Extraction of Copper and Zinc from Waste Printed Circuit Boards
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
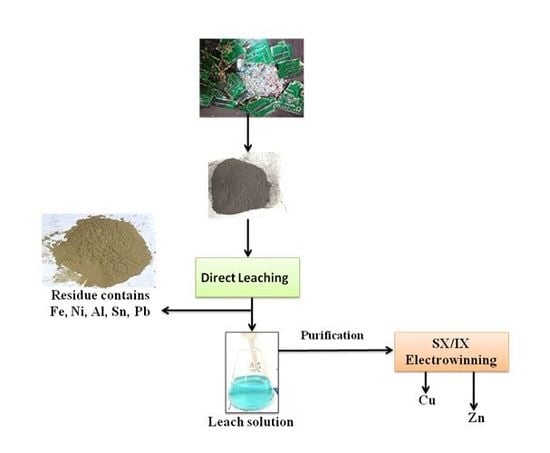
2.1. Sample Preparation
Material Pretreatment by Roasting
2.2. Characterization
Chemical Analysis
2.3. Experimental Studies
3. Results and Discussion
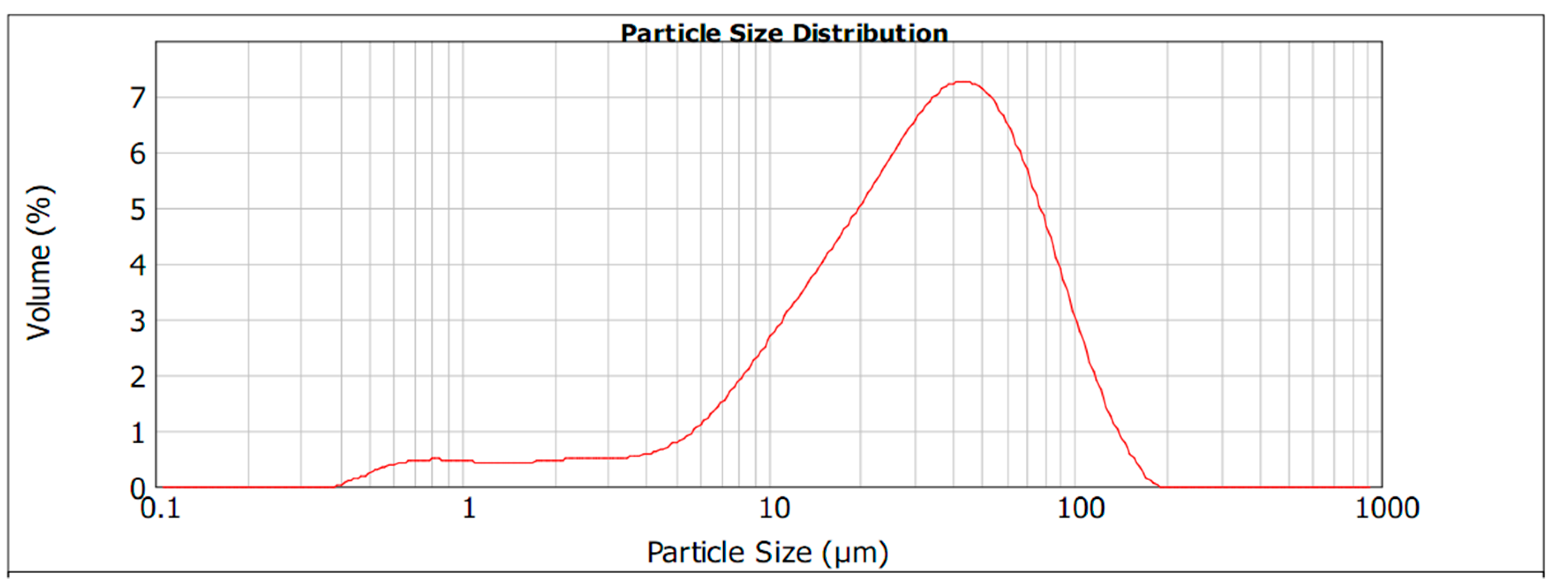
3.1. Physical and Chemical Characterization of Pulverized WPCBs
3.2. Extraction in Hydrochloric Acid
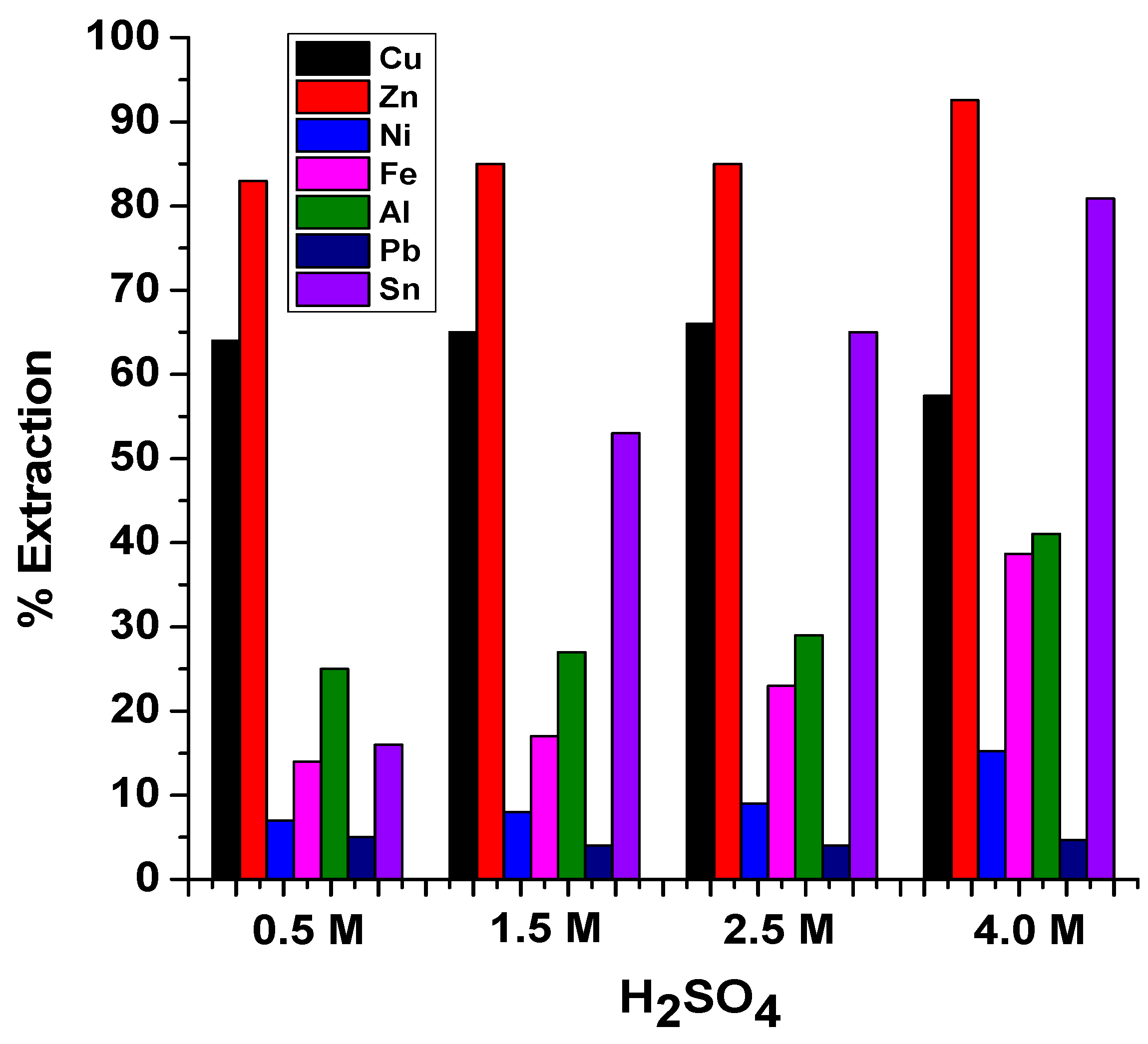
3.3. Extraction in Sulfuric Acid
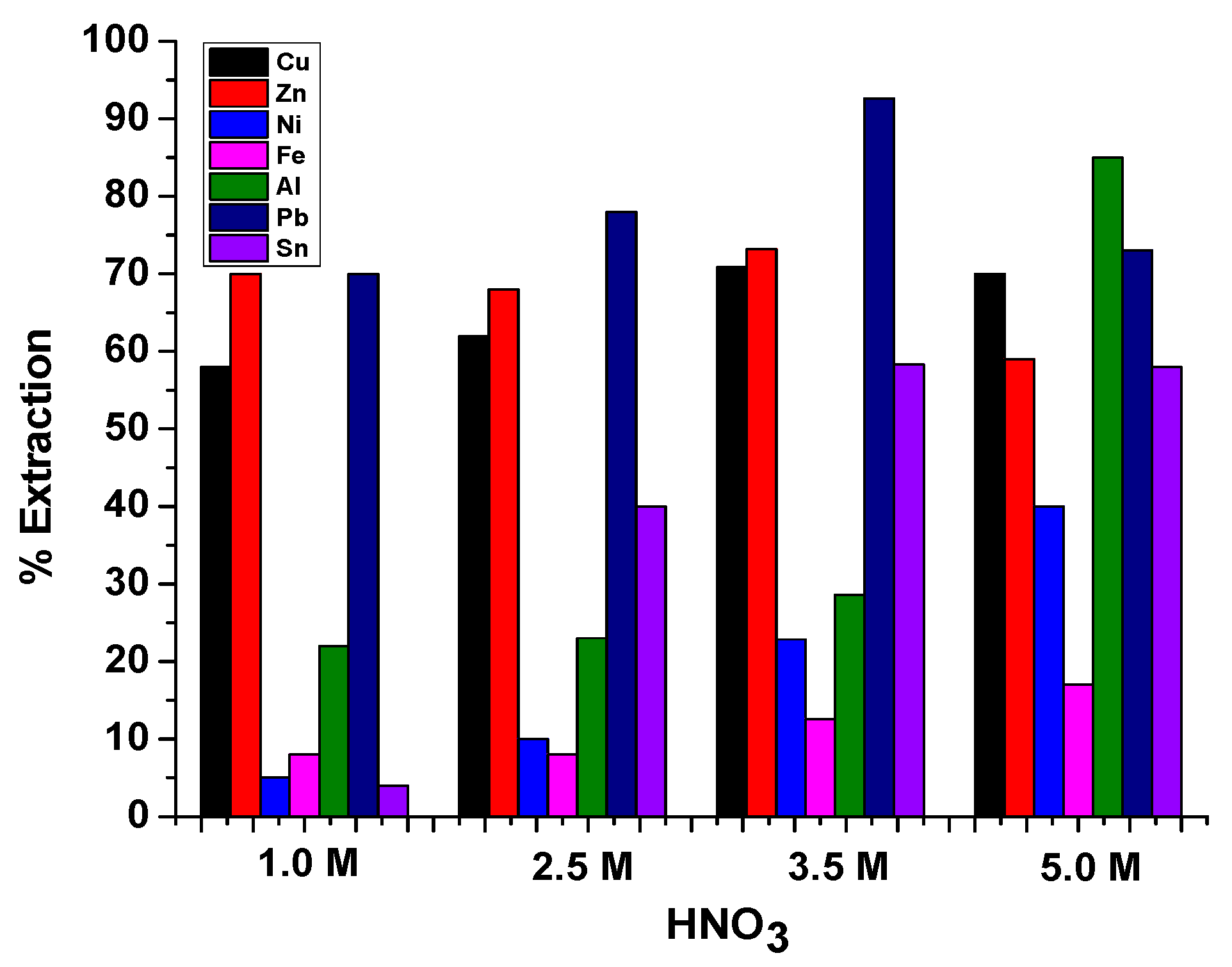
3.4. Extraction Study in Nitric Acid
3.5. Extraction in Trifluoromethanesulfonic Acid (TFMS)
3.6. Extraction in Chloride Media
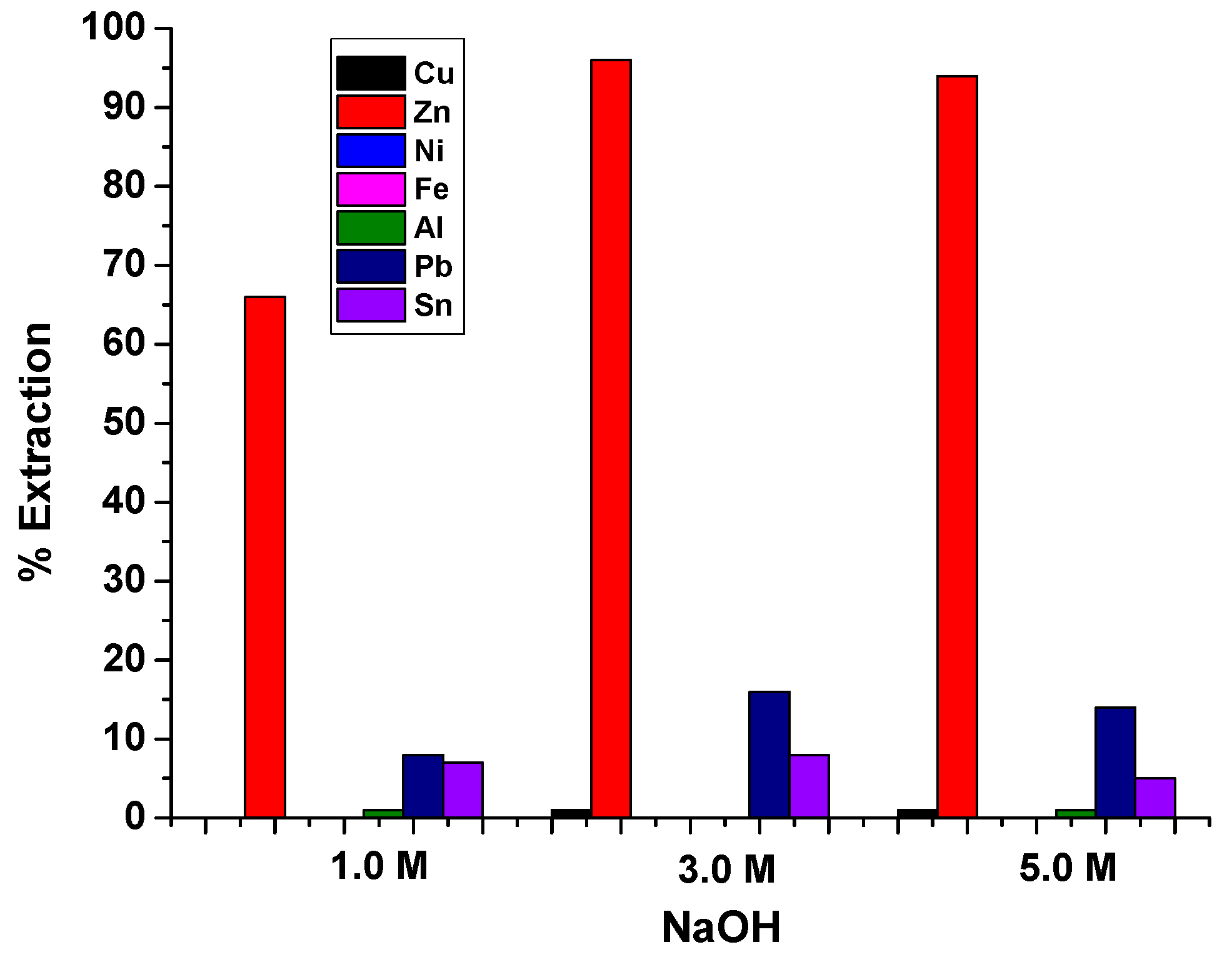
3.7. Extraction in Hydroxide Media
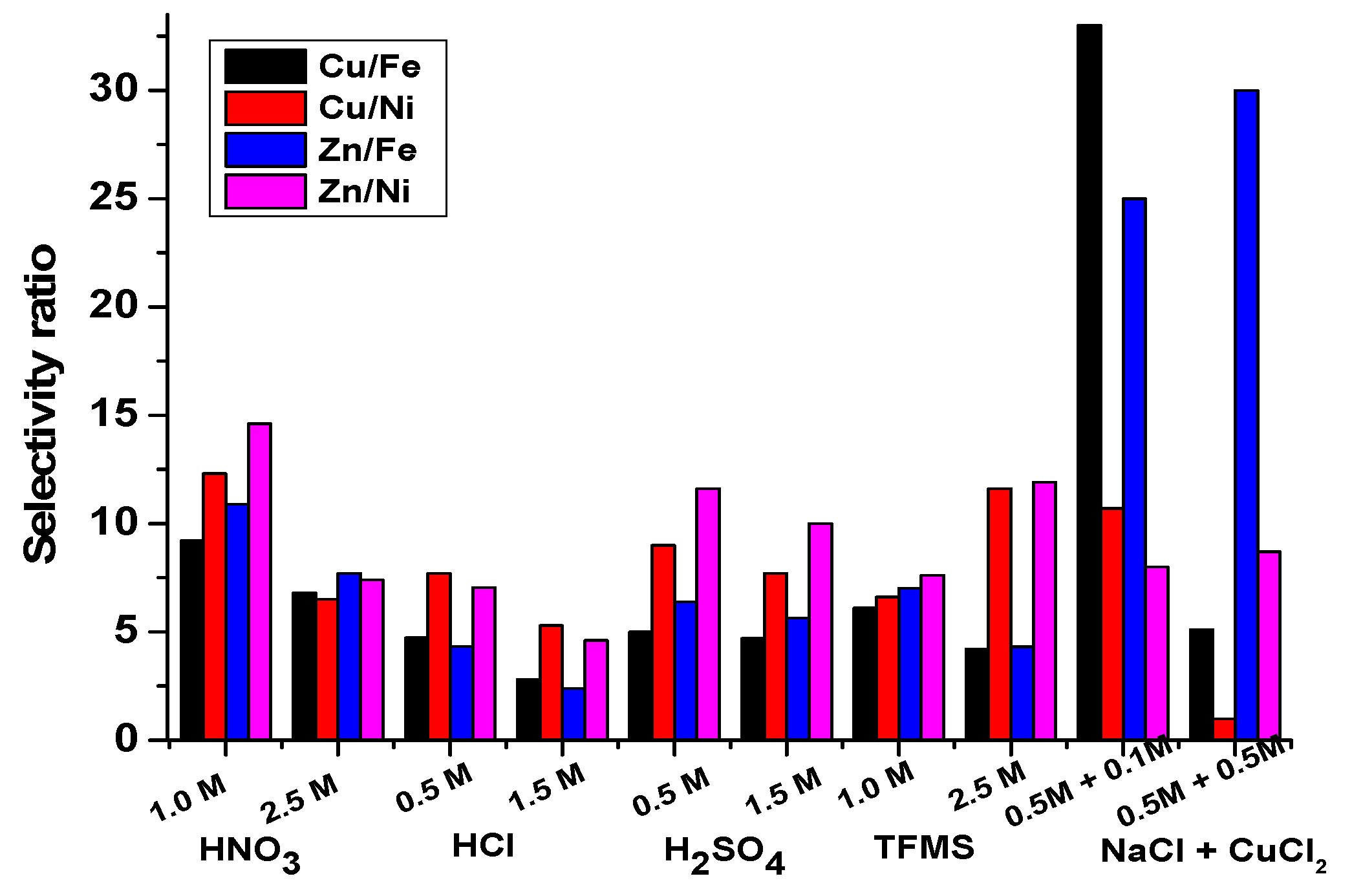
4. Selectivity Studies
5. Conclusions
- Cu and Zn were extracted with other metals in diluted HCl lixiviant, which resulted in a low selectivity ratio and made HCl lixiviants perform poorly for selective extraction.
- Diluted H2SO4, HNO3, and TFMS lixiviants performed excellently, with the highest selectivity of Cu and Zn toward Fe.
- The selective extraction of Zn without the extraction of other metals was achieved in NaOH lixiviants because Zn acted as an amphoteric oxide. The high selectivity of Zn toward Fe was achieved in 0.5 M NaCl + 0.5M CuCl2 lixiviant.
