Hyperthermia in Cancer Therapy
A topical collection in Cancers (ISSN 2072-6694). This collection belongs to the section "Cancer Therapy".
Viewed by 71549
Share This Topical Collection
Editors
 Prof. Dr. Holger Grüll
Prof. Dr. Holger Grüll
 Prof. Dr. Holger Grüll
Prof. Dr. Holger Grüll
E-Mail
Website
Collection Editor
Department of Radiology, University of Cologne, 50937 Cologne, Germany
Interests: hyperthermia; MR-HIFU; imaging
 Prof. Dr. Elizabeth Repasky
Prof. Dr. Elizabeth Repasky
 Prof. Dr. Elizabeth Repasky
Prof. Dr. Elizabeth Repasky
E-Mail
Website
Collection Editor
Department of Immunology, Roswell Park Comprehensive Cancer Center, Buffalo, NY 14263, USA
Interests: stress and tumor immunity; thermal stress; immunotherapy; tumor microenvironment and physiology
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
Moderate hyperthermia at 40–45 °C is a clinically proven radiosensitizer and chemosensitizer, and is used as a form of treatment at a number of tumor sites, including recurrent breast cancer, bladder cancer, cervical carcinoma, head and neck cancer, melanomas, peritoneal metastases, and soft tissue sarcomas. Adding hyperthermia to radiotherapy and chemotherapy improves the possibility for tumor control without increasing normal tissue toxicity. The effects of hyperthermia include re-oxygenation, the induction of the heat shock response, the inhibition of DNA-damage repair, and an enhanced immunological response. Ongoing research aims to comprehend more fully the effects of hyperthermia and further improve the clinical results.
This Topical Collection is pleased to invite submissions of manuscripts relating to multidisciplinary oncological research on therapeutic hyperthermia.
This Topical Collection invites submissions of papers, articles, and reviews on the relevant topics and innovative and original research related to hypothermia, which include advanced drug-delivery systems for targeted tumor therapy using nanoparticles or thermo-sensitive liposomes, cancer immune therapy, magnetic nanoparticle (MNP) and magnetic fluid hyperthermia, photothermal treatments, a combination with PARP inhibitors or HSP-90 inhibitors, thermal dosimetry, and biological modeling.
The areas of research may include (but are not limited to) biological and preclinical research; the clinical application and results of local, loco-regional, whole-body hyperthermia, HIPEC, and HIVEC; the development of new heating technology; hyperthermia simulations; and treatment planning.
We look forward to receiving your contributions.
Dr. Hans Crezee
Prof. Dr. Holger Grüll
Prof. Dr. Elizabeth Repasky
Collection Editors
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Cancers is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript.
The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2900 CHF (Swiss Francs).
Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's
English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- hyperthermia
- radiosensitization
- chemosensitization
- immunotherapy
- advanced drug delivery
- treatment planning
- modelling
- magnetic fluid hyperthermia
- nanomedicine
- multi-modality therapy
- particle therapy
- targeted drug delivery
- synthetic lethality
Published Papers (31 papers)
Open AccessArticle
A Validated Methodological Approach to Prove the Safety of Clinical Electromagnetic Induction Systems in Magnetic Hyperthermia
by
Maria Anastasia Rouni, Boaz Shalev, George Tsanidis, Ioannis Markakis, Sarah Kraus, Pazit Rukenstein, Doron Suchi, Ofer Shalev and Theodoros Samaras
Cited by 2 | Viewed by 1484
Abstract
The present study focuses on the development of a methodology for evaluating the safety of MNH systems, through the numerical prediction of the induced temperature rise in superficial skin layers due to eddy currents heating under an alternating magnetic field (AMF). The methodology
[...] Read more.
The present study focuses on the development of a methodology for evaluating the safety of MNH systems, through the numerical prediction of the induced temperature rise in superficial skin layers due to eddy currents heating under an alternating magnetic field (AMF). The methodology is supported and validated through experimental measurements of the AMF’s distribution, as well as temperature data from the torsos of six patients who participated in a clinical trial study. The simulations involved a computational model of the actual coil, a computational model of the cooling system used for the cooling of the patients during treatment, and a detailed human anatomical model from the Virtual Population family. The numerical predictions exhibit strong agreement with the experimental measurements, and the deviations are below the estimated combined uncertainties, confirming the accuracy of computational modeling. This study highlights the crucial role of simulations for translational medicine and paves the way for personalized treatment planning.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
Hyperthermia in Combination with Emerging Targeted and Immunotherapies as a New Approach in Cancer Treatment
by
Tine Logghe, Eke van Zwol, Benoît Immordino, Kris Van den Cruys, Marc Peeters, Elisa Giovannetti and Johannes Bogers
Cited by 3 | Viewed by 3213
Abstract
Despite significant advancements in the development of novel therapies, cancer continues to stand as a prominent global cause of death. In many cases, the cornerstone of standard-of-care therapy consists of chemotherapy (CT), radiotherapy (RT), or a combination of both. Notably, hyperthermia (HT), which
[...] Read more.
Despite significant advancements in the development of novel therapies, cancer continues to stand as a prominent global cause of death. In many cases, the cornerstone of standard-of-care therapy consists of chemotherapy (CT), radiotherapy (RT), or a combination of both. Notably, hyperthermia (HT), which has been in clinical use in the last four decades, has proven to enhance the effectiveness of CT and RT, owing to its recognized potency as a sensitizer. Furthermore, HT exerts effects on all steps of the cancer–immunity cycle and exerts a significant impact on key oncogenic pathways. Most recently, there has been a noticeable expansion of cancer research related to treatment options involving immunotherapy (IT) and targeted therapy (TT), a trend also visible in the research and development pipelines of pharmaceutical companies. However, the potential results arising from the combination of these innovative therapeutic approaches with HT remain largely unexplored. Therefore, this review aims to explore the oncology pipelines of major pharmaceutical companies, with the primary objective of identifying the principal targets of forthcoming therapies that have the potential to be advantageous for patients by specifically targeting molecular pathways involved in HT. The ultimate goal of this review is to pave the way for future research initiatives and clinical trials that harness the synergy between emerging IT and TT medications when used in conjunction with HT.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
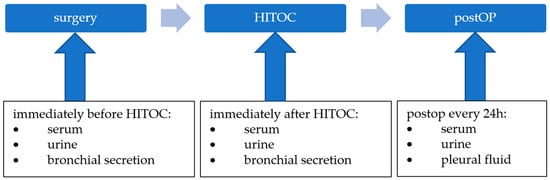
The Excretion of Cisplatin after Hyperthermic Intrathoracic Chemotherapy
by
Christopher Larisch, Till Markowiak, Michael Ried, Dennis Nowak, Hans-Stefan Hofmann and Stefan Rakete
Viewed by 1266
Abstract
Hyperthermic intrathoracic chemotherapy (HITOC) is an additional intraoperative treatment option within the multimodality therapy of pleural malignancies. A chemotherapy perfusion with high-dose cisplatin is performed over a period of 60 min after surgical cytoreduction to improve local tumour control through the eradication of
[...] Read more.
Hyperthermic intrathoracic chemotherapy (HITOC) is an additional intraoperative treatment option within the multimodality therapy of pleural malignancies. A chemotherapy perfusion with high-dose cisplatin is performed over a period of 60 min after surgical cytoreduction to improve local tumour control through the eradication of residual tumour cells. Although HITOC is increasingly used, there is only little scientific evidence about the necessary safety measures after HITOC. Therefore, the objective of this study was an analysis of cisplatin excretion via various body fluids after HITOC, with the aim of providing recommendations on occupational health and safety. Five patients undergoing HITOC were included. Before and after the HITOC, as well as during the following days, serum, urine, and bronchial secretion, as well as pleural effusion, were sampled. The platinum levels in the samples were measured using ICP-MS (inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry). Immediately after the HITOC, the mean levels of cisplatin increased dramatically in the serum (from 0.79 to 1349 µg/L), urine (from 3.48 to 10,528 µg/g creatinine), and bronchial secretion (from 0.11 to 156 µg/L). Thereafter, the cisplatin levels dropped to 133 µg/L in the serum and 994 µg/g creatinine in the urine within nine days after the HITOC. The AUC ratio shows 59% of the cisplatin being excreted via the urine after 48 h. The sampling of pleural effusion started 24 h after the HITOC, and the cisplatin levels decreased from 618 to 93 µg/L within nine days. Although the cisplatin levels in the body fluids of HITOC patients are much lower compared to patients receiving intravenous chemotherapy, a significant amount of cisplatin is excreted via these body fluids. Consequently, safety precautions must be implemented in the post-HITOC care of patients to avoid occupational exposure to cisplatin.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
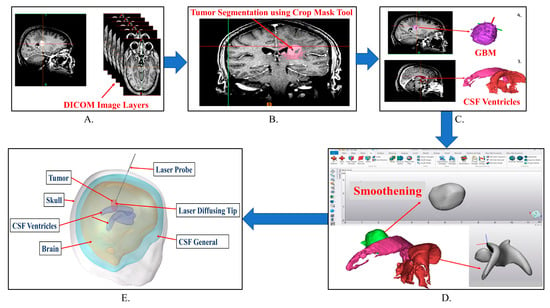
Development of a Treatment Planning Framework for Laser Interstitial Thermal Therapy (LITT)
by
Yash Lad, Avesh Jangam, Hayden Carlton, Ma’Moun Abu-Ayyad, Constantinos Hadjipanayis, Robert Ivkov, Brad E. Zacharia and Anilchandra Attaluri
Cited by 4 | Viewed by 1835
Abstract
Purpose: Develop a treatment planning framework for neurosurgeons treating high-grade gliomas with LITT to minimize the learning curve and improve tumor thermal dose coverage. Methods: Deidentified patient images were segmented using the image segmentation software Materialize MIMICS©. Segmented images were imported into the
[...] Read more.
