Extraction
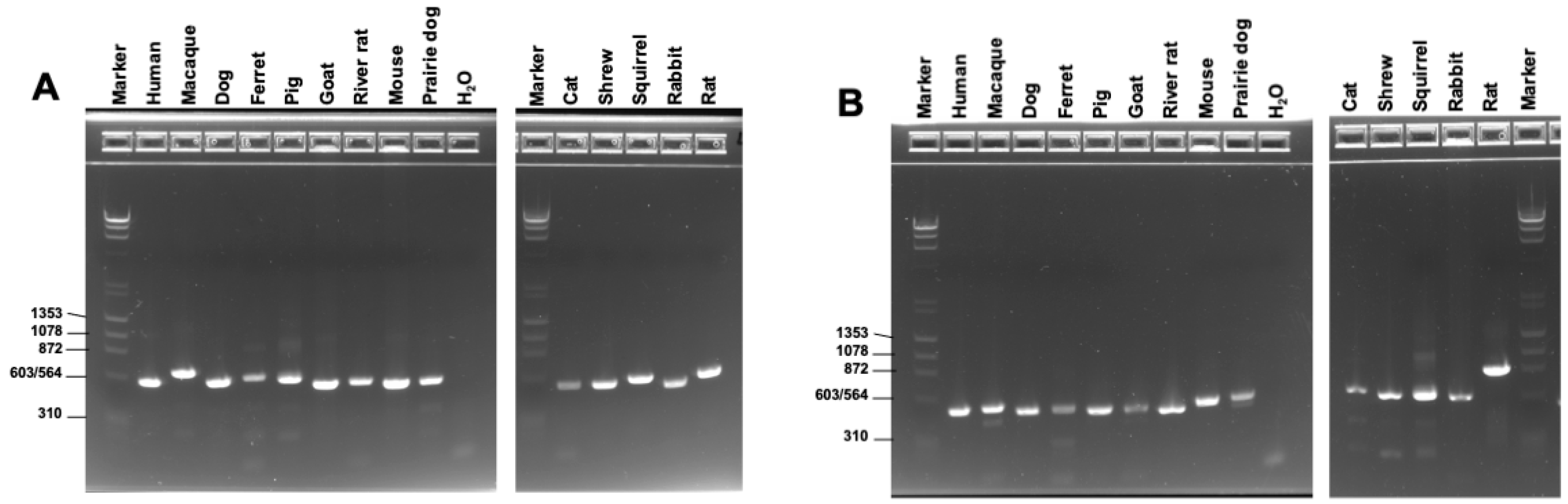
2.2. Design and Testing of Universal Primers for the Pneumocystis Genus
2.3. Determination of the Prevalence of Pneumocystis Infection in Hares and Rabbits by PCR
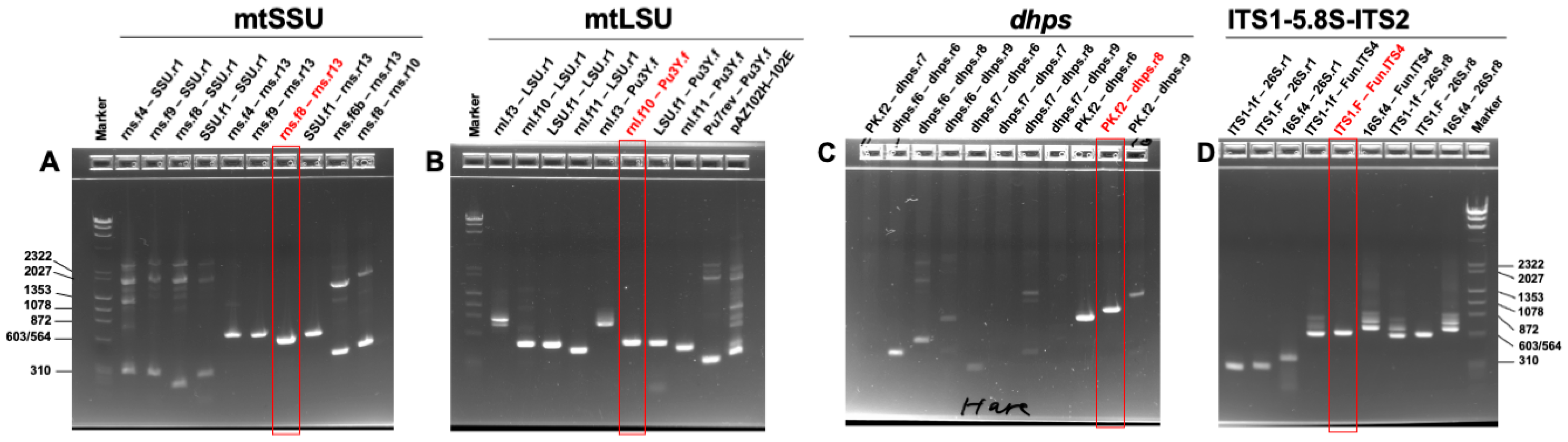
2.4. Genetic Divergence Analysis of Pneumocystis in Hares and Rabbits by Multi-Locus PCR and Sequencing
2.5. Sequencing of the Mitochondrial Genome (mtDNA) and Nuclear rRNA Operon (rDNA) of P. sp. ‘Townsendii’
2.6. Gene Annotation, Sequence Similarity, and Evolutionary Distance Estimation
2.7. Phylogenetic Analysis
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Universal Pneumocystis Primer Design
3.2. Prevalence of Pneumocystis in Hares and Rabbits
3.3. Genetic Variation of Pneumocystis in Hares and Rabbits
3.4. Phylogeny of Pneumocystis in Hares and Rabbits
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Weissenbacher-Lang, C.; Grenl, A.; Blasi, B. Meta-analysis and systematic literature review of the genus Pneumocystis in pet, farm, zoo, and wild mammal species. J. Fungi 2023, 9, 1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, L.; Cisse, O.H.; Kovacs, J.A. A molecular window into the biology and epidemiology of Pneumocystis spp. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2018, 31, e00009-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aliouat-Denis, C.M.; Chabe, M.; Demanche, C.; Aliouat, E.M.; Viscogliosi, E.; Guillot, J.; Delhaes, L.; Dei-Cas, E. Pneumocystis species, co-evolution and pathogenic power. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2008, 8, 708–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hugot, J.P.; Demanche, C.; Barriel, V.; Dei-Cas, E.; Guillot, J. Phylogenetic systematics and evolution of primate-derived Pneumocystis based on mitochondrial or nuclear DNA sequence comparison. Syst. Biol. 2003, 52, 735–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durand-Joly, I.; Aliouat, E.M.; Recourt, C.; Guyot, K.; Francois, N.; Wauquier, M.; Camus, D.; Dei-Cas, E. Pneumocystis carinii f. sp. hominis is not infectious for SCID mice. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2002, 40, 1862–1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carini, A.; Maciel, J. Ueber Pneumocystis carinii. Zentr. Bakt. Orig. 1916, 777, 46. [Google Scholar]
- Dei-Cas, E.; Chabe, M.; Moukhlis, R.; Durand-Joly, I.; Aliouat, E.M.; Stringer, J.R.; Cushion, M.; Noel, C.; de Hoog, G.S.; Guillot, J.; et al. Pneumocystis oryctolagi sp. nov., an uncultured fungus causing pneumonia in rabbits at weaning: Review of current knowledge, and description of a new taxon on genotypic, phylogenetic and phenotypic bases. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2006, 30, 853–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reinhardt, D.J.; Kaplan, W.; Chandler, F.W. Morphologic resemblance of zygomycete spores to Pneumocystis carinii cysts in tissue. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 1977, 115, 170–172. [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen, M.H.; Settnes, O.P.; Aliouat, E.M.; Cailliez, J.C.; Dei-Cas, E. Different ultrastructural morphology of Pneumocystis carinii derived from mice, rats, and rabbits. APMIS 1998, 106, 771–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palluault, F.; Pietrzyk, B.; Dei-Cas, E.; Slomianny, C.; Soulez, B.; Camus, D. Three-dimensional reconstruction of rabbit-derived Pneumocystis carinii from serial-thin sections. II: Intermediate precyst. J. Protozool. 1991, 38, 407–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palluault, F.; Pietrzyk, B.; Dei-Cas, E.; Slomianny, C.; Soulez, B.; Camus, D. Three-dimensional reconstruction of rabbit-derived Pneumocystis carinii from serial-thin sections. I: Trophozoite. J. Protozool. 1991, 38, 402–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cere, N.; Drouet-Viard, F.; Dei-Cas, E.; Chanteloup, N.; Coudert, P. In utero transmission of Pneumocystis carinii sp. f. oryctolagi. Parasite 1997, 4, 325–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez, C.A.; Chabe, M.; Aliouat, E.M.; Durand-Joly, I.; Gantois, N.; Conseil, V.; Lopez, C.; Duriez, T.; Dei-Cas, E.; Vargas, S.L. Exploring transplacental transmission of Pneumocystis oryctolagi in first-time pregnant and multiparous rabbit does. Med. Mycol. 2007, 45, 701–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dei-Cas, E.; Mazars, E.; Ferragut, C.O.; Durand, I.; Aliouat, E.M.; Dridba, M.; Palluault, F.; Cailliez, J.C.; Seguy, N.; Tibayrenc, M.; et al. Ultrastructural, genomic, isoenzymatic and biological features make it possible to distinguish rabbit Pneumocystis from other mammal Pneumocystis strains. J. Eukaryot. Microbiol. 1994, 41, 84S. [Google Scholar]
- Banerji, S.; Lugli, E.B.; Miller, R.F.; Wakefield, A.E. Analysis of genetic diversity at the arom locus in isolates of Pneumocystis carinii. J. Eukaryot. Microbiol. 1995, 42, 675–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazars, E.; Odberg-Ferragut, C.; Dei-Cas, E.; Fourmaux, M.N.; Aliouat, E.M.; Brun-Pascaud, M.; Mougeot, G.; Camus, D. Polymorphism of the thymidylate synthase gene of Pneumocystis carinii from different host species. J. Eukaryot. Microbiol. 1995, 42, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, M.; Morgenthaler, T.I.; Hoffman, O.A.; Standing, J.E.; Rohrbach, M.S.; Limper, A.H. Pneumocystis carinii induces the release of arachidonic acid and its metabolites from alveolar macrophages. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 1993, 9, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neese, L.W.; Standing, J.E.; Olson, E.J.; Castro, M.; Limper, A.H. Vitronectin, fibronectin, and gp120 antibody enhance macrophage release of TNF-alpha in response to Pneumocystis carinii. J. Immunol. 1994, 152, 4549–4556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamburrini, E.; Ortona, E.; Visconti, E.; Mencarini, P.; Margutti, P.; Zolfo, M.; Barca, S.; Peters, S.E.; Wakefield, A.E.; Siracusano, A. Pneumocystis carinii infection in young non-immunosuppressed rabbits. Kinetics of infection and of the primary specific immune response. Med. Microbiol. Immunol. 