Trajectory Control in Discrete-Time Nonlinear Coupling Dynamics of a Soft Exo-Digit and a Human Finger Using Input–Output Feedback Linearization
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- Analytical modeling formulation of quasi-static physical interaction between the human finger model and a soft robotic exo-digit with individually controlled joints was derived.
- A feedback linearization control algorithm was derived for a nonlinear discrete-time multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) state-space representation.
- The feedback linearizability and stability conditions of the nonlinear discrete-time state-space model of soft exo-digit and human finger physical interaction were studied.
- Experimental testing of the soft exo-digit interacting with a human finger model for tracking a desired trajectory was carried out.
2. Quasi-Static Model of Physical Human-Soft Robot Interaction
2.1. Kinematics of the Human Finger Model
2.2. Coupled Human–Robot Interaction Quasi-Static Model
3. Feedback Linearization Control
3.1. Nonlinear Discrete-Time State-Space Representation
3.2. Input–Output Feedback Linearization
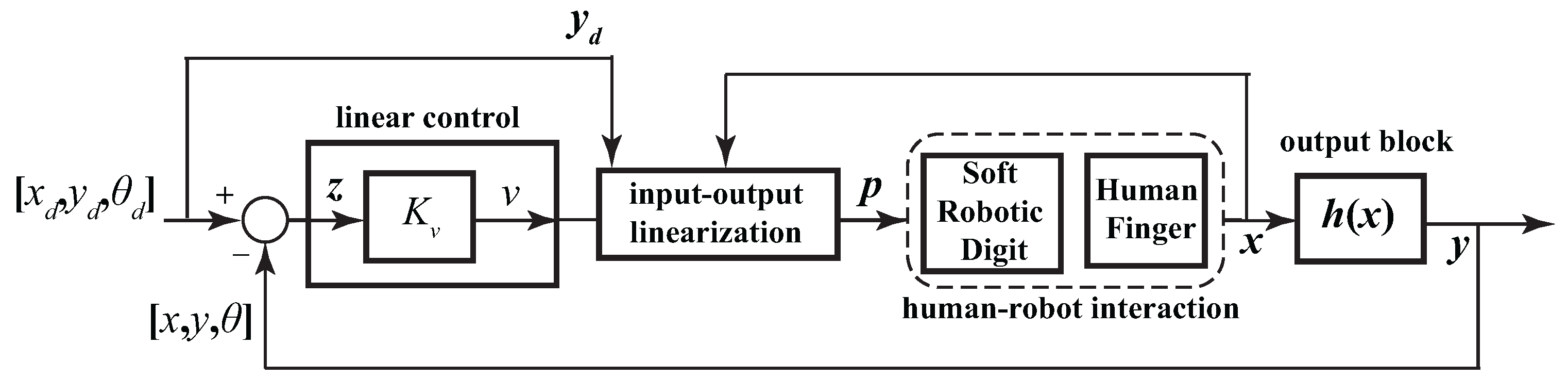
4. Control System Implementation
5. Results and Discussion
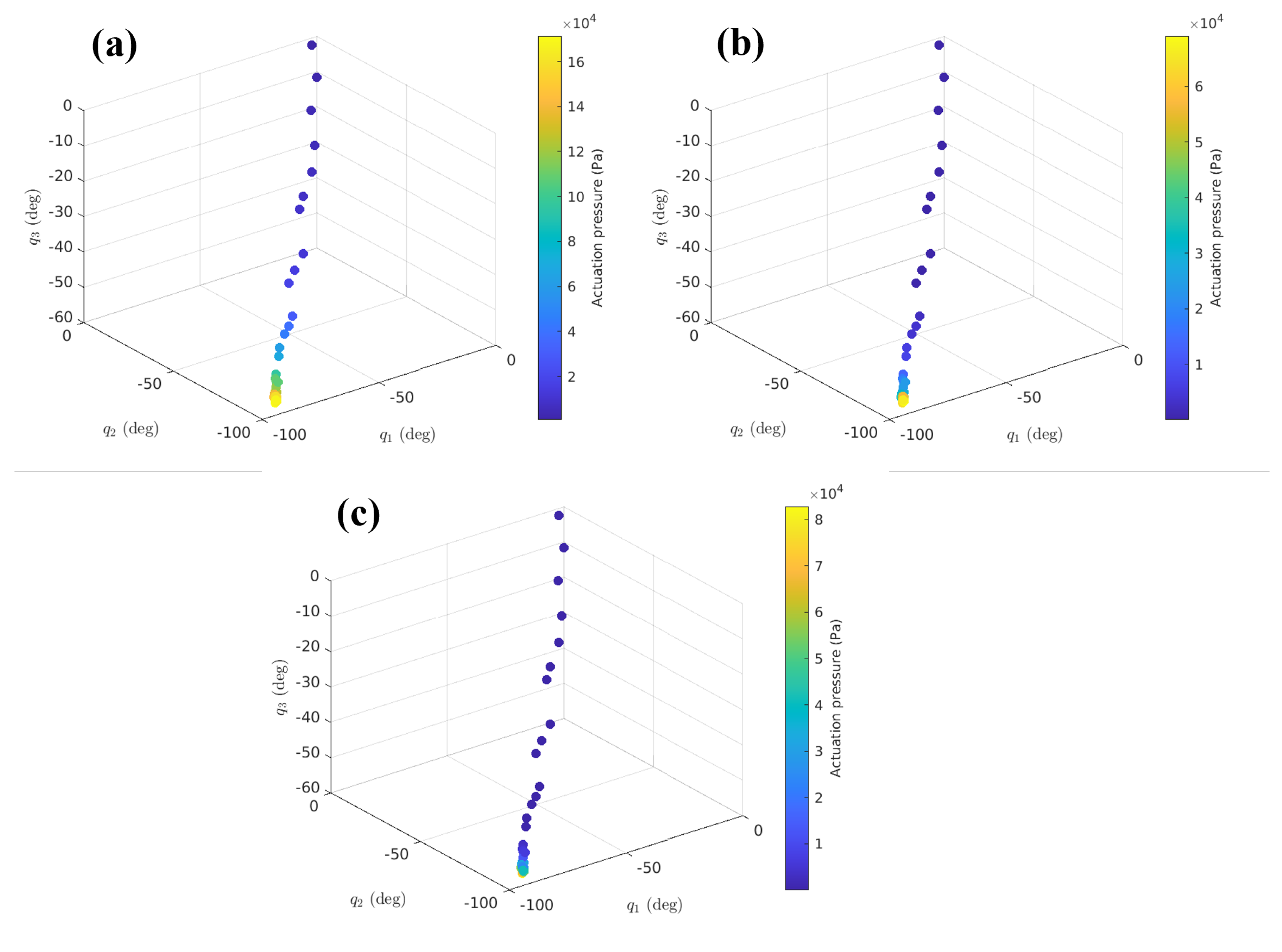
5.1. Analysis of the Control Law
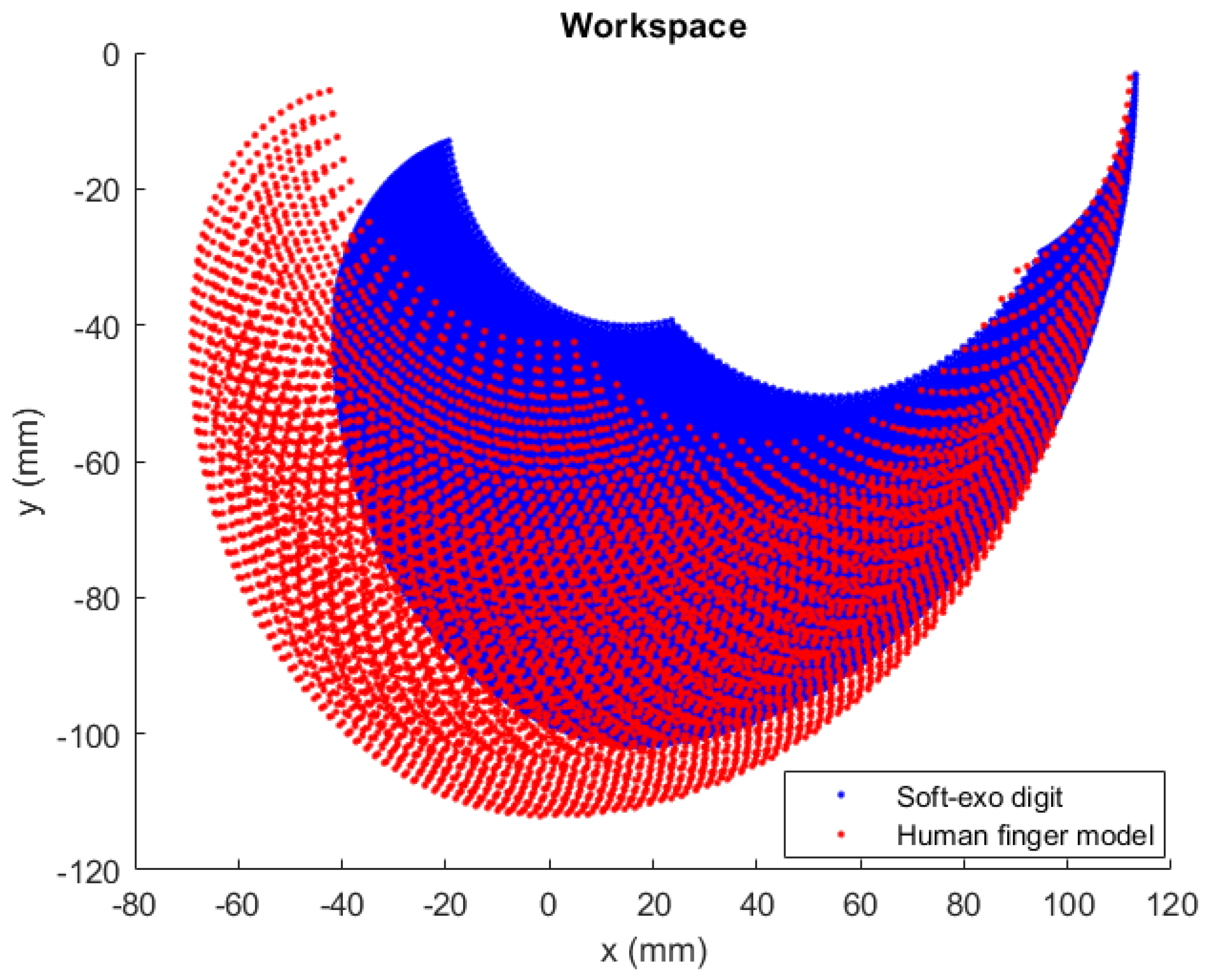
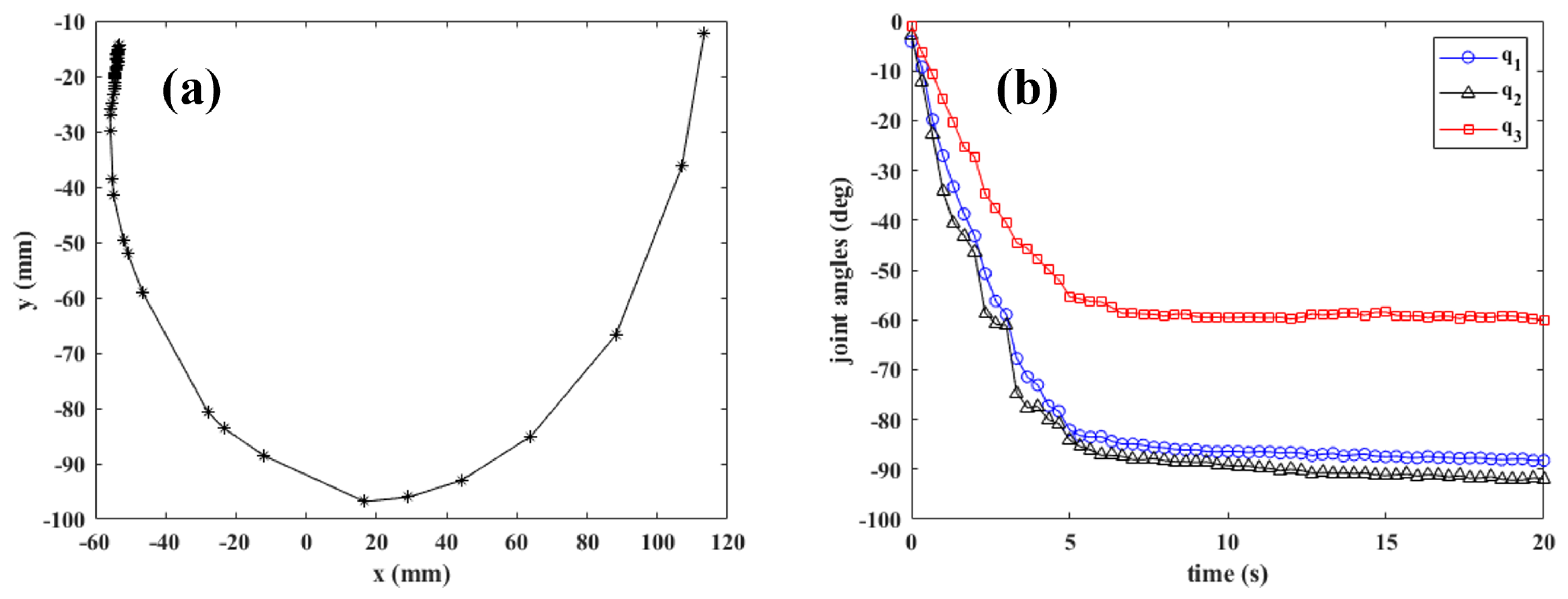
5.2. Trajectory Tracking of the Desired Fingertip Pose in Simulation
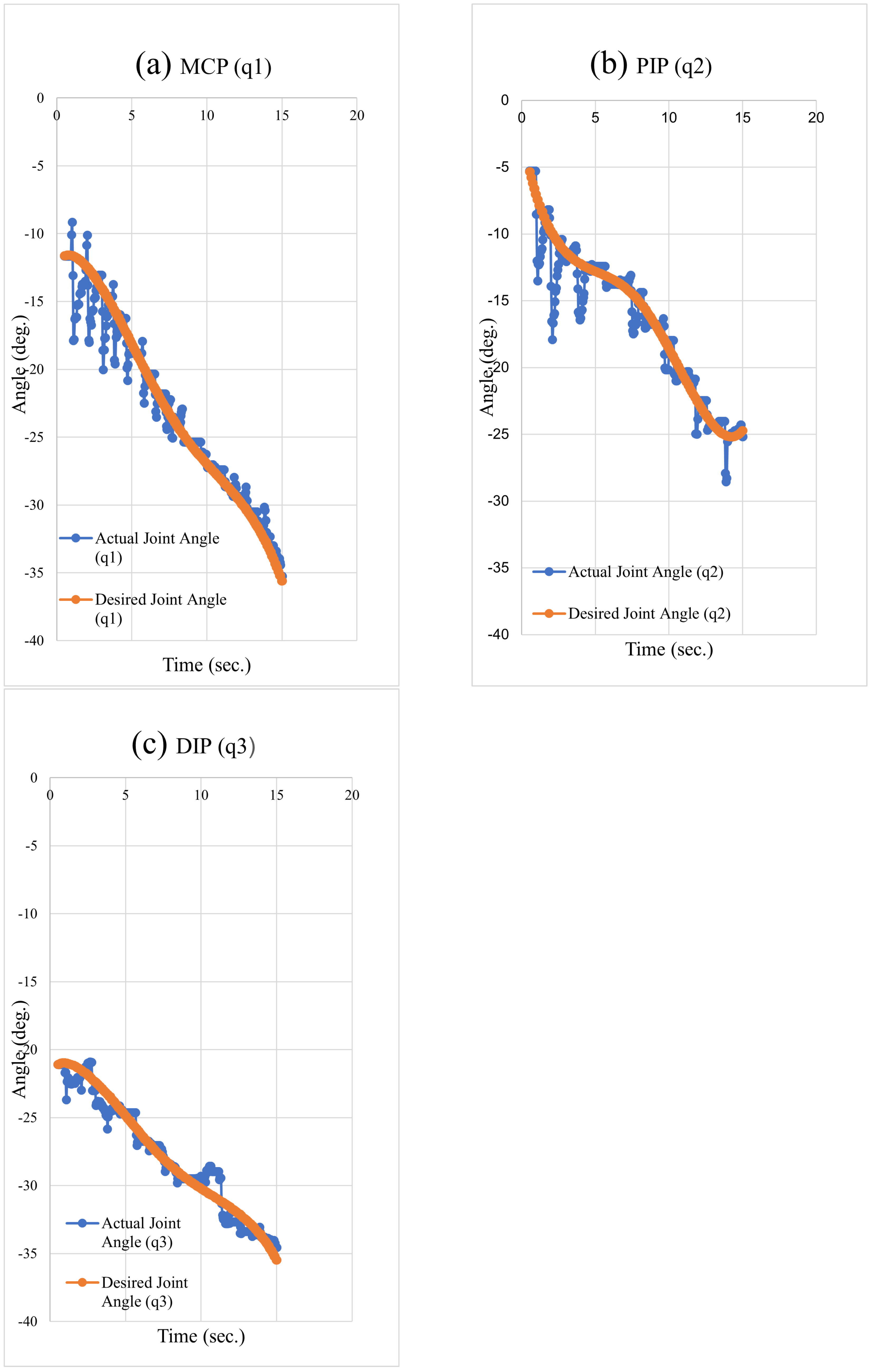
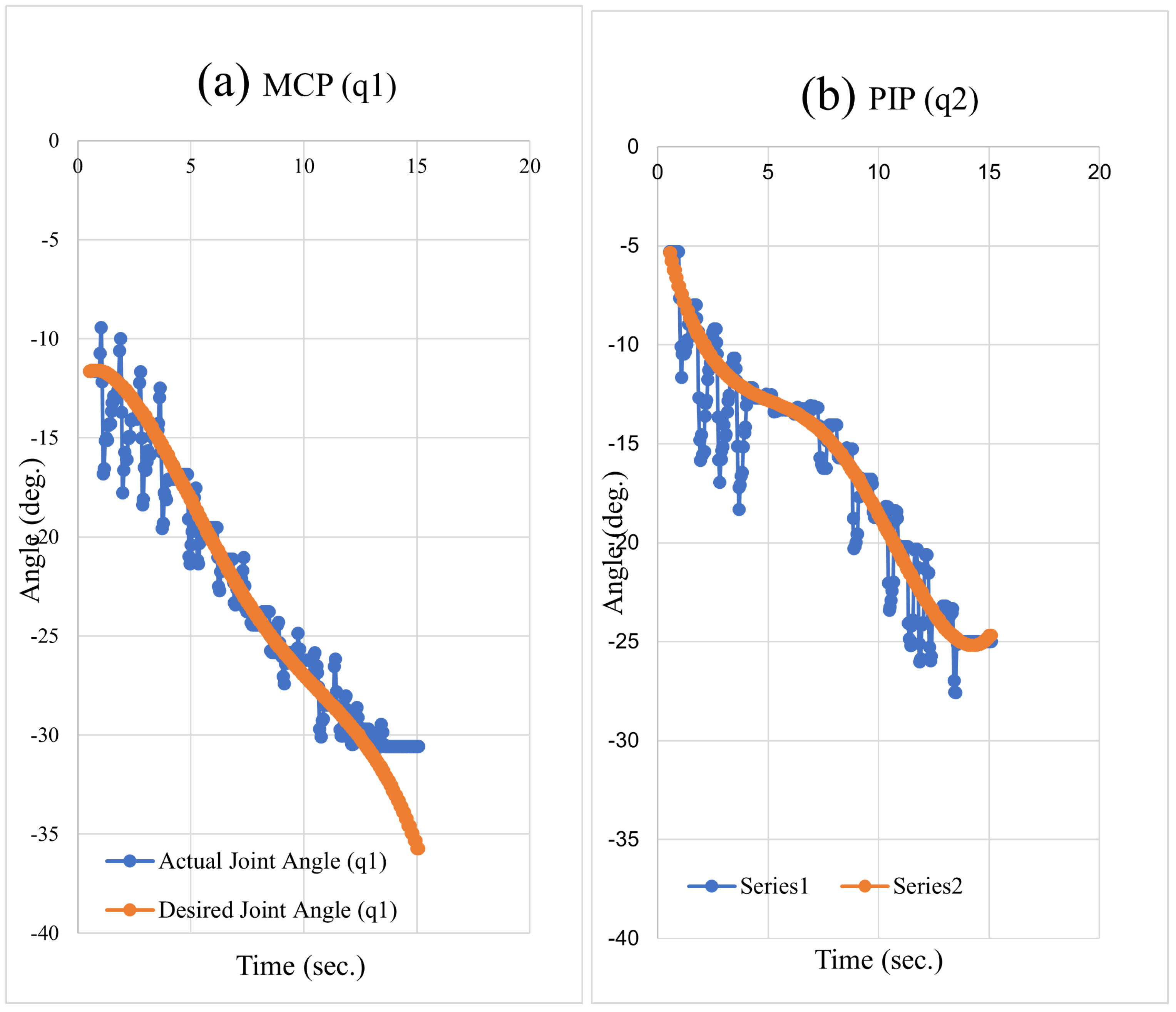
5.3. Trajectory Tracking of the Desired Fingertip Pose
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CPM | Continuous passive motion |
| 3D | Three dimensional |
| DOF | Degrees of freedom |
| pHRI | Physical human-robot interaction |
| SISO | single-input single-output |
| MIMO | multi-input multi-output |
| MCP | Metacarpophalangeal |
| DIP | Distal Interphalangeal |
| PIP | Proximal Interphalangeal |
| kPA | kilo Pascal |
| PWM | Pulse Width Modulation |
| IMU | Inertial Measurement Unit |
| RMSE | Root mean square error |
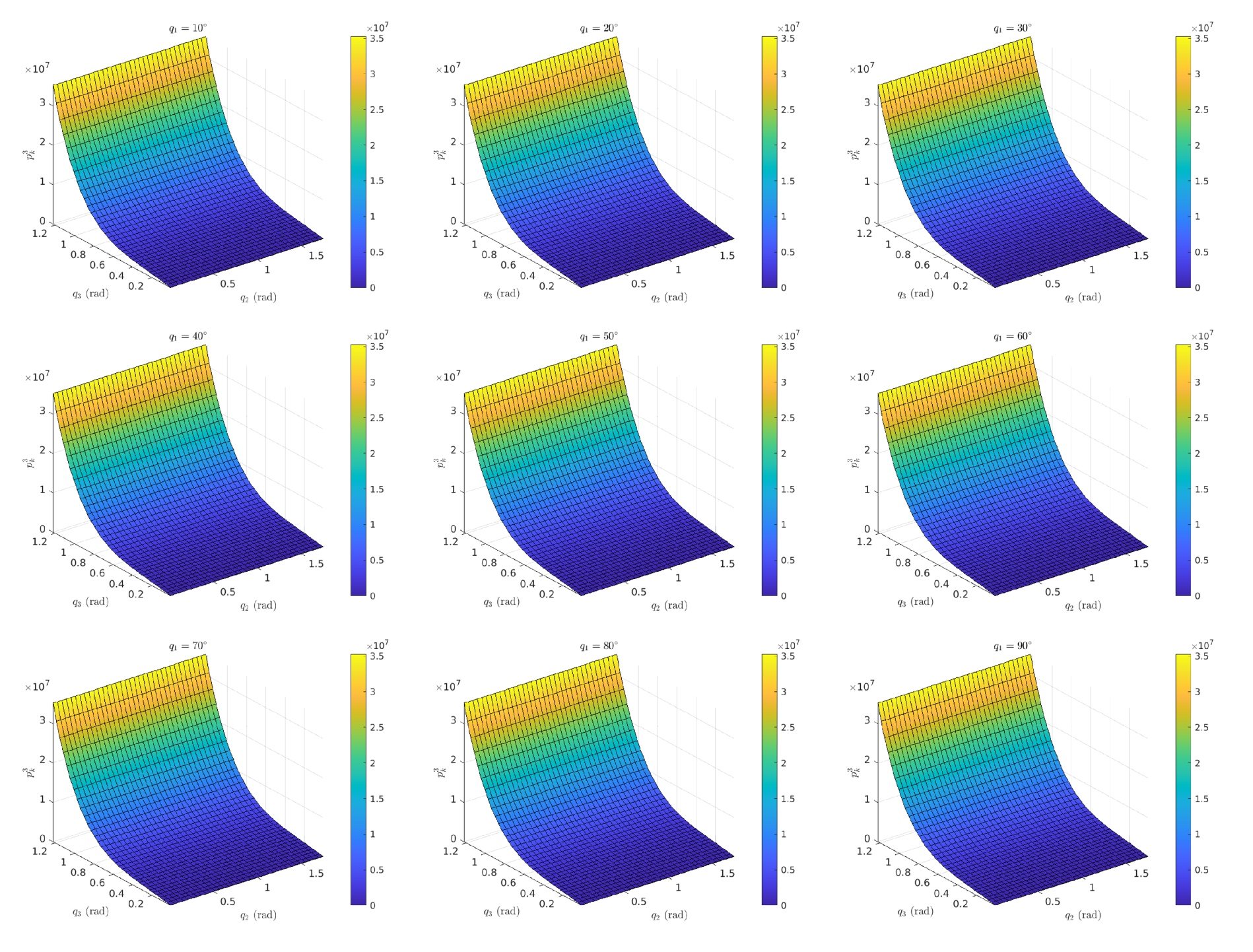
Appendix A. Lie Derivatives
Appendix A.1. Invertibility of
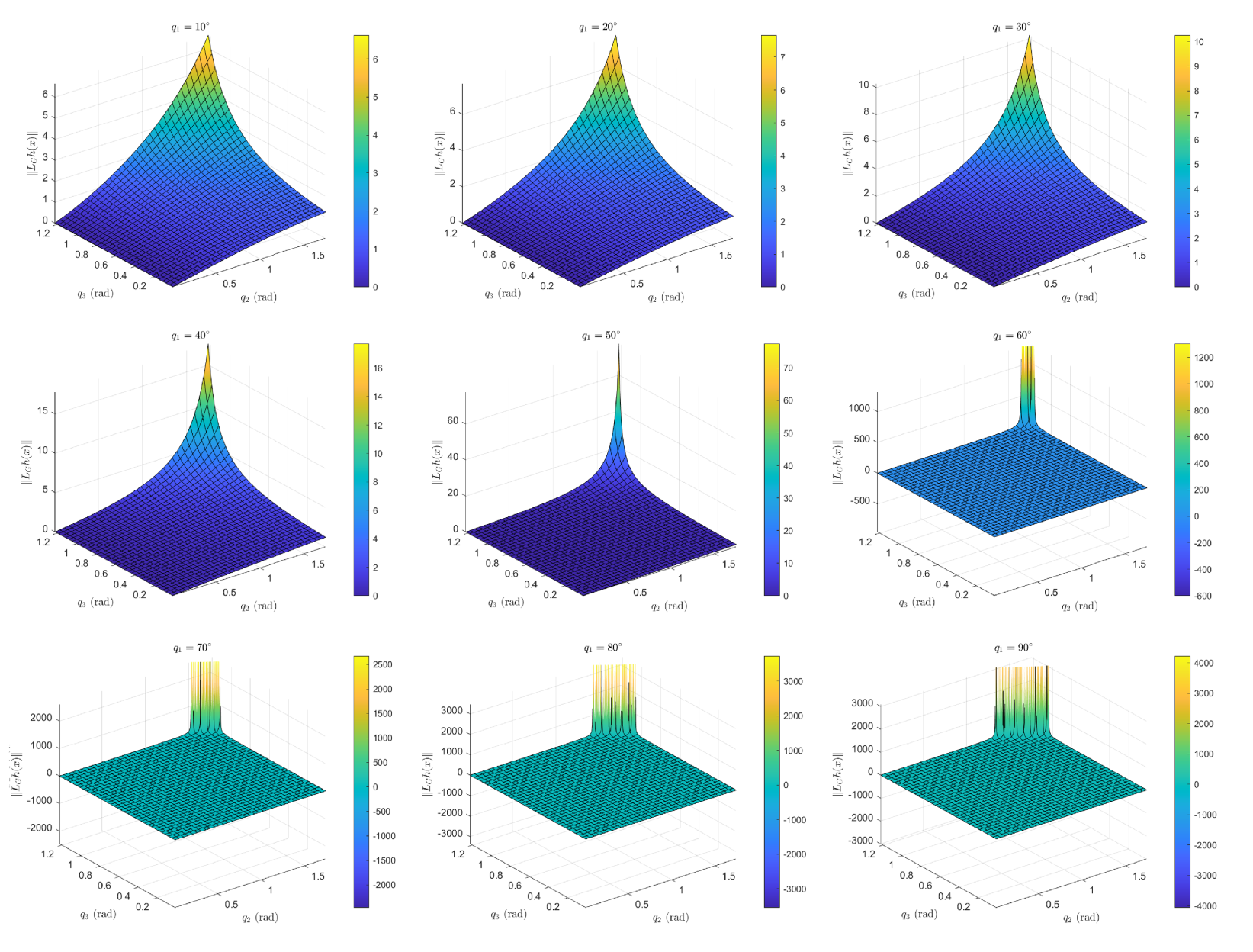

Appendix A.2. Symbolic Equations of
References
- Feigin, V.L.; Roth, G.A.; Naghavi, M.; Parmar, P.; Krishnamurthi, R.; Chugh, S.; Mensah, G.A.; Norrving, B.; Shiue, I.; Ng, M.; et al. Global burden of stroke and risk factors in 188 countries, during 1990-2013: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. Lancet Neurol. 2016, 15, 913–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanjuan, J.; Castillo, A.D.; Padilla, M.A.; Quintero, M.C.; Gutierrez, E.; Sampayo, I.P.; Hernandez, J.R.; Rahman, M.H. Cable driven exoskeleton for upper-limb rehabilitation: A design review. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2020, 126, 103445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobkin, B.H. Strategies for stroke rehabilitation. Lancet Neurol. 2004, 3, 528–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maciejasz, P.; Eschweiler, J.; Gerlach-Hahn, K.; Jansen-Troy, A.; Leonhardt, S. A survey on robotic devices for upper limb rehabilitation. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2014, 11, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, C. Human-in-the-loop development of soft wearable robots. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2018, 3, 78–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghshenas-Jaryani, M.; Carrigan, W.; Wijesundara, M.B.; Patterson, R.M.; Bugnariu, N.; Niacaris, T. Kinematic Study of a Soft-and-Rigid Robotic Digit for Rehabilitation and Assistive Applications. In Proceedings of the ASME 2016 International Design Engineering Technical Conferences and Computers and Information in Engineering Conference, Charlotte, NC, USA, 21–24 August 2016; American Society of Mechanical Engineers Digital Collection: New York, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Rus, D.; Tolley, M.T. Design, fabrication and control of soft robots. Nature 2015, 521, 467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polygerinos, P.; Correll, N.; Morin, S.A.; Mosadegh, B.; Onal, C.D.; Petersen, K.; Cianchetti, M.; Tolley, M.T.; Shepherd, R.F. Soft robotics: Review of fluid-driven intrinsically soft devices; manufacturing, sensing, control, and applications in human-robot interaction. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2017, 19, 1700016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polygerinos, P.; Wang, Z.; Galloway, K.C.; Wood, R.J.; Walsh, C.J. Soft robotic glove for combined assistance and at-home rehabilitation. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2015, 73, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghshenas-Jaryani, M.; Carrigan, W.; Nothnagle, C.; Wijesundara, M.B. Sensorized soft robotic glove for continuous passive motion therapy. In Proceedings of the 2016 6th IEEE International Conference on Biomedical Robotics and Biomechatronics (BioRob), Singapore, 26–29 June 2016; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 815–820. [Google Scholar]
- Haghshenas-Jaryani, M.; Nothnagle, C.; Patterson, R.M.; Bugnariu, N.; Wijesundara, M.B. Soft robotic rehabilitation exoskeleton (rehab glove) for hand therapy. In Proceedings of the ASME 2017 International Design Engineering Technical Conferences and Computers and Information in Engineering Conference, Cleveland, OH, USA, 6–9 August 2017; American Society of Mechanical Engineers Digital Collection: New York, NY, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Chu, C.Y.; Patterson, R.M. Soft robotic devices for hand rehabilitation and assistance: A narrative review. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2018, 15, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahid, T.; Gouwanda, D.; Nurzaman, S.G.; Gopalai, A.A. Moving toward soft robotics: A decade review of the design of hand exoskeletons. Biomimetics 2018, 3, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghshenas-Jaryani, M.; Pande, C.; Wijesundara, B.M. Soft Robotic Bilateral Hand Rehabilitation System for Fine Motor Learning. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE 16th International Conference on Rehabilitation Robotics (ICORR), Toronto, ON, Canada, 24–28 June 2019; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 337–342. [Google Scholar]