Purpose: Develop a treatment planning framework for neurosurgeons treating high-grade gliomas with LITT to minimize the learning curve and improve tumor thermal dose coverage. Methods: Deidentified patient images were segmented using the image segmentation software Materialize MIMICS©. Segmented images were imported into the commercial finite element analysis (FEA) software COMSOL Multiphysics© to perform bioheat transfer simulations. The laser probe was modeled as a cylindrical object with radius 0.7 mm and length 100 mm, with a constant beam diameter. A modeled laser probe was placed in the tumor in accordance with patient specific patient magnetic resonance temperature imaging (MRTi) data. The laser energy was modeled as a deposited beam heat source in the FEA software. Penne’s bioheat equation was used to model heat transfer in brain tissue. The cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) was modeled as a solid with convectively enhanced conductivity to capture heat sink effects. In this study, thermal damage-dependent blood perfusion was assessed. Pulsed laser heating was modeled based on patient treatment logs. The stationary heat source and pullback heat source techniques were modeled to compare the calculated tissue damage. The developed bioheat transfer model was compared to MRTi data obtained from a laser log during LITT procedures. The application builder module in COMSOL Multiphysics© was utilized to create a Graphical User Interface (GUI) for the treatment planning framework. Results: Simulations predicted increased thermal damage (10–15%) in the tumor for the pullback heat source approach compared with the stationary heat source. The model-predicted temperature profiles followed trends similar to those of the MRTi data. Simulations predicted partial tissue ablation in tumors proximal to the CSF ventricle. Conclusion: A mobile platform-based GUI for bioheat transfer simulation was developed to aid neurosurgeons in conveniently varying the simulation parameters according to a patient-specific treatment plan. The convective effects of the CSF should be modeled with heat sink effects for accurate LITT treatment planning.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
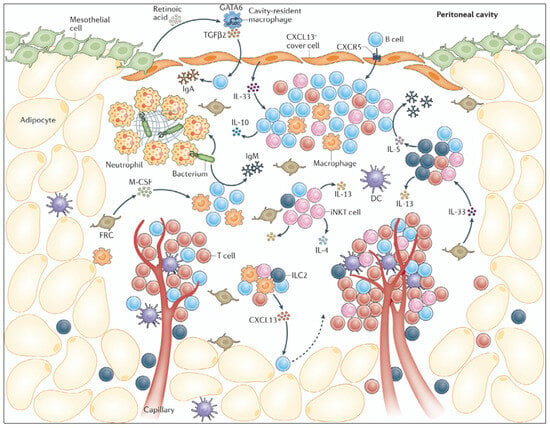
Effects of Hyperthermia and Hyperthermic Intraperitoneal Chemoperfusion on the Peritoneal and Tumor Immune Contexture
by
Daryl K. A. Chia, Jesse Demuytere, Sam Ernst, Hooman Salavati and Wim Ceelen
Cited by 2 | Viewed by 1907
Abstract
Hyperthermia combined with intraperitoneal (IP) drug delivery is increasingly used in the treatment of peritoneal metastases (PM). Hyperthermia enhances tumor perfusion and increases drug penetration after IP delivery. The peritoneum is increasingly recognized as an immune-privileged organ with its own distinct immune microenvironment.
[...] Read more.
Hyperthermia combined with intraperitoneal (IP) drug delivery is increasingly used in the treatment of peritoneal metastases (PM). Hyperthermia enhances tumor perfusion and increases drug penetration after IP delivery. The peritoneum is increasingly recognized as an immune-privileged organ with its own distinct immune microenvironment. Here, we review the immune landscape of the healthy peritoneal cavity and immune contexture of peritoneal metastases. Next, we review the potential benefits and unwanted tumor-promoting effects of hyperthermia and the associated heat shock response on the tumor immune microenvironment. We highlight the potential modulating effect of hyperthermia on the biomechanical properties of tumor tissue and the consequences for immune cell infiltration. Data from translational and clinical studies are reviewed. We conclude that (mild) hyperthermia and HIPEC have the potential to enhance antitumor immunity, but detailed further studies are required to distinguish beneficial from tumor-promoting effects.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
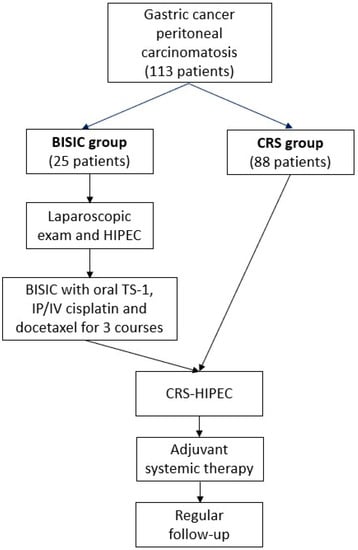
Benefit of Neoadjuvant Laparoscopic Hyperthermic Intraperitoneal Chemotherapy and Bidirectional Chemotherapy for Patients with Gastric Cancer with Peritoneal Carcinomatosis Considering Cytoreductive Surgery
by
Hsin-Hsien Yu, Yutaka Yonemura, Hui-Ji Ng, Ming-Che Lee, Bor-Chyuan Su and Mao-Chih Hsieh
Cited by 2 | Viewed by 1733
Abstract
Comprehensive treatment comprising neoadjuvant laparoscopic HIPEC (L-HIPEC) and bidirectional intraperitoneal and systemic induction chemotherapy (BISIC) followed by cytoreductive surgery (CRS) for gastric cancer with peritoneal carcinomatosis (PC) has been developed. However, its benefits and patient selection criteria have not been thoroughly investigated. We
[...] Read more.
Comprehensive treatment comprising neoadjuvant laparoscopic HIPEC (L-HIPEC) and bidirectional intraperitoneal and systemic induction chemotherapy (BISIC) followed by cytoreductive surgery (CRS) for gastric cancer with peritoneal carcinomatosis (PC) has been developed. However, its benefits and patient selection criteria have not been thoroughly investigated. We retrospectively reviewed 113 patients, with 25 having received comprehensive treatment (L-HIPEC, BISIC, and then CRS-HIPEC; the BISIC group) and 88 having received direct CRS-HIPEC (the CRS group). The BISIC group showed greater tumor clearance in terms of post-CRS peritoneal cancer index ((PCI) 6 vs. 14,
p = 0.002) compared to CRS group. The median survival was 20.0 months in the BISIC group and 8.6 months in the CRS group (
p = 0.031). Multivariable analysis revealed that the factors associated with increased survival were the BISIC protocol, age, and post-CRS tumor clearance. BISIC significantly improved survival in cases of moderate severity (PCI 11–20) and severe cases (PCI 21–39) without increasing the morbidity rate. We recommend the use of this neoadjuvant strategy for patients with gastric cancer-associated PC and an initial PCI of >10 to provide superior survival outcomes.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
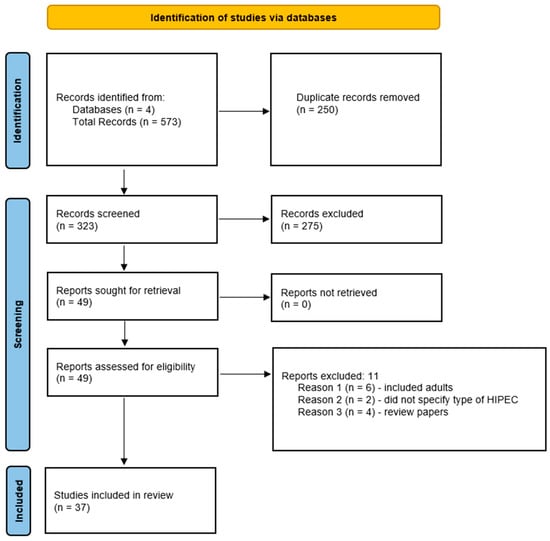
A Review of the Use of Hyperthermic Intraperitoneal Chemotherapy for Peritoneal Malignancy in Pediatric Patients
by
David J. Byrwa, Clare J. Twist, Joseph Skitzki, Elizabeth Repasky, P. Ben Ham III and Ajay Gupta
Cited by 1 | Viewed by 2287
Abstract
Hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy (HIPEC) can directly target microscopic peritoneal disease, has achieved regular consideration in the treatment of several adult cancer types, and is more recently being studied in pediatrics. This review paper provides an overview of the use of this modality in
[...] Read more.
Hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy (HIPEC) can directly target microscopic peritoneal disease, has achieved regular consideration in the treatment of several adult cancer types, and is more recently being studied in pediatrics. This review paper provides an overview of the use of this modality in pediatrics in order to identify medication choice, discuss post-operative morbidity and mortality, and evaluate impact on overall survival. Four databases were searched including Scopus, PubMed, Embase, and CINAHL and ultimately 37 papers documenting the use of this modality comprising 264 pediatric patients were included. Malignancies treated include desmoplastic small round cell tumor, rhabdomyosarcoma, angiosarcoma, colorectal carcinoma, and mesothelioma, with several rarer tumor types. Cisplatin was the most commonly used drug for HIPEC at varying concentrations for 30–90 min in duration at temperatures of approximately 41–42 °C. Reported toxicities were generally self-limited and there was no post-operative mortality. The impact on overall survival versus systemic chemotherapy and debulking surgery is uncertain due to lack of clinical trials and very small sample size across tumor subsets and the overall pediatric population. The relationship between degree of tumor burden and extent of surgical debulking needs to be further clarified. Future directions include prospective clinical trials, establishment of patient databases to facilitate standardization of HIPEC in pediatric patients, and additional approaches to optimize HIPEC.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
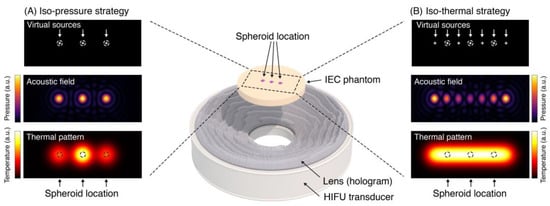
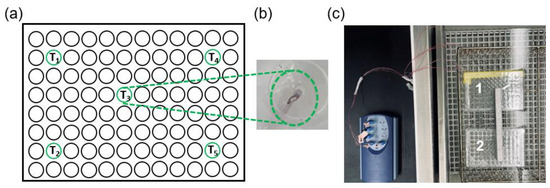
Holographic Focused Ultrasound Hyperthermia System for Uniform Simultaneous Thermal Exposure of Multiple Tumor Spheroids
by
Diana Andrés, Ian Rivens, Petros Mouratidis, Noé Jiménez, Francisco Camarena and Gail ter Haar
Cited by 7 | Viewed by 1984
Abstract
Hyperthermia is currently used to treat cancer due to its ability to radio- and chemo-sensitize and to stimulate the immune response. While ultrasound is non-ionizing and can induce hyperthermia deep within the body non-invasively, achieving uniform and volumetric hyperthermia is challenging. This work
[...] Read more.