1999, 188, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pifer, L.L.; Pifer, D.D.; Woods, D.R.; Joyner, R.E.; Edwards, C.C. Preliminary studies on the development of a vaccine for Pneumocystis carinii. I. Immunological and biochemical characterization. Vaccine 1986, 4, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gigliotti, F.; Hughes, W.T. Passive immunoprophylaxis with specific monoclonal antibody confers partial protection against Pneumocystis carinii pneumonitis in animal models. J. Clin. Investig. 1988, 81, 1666–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soulez, B.; Dei-Cas, E.; Charet, P.; Mougeot, G.; Caillaux, M.; Camus, D. The young rabbit: A nonimmunosuppressed model for Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia. J. Infect. Dis. 1989, 160, 355–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazars, E.; Guyot, K.; Durand, I.; Dei-Cas, E.; Boucher, S.; Abderrazak, S.B.; Banuls, A.L.; Tibayrenc, M.; Camus, D. Isoenzyme diversity in Pneumocystis carinii from rats, mice, and rabbits. J. Infect. Dis. 1997, 175, 655–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cisse, O.H.; Ma, L.; Dekker, J.P.; Khil, P.P.; Youn, J.H.; Brenchley, J.M.; Blair, R.; Pahar, B.; Chabe, M.; Van Rompay, K.K.A.; et al. Genomic insights into the host specific adaptation of the Pneumocystis genus. Commun. Biol. 2021, 4, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Settnes, O.P.; Elvestad, K.; Clausen, B. Pneumocystis carinii Delanoe & Delanoe, 1912 found in lungs of freeliving animals in Denmark at autopsy. Nord. Vet. Med. 1986, 38, 11–15. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Poelma, F.G. Pneumocystis carinii in hares, Lepus europaeus Pallas, in the Netherlands. Z. Parasitenkd. 1972, 40, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laakkonen, J.; Nyyssonen, T.; Hiltunen, M.; Kauhala, K.; Nikander, S.; Soveri, T. Effects of Protostrongylus sp. and Pneumocystis sp. on the pulmonary tissue and the condition of mountain and brown hares from Finland. J. Wildl. Dis. 2006, 42, 780–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blazek, K. Die Pneumocystis-pneumonie beim Feldhasen (Lepus europaeus Pallas). Zbl. allg. Path. path. Anat. 1960, 101, 484–489. [Google Scholar]
- Schoch, C.L.; Ciufo, S.; Domrachev, M.; Hotton, C.L.; Kannan, S.; Khovanskaya, R.; Leipe, D.; McVeigh, R.; O’Neill, K.; Robbertse, B.; et al. NCBI Taxonomy: A comprehensive update on curation, resources and tools. Database 2020, 2020, baaa062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Huang, D.W.; Cuomo, C.A.; Sykes, S.; Fantoni, G.; Das, B.; Sherman, B.T.; Yang, J.; Huber, C.; Xia, Y.; et al. Sequencing and characterization of the complete mitochondrial genomes of three Pneumocystis species provide new insights into divergence between human and rodent Pneumocystis. FASEB J. 2013, 27, 1962–1972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Chen, Z.; Huangda, W.; Kutty, G.; Ishihara, M.; Wang, H.; Abouelleil, A.; Bishop, L.; Davey, E.; Deng, R.; et al. Genome analysis of three Pneumocystis species reveals adaptation mechanisms to life exclusively in mammalian hosts. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 10740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, L.; Borio, L.; Masur, H.; Kovacs, J.A. Pneumocystis carinii dihydropteroate synthase but not dihydrofolate reductase gene mutations correlate with prior trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole or dapsone use. J. Infect. Dis. 1999, 180, 1969–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riebold, D.; Lubig, J.; Wolf, P.; Wolf, C.; Russow, K.; Loebermann, M.; Slevogt, H.; Mohr, E.; Feldhusen, F.; Reisinger, E.C. First molecular detection of Pneumocystis spp. in red foxes (Vulpes vulpeslinnaeus, 1758) and raccoon dogs (Nyctereutes procyonoidesgray, 1834). Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2020, 73, 101531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wakefield, A.E.; Pixley, F.J.; Banerji, S.; Sinclair, K.; Miller, R.F.; Moxon, E.R.; Hopkin, J.M. Detection of Pneumocystis carinii with DNA amplification. Lancet 1990, 336, 451–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weissenbacher-Lang, C.; Blasi, B.; Bauer, P.; Binanti, D.; Bittermann, K.; Ergin, L.; Hogler, C.; Hogler, T.; Klier, M.; Matt, J.; et al. Detection of Pneumocystis and morphological description of fungal distribution and severity of infection in thirty-six mammal species. J. Fungi 2023, 9, 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, T.J.; Bruns, T.; Lee, S.; Taylor, J. Amplification and direct sequencing of fungal ribosomal RNA genes for phylogenetics. In PCR Protocols: A Guide to Methods and Applications; Innis, M.A., Gelfand, D.H., Sninsky, J.J., White, T.J., Eds.; Academic Press, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1990; pp. 315–322. [Google Scholar]
- Danesi, P.; da Rold, G.; Rizzoli, A.; Hauffe, H.C.; Marangon, S.; Samerpitak, K.; Demanche, C.; Guillot, J.; Capelli, G.; de Hoog, S.G. Barcoding markers for Pneumocystis species in wildlife. Fungal Biol. 2016, 120, 191–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsolaki, A.G.; Beckers, P.; Wakefield, A.E. Pre-AIDS era isolates of Pneumocystis carinii f. sp. hominis: High genotype similarity with contemporary isolates. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1998, 36, 90–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wakefield, A.E. DNA sequences identical to Pneumocystis carinii f. sp. carinii and Pneumocystis carinii f. sp. hominis in samples of air spora. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1996, 34, 1754–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danesi, P.; Corro, M.; Falcaro, C.; Carminato, A.; Furlanello, T.; Cocchi, M.; Krockenberger, M.B.; Meyer, W.; Capelli, G.; Malik, R. Molecular detection of Pneumocystis in the lungs of cats. Med. Mycol. 2019, 57, 813–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danesi, P.; Falcaro, C.; Ravagnan, S.; Da Rold, G.; Porcellato, E.; Corro, M.; Iatta, R.; Cafarchia, C.; Frangipane di Regalbono, A.; Meyer, W.; et al. Real-time PCR assay for screening Pneumocystis in free-living wild squirrels and river rats in Italy. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2018, 30, 862–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, L.; Davis, A.S.; Kovacs, J.A. Pneumocystis ludoviciani from the Black-Tailed Prairie Dog (Registered in MycoBank with ID: MBT10019263). Available online: https://www.mycobank.org (accessed on 4 April 2024).