- Kadowaki, Y.; Noritsugu, T.; Takaiwa, M.; Sasaki, D.; Kato, M. Development of soft power-assist glove and control based on human intent. J. Robot. Mechatron. 2011, 23, 281–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thalman, C.; Artemiadis, P. A review of soft wearable robots that provide active assistance: Trends, common actuation methods, fabrication, and applications. Wearable Technol. 2020, 1, e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, J.; Khan, H.; Tsagarakis, N.G.; Caldwell, D.G. A novel exoskeleton robotic system for hand rehabilitation–conceptualization to prototyping. Biocybern. Biomed. Eng. 2014, 34, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lum, P.S.; Godfrey, S.B.; Brokaw, E.B.; Holley, R.J.; Nichols, D. Robotic approaches for rehabilitation of hand function after stroke. Am. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2012, 91, S242–S254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heo, P.; Gu, G.M.; Lee, S.J.; Rhee, K.; Kim, J. Current hand exoskeleton technologies for rehabilitation and assistive engineering. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. 2012, 13, 807–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, C.G.; O’Malley, M.K. Hybrid rigid-soft hand exoskeleton to assist functional dexterity. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2018, 4, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noritsugu, T.; Yamamoto, H.; Sasakil, D.; Takaiwa, M. Wearable power assist device for hand grasping using pneumatic artificial rubber muscle. In Proceedings of the SICE 2004 Annual Conference, Sapporo, Japan, 4–6 August 2004; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2004; Volume 1, pp. 420–425. [Google Scholar]
- Polygerinos, P.; Lyne, S.; Wang, Z.; Nicolini, L.F.; Mosadegh, B.; Whitesides, G.M.; Walsh, C.J. Towards a soft pneumatic glove for hand rehabilitation. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Tokyo, Japan, 3–7 November 2013; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2013; pp. 1512–1517. [Google Scholar]
- Yap, H.K.; Ang, B.W.; Lim, J.H.; Goh, J.C.; Yeow, C.H. A fabric-regulated soft robotic glove with user intent detection using EMG and RFID for hand assistive application. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Stockholm, Sweden, 16–21 May 2016; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 3537–3542. [Google Scholar]
- Noritsugu, T.; Takaiwa, M.; Sasaki, D. Power assist wear driven with pneumatic rubber artificial muscles. In Proceedings of the 2008 15th International Conference on Mechatronics and Machine Vision in Practice, Auckland, New Zealand, 2–4 December 2008; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2008; pp. 539–544. [Google Scholar]
- Cappello, L.; Meyer, J.T.; Galloway, K.C.; Peisner, J.D.; Granberry, R.; Wagner, D.A.; Engelhardt, S.; Paganoni, S.; Walsh, C.J. Assisting hand function after spinal cord injury with a fabric-based soft robotic glove. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2018, 15, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Jalving, J.; Huang, R.; Knepper, R.; Ruina, A.; Shepherd, R. A helping hand: Soft orthosis with integrated optical strain sensors and EMG control. IEEE Robot. Autom. Mag. 2016, 23, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Lin, L.; Yang, L.; Fu, Y. Variable impedance control of finger exoskeleton for hand rehabilitation following stroke. Ind. Robot. Int. J. Robot. Res. Appl. 2019, 47, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiota, K.; Kokubu, S.; Tarvainen, T.V.; Sekine, M.; Kita, K.; Huang, S.Y.; Yu, W. Enhanced Kapandji test evaluation of a soft robotic thumb rehabilitation device by developing a fiber-reinforced elastomer-actuator based 5-digit assist system. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2019, 111, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Chen, D.; Liu, P.; Jiao, X.; Ping, Z.; Xu, Z.; Li, J.; Xu, Y. Fishbone-inspired soft robotic glove for hand rehabilitation with multi-degrees-of-freedom. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Soft Robotics (RoboSoft), Livorno, Italy, 24–28 April 2018; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 394–399. [Google Scholar]
- Heung, K.H.; Tong, R.K.; Lau, A.T.; Li, Z. Robotic glove with soft-elastic composite actuators for assisting activities of daily living. Soft Robot. 2019, 6, 289–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popov, D.; Gaponov, I.; Ryu, J.H. Portable exoskeleton glove with soft structure for hand assistance in activities of daily living. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2016, 22, 865–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- In, H.; Kang, B.B.; Sin, M.; Cho, K.J. Exo-glove: A wearable robot for the hand with a soft tendon routing system. IEEE Robot. Autom. Mag. 2015, 22, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, B.B.; Choi, H.; Lee, H.; Cho, K.J. Exo-Glove Poly II: A Polymer-Based Soft Wearable Robot for the Hand with a Tendon-Driven Actuation System. Soft Robot. 2019, 6, 214–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghshenas-Jaryani, M.; Patterson, R.M.; Bugnariu, N.; Wijesundara, M.B. A pilot study on the design and validation of a hybrid exoskeleton robotic device for hand rehabilitation. J. Hand Ther. 2020, 33, 198–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, S.S.; Kang, B.B.; Cho, K.J. Exo-glove PM: An easily customizable modularized pneumatic assistive glove. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2017, 2, 1725–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerez, L.; Gao, G.; Dwivedi, A.; Liarokapis, M. A Hybrid, Wearable Exoskeleton Glove Equipped With Variable Stiffness Joints, Abduction Capabilities, and a Telescopic Thumb. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 173345–173358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, B.B.; Lee, H.; In, H.; Jeong, U.; Chung, J.; Cho, K.J. Development of a polymer-based tendon-driven wearable robotic hand. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Stockholm, Sweden, 16–21 May 2016; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 3750–3755. [Google Scholar]