- Selectivity of Cu and Zn toward Fe in 0.5 M NaCl + 0.1 M CuCl2 lixiviant was obtained. As the concentration of CuCl2 increased to 0.5 M, the Cu extraction efficiency decreased drastically.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- UNEP. E-Waste Inventory Assessment Manual; UNEP: Nairobi, Kenya, 2007; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Sheng, P.P.; Etsell, T.H. Recovery of gold from computer circuit boards. Waste Manag. Resour. 2007, 25, 380–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, N.V.; Lee, J.; Jha, M.K.; Yoo, K.; Jeong, J. Copper recovery from low concentration waste solution using Dowex G-26 resin. Hydrometallurgy 2009, 97, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebin, B.; Isik, M.I. Pyrometallurgical Processes for the Recovery of Metals from WEEE. In WEEE Recycling; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2006; pp. 107–137. [Google Scholar]
- Tuncuk, A.; Stazi, V.; Akcil, A.; Yazici, E.Y.; Deveci, H. Aqueous metal recovery techniques from e-scrap: Hydrometallurgy in recycling. Miner. Eng. 2012, 25, 28201337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryan, C.G.; Watkin, E.L.; McCredden, T.J.; Wong, Z.R.; Harrison, S.T.L.; Kaksonen, A.H. The use of pyrite as a source of lixiviant in the bioleaching of electronic waste. Hydrometallurgy 2015, 152, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Lee, J.C.; Kim, M.S.; Jeong, J.; Yoo, K. Leaching of metals from waste printed circuit boards (WPCBs) using sulfuric and nitric acids. Environ. Eng. Manag. J. 2014, 13, 2601–2607. [Google Scholar]