- Ma, L.; Imamichi, H.; Sukura, A.; Kovacs, J.A. Genetic divergence of the dihydrofolate reductase and dihydropteroate synthase genes in Pneumocystis carinii from 7 different host species. J. Infect. Dis. 2001, 184, 1358–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weissenbacher-Lang, C.; Fuchs-Baumgartinger, A.; Klang, A.; Kneissl, S.; Pirker, A.; Shibly, S.; von Ritgen, S.; Weissenbock, H.; Kunzel, F. Pneumocystis carinii infection with severe pneumomediastinum and lymph node involvement in a Whippet mixed-breed dog. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2017, 29, 757–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gits-Muselli, M.; White, P.L.; Mengoli, C.; Chen, S.; Crowley, B.; Dingemans, G.; Frealle, E.; Gorton, R.L.; Guiver, M.; Hagen, F.; et al. The Fungal PCR Initiative’s evaluation of in-house and commercial Pneumocystis jirovecii qPCR assays: Toward a standard for a diagnostics assay. Med. Mycol. 2020, 58, 779–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burger, G.; Gray, M.W.; Forget, L.; Lang, B.F. Strikingly bacteria-like and gene-rich mitochondrial genomes throughout jakobid protists. Genome Biol. Evol. 2013, 5, 418–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, P.P.; Lowe, T.M. tRNAscan-SE: Searching for tRNA Genes in Genomic Sequences. Methods Mol. Biol. 2019, 1962, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Kumar, S. MEGA11: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 11. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2021, 38, 3022–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sievers, F.; Higgins, D.G. Clustal Omega. Curr. Protoc. Bioinform. 2014, 48, 11–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, L.T.; Schmidt, H.A.; von Haeseler, A.; Minh, B.Q. IQ-TREE: A fast and effective stochastic algorithm for estimating maximum-likelihood phylogenies. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2015, 32, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korsgren, C.; Cohen, C.M. Organization of the gene for human erythrocyte membrane protein 4.2: Structural similarities with the gene for the a subunit of factor XIII. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1991, 88, 4840–4844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minh, B.Q.; Nguyen, M.A.; von Haeseler, A. Ultrafast approximation for phylogenetic bootstrap. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 1188–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wakefield, A.E.; Pixley, F.J.; Banerji, S.; Sinclair, K.; Miller, R.F.; Moxon, E.R.; Hopkin, J.M. Amplification of mitochondrial ribosomal RNA sequences from Pneumocystis carinii DNA of rat and human origin. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 1990, 43, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwok, S.; Kellogg, D.E.; McKinney, N.; Spasic, D.; Goda, L.; Levenson, C.; Sninsky, J.J. Effects of primer-template mismatches on the polymerase chain reaction: Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 model studies. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990, 18, 999–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guillot, J.; Chevalier, V.; Queney, G.; Berthelemy, M.; Polack, B.; Lacube, P.; Roux, P.; Chermette, R. Acquisition and biodiversity of Pneumocystis carinii in a colony of wild rabbits (Oryctolagus cuniculus). J. Eukaryot. Microbiol. 1999, 46, 100S–101S. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Palmer, R.J.; Settnes, O.P.; Lodal, J.; Wakefield, A.E. Population structure of rat-derived Pneumocystis carinii in Danish wild rats. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2000, 66, 4954–4961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norris, K.A.; Wildschutte, H.; Franko, J.; Board, K.F. Genetic variation at the mitochondrial large-subunit rRNA locus of Pneumocystis isolates from simian immunodeficiency virus-infected rhesus macaques. Clin. Diag. Lab. Immunol. 