Current and Prospective Protein Biomarkers of Lung Cancer
Abstract
:1. Introduction
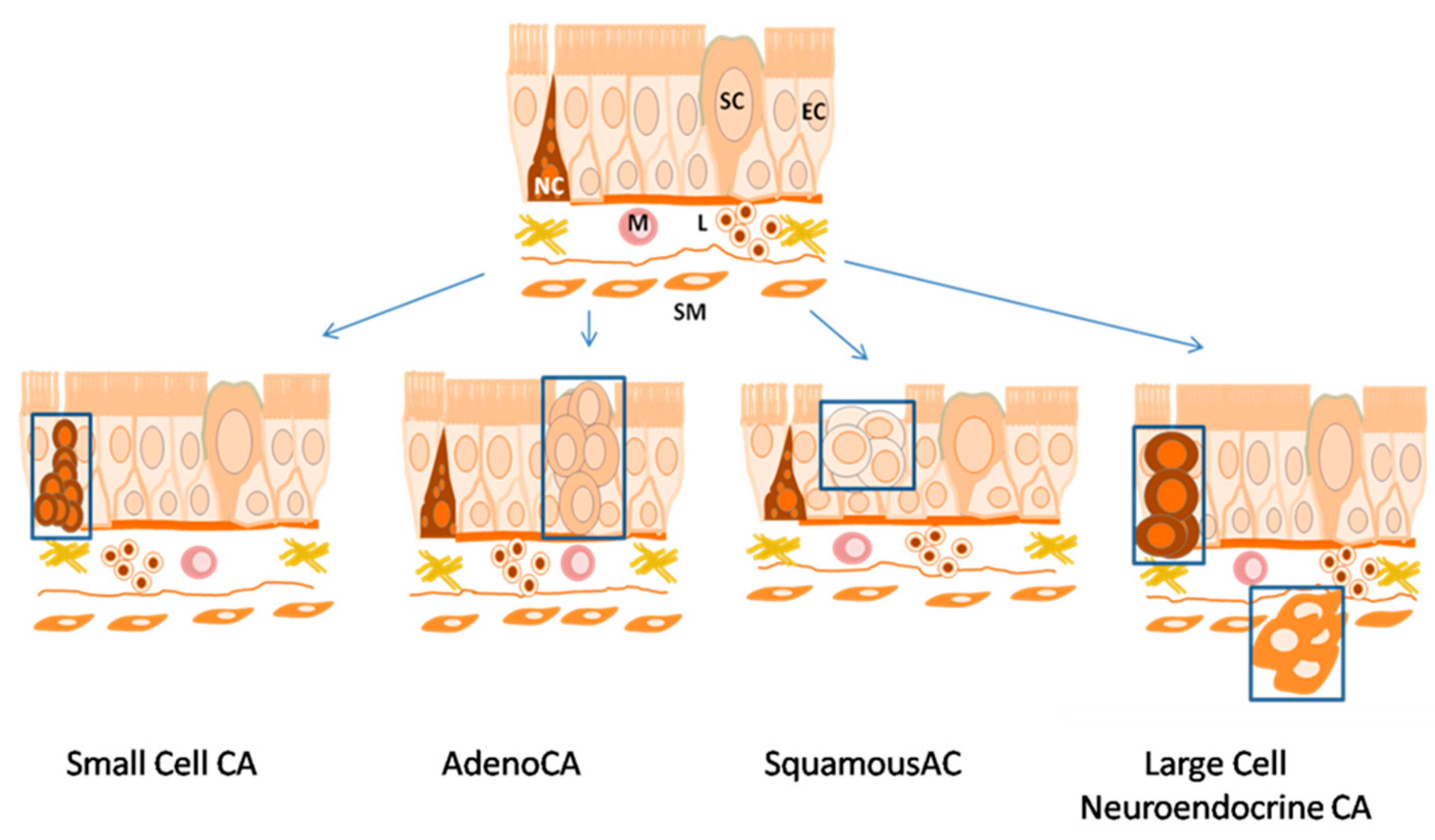
2. Histology of Lung Cancer Types
3. Methods Currently Employed to Diagnose Lung Cancer
4. Circulating Biomarkers of Carcinogenesis
5. Proteomic-Based Lung Cancer Biomarker Search
6. Protein Biomarkers Used in Lung Cancer Diagnosis
7. Aptamer-Based Affinity Enrichment Methods for Lung Cancer Biomarker Discovery
8. Lung Cancer Diagnosis Using Aptamers
Aptahistochemistry for Identification of Lung Cancer Biomarkers
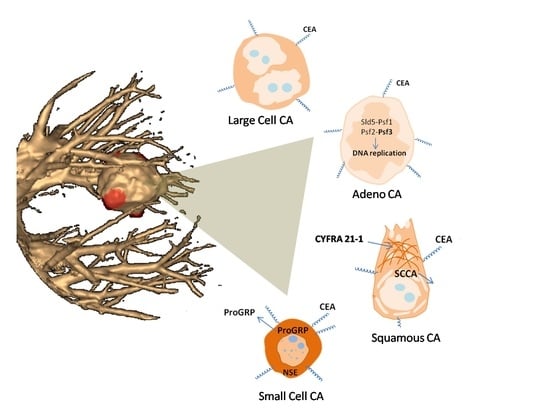
9. Biomarkers of Different Histological Lung Cancer Types
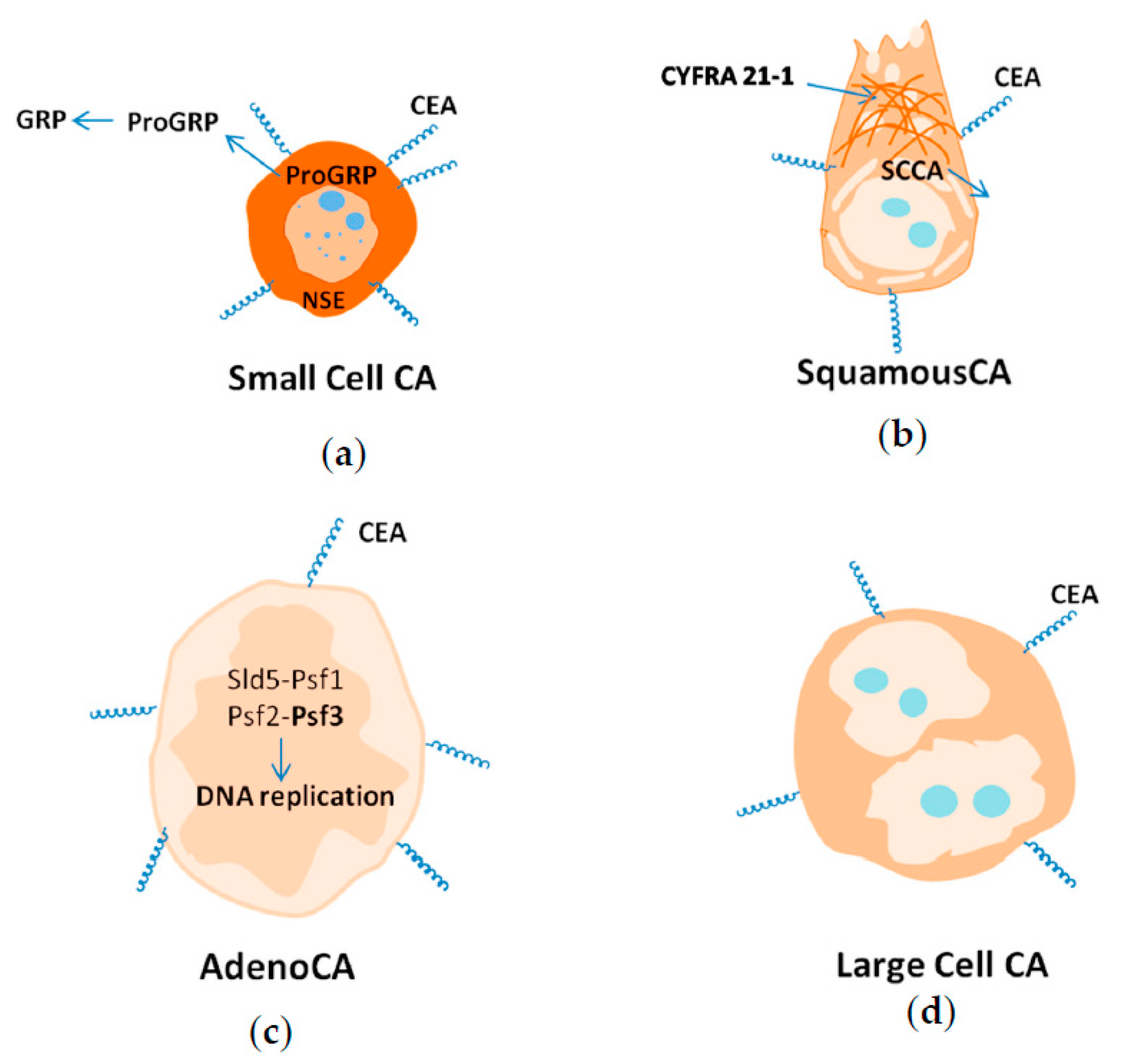
9.1. Small Cell Lung Cancer
9.2. Squamous Lung Cancer
9.3. Adenocarcinoma
9.4. Large Cell Carcinoma
9.5. Adenosquamous Carcinoma
9.6. Large Cell Neuroendocrine Carcinoma
9.7. Protein Biomarkers to Main Histological Types of Lung Cancer
- CEA is a biomarker specific for all lung cancer types;
- NSE is a biomarker of NSCLC, and a marker of metastasis;
- CYFRA21-1 is a general biomarker for screening for lung cancer, and a biomarker of squamous lung cancer in metastatic form;
- SCCA is a biomarker of squamous lung cancer;
- PSF3 is a biomarker of adenocarcinoma;
- ProGRP is a biomarker of SCLC;
- SCCA and mucin are biomarkers of adenosquamous carcinoma;
- SST is a biomarker of large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma.
10. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Arya, S.; Bhansali, S. Lung cancer and its early detection using biomarker-based biosensors. Chem. Rev. 2011, 111, 6783–6809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brambilla, E.; Travis, W.D. Lung cancer. In World Cancer Report; Stewart, B.W., Wild, C.P., Eds.; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Dikshit, R.; Eser, S.; Mathers, C.; Rebelo, M.; Parkin, D.; Forman, D.; Bray, F. Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: Sources, methods and major patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int. J. Cancer 2015, 136, E359–E386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sung, H.; Cho, J. Biomarkers for the lung cancer diagnosis and their advances in proteomics. BMB Rep. 2008, 41, 615–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiorentino, F.; Macaluso, M.; Miranda, F.; Montanari, M.; Russo, A.; Bagella, L.; Giordano, A. CTCF and BORIS regulate Rb2/p130 gene transcription: A novel mechanism and a new paradigm for understanding the biology of lung cancer. Mol. Cancer Res. 2011, 9, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, L.; Dowell, J.; Garwood, D.; Spangler, A.; Choy, H. Prophylactic cranial irradiation with combined modality therapy for patients with locally advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Semin. Oncol. 2005, 32, 293–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaspar, L.; Scott, C.; Rotman, M.; Asbell, S.; Phillips, T.; Wasserman, T.; McKenna, W.; Byhardt, R. Recursive partitioning analysis (RPA) of prognostic factors in three radiation therapy oncology group (RTOG) brain metastases trials. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 1997, 37, 745–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnabel, P.; Junker, K. Pulmonary neuroendocrine tumors in the new WHO 2015 classification. Start of breaking new grounds? Pathologe 2015, 36, 283–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Travis, W. Update on small cell carcinoma and its differentiation from squamous cell carcinoma and other non-small cell carcinomas. Mod. Pathol. 2012, 25, S18–S30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weynants, P.; Humblet, Y.; Canon, J.; Symann, M. Biology of small-cell lung-cancer—An overview. Eur. Respir. J. 1990, 3, 699–714. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Muller, K. Histological classification and histogenesis of lung-cancer. Eur. J. Respir. Dis. 1984, 65, 4–19. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dogan, S.; Shen, R.; Ang, D.; Johnson, M.; D’Angelo, S.; Paik, P.; Brzostowski, E.; Riely, G.; Kris, M.; Zakowski, M.; et al. Molecular epidemiology of EGFR and KRAS mutations in 3026 lung adenocarcinomas: Higher susceptibility of women to smoking-related KRAS-mutant cancers. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 18, 6169–6177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imyanitov, E.; Demidova, I.; Gordiev, M.; Filipenko, M.; Kekeyeva, T.; Moliaka, Y.; Gervas, P.; Kozhemyako, V.; Vodolazhskiy, D.; Sergeyeva, L.; et al. Distribution of EGFR mutations in 10,607 Russian patients with lung cancer. Mol. Diagn. Ther. 2016, 20, 401–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capelozzi, V. Role of immunohistochemistry in the diagnosis of lung cancer. Jornal Brasileiro De Pneumologia 2009, 35, 375–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marshall, H.; Bowman, R.; Yang, I.; Fong, K.; Berg, C. Screening for lung cancer with low-dose computed tomography: A review of current status. J. Thorac. Dis. 2013, 5, S524–S539. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vazquez, M.; Koizurni, J.; Henschke, C.; Yankelevitz, D. Reliability of cytologic diagnosis of early lung cancer. Cancer Cytopathol. 2007, 111, 252–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabinowits, G.; Gercel-Taylor, C.; Day, J.; Taylor, D.; Kloecker, G. Exosomal microrna: A diagnostic marker for lung cancer. Clin. Lung Cancer 2009, 10, 42–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitas, M.; Hoover, L.; Silvestri, G.; Reed, C.; Green, M.; Turrisi, A.; Sherman, C.; Mikhitarian, K.; Cole, D.; Block, M.; et al. Lunx is a superior molecular marker for detection of non-small lung cell cancer in peripheral blood. J. Mol. Diagn. 2003, 5, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, H.; Lewis, C.; Thomas, P. Exhaled breath analysis: Novel approach for early detection of lung cancer. Lung Cancer 2009, 63, 164–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jantus-Lewintre, E.; Usó, M.; Sanmartín, E.; Camps, C. Update on biomarkers for the detection of lung cancer. Lung Cancer Targ. Ther. 2012, 3, 21–29. [Google Scholar]