- Grause, G.; Ishibashi, J.; Kameda, T.; Bhaskar, T.; Yoshioka, T. Kinetic studies of the decomposition of flame retardant containing high-impact polystyrene. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2010, 95, 1129–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arshadi, M.; Mousavi, S.M. Simultaneous recovery of Ni and Cu from computer-printed circuit boards using bioleaching: Statistical evaluation and optimization. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 174, 233–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natarajan, G.; Ting, Y.P. Pretreatment of e-waste and mutation of alkali-tolerant cyanogenic bacteria promote gold biorecovery. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 152, 80–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saidan, M.; Brown, B.; Valix, M. Leaching of electronic waste using biometabolised acids. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2012, 20, 530–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Zhang, L. Metallurgy Recovery of Metals from Electronic Waste: A Review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 158, 228–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.C.; Gopala, P.; Krishna, D. Effect of Fe3+ during copper electrowinning at higher current density. Int. J. Miner. Process. 1996, 46, 91–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, D.R.; Dreisinger, D.B.; Lancaster, T.; Richmond, G.D.; Tomlinson, M. The commercialization of the FENIX iron control system for purifying copper electrowinning electrolytes. J. Mater. 2004, 38–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochromowicz, K.; Jeziorek, M.; Wejman, K. Copper (II) Extraction from ammonia leach solution. Physicochem. Probl. Miner. Process. 2014, 50, 327–335. [Google Scholar]
- Jergensen, G.V. Copper Leaching, Solvent Extraction and Electrowinning Technology; SME Inc.: Littleton, CO, USA, 1999; pp. 267–268. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, J.D.; Haung, H.H.; Pereira, E.F. Equilibrium and kinetics of copper extraction from ammonia solutions by hydroxyoximes with particular emphasis on transport phenomena. In Process and Fundamental Considerations of Selected Hydrometallurgical Systems; Society of Mining Engineers of American Institute of Mining, Metallurgical, and Petroleum Engineers: Englewood, CO, USA, 1981; pp. 221–241. [Google Scholar]
- Radmehr, V.; Koleini, S.M.J.; Khalesi, M.R.; Mohammadi, M.R.T. Ammonia leaching in the copper industry: A Review. In Proceedings of the International Mineral Processing Congress (IMPC), New Delhi, India, 23–28 September 2012; p. 487. [Google Scholar]
