Telehealth Transformation: COVID-19 and the Rise of Virtual Care, Connected Health and Virtual Community of Practice
Share This Topical Collection
Editors
 Prof. Dr. Jinan Fiaidhi
Prof. Dr. Jinan Fiaidhi
 Prof. Dr. Jinan Fiaidhi
Prof. Dr. Jinan Fiaidhi
E-Mail
Website
Collection Editor
Department of Computer Science, Lakehead University, Thunder Bay, ON P7B 5E1, Canada
Interests: collaborative learning; web intelligence; health informatics; learning analytics; thick data analytics
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
With the onset of the COVID-19 viral wave, strategies that shift care away from hospitals toward the home and community have gained momentum. Additionally, the guidelines to stay at home and work from home have led to increased awareness of new ways to manage care and interpersonal collaboration. As a result, we are witnessing a variety of apps and services covering areas from automated triage help via smart care chatbots to direct connection to care teams via services such as lightweight videoconferencing, remote monitoring systems, and medical alerts. All these new virtual care services along with the real time data streaming analysis are playing an increasing role in enabling virtual care, connected health, and supporting the interpersonal community of practice.
Prof. Dr. Jinan Fiaidhi
Prof. Dr. Sabah Mohammed
Collection Editors
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Healthcare is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript.
The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2700 CHF (Swiss Francs).
Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's
English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- Virtual consultation
- Care question answering and VQA
- Virtual community of practice
- Remote patient monitoring and management
- Telehealth, mHealth and eHealth
- Telehealth security
- Telecare robotics
- Connected health technologies
- IoMT and IoT for Virtual Care
- Telecare and wellbeing apps and services
- Real time care data analytics
- Virtual care medical records via FHIR
Published Papers (15 papers)
Open AccessReview
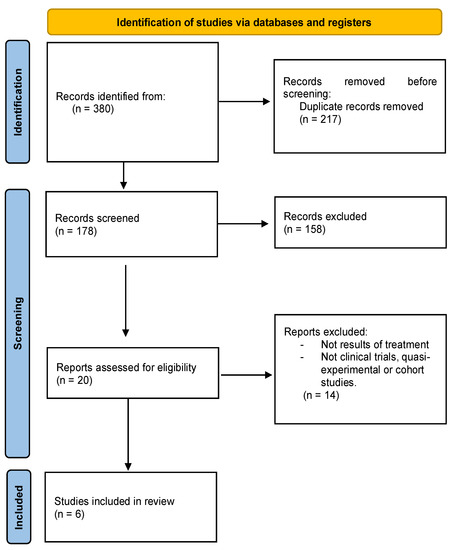
Telerehabilitation, A Viable Option in Patients with Persistent Post-COVID Syndrome: A Systematic Review
by
María Ángeles Valverde-Martínez, Remedios López-Liria, Jesús Martínez-Cal, María Jesús Benzo-Iglesias, Lucía Torres-Álamo and Patricia Rocamora-Pérez
Cited by 24 | Viewed by 4504
Abstract
The number of patients with post-COVID-19 syndrome continues to increase considerably, having serious healthcare, social and economic repercussions. The objective of this study is to describe the effectiveness of telerehabilitation to alleviate the symptoms of post-COVID-19 syndrome. A systematic review was conducted using
[...] Read more.
The number of patients with post-COVID-19 syndrome continues to increase considerably, having serious healthcare, social and economic repercussions. The objective of this study is to describe the effectiveness of telerehabilitation to alleviate the symptoms of post-COVID-19 syndrome. A systematic review was conducted using the information available on four databases (PubMed, Medline, Scielo and PEDRo) on these patients until November 2022. The MeSH search terms were: Post-COVID syndrome, Post-COVID-19, Long COVID, Telerehabilitation, Physiotherapy, Rehabilitation, Virtual, Home care. Six articles were included which provided information on 140 patients, detailing their symptomatology, assessment, treatment and monitoring. The variables measured were dyspnea, fatigue, physical performance and quality of life. All studies included aerobic and anaerobic exercises. Most notable among the techniques used were rib cage expansion exercises, respiratory control and thoracic cage stretching, patient education, Mindfulness and virtual reality games to address physical, mental and relaxation aspects. The use of telerehabilitation could be an effective tool for the treatment of persistent symptoms after suffering from COVID-19. It has been shown in these studies that patients improve both their physical performance and their quality of life.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
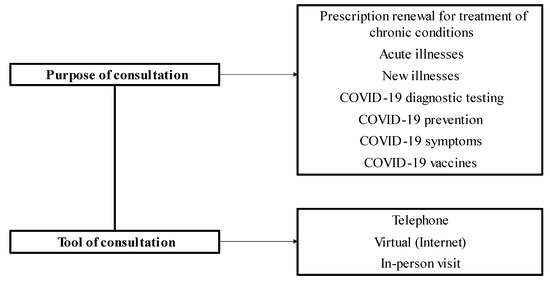
Consultation Management during the COVID-19 Pandemic: The Experience of Lithuanian Physicians
by
Aida Budrevičiūtė, Gediminas Raila, Renata Paukštaitienė, Leonas Valius and Marios Argyrides
Cited by 2 | Viewed by 1641
Abstract
Crises in the medicine sector such as the COVID-19 pandemic encourage the search for effective solutions for the provision of health care services, when conventional face-to-face consultations may be difficult to deliver effectively due to contact restrictions. The main objective of this study
[...] Read more.
