Estimation of the Effects of Achilles Tendon Geometry on the Magnitude and Distribution of Local Strain: A Finite Element Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
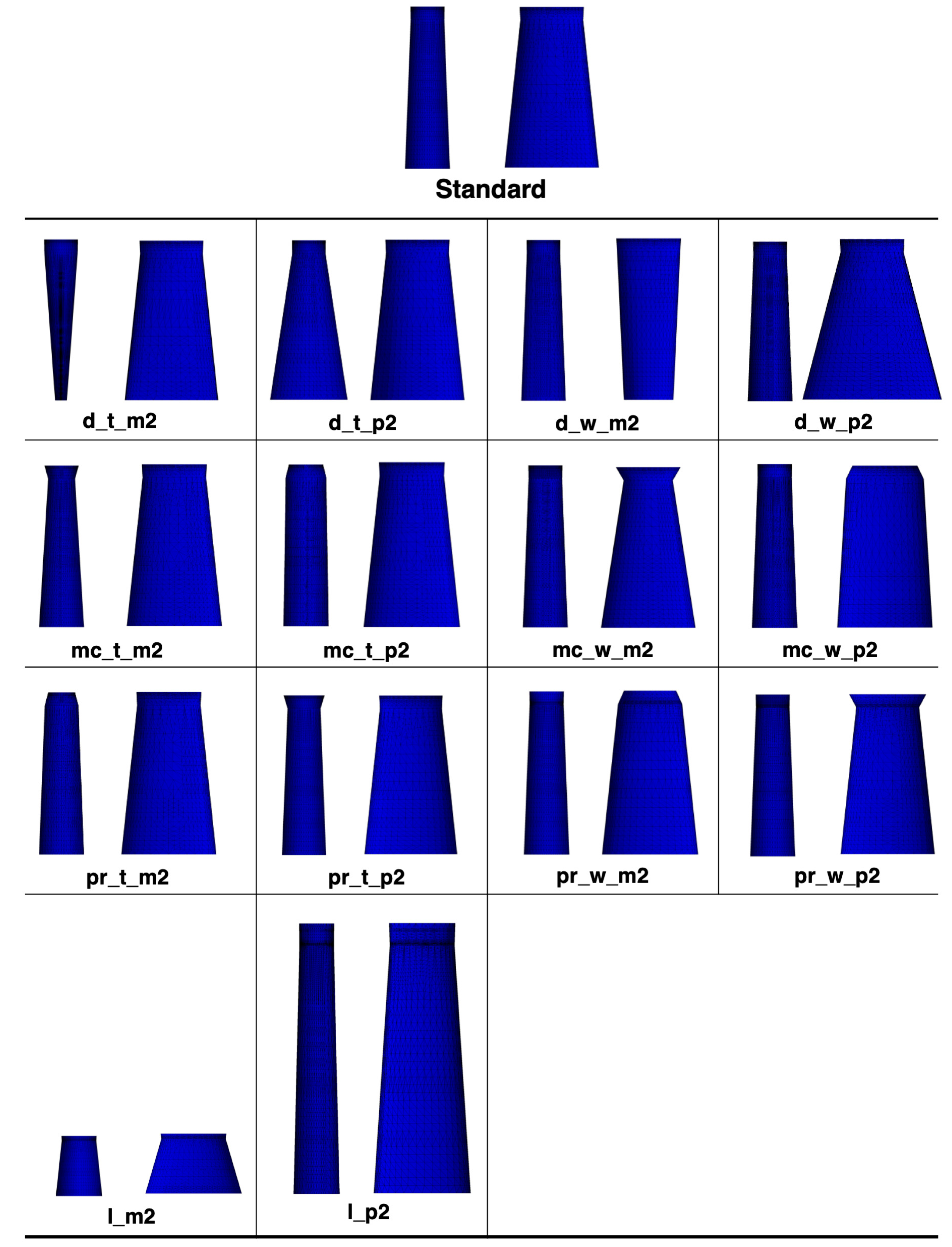
2.1. Mesh Generation
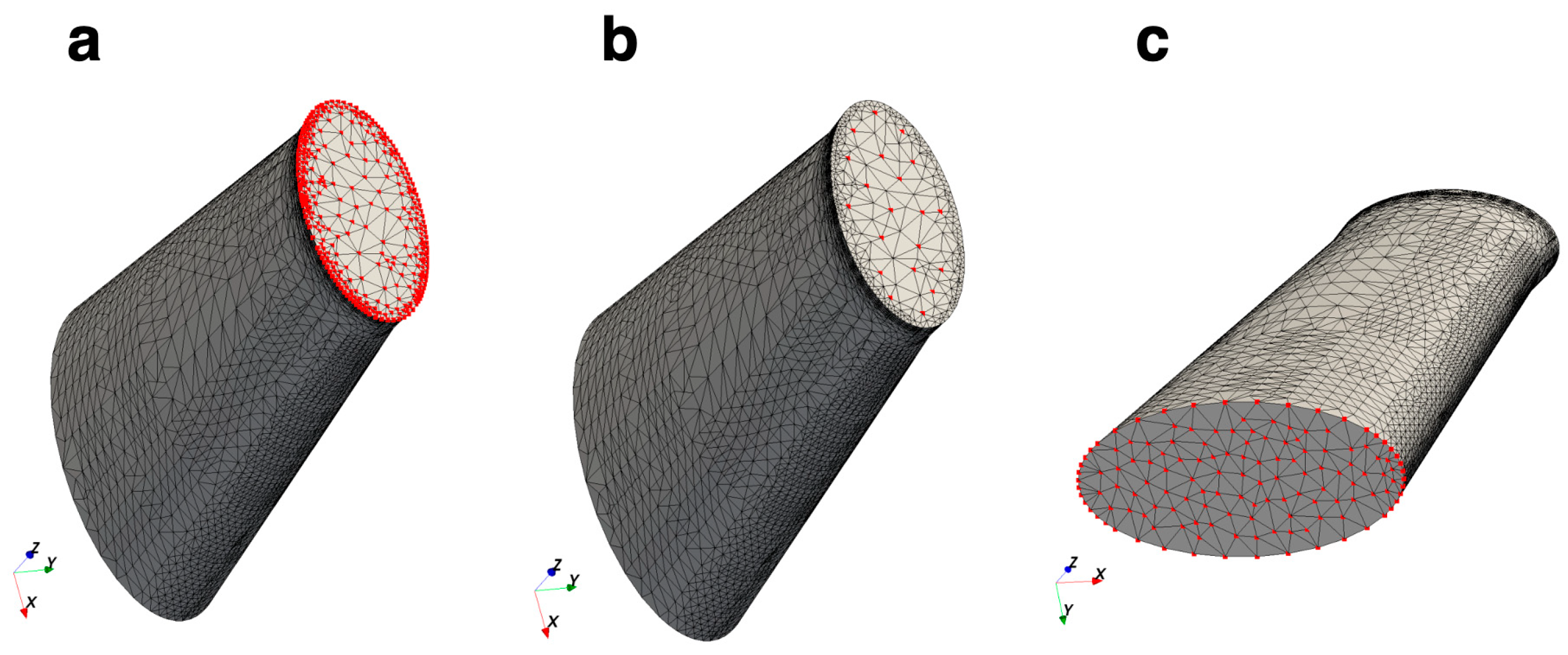
2.2. Mesh Convergence Test
2.3. Setting of Material Properties
2.4. Finite Element Analysis and Calculation of First Principal Strain
2.5. Validation of the Finite Element Model
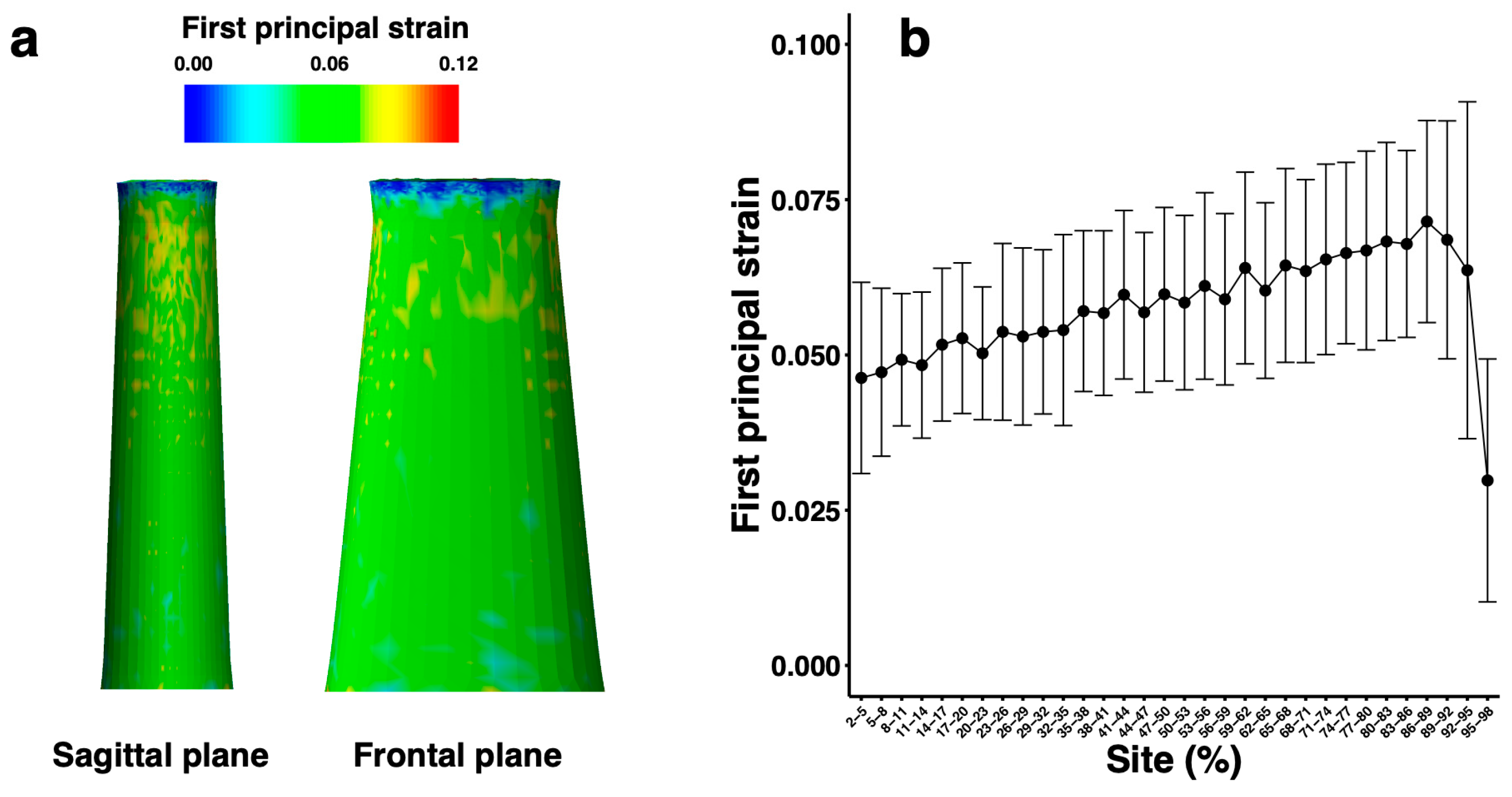
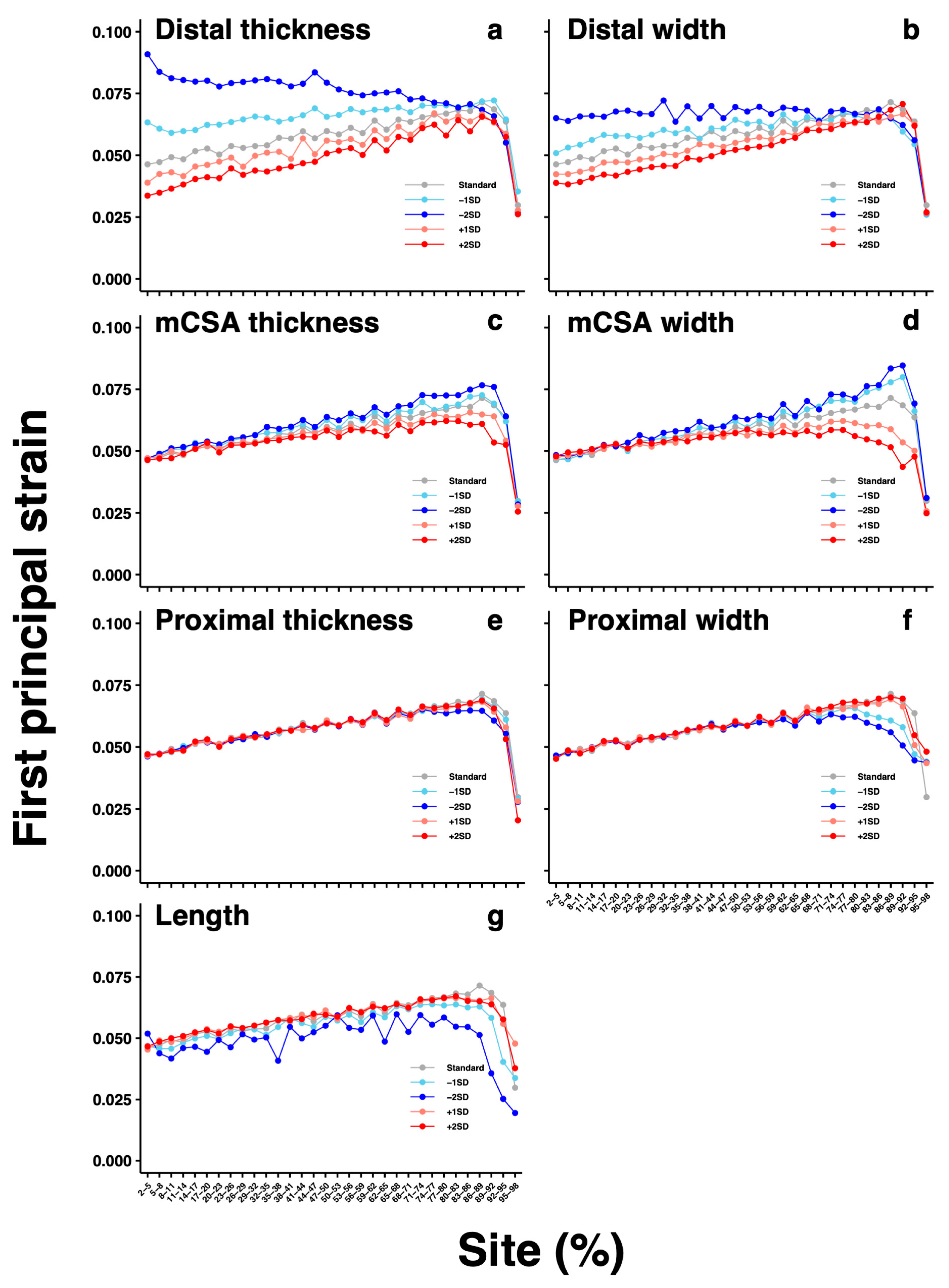
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alexander, R.M.; Bennet-Clark, H.C. Storage of elastic strain energy in muscle and other tissues. Nature 1977, 265, 114117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawakami, Y.; Muraoka, T.; Ito, S.; Kanehisa, H.; Fukunaga, T. In vivo muscle fibre behaviour during counter-movement exercise in humans reveals a significant role for tendon elasticity. J. Physiol. 2002, 540, 635–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maffulli, N.; Waterston, S.W.; Squair, J.; Reaper, J.; Douglas, A.S. Changing incidence of Achilles tendon rupture in Scotland: A 15-year study. Clin. J. Sport. Med. 1999, 9, 157–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houshian, S.; Tscherning, T.; Riegels-Nielsen, P. The epidemiology of Achilles