- Gehrmann, B.; Hattendorf, H.; Kolb-Telips, A.; Kramer, W.; Mottgen, W. Corrosion behavior of soft magnetic iron-nickel alloys. Mater. Corrossion 2004, 48, 535–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranitović, M.; Kamberović, Ž.; Korać, M.; Jovanović, N.; Mihjalović, A. Hydrometallurgical Recovery of tin and lead from waste printed circuit boards (WPCBs): Limitations and opportunities. Metalurgija 2016, 55, 153–156. [Google Scholar]
- Lui, W.K. Dissolution of Tin in Hydrochloric Acid. Electronic Theses and Dissertations 6311. Master’s Thesis, University of Windsor, Windsor, ON, Canada, 1962. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.G. Corrosion and Electrochemistry of Zinc; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida, T. Leaching of Zinc Oxide in Acidic Solution. Materials Transactions 2003, 44, 2489–2493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rusen, A.; Sunkar, A.S.; Topkaya, Y. Zinc and lead extraction from Cinkur leach residues by using hydrometallurgy method. Hydrometallurgy 2008, 93, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koltrly, S.; Sucha, L. Handbook of Chemical Equilibria in Analytical Chemistry; Ellis Horwood Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Salmimies, R.; Mannila, M.; Kallas, J.; Häkkinen, A.H. Acidic dissolution of magnetite: experimental study on the effects of acid concentration and temperature. Clays Clay Miner. 