Crises in the medicine sector such as the COVID-19 pandemic encourage the search for effective solutions for the provision of health care services, when conventional face-to-face consultations may be difficult to deliver effectively due to contact restrictions. The main objective of this study was to investigate consultation management provided by physicians during the COVID-19 pandemic in Lithuania. The dependence of diagnostic testing and vaccination of patients on the socio-demographic characteristics of physicians was also assessed. An anonymous survey was carried out during the COVID-19 pandemic, between 21 June 2021 and 17 September 2021, involving 191 physicians (9% of the total population) working in family physician teams in Lithuania. Thirty-nine Lithuanian Primary Health Care Institutions (PHCIs) were selected for this study, of which 11 were public and 28 were private. Private and public PHCIs employed 31% and 63% of the respondents, respectively, and 6% of respondents worked at both types of institutions. Concerning telemedicine, the physician-respondents frequently provided consultations over the telephone (79.6%) and in-person (63.9%), but less so via the Internet, with the latter option never being used at all by 57.1% of the respondents. Whilst telephone consultations were frequently provided by Lithuanian physicians, only half of the respondents chose to provide services over the Internet. Private, smaller, and rural-based PHCIs should more actively offer viral diagnostics and vaccination services.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
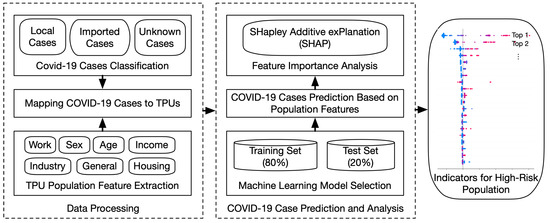
Identifying the High-Risk Population for COVID-19 Transmission in Hong Kong Leveraging Explainable Machine Learning
by
Zhihan Jiang, Ka-Man Yip, Xinchen Zhang, Jing Deng, Wilfred Wong, Hung-Kwan So and Edith C. H. Ngai
Viewed by 2972
Abstract
The worldwide spread of COVID-19 has caused significant damage to people’s health and economics. Many works have leveraged machine learning models to facilitate the control and treatment of COVID-19. However, most of them focus on clinical medicine and few on understanding the spatial
[...] Read more.
The worldwide spread of COVID-19 has caused significant damage to people’s health and economics. Many works have leveraged machine learning models to facilitate the control and treatment of COVID-19. However, most of them focus on clinical medicine and few on understanding the spatial dynamics of the high-risk population for transmission of COVID-19 in real-world settings. This study aims to investigate the association between population features and COVID-19 transmission risk in Hong Kong, which can help guide the allocation of medical resources and the implementation of preventative measures to control the spread of the pandemic. First, we built machine learning models to predict the number of COVID-19 cases based on the population features of different tertiary planning units (TPUs). Then, we analyzed the distribution of cases and the prediction results to find specific characteristics of TPUs leading to large-scale outbreaks of COVID-19. We further evaluated the importance and influence of various population features on the prediction results using SHAP values to identify indicators for high-risk populations for COVID-19 transmission. The evaluation of COVID-19 cases and the TPU dataset in Hong Kong shows the effectiveness of the proposed methods. The top three most important indicators are identified as people in accommodation and food services, low income, and high population density.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Evaluation of a Non-Face-to-Face Multidisciplinary Health Care Model in a Population with Rheumatoid Arthritis Vulnerable to COVID-19 in a Health Emergency Situation
by
Pedro Santos-Moreno, Gabriel-Santiago Rodríguez-Vargas, Rosangela Casanova, Jaime-Andrés Rubio-Rubio, Josefina Chávez-Chávez, Diana Patricia Rivera-Triana, Ruth Alexandra Castiblanco-Montañez, Sandra Milena Hernández-Zambrano, Laura Villareal and Adriana Rojas-Villarraga
Cited by 8 | Viewed by 3241
Abstract
This study evaluated a non-face-to-face-multidisciplinary consultation model in a population with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) during the COVID-19 pandemic. This is an analytical observational study of a prospective cohort with simple random sampling. RA patients were followed for 12 weeks (Jul–Oct 2020). Two groups
[...] Read more.