Hyperthermia is currently used to treat cancer due to its ability to radio- and chemo-sensitize and to stimulate the immune response. While ultrasound is non-ionizing and can induce hyperthermia deep within the body non-invasively, achieving uniform and volumetric hyperthermia is challenging. This work presents a novel focused ultrasound hyperthermia system based on 3D-printed acoustic holograms combined with a high-intensity focused ultrasound (HIFU) transducer to produce a uniform iso-thermal dose in multiple targets. The system is designed with the aim of treating several 3D cell aggregates contained in an International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) tissue-mimicking phantom with multiple wells, each holding a single tumor spheroid, with real-time temperature and thermal dose monitoring. System performance was validated using acoustic and thermal methods, ultimately yielding thermal doses in three wells that differed by less than 4%. The system was tested in vitro for delivery of thermal doses of 0–120 cumulative equivalent minutes at 43 °C (CEM
43) to spheroids of U87-MG glioma cells. The effects of ultrasound-induced heating on the growth of these spheroids were compared with heating using a polymerase chain reaction (PCR) thermocycler. Results showed that exposing U87-MG spheroids to an ultrasound-induced thermal dose of 120 CEM
43 shrank them by 15% and decreased their growth and metabolic activity more than seen in those exposed to a thermocycler-induced heating. This low-cost approach of modifying a HIFU transducer to deliver ultrasound hyperthermia opens new avenues for accurately controlling thermal dose delivery to complex therapeutic targets using tailored acoustic holograms. Spheroid data show that thermal and non-thermal mechanisms are implicated in the response of cancer cells to non-ablative ultrasound heating.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Advanced Radio Frequency Applicators for Thermal Magnetic Resonance Theranostics of Brain Tumors
by
Nandita Saha, Andre Kuehne, Jason M. Millward, Thomas Wilhelm Eigentler, Ludger Starke, Sonia Waiczies and Thoralf Niendorf
Cited by 5 | Viewed by 2990
Abstract
Thermal Magnetic Resonance (ThermalMR) is a theranostic concept that combines diagnostic magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) with targeted thermal therapy in the hyperthermia (HT) range using a radiofrequency (RF) applicator in an integrated system. ThermalMR adds a therapeutic dimension to a diagnostic MRI device.
[...] Read more.
Thermal Magnetic Resonance (ThermalMR) is a theranostic concept that combines diagnostic magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) with targeted thermal therapy in the hyperthermia (HT) range using a radiofrequency (RF) applicator in an integrated system. ThermalMR adds a therapeutic dimension to a diagnostic MRI device. Focused, targeted RF heating of deep-seated brain tumors, accurate non-invasive temperature monitoring and high-resolution MRI are specific requirements of ThermalMR that can be addressed with novel concepts in RF applicator design. This work examines hybrid RF applicator arrays combining loop and self-grounded bow-tie (SGBT) dipole antennas for ThermalMR of brain tumors, at magnetic field strengths of 7.0 T, 9.4 T and 10.5 T. These high-density RF arrays improve the feasible transmission channel count, and provide additional degrees of freedom for RF shimming not afforded by using dipole antennas only, for superior thermal therapy and MRI diagnostics. These improvements are especially relevant for ThermalMR theranostics of deep-seated brain tumors because of the small surface area of the head. ThermalMR RF applicators with the hybrid loop+SGBT dipole design outperformed applicators using dipole-only and loop-only designs, with superior MRI performance and targeted RF heating. Array variants with a horse-shoe configuration covering an arc (270°) around the head avoiding the eyes performed better than designs with 360° coverage, with a 1.3 °C higher temperature rise inside the tumor while sparing healthy tissue. Our EMF and temperature simulations performed on a virtual patient with a clinically realistic intracranial tumor provide a technical foundation for implementation of advanced RF applicators tailored for ThermalMR theranostics of brain tumors.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
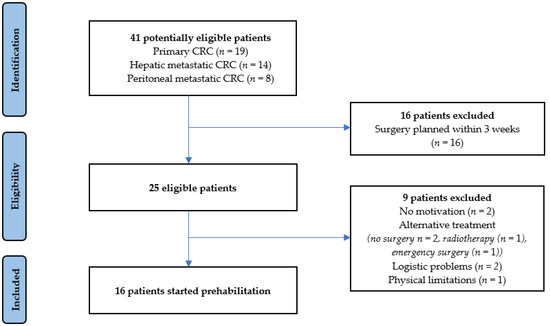
Multimodal Prehabilitation in Patients Undergoing Complex Colorectal Surgery, Liver Resection, and Hyperthermic Intraperitoneal Chemotherapy (HIPEC): A Pilot Study on Feasibility and Potential Efficacy
by
Dieuwke Strijker, Wilhelmus J. H. J. Meijerink, Linda A. G. van Heusden-Schotalbers, Manon G. A. van den Berg, Monique J. M. D. van Asseldonk, Luuk D. Drager, Johannes H. W. de Wilt, Kees J. H. M. van Laarhoven and Baukje van den Heuvel
Cited by 2 | Viewed by 2124
Abstract
Background: Surgery for complex primary and metastatic colorectal cancer (CRC), such as liver resection and hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy (HIPEC), in academic settings has led to improved survival but is associated with complications up to 75%. Prehabilitation has been shown to prevent complications in
[...] Read more.
Background: Surgery for complex primary and metastatic colorectal cancer (CRC), such as liver resection and hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy (HIPEC), in academic settings has led to improved survival but is associated with complications up to 75%. Prehabilitation has been shown to prevent complications in non-academic hospitals. This pilot study aimed to determine the feasibility and potential efficacy of a multimodal prehabilitation program in patients undergoing surgery in an academic hospital for complex primary and metastatic CRC. Methods: All patients awaiting complex colorectal surgery, liver resection, or HIPEC from July 2019 until January 2020 were considered potentially eligible. Feasibility was measured by accrual rate, completion rate, adherence to the program, satisfaction, and safety. To determine potential efficacy, postoperative outcomes were compared with a historical control group. Results: Sixteen out of twenty-five eligible patients (64%) commenced prehabilitation, and fourteen patients fully completed the intervention (88%). The adherence rate was 69%, as 11 patients completed >80% of prescribed supervised trainings. No adverse events occurred, and all patients expressed satisfaction with the program. The complication rate was significantly lower in the prehabilitation group (37.5%) than the control group (70.2%,
p = 0.020). There was no difference in the type of complications. Conclusion: This pilot study illustrates that multimodal prehabilitation is feasible in the majority of patients undergoing complex colorectal cancer, liver resection, and HIPEC in an academic setting.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Hyperthermia Treatment Monitoring via Deep Learning Enhanced Microwave Imaging: A Numerical Assessment
by
Álvaro Yago Ruiz, Marta Cavagnaro and Lorenzo Crocco
Viewed by 1733
Abstract
The paper deals with the problem of monitoring temperature during hyperthermia treatments in the whole domain of interest. In particular, a physics-assisted deep learning computational framework is proposed to provide an objective assessment of the temperature in the target tissue to be treated
[...] Read more.
The paper deals with the problem of monitoring temperature during hyperthermia treatments in the whole domain of interest. In particular, a physics-assisted deep learning computational framework is proposed to provide an objective assessment of the temperature in the target tissue to be treated and in the healthy one to be preserved, based on the measurements performed by a microwave imaging device. The proposed concept is assessed in-silico for the case of neck tumors achieving an accuracy above 90%. The paper results show the potential of the proposed approach and support further studies aimed at its experimental validation.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Design and Assessment of a Novel Biconical Human-Sized Alternating Magnetic Field Coil for MNP Hyperthermia Treatment of Deep-Seated Cancer
by
Levan Shoshiashvili, Irma Shamatava, David Kakulia and Fridon Shubitidze
Cited by 5 | Viewed by 2043
Abstract
Magnetic nanoparticle (MNP) hyperthermia therapy is a treatment technique that can be used alone or as an adjunct to radiation and/or chemotherapies for killing cancer cells. During treatment, MNPs absorb a part of electromagnetic field (EMF) energy and generate localized heat when subjected
[...] Read more.