2011, 59, 136–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, S.I.; Mazzafro, W.J. Nitric Acid; Wiley Online Library: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michael, D.G.; Min, W.; Thomas, B.; Patrick, J. Environmental benefits of methanesulfonic acid: comparative properties and advantages. Green Chem. 1999, 1, 127–140. [Google Scholar]
- Posternak, A.G.; Garlyauskayte, R.Y.; Polovinko, V.V.; Yagupolskii, M.L.; Yagupolskii, Y.L. New kinds of organic superacids. Bis (perfluoroalkylsulfonylimino)-trifluoromethanesulfonic acids and their trimethylsilyl esters. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borra, C.R.; Pontikes, Y.; Binnemans, K.; Van Gerven, T. Leaching of rare earths from bauxite residue (red mud). Miner. Eng. 2015, 76, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sampoli, M.; Marziano, N.C. Tortato, C. Dissociation of Tritluoromethanesutfonic Acid in Aqueous Solutions by Raman Spectroscopy. J. Phys. Chem. 1989, 93, 7252–7257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carneiro, M.F.C.; Leao, V.A. The role of sodium chloride on surface properties of chalcopyrite leached with ferric sulphate. Hydrometallurgy 2007, 87, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ashurst, K.G. The Thermodynamics of the Formation of Chlorocomplexes of Iron (III), Cobalt (II), Iron (II), Manganese (II) in Perchlorate Medium; National Institute of Metallurgy: Randburg, South Africa, 1976; Volume 1820, pp. 1–43. [Google Scholar]