- Andre, F.; Schartz, N.; Movassagh, M.; Flament, C.; Pautier, P.; Morice, P.; Pomel, C.; Lhomme, C.; Escudier, B.; Le Chevalier, T.; et al. Malignant effusions and immunogenic tumour-derived exosomes. Lancet 2002, 360, 295–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montani, F.; Marzi, M.; Dezi, F.; Dama, E.; Carletti, R.; Bonizzi, G.; Bertolotti, R.; Bellomi, M.; Rampinelli, C.; Maisonneuve, P.; et al. Mir-test: A blood test for lung cancer early detection. Cancer Res. 2015, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagrath, S.; Sequist, L.; Maheswaran, S.; Bell, D.; Irimia, D.; Ulkus, L.; Smith, M.; Kwak, E.; Digumarthy, S.; Muzikansky, A.; et al. Isolation of rare circulating tumour cells in cancer patients by microchip technology. Nature 2007, 450, 1235–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sozzi, G.; Boeri, M.; Rossi, M.; Verri, C.; Suatoni, P.; Bravi, F.; Roz, L.; Conte, D.; Grassi, M.; Sverzellati, N.; et al. Clinical utility of a plasma-based miRNA signature classifier within computed tomography lung cancer screening: A correlative MILD trial study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 32, 768–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sozzi, G.; Conte, D.; Leon, M.; Cirincione, R.; Roz, L.; Ratcliffe, C.; Roz, E.; Cirenei, N.; Bellomi, M.; Pelosi, G.; et al. Quantification of free circulating DNA as a diagnostic marker in lung cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2003, 21, 3902–3908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valenti, R.; Huber, V.; Filipazzi, P.; Pilla, L.; Sovena, G.; Villa, A.; Corbelli, A.; Fais, S.; Parmiani, G.; Rivoltini, L. Human tumor-released microvesicles promote the differentiation of myeloid cells with transforming growth factor-β-mediated suppressive activity on T lymphocytes. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 9290–9298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paci, M.; Rapicetta, C.; Maramotti, S. New biomarkers for lung cancer. Expert Opin. Med. Diagn. 2010, 4, 201–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, H. Expression and function of squamous cell carcinoma antigen. Anticancer Res. 1996, 16, 2149–2153. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Doseeva, V.; Colpitts, T.; Gao, G.; Woodcock, J.; Knezevic, V. Performance of a multiplexed dual analyte immunoassay for the early detection of non-small cell lung cancer. J. Transl. Med. 2015, 13, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Indovina, P.; Marcelli, E.; Maranta, P.; Tarro, G. Lung cancer proteomics: Recent advances in biomarker discovery. Int. J. Proteom. 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, S.; Sung, H.; Ahn, J.; Park, J.; Lee, S.; Park, C.; Cho, J. The haptoglobin β chain as a supportive biomarker for human lung cancers. Mol. Biosyst. 2011, 7, 1167–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maciel, C.; Junqueira, M.; Kawamura, M.; Paschoal, M.; Duarte, R.; Carvalho, M.; Domone, G. Differential proteomic serum pattern of low molecular weight proteins expressed by adenocarcinoma lung cancer patients. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2004, 3, S215. [Google Scholar]
- Kokkonen, N.; Ulibarri, I.; Kauppila, A.; Luosujarvi, H.; Rivinoja, A.; Pospiech, H.; Kellokumpu, I.; Kellokumpu, S. Hypoxia upregulates carcinoembryonic antigen expression in cancer cells. Int. J. Cancer 2007, 121, 2443–2450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ueda, K.; Saichi, N.; Takami, S.; Kang, D.; Toyama, A.; Daigo, Y.; Ishikawa, N.; Kohno, N.; Tamura, K.; Shuin, T.; et al. A comprehensive peptidome profiling technology for the identification of early detection biomarkers for lung adenocarcinoma. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e18567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, X.; Hood, B.; Sun, M.; Conrads, T.; Day, R.; Weissfeld, J.; Siegfried, J.; Bigbee, W. Lung cancer serum biomarker discovery using glycoprotein capture and liquid chromatography mass spectrometry. J. Proteome Res. 2010, 9, 6440–6449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bharti, A.; Ma, P.C.; Mauliketal, G. Haptoglobin α-subunit and hepatocyte growth factor can potentially serve as serum tumor biomarkers in small cell lung cancer. Anticancer Res. 2004, 24, 1031–1038. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dai, S.; Wang, X.; Liu, L.; Liu, J.; Wu, S.; Huang, L.; Xiao, X.; He, D. Discovery and identification of serum amyloid a protein elevated in lung cancer serum. Sci. China Ser. C Life Sci. 2007, 50, 305–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Liu, J.; Dai, S.; Wang, X.; Wu, S.; Wang, J.; Huang, L.; Xiao, X.; He, D. Reduced transthyretin expression in sera of lung cancer. Cancer Sci. 2007, 98, 1617–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Liu, J.; Wang, Y.; Dai, S.; Wang, X.; Wu, S.; Wang, J.; Huang, L.; Xiao, X.; He, D. A combined biomarker pattern improves the discrimination of lung cancer. Biomarkers 2011, 16, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howard, B.; Wang, M.; Campa, M.; Corro, C.; Fitzgerald, M.; Patz, E. Identification and validation of a potential lung cancer serum biomarker detected by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization-time of flight spectra analysis. Proteomics 2003, 3, 1720–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, G.; Wu, Q.; Liu, G.; Song, X.; Zhang, J. Psoriasin (S100A7) is a novel biomarker for lung squamous cell carcinoma in humans (retracted article. See vol. 16, 40, 2016). Cancer Cell Int. 2015, 15, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Z.; Chen, X.; Cui, L.; Si, H.; Lu, H.; Liu, S. Prediction of lung cancer based on serum biomarkers by gene expression programming methods. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2014, 15, 9367–9373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Liu, J.; Yue, D.; Gao, L.; Wang, D.; Zhang, H.; Wang, C. Clinical significance of E-cadherin, β-catenin, vimentin and S100A4 expression in completely resected squamous cell lung carcinoma. J. Clin. Pathol. 2013, 66, 937–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diamandis, E.; Goodglick, L.; Planque, C.; Thomquist, M. Pentraxin-3 is a novel biomarker of lung carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 2395–2399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goetsch, C.M. Genetic tumor profiling and genetically targeted cancer therapy. Semin. Oncol. Nurs. 2011, 27, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.; Oh, I.; Shin, M.; Park, J.; Choi, H.; Ban, H.; Kim, K.; Kim, Y.; Shin, J.; Ryang, D.; et al. Plasma proGRP concentration is sensitive and specific for discriminating small cell lung cancer from nonmalignant conditions or non-small cell lung cancer. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2011, 26, 625–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landi, M.; Zhao, Y.; Rotunno, M.; Koshiol, J.; Liu, H.; Bergen, A.; Rubagotti, M.; Goldstein, A.; Linnoila, I.; Marincola, F.; et al. Microrna expression differentiates histology and predicts survival of lung cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2010, 16, 430–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foa, P.; Fornier, M.; Miceli, R.; Seregni, E.; Santambrogio, L.; Nosotti, M.; Cataldo, I.; Sala, M.; Caldiera, S.; Bombardieri, E. Tumour markers CEA, NSE, SCC, TPA and CYFRA 21.1 in resectable non-small cell lung cancer. Anticancer Res. 1999, 19, 3613–3618. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tessitore, A.; Gaggiano, A.; Cicciarelli, G.; Verzella, D.; Capece, D.; Fischietti, M.; Zazzeroni, F.; Alesse, E. Serum biomarkers identication mass spectrometry in high-mortality tumors. Int. J. Proteom. 2013, 2013, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jett, J.; Peek, L.; Fredericks, L.; Jewell, W.; Pingleton, W.; Robertson, J. Audit of the autoantibody test, EarlyCDT®-Lung, in 1600 patients: An evaluation of its performance in routine clinical practice. Lung Cancer 2014, 83, 51–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chapman, C.; Thorpe, A.; Murray, A.; Parsy-Kowalska, C.; Allen, J.; Stafford, K.; Chauhan, A.; Kite, T.; Maddison, P.; Robertson, J. Immunobiomarkers in small cell lung cancer: Potential early cancer signals. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 1474–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizuguchi, S.; Nishiyama, N.; Iwata, T.; Nishida, T.; Izumi, N.; Tsukioka, T.; Inoue, K.; Uenishi, T.; Wakasa, K.; Suehiro, S. Serum Sialyl Lewis(x) and cytokeratin 19 fragment as predictive factors for recurrence in patients with stage I non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 2007, 58, 369–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pujol, J.; Grenier, J.; Daures, J.; Daver, A.; Pujol, H.; Michel, F. Serum fragment of cytokeratin subunit-19 measured by CYFRA-21-1 immunoradiometric assay as a marker of lung-cancer. Cancer Res. 1993, 53, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Okada, M.; Nishio, W.; Skaamoto, T.; Uchino, K.; Yuki, T.; Nakagawa, A.; Tsubota, N. Effect of hystologic type and smoking status on interpretation of serum carcinoembryonic antigen value in non-small cell lung carcinoma. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2004, 78, 1004–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arrieta, O.; Saavedra-Perez, D.; Kuri, R.; Aviles-Salas, A.; Martinez, L.; Mendoza-Posada, D.; Castillo, P.; Astorga, A.; Guzman, E.; de la Garza, J. Brain metastasis development and poor survival associated with carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) level in advanced non-small cell lung cancer: A prospective analysis. BMC Cancer 2009, 9, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ginsberg, M.; Grewal, R.; Heelan, R. Lung cancer. Radiol. Clin. N. Am. 2007, 45, 21–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuespert, K.; Pils, S.; Hauck, C. Ceacams: Their role in physiology and pathophysiology. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2006, 18, 565–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lakshmanan, I.; Ponnusamy, M.; Macha, M.; Haridas, D.; Majhi, P.; Kaur, S.; Jain, M.; Batra, S.; Ganti, A. Mucins in lung cancer diagnostic, prognostic, and therapeutic implications. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2015, 10, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okabe, N.; Ezaki, J.; Yamaura, T.; Muto, S.; Osugi, J.; Tamura, H.; Imai, J.; Ito, E.; Yanagisawa, Y.; Honma, R.; et al. FAM83B is a novel biomarker for diagnosis and prognosis of lung squamous cell carcinoma. Int. J. Oncol. 