Magnetic nanoparticle (MNP) hyperthermia therapy is a treatment technique that can be used alone or as an adjunct to radiation and/or chemotherapies for killing cancer cells. During treatment, MNPs absorb a part of electromagnetic field (EMF) energy and generate localized heat when subjected to an alternating magnetic field (AMF). The MNP-absorbed EMF energy, which is characterized by a specific absorption rate (SAR), is directly proportional to AMF frequency and the magnitude of transmitting currents in the coil. Furthermore, the AMF penetrates inside tissue and induces eddy currents in electrically conducting tissues, which are proportional to the electric field (
J = σ
E). The eddy currents produce Joule heating (<
J·
E> = 0.5·σ·E
2) in the normal tissue, the rate of energy transfer to the charge carriers from the applied electric fields. This Joule heating contains only the electric field because the magnetic field is always perpendicular to the velocity of the conduction charges, i.e., it does not produce work on moving charge. Like the SAR due to MNP, the electric field produced by the AMF coil is directly proportional to AMF frequency and the magnitude of transmitting currents in the coil. As a result, the Joule heating is directly proportional to the square of the frequency and transmitter current magnitude. Due to the fast decay of magnetic fields from an AMF coil over distance, MNP hyperthermia treatment of deep-seated tumors requires high-magnitude transmitting currents in the coil for clinically achievable MNP distributions in the tumor. This inevitably produces significant Joule heating in the normal tissue and becomes more complicated for a standard MNP hyperthermia approach for deep-seated tumors, such as pancreatic, prostate, liver, lung, ovarian, kidney, and colorectal cancers. This paper presents a novel human-sized AMF coil and MNP hyperthermia system design for safely and effectively treating deep-seated cancers. The proposed design utilizes the spatial distribution of electric and magnetic fields of circular coils. Namely, it first minimizes the SAR due to eddy currents in the normal tissue by moving the conductors away from the tissue (i.e., increasing coils’ radii), and second, it increases the magnetic field at the targeted area (z = 0) due to elevated coils (|z| > 0) by increasing the radius of the elevated coils (|z| > 0). This approach is a promising alternative aimed at overcoming the limitation of standard MNP hyperthermia for deep-seated cancers by taking advantage of the transmitter coil’s electric and magnetic field distributions in the human body for maximizing AMF in tumor regions and avoiding damage to normal tissue. The human-sized coil’s AMF, MNP activation, and eddy current distribution characteristics are investigated for safe and effective treatment of deep-seated tumors using numerical models. Namely, computational results such as AMF, Joule heating SAR, and temperature distributions are presented for a full-body, 3D human model. The SAR and temperature distributions clearly show that the proposed human-sized AMF coil can provide clinically relevant AMF to the region occupied by deep-seated cancers for the application of MNP hyperthermia therapy while causing less Joule heating in the normal tissues than commonly used AMF techniques.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Field and Temperature Shaping for Microwave Hyperthermia: Recent Treatment Planning Tools to Enhance SAR-Based Procedures
by
Martina T. Bevacqua, Rossella Gaffoglio, Gennaro G. Bellizzi, Marco Righero, Giorgio Giordanengo, Lorenzo Crocco, Giuseppe Vecchi and Tommaso Isernia
Cited by 2 | Viewed by 2111
Abstract
The aim of the article is to provide a summary of the work carried out in the framework of a research project funded by the Italian Ministry of Research. The main goal of the activity was to introduce multiple tools for reliable, affordable,
[...] Read more.
The aim of the article is to provide a summary of the work carried out in the framework of a research project funded by the Italian Ministry of Research. The main goal of the activity was to introduce multiple tools for reliable, affordable, and high-performance microwave hyperthermia for cancer therapy. The proposed methodologies and approaches target microwave diagnostics, accurate in vivo electromagnetic parameters estimation, and improvement in treatment planning using a single device. This article provides an overview of the proposed and tested techniques and shows their complementarity and interconnection. To highlight the approach, we also present a novel combination of specific absorption rate optimization via convex programming with a temperature-based refinement method implemented to mitigate the effect of thermal boundary conditions on the final temperature map. To this purpose, numerical tests were carried out for both simple and anatomically detailed 3D scenarios for the head and neck region. These preliminary results show the potential of the combined technique and improvements in the temperature coverage of the tumor target with respect to the case wherein no refinement is adopted.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
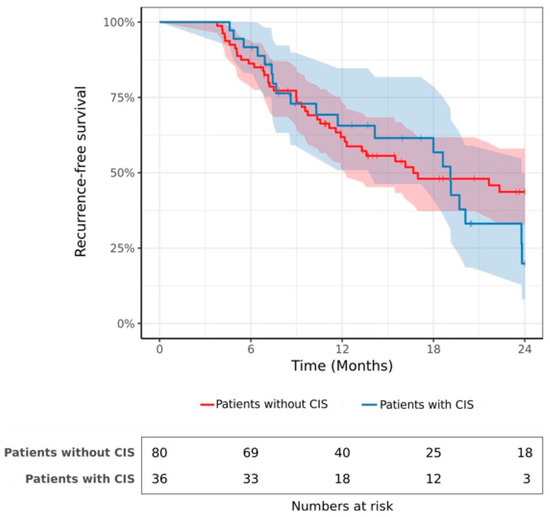
Is CIS a Contraindication to Hyperthermic Intravesical Chemotherapy (HIVEC) after BCG-Failure?
by
Vassili Anastay, Michael Baboudjian, Alexandra Masson-Lecomte, Cédric Lebacle, Alexandre Chamouni, Jacques Irani, Xavier Tillou, Thibaut Waeckel, Arnaud Monges, Céline Duperron, Gwenaelle Gravis, Jochen Walz, Eric Lechevallier and Géraldine Pignot
Cited by 4 | Viewed by 1825
Abstract
CIS of the bladder is associated with a high risk of progression. In the case of BCG failure, radical cystectomy should be performed. For patients who refuse or are ineligible, bladder-sparing alternatives are evaluated. This study aims to investigate the efficacy of Hyperthermic
[...] Read more.
CIS of the bladder is associated with a high risk of progression. In the case of BCG failure, radical cystectomy should be performed. For patients who refuse or are ineligible, bladder-sparing alternatives are evaluated. This study aims to investigate the efficacy of Hyperthermic IntraVesical Chemotherapy (HIVEC) depending on the presence or absence of CIS. This retrospective, multicenter study was conducted between 2016 and 2021. Patients with non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer (NMIBC) with BCG failure received 6–8 adjuvant instillations of HIVEC. The co-primary endpoints were recurrence-free survival (RFS) and progression-free survival (PFS). A total of 116 consecutive patients met our inclusion criteria of whom 36 had concomitant CIS. The 2-year RFS rate was 19.9% and 43.7% in patients with and without CIS, respectively (
p = 0.52). Fifteen patients (12.9%) experienced progression to muscle-invasive bladder cancer with no significant difference between patients with and without CIS (2-year PFS rate = 71.8% vs. 88.8%,
p = 0.32). In multivariate analysis, CIS was not a significant prognostic factor in terms of recurrence or progression. In conclusion, CIS may not be considered a contraindication to HIVEC, as there is no significant association between CIS and the risk of progression or recurrence after treatment.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
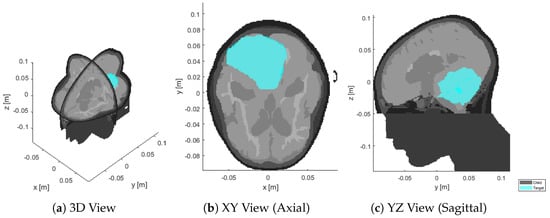
Antenna Arrangement in UWB Helmet Brain Applicators for Deep Microwave Hyperthermia
by
Massimiliano Zanoli, Erika Ek and Hana Dobšíček Trefná
Cited by 2 | Viewed by 1885
Abstract
Deep microwave hyperthermia applicators are typically designed as narrow-band conformal antenna arrays with equally spaced elements, arranged in one or more rings. This solution, while adequate for most body regions, might be sub-optimal for brain treatments. The introduction of ultra-wide-band semi-spherical applicators, with
[...] Read more.
Deep microwave hyperthermia applicators are typically designed as narrow-band conformal antenna arrays with equally spaced elements, arranged in one or more rings. This solution, while adequate for most body regions, might be sub-optimal for brain treatments. The introduction of ultra-wide-band semi-spherical applicators, with elements arranged around the head and not necessarily aligned, has the potential to enhance the selective thermal dose delivery in this challenging anatomical region. However, the additional degrees of freedom in this design make the problem non-trivial. We address this by treating the antenna arrangement as a global SAR-based optimization process aiming at maximizing target coverage and hot-spot suppression in a given patient. To enable the quick evaluation of a certain arrangement, we propose a novel E-field interpolation technique which calculates the field generated by an antenna at any location around the scalp from a limited number of initial simulations. We evaluate the approximation error against full array simulations. We demonstrate the design technique in the optimization of a helmet applicator for the treatment of a medulloblastoma in a paediatric patient. The optimized applicator achieves 0.3
C higher T90 than a conventional ring applicator with the same number of elements.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
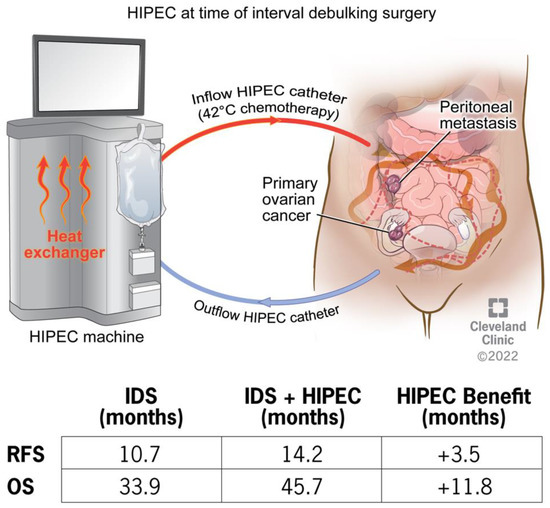
Mechanistic Insights on Hyperthermic Intraperitoneal Chemotherapy in Ovarian Cancer
by
Olivia G. Huffman, Danielle B. Chau, Andreea I. Dinicu, Robert DeBernardo and Ofer Reizes
Cited by 10 | Viewed by 4396
Abstract
Epithelial ovarian cancer is an aggressive disease of the female reproductive system and a leading cause of cancer death in women. Standard of care includes surgery and platinum-based chemotherapy, yet patients continue to experience a high rate of recurrence and metastasis. Hyperthermic intraperitoneal
[...] Read more.
