Advances in Integrative Medicine: Complementary Approaches and Therapies in Global Healthcare
A project collection of Healthcare (ISSN 2227-9032). This project collection belongs to the section "Health Assessments".
Papers displayed on this page all arise from the same project. Editorial decisions were made independently of project staff and handled by the Editor-in-Chief or qualified Editorial Board members.
Viewed by 68094Editors
Interests: biomedical sciences; global and integrative health; complementary therapy development; extracellular superconductor transmission; supplementary nutrition and natural diet; physical and respiratory movements; clinical trials; medicine advances on artificial and biological intelligence integration; biomineralization of biosynthetic membranes; calcification physiology mechanisms in mollusks
Interests: global and integrative health; complementary therapy development; supplementary nutrition and natural diet; clinical trials; human genetics; platelet activation; thrombosis and hemostasis
Project Overview
Dear Colleagues,
Currently, diagnostic and therapeutic systems in addition to methods to safeguard sustainable public and individual health are no longer compatible with isolated/closed or even prejudiced structures, mechanisms, and processes. Several external or internal factors to the human being interfere in a transversal and complex way, forcing new concepts and technical–scientific methodologies in order to overcome somatic or mental imbalances.
Thus, it is increasingly observed that psychic and physical or biopsychosomatic human well-being is a final result of several interactions from environmental agents in confrontation with the immunological and neurological response capacity of internal components. This state of affairs sometimes calls, whenever possible, for expeditious, simple, and natural methods, since access to healthcare is sometimes expensively unnecessary. Therefore, we can say that we need to build more flexible approaches, in addition to agile, reliable, and transversal health approaches for everyone.
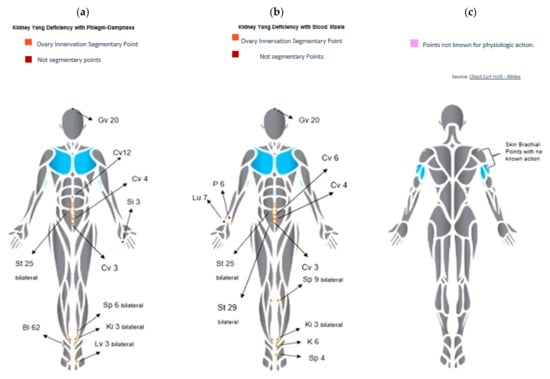
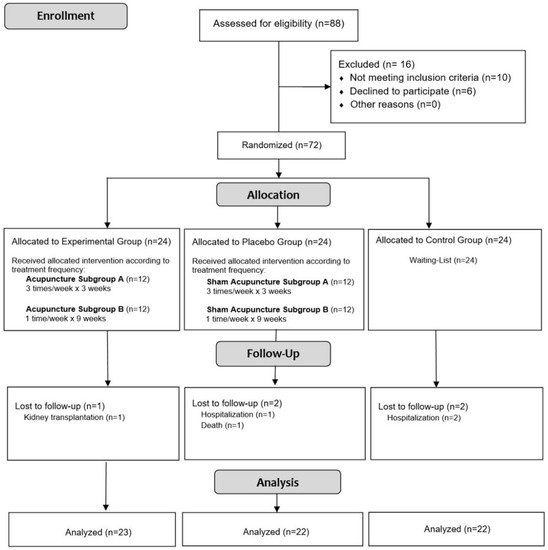
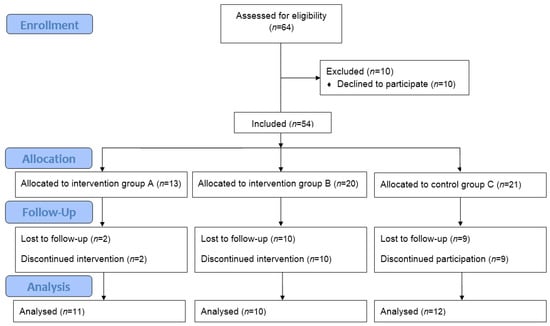
In this context, we are sufficiently motivated and proud to invite skilled scientists with an interest in global and integrative healthcare to present their studies in peer-reviewed papers in our Collection Project. Cross-disciplinary research will be important in the future. This issue will be open for all possible topics related to global health, e.g., reproductive health, occupational health, “forgotten health problems”, child and adolescent health, and infectious and chronic diseases, such as cancer, COVID-19 infection, obesity, diabetes, and metabolic, neurodegenerative, and immunodeficiency diseases. Thus, approaches on acupuncture effects, phytotherapy, decoctions, nutritional or dietetic supplements, Asian or Western physical and breathing exercises, as well as in silico intelligence medicine studies using bioresonance integrators are welcome.
The journal has excellent reviewers and adequate research specialists, with a rapidly increasing impact as well as a quick and thorough review process. Thus, you are welcome to join us in this interesting Project Collection.
Dr. Jorge P. Machado
Prof. Dr. Maria Begoña Criado
Collection Editors
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Healthcare is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2700 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- biomedical sciences
- global healthcare
- integrative health
- complementary therapy development
- phytotherapy
- acupuncture
- chronic and infectious disease
- nutrition and dietetic supplements
- biological–artificial intelligence integration
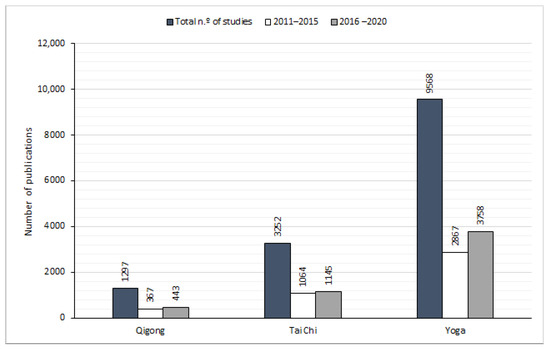
- physical and breathing exercises