Abstract
Although research on risk management (RM) in small- and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) in general and regarding supply chains (SCs) has increased recently, our understanding is still rather fragmented and underdeveloped. This refers particularly to new types of risks such as dynamic crises or emerging risks associated with digital transformation (DT). Therefore, the purpose of this exploratory paper is to investigate RM in SMEs in SCs. More precisely, the aim is to identify patterns that can be used to group SMEs according to their risk behavior (i.e., risk attitude and perception). Drawing from a data set of 181 European SMEs, this paper empirically conceptualizes a typology of SMEs. The typology consists of four distinct types of SMEs that emerged from a cluster analysis: collective risk eliminators, collective playing it safe seekers, collective risk-ignoring knights of fortune, and collective neglecting imperturbable ones. The findings indicate that different risk behavior leads to different degrees of collaboration within the SC. Furthermore, the close interconnection between RM as found in the different clusters and the respective firm’s innovation performance can be shown. By acknowledging the heterogeneity found in SMEs, this paper breaks away from mainstream research that tends to consider SMEs as a homogeneous entity.
1. Introduction
External crises, such as the COVID-19 pandemic, have a widespread impact on companies and their supply chains (SCs) and call for an even stronger emphasis on systematic risk management (RM) approaches [1]. Especially for small- and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) involved in SCs, RM is even more urgent, as their risk exposure increases within the SC [2,3]. Dynamic crises such as (cyber)wars and sanctions or the COVID-19 pandemic also act as accelerators for both digital transformation (DT) and the emergence of new types of risks [4,5,6]. Thus, the ongoing identification of risks and their handling is highly important, and not only essential for SMEs themselves but also in inter-organizational settings such as SCs [7]. The management of resulting SC risks is even more challenging as indirect effects on companies such as innovation performance or threats for the intellectual capital needs to be considered [8,9]. As SMEs are very heterogenous, a different behavior (attitude and perception) towards (SC) risks, must be expected and influences their applied (SC)RM and innovation performance. Resulting from this heterogeneity, standardized RM approaches among SMEs are uncommon [10]. Hence, a more differentiated view of risk behavior is needed. Furthermore, due to digitalization and the resulting digital SC [11], risk behavior, respectively RM within SMEs needs to be investigated more closely because newly emerging digitalization risks especially focusing on cybersecurity or intellectual capital have not been examined in detail yet [4,12].
Looking at current research, it appears that little is known about RM in SMEs in general and in the context of SCM, in particular [3]. Several studies, e.g., [13,14], showed that the size of companies matter when it comes to RM. In contrast to large companies (LEs), SMEs often face resource scarcity and are not able to put great effort into the timely identification and elimination of risks [10,13,14]. Nevertheless, the need for RM in SMEs is vital given that the probability of failure among such firms is higher [2]. Regarding risk behavior, existing research has found that reactive management of risks is more common than proactive one in SMEs [15,16,17]. SME owners are often in charge of the RM function too in addition to their other tasks [7]. According to [7], research is unclear to which extent SME owners’ experience influences their risk perception or how risk attitude changes with growing company size. Being active partners in SCs, SMEs are exposed to severe SC risks, e.g., incompatible information systems or loss of intellectual capital, and existing research has found collaborative RM as a suitable solution to addressing them [18,19]. Having a structured RM approach within the SC collaboration, can not only reduce the potential impact and severity of risks but also enhance innovation performance [20,21].
Even so, despite increasing research triggered by the COVID-19 pandemic, RM in SME has gained more and more attention, it is still an underdeveloped field, which calls for more research in general [3,7]; in the context of SC, in particular [22]. For these reasons, it will be necessary to look at RM in SMEs which have different risk perceptions and face different types of risks with different attitudes. As SMEs are heterogeneous and thus diverse approaches are likely [23], it can be expected that this situation not only influences the inflicted risk impact but, furthermore, the firms’ innovation performance. Thus, it not clear yet which approaches SMEs take to address (SC)RM and how these approaches can be grouped, to provide insight into their risk behavior.
To address this research gap, a survey was conducted and disseminated among SMEs located in selected EU countries. Due to the relevance of risks in SCs, and especially in relation to the DT, an improved understanding is very important as it will help to assess RM in SMEs. Based on cluster analysis, we identify patterns that help to gain deeper and more fine-grained insights into (SC)RM in SMEs and its characteristics which allows the grouping of the approaches taken in these firms. Acknowledging both the impact of size and sectoral affiliation, implications can be drawn that are relevant for theory and practice. Furthermore, implications for the innovation performance of SMEs are drawn in the existing research. This paper proceeds as follows. First, the theoretical background addresses the relevant literature regarding DT in (SC)RM in SMEs and its link with innovation performance. Next, the methodology is presented and in the following section, the results are presented and afterwards discussed. Finally, a conclusion is drawn, and limitations and prospects are mentioned.
2. Theoretical Background
2.1. Digital Transformation and Supply Chain
The DT offers a manifold of new opportunities to optimize SCs, which lead to innovations and improvements in industrial ecosystems, also in a SME scale [24,25]. In SCM, digitalization is referred to Industry 4.0 or Smart Manufacturing and the core aspect is efficiency, which is pushed further by data-driven decision support. As a result, industry is transforming more and more into a high-tech environment and SC are digitalized [26]. Industry 4.0 characterizes a manufacturing model in which machinery and products communicate autonomously. High customization and smart processes are key advantages within Industry 4.0 [27]. Digitalization enhances the number of connected devices intensely and data exchange has increased tremendously [26]. Even though this increased data exchange can contribute to certain benefits such as improved processes and planning it also bears several risks such as the loss of proprietary knowledge or unintended disclosure of business insights to other partners [11,28,29]. Further, the increasing digital integration of SCs bears the risk of being in the focus of cyber-attacks [30,31,32]. As digitalization not only depends on technology adoption, but also on the management within the company, SME owners, among many other things, also need to fill the gap from IT manager to risk manager [33]. SMEs need to quickly adopt to new technologies in order to cope with the market competition [34]. Regarding the shift towards more and more virtual environments, it must also be noted that digitization risks, or knowledge risks resulting from them, may become more and more relevant for SMEs and further increase risk exposure within the company and across its boundaries to a considerable extent [35,36]. It can thus be assumed that SMEs will continue to benefit from, respectively, practicing implementing systematic RM in the future, but, as research regarding SMEs in digital SCs is scarce, there is a need to investigate in more detail.