This study evaluated a non-face-to-face-multidisciplinary consultation model in a population with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) during the COVID-19 pandemic. This is an analytical observational study of a prospective cohort with simple random sampling. RA patients were followed for 12 weeks (Jul–Oct 2020). Two groups were included: patients in telemedicine care (TM), and patients in the usual face-to-face care (UC). Patients could voluntarily change the care model (transition model (TR)). Activity of disease, quality of life, disability, therapeutic adherence, and self-care ability were analyzed. Bivariate analysis was performed. A qualitative descriptive exploratory study was conducted. At the beginning, 218 adults were included: (109/TM-109/UC). The groups didn’t differ in general characteristics. At the end of the study, there were no differences in TM: (
n = 71). A significant (
p < 0.05) decrease in adherence, and increase in self-care ability were found in UC (
n = 18) and TR (
n = 129). Seven patients developed COVID-19. Four categories emerged from the experience of the subjects in the qualitative assessment (factors present in communication, information and communication technologies management, family support and interaction, and adherence to treatment). The telemedicine model keeps RA patients stable without major differences compared to the usual care or mixed model.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Patients’ Perceptions and Satisfaction with the Outpatient Telemedicine Clinics during COVID-19 Era in Saudi Arabia: A Cross-Sectional Study
by
Ashokkumar Thirunavukkarasu, Nasser Hanas Alotaibi, Ahmad Homoud Al-Hazmi, Mohammed Jayed Alenzi, Ziad Mansour Alshaalan, Mohammed Ghazi Alruwaili, Thamer Alshami Marghel Alruwaili, Hassan Alanazi and Turki Hanas Alosaimi
Cited by 18 | Viewed by 5931
Abstract
Successful implementation of virtual healthcare depends immensely on patients’ perceptions and satisfaction. This cross-sectional study assessed patients’ perceptions of, and factors associated with, poor and average satisfaction with the outpatient telemedicine clinics in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA). This questionnaire-based survey was
[...] Read more.
Successful implementation of virtual healthcare depends immensely on patients’ perceptions and satisfaction. This cross-sectional study assessed patients’ perceptions of, and factors associated with, poor and average satisfaction with the outpatient telemedicine clinics in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA). This questionnaire-based survey was conducted among 720 patients who attended outpatient telemedicine clinics from different regions of the KSA. Of the sample studied, 54.7% of the participants had high satisfaction and the most common disadvantage perceived by patients was technical issues (53.1%), followed by fewer personal interactions (30.4%). Around 75% of the participants desired to use telemedicine services even after the COVID-19 pandemic. Logistic regression analysis revealed that age group more than 40 years (OR = 1.59; 95% CI = 1.04–2.44,
p = 0.031), education less than university level (OR = 1.68; 95% CI = 1.07–2.15,
p = 0.025), and first-time participants (OR = 3.28; 95% CI = 2.32–4.65,
p < 0.001) were significantly associated with poor and average satisfaction ratings. The concerned authorities must make targeted action plans to circumvent the disadvantages perceived by patients accessing telemedicine. Furthermore, a multicenter, exploratory study that compares the virtual clinic with other telemedicine services in the KSA is warranted.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
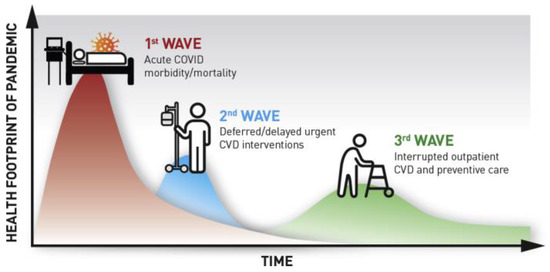
Preventive Cardiology in the Digital and COVID-19 Era: A Brave New World within the Veterans Health Administration
by
Sohil Khanna and Arash Harzand
Cited by 2 | Viewed by 2437
Abstract
The past year challenged patients, health care providers, and health systems alike to adapt and recalibrate to meet healthcare needs within pandemic constraints. The coronavirus 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic has radically interfered with the accessibility and delivery of cardiovascular care in the United States.
