Extraction and Composition of Lipids from Pomegranate Seed Oil from West Algeria †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Vegetable Matter
2.2. Reagents and Chemicals
2.3. Oil Extraction: Soxhlet
- Method A: A total of 20 g of Punica granatum seeds are placed in a Soxhlet apparatus with a flask containing 200 mL of solvent. Extraction is performed over 8 h. Afterward, the mixture is transferred to the rotary evaporator for complete solvent evaporation. The isolated oil is stored at −4 °C, and the yield is expressed as a percentage of the isolated oil weight relative to the weight of the ground seeds.
- Method B: In this modified protocol designed to shorten the extraction time, 20 g of Punica Granatum seeds are loaded into the extraction cartridge, which is then inserted into a flask containing 200 mL of solvent. After 30 min of refluxing, both the solvent and cartridge are transferred into a Soxhlet apparatus and refluxed for an additional 60 min. The mixture is then transferred to the rotary evaporator for complete solvent evaporation. The isolated oil is stored at −4 °C, and the yield is expressed as a percentage of the isolated oil weight relative to the weight of the ground seeds.
2.4. Physico-Chemical Analysis: Oil Quality Parameters
2.5. High-Performance Thin-Layer Chromatography (HPTLC)—Lipid Classes
2.6. Analysis by Gas Chromatography (GC)-FID
2.6.1. Preparation of Fatty Acid Methyl Esters (FAMEs)
2.6.2. FAMEs GC-FID Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Localization and Quantification
3.2. Soxhlet Approach to Oil-Extraction
3.3. PSO Physico-Chemical Indices
3.4. Chemical Composition of the PSO
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Verma, N.; Mohanty, A.; Lal, A. Pomegranate Genetic Resources and Germplasm Conservation. A Review. Fruit Veg. Cereal Sci. Biotechnol. 2010, 4, 120–125. [Google Scholar]
- Mohagheghi, M.; Rezaei, K.; Labbafi, M.; Mousavi, S.M.E. Pomegranate seed oil as a functional ingredient in beverages. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2011, 113, 730–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Melo, I.L.P.; Carvalho, E.B.T.; Mancini-Filho, J. Pomegranate Seed Oil (Punica granatum L.): A Source of Punicic Acid (Conjugated α-Linolenic Acid). J. Hum. Nutr. Food Sci. 2014, 2, 1024–1035. [Google Scholar]
- Holic, R.; Xu, Y.; Caldo, K.M.P.; Singer, S.D.; Field, C.J.; Weselake, R.J.; Chen, G. Bioactivity and biotechnological production of punicic acid. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 102, 102–3537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boroushaki, M.T.; Mollazadeh, H.; Afshari, A.R. Pomegranate seed oil: A comprehensive review on its therapeutic effects. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Res. 2016, 7, 430–442. [Google Scholar]
- Vroegrijk, I.O.; van Diepen, J.A.; van den Berg, S.; Westbroek, I.; Keizer, H.; Gambelli, L.; Havekes, L.M. Pomegranate seed oil, a rich source of punicic acid, prevents diet-induced obesity and insulin resistance in mice. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2011, 49, 1426–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AOCS Official Methods of Analysis. Methods Cd 3d-63; Cd 1b-87; Cd 8b-90; AOCS: Champaign, IL, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Youssef, S.; Fakhfakh, J.; Breil, C.; Abert-Vian, M.; Chemat, F.; Allouche, N. Green extraction procedures of lipids from Tunisian date palm seeds. Ind. Crops Prod. 2017, 108, 520–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrison, W.R.; Smith, L.M. Preparation of fatty acid methyl esters and dimethyl acetals from lipids with boron fluoridemethanol. J. Lipid Res. 1964, 5, 600–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandes, L.; Pereira, J.A.; Lopéz-Cortés, I.; Salazar, D.M.; Ramalhosa, E.; Casal, S. Fatty acid, vitamin E and sterols composition of seed oils from nine different pomegranate (Punica granatum L.) cultivars grown in Spain. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2015, 39, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Codex Alimentarius. 2001. Codex standard for named vegetable oils cx-stan 210. Named Veg. Oils 1999, 8, 11–25. [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman, M.; Wiesman, Z. Pomegranate Oil Analysis with Emphasis on MALDI-TOF/MS Triacylglycerol Fingerprinting. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 10405–10413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aruna, P.; Venkataramanamma, D.; Singh, A.K.; Singh, R.P. Health Benefits of Punicic Acid. A Review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2014, 15, 16–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kýralan, M.; Gölükcü, M.; Tokgöz, H. Oil and Conjugated Linolenic Acid Contents of Seeds from Important Pomegranate Cultivars (Punica granatum L.) Grown in Turkey. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2009, 86, 985–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pande, G.; Akoh, C.C. Antioxidant Capacity and Lipid Characterization of Six Georgia-Grown Pomegranate Cultivars. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 9427–9436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| % Arils (Seed + Pulp) | % of Dried Seeds | |
|---|---|---|
| Atmi | 62.5 | 6.1 |
| Valenciana | 65.8 | 7.9 |
| Mollar Elche | 53.1 | 4.7 |
| Solvent of Extraction | Solvent’s Boiling Point (°C) | Yield in Oil (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Method A | Method B | ||
| n-Hexane | 68.7 | 15.62 | 16.25 |
| Cyclohexane | 80.7 | 14.89 | 13.05 |
| Petroleum Ether | 40–65 | 13.68 | 11.84 |
| Chloroform | 62 | 13.3 | 16.5 |
| Isopropanol | 83 | 17.21 | 17.11 |
| Physico-Chemical Property | PSO of Atmi |
|---|---|
| Refractive Index (25 °C) | 1.5178 |
| Density at 20 °C | 0.943 |
| Iodine Index (g I2/100 g oil) | 153.04 |
| Acid Index (mg KOH/g) | 2.24 |
| Peroxide Index (meq O2/kg) | 1.69 |
| Saponification Index (mg KOH/g) | 196.40 |
| Viscosity(Pa.s) | 0.191 |
| Saturated Fatty Acids (SFA) | 4.16% |
|---|---|
| Mono-Unsaturated Fatty Acids (MUFA) | 6.12% |
| Poly-Unsaturated Fatty Acids (PUFA) | 89.72% |
| Σ Unsaturated Acids | 95.84% |
| Ratio SFA/(PUFA + MUFA) | 0.043 |
| Fatty Acid | Percentage % | |
|---|---|---|
| Saturated | ||
| Palmitic Acid | C16:0 | 2.43 |
| Stearic Acid | C18:0 | 1.73 |
| Mono-unsaturated | ||
| Oleic Acid (n-9) | C18:1 | 5.69 |
| Gondoic Acid (n-9) | C22:1 | 0.43 |
| Poly-unsaturated | ||
| Linoleic Acid (n-6) | C18:2 | 6.52 |
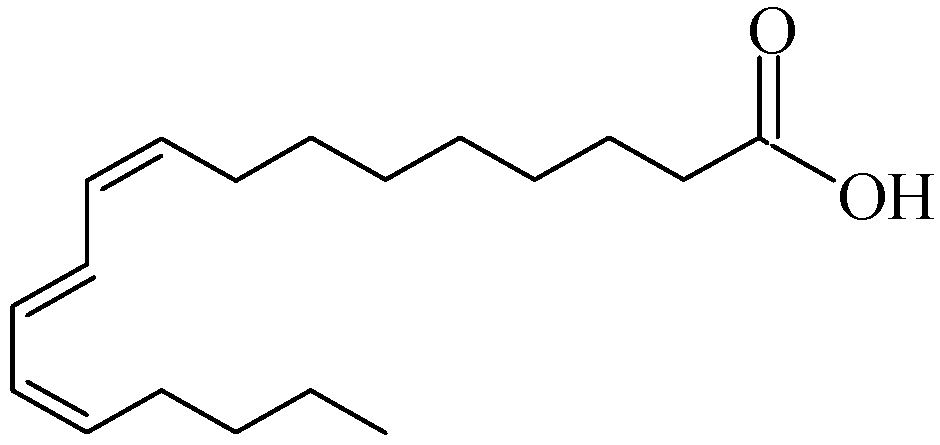
| Punicic Acid (n-5) | C18:3 | 83.20 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dib, S.; Mostefa-Kara, B.; Villemin, D. Extraction and Composition of Lipids from Pomegranate Seed Oil from West Algeria. Chem. Proc. 2023, 14, 78. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecsoc-27-16115
Dib S, Mostefa-Kara B, Villemin D. Extraction and Composition of Lipids from Pomegranate Seed Oil from West Algeria. Chemistry Proceedings. 2023; 14(1):78. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecsoc-27-16115
Chicago/Turabian StyleDib, Salima, Bachir Mostefa-Kara, and Didier Villemin. 2023. "Extraction and Composition of Lipids from Pomegranate Seed Oil from West Algeria" Chemistry Proceedings 14, no. 1: 78. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecsoc-27-16115
APA StyleDib, S., Mostefa-Kara, B., & Villemin, D. (2023). Extraction and Composition of Lipids from Pomegranate Seed Oil from West Algeria. Chemistry Proceedings, 14(1), 78. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecsoc-27-16115