2.2. Risk Management in Supply Chains in SMEs
RM aims to identify potential risks, reduce them and mitigate their effects, such as possible losses [3]. SMEs are exposed to risks in the same way as LEs, with the difference that they often do not have sufficient resources and capabilities to address them properly [7,10,14]. Thus, the application of RM in an SME environment is rather assessed as a reactive one, instead of a proactive one [16,17]. As there is often no particular RM division or a risk manager, RM is taken care of by the general management or it is the SME owner’s task [37]. However, applying a structured RM approach can, on the one hand, side help SMEs to overcome resource constraints and on the other hand side also increase their company profitability [38,39].
Companies participate together in SCs to create products or services and thus may face risks jointly. Collaboration can be vertical or horizonal [40], in this paper we focus on SC collaboration in general. SC risks are challenges linked to potential disturbances influencing SC partners that may directly influence an organization’s capability to operate, produce goods, or offer services [41]. As SMEs have fewer financial resources to cope with emerging risks and prevail over them upfront, the implementation of a proper RM within the SC lacks [19,22]. Supply chain risk management (SCRM) is an inter-organizational collaborative effort using quantitative and qualitative RM methodologies to identify, analyze, monitor, and mitigate if unexpected events or conditions could adversely affect any part of the SC [19,37,42,43]. SCs are becoming increasingly interconnected and globalized, and the importance of SC performance increases [44]. Within SCRM, risk information sharing is one of the most important key capabilities, and sharing information reduces SC risks [45,46]. The focus in this paper lies mainly on collaborative RM within a SC, as SMEs are highly dependent on their SC partners [16,47]. Due to their interwoven nature, their SCRM must have high priority and needs more investigation.
RM in SMEs is influenced by the risk behavior of the SME owner, manager or even employee. For the paper’s research purpose, we suppose that risk behavior consists of the general attitude towards risks and the perception of risks within the SME of the specific survey participant. Therefore, the manager’s or employee’s behavior towards risk is one of the main factors to keep in mind if RM in SMEs comes into play. Notably, SMEs show a different risk behavior compared to LEs. Instead of formal methods for individual risk scenarios, SMEs often try to carry out a holistic risk assessment, and their general attitude towards risk is more averse [7,10,48]. Their behavior towards risk is dependent on individual trade-offs; what is perceived as a tolerable level of risk, the estimated benefit, and the general attitude of the company concerning risk-taking. Managers or employees can be either way highly risk-averse or risk-takers. As it is an individual perception and attitude, it is connected to work experience, maturity, and other factors [9,10,19].
Heckmann et al. (2015) propose three groups of risk attitudes: risk-averse, risk-seeking, and risk-neutral. Individual behavior influences each decision-making process and the SC performance [49]. Regarding risk attitudes, it is important to not consider SMEs as a homogeneous group and that SMEs often use reactive strategies instead of preventive [10,16]. Further, attitudes can suddenly change, most possibly after facing heavy losses in business. To overcome such possible losses, risk awareness among employees is important. RM needs to be applied also outside of organizational boundaries, the collaborative efforts with partners must be held high, because by engaging in collaboration, SC performance increases, and risk mitigation takes effect, which leads to a different risk behavior [9,19,49,50]. Due to the lack of systematic RM in SMEs and their heterogeneity, represented through individual SME owners, the risk behavior perspective plays an important factor and needs further elaboration.
2.3. Risk Management and Innovation Performance in SMEs
Talking about performance, a lot of studies focus on SC or innovation performance, e.g., [51,52,53,54]. Innovation performance is often related to radical or incremental innovations [55] and is used for the purposes in this paper in the context of missing SCRM and associated perceived innovation slowdown due to poor RM. Innovation is a key driver to organizational or company performance. It goes hand in hand with new risks, and could also lead to unpredictable situations [56]. Furthermore, the risk-taking tendency has an indirect positive effect on a firm’s innovation performance [9]. Additionally, relationship learning and IT integration within the SC collaboration improve performance [57]. To achieve competitive advantage through technological innovation, companies must first establish appropriate technological infrastructures and organizational structures which support SC collaboration [52,58]. Due to resource constraints, this represents a dilemma in SMEs, and innovation performance always goes hand in hand with a trade-off regarding costs. Innovation is tightly connected to the SME owner’s risk behavior, which is also influenced by technological turbulence [48]. As a concept of a former decade technological turbulence has lost none of its relevance today [59]. Nowadays, production systems and SC become more connected, and more and more data is shared, accompanied by data security or even knowledge risks [11,60,61]. Information and communications technologies (ICT) can be a boost to innovation performance and firm performance [36,61,62].
Research about innovation performance and RM has rarely been considered as corollary factors. When they have been studied together, scholars have typically focused attention on large corporations with risks related to geographically complicated SCs [56]. Because of resource limitations and size factors [63], SMEs have different RM concerns that merit separate analyses [64]. Unfortunately, to our knowledge, there are no current studies that explore the interrelation between RM in SMEs and their innovation performance.
3. Research Methodology
Based on our literature review, we concluded that research on different types of SMEs regarding SCRM is missing. Hence, we decided to base our study on an exploratory research design. To gain a broad perspective regarding SCRM in different types of SMEs and to collect the necessary number of data required for doing a cluster analysis we decided to follow a quantitative research methodology. More precisely, data was collected in the form of an online survey disseminated among SMEs in selected European countries Austria, Estonia, Germany, Greece, Portugal and Spain). To get access to relevant SMEs, partners took advantage of available online databases in the respective countries and used their professional business contacts. To be considered suitable, the SMEs should fall under the EU’s definition of SMEs (see European Commission, 2021: https://ec.europa.eu/growth/smes/sme-definition_en, accessed on 17 January 2022). Additionally, as (SC)RM is viewed as relevant for all types of firms regardless of the industry, it was also tried to gather data from SMEs representing different industries. Given the exploratory nature of the study, this approach was deemed suitable. Thus, the sampling strategy followed the notion of criterion sampling [65].