[...] Read more.
The past year challenged patients, health care providers, and health systems alike to adapt and recalibrate to meet healthcare needs within pandemic constraints. The coronavirus 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic has radically interfered with the accessibility and delivery of cardiovascular care in the United States. With an emphasis on social distancing and stay-at-home orders in effect, many Americans delayed seeking routine medical care and treatment for acute cardiac symptoms due to fear of contracting the coronavirus. The COVID-19 pandemic compelled a rapid shift toward virtual care solutions across cardiovascular domains. The U.S Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) expanded virtual modalities, notably in specialty care and rehabilitation, which offered secure solutions to maintain treatment continuity. Within the VA and other health systems, virtual cardiac rehabilitation (CR) was embraced as an efficacious alternative to on-site cardiac rehabilitation that enabled patients to receive cardiac care remotely. Leveraging the infrastructure and lessons learned from the pandemic-induced expansion of virtual care carries enormous potential to refine virtual CR and revitalize future treatment paradigms for cardiovascular disease patients.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
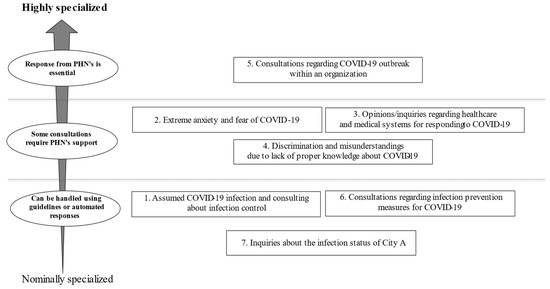
Content Analysis of the Free COVID-19 Telephone Consultations Available during the First Wave of the Pandemic in Japan
by
Kyoko Yoshioka-Maeda, Yuka Sumikawa, Noriha Tanaka, Chikako Honda, Riho Iwasaki-Motegi and Noriko Yamamoto-Mitani
Cited by 3 | Viewed by 2280
Abstract
This cross-sectional study aimed to (1) describe the unclassified contents of telephone consultation services provided by a public health center during the first wave of COVID-19 in Japan and (2) examine whether the contents required assistance from public health nurses (PHNs). We analyzed
[...] Read more.
This cross-sectional study aimed to (1) describe the unclassified contents of telephone consultation services provided by a public health center during the first wave of COVID-19 in Japan and (2) examine whether the contents required assistance from public health nurses (PHNs). We analyzed a total of 207 calls in which the purpose of the call was unclassified into pre-set categories. PHNs transcribed the exact text of the consultation conversations recorded from 25 March to 20 April 2020 in City A. Approximately half of the calls were from residents. Seven categories were extracted through a qualitative content analysis. The most common topic was infection control measures, where the presence of COVID-19 infection was assumed (
n = 62); the second most common was extreme anxiety and fear of infection (
n = 50). Questions about the COVID-19 response system (
n = 30), discrimination and misunderstandings about COVID-19 (
n = 24), and response measures for COVID-19 outbreaks within organizations (
n = 18) were also included. The unclassified consultations included various topics, several of which required the expertise of a PHN. Each local government should consider sharing and task-shifting telephone consultation services among PHNs and other staff to reduce their burden and allow them to concentrate on conducting infection control more effectively.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
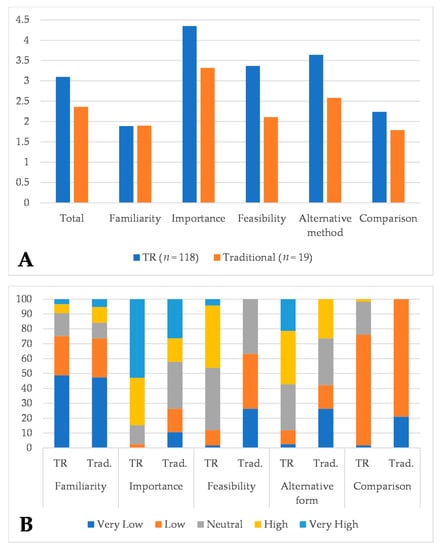
Feasibility, Acceptability and Limitations of Speech and Language Telerehabilitation during COVID-19 Lockdown: A Qualitative Research Study on Clinicians’ Perspectives
by
Luisa Cacciante, Błażej Cieślik, Sebastian Rutkowski, Anna Rutkowska, Katarzyna Kacperak, Tomasz Kuligowski and Pawel Kiper
Cited by 14 | Viewed by 3424
Abstract
The COVID-19 pandemic brought out the need to deliver health care services at a distance in the form of telerehabilitation (TR). This study aimed to analyse the Italian speech and language therapists’ (SLTs) opinions on the feasibility of the TR in the field
[...] Read more.