2015, 46, 999–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okamura, K.; Takayama, K.; Izumi, M.; Harada, T.; Furuyama, K.; Nakanishi, Y. Diagnostic value of CEA and CYFRA 21-1 tumor markers in primary lung cancer. Lung Cancer 2013, 80, 45–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wojcik, E.; Kulpa, J.; Sas-Korczynska, B.; Korzeniowski, S.; Jakubowicz, J. ProGRP and NSE in therapy monitoring in patients with small cell lung cancer. Anticancer Res. 2008, 28, 3027–3033. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zamay, G.; Kolovskaya, O.; Zamay, T.; Glazyrin, Y.; Krat, A.; Zubkova, O.; Spivak, E.; Wehbe, M.; Gargaun, A.; Muharemagic, D.; et al. Aptamers selected to postoperative lung adenocarcinoma detect circulating tumor cells in human blood. Mol. Ther. 2015, 23, 1486–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bastawisy, A.; Elazzouny, M.; Mohammed, G.; Awadallah, A.; Behiry, E. Serum cytokeratin 19 fragment in advanced lung cancer: Could we eventually have a serum tumor marker? Ecancer 2014, 394, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Berezovski, M.; Lechmann, M.; Musheev, M.; Mak, T.; Krylov, S. Aptamer-facilitated biomarker discovery (AptaBiD). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 9137–9143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Hayward, C.; Fong, P.; Dominguez, M.; Hunsucker, S.; Lee, L.; McLean, M.; Law, S.; Butler, H.; Schirm, M.; et al. A blood-based proteomic classifier for the molecular characterization of pulmonary nodules. Sci. Transl. Med. 2013, 5, 207ra142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molina, R.; Filella, X.; Auge, J. Progrp: A new biomarker for small cell lung cancer. Clin. Biochem. 2004, 37, 505–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stovold, R.; Blackhall, F.; Meredith, S.; Hou, J.; Dive, C.; White, A. Biomarkers for small cell lung cancer: Neuroendocrine, epithelial and circulating tumour cells. Lung Cancer 2012, 76, 263–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gandara, D.; Li, T.; Lara, P.; Mack, P.; Kelly, K.; Miyamoto, S.; Goodwin, N.; Beckett, L.; Redman, M. Algorithm for codevelopment of new drug-predictive biomarker combinations: Accounting for inter- and intrapatient tumor heterogeneity. Clin. Lung Cancer 2012, 13, 321–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyake, Y.; Kodama, T.; Yamaguchi, K. Pro-gastrin-releasing peptide(31–98) is a specific tumor-marker in patients with small-cell lung-carcinoma. Cancer Res. 1994, 54, 2136–2140. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shimizu, K.; Yukawa, T.; Okita, R.; Saisho, S.; Maeda, A.; Nojima, Y.; Nakata, M. Cyclooxygenase-2 expression is a prognostic biomarker for non-small cell lung cancer patients treated with adjuvant platinum-based chemotherapy. World J. Surg. Oncol. 2015, 13, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chee, J.; Naran, A.; Misso, N.; Thompson, P.; Bhoola, K. Expression of tissue and plasma kallikreins and kinin B1 and B2 receptors in lung cancer. Biol. Chem. 2008, 389, 1225–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pachter, J.; de Vries, H.; Fabry, Z. The blood-brain barrier and its role in immune privilege in the central nervous system. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2003, 62, 593–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fortes, D.; Allen, M.; Lowe, V.; Shen, K.; Wigle, D.; Cassivi, S.; Nichols, F.; Deschamps, C. The sensitivity of 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography in the evaluation of metastatic pulmonary nodules. Eur. J. Cardio Thorac. Surg. 2008, 34, 1223–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kikuchi, T.; Hassanein, M.; Amann, J.; Liu, Q.; Slebos, R.; Rahman, S.; Kaufman, J.; Zhang, X.; Hoeksema, M.; Harris, B.; et al. In-depth proteomic analysis of nonsmall cell lung cancer to discover molecular targets and candidate biomarkers. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2012, 11, 916–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tane, S.; Sakai, Y.; Hokka, D.; Okuma, H.; Ogawa, H.; Tanaka, Y.; Uchino, K.; Nishio, W.; Yoshimura, M.; Maniwa, Y. Significant role of Psf3 expression in non-small-cell lung cancer. Cancer Sci. 2015, 106, 1625–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hotta, K.; Segawa, Y.; Takigawa, N.; Kishino, D.; Saeki, H.; Nakata, M.; Mandai, K.; Eguchi, K. Evaluation of the relationship between serum carcinoembryonic antigen level and treatment outcome in surgically resected clinical-stage I patients with non-small-cell lung cancer. Anticancer Res. 2000, 20, 2177–2180. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tauchi, S.; Sakai, Y.; Fujimoto, S.; Ogawa, H.; Tane, S.; Hokka, D.; Tanaka, Y.; Nishio, W.; Yoshimura, M.; Yanagita, E.; et al. Psf3 is a prognostic biomarker in lung adenocarcinoma: A larger trial using tissue microarrays of 864 consecutive resections. Eur. J. Cardio Thorac. Surg. 2016, 50, 758–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sholl, L. Biomarkers in lung adenocarcinoma a decade of progress. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2015, 139, 469–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, D.; Kim, S.; Kang, J.; Hong, S.; Jeon, E.; Kim, Y.; Yoo, I.; Park, J.; Jang, H.; Lee, H.; et al. Serum carcinoembryonic antigen levels and the risk of whole-body metastatic potential in advanced non-small cell lung cancer. J. Cancer 2014, 5, 663–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bigbee, W.L.; Gopalakrishnan, V.; Weissfeld, J.L.; Wilson, D.O.; Dacic, S.; Lokshin, A.E.; Siegfried, J.M. A multiplexed serum biomarker immunoassay panel discriminates clinical lung cancer patients from high-risk individuals found to be cancer-free by CT screening. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2012, 7, 698–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patz, E.; Campa, M.; Gottlin, E.; Kusmartseva, I.; Guan, X.; Herndon, J. Panel of serum biomarkers for the diagnosis of lung cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2007, 25, 5578–5583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehan, M.; Ayers, D.; Thirstrup, D.; Xiong, W.; Ostroff, R.; Brody, E.; Walker, J.; Gold, L.; Jarvis, T.; Janjic, N.; et al. Protein signature of lung cancer tissues. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e35157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jantus-Lewintre, E.; Uso, M.; Sanmartin, E.; Gallach, S.; Sirera, R.; Hernando, A.; Martinez, N.; Figueroa, S.; Casimiro, E.; Camps, C. Ratios between VEGF ligands and receptors in tumor and stroma have impact on the outcome in resectable NSCLC. J. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 31, e22147. [Google Scholar]
- Patel, D.J.; Suri, A.K. Structure, recognition and discrimination in RNA aptamer complexes with cofactors, amino acids, drugs and aminoglycoside antibiotics. J. Biotechnol. 2000, 74, 39–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, F.; Liu, B.; Lu, J.; Li, F.; Li, D.; Liang, C.; Dang, L.; Liu, J.; He, B.; Badshah, S.; et al. Progress and challenges in developing aptamer-functionalized targeted drug delivery systems. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 23784–23822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lakhin, A.; Tarantul, V.; Gening, L. Aptamers: Problems, solutions and prospects. Acta Nat. 2013, 5, 34–43. [Google Scholar]
- Rozenblum, G.; Lopez, V.; Vitullo, A.; Radrizzani, M. Aptamers: Current challenges and future prospects. Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2016, 11, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zamay, G.S.; Ivanchenko, T.; Zamay, T.N.; Grigorieva, V.L.; Glazyrin, Y.E.; Kolovskaya, O.S.; Garanzha, I.; Barinov, A.; Krat, A.V.; Mironov, G.; et al. DNA-aptamers for characterization of histological structure of lung adenocarcinoma. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acid 2016, 6, 150–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lou, X.; Xiao, T.; Zhao, K.; Wang, H.; Zheng, H.; Lin, D.; Lu, Y.; Gao, Y.; Cheng, S.; Liu, S.; et al. Cathepsin D is secreted from M-B cells: Its potential role as a biomarker of lung cancer. J. Proteome Res. 2007, 6, 1083–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, S.; Wang, J.; Hou, L.; Li, J.; Chen, G.; Jing, B.; Zhang, X.; Yang, Z. Annexin A1, A2, A4 and A5 play important roles in breast cancer, pancreatic cancer and laryngeal carcinoma, alone and/or synergistically. Oncol. Lett. 2013, 5, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cole, A.; Clifton-Bligh, R.; Marsh, D. Histone h2b monoubiquitination: Roles to play in human malignancy. Endocrine-Related Cancer 2015, 22, T19–T33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Havel, L.; Kline, E.; Salgueiro, A.; Marcus, A. Vimentin regulates lung cancer cell adhesion through a VAV2-RAC1 pathway to control focal adhesion kinase activity. Oncogene 2015, 34, 1979–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kidd, M.; Shumaker, D.; Ridge, K. The role of vimentin intermediate filaments in the progression of lung cancer. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2014, 50, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richardson, F.; Young, G.; Sennello, R.; Wolf, J.; Argast, G.; Mercado, P.; Davies, A.; Epstein, D.; Wacker, B. The evaluation of E-Cadherin and vimentin as biomarkers of clinical outcomes among patients with non-small cell lung cancer treated with erlotinib as second- or third-line therapy. Anticancer Res. 2012, 32, 537–552. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Upton, M.; Hirohashi, S.; Tome, Y.; Miyazawa, N.; Suemasu, K.; Shimosato, Y. Expression of vimentin in surgically resected adenocarcinomas and large cell carcinomas of lung. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 1986, 10, 560–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chow, K.; Factor, R.; Ullman, K. The nuclear envelope environment and its cancer connections. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2012, 12, 196–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedl, P.; Wolf, K.; Lammerding, J. Nuclear mechanics during cell migration. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2011, 23, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machiels, B.; Ramaekers, F.; Kuijpers, H.; Groenewoud, J.; Oosterhuis, J.; Looijenga, L. Nuclear lamin expression in normal testis and testicular germ cell tumours of adolescents and adults. J. Pathol. 1997, 182, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, C.R.; Przyborski, S.A.; Wilson, R.G.; Hutchison, C.J. Lamins as cancer biomarkers. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2010, 38, 297–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parker, A.L.; Kavallaris, M.; McCarroll, J.A. Microtubules and their role in cellular stress in cancer. Front. Oncol. 