3.1. Data Collection and Questionnaire
Data collection was carried out through an online survey using the survey tool Qualtrics. Online surveys are particularly useful when data across countries are to be collected. The survey was open in the period April–May 2021. Potential companies were contacted by e-mail explaining the aim of the study and providing the link to the survey. In total, 223 people responded, and after the elimination of incomplete responses, the final number of responses to be analyzed was 181. As this study was an exploratory study, the aim was not to generalize from the data. The questionnaire developed for the study was based on existing research on (SC)RM. The questionnaire contained five blocks with 20 questions overall).
The first block was about the current overall risk situation in the company and covered topics of frequency of different risk scenarios, how those risks have an impact on the companies, and how often SMEs assess them. Differences in RM practices have been discussed in the literature and we used already elaborated survey items [10] to better capture the specific differences in this study as well. The second block contained questions about the current SC risks situation in the company. For an overview of how the frequency of perceived risks within the company and within the SC has changed in recent years, the participants were asked for their subjective opinion. Deducing from this, an assessment of the participants’ risk perception is possible, the items used were adapted from [66] and for the company’s attitude to risks from [19]. The third block revolved around topics of digitalization and the company. Additionally, the increasing data exchange increases the danger of information and knowledge leakages, thus we asked for an assessment, adapted from [67]. Block IV was about the company and its performance. Participants were asked how they self-assess the performance of their company compared to their key competitors. For this purpose, we used adapted items from [68]. Lastly, in Block V, information about the company and the participant were gathered. For the measurement of the relevant constructs, we used single- and multiple-choice types of response items and 5-point Likert scales. The developed questionnaire was pre-tested for validity by a consortium of researchers and slightly adapted afterward.
The data collected covers SMEs from different branches, e.g., information technology, transportation, logistics, architecture, and engineering. Regarding the size of the companies of the total sample, most companies were micro-enterprises with 1–9 employees, followed by small-sized enterprises, with 10–49 employees, and medium-sized enterprises. All participants were either SME owners, managers or involved in the firm’s RM.
3.2. Cluster Analysis
To analyze the collected data and thus to identify possible patterns advancing our understanding of (SC)RM in SMEs, a cluster analysis was used. This technique helps to classify multivariate data to arrange it by its common characteristics or patterns and was thus found to be the most appropriate for developing a typology of SCRM in SMEs. The different groups do not have to be known upfront, which is why this method can be used well for exploratory studies [69]. We used cluster analysis to identify clusters based on risk attitudes or perceptions, risk assessment, impact and frequency, and self-assessed innovation performance. The results of the cluster analysis are shown in Table 4.
A dendrogram was used to determine the number of clusters (see Figure 1). The dendrogram shown suggests a four-cluster solution.
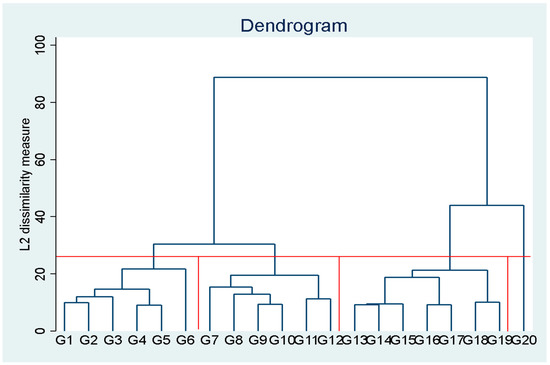
Figure 1.
Dendrogram for the cluster solution.
3.3. Verifying the Accuracy of the Clustering Process
To assess the validity and reliability of the findings put together from the cluster analysis, canonical discriminant analysis was carried out. Table 1 and Table 2 present the eigenvalues and the Wilks’ Lambda results for the three canonical discriminant functions. Table 2 reports Wilks’ Lambda of 0.0538, 0.2262, and 0.7052 for each of the functions. From the results, it is also observed that all three functions are significant (p-value = 0.000 < 0.05) indicating that the discriminant analysis is robust enough to assess the cluster analysis results. Furthermore, the results reveal eigenvalues of 3.201, 2.117, and 0.418 together with a canonical correlation of 0.873, 0.824, and 0.543 for each of the generated functions. These imply that the first, second, and third discriminant functions explain about 76.2%, 67.9%, and 29.5% (square of canonical correlation) of the variations in the model. Technically, the higher the eigenvalues the stronger the functions. With regards to our results, the discrimination level for this study is deemed efficient (eigenvalues are relatively higher).

Table 1.
Eigenvalues results for discriminant analysis.

Table 2.
Wilk’s Lambda results for discriminant analysis.
To finally check the validity and reliability of the cluster analysis conducted on the 4 clusters and 17 characteristics based on the Wilds’ linkage, the discriminant function classification (as presented by Table 3) was constructed using both the count and percentage. The results are as follows: for cluster 1, 58 out of 68 members are correctly classified representing 85.3% and the remaining 10 members incorrectly classified; for cluster 2, 40 out of 49 members are correctly classified representing 81.6% with the remaining 9 members incorrectly classified; for cluster 3, 44 out of 51 members are correctly classified representing 86.3% and the remaining 7 members incorrectly classified; and last but not least, for cluster 4, 13 out of 13 members are correctly classified indicating 100% with none incorrectly classified. Overall, 85.6% of the original grouped cases are correctly classified.

Table 3.
The discriminant function classification results.
4. Results
According to the result obtained from the clustering process in Section 3, 4 distinct clusters are presented by Table 4 with allocations: 68 SMEs for cluster 1, 49 SMEs for cluster 2, 51 SMEs for cluster 3, and 13 SMEs for cluster 4. This was based on the following items: the frequency of crisis, the level of risk impact, risk assessment, risks as opportunities, risks as threats, risks are difficult to control, risks can be minimized by involving SC partners, risks are costs, group risk elimination with SC partners, risk sharing with SC partners, risk insurance, self-eliminate risk, risk transfer to SC partner, ignore risk, innovation performance compared to competitors, number of employees, and annual turnover. The table values show the respective cluster mean (Table 4).