The COVID-19 pandemic brought out the need to deliver health care services at a distance in the form of telerehabilitation (TR). This study aimed to analyse the Italian speech and language therapists’ (SLTs) opinions on the feasibility of the TR in the field of speech-language therapy during the COVID-19 pandemic. We developed an anonymous survey to determine the SLTs’ opinions on feasibility of TR during lockdown caused by COVID-19. We analysed the survey’s answers provided by 136 SLTs. Cronbach’s alpha coefficient showed good reliability of the survey. The SLTs working previously with TR showed better judgements regarding this method. The comparison analysis between TR and face-to-face treatment delivery showed statistically significant differences as follows: “importance” (4.35 vs. 3.32,
p = 0.001), “feasibility” (3.37 vs. 2.11,
p < 0.001), “alternative form” (3.64 vs. 2.58,
p = 0.001) and “comparison” (2.24 vs. 1.69,
p < 0.001), but not with “familiarity” (
p = 0.81). The survey showed that most of the Italian SLTs were not satisfied with TR systems. SLTs who used TR previously had a better opinion on this treatment modality. Experience and familiarity with TR systems were key factors for the use of this new rehabilitation modality.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
Connecting the World of Healthcare Virtually: A Scoping Review on Virtual Care Delivery
by
Cindy (Zhirui) Li, Elizabeth M. Borycki and Andre W. Kushniruk
Cited by 29 | Viewed by 6378
Abstract
Virtual care extends beyond the walls of healthcare organizations to provide care at a distance. Although virtual care cannot be regarded as a solution for all health-related inquiries, it provides another care delivery channel for specific patient populations with appointments that do not
[...] Read more.
Virtual care extends beyond the walls of healthcare organizations to provide care at a distance. Although virtual care cannot be regarded as a solution for all health-related inquiries, it provides another care delivery channel for specific patient populations with appointments that do not require in-person physical examinations or procedures. A scoping review was conducted to define the meaning of virtual care, understand how virtual care has influenced the healthcare industry and is being expanded to complement the existing healthcare system, and describe the outcomes of using virtual care for patients and providers. Findings from the scoping review suggest that virtual care encompasses the provision of care using advanced video conferencing technology to support remote care that takes place between patients and providers and the use of virtual reality technology to simulate care environments. Some of virtual care’s use in healthcare includes application to pain and anxiety management, virtual consultations and follow-up visits, rehabilitation and therapy services, outpatient clinics, and emergency services. Lastly, from a provider and patient perspective, while both saw benefits of virtual care and scored the service relatively high on satisfaction after using virtual care, the greatest barrier to using virtual care may be technological challenges.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
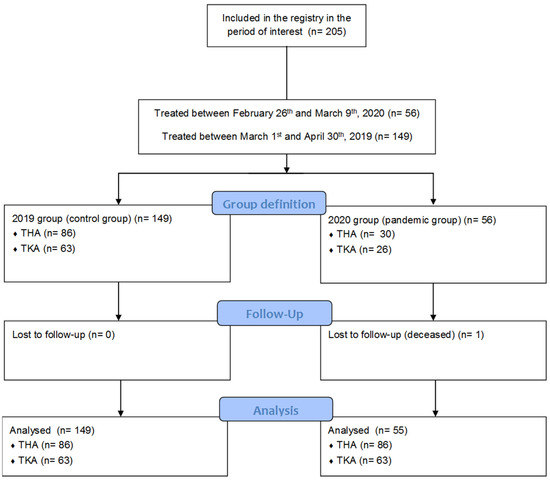
Remote Management of Patients after Total Joint Arthroplasty via a Web-Based Registry during the COVID-19 Pandemic
by
Michele Ulivi, Luca Orlandini, Valentina Meroni, Mario D’Errico, Arianna Fontana, Marco Viganò, Laura Mangiavini, Roberto D’Anchise, Franco Parente, Roberto Pozzoni, Valerio Sansone, Luigi Zagra and Giuseppe M. Peretti
Cited by 9 | Viewed by 2281
Abstract
Background: In 2020, due to the outbreak of the COVID-19 (Coronavirus Disease 2019) pandemic, patients who underwent total joint arthroplasty were not able to undergo the proper postoperative surgical and rehabilitative care. This study aims to evaluate the potential of a web-cloud-based database
[...] Read more.