2014, 4, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aarbiou, J.; Verhoosel, R.; van Wetering, S.; de Boer, W.; van Krieken, J.; Litvinov, S.; Rabe, K.; Hiemstra, P. Neutrophil defensins enhance lung epithelial wound closure and MUCIN gene expression in vitro. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2004, 30, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holterman, D.; Diaz, J.; Blackmore, P.; Davis, J.; Schellhammer, P.; Corica, A.; Semmes, O.; Vlahou, A. Overexpression of α-defensin is associated with bladder cancer invasiveness. Urol. Oncol. Semin. Orig. Investig. 2006, 24, 97–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zamay, G.S.; Zamay, T.N.; Kolovskii, V.A.; Shabanov, A.V.; Glazyrin, Y.E.; Veprintsev, D.V.; Krat, A.V.; Zamay, S.S.; Kolovskaya, O.S.; Gargaun, A.; et al. Electrochemical aptasensor for lung cancer-related protein detection in crude blood plasma samples. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 34350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gold, L.; Ayers, D.; Bertino, J.; Bock, C.; Bock, A.; Brody, E.N.; Carter, J.; Dalby, A.B.; Eaton, B.E.; Fitzwater, T.; et al. Aptamer-based multiplexed proteomic technology for biomarker discovery. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e15004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prakash, J.; Rajamanickam, K. Aptamers and their significant role in cancer therapy and diagnosis. Biomedicines 2015, 3, 248–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Han, D.; Ocsoy, I.; Tan, W. Aptamers selected by cell-selex for application in cancer studies. Bioanalysis 2010, 2, 907–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Zhang, Y.; Cai, J.; Cai, W.; Gao, T. Aptamer-based fluorescent biosensors. Curr. Med. Chem. 2011, 18, 4175–4184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Medley, C.; Sefah, K.; Shangguan, D.; Tang, Z.; Meng, L.; Smith, J.; Tan, W. Molecular recognition of small-cell lung cancer cells using aptamers. Chemmedchem 2008, 3, 991–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kunii, T.; Ogura, S.; Mie, M.; Kobatake, E. Selection of DNA aptamers recognizing small cell lung cancer using living cell-selex. Analyst 2011, 136, 1310–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jimenez, E.; Sefah, K.; Lopez-Colon, D.; Van Simaeys, D.; Chen, H.; Tockman, M.; Tan, W. Generation of lung adenocarcinoma DNA aptamers for cancer studies. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e46222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.; Zhao, Z.; Liu, Q.; Ye, M.; Hu, B.; Wang, J.; Tan, W. Study of the function of G-Rich aptamers selected for lung adenocarcinoma. Chem. Asian J. 2015, 10, 1519–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, Z.; Liu, Q.; Tan, W.; Fang, X. Cellular internalization and cytotoxicity of aptamers selected from lung cancer cell. Am. J. Biomed. Sci. 2013, 5, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamay, A.; Zamay, G.; Glazyrin, Y.; Zamay, T.; Krat, A.; Modestov, A.; Zubkova, O.; Spivak, E.; Sukhovolskaia, M.; Kuznetsova, S.; et al. DNA aptamer to human lung adenocarcinoma shows antitumor effect. Oligos Pept. Chim. Oggi Chem. Today 2014, 32, 24–28. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Y.; Duan, J.; Zhan, Q.; Wang, F.; Lu, X.; Yang, X. Novel MUC1 aptamer selectively delivers cytotoxic agent to cancer cells in vitro. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e31970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurosaki, T.; Higuchi, N.; Kawakami, S.; Higuchi, Y.; Nakamura, T.; Kitahara, T.; Hashida, M.; Sasaki, H. Self-assemble gene delivery system for molecular targeting using nucleic acid aptamer. Gene 2012, 491, 205–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esposito, C.; Cerchia, L.; Catuogno, S.; De Vita, G.; Dassie, J.; Santamaria, G.; Swiderski, P.; Condorelli, G.; Giangrande, P.; de Franciscis, V. Multifunctional aptamer-miRNA conjugates for targeted cancer therapy. Mol. Ther. 2014, 22, 1151–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iaboni, M.; Russo, V.; Fontanella, R.; Roscigno, G.; Fiore, D.; Donnarumma, E.; Esposito, C.; Quintavalle, C.; Giangrande, P.; de Franciscis, V.; et al. Aptamer-miRNA-212 conjugate sensitizes NSCLC cells to trail. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2016, 5, e289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, W.; Wang, W.; Chang, Y.; Chang, C.; Yang, P.; Peck, K. Synergistic inhibition of lung cancer cell invasion, tumor growth and angiogenesis using aptamer-siRNA chimeras. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 2905–2914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Zheng, H.; Bates, P.; Malik, T.; Li, X.; Trent, J.; Ng, C. Aptamer imaging with CU-64 labeled AS1411: Preliminary assessment in lung cancer. Nucl. Med. Biol. 2014, 41, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.; Xu, L.; Shi, X.; Tan, W.; Fang, X.; Shangguan, D. Recognition of subtype non-small cell lung cancer by DNA aptamers selected from living cells. Analyst 2009, 134, 1808–1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rekhtman, N.; Ang, D.; Sima, C.; Travis, W.; Moreira, A. Immunohistochemical algorithm for differentiation of lung adenocarcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma based on large series of whole-tissue sections with validation in small specimens. Mod. Pathol. 