Table 4.
Result of the cluster analysis.
Typology of SME’s Risk Management
Based on the scores of the K-means clustering, the results of the survey have led to an allocation of several clusters. For successful cluster analysis, a maximum of four clusters was required which describe SMEs attitudes and perceptions of risks. The findings of this explorative research are described briefly in the following and then discussed. The main aim of the study is to identify patterns that can be used to cluster SMEs according to their risk behavior (attitude and perception). This can lead to a better understanding of SMEs RM within and across companies and their behavior towards risks, respectively, their self-assessed innovation performance.
- Cluster 1 (Collective risk eliminators)
The total number of SMEs in this cluster is 68 (37.6%) and mainly small enterprises, representing the information technology sector, among others. They have an average of 10 to 49 employees as of 2020, and an annual turnover of 2–10 million euros. Most of these firms seem to allocate a considerable amount of their annual revenue in innovation, as they perceive them to be more innovative than competitors. According to the cluster analysis in Table 4, it is observed that these firms view risks more as a threat than an opportunity. Moreover, one peculiar and distinct feature about this group of firms is their collaborative efforts to eliminate risk whenever possible, instead of just ignoring it or trying to transfer it to another. Since this group of firms normally experience less frequency of risk, they rarely assess them, and when confronted with it, most of these risks tend to have high negative implications on their businesses. Still, somehow, they rather perceive risks as something that can be minimized together.
- Cluster 2 (Collective playing it safe seekers)
There are 49 SMEs in this group, representing about 27.1% of the total sample size. Within this group, the average number of employees falls within the range of 50 to 249, with an average annual turnover between 10–20 million euros as of 2020. Firms within this cluster are touted as innovators. This is especially interesting, because the largest part of this group is active in the services sector, such as logistics or transport or other services. They as well encourage risk-sharing among groups for effective minimization of risk. Since they regard risks as something difficult to control and at the same time as expensive, they often opt for insurance. In this group, SMEs associate risks with threats rather than opportunities. SMEs within this cluster experience the lowest crisis frequency, which may also be related to the fact that risks are assessed most regularly within this group. Nevertheless, when a risk occurs, the impact is high, and thus this group has the attitude to not ignore risks.
- Cluster 3 (Collective risk-ignoring knights of fortune)
SMEs within this group are majorly micro-enterprises, with the smallest annual turnover, with less than two million euros per year (2020), and the smallest employees’ number, ranging from 1–9. This group has the second largest membership among all the clusters. It constitutes 51 SMEs holding a 28.2 percentage of the sample size. Firms under this group primarily view risks as opportunities, rather than threats; however, they have the culture of ignoring risks and score lowest regarding the innovative performance assessment, still they see them as more innovative than competitors, as seen in Table 4. They also engage in other activities such as risk transfer to SC partners, self-risk elimination over group risk elimination, and risk-sharing in the SC. They do little to assess the severity of the risk and for that reason whenever there is a risk, it normally has a strong impact on their operations. It appears that their assessment of risk is fragmented, that is, only targeting the frequency of risk rather than its severity. Lots of the micro-enterprises within this group can be found in the architecture and/or engineering sectors.
- Cluster 4 (Collective neglecting imperturbable ones)
This group has the smallest number of SMEs as far as this study is concerned. It consists of 13 SMEs (7.1%), specifically medium-sized enterprises. Although they have the least number of members, they are the group with the highest annual turnover of up to 100 million euros as of 2020. Furthermore, they have the largest number of employees, close to 250. One striking characteristic of these firms is their unresponsive attitude towards risk, although they perceive risks more as a threat than an opportunity. That, however, corresponds to the severity they tend to experience in the aftermath of the occurrence of risks, although, at the same time, they perceive risks as something to be minimized. They do little assessments and do not perceive risks as costs. Furthermore, they do not eliminate risks as a group, so due to their size, the RM collaboration within the SC seems to be rather neglected. They assess themselves as more innovative than their competitors, and their attitude towards risk control such as risk sharing, and risk insurance is rather neglected. Various sectors are represented in this small cluster, and particularly prominent are the education and training sectors which stands out.
The following section compares and discusses the findings.
5. Discussion
Coming with complex business, environmental and digitalization challenges caused by DT, new opportunities and risks emerge simultaneously, which can either be seen as opportunities or as threats. Therefore, SMEs are forced to position themselves in the continuum between a systematic and continuous RM or dealing with risks on the fly. As the results show, four different clusters were identified, which need to be discussed in the context of managing the DT in the context of SCM and SMEs. Regarding the perception of the different clusters, it can be said that, except cluster 3 (Collective risk-ignoring knights of fortune), all the clusters perceive risks more as a threat than an opportunity (see Table 4), but still, continuous risk assessment suffers. This can result from a variety of reasons. Very often, a risk assessment in SMEs is neglected due to employees’ limited capability of RM knowledge. When it comes to proper identification of risks, and implementing them in business planning, SMEs often lack defined processes, which may result from the general lack of a risk manager [10]. Since in SMEs the owner often is the risk manager at the same time, gut feeling and the individual risk attitude play a central role and also link to innovative performance [7,9]. Furthermore, all clusters perceive risks as something which can be minimized and controlled, but looking at the impact of experienced risk scenarios, this is clearly misperceived [70]. Thus, in summary, the findings suggest that there are clear deficits regarding RM in all surveyed SMEs.