Background: In 2020, due to the outbreak of the COVID-19 (Coronavirus Disease 2019) pandemic, patients who underwent total joint arthroplasty were not able to undergo the proper postoperative surgical and rehabilitative care. This study aims to evaluate the potential of a web-cloud-based database on patients’ follow-up in extraordinary situations, when a traditional in-person follow-up cannot be warranted. Methods: Patients who underwent joint arthroplasty at our Institute between 21 February and 16 March 2020 were included in the study group and were matched to a similar population undergoing joint arthroplasty in February/March 2019. All patients routinely complete questionnaires before and after treatment, including patient-reported outcome measures such as the Visual Analogues Scale (VAS), Knee/Hip Injury and Osteoarthritis Outcome Score Physical Function Short Form (KOOS-PS/HOOS-PS) and Short-Form Health Survey (SF-12) for the monitoring of clinical improvements. Results: 56 (study group) and 144 (control group) patients were included in the study. Both groups demonstrated significant improvements at 3 months. HOOS-PS improvement was significantly reduced in the 2020 group compared to 2019 (21.7 vs. 33.9,
p < 0.001). This reduction was related to intense physical activities. Similarly, the functional score improvement related to these activities was reduced for patients undergoing knee replacement (8 vs. 10,
p < 0.05). Conclusions: The web-based Institute Registry emerged as a meaningful and sensitive tool during an extraordinary situation such as the COVID-19 pandemic to monitor patients’ progression after total joint arthroplasties. Thanks to this tool, it was possible to observe that the prevention of usual postoperative care due to pandemic-related restrictions did not alter the benefits observed after joint replacement surgeries, even if this condition reduced the postoperative improvements in the most burdensome physical activities. A broader use of this kind of tool would improve and potentially reduce the burden and costs of postoperative patients’ monitoring in standard and extraordinary conditions. In addition, the systematic remote collection of data would allow for the identification of relevant differences in clinical outcomes in specific conditions or following the modification of treatment and rehabilitation protocols.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
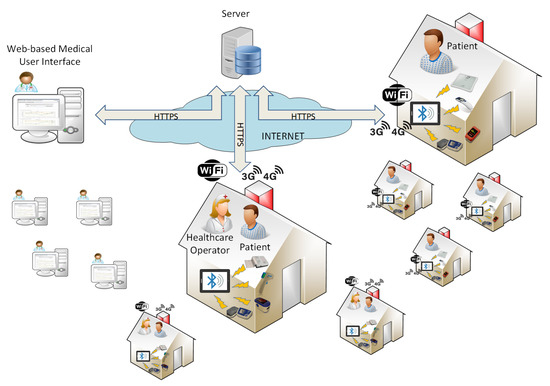
Telemonitoring in the Covid-19 Era: The Tuscany Region Experience
by
Silvia Panicacci, Massimiliano Donati, Alberto Lubrano, Annamaria Vianello, Alessio Ruiu, Luca Melani, Antonella Tomei and Luca Fanucci
Cited by 16 | Viewed by 3494
Abstract
Covid-19 has brought many difficulties in the management of infected and high-risk patients. Telemedicine platforms can really help in this situation, since they allow remotely monitoring Covid-19 patients, reducing the risk for the doctors, without decreasing the efficiency of the therapies and while
[...] Read more.