- Jeong, U.; In, H.; Lee, H.; Kang, B.B.; Cho, K. Investigation on the control strategy of soft wearable robotic hand with slack enabling tendon actuator. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Seattle, WA, USA, 26–30 May 2015; pp. 5004–5009. [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson, M.; Ingvast, J.; Wikander, J.; von Holst, H. The Soft Extra Muscle system for improving the grasping capability in neurological rehabilitation. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE-EMBS Conference on Biomedical Engineering and Sciences, Langkawi, Malaysia, 17–19 December 2012; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2012; pp. 412–417. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.W.; Landers, K.A.; Park, H.S. Development of a biomimetic hand exotendon device (BiomHED) for restoration of functional hand movement post-stroke. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2014, 22, 886–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borboni, A.; Mor, M.; Faglia, R. Gloreha—Hand robotic rehabilitation: Design, mechanical model, and experiments. J. Dyn. Syst. Meas. Control 2016, 138, 111003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nycz, C.J.; Delph, M.A.; Fischer, G.S. Modeling and design of a tendon actuated soft robotic exoskeleton for hemiparetic upper limb rehabilitation. In Proceedings of the 2015 37th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Milan, Italy, 25–29 August 2015; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2015; pp. 3889–3892. [Google Scholar]
- Meeker, C.; Park, S.; Bishop, L.; Stein, J.; Ciocarlie, M. EMG pattern classification to control a hand orthosis for functional grasp assistance after stroke. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Rehabilitation Robotics (ICORR), London, UK, 17–20 July 2017; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 1203–1210. [Google Scholar]
- Park, S.; Weber, L.; Bishop, L.; Stein, J.; Ciocarlie, M. Design and development of effective transmission mechanisms on a tendon driven hand orthosis for stroke patients. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Brisbane, Australia, 21–25 May 2018; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 2281–2287. [Google Scholar]
- Xiloyannis, M.; Cappello, L.; Binh, K.D.; Antuvan, C.W.; Masia, L. Preliminary design and control of a soft exosuit for assisting elbow movements and hand grasping in activities of daily living. J. Rehabil. Assist. Technol. Eng. 2017, 4, 2055668316680315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grosu, S.; Rodriguez-Guerrero, C.; Grosu, V.; Vanderborght, B.; Lefeber, D. Evaluation and Analysis of Push-Pull Cable Actuation System Used for Powered Orthoses. Front. Robot. AI 2018, 5, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghshenas-Jaryani, M.; Carrigan, W.; Wijesundara, M.B. Design and Development of a Novel Soft-and-Rigid Hybrid Actuator System for Robotic Applications. In Proceedings of the ASME 2015 International Design Engineering Technical Conferences and Computers and Information in Engineering Conference, Boston, MA, USA, 2–5 August 2015; American Society of Mechanical Engineers: New York, NY, USA, 2015; Volume 5A, pp. V05AT08A047–V05AT08A053. [Google Scholar]
- Kadivar, Z.; Beck, C.E.; Rovekamp, R.N.; O’Malley, M.K.; Joyce, C.A. On the efficacy of isolating shoulder and elbow movements with a soft, portable, and wearable robotic device. In Wearable Robotics: Challenges and Trends; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; pp. 89–93. [Google Scholar]
