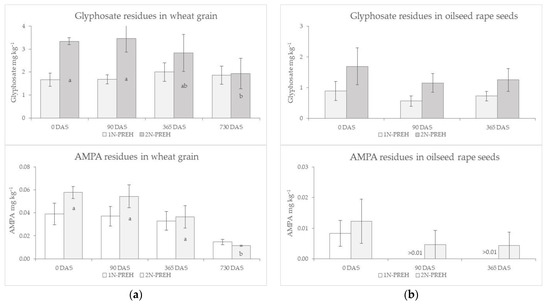
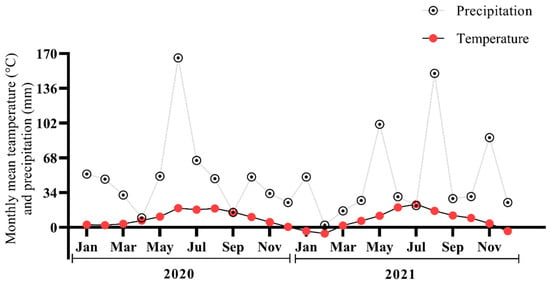
Selected Papers from Lithuanian Research Centre for Agriculture and Forestry
A topical collection in Plants (ISSN 2223-7747). This collection belongs to the section "Horticultural Science and Ornamental Plants".
Viewed by 30496Editors
Interests: photophysiology; physiology of plant productivity; metabolism; phytochemistry
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Interests: soil science; agricultural plant science; agrophysics
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
2. Department of Horticulture, Norwegian Institute of Bioeconomy Research—NIBIO Ullensvang, Ullensvangvegen 1005, NO-5781 Lofthus, Norway
Interests: fruit tree cultivars; rootstocks; fruit physiology; crop load regulation; preharvest fruit quality
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Interests: horticultural plant diseases; plant protection; disease forecasting
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
In modern agriculture, in the context of a climate change, it is important to find solutions for obtaining high productivity for crops of proper quality, which are both safe for humans and, at the same time, not harmful to the environment. To achieve these goals, many aspects must be foreseen and evaluated.
The work carried out in the Lithuanian Research Centre for Agriculture and Forestry (LAMMC) is covering a broad spectrum of R&D in the fields of agronomy and forestry and the related fields of ecology and environmental sciences, biology, biophysics, botany, and micro and macro fauna. The results obtained in the Centre are of great importance for better understanding the future perspectives in agriculture, horticulture, and forestry.
This Topical Collection will include publications on the recent research carried out in the LAMMC related to plant science.
Topics of interest include but are not limited to:
- Plant Physiology and Metabolism
- Phytochemistry
- Plant Protection and Biotic Interactions
- Plant Molecular Biology
- Plant Development and Morphogenesis
- Plant Ecology
- Plant Cell Biology
- Plant Systematics, Taxonomy, Nomenclature, and Classification
- Plant Genetics, Genomics and Biotechnology
- Plant Modeling
- Plant Response to Abiotic Stress and Climate Change
- Plant Nutrition
- Plant–Soil Interactions
- Crop Physiology and Crop Production
- Plant Genetic Resources
- Horticultural Science and Ornamental Plants
Dr. Giedrė Samuolienė
Dr. Gražina Kadžienė
Dr. Darius Kviklys
Dr. Neringa Rasiukeviciute
Collection Editors
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Plants is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2700 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- plant physiology
- plant nutrition
- plant-soil interactions
- plant genetics
- genomics and biotechnology
- plant protection
- plant breeding
- postharvest and processing