- Peek, E.M.; Van Weert, G. Chloride metallurgy. In Proceedings of the 32nd Annual Hydrometallurgy Meeting and International Conference of the Practice and Theory of Chloride/Metal interaction, Montreal, QC, Canada, 19–23 October 2002; Volume 23, pp. 760–780. [Google Scholar]
- Misawa, T. The thermodynamics consideration for Fe-H2O system at 25 °C. Corros. Sci. 1973, 13, 659–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darwish, N.A.; Hilbert, F.; Lorenz, W.J.; Rosswag, H. The influence of chloride ions on the kinetics of iron dissolution. Electrochim. Acta 1973, 18, 421–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, A.; Xu, D.; Chen, X.; Zhang, W.; Liu, X. Measurements of zinc oxide solubility in sodium hydroxide solution from 25 to 100 °C. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2012, 22, 1513–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

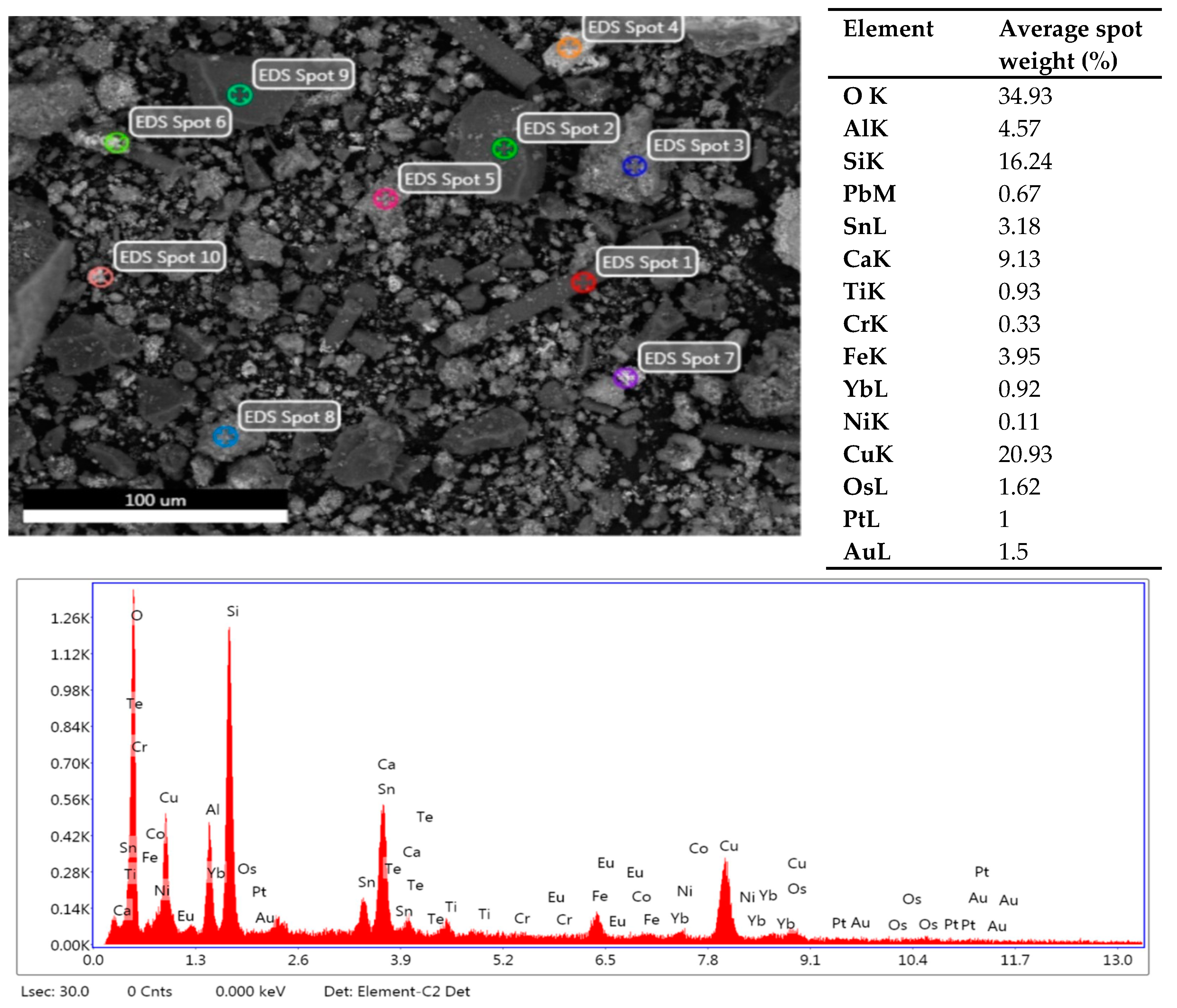



 | Elements | Weight (%) |
| Fe | 11.118 | |
| Cu | 41.64 | |
| Ni | 2.28 | |
 | Al | 5.05 |
| Zn | 1.79 | |
| Pb | 1.09 | |
| Sn | 1.63 | |
| Ti | 0.18 |
| Solutions | Concentrations | Chemical Strength | Manufacturer |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hydrochloric Acid (HCl) | 0.5 M 1.5 M 2.5 M 4.5 M 5.0 M | Percent purity: 35.4%, specific gravity: 1.18 g/cm3, percent weight: 36.46 g/mole | Finar Chemical |
| Sulfuric Acid (H2SO4) | 0.5 M 1.5 M 2.5 M 4.0 M | Percent purity: 98.0%, specific gravity: 1.84 g/cm3, percent weight: 98.08 g/mole | Merck Specialities Private |