- Marchese, A.D.; Tedrake, R.; Rus, D. Dynamics and trajectory optimization for a soft spatial fluidic elastomer manipulator. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Seattle, WA, USA, 26–30 May 2015; pp. 2528–2535. [Google Scholar]
- Santina, C.D.; Katzschmann, R.K.; Biechi, A.; Rus, D. Dynamic control of soft robots interacting with the environment. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Soft Robotics (RoboSoft), Livorno, Italy, 24–28 April 2018; pp. 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George Thuruthel, T.; Ansari, Y.; Falotico, E.; Laschi, C. Control strategies for soft robotic manipulators: A survey. Soft Robot. 2018, 5, 149–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.Q.; Heung, H.L.; Shi, X.Q.; Tong, K.Y.; Li, Z. Probabilistic Model-Based Learning Control of a Soft Pneumatic Glove for Hand Rehabilitation. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2022, 69, 1016–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiboni, M.; Amici, C. Soft Gloves: A Review on Recent Developments in Actuation, Sensing, Control and Applications. Actuators 2022, 11, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- du Plessis, T.; Djouani, K.; Oosthuizen, C. A review of active hand exoskeletons for rehabilitation and assistance. Robotics 2021, 10, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrow, N.; Correll, N. A soft pneumatic actuator that can sense grasp and touch. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Hamburg, Germany, 28 September–2 October 2015; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2015; pp. 2317–2323. [Google Scholar]
- Bilodeau, R.A.; White, E.L.; Kramer, R.K. Monolithic fabrication of sensors and actuators in a soft robotic gripper. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Hamburg, Germany, 28 September–2 October 2015; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2015; pp. 2324–2329. [Google Scholar]
- Case, J.C.; White, E.L.; Kramer, R.K. Sensor enabled closed-loop bending control of soft beams. Smart Mater. Struct. 2016, 25, 045018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correll, N.; Önal, Ç.D.; Liang, H.; Schoenfeld, E.; Rus, D. Soft autonomous materials—Using active elasticity and embedded distributed computation. In Proceedings of the Experimental Robotics, Bali, Indonesia, 5–10 December 2014; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 227–240. [Google Scholar]
- Ha, J.; Kim, D.; Jo, S. Use of deep learning for position estimation and control of soft glove. In Proceedings of the 2018 18th International Conference on Control, Automation and Systems (ICCAS), PyeongChang, Republic of Korea, 17–20 October 2018; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 570–574. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, C.L.; Wang, F.; Morrison, R.; Sarkar, N.; Kamper, D.G. Design and development of the cable actuated finger exoskeleton for hand rehabilitation following stroke. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2012, 19, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneishi, D.; Matthew, R.P.; Leu, J.E.; O’Donnell, J.; Zhang, B.; Tomizuka, M.; Stuart, H. Hybrid control interface of a semi-soft assistive glove for people with spinal cord injuries. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE 16th International Conference on Rehabilitation Robotics (ICORR), Toronto, ON, Canada, 24–28 June 2019; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 132–138. [Google Scholar]
