Multidimensional Particle Properties: Characterization, Description, Separation
A topical collection in Powders (ISSN 2674-0516).
Viewed by 22822Editors
Interests: mechanical separation processes; solid liquid separation; recycling and mineral processing; particle-particle interactions; particle characterization
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Interests: particle classification; surface modifications; mechanical properties; charging behavior; cold and hot plasmas
Interests: nanoparticles; aerosols; nanomaterials and thin films; aerosol reactors; population balances; size classification; aerosol instrumentation; deep learning
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
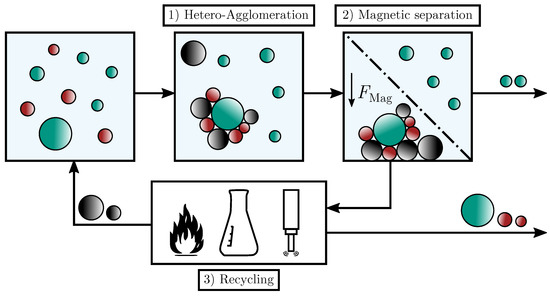
In 2016 the Senate of the German Science Foundation implemented the priority program 2045 “MehrDimPart - highly specific multidimensional fractionation of fine particles with technical relevance”. The joint research within the priority program aims at the research on and development of technological approaches which allow the separation/fractionation of fine particles below 10 μm. This separation has to meet more than one separation criteria (e.g., size and composition or size and shape), which ultimately allows the production of highly specific particle systems.
Highly specific particle systems form the basis for high-quality industrial products. Intermediate particle systems with defined multi-dimensional specifications are essential and quality-determining for the production of ceramic and powder metallurgical components, coatings, printed products, porous functional structures, particle-reinforced polymers, electrodes in electrochemical energy storage systems or electronic assemblies, for example, in the field of printed electronics.
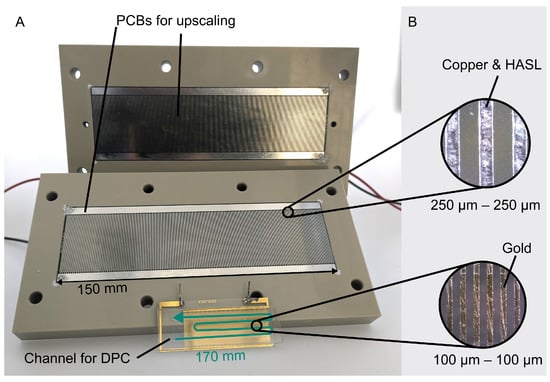
Downstream of particle production via synthesis or comminution, the particle systems have to undergo further process steps to reach the specified quality (i.e., size distribution and distribution of further properties). These steps include fractionation, that is, the selective separation of the particle system according to particle characteristics. Comparable processes are also used in mineral processing technology to extract particles containing valuable substances from natural or secondary raw materials.
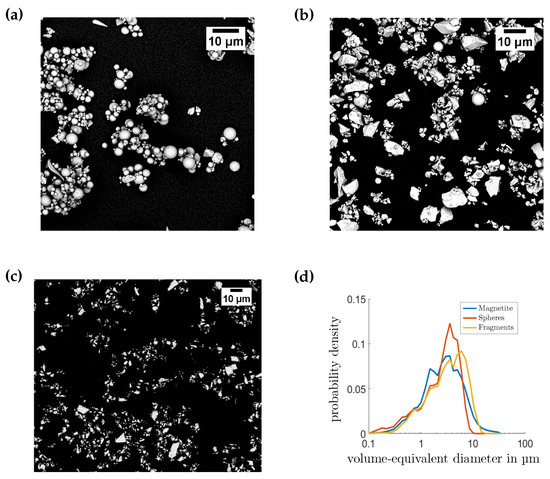
Since the characteristic lengths of both the technical structures and the primary and secondary raw materials are continuously decreasing, fine, highly specific particle systems will have to be processed or produced in the future. The technology required for this is reaching its limits since in this size range the physical separation principles used lose their effectiveness and selectivity.
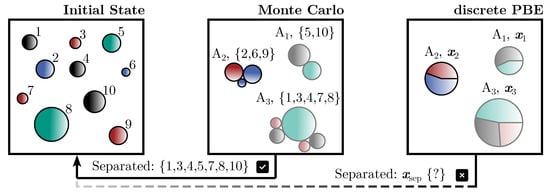
This Topical Collection addresses the characterization and separation/fractionation of particle systems with multi-dimensional properties. The separation/fractionation is therefore following more than one particle property, and thus is multi-dimensional. Different technological approaches will be presented, as will fundamental methods for process control and multidimensional particle characterization. The processes, technologies, and approaches are grouped into three classes: investigations on fundamental mechanisms for separation, applications of new process concepts and applications of established separation/fractionation concepts adopted to the size scale.
Prof. Dr. Urs Alexander Peuker
Prof. Dr. Alfred P. Weber
Prof. Dr. Einar Kruis
Prof. Dr. Doris Segets
Collection Editors
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Powders is an international peer-reviewed open access quarterly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 1000 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- multidimensional particle properties
- separation features
- multidimensional separation function
- multidimensional tromp curve
- selective agglomeration
- flow field fractionation
- electrostatic separation
- forced triboelectric charging
- separation at interfaces
- particle characterization
- aspect ratio/intergrowth
- flotation
- electrophoresis
- multivariate transfer function