2003, 10, 1037–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Wu, W.; Tian, X.; Hou, X.; Cui, X.; Xiao, Y.; Jiao, Q.; Zhou, P.; Liu, L.; Shi, W.; et al. A total infectome approach to understand the etiology of infectious disease in pigs. Microbiome 2022, 10, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanches, E.M.; Ferreiro, L.; Barbosa, M.R.; Spanamberg, A.; Ravazzolo, A.P.; Santurio, J.M.; Driemeier, D.; Barcellos, D.E.S.N.; Berthelemy, M.; Guillot, J. Phylogenetic analysis of Pneumocystis from pig lungs obtained from slaughterhouses in southern and midwestern regions of Brazil. Arq. Bras. Med. Vet. Zootec. 2011, 63, 1154–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Icenhour, C.R.; Arnold, J.; Medvedovic, M.; Cushion, M.T. Competitive coexistence of two Pneumocystis species. Infect Genet. Evol. 2006, 6, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honeycutt, R.J.; Adkins, R.M. Higher level systematics of eutherian mammals: An assessment of molecular characters and phylogenetic hypotheses. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 1993, 24, 279–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitazoe, Y.; Kishino, H.; Waddell, P.J.; Nakajima, N.; Okabayashi, T.; Watabe, T.; Okuhara, Y. Robust time estimation reconciles views of the antiquity of placental mammals. PLoS ONE 2007, 2, e384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Sun, F.; Xu, S.; Yang, G.; Li, M. The position of tree shrews in the mammalian tree: Comparing multi-gene analyses with phylogenomic results leaves monophyly of Euarchonta doubtful. Integr. Zool. 2015, 10, 186–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graur, D.; Duret, L.; Gouy, M. Phylogenetic position of the order Lagomorpha (rabbits, hares and allies). Nature 1996, 379, 333–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.H.; Gouy, M.; Sharp, P.M.; O’HUigin, C.; Yang, Y.W. Molecular phylogeny of Rodentia, Lagomorpha, Primates, Artiodactyla, and Carnivora and molecular clocks. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1990, 87, 6703–6707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Misawa, K.; Janke, A. Revisiting the Glires concept—Phylogenetic analysis of nuclear sequences. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2003, 28, 320–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the NIH. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, L.; Lin, I.; Hunter, S.T.; Blasi, B.; Danesi, P.; Weissenbacher-Lang, C.; Cisse, O.H.; Rothenburger, J.L.; Kovacs, J.A. Development of Highly Efficient Universal Pneumocystis Primers and Their Application in Investigating the Prevalence and Genetic Diversity of Pneumocystis in Wild Hares and Rabbits. J. Fungi 2024, 10, 355. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof10050355
Ma L, Lin I, Hunter ST, Blasi B, Danesi P, Weissenbacher-Lang C, Cisse OH, Rothenburger JL, Kovacs JA. Development of Highly Efficient Universal Pneumocystis Primers and Their Application in Investigating the Prevalence and Genetic Diversity of Pneumocystis in Wild Hares and Rabbits. Journal of Fungi. 2024; 10(5):355. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof10050355
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Liang, Isabella Lin, Summer T. Hunter, Barbara Blasi, Patrizia Danesi, Christiane Weissenbacher-Lang, Ousmane H. Cisse, Jamie L. Rothenburger, and Joseph A. Kovacs. 2024. "Development of Highly Efficient Universal Pneumocystis Primers and Their Application in Investigating the Prevalence and Genetic Diversity of Pneumocystis in Wild Hares and Rabbits" Journal of Fungi 10, no. 5: 355. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof10050355