The occurring risks have a strong impact on the businesses, this seems to apply to all companies in the clusters. Thus, even though SMEs perceive the risks imposed by DT they are currently not ready or in the position to respond in an appropriate manner. Hence, specific trainings, DT guidance and financial support are needed to support SMEs for developing (and upskilling) the necessary capabilities [34] and implementing a risk culture. What differs, however, are the respective views on risks in the SMEs studied our study provides an overview of the interdependence of risk behavior and innovation performance. Based on this, it seems important if the proposed training measures also discuss the connection between risk management and innovation performance. Looking at cluster 2 (Collective playing it safe seekers), collective efforts to eliminate risks, or risk-sharing within the SC lead to a strong (self-assessed) innovation performance. Notably, most companies within this cluster are medium-sized. It is, therefore, reasonable to assume that not only RM works within the SC, but that innovation efforts are also openly pursued with the partners. These findings are in line with the literature, which shows the positive relationship between collaborative RM and innovation activities, e.g., [20,71]. In cluster 4 (Collective neglecting imperturbable ones) there is an ignoring attitude towards risk. Although they perceive risks as threats, they see them as controllable threats and rather ignore them instead of opting out for insurance or group elimination, still, they see themselves as an innovative market player. In collective risk-ignoring knights of fortune, we observe mainly micro-enterprises that tend to perceive risks as opportunities, but also ignore risks, when it comes to managing them. A majority within this cluster is located in the engineering sector, less of them in the construction sector. It can be assumed that sectors that are more digital pioneers, such as engineering, have already made slightly more efforts regarding structured RM. In contrast to that, the more digital laggards such as the construction sector are rather even more behind [10,72,73]. Collective neglecting imperturbable ones grouped all larger medium-sized enterprises, who favor ignoring risks, but face a high risk impact, if one does occur. Within this small cluster, there are different sectors represented, but a large part is located in the education and training sector. So, as we can see, the heterogeneity of SMEs is consistent with the diversity of different sectors, i.e., each of which deals with risks in a different way.
The clusters for the most part also summarize the different company sizes, namely micro-, small-, and medium-sized enterprises. The biggest cluster (cluster 1, collective risk eliminators) of the survey participants represented small-sized enterprises to a large extent together with representatives of micro-enterprises (mostly represented in collective risk-ignoring knights of fortune), they made up two-thirds of the participants. The results show that micro- and small-sized enterprises rather view risks as opportunities (and at the same time as threats) than medium-sized enterprises do. On the opposite, collective neglecting imperturbable ones rather tends to minimize risks and take control over them, which can be explained by the fact that the larger companies become, the more they have a structured approach to RM or even have their staff for this purpose [3]. With regards to the collaborative RM, collective risk eliminators (mostly small-sized) and collective playing it safe seekers (mostly medium-sized) opted for group risk elimination within the SC, whereas collective risk-ignoring knights of fortune (mostly micro-sized) and collective neglecting imperturbable ones (mostly at the tipping point to large enterprises) did not. Notably, the last two clusters tend to have rather frequent crises occurring in their companies and are ignoring risks. To establish an effective RM within the SC, collaboration is the key to general success [19]. It can be concluded that the respective company size influences the risk behavior. The fact that the implementation of RM depends, among other things, on the size of the company has already been proven in various studies, e.g., [13,14], our study adds another confirmation.
Another result regarding size is that medium-sized companies assess themselves a higher innovation performance to their competitors than micro- and small-sized companies do. This linkage between size and innovation performance is not a matter of course. Scholars come to different conclusions when it comes to the relationship between size and innovation performance, e.g., [20,74]. However, it must also be considered here that there are different types of innovation, such as radical, incremental, or disruptive innovation. In the context of this study, innovation performance in the market environment was generally asked about. Notably, medium-sized enterprises in collective playing it safe seekers self-assessed their innovation performance to competitors as high and aimed at collaborative RM within the SC, such as group risk elimination or risk-sharing with partners. To conclude, the results show that SC collaboration positively affects innovation performance, such as the joint development of new products [75]. However, collaboration without caution is not recommended and risk management is highly relevant especially during the creation of data-driven business models [76].
Interestingly, the results also show that, across cluster boundaries, there is awareness of the threat of both digitalization and knowledge risks. With upcoming new technologies in the course of DT, more and more data are exchanged within the SC and information sharing is crucial. More and more SMEs are also involved in global SCs, where data exchange leads to new kinds of risks, emerging out of the digitalized SC setting [29,60,77]. To assess this exchange, awareness is needed, on the one hand, and tools to support decision making or modification, on the other hand [60,76]. Furthermore, qualified staff are non-substitutable, and training leads to an improvement of operational performance and quicker responses to threats [78,79]. Using data analytics tools not only fosters robustness in SCs but also innovation [51]. For SMEs, accessible programs are necessary, because SMEs mostly suffer from resource scarcity and it is difficult for the owner to get the commitment of the staff [10].
Answering the question of how industries differ in risk perception, proposed by [7], we conclude that companies from almost all sectors tend to perceive risks rather as threats than opportunities. Only collective risk-ignoring knights of fortune, which represented lots of companies within the architecture and engineering sector, perceived risks rather positively. Additionally, this exploratory study further confirms that structured RM remains underdeveloped or lacking in SMEs, even if SMEs perceive the risks caused by DT. We propose that sectors with more complex technology, such as engineering, have already made some progress regarding structured RM. In contrast to that, the more conservative sectors such as construction are rather even more behind. Regarding the attitude of group risk elimination or risk-sharing within the SC, we show that the more risks that are taken seriously and tried to be avoided, the more collaboration within the SC is fostered. Furthermore, the low frequency of risk incidents, but the big impact (in terms of severity certain risks may cause) should remind decision-makers in small firms that a dedicated approach to (SC)RM is vital to all firms and may facilitate the transition to DT.
6. Conclusions
This paper, reporting about an explorative study, identified patterns that can be used to cluster SMEs according to their risk behavior (i.e., attitude and perception). The study shows that SMEs perceive risks in the context of DT but are not ready to respond appropriately. Using a sample of 181 SMEs from selected EU countries, this paper has elaborated a typology of different SME groups which can be used to analyze this phenomenon in a more nuanced and detailed way.
The cluster analysis shows that four different groups of SMEs are identified. Each cluster shows its characteristics regarding the frequency of crisis, assessment, and impact of risks. Furthermore, risk behavior (attitude and perception) is clustered, as well as self-assessed innovation performance to competitors. Risks are rather perceived as threats, by all clusters, and only one cluster sees them more as opportunities than threats. Even though all four clusters reveal different risk behavior, they all see a positive innovation performance compared to their competitors.