2011, 24, 1348–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reiber, H. Dynamics of brain-derived proteins in cerebrospinal fluid. Clin. Chim. Acta 2001, 310, 173–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiber, H.; Jacobi, C.; Felgenhauer, K. Sensitive quantitation of carcinoembrionic antigen in cerebrospinal fluid and its barrier-dependent differentiation. Clin. Chim. Acta 1986, 156, 259–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grunnet, M.; Sorensen, J. Carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) as tumor marker in lung cancer. Lung Cancer 2012, 76, 138–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papadopoulos, E.; Petraki, C.; Gregorakis, A.; Chra, E.; Fragoulis, E.; Scorilas, A. l-Dopa decarboxylase mRNA levels provide high diagnostic accuracy and discrimination between clear cell and non-clear cell subtypes in renal cell carcinoma. Clin. Biochem. 2015, 48, 590–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stieber, P.; Dienemann, H.; Hasholzner, U.; Muller, C.; Poley, S.; Hofmann, K.; Fatehmoghadam, A. Comparison of cytokeratin fragment 19 (CYFRA 21-1), tissue polypeptide antigen (TPA) and tissue polypeptide specific antigen (TPS) as tumor-markers in lung-cancer. Eur. J. Clin. Chem. Clin. Biochem. 1993, 31, 689–694. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Yi, Y.; Li, B.; Wang, Z.; Sun, H.; Zhang, P.; Huang, W. CYFRA 21-1 can predict the sensitivity to chemoradiotherapy of non-small-cell lung carcinoma. Biomarkers 2010, 15, 594–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrigno, D.; Buccheri, G.; Biggi, A. Serum tumor-markers in lung-cancer: History, biology and clinical-applications. Eur. Respir. J. 1994, 7, 186–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, H.; Tamai, K.; Magaya, T. Clinical value of SCC-antigen, a subfraction of tumor antigen TA-4, in the manage-ment of cervical cancer. Gan No Rinsho. 1985, 31, 594–599. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Suminami, Y.; Nawata, S.; Kato, H. Biological role of SCC antigen. Tumor Biol. 1998, 19, 488–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hokka, D.; Maniwa, Y.; Tane, S.; Nishio, W.; Yoshimura, M.; Okita, Y.; Ohbayashi, C.; Sakai, Y.; Chen, X.; Hayashi, Y. Psf3 is a prognostic biomarker in lung adenocarcinoma. Lung Cancer 2013, 79, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bermudez, V.; Farina, A.; Raghavan, V.; Tappin, I.; Hurwitz, J. Studies on human DNA polymerase epsilon and GINS complex and their role in DNA replication. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 28963–28977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makino, T.; Mikami, T.; Hata, Y.; Otsuka, H.; Koezuka, S.; Isobe, K.; Tochigi, N.; Shibuya, K.; Homma, S.; Iyoda, A. Comprehensive biomarkers for personalized treatment in pulmonary large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma: A comparative analysis with adenocarcinoma. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2016, 102, 1694–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, C.; Yang, K.; Tang, H.; Chen, D. Diagnostic values of serum tumor markers CYFRA 21-1, SCCAg, ferritin, CEA, CA19-9, and AFP in oral/oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 9, 3381–3386. [Google Scholar]
- Pastor, A.; Menendez, R.; Cremades, M.; Pastor, V.; Llopis, R.; Aznar, J. Diagnostic value of SCC, CEA and CYFRA 21.1 in lung cancer: A bayesian analysis. Eur. Respir. J. 1997, 10, 603–609. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, H.; Kawasaki, N.; Taguchi, M.; Kabasawa, K. Survival impact of epidermal growth factor receptor overexpression in patients with non-small cell lung cancer: A meta-analysis. Thorax 2006, 61, 140–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Lung Cancer Type | Protein Biomarkers of Lung Cancer | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| NSCLC, SCLC | AGER, C10orf116, ADD2, PRX, LAMB3, SYNM, SPTA1, ANK1, HBE1, HBG1, CA1, TNXB, MMRN2, HBA1, CAV1, HBB, COL6A6, C1orf198, CLIC2, SDPR, EHD2, APOA2, NDUFB7, PRKCDBP, LAMA3, LBN | [33,34,35] |
| ACT, 3 IGFBP3, L-PGDS | [35] | |
| SAA | [36] | |
| SAA, HAP, HGF | [36,37] | |
| TTR | [38,39] | |
| SAA, AAG1/2, CLU, SSA, AAG1, SAA, TTR | [6,35,37,40,41] | |
| APOA4, FIBA, LBN, SAA, CP, HP, TTR, KRT2A, GLT1B, CK1, AKT, MBL2, AAG1-2, FGA | [42] | |
| GSN, HP, FCN3, CNDP1 | [43] | |
| Lung adenocarcinoma | CALCA, CPS1, CHGB, IVL, AGR2, NASP, PFKP, THBS2, TXNDC17, PCSK1, CRABP2, ACBD3, DSG2, LRBA, STRAP, VGF, NOP2, LCN2, CKMT1B, AKR1B10, PCNA, CPD, PSME3, VIL1 | [44,45,46,47] |
| Squamous lung cancer | SERPINB5, RPL5, PKP1, RPL10, AKR1B10, AKR1C1, PCNA, RPS2, AKR1C3, THBS2, ACBD3, VSNL1, AHCY, IMMP10, PAK2, IVL, IARS, PSMD2, GBP5, MCM6, NDRG1, NOP58, S100A2, NRG1-2, CNDP1 | [45,47] |
| UCRP, CER, UPA, MT1-MMP, SFN, TF, ALB, S100A9, STMN, ENO, PLAU, IGFBP7, MMP14, THBS1, TTR | [48] |
| № | Protein Biomarkers of Lung Cancer | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | CEACAM (Carcinoembryonic Antigen) | [5,34,38,40,43,55,56,57,58,59,60,61,62] |
| 2 | CYFRA21-1 (Cytokeratin-19 fragments) | [5,8,26,34,38,43,55,56,58,61,62,63,64,65,66,67] |
| 3 | CA125 (Cancer Antigen 125) | [68] |
| 4 | PKLK (Plasma kallikrein) | [51] |
| 5 | ProGRP (Pro-gastrin-releasingpeptide) | [17,56,69,70] |
| 6 | NSE (Neuron-specific enolase) | [56,61,70,71,72] |
| 7 | ТРА 6, 7, 8 | [23,43] |
| 8 | NRG2, 100 | [43] |
| 9 | CNDP | [43] |
| 10 | APOВ100 | [43] |
| 11 | SCC (Squamous cell carcinoma antigen) | [73,74] |
| 12 | VEGF (Vascularendothelial growth factor) | [56] |
| 13 | EGFR (Epidermal Growth Factor) | [50] |
| 14 | PIK3CA, HER2, BRAF, ROS, RET, NRAS, MET, MEK1 | [6,7] |
| 15 | HER2 | [75] |
| 17 | C4.4A | [20] |
| 18 | PSF3 | [76,77] |
| 19 | FAM83B | [54] |
| 20 | ECD, CTNNB , VIM, S100A4 | [47] |
| 21 | S100A7 | [32] |
| 22 | COX2 | [78] |