Epithelial ovarian cancer is an aggressive disease of the female reproductive system and a leading cause of cancer death in women. Standard of care includes surgery and platinum-based chemotherapy, yet patients continue to experience a high rate of recurrence and metastasis. Hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy (HIPEC) treatment in highly selective patients extends overall survival by nearly 12 months. The clinical studies are highly supportive of the use of HIPEC in the treatment of ovarian cancer, though the therapeutic approach is limited to academic medical centers. The mechanism underlying HIPEC benefit remains unknown. The efficacy of HIPEC therapy is impacted by several procedural and patient/tumor factors including the timing of surgery, platinum sensitivity, and molecular profiling such as homologous recombination deficiency. The present review aims to provide insight into the mechanistic benefit of HIPEC treatment with a focus on how hyperthermia activates the immune response, induces DNA damage, impairs DNA damage repair pathways, and has a synergistic effect with chemotherapy, with the ultimate outcome of increasing chemosensitivity. Identifying the points of fragility unmasked by HIPEC may provide the key pathways that could be the basis of new therapeutic strategies for ovarian cancer patients.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
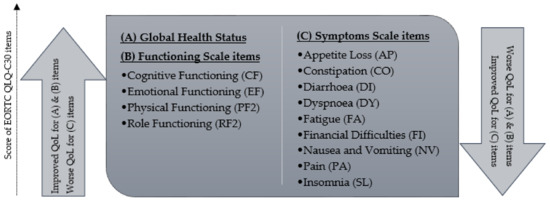
Real World Analysis of Quality of Life and Toxicity in Cancer Patients Treated with Hyperthermia Combined with Radio(chemo)therapy
by
Adela Ademaj, Emsad Puric, Olaf Timm, David Kurti, Dietmar Marder, Thomas Kern, Roger A. Hälg, Susanne Rogers and Oliver Riesterer
Cited by 2 | Viewed by 1600
Abstract
Hyperthermia (HT) in combination with radio(chemo)therapy (RCT) is a well-established cancer treatment strategy. This report analyses the quality of life (QoL), toxicity and survival outcomes in patients with different tumor entities who received HT in combination with RCT. The primary endpoint of this
[...] Read more.
Hyperthermia (HT) in combination with radio(chemo)therapy (RCT) is a well-established cancer treatment strategy. This report analyses the quality of life (QoL), toxicity and survival outcomes in patients with different tumor entities who received HT in combination with RCT. The primary endpoint of this study was the assessment of QoL scale items 3 and 12 months after treatment in patients who were treated with palliative intent and curative intent, respectively. The secondary endpoints of this study were acute toxicities, 1-year overall survival (OS), and local progression-free survival (LPFS). Patients treated with curative intent experienced significant improvement in emotional functioning (EF), social functioning (SF), financial difficulties (FI) and insomnia (SL) 12 months after treatment. Patients had significantly improved FI and pain (PA) three months after palliative treatment. Acute toxicity of grade 3 or more was 26% during treatment and 4% after three months. The 1-year OS rates were 90% (95% CI: 79–96%) and 44% (95% CI: 31–59%) for patients treated with curative and palliative RCT combined with HT, respectively. Moreover, the 1-year LPFS rates were 94% (95% CI: 84–98%) for patients treated with curative intent and 64% (95% CI: 50–77%) for palliative patients. In summary, combined RCT and HT stabilized or improved QoL scale items for both curative and palliative indications.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
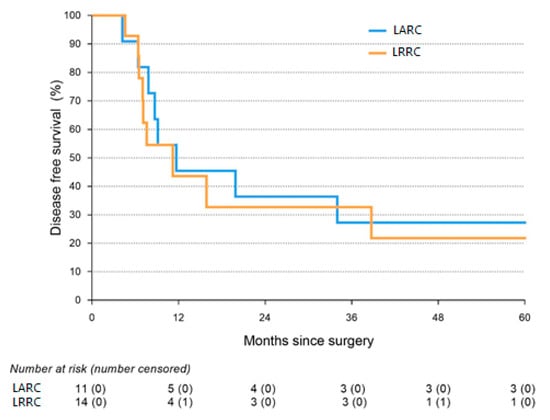
Cytoreductive Surgery and Hyperthermic Intraperitoneal Chemotherapy with Intra-Operative Radiotherapy for Patients with Locally Advanced or Locally Recurrent Rectal Cancer and Peritoneal Metastases
by
Vincent C. J. van de Vlasakker, Teun B. M. van den Heuvel, Anouk Rijken, Simon W. Nienhuijs, Stijn H. J. Ketelaers, An-Sofie E. Verrijssen, Harm J. Rutten, Grard A. P. Nieuwenhuijzen, Jacobus W. A. Burger and Ignace H. J. T. de Hingh
Cited by 4 | Viewed by 1842
Abstract
Purpose: To assess the safety and long-term outcome of a multimodality treatment consisting of radical surgery, intra-operative radiotherapy (IORT), and cytoreductive surgery with hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy (CRS-HIPEC) for patients with locally advanced rectal cancer (LARC) or locally recurrent rectal carcinoma (LRRC) and
[...] Read more.
Purpose: To assess the safety and long-term outcome of a multimodality treatment consisting of radical surgery, intra-operative radiotherapy (IORT), and cytoreductive surgery with hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy (CRS-HIPEC) for patients with locally advanced rectal cancer (LARC) or locally recurrent rectal carcinoma (LRRC) and peritoneal metastases (PM).
Methods: The present study was a single-center cohort study, including all consecutive patients undergoing this treatment in a tertiary referral center for LARC, LRRC, and PM. Postoperative complications, intensive care stay (ICU stay), and re-admission rates were assessed as well as disease-free survival (DFS) and overall survival (OS).
Results: A total of 14 LARC and 16 LRRC patients with PM were included in the study. The median ICU stay was 1 day, and 57% of patients developed a severe postoperative complication. No 90-day mortality was observed. Median DFS was 10.0 months (Interquartile Range 7.1–38.7), and median OS was 31.0 months (Interquartile Range 15.9–144.3).
Conclusions: As postoperative complications and survival were in line with treatments that are accepted for LARC or LRRC and PM as separate procedures, we conclude that combined treatment with IORT and CRS-HIPEC should be considered as a treatment option for selected patients with LARC or LRRC and peritoneal metastases in tertiary referral centers.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
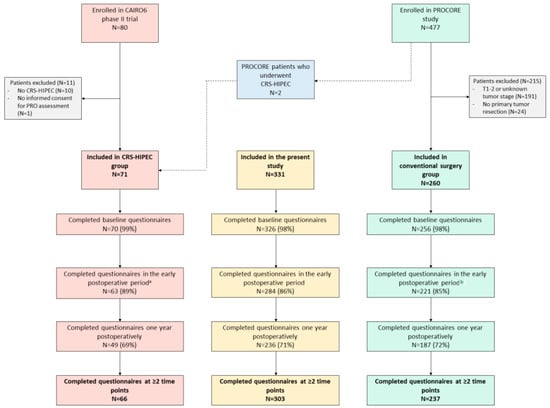
The Impact of Cytoreductive Surgery and Hyperthermic Intraperitoneal Chemotherapy (CRS-HIPEC) versus Conventional Surgery on Patient-Reported Outcomes: A Comparative Cohort Study between the CAIRO6 Trial and the PROCORE Study
by
Checca Bakkers, Vincent C. J. van de Vlasakker, Koen P. B. Rovers, Robin J. Lurvink, Simon W. Nienhuijs, Jacobus W. A. Burger, Geert-Jan M. Creemers, Cynthia S. Bonhof, Floortje Mols and Ignace H. J. T. de Hingh
Cited by 2 | Viewed by 1911
Abstract
Purpose—To compare patient-reported outcomes (PROs) of patients undergoing cytoreductive surgery and hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy (CRS-HIPEC) for colorectal peritoneal metastases to PROs of colorectal cancer (CRC) patients undergoing conventional surgery. Methods—Data were extracted from the CAIRO6 trial (CRS-HIPEC group) and the PROCORE study (conventional
[...] Read more.
Purpose—To compare patient-reported outcomes (PROs) of patients undergoing cytoreductive surgery and hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy (CRS-HIPEC) for colorectal peritoneal metastases to PROs of colorectal cancer (CRC) patients undergoing conventional surgery. Methods—Data were extracted from the CAIRO6 trial (CRS-HIPEC group) and the PROCORE study (conventional surgery group). Nine predefined PROs (derived from the EORTC QLQ-C30 questionnaire) were compared at baseline, in the early postoperative period and one year postoperatively, with correction for treatment with systemic therapy using linear mixed modeling. Results—In total, 331 patients were included: 71 in the CRS-HIPEC group and 260 in the conventional surgery group. All predefined PROs (fatigue, diarrhea, C30 summary score, Global Health Status, physical, role, emotional, cognitive, and social functioning) did not differ significantly between the groups at all three timepoints, and differential effects over time for all PROs did not differ significantly between the groups. Significant worsening of fatigue, C30 summary score, physical and role functioning (both groups), and cognitive and social functioning (conventional surgery group only) was present in the early postoperative period. All scores returned to baseline at one year postoperatively, except for physical and cognitive functioning in the conventional surgery group. Emotional functioning improved postoperatively in both groups compared to baseline. Conclusion—Despite a more extensive procedure with greater risk of morbidity, CRS-HIPEC in patients with colorectal peritoneal metastases did not have a greater negative impact on PROs than conventional surgery in patients with CRC. Further, systemic therapy did not affect these PROs. These findings may facilitate future patient counseling and shared decision making in clinical practice.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessSystematic Review
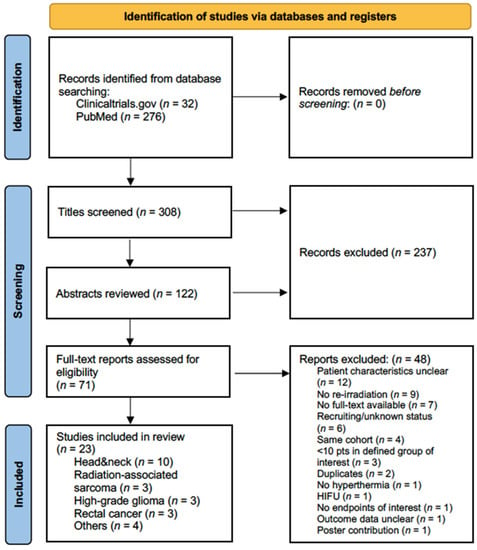
Combined Hyperthermia and Re-Irradiation in Non-Breast Cancer Patients: A Systematic Review
by
Ji-Young Kim, Sebastian Zschaeck, Jürgen Debus and Fabian Weykamp
Cited by 1 | Viewed by 1987
Abstract
Purpose: This systematic literature review summarizes clinical studies and trials involving combined non-ablative hyperthermia and re-irradiation in locoregionally recurrent cancer except breast cancer. Methods: One database and one registry, MEDLINE and clinicaltrials.gov, respectively, were searched for studies on combined non-ablative hyperthermia and re-irradiation
[...] Read more.