The identified four clusters are the key contribution of our study. The respective clusters identified provide relevant insights into how different perceptions of risks on the one hand and different risk attitudes of different types of SMEs, on the other hand, lead to different RM behavior. Thus, by acknowledging the heterogeneity found in SMEs in the study’s research design right from the beginning, the findings obtained can be considered as stronger and more fine-grained compared with other research that treats SMEs as a generic size. In fact, the clusters identified indicate that RM depends on the size of the company which in turn underlines once more that there is no standard solution for SMEs.
The findings presented are expected to be useful for practice too. This study offers insights into different RM approaches in SMEs underlining that SMEs differ and thus cannot be treated as one generic entity. SME owners must be aware that the infrequency of incidents should not lead to neglecting regular assessments. Rather, it must be noted that the pursuit of joint elimination of risks within the SC is of great benefit and can definitely mitigate the severity of risk scenarios that occur. The study shows that despite the low frequency, the impact of the risk scenarios that have occurred always represents a serious threat. Furthermore, for better innovation performance, it was shown that eliminating risks within SC leads to a better perception of one’s innovativeness. For all these reasons, SMEs should seek out collaboration with their SC partners because the joint management of risks that arise can always be seen in the SME’s favor. Policymakers may find the findings relevant too as they can help to develop and offer more specific RM-related measures for different types of SMEs.
Like any research, this paper does have limitations. First, considering that SMEs from a subset of EU countries were investigated, the findings presented should be taken with caution (although different types of SMEs operating in different sectors were involved). Given the exploratory nature of the study, no consideration was given to cultural or other contextual differences, yet considering the relevance of context, future research should be developed accordingly. Second, the number of participants is suitable for an exploratory study and the cluster analysis and, representativeness was not the purpose of the study but to further develop a still under-researched area of research. Scholars may be encouraged to conduct a follow-up study in representative samples to test the robustness of t. Nevertheless, the cluster analysis was found to be valid and 85.6% of original grouped cases are correctly classified (see Table 3). Third, even though different categories of SMEs were involved in the study, the sample in this paper is skewed as it does not present SMEs according to their percentage share of the total number of all SMEs in Europe. Finally, this survey represents only a snapshot of RM; considering the dynamic nature of risks and thus the requirements regarding RM, there is a need for longitudinal studies to better understand risk behavior over time. Regarding digitalization and knowledge risks, it would be a suitable opportunity for future research to go into this more deeply and to look explicitly for risk perception and attitudes in this area.
The conclusion to be drawn is that research on RM in SMEs should be further intensified. We hope that the findings presented will encourage more fine-grained research that takes into consideration the heterogeneity found in SMEs and based on that breaks away from suggesting general approaches for all types of SMEs.
Author Contributions
The conceptualization originated from the idea of all three authors during a joint project. Additionally, the methodology was decided by J.P.Z., S.D. and S.T. and after shared investigation and data collection, formal analysis was conducted by S.D. and validated by J.P.Z. and S.T. The original draft writing was carried out by J.P.Z.; further writing, reviewing and editing was performed by S.D., S.T. and J.P.Z. Project administration was shared by all three authors. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The authors greatly acknowledge the financial support from the European Union’s Erasmus + Programme under Project Reference: 2020-1-EE01-KA202-077891. The authors further greatly acknowledge the efforts of the other partners in this project as otherwise this paper would not have been possible. “Open Access Funding by the University of Graz”.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the financial support by the University of Graz.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- El Baz, J.; Ruel, S. Can supply chain risk management practices mitigate the disruption impacts on supply chains’ resilience and robustness? Evidence from an empirical survey in a COVID-19 outbreak era. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2021, 233, 107972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finch, P. Supply chain risk management. Supply Chain Manag. 2004, 9, 183–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Araújo Lima, P.F.; Crema, M.; Verbano, C. Risk management in SMEs: A systematic literature review and future directions. Eur. Manag. J. 2020, 38, 78–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colicchia, C.; Creazza, A.; Menachof, D.A. Managing cyber and information risks in supply chains: Insights from an exploratory analysis. Supply Chain Manag. 2019, 24, 215–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soto-Acosta, P. COVID-19 Pandemic: Shifting Digital Transformation to a High-Speed Gear. Inf. Syst. Manag. 2020, 37, 260–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraus, S.; Durst, S.; Ferreira, J.J.; Veiga, P.; Kailer, N.; Weinmann, A. Digital transformation in business and management research: An overview of the current status quo. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2022, 63, 102466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falkner, E.M.; Hiebl, M.R. Risk management in SMEs: A systematic review of available evidence. J. Risk Financ. 2015, 16, 122–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shou, Y.; Prester, J.; Li, Y. The Impact of Intellectual Capital on Supply Chain Collaboration and Business Performance. IEEE Trans. Eng. Manag. 2020, 67, 92–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llopis, O.; Garcia-Granero, A.; Fernández-Mesa, A.; Alegre, J. Managers’ risk taking propensity and innovation in organizations: The mediating influence of employees’ perceived risk taking climate. In Proceedings of the 2013 35th DRUID Celebration Conference, Barcelona, Spain, 17–19 June 2013; pp. 17–19. [Google Scholar]
- Henschel, T.; Durst, S. Risk management in Scottish, Chinese and German small and medium-sized enterprises: A country comparison. IJESB 2016, 29, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeiringer, J.P.; Thalmann, S. Knowledge Risks in Digital Supply Chains: A Literature Review. In Proceedings of the Wirtschaftsinformatik 2020, Potsdam, Germany, 9–11 March 2020; GITO Verlag: Berlin, Germany, 2020; pp. 370–385, ISBN 9783955453350. [Google Scholar]
- Zeiringer, J.P. Tackling Knowledge Risks in Data-centric Collaborations: A Literature Review. In Proceedings of the Pacific Asia Conference on Information Systems (PACIS), Dubai, United Arab Emirates, 12–14 July 2021; ISBN 978-1-7336325-7-7. [Google Scholar]