tendon rupture in a Danish county. Injury 1998, 29, 651–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kujala, U.M.; Sarna, S.; Kaprio, J. Cumulative incidence of achilles tendon rupture and tendinopathy in male former elite athletes. Clin. J. Sport. Med. 2005, 15, 133–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metz, R.; Verleisdonk, E.J.; van der Heijden, G.J.; Clevers, G.J.; Hammacher, E.R.; Verhofstad, M.H.; van der Werken, C. Acute Achilles tendon rupture: Minimally invasive surgery versus nonoperative treatment with immediate full weightbearing—A randomized controlled trial. Am. J. Sports Med. 2008, 36, 1688–1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zellers, J.A.; Carmont, M.R.; Grävare Silbernagel, K. Return to play post-Achilles tendon rupture: A systematic review and meta-analysis of rate and measures of return to play. Br. J. Sports Med. 2016, 50, 1325–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habets, B.; van den Broek, A.G.; Huisstede, B.M.A.; Backx, F.J.G.; van Cingel, R.E.H. Return to Sport in Athletes with Midportion Achilles Tendinopathy: A Qualitative Systematic Review Regarding Definitions and Criteria. Sports Med. 2018, 48, 705–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maffulli, N.; Sharma, P.; Luscombe, K.L. Achilles tendinopathy: Aetiology and