Purpose: This systematic literature review summarizes clinical studies and trials involving combined non-ablative hyperthermia and re-irradiation in locoregionally recurrent cancer except breast cancer. Methods: One database and one registry, MEDLINE and clinicaltrials.gov, respectively, were searched for studies on combined non-ablative hyperthermia and re-irradiation in non-breast cancer patients. Extracted study characteristics included treatment modalities and re-irradiation dose concepts. Outcomes of interest were tumor response, survival measures, toxicity data and palliation. Within-study bias assessment included the identification of conflict of interest (COI). The final search was performed on 29 August 2022. Results: Twenty-three articles were included in the final analysis, reporting on 603 patients with eight major tumor types. Twelve articles (52%) were retrospective studies. Only one randomized trial was identified. No COI statement was declared in 11 studies. Four of the remaining twelve studies exhibited significant COI. Low study and patient numbers, high heterogeneity in treatment modalities and endpoints, as well as significant within- and across-study bias impeded the synthesis of results. Conclusion: Outside of locoregionally recurrent breast cancer, the role of combined moderate hyperthermia and re-irradiation can so far not be established. This review underscores the necessity for more clinical trials to generate higher levels of clinical evidence for combined re-irradiation and hyperthermia.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
In Vitro Measurement and Mathematical Modeling of Thermally-Induced Injury in Pancreatic Cancer Cells
by
Faraz Chamani, Marla M. Pyle, Tej B. Shrestha, Jan Sebek, Stefan H. Bossmann, Matthew T. Basel, Rahul A. Sheth and Punit Prakash
Cited by 6 | Viewed by 2105
Abstract
Thermal therapies are under investigation as part of multi-modality strategies for the treatment of pancreatic cancer. In the present study, we determined the kinetics of thermal injury to pancreatic cancer cells in vitro and evaluated predictive models for thermal injury. Cell viability was
[...] Read more.
Thermal therapies are under investigation as part of multi-modality strategies for the treatment of pancreatic cancer. In the present study, we determined the kinetics of thermal injury to pancreatic cancer cells in vitro and evaluated predictive models for thermal injury. Cell viability was measured in two murine pancreatic cancer cell lines (KPC, Pan02) and a normal fibroblast (STO) cell line following in vitro heating in the range 42.5–50 °C for 3–60 min. Based on measured viability data, the kinetic parameters of thermal injury were used to predict the extent of heat-induced damage. Of the three thermal injury models considered in this study, the Arrhenius model with time delay provided the most accurate prediction (root mean square error = 8.48%) for all cell lines. Pan02 and STO cells were the most resistant and susceptible to hyperthermia treatments, respectively. The presented data may contribute to studies investigating the use of thermal therapies as part of pancreatic cancer treatment strategies and inform the design of treatment planning strategies.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessSystematic Review
DNA and RNA Alterations Associated with Colorectal Peritoneal Metastases: A Systematic Review
by
Danique J. I. Heuvelings, Anne G. W. E. Wintjens, Julien Luyten, Guus E. W. A. Wilmink, Laura Moonen, Ernst-Jan M. Speel, Ignace H. J. T. de Hingh, Nicole D. Bouvy and Andrea Peeters
Cited by 4 | Viewed by 2712
Abstract
Background: As colorectal cancer (CRC) patients with peritoneal metastases (PM) have a poor prognosis, new treatment options are currently being investigated for CRC patients. Specific biomarkers in the primary tumor could serve as a prediction tool to estimate the risk of distant metastatic
[...] Read more.
Background: As colorectal cancer (CRC) patients with peritoneal metastases (PM) have a poor prognosis, new treatment options are currently being investigated for CRC patients. Specific biomarkers in the primary tumor could serve as a prediction tool to estimate the risk of distant metastatic spread. This would help identify patients eligible for early treatment. Aim: To give an overview of previously studied DNA and RNA alterations in the primary tumor correlated to colorectal PM and investigate which gene mutations should be further studied. Methods: A systematic review of all published studies reporting genomic analyses on the primary tissue of CRC tumors in relation to PM was undertaken according to PRISMA guidelines. Results: Overall, 32 studies with 18,906 patients were included.
BRAF mutations were analyzed in 17 articles, of which 10 found a significant association with PM. For all other reported genes, no association with PM was found. Two analyses with broader cancer panels did not reveal any new biomarkers. Conclusion: An association of specific biomarkers in the primary tumors of CRC patients with metastatic spread into peritoneum could not be proven. The role of
BRAF mutations should be further investigated. In addition, studies searching for potential novel biomarkers are still required.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
Review of the Delivery Kinetics of Thermosensitive Liposomes
by
Dieter Haemmerich, Krishna K. Ramajayam and Danforth A. Newton
Cited by 4 | Viewed by 2926
Abstract
Thermosensitive liposomes (TSL) are triggered nanoparticles that release the encapsulated drug in response to hyperthermia. Combined with localized hyperthermia, TSL enabled loco-regional drug delivery to tumors with reduced systemic toxicities. More recent TSL formulations are based on intravascular triggered release, where drug release
[...] Read more.
Thermosensitive liposomes (TSL) are triggered nanoparticles that release the encapsulated drug in response to hyperthermia. Combined with localized hyperthermia, TSL enabled loco-regional drug delivery to tumors with reduced systemic toxicities. More recent TSL formulations are based on intravascular triggered release, where drug release occurs within the microvasculature. Thus, this delivery strategy does not require enhanced permeability and retention (EPR). Compared to traditional nanoparticle drug delivery systems based on EPR with passive or active tumor targeting (typically <5%ID/g tumor), TSL can achieve superior tumor drug uptake (>10%ID/g tumor). Numerous TSL formulations have been combined with various drugs and hyperthermia devices in preclinical and clinical studies over the last four decades. Here, we review how the properties of TSL dictate delivery and discuss the advantages of rapid drug release from TSL. We show the benefits of selecting a drug with rapid extraction by tissue, and with quick cellular uptake. Furthermore, the optimal characteristics of hyperthermia devices are reviewed, and impact of tumor biology and cancer cell characteristics are discussed. Thus, this review provides guidelines on how to improve drug delivery with TSL by optimizing the combination of TSL, drug, and hyperthermia method. Many of the concepts discussed are applicable to a variety of other triggered drug delivery systems.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
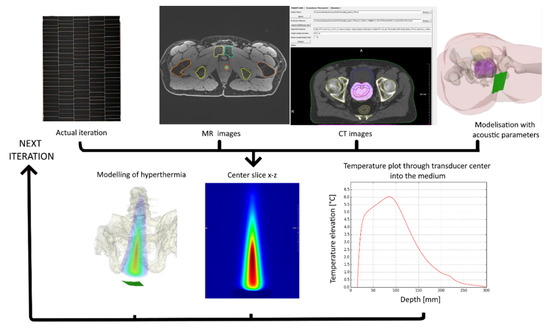
A Novel Concept of Transperineal Focused Ultrasound Transducer for Prostate Cancer Local Deep Hyperthermia Treatments
by
Pauline Coralie Guillemin, David Sinden, Yacine M’Rad, Michael Schwenke, Jennifer Le Guevelou, Johannes W. E. Uiterwijk, Orane Lorton, Max Scheffler, Pierre-Alexandre Poletti, Juergen Jenne, Thomas Zilli and Rares Salomir
Cited by 3 | Viewed by 2281
Abstract
Design, embodiment, and experimental study of a novel concept of extracorporeal phased array ultrasound transducer for prostate cancer regional deep hyperthermia treatments using a transperineal acoustic window is presented. An optimized design of hyperthermia applicator was derived from a modelling software where acoustic
[...] Read more.
Design, embodiment, and experimental study of a novel concept of extracorporeal phased array ultrasound transducer for prostate cancer regional deep hyperthermia treatments using a transperineal acoustic window is presented. An optimized design of hyperthermia applicator was derived from a modelling software where acoustic and thermal fields were computed based on anatomical data. Performance tests have been experimentally conducted on gel phantoms and tissues, under 3T MRI guidance using PRFS thermometry. Feedback controlled hyperthermia (ΔT = 5 °C during 20min) was performed on two ex vivo lamb carcasses with prostate mimicking pelvic tissue, to demonstrate capability of spatio-temporal temperature control and to assess potential risks and side effects. Our optimization approach yielded a therapeutic ultrasound transducer consisting of 192 elements of variable shape and surface, pseudo randomly distributed on 6 columns, using a frequency of 700 kHz. Radius of curvature was 140 mm and active water circulation was included for cooling. The measured focusing capabilities covered a volume of 24 × 50 × 60 mm
3. Acoustic coupling of excellent quality was achieved. No interference was detected between sonication and MR acquisitions. On ex vivo experiments the target temperature elevation of 5 °C was reached after 5 min and maintained during another 15 min with the predictive temperature controller showing 0.2 °C accuracy. No significant temperature rise was observed on skin and bonny structures. Reported results represent a promising step toward the implementation of transperineal ultrasound hyperthermia in a pilot study of reirradiation in prostate cancer patients.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessSystematic Review
The Effects of Heat Stress on the Transcriptome of Human Cancer Cells: A Meta-Analysis
by
Enzo M. Scutigliani, Fernando Lobo-Cerna, Sergio Mingo Barba, Stephan Scheidegger and Przemek M. Krawczyk
Cited by 3 | Viewed by 3026
Abstract
Hyperthermia is clinically applied cancer treatment in conjunction with radio- and/or chemotherapy, in which the tumor volume is exposed to supraphysiological temperatures. Since cells can effectively counteract the effects of hyperthermia by protective measures that are commonly known as the heat stress response,
[...] Read more.