- Colquitt, L.L.; Hoyt, R.E.; Lee, R.B. Integrated Risk Management and the Role of the Risk Manager. Risk Manag. Insur. Rev. 1999, 2, 43–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatzert, N.; Martin, M. Determinants and Value of Enterprise Risk Management: Empirical Evidence From the Literature. Risk Manag. Insur. Rev. 2015, 18, 29–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brustbauer, J. Enterprise risk management in SMEs: Towards a structural model. Int. Small Bus. J. 2016, 34, 70–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thun, J.-H.; Drüke, M.; Hoenig, D. Managing uncertainty—An empirical analysis of supply chain risk management in small and medium-sized enterprises. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2011, 49, 5511–5525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahroun, M.; Harbi, S. Risk management in the modern retail supply chain: Lessons from a case study and literature review. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Industrial Engineering and Systems Management (IESM)—The Road Ahead, Seville, Spain, 21–23 October 2015; pp. 1161–1170. [Google Scholar]
- Li, G.; Fan, H.; Lee, P.K.; Cheng, T. Joint supply chain risk management: An agency and collaboration perspective. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2015, 164, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavastre, O.; Gunasekaran, A.; Spalanzani, A. Supply chain risk management in French companies. Decis. Support Syst. 2012, 52, 828–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durst, S.; Temel, S.; Hinteregger, C. Influence of network partners on SMEs’ innovation activities. Int. J. Bus. Environ. 2020, 11, 369–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revilla, E.; Saenz, M.J. The impact of risk management on the frequency of supply chain disruptions. Int. J. Oper. Prod. Manag. 2017, 37, 557–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanco, M.; Jurburg, D.; Escuder, M. Main difficulties hindering supply chain performance: An exploratory analysis at Uruguayan SMEs. Supply Chain Manag. 2015, 20, 11–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curran, J.; Blackburn, R.A. Researching the Small Enterprise; Online-Ausg; Sage: London, UK, 2001; ISBN 9780761952954. [Google Scholar]
- Vial, G. Understanding digital transformation: A review and a research agenda. J. Strateg. Inf. Syst. 2019, 28, 118–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouwman, H.; Nikou, S.; de Reuver, M. Digitalization, business models, and SMEs: How do business model innovation practices improve performance of digitalizing SMEs? Telecommun. Policy 2019, 43, 101828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kagermann, H. Change Through Digitization—Value Creation in the Age of Industry 4.0. In Management of Permanent Change; Albach, H., Meffert, H., Pinkwart, A., Reichwald, R., Eds.; Springer Fachmedien Wiesbaden: Wiesbaden, Germany, 2015; pp. 23–45. ISBN 978-3-658-05013-9. [Google Scholar]
- Ivanov, D.; Dolgui, A.; Sokolov, B. The impact of digital technology and Industry 4.0 on the ripple effect and supply chain risk analytics. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2019, 57, 829–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaiser, R.; Thalmann, S.; Pammer-Schindler, V. An Investigation of Knowledge Protection Practices in Inter-organisational Collaboration. Protecting Specialised Engineering Knowledge with a Practice Based on Grey-box Modelling. VINE J. Inf. Knowl. Manag. Syst. 2020, 51, 713–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- North, K.; de Carvalho, A.; Braccini, A.; Durst, S.; Carvalho, J.; Gräslund, K.; Thalmann, S. Information and knowledge risks in supply chain interactions of SMEs. In Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Practical Knowledge Management, Potsdam, Germany, 2–4 September 2019. Lecture notes on Informatics. [Google Scholar]
- Pfeifer, M.R. IT security in SMEs—Threats and Chances for Supply Chains. J. Supply Chain. Cust. Relatsh. Manag. 2021, 2021, 435883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, S.; Singh, R.K.; Gunasekaran, A.; Kaushik, A. Cyber security risks in globalized supply chains: Conceptual framework. J. Glob. Oper. Strateg. Sourc. 2020, 13, 103–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghadge, A.; Weiß, M.; Caldwell, N.D.; Wilding, R. Managing cyber risk in supply chains: A review and research agenda. Supply Chain Manag. 2019, 25, 223–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- North, K.; Aramburu, N.; Lorenzo, O.J. Promoting digitally enabled growth in SMEs: A framework proposal. J. Enterp. Inf. Manag. 2020, 33, 238–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, I.; North, K.; Thalmann, S.; Aramburu, N.; Hermann, A.; Gräslund, K.; Barros, V. Using Simulation to Leverage Digital Transformation of SMEs: A European Perspective. In Proceedings of the 55th Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences, Hawaii, HI, USA, 4–7 June 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Zeiringer, J.P.; Thalmann, S. Knowledge sharing and protection in data-centric collaborations: An exploratory study. Knowl. Manag. Res. Pract. 2021, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birkel, H.; Veile, J.; Müller, J.; Hartmann, E.; Voigt, K.-I. Development of a Risk Framework for Industry 4.0 in the Context of Sustainability for Established Manufacturers. Sustainability 2019, 11, 384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, W.; Zheng, T.; Yildiz, H.; Talluri, S. Supply chain risk management: A literature review. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2015, 53, 5031–5069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lepistö, K.; Saunila, M.; Ukko, J. Facilitating SMEs’ profitability through total quality management: The roles of risk management, digitalization, stakeholder management and system deployment. TQM J. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smit, Y.; Watkins, J.A. A literature review of small and medium enterprises (SME) risk management practices in South Africa. Afr. J. Bus. Manag. 2012, 6, 6324–6330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barratt, M. Understanding the meaning of collaboration in the supply chain. Supply Chain Manag. 2004, 9, 30–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogulin, R.; Selen, W.; Ashayeri, J. Determinants of informal coordination in networked supply chains. J. Enterp. Inf. Manag. 2012, 25, 328–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Stevenson, M. A review of supply chain risk management: Definition, theory, and research agenda. Int. J. Phys. Distrib. Logist. Manag. 2018, 48, 205–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, S.M.; Bode, C. Dominant Risks and Risk Management Practices in Supply Chains. In Supply Chain Risk; Hillier, F.S., Zsidisin, G.A., Ritchie, B., Eds.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2009; pp. 271–290. ISBN 978-0-387-79933-9. [Google Scholar]