- Sierotowicz, M.; Lotti, N.; Nell, L.; Missiroli, F.; Alicea, R.; Zhang, X.; Xiloyannis, M.; Rupp, R.; Papp, E.; Krzywinski, J.; et al. EMG-Driven Machine Learning Control of a Soft Glove for Grasping Assistance and Rehabilitation. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2022, 7, 1566–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghshenas-Jaryani, M. Adaptive Quasi-Static Motion Control of a Soft Robotic Exo-Digit in physical Human-Wearable-Soft-Robot-Interaction. In Proceedings of the IEEE 18th International Conference on Automation Science and Engineering (CASE), Mexico City, Mexico, 20–24 August 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Kamper, D.G.; Rymer, W.Z. Quantitative features of the stretch response of extrinsic finger muscles in hemiparetic stroke. Muscle & Nerve Off. J. Am. Assoc. Electrodiagn. Med. 2000, 23, 954–961. [Google Scholar]
- Kamper, D.; Rymer, W.Z. Impairment of voluntary control of finger motion following stroke: Role of inappropriate muscle coactivation. Muscle Nerve Off. J. Am. Assoc. Electrodiagn. Med. 2001, 24, 673–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polygerinos, P.; Wang, Z.; Overvelde, J.T.; Galloway, K.C.; Wood, R.J.; Bertoldi, K.; Walsh, C.J. Modeling of soft fiber-reinforced bending actuators. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2015, 31, 778–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolov, S.; Kotev, V.; Kostadinov, K.; Wang, F.; Liang, C.; Tian, Y. Model-based design optimization of soft fiber-reinforced bending actuators. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Manipulation, Manufacturing and Measurement on the Nanoscale (3M-NANO), Chongqing, China, 18–22 July 2016; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 136–140. [Google Scholar]
- Haghshenas-Jaryani, M.; Wijesundara, M.B. A Quasi-Static Model for Studying Physical Interaction Between a Soft Robotic Digit and a Human Finger. In Proceedings of the ASME 2018 International Design Engineering Technical Conferences and Computers and Information in Engineering Conference, Quebec City, QC, Canada, 26–29 August 2018; American Society of Mechanical Engineers Digital Collection: New York, NY, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Haghshenas-Jaryani, M.; Manvar, M.; Wijesundara, M.B. Torque Characterization of a Novel Pneumatic Soft-and-Rigid Hybrid Actuator. In Proceedings of the ASME 2017 Dynamic Systems and Control Conference, Tysons Corner, VA, USA, 11–13 October 2017; American Society of Mechanical Engineers Digital Collection: New York, NY, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Haghshenas-Jaryani, M. Quasi-Static Model-based Control of Human-Soft-Robot Interaction for Assisted Hand Motion. In Proceedings of the 2020 8th IEEE RAS/EMBS International Conference for Biomedical Robotics and Biomechatronics (BioRob), New York City, NY, USA, 29 November–1 December 2020; pp. 370–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, H.K. Nonlinear Control, 3rd ed.; Pearson: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Isidori, A. Nonlinear Control Systems: An Introduction; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Jayaraman, G.; Chizeck, H.J. Feedback linearization of discrete-time systems. In Proceedings of the 32nd IEEE Conference on Decision and Control, San Antonio, TX, USA, 15–17 December 1993; Volume 4, pp. 2972–2977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