management. J. R. Soc. Med. 2004, 97, 472–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theobald, P.; Benjamin, M.; Nokes, L.; Pugh, N. Review of the vascularisation of the human Achilles tendon. Injury 2005, 36, 1267–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oda, T.; Kawakami, Y.; Kataoka, H.; Yokota, H.; Himeno, R. Estimation of local strain and stress in human Achilles tendon tissue during jumping. Jpn. J. Biomech. Sport Exerc. 2012, 16, 54–63. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Hisano, T.; Kusumoto, K.; Kurihara, T.; Ishikawa, M.; Kawakami, Y.; Oda, T. Estimation of local strain of Achilles tendon during exercise with individual structure geometry and tendon force date by finite element analysis. Jpn. J. Biomech. Sport Exerc. 2015, 19, 2–10. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Funaro, A.; Shim, V.; Crouzier, M.; Mylle, I.; Vanwanseele, B. Subject-Specific 3D Models to Investigate the Influence of Rehabilitation Exercises and the Twisted Structure on Achilles Tendon Strains. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 914137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szaro, P.; Ghali Gataa, K. The correlations between dimensions of the normal tendon and tendinopathy changed Achilles tendon in routine magnetic resonance imaging. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 6131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, J.L.; Yamamura, N.; Oda, T.; Teodosiu, C. Numerical simulation of musculoskeletal systems by V-Biomech. In Proceedings of the CMBBE2010, Valencia, Spain, 24–27 February 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, A.C.; Wilcox, R.K. Finite element analysis of the spine: Towards a framework of verification, validation and sensitivity analysis. Med. Eng. Phys. 2008, 30, 1287–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Xu, G.; Yang, J.; Lin, X. Finite element study of the biomechanical effects on the rotator cuff under load. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2023, 11, 1193376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamura, N.; Alves, J.L.; Oda, T.; Kinugasa, R.; Takagi, S. Effect of tendon stiffness on the generated force at the Achilles tendon-3D finite element simulation of a human triceps surae muscle during isometric contraction. J. Biomech. Sci. Eng. 2014, 9, 13–00294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Louis-Ugbo, J.; Leeson, B.; Hutton, W.C. Tensile properties of fresh human calcaneal (Achilles) tendons. Clin. Anat. 2004, 17, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukashiro, S.; Komi, P.V.; Järvinen, M.; Miyashita, M. In vivo Achilles tendon loading during jumping in humans. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. Occup. Physiol. 1995, 71, 453–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinugasa, R.; Yamamura, N.; Sinha, S.; Takagi, S. Influence of intramuscular fiber orientation on the Achilles tendon curvature using three-dimensional finite element modeling of contracting skeletal muscle. J. Biomech. 2016, 49, 3592–3595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kongsgaard, M.; Nielsen, C.H.; Hegnsvad, S.; Aagaard, P.; Magnusson, S.P. Mechanical properties of the human Achilles tendon, in vivo. Clin. Biomech. 2011, 26, 772–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, W.; Shim, V.B.; Obst, S.; Lloyd, D.G.; Newsham-West, R.; Barrett, R.S. Achilles tendon stress is more sensitive to subject-specific geometry than subject-specific material properties: A finite element analysis. J. Biomech. 2017, 56, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obst, S.J.; Renault, J.B.; Newsham-West, R.; Barrett, R.S. Three-dimensional deformation and transverse rotation of the human free Achilles tendon in vivo during isometric plantarflexion contraction. J. Appl. Physiol. 2014, 116, 376–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohatgi, A. WebPlotDigitizer. Available online: https://automeris.io/WebPlotDigitizer (accessed on 24 October 2023).