- Arnold, V.; Benford, T.; Hampton, C.; Sutton, S.G. Competing pressures of risk and absorptive capacity potential on commitment and information sharing in global supply chains. Eur. J. Inf. Syst. 2010, 19, 134–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friday, D.; Ryan, S.; Sridharan, R.; Collins, D. Collaborative risk management: A systematic literature review. Int. J. Phys. Distrib. Logist. Manag. 2018, 48, 231–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Sohal, A.S.; Prajogo, D.I. Supply chain operational risk mitigation: A collaborative approach. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2013, 51, 2186–2199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huong Tran, T.T.; Childerhouse, P.; Deakins, E. Supply chain information sharing: Challenges and risk mitigation strategies. J. Manuf. Technol. Manag. 2016, 27, 1102–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acar, E.; Göç, Y. Prediction of risk perception by owners’ psychological traits in small building contractors. Constr. Manag. Econ. 2011, 29, 841–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heckmann, I.; Comes, T.; Nickel, S. A critical review on supply chain risk—Definition, measure and modeling. Omega 2015, 52, 119–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Um, J.; Han, N. Understanding the relationships between global supply chain risk and supply chain resilience: The role of mitigating strategies. Supply Chain Manag. 2021, 26, 240–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamout, M.D. The nexus between supply chain analytic, innovation and robustness capability. VINE J. Inf. Knowl. Manag. Syst. 2020, 51, 163–176, ahead-of-print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Dai, J.; Cui, L. The impact of digital technologies on economic and environmental performance in the context of industry 4.0: A moderated mediation model. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2020, 229, 107777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, X.; Song, M. Does knowledge management enhance or impede innovation speed? J. Knowl. Manag. 2020, 24, 1393–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, S.X.; Xie, X.M.; Tam, C.M. Relationship between cooperation networks and innovation performance of SMEs. Technovation 2010, 30, 181–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oke, A. Innovation types and innovation management practices in service companies. Int. J. Oper. Prod. Manag. 2007, 27, 564–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, D.-W.; Seo, Y.-J.; Mason, R. Investigating the relationship between supply chain innovation, risk management capabilities and competitive advantage in global supply chains. Int. J. Oper. Prod. Manag. 2018, 38, 2–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connor, N.O.; Lowry, P.B.; Treiblmaier, H. Interorganizational cooperation and supplier performance in high-technology supply chains. Heliyon 2020, 6, e03434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wei, Z.; Li, B. Supply chain collaboration for ERP implementation. Int. J. Oper. Prod. Manag. 2017, 37, 1327–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaworski, B.J.; Kohli, A.K. Market Orientation: Antecedents and Consequences. J. Mark. 1993, 57, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colicchia, C.; Creazza, A.; Noè, C.; Strozzi, F. Information sharing in supply chains: A review of risks and opportunities using the systematic literature network analysis (SLNA). Supply Chain Manag. 2019, 24, 5–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inkinen, H.T.; Kianto, A.; Vanhala, M. Knowledge management practices and innovation performance in Finland. Balt. J. Manag. 2015, 10, 432–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamel, G. The why, what, and how of management innovation. Harv. Bus. Rev. 2006, 84, 72–84, 163. [Google Scholar]
- Woschke, T.; Haase, H.; Kratzer, J. Resource scarcity in SMEs: Effects on incremental and radical innovations. Manag. Res. Rev. 2017, 40, 195–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verbano, C.; Venturini, K. Managing Risks in SMEs: A Literature Review and Research Agenda. J. Technol. Manag. Innov. 2013, 8, 33–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patton, M.Q. Qualitative Research & Evaluation Methods, 3rd ed.; Sage: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2009; ISBN 9780761919711. [Google Scholar]
- Markmann, C.; Darkow, I.-L.; Gracht, H. von der. A Delphi-based risk analysis—Identifying and assessing future challenges for supply chain security in a multi-stakeholder environment. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2013, 80, 1815–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fawad Sharif, S.M.; Naiding, Y.; Xu, Y.; Rehman, A.u. The effect of contract completeness on knowledge leakages in collaborative construction projects: A moderated mediation study. J. Knowl. Manag. 2020, 24, 2057–2078, ahead-of-print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durst, S.; Hinteregger, C.; Zieba, M. The linkage between knowledge risk management and organizational performance. J. Bus. Res. 2019, 105, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Everitt, B. Cluster Analysis, 5th ed.; Wiley: Chichester, UK, 2011; ISBN 1280767952. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, S.S.; Sung, M.C.; Zhang, J. Risk management capability building in SMEs: A social capital perspective. Int. Small Bus. J. 2013, 31, 677–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roldán Bravo, M.I.; Ruiz Moreno, A.; Llorens-Montes, F.J. Supply network-enabled innovations. An analysis based on dependence and complementarity of capabilities. Supply Chain Manag. 2016, 21, 642–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oduoza, C.F.; Odimabo, O.; Tamparapoulos, A. Framework for Risk Management Software System for SMEs in the Engineering Construction Sector. Procedia Manuf. 2017, 11, 1231–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Rostami, A.; Sommerville, J.; Wong, I.L.; Lee, C. Risk management implementation in small and medium enterprises in the UK construction industry. Eng. Constr. Archit. Manag. 2015, 22, 91–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Löfsten, H. Product innovation processes and the trade-off between product innovation performance and business performance. Eur. J. Innov. Manag. 2014, 17, 61–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patrucco, A.S.; Luzzini, D.; Ronchi, S. Achieving innovation through supplier collaboration: The role of the purchasing interface. Bus. Process Manag. J. 2017, 23, 1270–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fruhwirth, M.; Pammer-Schindler, V.; Thalmann, S. A Network-based Tool for Identifying Knowledge Risks in Data-Driven Business Models. In Proceedings of the 54th Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences, Hawaii, HI, USA, 5 January 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Vuković, M.; Thalmann, S. Causal Discovery in Manufacturing: A Structured Literature Review. J. Manuf. Mater. Processing 2022, 6, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flöthmann, C.; Hoberg, K.; Gammelgaard, B. Disentangling supply chain management competencies and their impact on performance. Int. J. Phys. Distrib. Logist. Manag. 2018, 48, 630–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riley, J.M.; Klein, R.; Miller, J.; Sridharan, V. How internal integration, information sharing, and training affect supply chain risk management capabilities. Int. J. Phys. Distrib. Logist. Manag. 2016, 46, 953–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).