Hyperthermia is clinically applied cancer treatment in conjunction with radio- and/or chemotherapy, in which the tumor volume is exposed to supraphysiological temperatures. Since cells can effectively counteract the effects of hyperthermia by protective measures that are commonly known as the heat stress response, the identification of cellular processes that are essential for surviving hyperthermia could lead to novel treatment strategies that improve its therapeutic effects. Here, we apply a meta-analytic approach to 18 datasets that capture hyperthermia-induced transcriptome alterations in nine different human cancer cell lines. We find, in line with previous reports, that hyperthermia affects multiple processes, including protein folding, cell cycle, mitosis, and cell death, and additionally uncover expression changes of genes involved in KRAS signaling, inflammatory responses, TNF-a signaling and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT). Interestingly, however, we also find a considerable inter-study variability, and an apparent absence of a ‘universal’ heat stress response signature, which is likely caused by the differences in experimental conditions. Our results suggest that gene expression alterations after heat stress are driven, to a large extent, by the experimental context, and call for a more extensive, controlled study that examines the effects of key experimental parameters on global gene expression patterns.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
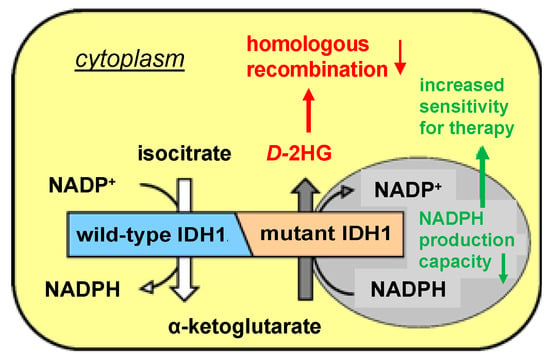
Hyperthermia as a Potential Cornerstone of Effective Multimodality Treatment with Radiotherapy, Cisplatin and PARP Inhibitor in IDH1-Mutated Cancer Cells
by
Mohammed Khurshed, Elia Prades-Sagarra, Sarah Saleh, Peter Sminia, Johanna W. Wilmink, Remco J. Molenaar, Hans Crezee and Cornelis J. F. van Noorden
Cited by 3 | Viewed by 1793
Abstract
Mutations in the isocitrate dehydrogenase 1 (
IDH1MUT) gene occur in various types of malignancies, including ~60% of chondrosarcomas, ~30% of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinomas and >80% of low-grade gliomas.
IDH1MUT are causal in the development and progression of these types of
[...] Read more.
Mutations in the isocitrate dehydrogenase 1 (
IDH1MUT) gene occur in various types of malignancies, including ~60% of chondrosarcomas, ~30% of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinomas and >80% of low-grade gliomas.
IDH1MUT are causal in the development and progression of these types of cancer due to neomorphic production of the oncometabolite
D-2-hydroxyglutarate (
D-2HG). Intracellular accumulation of
D-2HG has been implicated in suppressing homologous recombination and renders
IDH1MUT cancer cells sensitive to DNA-repair-inhibiting agents, such as poly-(adenosine 5′-diphosphate–ribose) polymerase inhibitors (PARPi). Hyperthermia increases the efficacy of DNA-damaging therapies such as radiotherapy and platinum-based chemotherapy, mainly by inhibition of DNA repair. In the current study, we investigated the additional effects of hyperthermia (42 °C for 1 h) in the treatment of
IDH1MUT HCT116 colon cancer cells and hyperthermia1080 chondrosarcoma cancer cells in combination with radiation, cisplatin and/or a PARPi on clonogenic cell survival, cell cycle distribution and the induction and repair of DNA double-strand breaks. We found that hyperthermia in combination with radiation or cisplatin induces an increase in double-strand breaks and cell death, up to 10-fold in
IDH1MUT cancer cells compared to
IDH1 wild-type cells. This vulnerability was abolished by the
IDH1MUT inhibitor AGI-5198 and was further increased by the PARPi. In conclusion, our study shows that
IDH1MUT cancer cells are sensitized to hyperthermia in combination with irradiation or cisplatin and a PARPi. Therefore, hyperthermia may be an efficacious sensitizer to cytotoxic therapies in tumors where the clinical application of hyperthermia is feasible, such as
IDH1MUT chondrosarcoma of the extremities.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
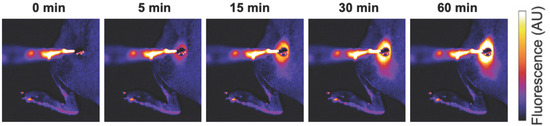
Interventional Oncolytic Immunotherapy with LTX-315 for Residual Tumor after Incomplete Radiofrequency Ablation of Liver Cancer
by
Guanhui Zhou, Xuefeng Kan, Feng Zhang, Hongxiu Ji, Junhui Sun and Xiaoming Yang
Cited by 3 | Viewed by 1919
Abstract
Objective: To investigate the feasibility of interventional oncolytic immunotherapy with LTX-315 for residual tumors after incomplete radiofrequency ablation (iRFA) of VX2 liver tumors in a rabbit model. Methods: For in vitro experiments, VX2 tumor cells were treated with: (1) phosphate buffered saline, (2)
[...] Read more.
Objective: To investigate the feasibility of interventional oncolytic immunotherapy with LTX-315 for residual tumors after incomplete radiofrequency ablation (iRFA) of VX2 liver tumors in a rabbit model. Methods: For in vitro experiments, VX2 tumor cells were treated with: (1) phosphate buffered saline, (2) radiofrequency hyperthermia (RFH), (3) LTX-315, and (4) RFH plus LTX-315. The residual tumors after iRFA of VX2 liver tumors were treated with: (1) phosphate buffered saline served as control, (2) 2 mg LTX-315, and (3) 4 mg LTX-315. MTS assay, fluorescence microscopy, and flow cytometry were used to compare cell viabilities and apoptosis among different groups. Ultrasound imaging was used to follow up the tumor growth, which were correlated with the optical imaging and subsequent histology. Results: For in vitro experiments, compared with the other three groups, MTS assay demonstrated the lowest cell viability, fluorescence microscopy showed the least survival cells, and apoptosis analysis revealed the highest percentage of apoptosis cells in the combination treatment groups (
p < 0.001). For in vivo experiments, ultrasound imaging showed the smallest tumor volume in the group with 4 mg LTX-315 therapy compared with the other two groups (
p < 0.001). The optical imaging and histopathological analysis showed complete necrosis of the tumors in the group with 4 mg LTX-315 therapy. A significant increase of CD8
+ T cells and HSP70 and a significant decrease of Tregs were observed in residual tumors in the group with 2 mg LTX-315 therapy compared with the control group (
p < 0.001). Conclusion: Interventional oncolytic immunotherapy with LTX-315 for residual tumors after iRFA of liver cancer is feasible, which may open up new avenues to prevent residual tumors after RFA of intermediate-to-large liver cancers.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
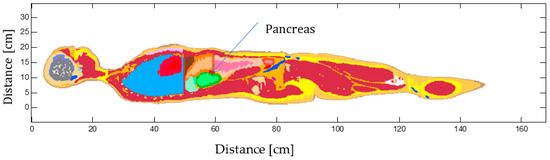
Gold Nanoparticles-Mediated Photothermal Therapy of Pancreas Using GATE: A New Simulation Platform
by
Somayeh Asadi, Leonardo Bianchi, Martina De Landro and Paola Saccomandi
Cited by 1 | Viewed by 2333
Abstract
This work presents the first investigation of gold nanorods (GNRs)-based photothermal therapy of the pancreas tumor using the Monte Carlo-based code implemented with Geant4 Application for Emission Tomography (GATE). The model of a human pancreas was obtained by segmenting an abdominal computed tomography
[...] Read more.
This work presents the first investigation of gold nanorods (GNRs)-based photothermal therapy of the pancreas tumor using the Monte Carlo-based code implemented with Geant4 Application for Emission Tomography (GATE). The model of a human pancreas was obtained by segmenting an abdominal computed tomography (CT) scan, and its physical and chemical properties, were obtained from experimental and theoretical data. In GATE, GNRs-mediated hyperthermal therapy, simple heat diffusion as well as interstitial laser ablation were then modeled in the pancreas tumor by defining the optical parameters of this tissue when it is loaded with GNRs. Two different experimental setups on ex vivo pancreas tissue and GNRs-embedded water were devised to benchmark the developed Monte Carlo-based model for the hyperthermia in the pancreas alone and with GNRs, respectively. The influence of GNRs on heat distribution and temperature increase within the pancreas tumor was compared for two different power values (1.2 W and 2.1 W) when the tumor was exposed to 808 nm laser irradiation and with two different laser applicator diameters. Benchmark tests demonstrated the possibility of the accurate simulating of NPs-assisted thermal therapy and reproducing the experimental data with GATE software. Then, the output of the simulated GNR-mediated hyperthermia emphasized the importance of the precise evaluation of all of the parameters for optimizing the preplanning of cancer thermal therapy. Simulation results on temperature distribution in the pancreas tumor showed that the temperature enhancement caused by raising the power was increased with time in both the tumor with and without GNRs, but it was higher for the GNR-load tumor compared to tumor alone.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
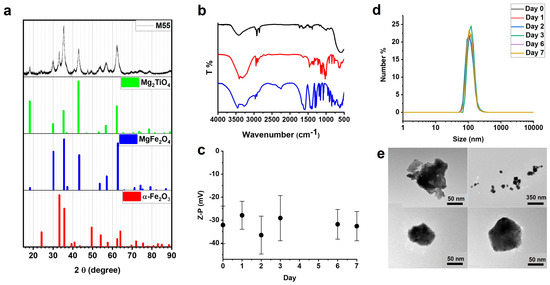
Doped Ferrite Nanoparticles Exhibiting Self-Regulating Temperature as Magnetic Fluid Hyperthermia Antitumoral Agents, with Diagnostic Capability in Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Magnetic Particle Imaging
by
Federica Vurro, Marco Gerosa, Alice Busato, Matilde Muccilli, Emil Milan, Jeff Gaudet, Patrick Goodwill, James Mansfield, Enrico Forlin, Alessandro Negri, Filippo Gherlinzoni, Giovanni Morana, Michele Gottardi, Paolo Matteazzi, Max Wintermark, Adolfo Speghini and Pasquina Marzola
Cited by 6 | Viewed by 2133
Abstract
This paper reports a comprehensive investigation of a magnetic nanoparticle (MNP), named M55, which belongs to a class of innovative doped ferrite nanomaterials, characterized by a self-limiting temperature. M55 is obtained from M48, an MNP previously described by our group, by implementing an
[...] Read more.
This paper reports a comprehensive investigation of a magnetic nanoparticle (MNP), named M55, which belongs to a class of innovative doped ferrite nanomaterials, characterized by a self-limiting temperature. M55 is obtained from M48, an MNP previously described by our group, by implementing an additional purification step in the synthesis. M55, after citrate and glucose coating, is named G-M55. The present study aimed to demonstrate the properties of G-M55 as a diagnostic contrast agent for MRI and magnetic particle imaging (MPI), and as an antitumoral agent in magnetic fluid hyperthermia (MFH). Similar specific absorption rate values were obtained by standard MFH and by an MPI apparatus. This result is of interest in relation to the application of localized MFH by MPI apparatus. We demonstrated the biocompatibility of G-M55 in a triple-negative human breast cancer line (MDA-MB-231), and its efficacy as an MFH agent in the same cell line. We also demonstrated the efficacy of MFH treatment with G-M55 in an experimental model of breast cancer. Overall, our results pave the way for the clinical application of G-M55 as an MFH agent in breast cancer therapy, allowing not only efficient treatment by both standard MFH apparatus and MPI but also temperature monitoring.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
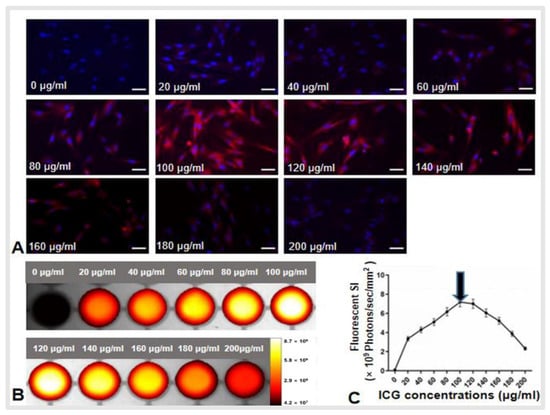
Development of a Three-Dimensional Multi-Modal Perfusion-Thermal Electrode System for Complete Tumor Eradication
by
Hui Zheng, Peicheng Li, Ruidong Ma, Feng Zhang, Hongxiu Ji, Wayne L. Monsky, Evan Johnson, Weizhu Yang, Caifang Ni, Dayong Gao and Xiaoming Yang
Cited by 1 | Viewed by 1863
Abstract
Background: Residual viable tumor cells after ablation at the tumor periphery serve as the source for tumor recurrence, leading to treatment failure. Purpose: To develop a novel three-dimensional (3D) multi-modal perfusion-thermal electrode system completely eradicating medium-to-large malignancies. Materials and Methods: This study included
[...] Read more.
Background: Residual viable tumor cells after ablation at the tumor periphery serve as the source for tumor recurrence, leading to treatment failure. Purpose: To develop a novel three-dimensional (3D) multi-modal perfusion-thermal electrode system completely eradicating medium-to-large malignancies. Materials and Methods: This study included five steps: (i) design of the new system; (ii) production of the new system; (iii) ex vivo evaluation of its perfusion-thermal functions; (iv) mathematic modeling and computer simulation to confirm the optimal temperature profiles during the thermal ablation process, and; (v) in vivo technical validation using five living rabbits with orthotopic liver tumors. Results: In ex vivo experiments, gross pathology and optical imaging demonstrated the successful spherical distribution/deposition of motexafin gadolinium administered through the new electrode, with a temperature gradient from the electrode core at 80 °C to its periphery at 42 °C. An excellent repeatable correlation of temperature profiles at varying spots, from the center to periphery of the liver tumor, was found between the mathematic simulation and actual animal tumor models (Pearson coefficient ≥0.977). For in vivo validation, indocyanine green (ICG) was directly delivered into the peritumoral zones during simultaneous generation of central tumoral lethal radiofrequency (RF) heat (>60 °C) and peritumoral sublethal RF hyperthermia (<60 °C). Both optical imaging and fluorescent microscopy confirmed successful peritumoral ICG distribution/deposition with increased heat shock protein 70 expression. Conclusion: This new 3D, perfusion-thermal electrode system provided the evidence on the potential to enable simultaneous delivery of therapeutic agents and RF hyperthermia into the difficult-to-treat peritumoral zones, creating a new strategy to address the critical limitation, i.e., the high incidence of residual and recurrent tumor following thermal ablation of unresectable medium-to-large and irregular tumors.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Proposal of New Safety Limits for In Vivo Experiments of Magnetic Hyperthermia Antitumor Therapy
by
Borja Herrero de la Parte, Irati Rodrigo, Jon Gutiérrez-Basoa, Sira Iturrizaga Correcher, Carmen Mar Medina, Jose Javier Echevarría-Uraga, Jose Angel Garcia, Fernando Plazaola and Ignacio García-Alonso
Cited by 34 | Viewed by 3107
Abstract
Background: Lately, major advances in crucial aspects of magnetic hyperthermia (MH) therapy have been made (nanoparticle synthesis, biosafety, etc.). However, there is one key point still lacking improvement: the magnetic field-frequency product (
H × f = 4.85 × 10
8 Am
−1
[...] Read more.
Background: Lately, major advances in crucial aspects of magnetic hyperthermia (MH) therapy have been made (nanoparticle synthesis, biosafety, etc.). However, there is one key point still lacking improvement: the magnetic field-frequency product (
H × f = 4.85 × 10
8 Am
−1s
−1) proposed by Atkinson–Brezovich as a limit for MH therapies. Herein, we analyze both local and systemic physiological effects of overpassing this limit. Methods: Different combinations of field frequency and intensity exceeding the Atkinson–Brezovich limit (591–920 kHz, and 10.3–18 kA/m) have been applied for 21 min to WAG/RijHsd male rats, randomly distributed to groups of 12 animals; half of them were sacrificed after 12 h, and the others 10 days later. Biochemical serum analyses were performed to assess the general, hepatic, renal and/or pancreatic function. Results: MH raised liver temperature to 42.8 ± 0.4 °C. Although in five of the groups the exposure was relatively well tolerated, in the two of highest frequency (928 kHz) and intensity (18 kA/m), more than 50% of the animals died. A striking elevation in liver and systemic markers was observed after 12 h in the surviving animals, independently of the frequency and intensity used. Ten days later, liver markers were almost recovered in all of the animals. However, in those groups exposed to 591 kHz and 16 kA/m, and 700 kHz and 13.7 kA/m systemic markers remained altered. Conclusions: Exceeding the Atkinson–Brezovich limit up to 9.59 × 10
9 Am
−1s
−1 seems to be safe, though further research is needed to understand the impact of intensity and/or frequency on physiological conditions following MH.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Planned Papers
The below list represents only planned manuscripts. Some of these
manuscripts have not been received by the Editorial Office yet. Papers
submitted to MDPI journals are subject to peer-review.
Title: Hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy (HIPEC) for peritoneal carcinomatosis and the peritoneal immune microenvironment
Authors: Wim P Ceelen
Affiliation: Department of GI Surgery, Ghent University Hospital
Abstract: Hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy (HIPEC) in addition to cytoreductive surgery for peritoneal carcinomatosis (PC) treats residual microscopic disease. Hyperthermia purportedly improves drug distribution and penetration in the peritoneal cavity; It is being incorporated into emerging peritoneal-directed therapies. The peritoneum is also increasingly recognized as an immune-privileged organ with its own distinct immune microenvironment that have been shown to correlate with clinical prognosis. However, as shown by increased levels of damage associated molecular patterns (DAMPs) such as heat-shock proteins, hyperthermia induces direct injury to the peritoneum. There may also be deleterious effect on the peritoneal immune response via indirect and direct mechanisms. Indirect mechanisms such as cytokine mediated chemotaxis and paracrine immune modulation may be negatively affected by hyperthermia. Direct hyperthermia-induced damage to key immune cell populations may also allow for the establishment and propagation of PC. While hyperthermia has both stimulatory and suppressive actions, the overall net effect on PC and impact on prognosis remains unknown. Newer modalities of peritoneal treatment utilizing live viruses or immune-modulatory molecules may also be temperature sensitive and hence, not amenable to delivery with hyperthermia. Emerging evidence suggests that hyperthermia in treatment of PC is not entirely innocuous. The impact of temperature on the peritoneum and its unique microenvironment needs to be more accurately defined to determine its benefit in the management of PC.
Title: Combine human-sized alternating magnetic field coil and MNP hyperthermia for deep seated can-cer treatment
Author:
Highlights: An AMF coil is presented for deep seated tumors MNP hyperthermia and avoiding damage normal tissues by eddy currents heating. The studies are done for pancreatic cancer. The results show that the proposed human-sized coil can provide clinically relevant AMF at deeply seated cancers during MNP hyperthermia therapy, while causing less eddy currents heating in the normal tissues.