Covid-19 has brought many difficulties in the management of infected and high-risk patients. Telemedicine platforms can really help in this situation, since they allow remotely monitoring Covid-19 patients, reducing the risk for the doctors, without decreasing the efficiency of the therapies and while alleviating patients’ mental issues. In this paper, we present the entire architecture and the experience of using the Tel.Te.Covid19 telemedicine platform. Projected for the treatment of chronic diseases, it has been technologically updated for the management of Covid-19 patients with the support of a group of doctors in the territory when the pandemic arrived, introducing new sensors and functionalities (e.g., the familiar use and video calls). In Tuscany (Central Italy), during the first wave of outbreak, a model for enrolling patients was created and tested. Because of the positive results, the latter has been then adopted in the second current wave. The Tel.Te.Covid19 platform has been used by 40 among general practitioners and doctors of continuity care and about 180 symptomatic patients since March 2020. Both patients and doctors have good opinion of the platform, and no hospitalisations or deaths occurred for the monitored patients, reducing also the impact on the National Healthcare System.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
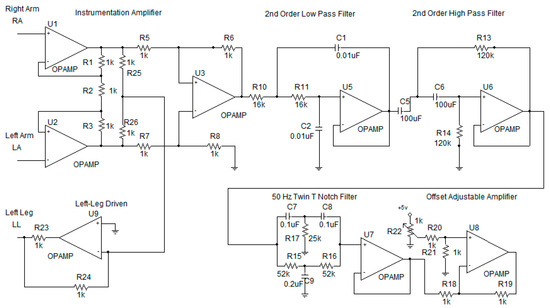
Multi-Parameter Vital Sign Telemedicine System Using Web Socket for COVID-19 Pandemics
by
Chuchart Pintavirooj, Tanapon Keatsamarn and Treesukon Treebupachatsakul
Cited by 6 | Viewed by 3868
Abstract
Telemedicine has become an increasingly important part of the modern healthcare infrastructure, especially in the present situation with the COVID-19 pandemics. Many cloud platforms have been used intensively for Telemedicine. The most popular ones include PubNub, Amazon Web Service, Google Cloud Platform and
[...] Read more.
Telemedicine has become an increasingly important part of the modern healthcare infrastructure, especially in the present situation with the COVID-19 pandemics. Many cloud platforms have been used intensively for Telemedicine. The most popular ones include PubNub, Amazon Web Service, Google Cloud Platform and Microsoft Azure. One of the crucial challenges of telemedicine is the real-time application monitoring for the vital sign. The commercial platform is, by far, not suitable for real-time applications. The alternative is to design a web-based application exploiting Web Socket. This research paper concerns the real-time six-parameter vital-sign monitoring using a web-based application. The six vital-sign parameters are electrocardiogram, temperature, plethysmogram, percent saturation oxygen, blood pressure and heart rate. The six vital-sign parameters were encoded in a web server site and sent to a client site upon logging on. The encoded parameters were then decoded into six vital sign signals. Our proposed multi-parameter vital-sign telemedicine system using Web Socket has successfully remotely monitored the six-parameter vital signs on 4G mobile network with a latency of less than 5 milliseconds.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
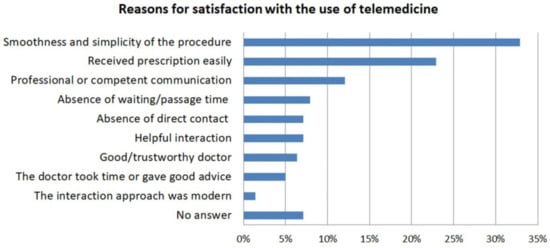
Telehealth in Times of COVID-19: Spotlight on Austria
by
Maria Kletečka-Pulker, Sabine Völkl-Kernstock, Anna Fassl, Elisabeth Klager, Harald Willschke, Sophie Klomfar, Thomas Wochele-Thoma, Eva Schaden and Atanas G. Atanasov
Cited by 8 | Viewed by 5026
Abstract
Introduction: With the spread of Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), the world has been experiencing an extraordinary state of emergency. As patients entering a doctor’s practice can potentially infect medical staff and other patients, using digital alternatives wherever possible is a potential solution to
[...] Read more.