| Nitric Acid (HNO3) | 1.0 M 2.5 M 3.5 M 5.0 M | Percent purity: 69.0%, specific gravity: 1.42g/cm3, percent weight: 63.01 g/mole | HiMedia Laboratories Pvt. Ltd. |
| Trifluoromethanesulfonic Acid (TFMS) | 1.0 M 2.5 M | ||
| Sodium Hydroxide | 1.0 M 2.0 M 5.0 M | NaOH | |
| Copper (II) Chloride, pH 1 | 0.5 M NaCl + 0.1M CuCl2 4.5M NaCl + 0.5 M CuCl2 4.5 M NaCl + 0.1 M CuCl2 4.5 M NaCl + 1.0 M CuCl2 | CuCl2 2H2O |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ajiboye, A.E.; Olasehinde, F.E.; Adebayo, O.A.; Ajayi, O.J.; Ghosh, M.K.; Basu, S. Extraction of Copper and Zinc from Waste Printed Circuit Boards. Recycling 2019, 4, 36. https://doi.org/10.3390/recycling4030036
Ajiboye AE, Olasehinde FE, Adebayo OA, Ajayi OJ, Ghosh MK, Basu S. Extraction of Copper and Zinc from Waste Printed Circuit Boards. Recycling. 2019; 4(3):36. https://doi.org/10.3390/recycling4030036
Chicago/Turabian StyleAjiboye, Ayorinde Emmanuel, Folorunsho Emmanuel Olasehinde, Ojo Albert Adebayo, Olubode John Ajayi, Malay Kumar Ghosh, and Suddhasatwa Basu. 2019. "Extraction of Copper and Zinc from Waste Printed Circuit Boards" Recycling 4, no. 3: 36. https://doi.org/10.3390/recycling4030036
APA StyleAjiboye, A. E., Olasehinde, F. E., Adebayo, O. A., Ajayi, O. J., Ghosh, M. K., & Basu, S. (2019). Extraction of Copper and Zinc from Waste Printed Circuit Boards. Recycling, 4(3), 36. https://doi.org/10.3390/recycling4030036