- Rosager, S.; Aagaard, P.; Dyhre-Poulsen, P.; Neergaard, K.; Kjaer, M.; Magnusson, S.P. Load-displacement properties of the human triceps surae aponeurosis and tendon in runners and non-runners. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2002, 12, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devaprakash, D.; Obst, S.J.; Lloyd, D.G.; Barrett, R.S.; Kennedy, B.; Ball, I.; Adams, K.L.; Collings, T.J.; Davico, G.; Hunter, A.; et al. The Free Achilles Tendon Is Shorter, Stiffer, Has Larger Cross-Sectional Area and Longer T2* Relaxation Time in Trained Middle-Distance Runners Compared to Healthy Controls. Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milgrom, Y.; Milgrom, C.; Altaras, T.; Globus, O.; Zeltzer, E.; Finestone, A.S. Achilles tendons hypertrophy in response to high loading training. Foot Ankle Int. 2014, 35, 1303–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geremia, J.M.; Baroni, B.M.; Bobbert, M.F.; Bini, R.R.; Lanferdini, F.J.; Vaz, M.A. Effects of high loading by eccentric triceps surae training on Achilles tendon properties in humans. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2018, 118, 1725–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, D.L.; Grood, E.S.; Noyes, F.R.; Zernicke, R.F. Biomechanics of ligaments and tendons. Exerc. Sport. Sci. Rev. 1978, 6, 125–181. [Google Scholar]
- Wren, T.A.; Yerby, S.A.; Beaupré, G.S.; Carter, D.R. Mechanical properties of the human achilles tendon. Clin. Biomech. 2001, 16, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruse, A.; Stafilidis, S.; Tilp, M. Ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging are not interchangeable to assess the Achilles tendon cross-sectional-area. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2017, 117, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnusson, S.P.; Beyer, N.; Abrahamsen, H.; Aagaard, P.; Neergaard, K.; Kjaer, M. Increased cross-sectional area and reduced tensile stress of the Achilles tendon in elderly compared with young women. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2003, 58, B123–B127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slane, L.C.; Martin, J.; DeWall, R.; Thelen, D.; Lee, K. Quantitative ultrasound mapping of regional variations in shear wave speeds of the aging Achilles tendon. Eur. Radiol. 2017, 27, 474–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coombes, B.K.; Tucker, K.; Vicenzino, B.; Vuvan, V.; Mellor, R.; Heales, L.; Nordez, A.; Hug, F. Achilles and patellar tendinopathy display opposite changes in elastic properties: A shear wave elastography study. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2018, 28, 1201–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crawford, S.K.; Thelen, D.; Yakey, J.M.; Heiderscheit, B.C.; Wilson, J.J.; Lee, K.S. Regional shear wave elastography of Achilles tendinopathy in symptomatic versus contralateral Achilles tendons. Eur. Radiol. 2023, 33, 720–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edama, M.; Kubo, M.; Onishi, H.; Takabayashi, T.; Inai, T.; Yokoyama, E.; Hiroshi, W.; Satoshi, N.; Kageyama, I. The twisted structure of the human Achilles tendon. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2015, 25, e497–e503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handsfield, G.G.; Greiner, J.; Madl, J.; Rog-Zielinska, E.A.; Hollville, E.; Vanwanseele, B.; Shim, V. Achilles Subtendon Structure and Behavior as Evidenced From Tendon Imaging and Computational Modeling. Front. Sports Act. Living 2020, 2, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knaus, K.R.; Blemker, S.S. 3D Models Reveal the Influence of Achilles Subtendon Twist on Strain and Energy Storage. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 5, 539135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shim, V.B.; Handsfield, G.G.; Fernandez, J.W.; Lloyd, D.G.; Besier, T.F. Combining in silico and in vitro experiments to characterize the role of fascicle twist in the Achilles tendon. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 13856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Parameter | Mean | Standard Deviation | Minimum | Maximum | Unit | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Proximal | Width | 14.2 | 1.4 | 12.2 | 16.9 | mm |
| Thickness | 7.5 | 0.8 | 6.2 | 9.1 | mm | |
| Minimum cross- sectional area | Width | 13.9 | 1.5 | 11.5 | 16.9 | mm |
| Thickness | 7.4 | 0.7 | 6.2 | 8.9 | mm | |
| Distal | Width | 20.8 | 4.9 | 8.0 | 30.6 | mm |
| Thickness | 9.9 | 3.7 | 6.4 | 23.6 | mm | |
| Length | 35.5 | 11.3 | 12.0 | 54.0 | mm | |
| Position of minimum cross-sectional area | 91.7 | 16.7 | 44.6 | 100.0 | % | |
| a10 | a01 | a20 | a11 | a02 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.24E1 | 3.62E0 | 5.83E2 | 1.80E3 | 3.11E3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Enomoto, S.; Oda, T. Estimation of the Effects of Achilles Tendon Geometry on the Magnitude and Distribution of Local Strain: A Finite Element Analysis. Biomechanics 2023, 3, 583-595. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomechanics3040047
Enomoto S, Oda T. Estimation of the Effects of Achilles Tendon Geometry on the Magnitude and Distribution of Local Strain: A Finite Element Analysis. Biomechanics. 2023; 3(4):583-595. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomechanics3040047
Chicago/Turabian StyleEnomoto, Shota, and Toshiaki Oda. 2023. "Estimation of the Effects of Achilles Tendon Geometry on the Magnitude and Distribution of Local Strain: A Finite Element Analysis" Biomechanics 3, no. 4: 583-595. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomechanics3040047
APA StyleEnomoto, S., & Oda, T. (2023). Estimation of the Effects of Achilles Tendon Geometry on the Magnitude and Distribution of Local Strain: A Finite Element Analysis. Biomechanics, 3(4), 583-595. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomechanics3040047