Introduction: With the spread of Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), the world has been experiencing an extraordinary state of emergency. As patients entering a doctor’s practice can potentially infect medical staff and other patients, using digital alternatives wherever possible is a potential solution to avoiding face-to-face encounters. In these conditions, telemedicine is becoming increasingly relevant. Hence, the aim of this study was to examine telemedicine use and gathered experiences during the COVID-19 pandemic in Austria. Materials and Methods: In June 2020, a representative group of Austrian respondents (
n = 1000) was asked via online survey whether they had contacted a doctor during spring of 2020, and, if so, whether they had used a telemedical method to do so. The survey also reflected gathered experiences and degrees of satisfaction with the use of telemedicine. Results: A third (33%) of those who contacted a doctor during the target period did so using telemedical tools. The majority of those with previous telehealth experience were satisfied with the help they received. Patients commonly used a telephone to contact their doctors. The overall assessment of telemedical aids tended to be positive, with more than half (53%) of those surveyed seeing significant advantages, and a 90% satisfaction rate among the respondents who used telehealth services. Conclusion: The outcomes from this work hint at fairly high acceptance of telemedical communication tools in the studied group of the Austrian population. Based on the high rate of satisfaction among patients who used telehealth, it is expected that the use of telehealth services will increase further in the near future.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessCommentary
Perspectives of Registered Dietitian Nutritionists on Adoption of Telehealth for Nutrition Care during the COVID-19 Pandemic
by
Cory Brunton, Mary Beth Arensberg, Susan Drawert, Christina Badaracco, Wendy Everett and Sharon M. McCauley
Cited by 39 | Viewed by 6077
Abstract
Widespread transmission of the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection has resulted in a global coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic that is straining medical resources worldwide. In the United States (US), hospitals and clinics are challenged to accommodate surging patient populations
[...] Read more.
Widespread transmission of the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection has resulted in a global coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic that is straining medical resources worldwide. In the United States (US), hospitals and clinics are challenged to accommodate surging patient populations and care needs while preventing further infection spread. Under such conditions, meeting with patients via telehealth technology is a practical way to help maintain meaningful contact while mitigating SARS-CoV-2 transmission. The application of telehealth to nutrition care can, in turn, contribute to better outcomes and lower burdens on healthcare resources. To identify trends in telehealth nutrition care before and during the pandemic, we emailed a 20-question, qualitative, structured survey to approximately 200 registered dietitian nutritionists (RDNs) from hospitals and clinics that have participated in the Malnutrition Quality Improvement Initiative (MQii). RDN respondents reported increased use of telehealth-based care for nutritionally at-risk patients during the pandemic. They suggested that use of such telehealth nutrition programs supported positive patient outcomes, and some of their sites planned to continue the telehealth-based nutrition visits in post-pandemic care. Nutrition care by telehealth technology has the potential to improve care provided by practicing RDNs, such as by reducing no-show rates and increasing retention as well as improving health outcomes for patients. Therefore, we call on healthcare professionals and legislative leaders to implement policy and funding changes that will support improved access to nutrition care via telehealth.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Developing the eMedical Student (eMS)—A Pilot Project Integrating Medical Students into the Tele-ICU during the COVID-19 Pandemic and beyond
by
Joshua Ho, Philip Susser, Cindy Christian, Horace DeLisser, Michael J. Scott, Lynn A. Pauls, Ann M. Huffenberger, C. William Hanson III, John M. Chandler, Lee A. Fleisher and Krzysztof Laudanski
Cited by 12 | Viewed by 3407
Abstract
The COVID-19 pandemic has accelerated the demand for virtual healthcare delivery and highlighted the scarcity of telehealth medical student curricula, particularly tele-critical care. In partnership with the Penn E-lert program and the Department of Anesthesiology and Critical Care, the Perelman School of Medicine
[...] Read more.
The COVID-19 pandemic has accelerated the demand for virtual healthcare delivery and highlighted the scarcity of telehealth medical student curricula, particularly tele-critical care. In partnership with the Penn E-lert program and the Department of Anesthesiology and Critical Care, the Perelman School of Medicine (PSOM) established a tele-ICU rotation to support the care of patients diagnosed with COVID-19 in the Intensive Care Unit (ICU). The four-week course had seven elements: (1) 60 h of clinical engagement; (2) multiple-choice pretest; (3) faculty-supervised, student-led case and topic presentations; (4) faculty-led debriefing sessions; (5) evidence-based-medicine discussion forum; (6) multiple-choice post-test; and (7) final reflection. Five third- and fourth-year medical students completed 300 h of supervised clinical engagement, following 16 patients over three weeks and documenting 70 clinical interventions. Knowledge of critical care and telehealth was demonstrated through improvement between pre-test and post-test scores. Professional development was demonstrated through post-course preceptor and learner feedback. This tele-ICU rotation allowed students to gain telemedicine exposure and participate in the care of COVID patients in a safe environment.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures