New Trends in Plant Science in Italy
A topical collection in Plants (ISSN 2223-7747).
Viewed by 35451
Share This Topical Collection
Editor
 Dr. Massimo Galbiati
Dr. Massimo Galbiati
 Dr. Massimo Galbiati
Dr. Massimo Galbiati
E-Mail
Website
Collection Editor
Istituto di Biologia e Biotecnologia Agraria - IBBA - Consiglio Nazionale delle Ricerche - CNR - Via A. Corti 12, 20133 Milano, Italy
Interests: plant genetics; functional genomics; biotechnology; drought stress; stomata; transcription factors; regulation of gene expression
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
This Topical Collection aims to highlight recent advancements in fundamental and applied research in plant science, delivered by Italian scientists. We invite original Research Articles, Short Communications and Systematic Reviews in all fields of plant biology. Topics include, but are not limited to:
- Plant genetics and genomics
- Plant breeding
- Plant physiology
- Development and morphogenesis
- Reproduction
- Stress resistance
- Plant pathology
- Plant nutrition
- Crop production
- Food quality
- New breeding techniques
- Plant biotechnology
Dr. Massimo Galbiati
Collection Editor
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Plants is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript.
The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2700 CHF (Swiss Francs).
Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's
English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- plant biology
- plant physiology
- plant pathology
- plant genetics and genomics
- plant biotechnology
- plant breeding
- crop productivity
- food quality
Published Papers (13 papers)
Open AccessArticle
Exploring the Anticancer Potential of Premna resinosa (Hochst.) Leaf Surface Extract: Discovering New Diterpenes as Heat Shock Protein 70 (Hsp70) Binding Agents
by
Valentina Parisi, Giuliana Donadio, Maria Laura Bellone, Soumia Belaabed, Ammar Bader, Angela Bisio, Valeria Iobbi, Erica Gazzillo, Maria Giovanna Chini, Giuseppe Bifulco, Immacolata Faraone and Antonio Vassallo
Viewed by 1771
Abstract
Premna, a genus consisting of approximately 200 species, predominantly thrives in tropical and subtropical areas. Many of these species have been utilized in ethnopharmacology for diverse medicinal applications. In Saudi Arabia,
Premna resinosa (Hochst.) Schauer (Lamiaceae) grows wildly, and its slightly viscid
[...] Read more.
Premna, a genus consisting of approximately 200 species, predominantly thrives in tropical and subtropical areas. Many of these species have been utilized in ethnopharmacology for diverse medicinal applications. In Saudi Arabia,
Premna resinosa (Hochst.) Schauer (Lamiaceae) grows wildly, and its slightly viscid leaves are attributed to the production of leaf accession. In this study, we aimed to extract the surface accession from fresh leaves using dichloromethane to evaluate the anticancer potential. The plant exudate yielded two previously unknown labdane diterpenes, Premnaresone A and B, in addition to three already described congeners and four known flavonoids. The isolation process was accomplished using a combination of silica gel column chromatography and semi-preparative HPLC, the structures of which were identified by NMR and HRESIMS analyses and a comparison with the literature data of associated compounds. Furthermore, we employed a density functional theory (DFT)/NMR approach to suggest the relative configuration of different compounds. Consequently, we investigated the possibility of developing new chaperone inhibitors by subjecting diterpenes
1–
5 to a Surface Plasmon Resonance-screening, based on the knowledge that oridonin, a diterpene, interacts with Heat Shock Protein 70 (Hsp70) 1A in cancer cells. Additionally, we studied the anti-proliferative activity of compounds
1–
5 on human Jurkat (human T-cell lymphoma) and HeLa (epithelial carcinoma) cell lines, where diterpene 3 exhibited activity in Jurkat cell lines after 48 h, with an IC
50 of 15.21 ± 1.0 µM. Molecular docking and dynamic simulations revealed a robust interaction between compound
3 and Hsp70 key residues.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Phytochemical Profile and In Vitro Bioactivities of Plant-Based By-Products in View of a Potential Reuse and Valorization
by
Ilaria Chiocchio, Manuela Mandrone, Massimo Tacchini, Alessandra Guerrini and Ferruccio Poli
Cited by 8 | Viewed by 1989
Abstract
Wastes and by-products of plant origin are of particular interest to develop a circular economy approach, which attempts to turn them into resources. In this work, thirty-seven neglected plant matrices, including agricultural residues, pest plants, and by-products from the herbal and food industry
[...] Read more.
Wastes and by-products of plant origin are of particular interest to develop a circular economy approach, which attempts to turn them into resources. In this work, thirty-seven neglected plant matrices, including agricultural residues, pest plants, and by-products from the herbal and food industry were extracted and tested for their in vitro anti-tyrosinase, antioxidant, and antibacterial activity against the phytopathogens
Pseudomonas syringae pv.
syringae ATCC 19310 and
Clavibacter michiganensis subsp.
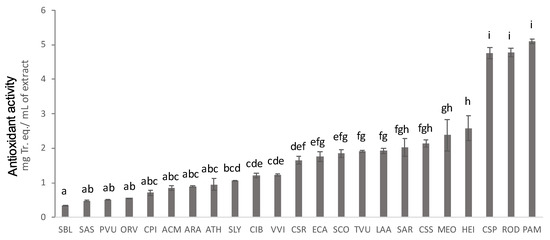
nebraskense ATCC 27822. Antioxidant activity ranged from 0.3 to 5 mg of Tr. eq/mL of plant extract, and extract of
Castanea sativa pericarp (Csp),
Rosa damascena buds (post-distillation) (Rod), and
Prunus amygdalus exocarp and mesocarp (Pam) were the most powerful ones. Csp was also capable of inhibiting tyrosinase (IC
50 = 16.5 µg/mL), as well as three distillation by-products, namely:
Cupressus sempervirens (Css) (IC
50 = 95.5 µg/mL),
Salvia officinalis (Sco) (IC
50 = 87.6 µg/mL), and
Helichrysum italicum (Hei) (IC
50 = 90.1 µg/mL). Five residues from distillation showed antibacterial activity against
C. michiganensis (MICs ranging from 0.125 to 1 mg/mL), namely:
Salvia sclarea L. (Sas),
Salvia rosmarinus Schleid (Sar), Sco, Hei, and Css. The
1H NMR fingerprinting of the bioactive matrices was acquired, detecting primary and secondary metabolites (rosmarinic acid, shikimic acid, sclareol, and hydroxycinnamic acids).
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
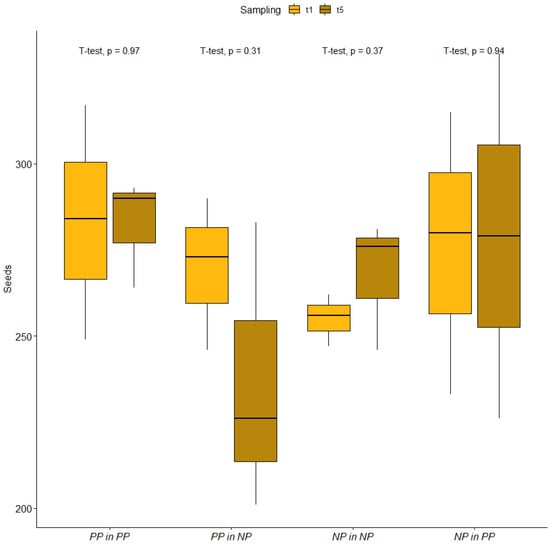
Root and Shoot Growth of a Modern and an Old Tall Durum Wheat (Triticum durum Desf.) Variety under Dual-Purpose Management
by
Roberta Rossi, Giovanni Bitella, Rocco Bochicchio, Rosanna Labella, Francesco Angerame, Marcella Urbano and Mariana Amato
Cited by 2 | Viewed by 2029
Abstract
In dual-purpose cereal systems, the co-production of fodder and grain can increase farm profitability and reduce farming risks. Our work evaluated shoot and root growth in durum wheat (
Triticum durum Desf.) under dual-purpose management in a medium-high rainfall area of southern Italy.
[...] Read more.
In dual-purpose cereal systems, the co-production of fodder and grain can increase farm profitability and reduce farming risks. Our work evaluated shoot and root growth in durum wheat (
Triticum durum Desf.) under dual-purpose management in a medium-high rainfall area of southern Italy. We compared a modern variety (Core) with a tall ancient variety (Saragolle lucana) under traditional (NDP) and dual-purpose (DP) management and tested the hypothesis that clipping plants during the vegetative stage would reduce root growth and dewatering before anthesis, which is advantageous in drought-prone environments. Experiments were conducted in Bella (PZ), Basilicata region, southern Italy (40°42′ N, 15°32′ E) on a clay loam soil in 2021 in a split-plot design on 2 × 2 main plots and 1 × 2 split-plots with 6 replicates. The DP treatment consisted of simulated grazing by clipping plants at 5 cm from the ground 3 months after sowing (at first hollow stem). Forage Biomass was not different at
p = 0.05 between varieties, with an average of 0.58 t ha
−1 DM. Grain yield was not penalized by clipping (
p = 0.05) and did not differ significantly between varieties. SPAD was always lower in the Saragolle variety and lowered by clipping. Defoliation delayed phenology in both cultivars but did not reduce the final number of spikes per square meter. Stomatal conductance was correlated to temperature, did not differ between cultivars, and was not influenced by clipping. Soil water depletion was monitored in modern wheat from the booting stage to the beginning of grain filling. Clipping did not result in a reduction in pre-anthesis water depletion, possibly due to evaporative losses. Root density was markedly reduced by clipping in core variety between 0.20 and 0.60 m and much less in Saragolle. Unclipped Saragolle produced thicker roots and higher root masses compared to clipped plants. Defoliated Saragolle shifted to finer roots, reducing root mass more than length. This may have reduced the metabolic cost of soil exploration, thereby increasing root foraging efficiency.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessEditor’s ChoiceReview
Genetic Improvement of Camelina sativa (L.) Crantz: Opportunities and Challenges
by
Martina Ghidoli, Elena Ponzoni, Fabrizio Araniti, Daniela Miglio and Roberto Pilu
Cited by 13 | Viewed by 3855
Abstract
In recent years, a renewed interest in novel crops has been developing due to the environmental issues associated with the sustainability of agricultural practices. In particular, a cover crop,
Camelina sativa (L.) Crantz, belonging to the Brassicaceae family, is attracting the scientific community’s
[...] Read more.
In recent years, a renewed interest in novel crops has been developing due to the environmental issues associated with the sustainability of agricultural practices. In particular, a cover crop,
Camelina sativa (L.) Crantz, belonging to the Brassicaceae family, is attracting the scientific community’s interest for several desirable features. It is related to the model species
Arabidopsis thaliana, and its oil extracted from the seeds can be used either for food and feed, or for industrial uses such as biofuel production. From an agronomic point of view, it can grow in marginal lands with little or no inputs, and is practically resistant to the most important pathogens of
Brassicaceae. Although cultivated in the past, particularly in northern Europe and Italy, in the last century, it was abandoned. For this reason, little breeding work has been conducted to improve this plant, also because of the low genetic variability present in this hexaploid species. In this review, we summarize the main works on this crop, focused on genetic improvement with three main objectives: yield, seed oil content and quality, and reduction in glucosinolates content in the seed, which are the main anti-nutritional substances present in camelina. We also report the latest advances in utilising classical plant breeding, transgenic approaches, and CRISPR-Cas9 genome-editing.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Subterranean Clover and Sulla as Valuable and Complementary Sources of Bioactive Compounds for Rainfed Mediterranean Farming Systems
by
Maria Giovanna Molinu, Leonardo Sulas, Giuseppe Campesi, Giovanni Antonio Re, Federico Sanna and Giovanna Piluzza
Cited by 4 | Viewed by 2121
Abstract
Mediterranean pasture and forage legumes are important components of sustainable production systems. Subterranean clover and sulla represent key species having proven high agronomic value and traits for production and multiple services. Our research investigated the potential of the abovementioned species as a source
[...] Read more.
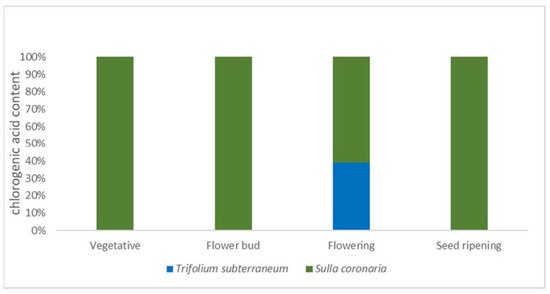
Mediterranean pasture and forage legumes are important components of sustainable production systems. Subterranean clover and sulla represent key species having proven high agronomic value and traits for production and multiple services. Our research investigated the potential of the abovementioned species as a source of phenolic compounds and antioxidants for contributing to support their full exploitation in the fodder, animal welfare, and nutraceutical sectors. Antioxidant capacity, as well as the content of total phenolic compounds and individual phenolic compounds, was determined in subterranean clover and sulla shoots at the vegetative, flower bud, flowering, and seed ripening phenological stages. The antioxidant capacity and the phenolic content were affected significantly by harvest time. In subterranean clover, 10 individual phenolic compounds were detected, and isoflavones were the most abundant (3.19–18.27 mg·g
−1 DM). Eleven phenolic compounds were identified in sulla shoots, and chlorogenic acid (0.76–3.43 mg·g
−1 DM) and diosmin (3.64–4.94 mg·g
−1 DM) were the most represented compounds at the vegetative and flower bud stage. On the basis of our findings, a complementary utilization of both legume species is suggested; this might ensure the exploitation of all phenolic compounds in view of the potential benefits for animal production and health.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Involvement of miRNAs in Metabolic Herbicide Resistance to Bispyribac-Sodium in Echinochloa crus-galli (L.) P. Beauv.
by
Carlo Maria Cusaro, Carolina Grazioli, Enrica Capelli, Anna Maria Picco, Marta Guarise, Enrico Gozio, Pietro Zarpellon and Maura Brusoni
Cited by 2 | Viewed by 2604
Abstract
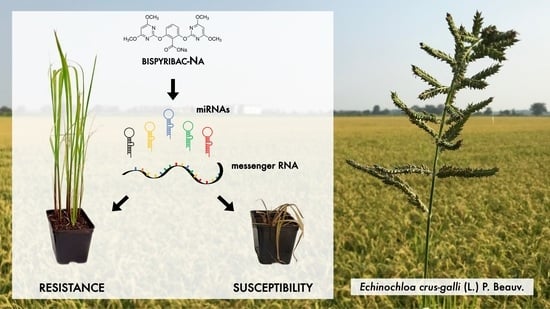
Several mechanisms involved in weed herbicide resistance are unknown, particularly those acting at the epigenetic level, such as the capacity of small-non-coding RNAs (sncRNAs) to target messenger RNAs of genes involved in herbicide detoxification. The transcription of these sncRNAs is stimulated by epigenetic
[...] Read more.
Several mechanisms involved in weed herbicide resistance are unknown, particularly those acting at the epigenetic level, such as the capacity of small-non-coding RNAs (sncRNAs) to target messenger RNAs of genes involved in herbicide detoxification. The transcription of these sncRNAs is stimulated by epigenetic factors, thereby affecting gene expression. This study was carried out in order to evaluate, for the first time in
Echinochloa crus-galli (L.) P. Beauv. (barnyardgrass), the capacity of miRNAs to regulate the expression of genes associated with bispyribac-sodium detoxification. The expression profiles of eight miRNAs with a high degree of complementarity (≥80%) with mRNAs of genes involved in herbicide detoxification (CYP450, GST and eIF4B) were determined by qRT-PCR before and after herbicide spraying. Five of the miRNAs studied (gra-miR7487c, gma-miR396f, gra-miR8759, osa-miR395f, ath-miR847) showed an increased expression after herbicide application in both susceptible and resistant biotypes. All the miRNAs, except gra-miR8759, were more highly expressed in the herbicide-resistant biotypes. In specimens with increased expression of miRNAs, we observed reduced expression of the target genes. The remaining three miRNAs (ata-miR166c-5p, ath-miR396b-5p and osa-miR5538) showed no over-expression after herbicide treatment, and no difference in expression was recorded between susceptible and resistant biotypes. Our results represent a first overview of the capacity of miRNAs to regulate the expression of genes involved in bispyribac-sodium detoxification in the genus
Echinochloa. Further research is required to identify novel miRNAs and target genes to develop more focused and sustainable strategies of weed control.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Seed Bank Conservation and Incipient Seed Development in Orchids Colonizing Mining Wastes: Results of a Field Pilot Experiment
by
Antonio De Agostini, Donatella Cogoni, Annalena Cogoni, Andrea Vacca, Giuseppe Fenu and Pierluigi Cortis
Cited by 1 | Viewed by 1965
Abstract
As they represent actual or potential risks to human and environmental safety and health, abandoned mines are a major global problem. The heavy metal-polluted tailings dump of Barraxiutta (Domusnovas, southwestern Sardinia, Italy) is home to a metallicolous population of
Epipactis tremolsii (Orchidaceae). A
[...] Read more.
As they represent actual or potential risks to human and environmental safety and health, abandoned mines are a major global problem. The heavy metal-polluted tailings dump of Barraxiutta (Domusnovas, southwestern Sardinia, Italy) is home to a metallicolous population of
Epipactis tremolsii (Orchidaceae). A reclamation of the abandoned mine area seems to be approaching, and such an intervention may pose a serious risk for the maintenance of the unique orchid population colonizing the mine wastes. In the present work, the seed packet technique was implemented for the first time to observe orchid seed development in mine wastes. This approach allowed us to explore different seed-based conservation options for the metallicolous orchid population and to gain a deeper grasp of population dynamics and ecology. Four different sowing treatments were set up in the tailing dump and in a near unpolluted site (control site). The field phase of the experiment lasted for 10 months, a period in which the experimental seed bank preservation and incipient seed development were observed and statistically approached. Our findings observed no significant seed loss happening during the experiment, demonstrating the suitability of the seed packet technique to also explore seed bank conservation and development in extreme environmental conditions (i.e., polluted mine wastes). This field method will be a useful tool to further explore the more effective translocation and quasi in situ conservation alternatives for the
E. tremolsii metallicolous population. Incipient and site-specific seed development (non-mycorrhizal stage) was observed during the experiment. A plant–soil fungus interaction at the seed level was also observed, the nature of which remains to be ascertained in further studies providing a longer duration for the field phases.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
A Multi-Level Approach as a Powerful Tool to Identify and Characterize Some Italian Autochthonous Common Bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) Landraces under a Changing Environment
by
Martina Falcione, Melissa Simiele, Alessandra Renella, Gabriella Stefania Scippa, Paolo Di Martino and Dalila Trupiano
Cited by 2 | Viewed by 1744
Abstract
A prime role in matters of agrobiodiversity is held by landraces, which serve as a repository gene pool able to meet sustainable development goals and to face the ongoing challenges of climate change. However, many landraces are currently endangered due to environmental and
[...] Read more.
A prime role in matters of agrobiodiversity is held by landraces, which serve as a repository gene pool able to meet sustainable development goals and to face the ongoing challenges of climate change. However, many landraces are currently endangered due to environmental and socio-economic changes. Thus, effective characterization activities and conservation strategies should be undertaken to prevent their genetic and cultural erosion. In the current study, the morphological, genetic, and biochemical analyses were integrated with stress response-related studies to characterize the diversity of seven Italian autochthonous common bean landraces. The results showed that the morphological descriptors and the neutral molecular markers represent powerful tools to identify and distinguish diversity among landrace populations, but they cannot correlate with the stress tolerance pattern of genetically similar populations. The study also supported the use of proline as a biochemical marker to screen the most salt-sensitive bean landraces. Thus, to fully elucidate the future dynamics of agrobiodiversity and to establish the basis for safeguarding them while promoting their utilization, a multi-level approach should always be included in any local and national program for the characterization/conservation/use of genetic resources. This study should represent the basis for further joint research that effectively contributes to set/achieve Italian priorities towards sustainability in the framework of emerging environmental, societal, and economic challenges.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
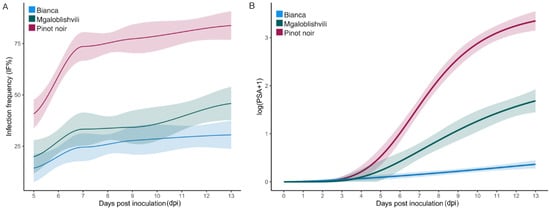
Pathogen Adaptation to American (Rpv3-1) and Eurasian (Rpv29) Grapevine Loci Conferring Resistance to Downy Mildew
by
Elena Marone Fassolo, Beatrice Lecchi, Demetrio Marcianò, Giuliana Maddalena and Silvia Laura Toffolatti
Cited by 2 | Viewed by 1836
Abstract
Durable resistance is a key objective in genetic improvement for disease resistance in grapevines, which must survive for years in the field in the presence of adaptable pathogen populations. In this study, the adaptation of 72 Northern Italian isolates of
Plasmopara viticola,
[...] Read more.
Durable resistance is a key objective in genetic improvement for disease resistance in grapevines, which must survive for years in the field in the presence of adaptable pathogen populations. In this study, the adaptation of 72 Northern Italian isolates of
Plasmopara viticola, the downy mildew agent, has been investigated into Bianca, possessing
Rpv3-1, the most frequently exploited resistance
locus for genetic improvement, and Mgaloblishvili, a
Vitis vinifera variety possessing the newly discovered
Rpv29 locus. Infection parameters (latency period, infection frequency, and disease severity) and oospore production and viability were evaluated and compared to those of Pinot noir, the susceptible reference. The expected levels of disease control were achieved by both resistant cultivars (>90% on Bianca; >25% on Mgaloblishvili), despite the high frequency of isolates able to grow on one (28%) or both (46%) accessions. The disease incidence and severity were limited by both resistant cultivars and the strains able to grow on resistant accessions showed signatures of fitness penalties (reduced virulence, infection frequency, and oospore density). Together, these results indicate an adequate pathogen control but suitable practices must be adopted in the field to prevent the diffusion of the partially adapted
P. viticola strains to protect resistance genes from erosion.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessEditor’s ChoiceArticle
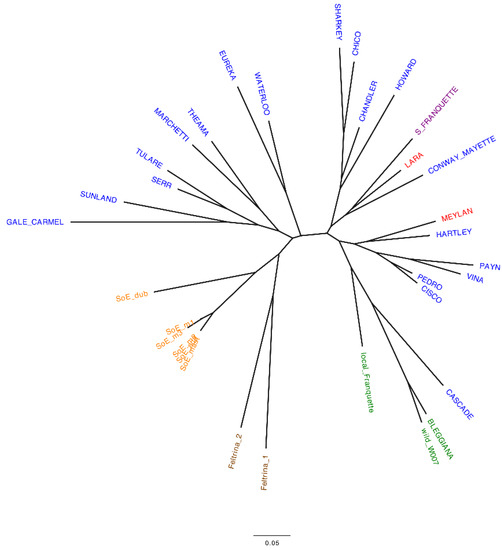
Valorization of Traditional Italian Walnut (Juglans regia L.) Production: Genetic, Nutritional and Sensory Characterization of Locally Grown Varieties in the Trentino Region
by
Erica A. Di Pierro, Pietro Franceschi, Isabella Endrizzi, Brian Farneti, Lara Poles, Domenico Masuero, Iuliia Khomenko, Francesco Trenti, Annarita Marrano, Urska Vrhovsek, Flavia Gasperi, Franco Biasioli, Graziano Guella, Luca Bianco and Michela Troggio
Cited by 14 | Viewed by 3412
Abstract
Juglans regia (L.) is cultivated worldwide for its nutrient-rich nuts. In Italy, despite the growing demand, walnut cultivation has gone through a strong decline in recent decades, which led to Italy being among the top five net importing countries. To promote the development
[...] Read more.
Juglans regia (L.) is cultivated worldwide for its nutrient-rich nuts. In Italy, despite the growing demand, walnut cultivation has gone through a strong decline in recent decades, which led to Italy being among the top five net importing countries. To promote the development of local high-quality Italian walnut production, we devised a multidisciplinary project to highlight the distinctive traits of three varieties grown in the mountainous region Trentino (northeast of Italy): the heirloom ‘Bleggiana’, a second local accession called
local Franquette and the French cultivar ‘Lara’, recently introduced in the local production to increase yield. The genetic characterization confirmed the uniqueness of ‘Bleggiana’ and revealed
local Franquette as a newly described autochthonous variety, thus named ‘Blegette’. The metabolic profiles highlighted a valuable nutritional composition of the local varieties, richer in polyphenols and with a lower ω-6/ω-3 ratio than the commercial ‘Lara’. ‘Blegette’ obtained the highest preference scores from consumers for both the visual aspect and tasting; however, the volatile organic compound profiles did not discriminate among the characterized cultivars. The described local varieties represent an interesting reservoir of walnut genetic diversity and quality properties, which deserve future investigation on agronomically useful traits (e.g., local adaptation and water usage) for a high-quality and sustainable production.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Insight into Carbohydrate Metabolism and Signaling in Grapevine Buds during Dormancy Progression
by
Valeria De Rosa, Rachele Falchi, Erica Moret and Giannina Vizzotto
Cited by 5 | Viewed by 2764
Abstract
Perennial fruit crops enter dormancy to ensure bud tissue survival during winter. However, a faster phenological advancement caused by global warming exposes bud tissue to a higher risk of spring frost damage. Tissue dehydration and soluble sugars accumulation are connected to freezing tolerance,
[...] Read more.
Perennial fruit crops enter dormancy to ensure bud tissue survival during winter. However, a faster phenological advancement caused by global warming exposes bud tissue to a higher risk of spring frost damage. Tissue dehydration and soluble sugars accumulation are connected to freezing tolerance, but non-structural carbohydrates also act as metabolic substrates and signaling molecules. A deepened understanding of sugar metabolism in the context of winter freezing resistance is required to gain insight into adaptive possibilities to cope with climate changes. In this study, the soluble sugar content was measured in a cold-tolerant grapevine hybrid throughout the winter season. Moreover, the expression of drought-responsive hexose transporters
VvHT1 and
VvHT5, raffinose synthase
VvRS and grapevine ABA-, Stress- and Ripening protein
VvMSA was analyzed. The general increase in sugars in December and January suggests that they can participate in protecting bud tissues against low temperatures. The modulation of
VvHT5,
VvINV and
VvRS appeared consistent with the availability of the different sugar species; challenging results were obtained for
VvHT1 and
VvMSA, suggesting interesting hypotheses about their role in the sugar–hormone crosstalk. The multifaceted role of sugars on the intricate phenomenon, which is the response of dormant buds to changing temperature, is discussed.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
The Delay of Raphanus raphanistrum subsp. sativus (L.) Domin Seed Germination Induced by Coumarin Is Mediated by a Lower Ability to Sustain the Energetic Metabolism
by
Fabrizio Araniti, Bhakti Prinsi and Luca Espen
Cited by 3 | Viewed by 2234
Abstract
In the present study, the mode of action of coumarin using the germination process as a target was investigated. A dose–response curve, built using a range of concentrations from 0 to 800 µM, allowed us to identify a key concentration (400 µM) inhibiting
[...] Read more.
In the present study, the mode of action of coumarin using the germination process as a target was investigated. A dose–response curve, built using a range of concentrations from 0 to 800 µM, allowed us to identify a key concentration (400 µM) inhibiting the germination process, reducing its speed without compromising seed development. Successively, short time-course (0–48 h) experiments were carried out to evaluate the biochemical and metabolic processes involved in coumarin-induced germination delay. The results pointed out that coumarin delayed K
+, Ca
2+, and Mg
2+ reabsorption, suggesting a late membrane reorganisation. Similarly, seed respiration was inhibited during the first 24 h but recovered after 48 h. Those results agreed with ATP levels, which followed the same trend. In addition, the untargeted metabolomic analysis allowed to identify, among the pathways significantly impacted by the treatment, amino acids metabolism, the TCA cycle, and the glyoxylate pathway. The results highlighted that coumarin was able to interact with membranes reorganisation, delaying them and reducing the production of ATP, as also supported by pathway analysis and cell respiration. The in vivo
31P-NMR analysis supported the hypothesis that the concentration chosen was able to affect plant metabolism, maintaining, on the other hand, its viability, which is extremely important for studying natural compounds’ mode of action.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
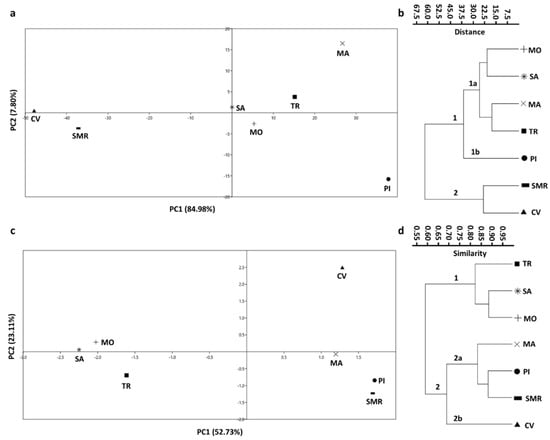
A ddRADseq Survey of the Genetic Diversity of Rye (Secale cereale L.) Landraces from the Western Alps Reveals the Progressive Reduction of the Local Gene Pool
by
Martino Adamo, Massimo Blandino, Luca Capo, Simone Ravetto Enri, Anna Fusconi, Michele Lonati and Marco Mucciarelli
Cited by 4 | Viewed by 2534
Abstract
Rye (
Secale cereale L.) has been at the basis of agriculture for centuries in most mountainous and northern areas of Eurasia, because it is more resistant than other cereals to low temperatures and poor soils. Rye deserves to be re-evaluated as a
[...] Read more.
Rye (
Secale cereale L.) has been at the basis of agriculture for centuries in most mountainous and northern areas of Eurasia, because it is more resistant than other cereals to low temperatures and poor soils. Rye deserves to be re-evaluated as a source of “environmentally resilient” genes in the future as well, and particularly in a perspective to grow cereals able to withstand global warming. According to recent studies, modern rye varieties have a relatively narrow genetic pool, a condition that is worsening in the most recent breeding processes. The preservation of local landraces as unique sources of genetic diversity has therefore become important, in order to preserve the genetic heritage of rye. In this study, genetic diversity of rye landraces collected in a sector of the Italian Alps particularly suited to traditional agriculture was investigated using the ddRADseq technique. A few landraces still managed with family farming turned out to be genetically distant from the commercial varieties currently in use, highlighting that the phenomenon of homogenization of the local genetic pool can be still circumvented. Ex situ conservation of genetically divergent landraces is a valid tool to avoid the dissipation of an as yet unexplored genetic potential.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Planned Papers
The below list represents only planned manuscripts. Some of these
manuscripts have not been received by the Editorial Office yet. Papers
submitted to MDPI journals are subject to peer-review.
Title: Valorisation of traditional walnut (Juglans regia L.) production: genetic, nutritional and sensory characterization of locally grown varieties
Authors: Di Pierro Erica
Affiliation: Research and Innovation Centre, Fondazione Edmund Mach, Via E. Mach 1, 38098 San Michele all’Adige, Italy
Abstract: Juglans regia (L.), commonly named Persian or English walnut, is cultivated worldwide for its nutrient-rich nuts. Walnut world production keeps increasing, exceeding three million tons since 2011, with China, USA and Iran as leading producing countries. In Italy, despite the constantly growing demand, walnut cultivation went through a strong decline in the last decades. However, the climate and the environmental conditions of the Italian peninsula are well suited to walnut cultivation of both traditional local Italian accessions and international commercial varieties. To undertake one step in the valorisation of the Italian walnut production, we devised a multidisciplinary project to characterize three selected varieties, locally grown in a restricted area of the mountainous region Trentino, in the north-east of Italy: the known traditional Bleggiana variety, locally cultivated and propagated by grafting since decades; a second heirloom accession (local Franquette), traditionally propagated by grafting by local growers, and the commercial variety ‘Lara’, recently introduced in the local production. In order to highlight distinctive traits that uniquely define each variety, and to address the consumer’s choice and orientation, each accession was described by means of i) genetic profiles, to better understand how they relate to one another − both locally and globally; ii) metabolic (polyphenols and lipids) and volatiles profiles and iii) sensory evaluation.