| 23 | MUC1 | [74,79] |
| Aptamers | Target Cells | Protein Target | Application | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Small cell lung cancer | ||||
| HCA12 HCC03 HCH07 HCH01 | Cell lines: NCI–H69 NCI–H146 NCI–H128 | Not determined | Formalin-fixed, Paraffin-embedded Tissue Array; Extraction and Detection with Aptamer Conjugated Magnetic/Fluorescent Nanoparticles using fluorescence microscopy and flow cytometry | [108] |
| 16-1 | SBC3 cell line | Not determined | Fluorescence microscopy and flow cytometry | [109] |
| Lung Adenocarcinoma | ||||
| EJ7 ADE2 | H23 cell line H23, A549 cell line | Not determined | Flow cytometry | [110] |
| S13, S50 | EGFR-transfected A549 cell line | EGFR | Antiproliferative activity | [111] |
| R50 | A549 cells transfected with EGFR-GFP | NCL | Apoptosis induction | [112] |
| LC-17 | Post-operative tissue | TUB | Aptahistochemical analyses of tissues Isolation of circulating tumor cells | [62,88] |
| LC-18, | Post-operative tissue | VIM, LMN | Aptahistochemical analyses of tissues Isolation of circulating tumor cells Electrochemical detection of protein biomarkers in human blood plasma | [62,88,103] |
| LC-224 | Post-operative tissue | ACT methylated at position 73 | Aptahistochemical analyses of tissues | [88] |
| LC-110 | Post-operative tissue | CLU H2B | Isolation of circulating tumor cells | [62] |
| LC-183 | Post-operative tissue | CTSD | Isolation of circulating tumor cells Inhibition of growth of primary cancer cell cultures | [62,113] |
| MA3 | Сell lines: A549, MCF-7 | MUC1 | Targeted delivery of doxorubicin | [114] |
| MUC-1 aptamer | A549 cell line | MUC1 | Targeted delivery of plasmid DNA | [115] |
| GL21.T | A549 (Axl+) cell line | AXL | Aptamer used as carriers for cell-targeted delivery of a miRNA with tumor suppressor function, let-7g; miR-212 | [116,117], |
| Other | ||||
| aptNCL | CL1-5 cell line | NC L | Targeted delivery of siRNA chimeras | [118] |
| AS1411 | Multiple cancer cell types | NC L | PET imaging of lung cancer with Cu-64 labeled aptamer | [119] |
| S1, S6, S11e, S15 | NSLC | Not determined | [120] | |
| Tumor-Associated Protein | NSCLC | SCLC | Normal |
|---|---|---|---|
| LDH | 525.079 ± 24.817 ng mL−1 [134] | 209.880 ± 161.322 ng mL−1 [134] | <245 ng mL−1 [134] |
| CRP | 25.079 ± 24.817 ng mL−1 [134] | 14.935 ± 21.078 ng mL−1 [134] | <8 ng mL−1 [134] |
| CEA | 51.493 ± 77.529 ng mL−1 [134] 78.5 ng mL−1 [23] ≥ 100 ng mL−1 [65] | 25.074 ± 40.957 [134] | <5.0 ng mL−1 5.0 ng mL−1 [23,61] <20.9 ng mL−1 6.5 ng mL−1 [66] |
| NSE | 13.638 ± 5.571 ng mL−1 [134] >6.4 ng mL−1 [19] 5–35 ng mL−1 17.95 ng mL−1 [61] 0–170 ng mL−1 [23] | 62.972 ± 63.012 [134] 50.8 ng mL−1 [61] 15–173 ng mL−1 [23] | 15.7–17.1 ng mL−1 15.2 ng mL−1 13 ng mL−1 [65] |
| CYFRA21-1 | 12.447 ± 15.814 ng mL−1 [134] 81.7 ng mL−1 [23] | 6.418 ± 9.567 ng mL−1 [134] | <3.3 ng mL−1 [134] 3.3 ng mL−1 [35] 3.3 ng mL−1 [61,65] 0.5 ng mL−1 [65] 2.0 ng mL−1 [23] |
| SCCA | 0.22–3.79 ng mL−1 [61] 0.5–1.7 >2 ng mL−1 [135] | 0.15 ng mL−1 [61] | 1.5 ng mL−1 [23] |
| TPS | 0–3842 ng mL−1 [136] | 12.5–773 ng mL−1 [23] | 34.9 ng mL−1 UL−1 [23] |
| ProGRP | <35 pg mL−1 [22] | >200 pg mL−1 [22] | <35 pg mL−1 [22] |
| Tumor-Associated Protein | Adenocarcinoma | Squamous Carcinoma | Normal |
|---|---|---|---|
| CEA | 30.76 ng mL−1 [61] 0.6–588 ng mL−1 [23] 3.5–11.1 ng mL−1 [66] | 4.49 ng mL−1 [134] 0.8–587 ng mL−1 [23] | <5.0 ng mL−1 5.0 ng mL−1 [23,61] <20.9 ng mL−1 6.5 ng mL−1 [66] |
| NSE | 17.95 ng mL−1 [134] | 16.83 ng mL−1 [134] | 15.7–17.1 ng mL−1 15.2 ng mL−1 13 ng mL−1 [23] |
| CYFRA21-1 | 4.00 ng mL−1 [61] 5.79 ± 6.75 ng mL−1 [63] 1.3–4.4 ng mL−1 [66] | 10.34 ng mL−1 [61] | <3.3 [134] 3.3 ng mL−1 [23,61] 0.5 ng mL−1 [23] 2.0 ng mL−1 [66] |
| SCCA | 0.22 ng mL−1 [61] 0.5–1.7 >2 ng mL−1 [66] | 3.79 ng mL−1 [61] | 1.5 ng mL−1 [66] |
| TPS | 10–3842 ng mL−1 [23] | 0–3000 ng mL−1 [23] | 34.9 ng mL−1 [23] |
| Biomarker | CEA ngmL−1 | NSE ngmL−1 | ProGRP pgmL−1 | PSF3 | CYFRA21-1 ngmL−1 | SCCA ngmL−1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Small Cell CA | 25.07 ± 41.1 | 50.8–173 | >200 | normal | 6.42 ± 9.57 | 0.15 |
| AdenoCA | 0.6–588 | 17.95 | ~35 | overexpression | 1.3–5.79 | 0.22–2.0 |
| SquamousCA | 0.8–587 | 16.83 | ~35 | normal | 10.34 | 3.79 |
| Large Cell CA | 51.5–100 | 4.6–17.95 | ~35 | normal | 1.3–5.79 | 0.22–2.0 |
| Healthy | 5–20.9 | 13–17.1 | ~35 | normal | 0.5–1.3 | 1.5 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zamay, T.N.; Zamay, G.S.; Kolovskaya, O.S.; Zukov, R.A.; Petrova, M.M.; Gargaun, A.; Berezovski, M.V.; Kichkailo, A.S. Current and Prospective Protein Biomarkers of Lung Cancer. Cancers 2017, 9, 155. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers9110155
Zamay TN, Zamay GS, Kolovskaya OS, Zukov RA, Petrova MM, Gargaun A, Berezovski MV, Kichkailo AS. Current and Prospective Protein Biomarkers of Lung Cancer. Cancers. 2017; 9(11):155. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers9110155
Chicago/Turabian StyleZamay, Tatiana N., Galina S. Zamay, Olga S. Kolovskaya, Ruslan A. Zukov, Marina M. Petrova, Ana Gargaun, Maxim V. Berezovski, and Anna S. Kichkailo. 2017. "Current and Prospective Protein Biomarkers of Lung Cancer" Cancers 9, no. 11: 155. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers9110155
APA StyleZamay, T. N., Zamay, G. S., Kolovskaya, O. S., Zukov, R. A., Petrova, M. M., Gargaun, A., Berezovski, M. V., & Kichkailo, A. S. (2017). Current and Prospective Protein Biomarkers of Lung Cancer. Cancers, 9(11), 155. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers9110155