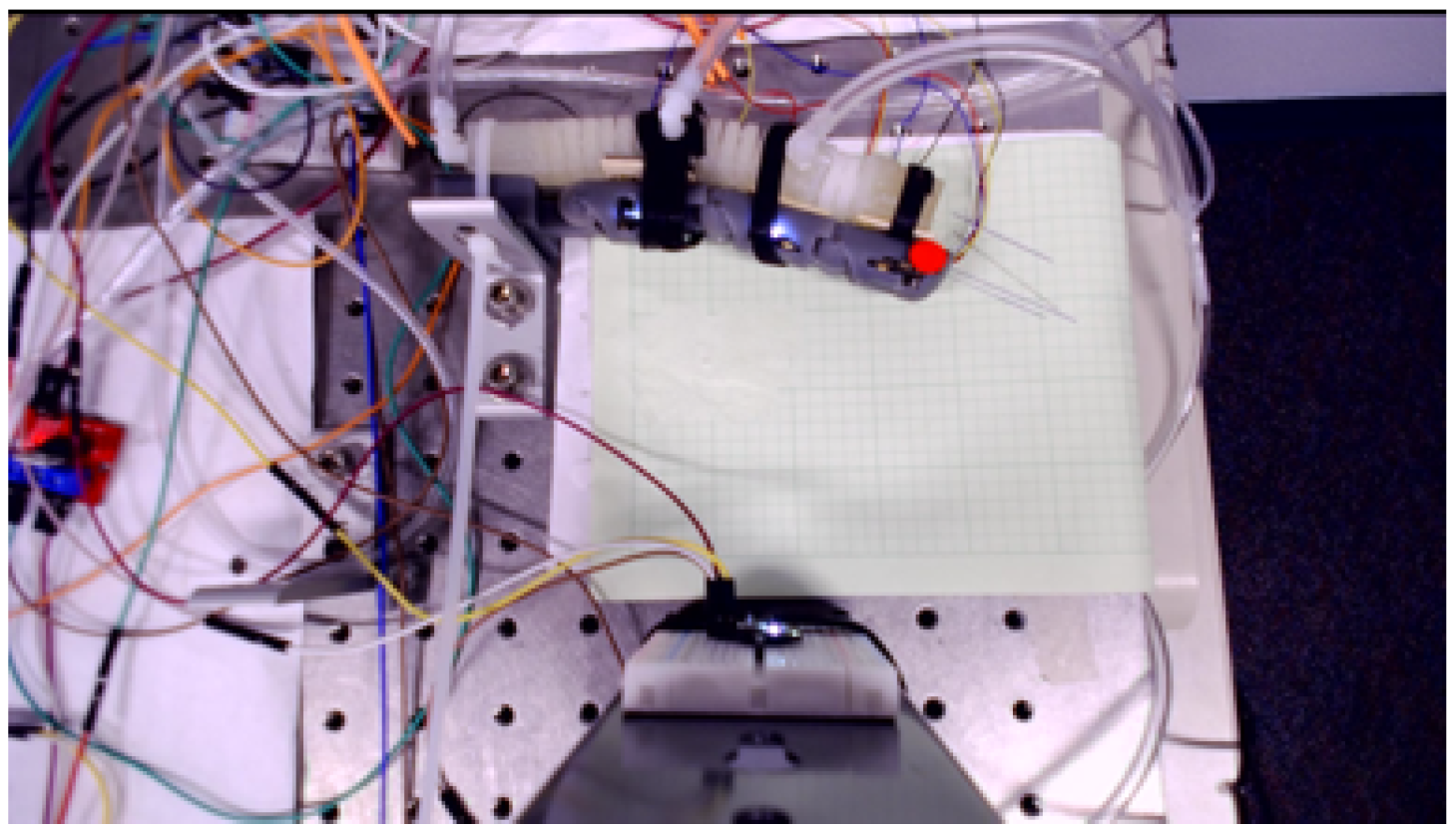



| No. | General Name | Specification | Amount | Description | Justification |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Arduino | MEGA 2560 | 1 | Controls overall operation, receives and transmits commands using control algorithms | Provides 5 V power to the I/O pin necessary to operate the valves |
| 2. | 3-way valve | FA0520E | 3 | Provides proportional input control value (pressurized air) to achieve the pressure change | Suitable for the logic of the system |
| 3. | 2-way valve | FA0520D | 3 | Controls the pressure relief process | Suitable for the logic of the system |
| 4. | Pressure sensor | MPRLS, Honeywell | 3 | Measures the internal pressure of each soft actuator segment | Suitable to measure inside air pressure of the tube |
| 5. | IMU | 6-DOF MPU6050 | 4 | Measures the angular position and velocity of moving links | Provides enough data for planar finger motion’s angular position and velocity calculation |
| 6. | I2C Multiplexer | TCA9548A | 1 | Connects the pressure sensors and the IMUs with the Arduino | Ideal for IMU, pressure sensor, and Arduino with I2C interface communication |
| 7. | MOS module | HM MOS module | 6 | Turns on and off the 3-way and 2-way valves | Suitable for the logic of the sytem |
| 8. | Finger model | Human finger model | 1 | 3D-printed human finger model that interacts with the soft exo-digit | Remains passive, provides only resistive reaction force to the soft exo-digit’s motion, ideal for testing current control algorithm |
| 9. | Robotic exo-digit | Soft silicone exo-digit | 1 | Soft silicone module fabricated with RTV silicone rubber | Suitable for safe physical interaction with human body |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alam, U.K.; Shedd, K.; Haghshenas-Jaryani, M. Trajectory Control in Discrete-Time Nonlinear Coupling Dynamics of a Soft Exo-Digit and a Human Finger Using Input–Output Feedback Linearization. Automation 2023, 4, 164-190. https://doi.org/10.3390/automation4020011
Alam UK, Shedd K, Haghshenas-Jaryani M. Trajectory Control in Discrete-Time Nonlinear Coupling Dynamics of a Soft Exo-Digit and a Human Finger Using Input–Output Feedback Linearization. Automation. 2023; 4(2):164-190. https://doi.org/10.3390/automation4020011
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlam, Umme Kawsar, Kassidy Shedd, and Mahdi Haghshenas-Jaryani. 2023. "Trajectory Control in Discrete-Time Nonlinear Coupling Dynamics of a Soft Exo-Digit and a Human Finger Using Input–Output Feedback Linearization" Automation 4, no. 2: 164-190. https://doi.org/10.3390/automation4020011
APA StyleAlam, U. K., Shedd, K., & Haghshenas-Jaryani, M. (2023). Trajectory Control in Discrete-Time Nonlinear Coupling Dynamics of a Soft Exo-Digit and a Human Finger Using Input–Output Feedback Linearization. Automation, 4(2), 164-190. https://doi.org/10.3390/automation4020011







